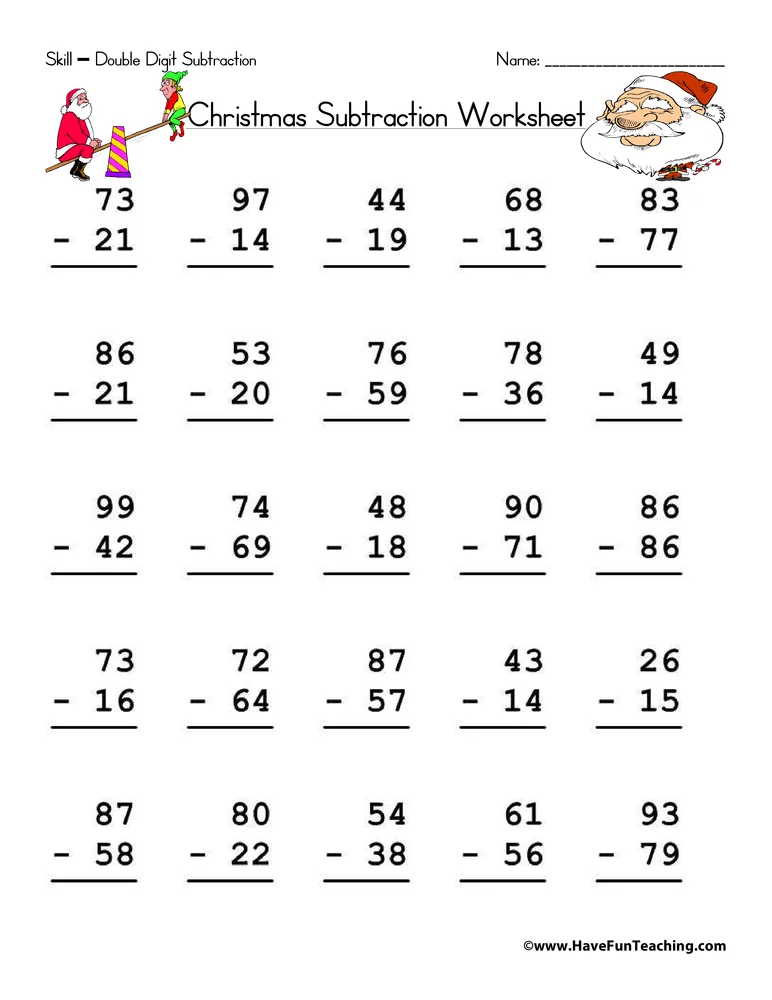
How to teach a child double digit subtraction
How to Teach Those Tricky 2 Digit Subtraction Strategies
As part of common core, we give students many strategies to help them find the answer to 2 digit subtraction problems. I like how these 2 digit subtraction strategies give students choices on how they can solve a problem. They help build meaning and number sense within the operation.
But here’s the thing… They can be a lot! Sometimes our curriculum goes too fast for students and they don’t quite master them and end up confused. That is why I am sharing the way I teach these strategies and the activities I give to my students to help them get the practice they need.
Before we get started, for students to truly be successful with these strategies they need a solid foundation with math facts. If students have to take time to recall or figure out a math fact, it can get them confused for what they are doing with the 2 digit subtraction strategy.
So no worries, I’ve got something special for you. I’m sharing my 7 Steps to Ensure Math Fact Fluency in a free workbook for 1st and 2nd grade teachers. Download your free copy here.
Okay, let’s get started with the 2 digit subtraction strategies I teach in my classroom.
2 digit subtraction strategies can be tricky for students, but there are little tricks you can do to help students build number sense and understanding when it comes to these 2 digit subtraction strategies.
Hundreds Chart
First, we have students working with a hundred’s chart for them to solve 2 digit subtraction problems. For this strategy, I really need to make sure that students understand the patterns with the hundreds chart.
I want my students to know that if they go up on the hundred’s chart, they are subtracting by tens. They need to know if they go left on the hundred’s chart, they are subtracting by by ones.
This 2 digit subtraction strategy helps students use patterns to solve them math problems.
When I have my students look at a 2 digit subtraction problem like 72-35, I first ask what number we start with on the hundred’s chart.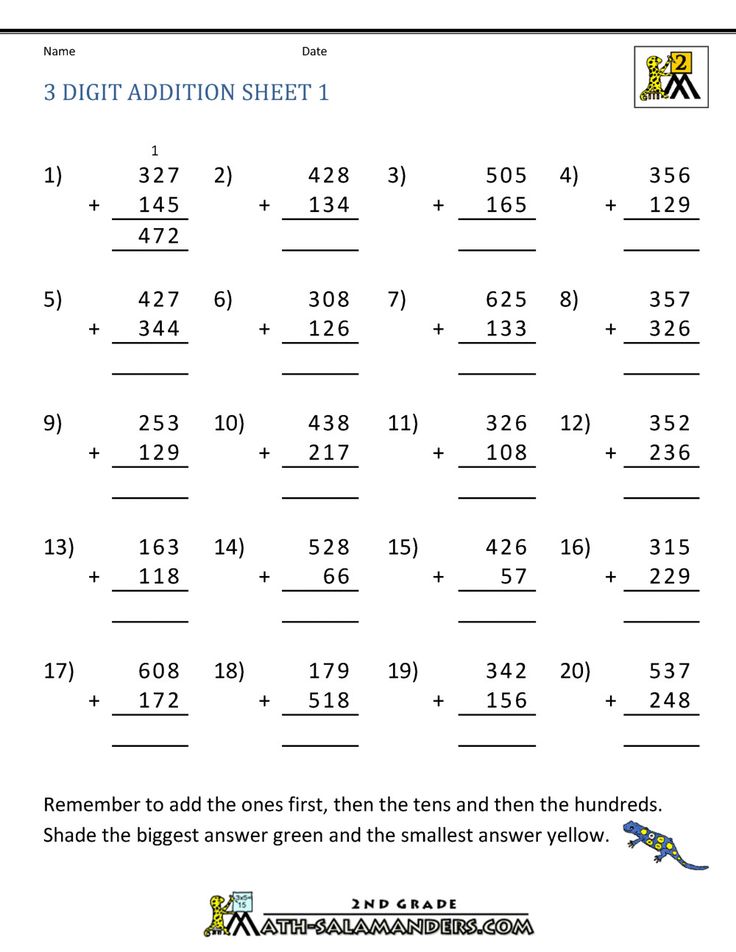 They need to know with subtraction, we have to start with the bigger number.
They need to know with subtraction, we have to start with the bigger number.
Then I ask how many tens are in 35. Three tens. So we go up three rows on the hundreds chart. We still need to take away the ones in 35. How many ones are in 35? There are 5 ones. So we go left 5 ones. We land on 37 so that is our answer.
I have students get lots of practice with this. It’s important that they have plenty of space on clean hundreds charts to not get confused. So I have them work on hundred chart worksheets and fun scoot activities. They can be used as centers or whole group activities. Find these Subtraction Hundreds Chart Activities here.
Open Number Line
With this 2 digit subtraction strategy, students make jumps back on a number line. They can also count on to subtract on a number line. This can be confusing to students at first, but if they have a good foundation with fact families, it makes sense that they can use addition to subtract. To learn more about fact families, read this blog post: 3 Reasons You Need To Teach Fact Families
The open number line 2 digit subtraction strategy can be extra tricky for students.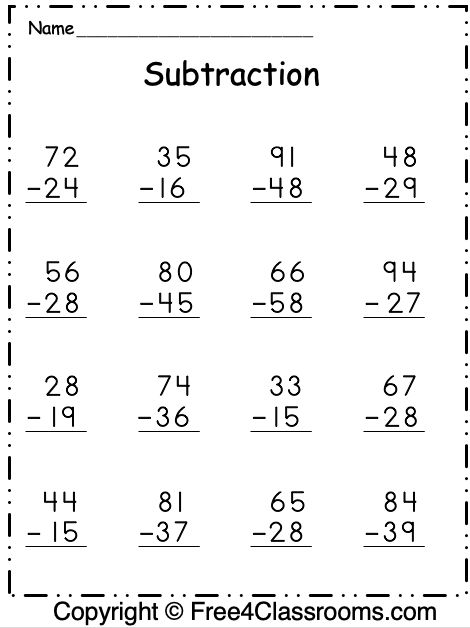 That is why I give my students lots of practice with this 2 digit subtraction strategy.
That is why I give my students lots of practice with this 2 digit subtraction strategy.
For teaching this strategy, I draw a number line on the board and write an equation. Let’s use the example of 63-24. I show my students that if we are counting back on the number line, I will start by putting 63 on the right side.
Then I ask how many tens are in 24. There are 2 tens so I will make two jumps back and label them.
Next I ask how many ones are in 24. There are 4 ones so I will make 4 jumps back and label them. I landed on 39 so that is the answer.
Students really need a lot of practice with this strategy. I find it helpful when I give them enough space on a number line and remind them to leave spaces in between their numbers so they can actually read their writing.
I have my students practice with worksheets and scoot activities. Find the 2 Digit Subtraction Number Line Activities resource I use here.
Break Apart
This 2 digit subtraction strategy is often a favorite with my students. In this strategy, students break the number being subtracted into tens and ones. Then break apart the ones another time if needed to get down to the next tens to make it easy.
In this strategy, students break the number being subtracted into tens and ones. Then break apart the ones another time if needed to get down to the next tens to make it easy.
The break apart strategy is a student favorite in my classroom!
This takes some practice. I just start by having my students practice break apart the ones so that they can get to the next tens. For example, I may show them if we have 45-9, I’m going to break apart the 9 into 4 and 5. Then I can think about it as 45-5=40 and 40-4=36.
Then I’ll add the tens into it, like 45-19. They would just take away a ten first so it would look like 45-10=35. 35-5=30. 30-4=26.
I like to provide my students with worksheets that have boxes that help them think about breaking apart the number. Find the worksheets and other activities I give my students here.
Tens and Ones Chart
This strategy is the regular 2 digit subtraction algorithm. For students to truly understand the meaning behind the steps, we use models, draw pictures, and then just use numbers.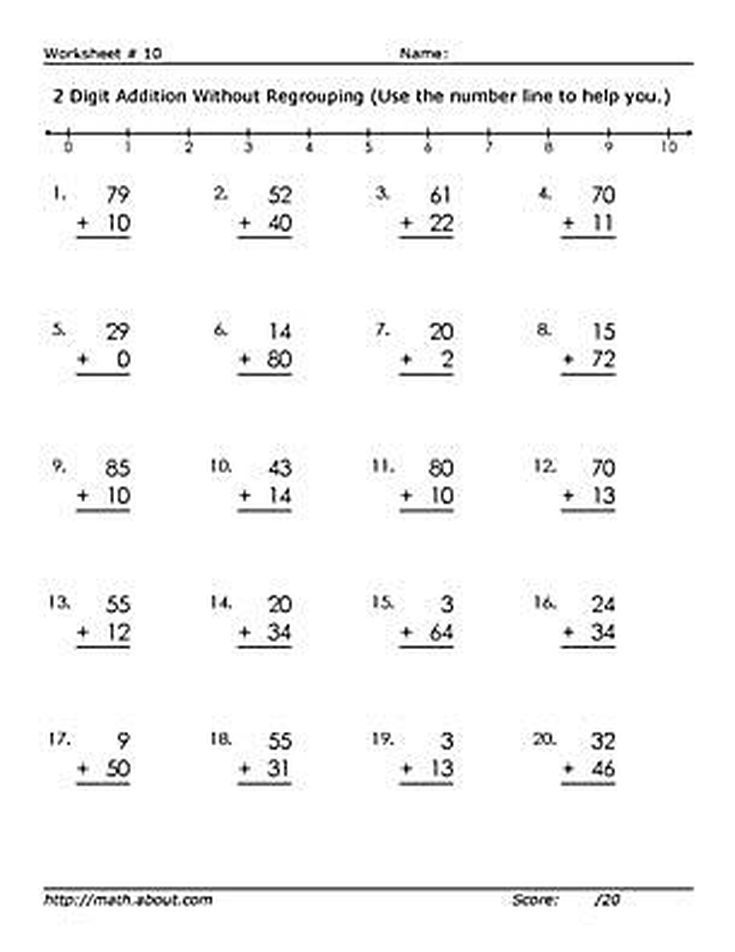
When it comes to 2 digit subtraction with regrouping, students needs lots of practice with models, pictures, and using tens and ones charts.
I like to show my students when we need to regroup. I often say something like, “If I have 5 ones, can I take away 8? Nope, I need to regroup.”
Find the worksheets and activities I use to help students answer 2 digit subtraction with regrouping here.
I hope that you have found many tips in helping students master these 2 digit subtraction strategies. It comes by teaching to build number sense and giving students a lot of practice. Find all of my 2 digit addition and subtraction strategies all in one bundle here.
For more on how to teach 2 digit addition strategies, read this blog post: 2 Digit Addition Strategies That Work
For extra help for getting students to fluently add and subtract 2 digit numbers, they need to be fluent in math facts 1-20. Download my free workbook for help: 7 Steps to Ensure Math Fact Fluency.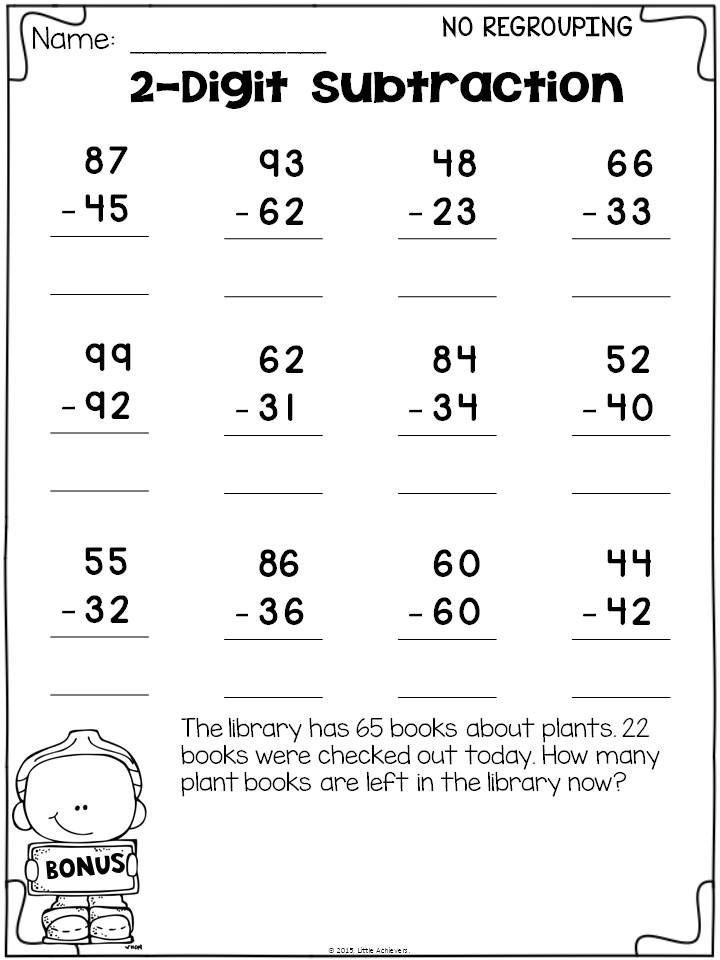
Download it here.
4 Methods for Teaching Double Digit Subtraction Without Regrouping
Second grade is a very important year when it comes to fact fluency. This is the time when they are learning to become familiar with two-digit addition and subtraction facts. In my previous post, I shared four addition strategies that I focus on Today, I’ll be sharing four subtraction strategies used for introducing 2 digit subtraction without regrouping.
Just like introducing 2-digit addition, I expose my students to multiple strategies and models they can use to solve subtraction problems. We spend lots of time focusing on WHY something is done before we teach HOW something is done. Giving students choice in their learning by providing them with multiple ways to solve problems is helping them succeed. Flexibility is key because every child learns differently.
The Texas TEK for two-digit subtraction states:
2.4B: Add up to four two-digit numbers and subtract two-digit numbers using mental strategies and algorithms based on place value and properties of operations.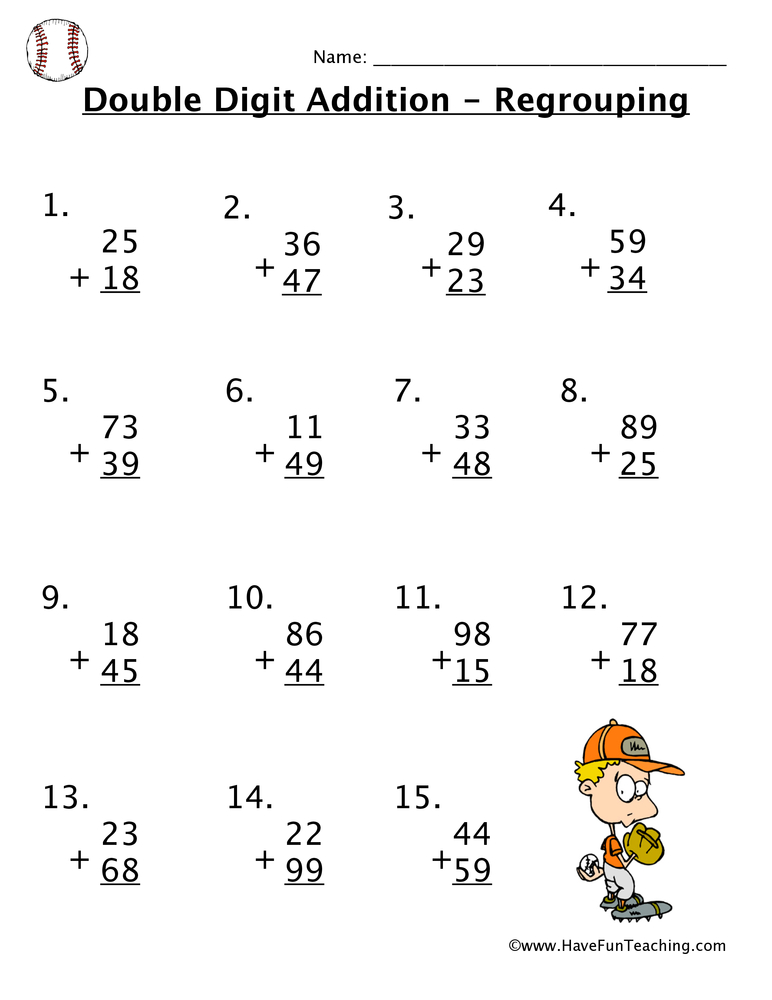
The Common Core Standard for two-digit subtraction states:
2.NBT.B.5: Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
Note that the bolded text above says nothing about the standard algorithm we learned growing up years ago. Keep reading to learn about four subtraction strategies I introduce and teach my students when focusing on double digit subtraction without regrouping. Also, note that these strategies will not focus on regrouping. Students need a strong understanding of place value AND simple subtraction before moving onto that task.
2 Digit Subtraction Without Regrouping Anchor ChartAt the beginning of our subtraction unit, I always make this subtraction without regrouping anchor chart. As we learn a new strategy, such as double digit subtraction without regrouping, it is added to our whole group chart.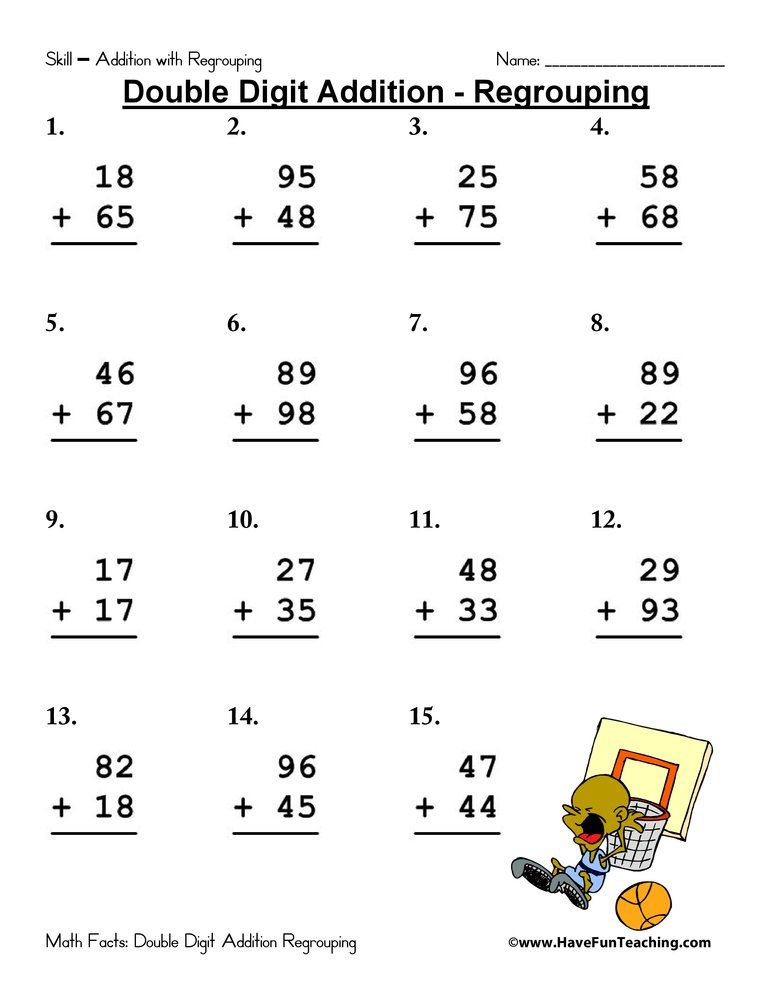 My students keep a matching copy of this in their math journals to use later on when they need extra support.
My students keep a matching copy of this in their math journals to use later on when they need extra support.
Before we get started, I want you to make sure you are familiar with the vocabulary that will be used.
Throughout this post, you will hear the terms minuend, subtrahend, and difference. In the problem 67-33=34, 67 is the minuend, 33 is the subtrahend, and 34 is the difference.
Base Ten Model for Double Digit Subtraction without RegroupingWhen introducing 2 digit subtraction without regrouping, I always start with the base ten models. In addition to using base ten blocks, I also teach them to draw the blocks out on paper. This is because students won’t always have access to manipulatives, but they will have a pencil and paper.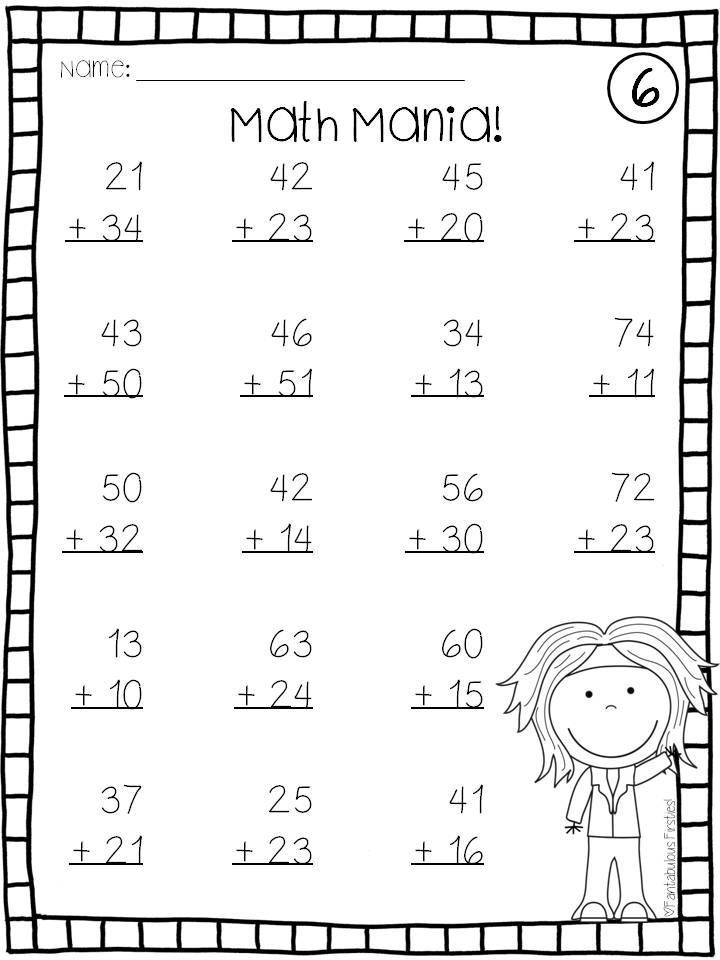 I always give my students a place value mat placed inside a plastic sleeve. This allows students to also write or draw using a dry erase marker and they can be used over and over again. Here is how this strategy works using the example 59-15=44
I always give my students a place value mat placed inside a plastic sleeve. This allows students to also write or draw using a dry erase marker and they can be used over and over again. Here is how this strategy works using the example 59-15=44
- Build/draw out the minuend (59) with base ten blocks.
- Take away the amount of the subtrahend (15). Remove 5 ones blocks and 1 tens block.
- Count the remaining blocks left and solve for the difference.
For students to draw out this strategy it works the same way. We draw “sticks” to represent the tens and “dots” to represent the ones. I also teach them to take away or cross out the ones first followed by the tens. This will help when regrouping is introduced later on.
Expanded Form Method 2 Digit Subtraction without RegroupingThe second subtraction strategy that I introduce is the Expanded Form Method. Your students need a strong understanding of place value and expanding numbers for them to be successful using this strategy.
The minuend and subtrahend of the subtraction problem will be expanded and lined up vertically. I always have my students circle the minus sign to help them remember to subtract rather than add.
Here is how it works using the example 86-43.
Expand the minuend. >>> 80+6
Expand the subtrahend and write it vertically underneath the minuend. >>> 40+3
Circle the minus sign.
Subtract and solve vertically based on place value starting with the ones, then the tens.
Solve for the difference. >>> 40+3=43
Number Line Model for Double Digit Subtraction without RegroupingThe number line model subtraction strategy tends to be more challenging for students. They need a strong knowledge of mental math and skip counting for this method to come easily for them.
I often use skip counting as a warm-up for our math block. Example: Have students stand in a circle. Choose a student to go first and skip count by 10’s starting with the number 35. The first person says 35, the next says 45, and so on. For the ones that struggle I will often let them hold a hundred chart in their hand to help. You can have them do this counting forwards or backward.
The first person says 35, the next says 45, and so on. For the ones that struggle I will often let them hold a hundred chart in their hand to help. You can have them do this counting forwards or backward.
Another way to squeeze in counting practice is to have them chant while they are lining up. Example: Class, let’s skip count by 2’s as we line up. We will start with the number 40 and see how high we can count. When everyone is lined up correctly, we will stop. The number line strategy focuses on students “hopping” and “skipping” backward on a number line to solve for the difference of a given problem. I call the 10’s hops, and the 1’s skips.
I’ve also found it helpful for students to write out their steps before solving the problem.
Here is how it works using the example 57-26.
- Draw an open number line.
- Write the minuend at the end of the number line. >>> 57
- Determine how many hops and skips you need to take.
- The subtrahend is 27.
 You need to draw 2 large hops and 6 small skips.
You need to draw 2 large hops and 6 small skips. - Skip count backward to solve for the difference.
- 57-26=31
This traditional method is probably how you learned two-digit subtraction growing up and is what our children’s parents are most familiar with.
For this strategy, students need to line up both numbers vertically underneath each other. The minuhend (larger number) goes on top and the subtrahend (smaller number) goes on the bottom. They will subtract the ones place first and then the tens place to solve for the difference.
One tip that can be helpful when first learning this strategy is to have students use a highlighter to highlight the ones place or have them circle the numbers in the ones place first. This helps them visualize where they need to start first. This concept can be more complicated for them than we realize because they are trained to read and write from left to right.
Reviewing Double Digit Subtraction Strategies
At the end of our unit, we always make these Subtraction Strategy Flipbooks to help us review. They can keep these to use later as a reference when needed.
Whew! That may seem like a lot of information to process.
We all learn concepts in different ways and the subtraction strategies that I have shared are what I have found to be beneficial for my own students. There is no right or wrong strategy when it comes to solving two-digit subtraction problems.
Allow your students to choose the method that works best for them and have them stick with it. Once they have found a method that they are comfortable with, it is important to provide them with multiple opportunities to practice.
Below are some resources that you may find helpful.
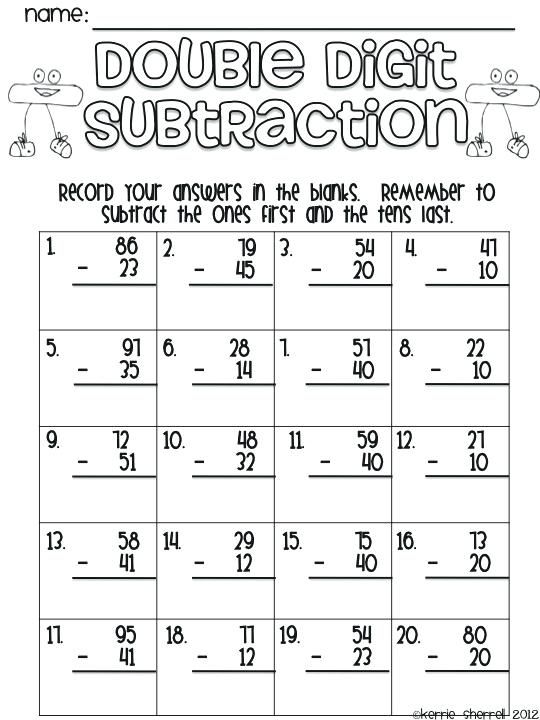
Addition and Subtraction without Regrouping Unit This unit features 10 days worth of hands-on and engaging activities for your students to practice all the subtraction strategies for double digit subtraction without regrouping that I have listed above.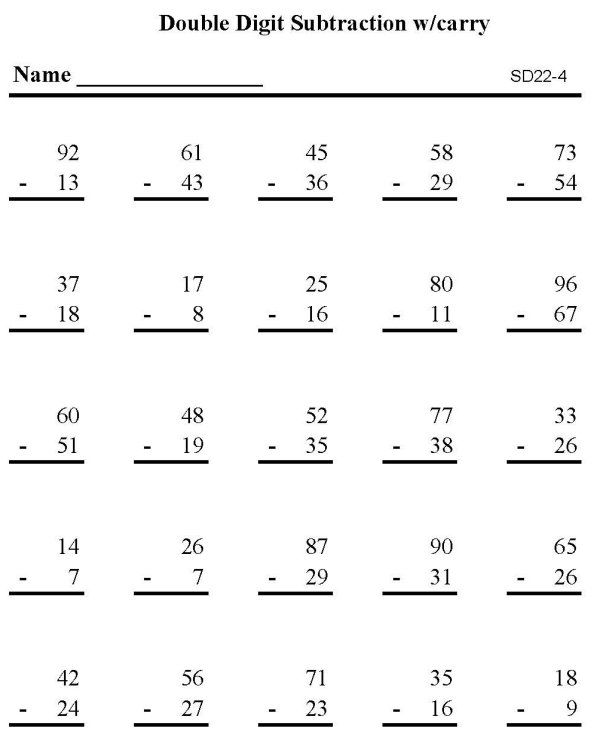 There are daily addition and subtraction word problems, interactive notebook prompts, subtraction without regrouping games and so much more.
There are daily addition and subtraction word problems, interactive notebook prompts, subtraction without regrouping games and so much more.
Want to save these subtraction strategies ideas for later? Pin the image below!
5 Free Festive Winter Math Activities
The holiday season is my absolute favorite time of year! I love the magic of the holidays and making memories with my family, friends, and
Read More »
10 Undeniable Reasons Why Teachers Are The Best: Celebrating 10 Years of Saddle Up For 2nd Grade
If you would have asked me 10 or even 20 years ago what I would be doing today, I would not have said a curriculum
Read More »
How to Teach Comparing Numbers With Ease Using The Dot Method Strategy
The skill of comparing numbers requires a deep understanding of place value. Students develop this understanding over time as they are exposed to multiple representations
Students develop this understanding over time as they are exposed to multiple representations
Read More »
How to explain subtraction and addition of two-digit numbers to a child
Location map
Contacts
Home
Blog
Teaching a child to subtract and add is a complex, multi-stage process, starting with the study of single-digit numbers and turning into two-digit ones, with a gradual study of the moments when the transition occurs through a dozen. To teach a child to quickly count two-digit numbers, you should go through each stage sequentially. The use of different learning methods, mainly in a playful way, makes it possible to make the whole process interesting for the baby, which will positively affect the results.
Subtraction of two-digit numbers with jump through the digit
It is easier to explain to a child the subtraction of two-digit numbers using game methods.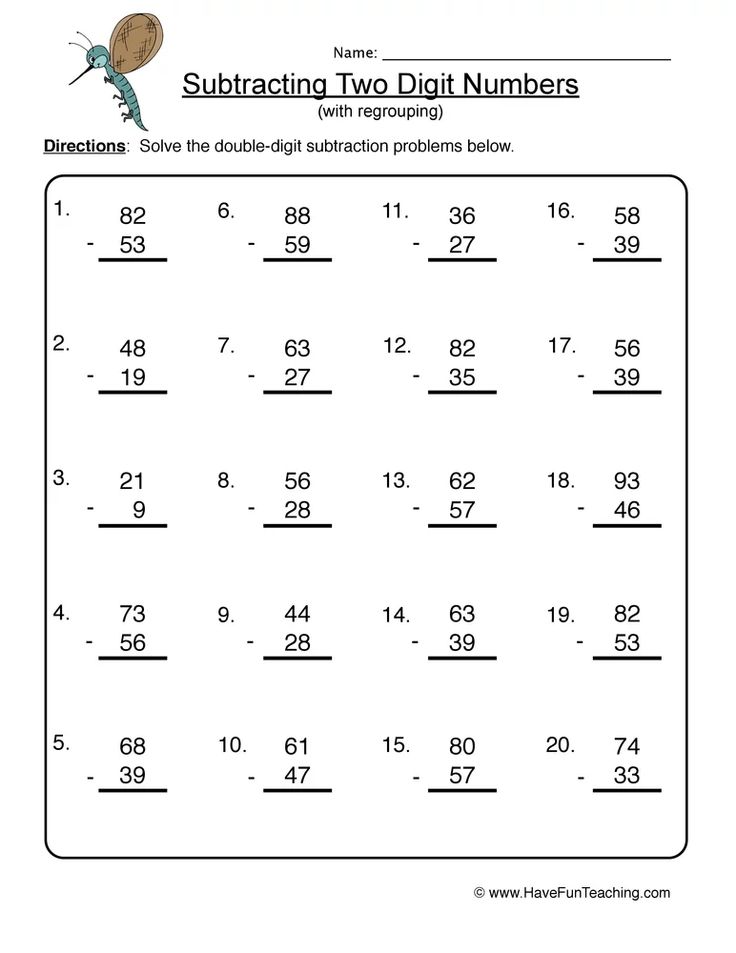 This will allow you to focus on the process and improve the assimilation of the material covered. You should not immediately start with large numbers, it is better to start the first steps with the minimum numbers, gradually increasing.
This will allow you to focus on the process and improve the assimilation of the material covered. You should not immediately start with large numbers, it is better to start the first steps with the minimum numbers, gradually increasing.
Such a moment is important - the child will not be able to immediately count in his mind, even when it comes to small numbers. It is better to use a piece of paper, parts of the designer, a computer or other additional means where the baby can make the required notes. Attention should be paid to the study of the order of formation of tens, up to a hundred. This will help when learning addition and subtraction with the transition through the digit, and not just within one ten. Having mastered the count within ten, you can proceed to the study of more complex actions, using one of the methods or combining them.
Dividing numbers when subtracting
When subtracting a single-digit number from a two-digit number with a transition through the discharge, division can be used. Explain to the child that it will be easier to subtract from a whole ten, and it is enough to divide a single-digit number in such a way that by subtracting one of its parts to get 10, and only then subtract the second part. As a result, the child will quickly master such an account, learning how to correctly divide numbers and get the final result.
Explain to the child that it will be easier to subtract from a whole ten, and it is enough to divide a single-digit number in such a way that by subtracting one of its parts to get 10, and only then subtract the second part. As a result, the child will quickly master such an account, learning how to correctly divide numbers and get the final result.
This method is well suited in cases where a count of up to 10 has been mastered, and the baby is also familiar with numbers up to at least 20. Classes should be conducted in a playful way, using consumables or special computer games.
Using geometric shapes to visualize numbers
A common option is when tens are indicated by triangles, and units by dots. It is enough to explain to the child the meaning of the figures and give a few examples. After that, you can start training, starting with simple tasks, using numbers up to 20, gradually complicating them.
For the entry-level, this is a suitable option that allows you to carry out calculations quickly and clearly. However, difficulty can arise when an additional ten should be subtracted when subtracting (for example, 54-35 \u003d 19). It is important to explain the subtlety of such a moment to the baby. Subtracting two-digit numbers in this way is better, avoiding such situations, or regularly showing examples to the child for better development.
However, difficulty can arise when an additional ten should be subtracted when subtracting (for example, 54-35 \u003d 19). It is important to explain the subtlety of such a moment to the baby. Subtracting two-digit numbers in this way is better, avoiding such situations, or regularly showing examples to the child for better development.
Lego Subtraction
To apply this method, you can use Lego Duplo, designed for this purpose, or ordinary designer cubes, having previously numbered them. With their help, you can solve complex problems, including those in which there is a transition through a dozen.
It is enough to display the required numbers using the appropriate numbers (eg 25-19). In order to explain the subtlety more clearly to the child, it is enough to divide them into smaller ones (10,10, 5 and 10, 5, 4). The child easily learns that 10-10 = 0, and will be able to remove the extra tens. The remaining equation is further solved easily (10 and 5 - 5 and 4). It remains for the child to count 10-4, having received the final result.
It remains for the child to count 10-4, having received the final result.
Two-digit addition
It is usually easier to explain to a child the addition of two-digit numbers than the subtraction, even in cases where there is an addition of an additional ten after addition. There are enough ways to learn to choose the most suitable for your baby. Important - the lesson of all preschool children should take place in a playful way.
Dividing numbers
One easy way to learn is to divide numbers into tens and ones. This also helps when adding ten after adding units. For example, 25 + 36 the child will write down as 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 6 + 5 and get the result 50 + 5 + 6. After that, the addition 5 + 6 = 11 takes place. Again, decomposing 11 by 10 + 1, we get 50 + 10 + 1 = 61. Children easily perceive this method and quickly learn to use it even when calculating in their minds.
Use stacked solution
This will make the counting process much easier for your little one.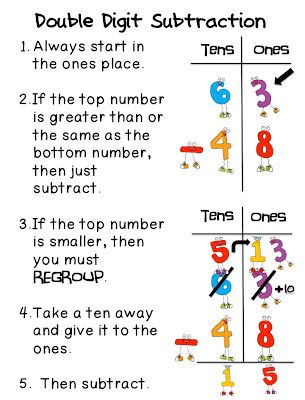 So the child perceives tens and ones more easily, can make notes about additional tens and other necessary records. Adding two-digit numbers in this way is easier and soon the child will be able to carry out the necessary operations in the mind.
So the child perceives tens and ones more easily, can make notes about additional tens and other necessary records. Adding two-digit numbers in this way is easier and soon the child will be able to carry out the necessary operations in the mind.
This method can also be used to study the deduction.
Using online games for learning
Today, there are many mini-games that are aimed at helping parents in teaching their child. Their use allows the baby to quickly and with interest learn the basic basics of counting, including cases when there is an addition of two-digit numbers with a transition through the discharge.
Solving examples with two-digit numbers in this way is quite easy, because in most cases at the first stage there is an explanation of how all actions should be carried out, examples are shown, and only then you can start solving tasks. You can use the option when the game offers answer options, however, in this case, the child may try to guess the correct answer without making calculations.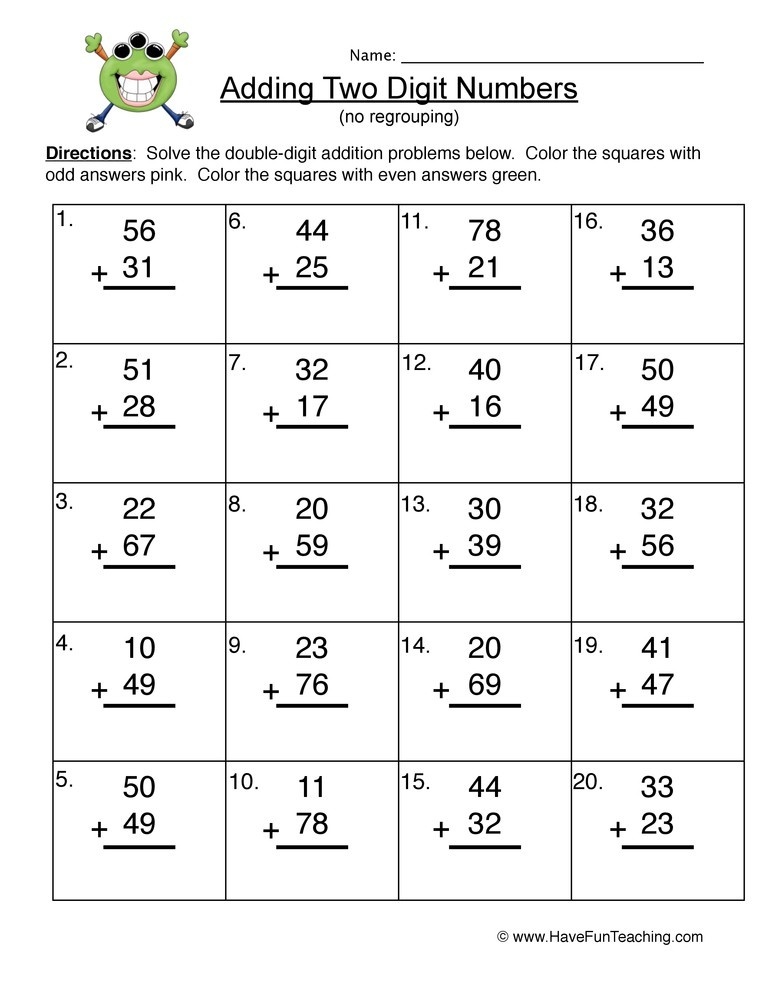 In case of a mistake, it is necessary to help the child understand why he made it, and explain how to do it right.
In case of a mistake, it is necessary to help the child understand why he made it, and explain how to do it right.
The online flash math game "Two Digit Numbers" generates random two digit numbers that the child has to sum up and choose the correct result. You can also enter it manually, using the mouse or the numeric keypad.
Teaching a child to add and subtract two-digit numbers is actually not difficult. It is enough to conduct regular classes, the duration of which will be 10-20 minutes, and after a short period of time your baby will achieve good results. The use of training tasks in everyday life will allow you to better learn all the rules and quickly develop the ability to count even large two-digit numbers in your head.
More from the blog:
What to do with a child from 5 to 8 years old at home and on the street
Read more
Books for children from 2 months to 14 years old - what to read
Read more
What to do with a child in summer?
Read more
Gifted children - how to identify and develop their abilities
Read more
Latest news
Master class in TRINITI shopping center
Leave a request and we will contact you
Leave your phone, we will call you backAddition and subtraction of two-digit numbers
Teaching a child arithmetic is quite difficult, because it consists of three stages.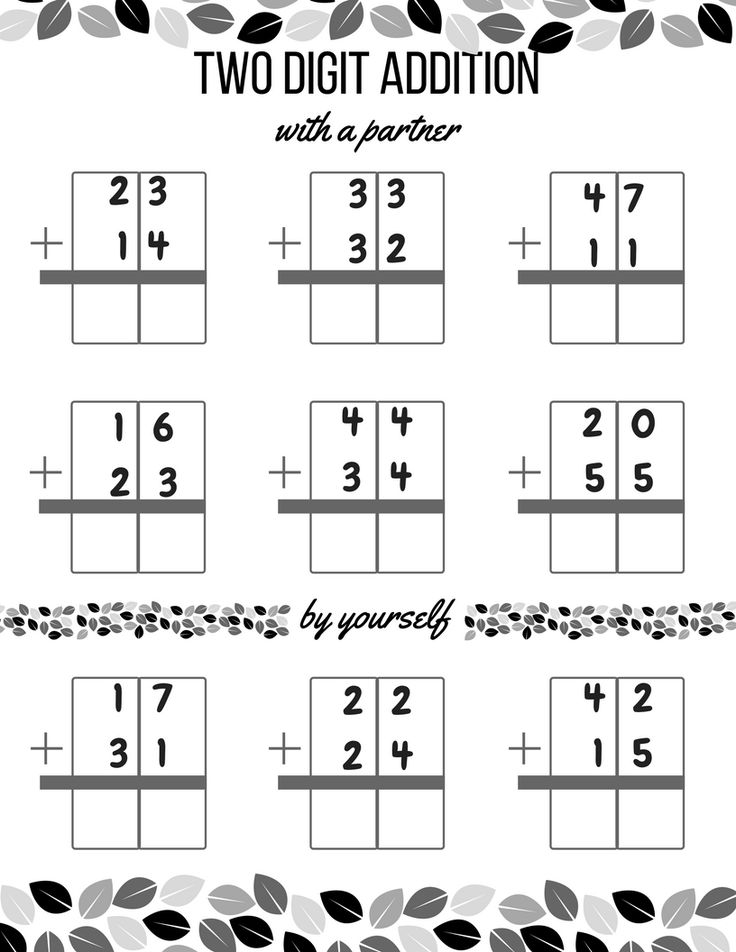 First you have to figure out the numbers from 0 to 9and then everything else. However, even with two-digit numbers, you need to work in stages. Have the child work through actions with numbers from 10 to 20, then from 20 to 30, and so on. If you apply the right methods and organize learning in a playful way, the child will quickly learn complex arithmetic.
First you have to figure out the numbers from 0 to 9and then everything else. However, even with two-digit numbers, you need to work in stages. Have the child work through actions with numbers from 10 to 20, then from 20 to 30, and so on. If you apply the right methods and organize learning in a playful way, the child will quickly learn complex arithmetic.
So, training takes place in several stages.
Preparation
At this stage, the child learns to add and subtract two-digit numbers. Let the child first work with round numbers (learn how to add and subtract them). Then teach him to highlight bit terms in numbers (34=30+4). Try to explain to him that in the number 34 you get 3 tens and 4 ones. Counting sticks will help you deal with this. This is a fairly practical method that has been used in schools for a long time.
Please note that counting sticks can be easily replaced with Lego pieces or some kind of constructor: small pieces are units, larger pieces are tens.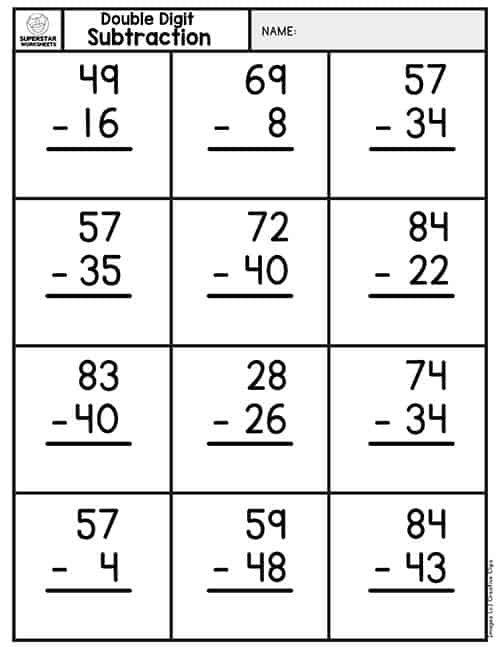 Immediately after that, you can proceed to the addition and subtraction of round numbers.
Immediately after that, you can proceed to the addition and subtraction of round numbers.
Adding and subtracting round numbers
There are different ways to teach a child to add and subtract round numbers.
In the same way, sort out the subtraction of round numbers. As soon as the baby learns these simple manipulations, you can move on.
Adding and subtracting numbers without crossing the digit
To understand this step, you will have to explain the steps in practice. Let's say we want to perform the following action: 24+31 . Here we have to learn one more way of addition/subtraction. We lay out the sticks along a horizontal line - these will be our dozens; and vertically laid out sticks are units. Now stack the vertical sticks with the vertical ones, and the horizontal sticks with the horizontal ones. So we lay out 2 sticks horizontally and 4 vertically, and next to them - 3 horizontal and 1 vertical stick.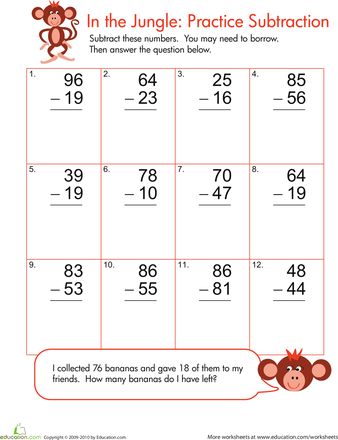 Adding them up, we get 5 horizontal sticks and 5 vertical ones, that is, the final answer is 55. Gradually, the child will learn that units need to be added to units, and tens are added to tens.
Adding them up, we get 5 horizontal sticks and 5 vertical ones, that is, the final answer is 55. Gradually, the child will learn that units need to be added to units, and tens are added to tens.
The next thing you can do with your baby is to learn how to add and subtract in columns. Here it is necessary to explain to the future student that units are written under units, and tens under tens. It may be useful to first lay out the Lego pieces and find the result, and then carry out the calculation in a column.
Subtraction can be parsed in the same way (using sticks, Lego pieces and writing in a column). If a child has mastered the technique of addition, it will not be difficult for him to cope with subtraction.
Addition and subtraction of numbers with the transition through the digit
The complexity of the addition and subtraction of numbers through the digit is that here you have to "borrow" and "memorize" the numbers.
Let's try to solve the following example (26+35) with sticks.
- Lay out the numbers with sticks and add them by digits. We have 5 horizontal and 11 vertical sticks.
- Now remind your child that when doing arithmetic, 10 ones equals 1 ten. It turns out that 10 vertical sticks can be replaced by 1 horizontal stick.
- There are 6 tens and 1 unit.
- This shows that when adding units, we have a number greater than 10. We replace these 10 units with 1 ten. Now we show the child that when performing addition and subtraction, you need to start with units. And if there are 10 or more of them, we select a dozen here and add it to the other dozens.
Once this stage is passed, you can consider other options for adding two-digit numbers.
- first add tens to the number, and then ones. (26+30+5=61)
- make the first term round, then add the second term to it and subtract the number that was added initially. (26+4=30; 30+35=65; 65-4=61)
- plus units with units, and tens with tens.
 Remember, if there are more than 10 units, then add 1 ten. (20+30=50; 6+5=11; 50+10=60) The total is 61.
Remember, if there are more than 10 units, then add 1 ten. (20+30=50; 6+5=11; 50+10=60) The total is 61.
Also show subtraction with a good example. Let's say 53-27.
- Making the first number (5 tens and 3 ones) and the second (2 tens and 7 ones)
- We see that it is impossible to subtract 7 units from 3 units. So we take 1 ten = 10 units.
- Now we can subtract 7 units from 13 units. And now subtract tens. Here it is important to remind the child that we have 1 less tens. So we subtract 2 from 4.
- In total we get 13-7=6 and 4-2=2. So, it turns out 53-27=26.
After completing the visual method, start counting in other ways:
- first subtract in a column: remind the child that units are subtracted and added to units, and tens to tens. 53-27=26
- and now we subtract tens, and after one.
To explain to your child the subtleties of arithmetic, take an abacus to help.