Process of inducing labour
Inducing labour - NHS
An induced labour is one that's started artificially. Every year, 1 in 5 labours are induced in the UK.
Sometimes labour can be induced if your baby is overdue or there's any risk to you or your baby's health.
This risk could be if you have a health condition such as high blood pressure, for example, or your baby is not growing.
Induction will usually be planned in advance. You'll be able to discuss the advantages and disadvantages with your doctor and midwife, and find out why they think your labour should be induced.
It's your choice whether to have your labour induced or not.
If your pregnancy lasts longer than 42 weeks and you decide not to have your labour induced, you should be offered increased monitoring to check your baby's wellbeing.
Why you might be induced
- if you're overdue
- if your waters have broken
- if you or your baby have a health problem
If you're overdue
Induction will be offered if you do not go into labour naturally by 42 weeks, as there will be a higher risk of stillbirth or problems for the baby.
If your waters break early
If your waters break more than 24 hours before labour starts, there's an increased risk of infection to you and your baby.
If your waters break after 34 weeks, you'll have the choice of induction or expectant management.
Expectant management is when your healthcare professionals monitor your condition and your baby's wellbeing, and your pregnancy can progress naturally as long as it's safe for both of you.
Your midwife or doctor should discuss your options with you before you make a decision.
They should also let you know about the newborn (neonatal) special care hospital facilities in your area.
If your baby is born earlier than 37 weeks, they may be vulnerable to problems related to being premature.
If your waters break before 34 weeks, you'll only be offered induction if there are other factors that suggest it's the best thing for you and your baby.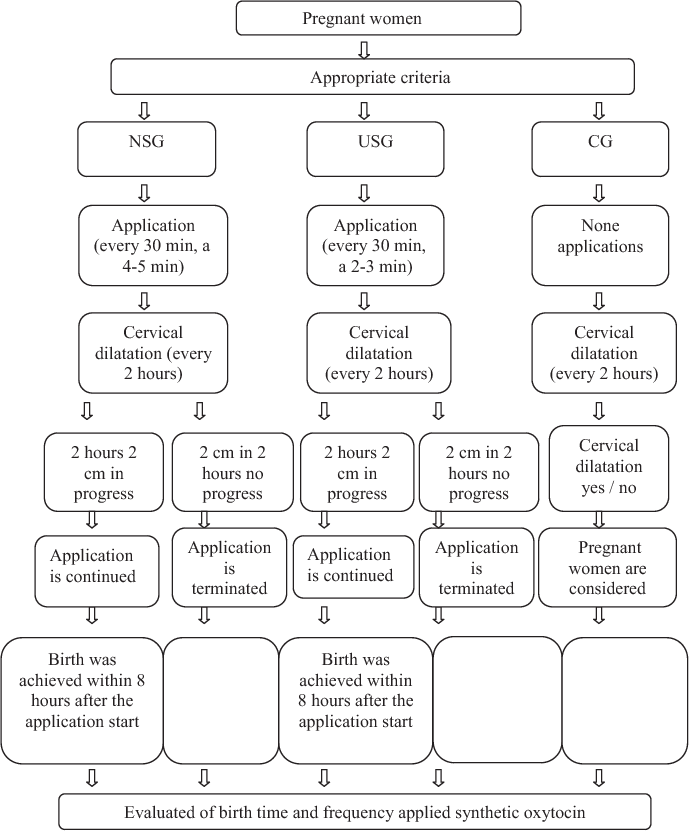
If you have a health condition or your baby is not thriving
You may be offered an induction if you have a condition that means it'll be safer to have your baby sooner, such as diabetes, high blood pressure or intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
If this is the case, your doctor and midwife will explain your options to you so you can decide whether or not to have your labour induced.
Membrane sweep
Before inducing labour, you'll be offered a membrane sweep, also known as a cervical sweep, to bring on labour.
To carry out a membrane sweep, your midwife or doctor sweeps their finger around your cervix during an internal examination.
This action should separate the membranes of the amniotic sac surrounding your baby from your cervix. This separation releases hormones (prostaglandins), which may start your labour.
Having a membrane sweep does not hurt, but expect some discomfort or slight bleeding afterwards.
If labour does not start after a membrane sweep, you'll be offered induction of labour.
Induction is always carried out in a hospital maternity unit. You'll be looked after by midwives and doctors will be available if you need their help.
How labour is induced
If you're being induced, you'll go into the hospital maternity unit.
Contractions can be started by inserting a tablet (pessary) or gel into your vagina.
Induction of labour may take a while, particularly if the cervix (the neck of the uterus) needs to be softened with pessaries or gels.
You will usually stay in the hospital maternity unit while you wait for it to work.
If you've had no contractions after 6 hours, you may be offered another tablet or gel.
If you have a controlled-release pessary inserted into your vagina, it can take 24 hours to work. If you are not having contractions after 24 hours, you may be offered another dose.
Sometimes a hormone drip is needed to speed up the labour. Once labour starts, it should proceed normally, but it can sometimes take 24 to 48 hours to get you into labour.
What induced labour feels like
Induced labour is usually more painful than labour that starts on its own, and you may want to ask for an epidural.
Your pain relief options during labour are not restricted by being induced. You should have access to all the pain relief options usually available in the maternity unit.
If you are induced you'll be more likely to have an assisted delivery, where forceps or ventouse suction are used to help the baby out.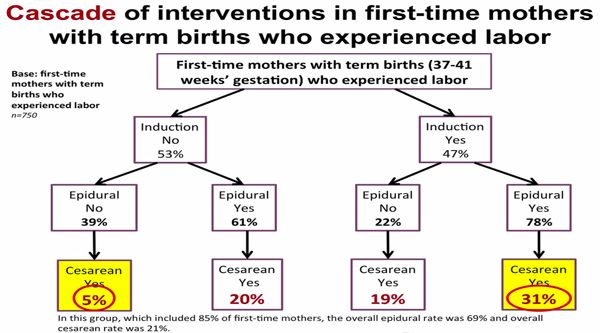
If induction of labour does not work
Induction is not always successful, and labour may not start.
Your obstetrician and midwife will assess your condition and your baby's wellbeing, and you may be offered another induction or a caesarean section.
Your midwife and doctor will discuss all your options with you.
Natural ways to start labour
There are no proven ways of starting your labour yourself at home.
You may have heard that certain things can trigger labour, such as herbal supplements and having sex, but there's no evidence that these work.
Other methods that are not supported by scientific evidence include acupuncture, homeopathy, hot baths, castor oil and enemas.
Having sex will not cause harm, but you should avoid having sex if your waters have broken as there's an increased risk of infection.
For more information on induction, you can read the NICE information for the public on induction of labour.
Video: When would I be induced and what's involved?
In this video, a midwife describes what an induction of labour is and what is involved.
Media last reviewed: 20 March 2020
Media review due: 20 March 2023
Labor induction - Mayo Clinic
Overview
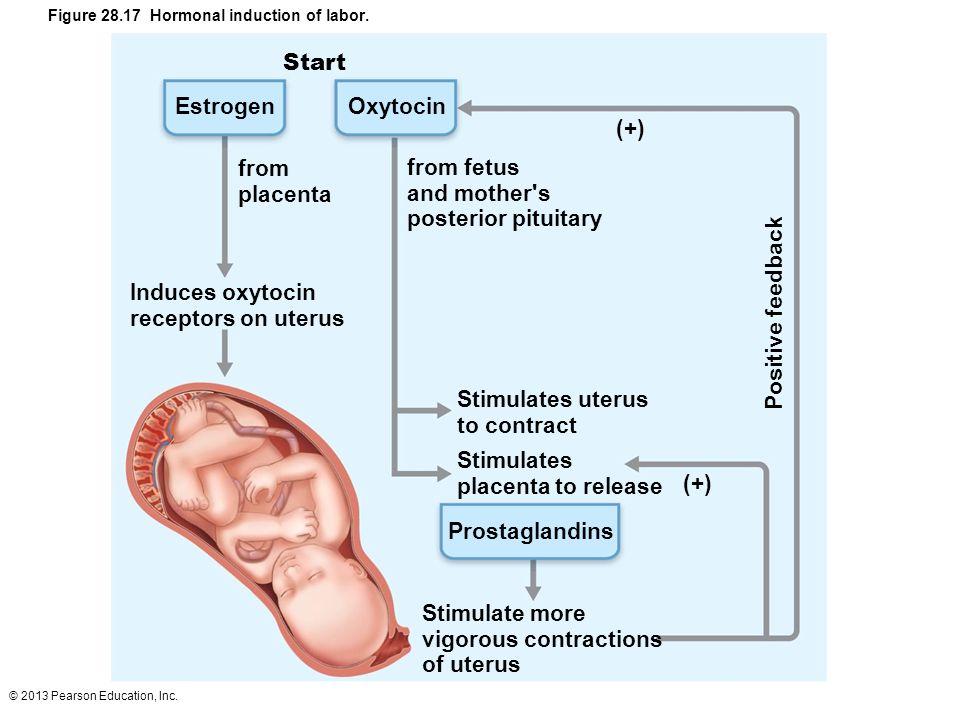
Labor induction — also known as inducing labor — is prompting the uterus to contract during pregnancy before labor begins on its own for a vaginal birth.
A health care provider might recommend inducing labor for various reasons, primarily when there's concern for the mother's or baby's health. An important factor in predicting whether an induction will succeed is how soft and expanded the cervix is (cervical ripening). The gestational age of the baby as confirmed by early, regular ultrasounds also is important.
The gestational age of the baby as confirmed by early, regular ultrasounds also is important.
If a health care provider recommends labor induction, it's typically because the benefits outweigh the risks. If you're pregnant, understanding why and how labor induction is done can help you prepare.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Why it's done
To determine if labor induction is necessary, a health care provider will likely evaluate several factors. These include the mother's health and the status of the cervix. They also include the baby's health, gestational age, weight, size and position in the uterus. Reasons to induce labor include:
- Nearing 1 to 2 weeks beyond the due date without labor starting (postterm pregnancy).
- When labor doesn't begin after the water breaks (prelabor rupture of membranes).
- An infection in the uterus (chorioamnionitis).
- When the baby's estimated weight is less than the 10th percentile for gestational age (fetal growth restriction).
- When there's not enough amniotic fluid surrounding the baby (oligohydramnios).
- Possibly when diabetes develops during pregnancy (gestational diabetes), or diabetes exists before pregnancy.
- Developing high blood pressure in combination with signs of damage to another organ system (preeclampsia) during pregnancy. Or having high blood pressure before pregnancy, developing it before 20 weeks of pregnancy (chronic high blood pressure) or developing the condition after 20 weeks of pregnancy (gestational hypertension).
- When the placenta peels away from the inner wall of the uterus before delivery — either partially or completely (placental abruption).
- Having certain medical conditions. These include heart, lung or kidney disease and obesity.
Elective labor induction is the starting of labor for convenience when there's no medical need. It can be useful for women who live far from the hospital or birthing center or who have a history of fast deliveries.
It can be useful for women who live far from the hospital or birthing center or who have a history of fast deliveries.
A scheduled induction might help avoid delivery without help. In such cases, a health care provider will confirm that the baby's gestational age is at least 39 weeks or older before induction to reduce the risk of health problems for the baby.
As a result of recent studies, women with low-risk pregnancies are being offered labor induction at 39 to 40 weeks. Research shows that inducing labor at this time reduces several risks, including having a stillbirth, having a large baby and developing high blood pressure as the pregnancy goes on. It's important that women and their providers share in decisions to induce labor at 39 to 40 weeks.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Risks
Uterine incisions used during C-sections
Uterine incisions used during C-sections
A C-section includes an abdominal incision and a uterine incision.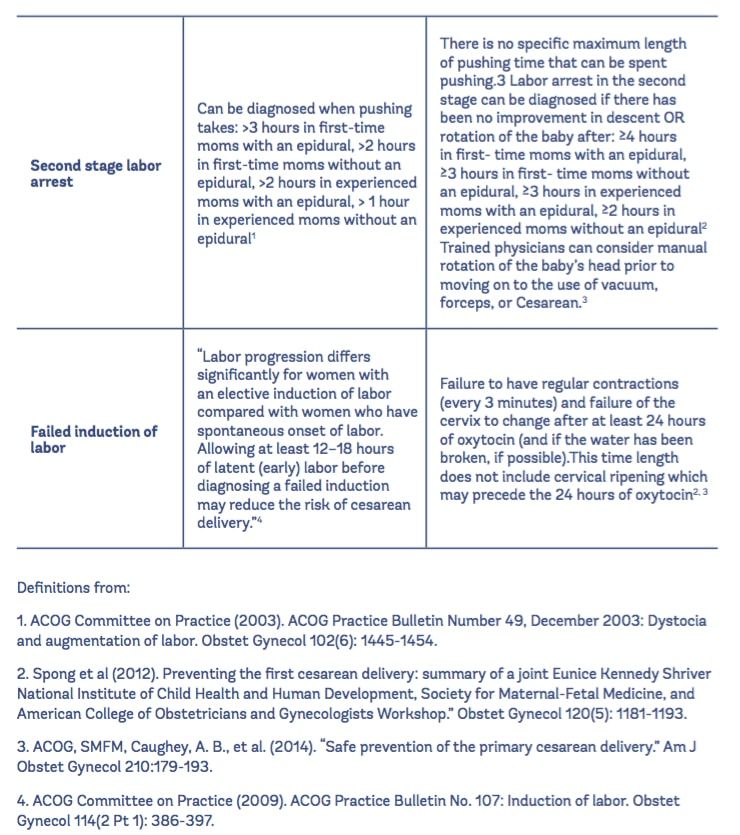 After the abdominal incision, the health care provider will make an incision in the uterus. Low transverse incisions are the most common (top left).
After the abdominal incision, the health care provider will make an incision in the uterus. Low transverse incisions are the most common (top left).
Labor induction carries various risks, including:
- Failed induction. An induction might be considered failed if the methods used don't result in a vaginal delivery after 24 or more hours. In such cases, a C-section might be necessary.
- Low fetal heart rate. The medications used to induce labor — oxytocin or a prostaglandin — might cause the uterus to contract too much, which can lessen the baby's oxygen supply and lower the baby's heart rate.
- Infection. Some methods of labor induction, such as rupturing the membranes, might increase the risk of infection for both mother and baby. The longer the time between membrane rupture and labor, the higher the risk of an infection.
-
Uterine rupture. This is a rare but serious complication in which the uterus tears along the scar line from a prior C-section or major uterine surgery.
 Rarely, uterine rupture can also occur in women who have not had previous uterine surgery.
Rarely, uterine rupture can also occur in women who have not had previous uterine surgery.An emergency C-section is needed to prevent life-threatening complications. The uterus might need to be removed.
- Bleeding after delivery. Labor induction increases the risk that the uterine muscles won't properly contract after giving birth, which can lead to serious bleeding after delivery.
Labor induction isn't for everyone. It might not be an option if:
- You've had a C-section with a classical incision or major uterine surgery
- The placenta is blocking the cervix (placenta previa)
- Your baby is lying buttocks first (breech) or sideways (transverse lie)
- You have an active genital herpes infection
- The umbilical cord slips into the vagina before delivery (umbilical cord prolapse)
If you have had a C-section and have labor induced, your health care provider is likely to avoid certain medications to reduce the risk of uterine rupture.
How you prepare
Labor induction is typically done in a hospital or birthing center. That's because mother and baby can be monitored there, and labor and delivery services are readily available.
What you can expect
During the procedure
There are various ways of inducing labor. Depending on the circumstances, the health care provider might use one of the following ways or a combination of them. The provider might:
-
Ripen the cervix. Sometimes prostaglandins, versions of chemicals the body naturally produces, are placed inside the vagina or taken by mouth to thin or soften (ripen) the cervix. After prostaglandin use, the contractions and the baby's heart rate are monitored.
In other cases, a small tube (catheter) with an inflatable balloon on the end is inserted into the cervix. Filling the balloon with saline and resting it against the inside of the cervix helps ripen the cervix.
- Sweep the membranes of the amniotic sac.
 With this technique, also known as stripping the membranes, the health care provider sweeps a gloved finger over the covering of the amniotic sac near the fetus. This separates the sac from the cervix and the lower uterine wall, which might help start labor.
With this technique, also known as stripping the membranes, the health care provider sweeps a gloved finger over the covering of the amniotic sac near the fetus. This separates the sac from the cervix and the lower uterine wall, which might help start labor. -
Rupture the amniotic sac. With this technique, also known as an amniotomy, the health care provider makes a small opening in the amniotic sac. The hole causes the water to break, which might help labor go forward.
An amniotomy is done only if the cervix is partially dilated and thinned, and the baby's head is deep in the pelvis. The baby's heart rate is monitored before and after the procedure.
- Inject a medication into a vein. In the hospital, a health care provider might inject a version of oxytocin (Pitocin) — a hormone that causes the uterus to contract — into a vein. Oxytocin is more effective at speeding up labor that has already begun than it is as at cervical ripening.
 The provider monitors contractions and the baby's heart rate.
The provider monitors contractions and the baby's heart rate.
How long it takes for labor to start depends on how ripe the cervix is when the induction starts, the induction techniques used and how the body responds to them. It can take minutes to hours.
After the procedure
In most cases, labor induction leads to a vaginal birth. A failed induction, one in which the procedure doesn't lead to a vaginal birth, might require another induction or a C-section.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Products & Services
Induction of labor or induction of labor
The purpose of this informational material is to familiarize the patient with the induction of labor procedure and to provide information on how and why it is performed.
In most cases, labor begins between the 37th and 42nd weeks of pregnancy. Such births are called spontaneous. If drugs or medical devices are used before the onset of spontaneous labor, then the terms "stimulated" or "induced" labor are used in this case.
Labor should be induced when further pregnancy is for some reason unsafe for the mother or baby and it is not possible to wait for spontaneous labor to begin.
The purpose of stimulation is to start labor by stimulating uterine contractions.
When inducing labor, the patient must be in the hospital so that both mother and baby can be closely monitored.
Labor induction methods
The choice of labor induction method depends on the maturity of the cervix of the patient, which is assessed using the Bishop scale (when viewed through the vagina, the position of the cervix, the degree of its dilatation, consistency, length, and the position of the presenting part of the fetus in the pelvic area are assessed). Also important is the medical history (medical history) of the patient, for example, a past caesarean section or operations on the uterus.
The following methods are used to induce (stimulate) labor:
- Oral misoprostol is a drug that is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandins found in the body.
 It prepares the body for childbirth, under its action the cervix becomes softer and begins to open.
It prepares the body for childbirth, under its action the cervix becomes softer and begins to open. - Balloon Catheter - A small tube is placed in the cervix and the balloon attached to the end is filled with fluid to apply mechanical pressure to the cervix. When using this method, the cervix becomes softer and begins to open. The balloon catheter is kept inside until it spontaneously exits or until the next gynecological examination.
- Amniotomy or opening of the fetal bladder - in this case, during a gynecological examination, when the cervix has already dilated sufficiently, the fetal bladder is artificially opened. When the amniotic fluid breaks, spontaneous uterine contractions will begin, or intravenous medication may be used to stimulate them.
- Intravenously injected synthetic oxytocin - acts similarly to the hormone of the same name produced in the body. The drug is given by intravenous infusion when the cervix has already dilated (to support uterine contractions).
 The dose of the drug can be increased as needed to achieve regular uterine contractions.
The dose of the drug can be increased as needed to achieve regular uterine contractions.
When is it necessary to induce labor?
Labor induction is recommended when the benefits outweigh the risks.
Induction of labor may be indicated in the following cases:
- The patient has a comorbid condition complicating pregnancy (eg, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, preeclampsia, or some other condition).
- The duration of pregnancy is already exceeding the norm - the probability of intrauterine death of the fetus increases after the 42nd week of pregnancy.
- Fetal problems, eg, problems with fetal development, abnormal amount of amniotic fluid, changes in fetal condition, various fetal disorders.
- If the amniotic fluid has broken and uterine contractions have not started within the next 24 hours, there is an increased risk of inflammation in both the mother and the fetus. This indication does not apply in case of preterm labor, when preparation of the baby's lungs with a special medicine is necessary before delivery.

- Intrauterine fetal death.
What are the risks associated with labor induction?
Labor induction is not usually associated with significant complications.
Occasionally, after receiving misoprostol, a patient may develop fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and too frequent uterine contractions (tachysystole). In case of too frequent contractions to relax the uterus, the patient is injected intravenously relaxing muscles uterus medicine. It is not safe to use misoprostol if you have had a previous caesarean section as there is a risk of rupture of the uterine scar.
The use of a balloon catheter increases the risk of inflammation inside the uterus.
When using oxytocin, the patient may rarely experience a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), hyponatremia (lack of sodium in the blood), which may result in headache, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, depression strength and sleepiness.
Induction of labor compared with spontaneous labor increases the risk of prolonged labor, the need for instrumental intervention
(use of vacuum or forceps), postpartum hemorrhage, uterine rupture, the onset of too frequent uterine contractions and the associated deterioration of the fetus, prolapse umbilical cord, as well as premature detachment of the placenta.
If induction of labor is not successful
The time frame for induction of labor may vary from patient to patient, on average labor begins within 24-72 hours. Sometimes more than one method is required.
The methods used do not always work on different patients in the same way and quickly. If the cervix does not dilate as a result of induction of labor, your doctor will tell you about your next options (which may include inducing labor later, using a different method, or delivering by caesarean section).
ITK833
This informational material was approved by the Women's Clinic on 01/01/2022.
Labor induction at home and in hospital
What is the problem?
Based on the results of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), we wanted to find out whether women preferred to return home or stay in the facility while waiting for labor after induction of labor in a medical facility. In addition, it needs to be established whether this has an impact on clinical outcomes for both women and their infants.
Why is this important?
Induction of labor at the end of pregnancy involves the artificial induction of labor to initiate the process of labor. There are maternal and infant health risks associated with labor induction, but sometimes the risks of prolonged pregnancy far outweigh them.
However, induction of labor can be a very difficult challenge for women, as they may feel they are deprived of comfort, support, and control over the process. The use of home induction of labor can improve the conditions of labor for women, reduce length of hospital stay, and reduce overall costs. The safety of both mother and child is a critical factor to consider. Only certain forms of induction are suitable for home induction (stimulation) of labor, such as vaginal prostaglandins or balloon/Foley catheters.
The safety of both mother and child is a critical factor to consider. Only certain forms of induction are suitable for home induction (stimulation) of labor, such as vaginal prostaglandins or balloon/Foley catheters.
What evidence did we find?
We searched for evidence on 31 January 2020 and found seven RCTs, six of which provided data on 1610 women and their infants. All of these studies were conducted in high-income countries. The certainty of the evidence was generally very low, mainly due to the limited number of trials, some of which were small, and the lack of clarity on study design.
Labor induction was performed in all trial participants at initial hospital follow-up. Women in the home labor induction group could then go home to wait for active labor to begin, or for a set period of time. Women belonging to the group giving birth in a medical facility remained in the hospital.
Two trials were found involving 1022 women and their infants who were given vaginal prostaglandin (PGE2) to induce labor. The difference in women's satisfaction with waiting to give birth at home or in hospital may be minimal or non-existent, although women were generally more satisfied with waiting at home. Outcomes for women: There may not be clear differences in the number of women with spontaneous vaginal delivery, or with uterine hyperstimulation, or in the number of deliveries by caesarean section. Infant outcomes: There may be similar rates of infection and admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). At home, costs may be less.
The difference in women's satisfaction with waiting to give birth at home or in hospital may be minimal or non-existent, although women were generally more satisfied with waiting at home. Outcomes for women: There may not be clear differences in the number of women with spontaneous vaginal delivery, or with uterine hyperstimulation, or in the number of deliveries by caesarean section. Infant outcomes: There may be similar rates of infection and admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). At home, costs may be less.
For labor induction with controlled vaginal release prostaglandin (PGE2), we found only one study involving 299 women and their infants, but the results probably indicate little or no difference.
On the use of a balloon catheter or Foley catheter for induction, we found three studies providing data on 289 women and their infants. Two studies reported on women's satisfaction and showed a tendency to prefer home environments, but the mode of data collection was unclear.