Rash on face white bumps
White Spots on Face: What’s Causing It?
Is this cause for concern?
Skin discolorations are common, especially on the face. Some people develop red acne patches, and others may develop dark age spots. But one particular skin discoloration might have you scratching your head.
You may notice white spots speckled across your cheeks or elsewhere on your face. Sometimes, these spots can cover a large surface area and may even extend to other parts of your body.
A number of conditions can cause white spots to form on your face, and they generally aren’t cause for concern. Here’s a look at the most common causes and how to handle them.
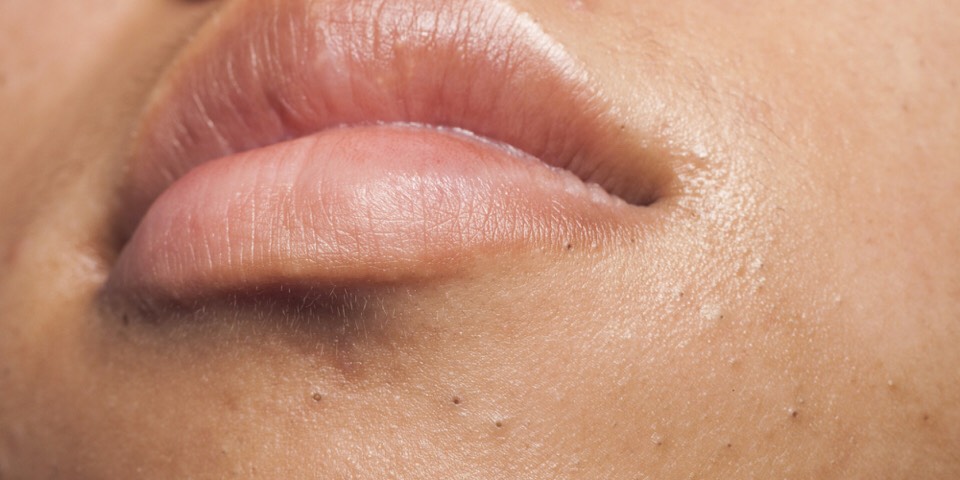
Milia develops when keratin gets trapped under the skin. Keratin is a protein that makes up the outer layer of skin. This causes the formation of tiny white-colored cysts on the skin. This condition most often occurs in children and adults, but it’s also seen in newborn babies.
When white spots are caused by entrapped keratin, it’s called primary milia. However, these tiny white cysts can also form on skin as the result of a burn, sun damage, or poison ivy. Cysts may also develop after a skin resurfacing procedure or after using a topical steroid cream.
Milia can develop on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and around the eyes. Some people also form cysts in their mouths. These bumps usually aren’t painful or itchy, and the condition typically resolves itself without treatment within a few weeks.
If your condition doesn’t improve within a few months, your doctor may prescribe a topical retinoid cream or recommend microdermabrasion or an acid peel to repair damaged skin. Your doctor can also use a special tool to extract the bumps.
Learn more: Baby acne or rash? 5 types and how to treat them »
Pityriasis alba is a type of eczema that causes a flaky, oval patch of discolored white skin to appear. This skin disorder affects about 5 percent of children around the world, primarily between the ages of 3 and 16.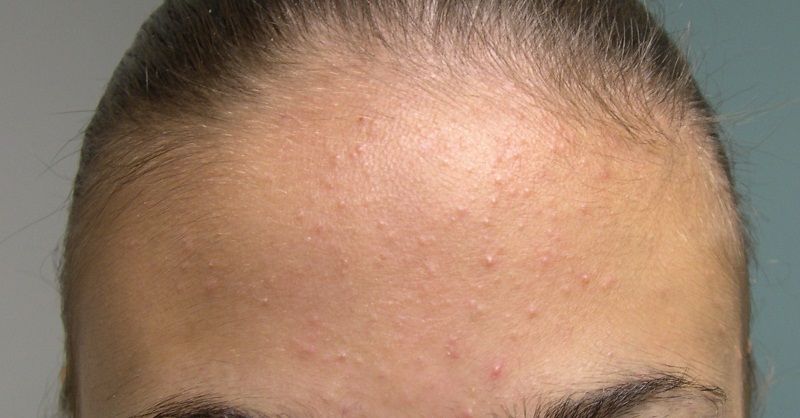
The exact cause of this condition is unknown. It’s usually seen in the setting of atopic dermatitis. It may be connected to sun exposure or a yeast that causes hypopigmentation.
Pityriasis alba often clears on its own within a few months, although discoloration can last up to three years.
If you’re experiencing symptoms, apply moisturizing cream on any dry spots and use an over-the-counter (OTC) topical steroid, such as hydrocortisone, to relieve any itchiness or redness.
Vitiligo is a skin disorder caused by loss of pigmentation. These patches of depigmented skin can form anywhere on the body. This includes your:
- face
- arms
- hands
- legs
- feet
- genitals
These patches may be small in size initially and gradually increase until white areas cover a large percentage of the body. However, widespread white spots don’t occur in all cases.
This condition can develop at any age, although most people don’t show symptoms of the disease until their 20s. Your risk for vitiligo increases if there’s a family history of the disease.
Your risk for vitiligo increases if there’s a family history of the disease.
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. Your doctor may recommend topical creams, ultraviolet light therapy, or oral medication to help restore skin color and stop the spread of white patches.
Skin grafts are also effective for getting rid of small patches of white skin. To do this, your doctor will remove skin from one part of your body and attach it to another part of your body.
Tinea versicolor, also known as pityriasis versicolor, is a skin disorder caused by an overgrowth of yeast. Yeast is a common type of fungus on the skin, but in some it can cause a rash. Tinea versicolor spots can appear scaly or dry and vary in color.
Some people with this condition develop pink, red, or brown spots, and others develop white spots. If you have lighter skin, white spots may be unnoticeable until your skin tans.
This skin disorder can occur in people of all ages, but it commonly affects people who live in humid climates, as well as people who have oily skin or a compromised immune system.
Because tinea vesicular is caused by an overgrowth of yeast, antifungal medications are the primary line of defense. Talk to your doctor about OTC or prescription antifungal products. This includes shampoos, soaps, and creams. Apply as directed until white spots improve.
Your doctor can also prescribe an oral antifungal medication, such as fluconazole, to stop and prevent the overgrowth of yeast.
White patches typically disappear once the fungus is under control. It can take weeks or months for skin to return to its normal color. Without consistent treatment with topicals, it often recurs.
Learn more: Is it psoriasis or tinea versicolor? »
Tinea versicolor and pregnancy
Your body goes through a lot of changes during pregnancy, including skin changes. In addition to developing dark spots, stretch marks, and acne, some expecting women develop tinea versicolor. This generally isn’t a cause for concern. Skin color usually returns once hormone levels return to normal.
Learn more: The second trimester of pregnancy: Changes in skin, vision, and gums »
If you want to more quickly fade any spots you may be experiencing, talk to your doctor about antifungal treatments that are safe to use during pregnancy.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, or sun spots, are white spots that form on the skin as a result of long-term UV exposure. The number and size of white spots vary, but they’re generally round, flat, and between 2 and 5 millimeters.
These spots can develop on different parts of the body including your:
- face
- arms
- back
- legs
This condition is more evident in people with fair skin, and your risk for sun spots increases with age. Women often develop spots at an earlier age than men.
Because these white spots are caused by UV exposure, you should use sun protection to prevent sun spots from worsening. This may help prevent new ones from forming.
Different treatments can reduce the appearance of white spots and restore color.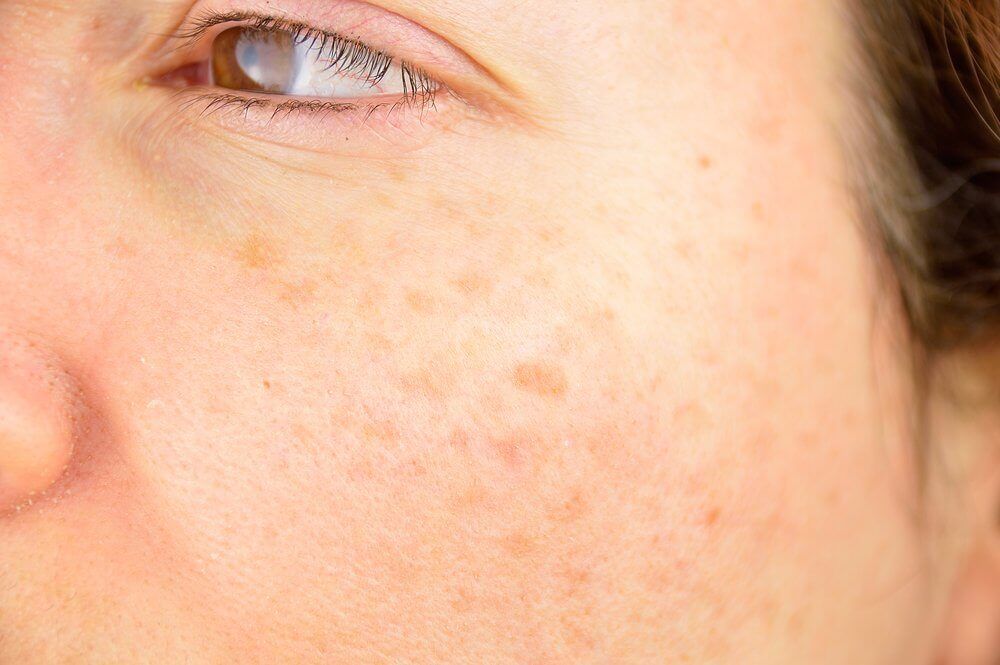 Options include topical steroids to reduce skin inflammation and retinoids to stimulate cell growth and hyperpigmentation.
Options include topical steroids to reduce skin inflammation and retinoids to stimulate cell growth and hyperpigmentation.
Most white spots on the skin aren’t a major cause for concern. Still, it’s important to see a doctor or dermatologist for a diagnosis, especially if the white spots spread or don’t respond to home treatment after a couple of weeks.
You might shrug off a white spot that doesn’t itch or hurt, but continue to monitor your skin. With early intervention, your doctor can recommend products to possibly restore pigmentation.
White spots on the face: Possible causes and treatments
Many people experience white spots on their face at some point during their lives. The affected areas may just be on the face, or they may appear on the chest or arms as well.
White spots can take different forms. They could be patches of discoloration on the face or small hard bumps.
In this article, we will examine the five main possible causes of white spots on the face. Read on for more about them, what causes them, and treatment options.
Read on for more about them, what causes them, and treatment options.
Milia are small round, hard, white bumps on the face that are often mistaken for whiteheads. They develop when keratin — a protein found in the upper layer of skin — and other dead skin cells components get trapped below the skin surface.
The most common areas for milia to appear are around the eyes, the cheeks, and on the nose.
Milia can occur at all ages in both men and women. They occur most often in very young babies, and the condition is also called milk spots.
Causes
Milia can be triggered by an allergic reaction to harsh products, by face cream that is irritating, and by sun damage.
Treatment
Milia usually get better without treatment within a few weeks. Dermatologists recommend not squeezing or piercing the bumps at home.
A change in face cream or other products that might have caused a reaction may help. A good skincare routine, including dead skin removal with exfoliants and wearing sun protection cream, is also advisable for adults.
A good skincare routine, including dead skin removal with exfoliants and wearing sun protection cream, is also advisable for adults.
If the condition does not improve on its own, a doctor or dermatologist can treat milia in a variety of ways:
- Lancing. The doctor or dermatologist will use a medical-grade fine needle to extract the keratin.
- Applying a retinoid cream. People can use this on their face but not around their eyes.
- Microdermabrasion. This is a procedure which removes the uppermost layers of the affected area.
- Skin peel. A treatment that removes the top layer of skin and can be used to remove milia.
Milia is not a dangerous condition and causes no discomfort, pain, or stinging.
If the white bumps do not disappear on their own, or if a person finds them unsightly, talk to a doctor about having them removed.
Pityriasis alba is thought to be a type of eczema. It appears as pale pink or red, scaly areas on the skin, which clear to smooth white (hypopigmented) patches.
There can be as many as 20 patches, often on the face and arms. Pityriasis alba is more noticeable on people with dark skin or after sun exposure.
The condition is mostly found in children and adolescents, with 5 percent of children worldwide developing the condition at some point.
Causes
Doctors do not know what causes pityriasis alba.
Treatment
The patches usually disappear within a few months but can last up to a few years. There is no specific treatment for pityriasis alba, but a doctor may treat any symptoms of itching or discomfort with a steroid or non-steroid cream.
If the patches start to itch or feel uncomfortably dry, a person should consult a doctor.
Share on PinterestVitiligo may occur in people of all skin colors and might be inherited.
Vitiligo appears as patches of skin that have lost their color pigment. It can occur anywhere on the body, including the face. It affects around 1 percent of people worldwide.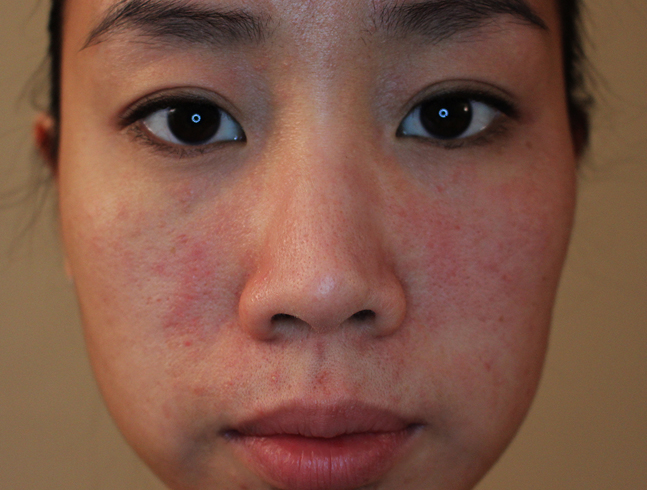
The white patches may start small and sometimes remain this way, but they can also slowly increase until the patch covers a large part of the body. Occasionally, some color may return to the affected area but rarely completely.
Vitiligo can occur at any age, but around half of the people with the condition develop it before their 20s.
Causes
Anyone can get vitiligo, though the chances increase somewhat if someone else in the family has it. The factor of inheritance has yet to be fully understood, so the children of a person who has vitiligo will not necessarily develop it as well.
Vitiligo occurs in people of all skin colors, but it is most noticeable on black skin. It is not contagious.
Skin cells make a pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its color. Some scientists believe that the skin affected by vitiligo develops when the body forms an antibody against melanin and destroys it.
Treatment
There are several possible treatments for vitiligo. The type offered depends on the severity of the condition.
The type offered depends on the severity of the condition.
People with vitiligo should wear sunscreen at all times and cover-up in the sun as the affected skin will burn more easily.
If a person wants, they can use colored skin creams to hide areas of vitiligo, and a doctor will be able to recommend the best creams available.
The doctor may also recommend anti-inflammatory creams, such as a higher strength corticosteroid, to help restore missing pigment.
Long-term use of corticosteroids, however, can bring undesirable side effects, such as thinning of the skin, so doctors may prescribe other types of anti-inflammatory creams.
Artificial ultraviolet (UV) light treatment or phototherapy may be used, often over a period of several months. Laser treatment may also be used to treat some skin areas.
Surgical treatments are being developed but are not yet common practice.
Share on PinterestAn overgrowth of yeast on the skin may change its color, causing pityriasis versicolor.
Pityriasis versicolor is a common condition, due to a yeast infection, that causes lighter or darker patches on the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body and may itch or feel dry or scaly.
Sometimes, the spots are tiny and sometimes only noticeable when the skin is tanned.
Pityriasis versicolor is more commonly found in adolescents and younger adults and frequently in the tropics and sub-tropical areas. In temperate climates, the discolored patches may disappear in the cooler months.
Causes
Over 90 percent of adults have a yeast called Malassezia living on their skin. It is a natural occurrence and does not usually cause any problems.
Sometimes, however, the yeast overgrows. When this happens, it changes the color of the skin, thus causing pityriasis versicolor. This can be due to several factors, such as:
- hot and humid weather
- oily skin
- a weak immune system
- hormonal changes
Pityriasis versicolor can occur during pregnancy but poses no danger.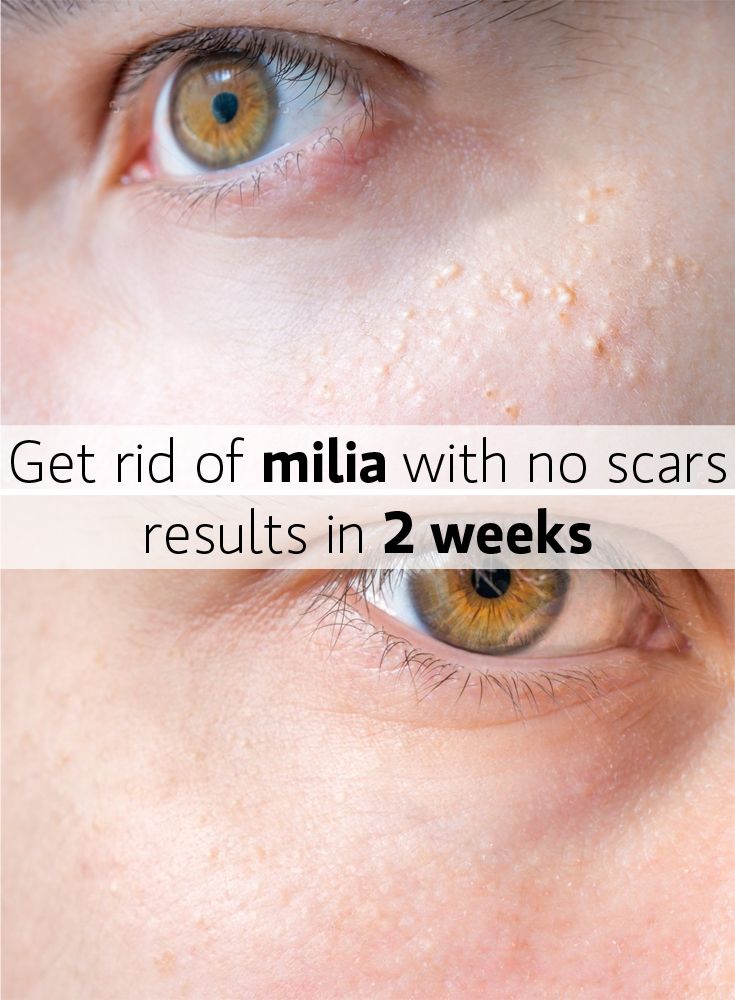 One study showed that the yeast that causes pityriasis versicolor was more abundant during the later stages of pregnancy and right after the birth.
One study showed that the yeast that causes pityriasis versicolor was more abundant during the later stages of pregnancy and right after the birth.
Treatment
There are a variety of different ways to successfully treat tinea versicolor. The patches may take some months to return to their former color, and sun cream should be used to protect the skin from the sun.
Medications that can help include:
- anti-fungal creams and lotions applied to the skin
- a medicated anti-fungal cleanser that will help the yeast growing out of control
- anti-fungal pills prescribed by a doctor if the pityriasis versicolor covers a large area of the body.
It is possible that pityriasis versicolor can return even after treatment, especially if the person travels to hot and humid climates.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, also known as white sun spots, causes flat white spots that can be 1 to 10 millimeters in diameter.
These spots can occur on the face, arms, upper back, and the shins.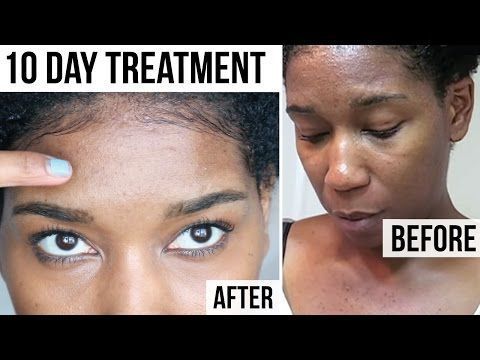 Although they are most often develop in people with fair skin, people with dark skin can develop them as well.
Although they are most often develop in people with fair skin, people with dark skin can develop them as well.
The spots are not harmful.
Causes
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis appears to occur in relation to prolonged exposure to the sun over time. However, the reason why there is a decrease in melanin in the affected areas is not yet known.
This skin condition appears more frequently in people over the age of 40, but this is likely to be due to the length of time the condition takes to develop.
Treatment
No treatment is needed or available to remove the condition.
Steroid creams, camouflage creams, and dermabrasion can reduce the appearance of the spots.
Many of these common conditions can be treated easily. Most conditions that cause white spots on the face are also harmless.
If anyone has any concerns about the appearance of white spots on their face, for health or cosmetic reasons, they should speak to a healthcare professional. They will be able to offer reassurance and treatment advice if necessary.
They will be able to offer reassurance and treatment advice if necessary.
Milia on the face - causes and treatment, how to remove whiteheads on the face
Contents
- What are milia
- Types and causes of whiteheads
- How to get rid of milia on the face with cosmetic methods
- Can it be removed milia at home
- Prevention of whiteheads
Whiteheads or milia are difficult to remove, but, fortunately, there are effective ways to get rid of this defect.
But, fortunately, there are effective ways to get rid of this defect.
Milia are cystic formations of the mouth of the hair follicle, which look like a small white grain. They are also called "millet", as they resemble millet grains in color and size. Usually they appear where the skin is relatively thin (periorbital zone, zygomatic part, eyelids, forehead) and do not cause any physical discomfort.
The content that accumulates in the milia is a mixture of sebum, keratin, and keratinized particles. The nature of the rashes is non-inflammatory in nature, so they do not cause harm to the body. They can appear both singly and form a focus.
The appearance of primary milia is associated with the functioning of the sebaceous gland. With its hyperfunction, the composition of sebum changes, there is a deficiency of valuable lipids, which creates a favorable background for the appearance of whiteheads.
Secondary (they are often called Balser's pseudomylia) may be the result of trauma to the surface of the skin.
Since milia are comedogenic phenomena, the following factors can influence their appearance:
-
Hereditary predisposition.
The peculiarity of the functioning of the sebaceous gland, the sensitivity of receptors to hormones, the tendency to acne are determined and encoded by a large number of genes.

-
Hormonal imbalance.
The sebaceous gland is hormone-dependent. First of all, from testosterone and its active forms. Therefore, with hyperandrogenism, diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, the appearance of oily sheen, black dots, acne, milia is observed. They can also occur in newborns, as they go through a hormonal crisis, but disappear after about a month.
-
Hyperkeratosis.
These are thickenings of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. May occur as a result of vitamin A deficiency, adverse external factors, intoxication in hazardous production. Hyperkeratosis leads to a slowdown in the rate of exfoliation of dead cells, resulting in blockage of the sebaceous gland.
-
Disorders of metabolic processes.
The disease is based on the development of insulin resistance, for example, against the background of obesity. This can be facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle, frequent consumption of foods with a high glycemic index, psychological distress, hormonal disorders (hypothyroidism).

-
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The appearance of a large number of milia can be affected by diseases associated with a violation of the outflow of bile: biliary dyskinesia, cholecystitis, bile stasis.
-
Unsuitable cosmetic treatment.
Neglect of hygiene rules or, on the contrary, the use of aggressive products can harm the skin. In the periorbital area, "milk" may appear due to the use of products that are not intended for the area around the eyes.
The main method of treatment is the opening and removal of the contents of milia. It should be carried out exclusively in the office of a competent and experienced cosmetologist.
- At the initial stage, superficial chemical peeling will help to partially unblock the head of the wen. Under the influence of fruit acids, dead skin cells dissolve, which gives a signal to renew the epidermis.
 Depending on the existing problems and skin type, the peeling course is from 5 to 7 sessions.
Depending on the existing problems and skin type, the peeling course is from 5 to 7 sessions. - Mechanical method (opening and curettage). Getting rid of milia is carried out by a puncture method with a needle. If the white wen is of medium size, then Vidal's needle is used. With smaller white dots, an insulin and mesotherapy syringe allows you to work. The beautician opens the shell of the wen and removes the keratin clot with the help of a curette and a Uno spoon. This method allows you to completely remove the contents and prevent the formation of new cysts.
However, milia may appear on the face and body, the size of which will not allow them to be opened. In this case, help:
- Electrocoagulation. The procedure involves drying the wen with a high-frequency electric current, as a result of which they themselves fall off.
- Laser removal. Used for multiple localization and hard-to-reach milia. The wen is removed with a laser, and the wound heals under a dry crust in 7-14 days.
 Thus, the skin is cured of cystic formations.
Thus, the skin is cured of cystic formations.
The exact and confident answer is no .
The upper part of the milia is completely clogged, which makes it difficult to remove them even with specialized equipment. In no case should you try to squeeze out the formations on your own, as you can introduce an infection and provoke inflammation. Incorrect and unprofessional exposure will lead to the appearance of even greater cosmetic defects - scars.
Prevention of milia does not differ from classical and high-quality care. Therefore, following some rules will become a multifunctional approach on the way to healthy and beautiful skin of the face and body.
- With the help of a beautician, choose a set of cosmetics that suits your skin type. We remind you that it should include cleansing, toning and moisturizing + the use of peels and masks 1-2 times a week.
- Hand over analyses. Deficiency or excess of certain elements can significantly harm the quality of the skin.
- Regularly visit a cosmetologist, in whose office you will undergo monthly care procedures: facial cleansing, peeling.
- Review the food you eat and start keeping a food diary. So you will know exactly what foods are present in the diet in excess. It is advisable to completely exclude fried, salty, junk food, as well as foods rich in preservatives and dyes.
- Protect your skin from harmful UV rays with a 30-50 spf cream.
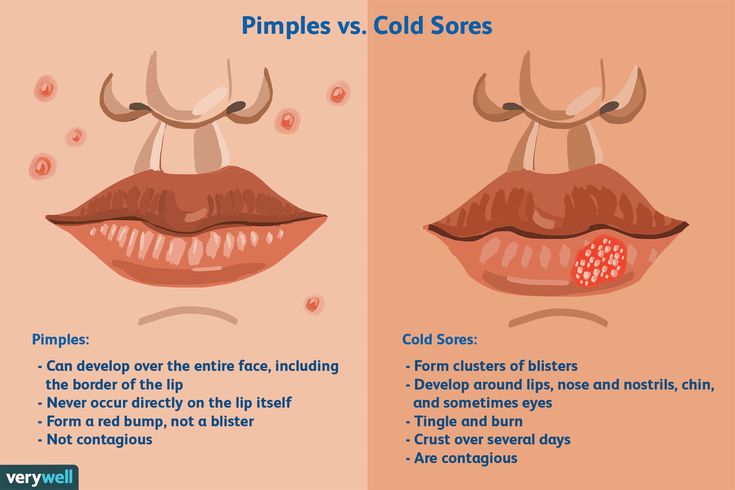
White pimples
Millet - this is sometimes called small white pimples that appear under the skin of the face. This type of acne resembles millet grains and is a dense nodules, located both singly and in groups. On the face, white acne is most often localized on the forehead, cheekbones, nose, chin, lips. Sometimes they pour out on the legs, neck, back, chest.
Most often, whiteheads occur in adolescents, as well as in adults with combination and oily skin types. The mechanism of the appearance of these formations is simple: the pores are clogged with sebum, clogged with particles of dead epithelium and sweat.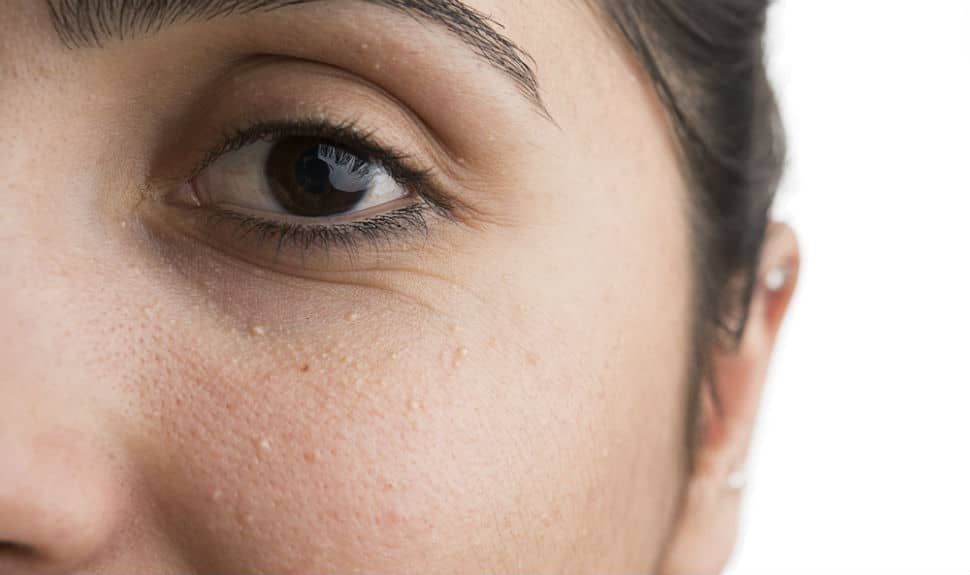 Such a cork is an ideal breeding ground for bacteria that actively multiply, as a result of which a knot forms under the skin within a short time.
Such a cork is an ideal breeding ground for bacteria that actively multiply, as a result of which a knot forms under the skin within a short time.
Whiteheads on the face: causes
Violations in the sebaceous glands occur due to:
- hormonal failures;
- lack of zinc in the body;
- increased sweating;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor skin care;
- use of unsuitable hygiene and cosmetic products;
- unbalanced diet - an excess of salty, sweet and fatty foods.
The appearance of white pimples is provoked by problems in the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract, helminthic invasion. The causes of subcutaneous nodes can also be skin diseases - seborrhea, demodicosis.
Prevention of whiteheads
Cleanse the skin twice a day with a lotion or gel cleanser according to the type of skin. The composition of the funds should include alpha hydroxy acids and salicylic acid. Every other day, dead skin particles should be removed using a soft scrub. Your skin needs to be moisturized daily.
Every other day, dead skin particles should be removed using a soft scrub. Your skin needs to be moisturized daily.
Steam baths lasting five to seven minutes are shown once a week. This procedure
- expands the pores;
- cleans them from accumulations of grease and dirt;
- removes dead cells;
- softens the skin.
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to flush out toxins from your body. Before going to bed, be sure to remove makeup so that the pores are not clogged. Avoid oil-based cosmetics.
The biggest mistake is trying to squeeze a pimple: this leads to the fact that the infection spreads to new areas of the skin. In addition, in the most unfavorable cases, blood poisoning can begin.
How is white pimples on the face treated?
Since purulent formations are located under a layer of skin, it is almost impossible to remove or cure them on your own. Contact the specialists of the clinic "Private practice".