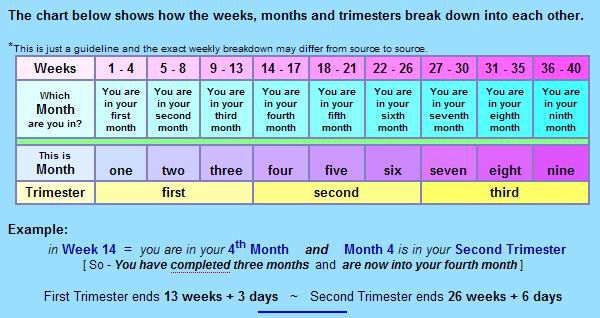
First trimester duration
Everything you need to know about the first trimester (weeks 1 to 12)
Tommy's PregnancyHub
You’re pregnant: congratulations! The first weeks of your pregnancy are a vital time as your body gets busy building a baby. How exciting!
First trimester: key stages
The first trimester begins on the first day of your last period and lasts until the end of week 12. This means that by the time you know for sure you're pregnant, you might already be five or six weeks pregnant!
A lot happens during these first three months. The fertilised egg rapidly divides into layers of cells and implants in the wall of your womb where it carries on growing. These layers of cells become an embryo, which is what the baby is called at this stage.
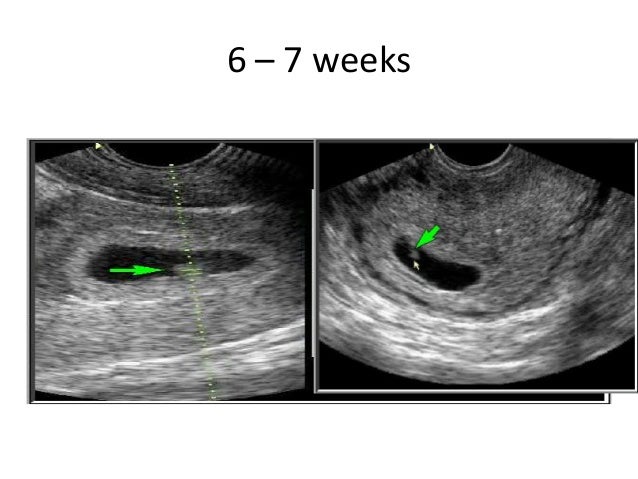
During this trimester, your baby grows faster than at any other time. By six weeks, a heartbeat can usually be heard and by the end of week 12, your baby's bones, muscles and all the organs of the body have formed. At this point, your baby looks like a tiny human being and is now called a fetus. He or she will even be practising swallowing!
Try our Healthy Pregnancy Tool to find out everything you need to know about your pregnancy
When am I due?
Find out your due date using our due date calculator!
When will I see a midwife?
Your first midwife appointment (also known as antenatal appointment) is the 'booking' appointment. This usually happens between week 8 and 10 of your pregnancy. Find out how to register with a midwife and when your appointments will be here.
Keeping your baby safe
There are some things that you can do during pregnancy that have an effect on your baby. Find out about them by clicking the link below.
Find the complete list of pregnancy dos and don'ts (and reasons why) here
Not sure whether you are pregnant?
Find out about the symptoms that mean you may be pregnant here.
Your physical and mental health in pregnancy
We also have lots of useful tips for coping with everyday pregnancy niggles. It’s common for women to experience symptoms such as morning sickness, cramp and indigestion during the first trimester.
It’s common for women to experience symptoms such as morning sickness, cramp and indigestion during the first trimester.
Don't forget that your mental health is just as important as your physical health. It's normal to feel some anxiety and stress but it shouldn't be ongoing. If what you’re feeling isn’t normal for you, talk to your GP or midwife about it. They are there to help.
Exercise, such as yoga, has been shown to reduce anxiety and is a great way to stay active during your pregnancy, too.
Read more about mental wellbeing in pregnancy
Read more about diabetes and pregnancy
Read more about pregnancy with a high BMI
Read more about exercise and pregnancy
Read about the symptoms to look out for in pregnancy
Track your baby's development
Sign up to a free pregnancy email from our midwives to track your baby's development and give you reminders of all you need to know through the 9 months of pregnancy. Click here to sign up.
Review dates
Reviewed: 28 June 2018 | Next review: 28 June 2021
This content is currently being reviewed by our team. Updated information will be coming soon.
Updated information will be coming soon.
Back to top
The First Trimester | Johns Hopkins Medicine
What You Need to Know
- At your first prenatal visit, you will undergo a physical exam as well as certain tests and screenings to assess the health of you and your unborn baby.
- First trimester symptoms vary from woman to woman, with some experiencing all known symptoms and others only a few. Duration of symptoms can vary as well.
- After eight weeks, the embryo is referred to as a fetus.
- Although the fetus is only 1 to 1.5 inches long at this point, all major organs and systems have been formed.
- During the first trimester, the fetus is most susceptible to damage from substances, like alcohol, drugs and certain medicines, and illnesses, like rubella (German measles).

Your First Prenatal Visit
Your first prenatal visit is the most thorough. A complete medical history is taken, a physical exam is done, and certain tests and procedures are performed to assess the health of both you and your unborn baby. Your first prenatal visit may include:
-
Personal medical history. This may include taking record of any of the following:
-
Previous and current medical conditions, like diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), anemia and/or allergies
-
Current medicines (prescription, over-the-counter and nutritional supplements)
-
Previous surgeries
-
-
Maternal and paternal family medical history, including illnesses, intellectual or developmental disabilities, and genetic disorders, like sickle cell disease or Tay-Sachs disease
-
Personal gynecological and obstetrical history, including past pregnancies (stillbirths, miscarriages, deliveries, terminations) and menstrual history (length and duration of menstrual periods)
-
Education, including a discussion regarding the importance of proper nutrition and expected weight gain in pregnancy; regular exercise; the avoidance of alcohol, drugs and tobacco during pregnancy; and a discussion of any concerns about domestic violence
-
Pelvic exam.
 This exam may be done for one or all of the following reasons:
This exam may be done for one or all of the following reasons:-
To note the size and position of the uterus
-
To determine the age of the fetus
-
To check the pelvic bone size and structure
-
To perform a Pap test (also called Pap smear) to find the presence of abnormal cells
-
-
Lab tests, including the following:
-
Urine tests. These are done to screen for bacteria, glucose and protein.
-
Blood tests. These are done to determine your blood type.
-
All pregnant women are tested for the Rh factor during the early weeks of pregnancy. Rh incompatibility happens when the mother’s blood is Rh-negative, the father’s blood is Rh-positive and the fetus’ blood is Rh-positive.
 The mother may make antibodies against the Rh-positive fetus, which may lead to anemia in the fetus. Incompatibility problems are watched and appropriate medical treatment is available to prevent the formation of Rh antibodies during pregnancy. There are also other blood antibodies that may cause problems in pregnancy that are screened for on the first visit.
The mother may make antibodies against the Rh-positive fetus, which may lead to anemia in the fetus. Incompatibility problems are watched and appropriate medical treatment is available to prevent the formation of Rh antibodies during pregnancy. There are also other blood antibodies that may cause problems in pregnancy that are screened for on the first visit.
-
-
-
Blood screening tests. These are done to find diseases that could have an effect on the pregnancy. One example is rubella, an infectious disease that is also called German measles.
-
Genetic tests. These are done to find inherited diseases, like sickle cell disease and Tay-Sachs disease.
-
Other screening tests. These are performed to find infectious diseases, like sexually transmitted diseases and urinary tract infections.
The first prenatal visit is also an opportunity to ask any questions or discuss any concerns that you may have about your pregnancy.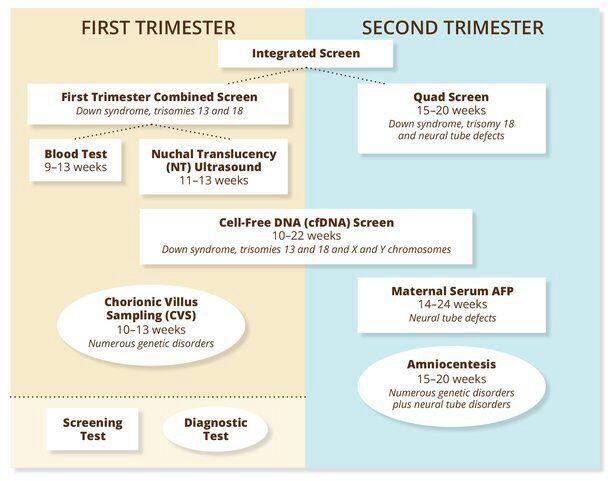
The First Trimester: What to Expect
A healthy first trimester is crucial to the normal development of the fetus. You may not be showing much on the outside yet, but on the inside, all of the major body organs and systems of the fetus are forming.
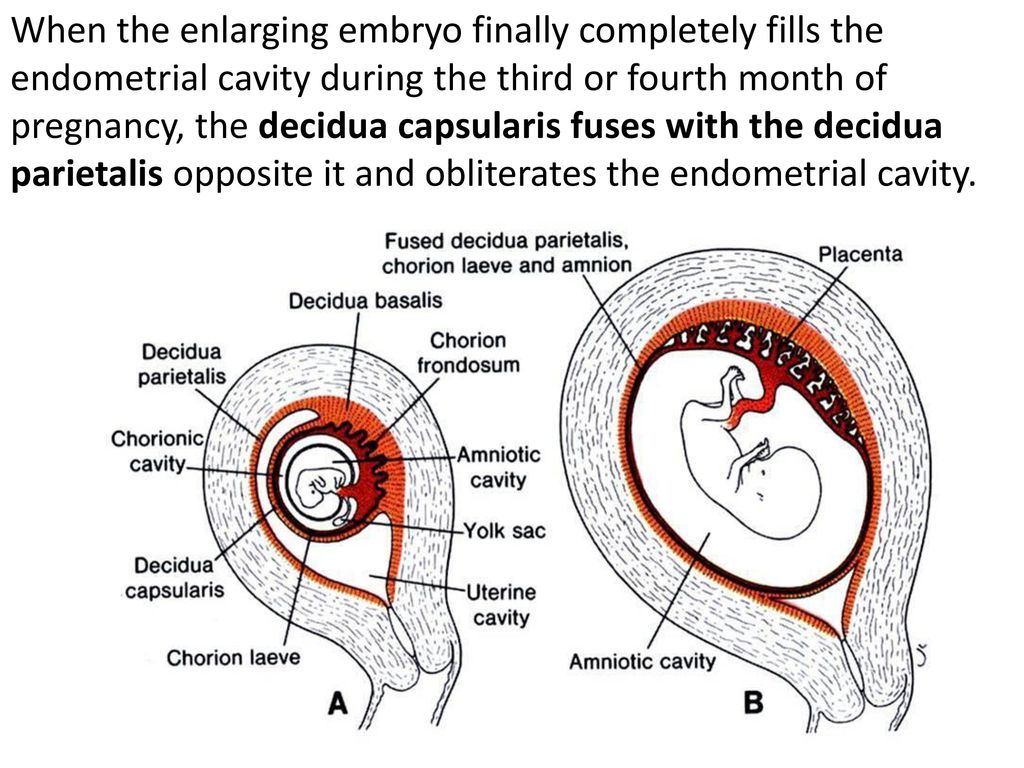
As the embryo implants itself into the uterine wall, several developments take place, including the formation of the:
-
Amniotic sac. A sac filled with amniotic fluid, called the amniotic sac, surrounds the fetus throughout the pregnancy. The amniotic fluid is liquid made by the fetus and the amnion (the membrane that covers the fetal side of the placenta) that protects the fetus from injury. It also helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus.
-
Placenta. The placenta is an organ shaped like a flat cake that only grows during pregnancy. It attaches to the uterine wall with tiny projections called villi. Fetal blood vessels grow from the umbilical cord into these villi, exchanging nourishment and waste products with your blood.
 The fetal blood vessels are separated from your blood supply by a thin membrane.
The fetal blood vessels are separated from your blood supply by a thin membrane. -
Umbilical cord. The umbilical cord is a ropelike cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. The umbilical cord contains two arteries and a vein, which carry oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and waste products away from the fetus.
It is during this first trimester that the fetus is most susceptible to damage from substances, like alcohol, drugs and certain medicines, and illnesses, like rubella (German measles).
During the first trimester, your body and your baby’s body are changing rapidly.
Johns Hopkins Hospital Designated as Baby-Friendly
The Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, a global program launched by the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund, has designated The Johns Hopkins Hospital as Baby-Friendly. This designation is given to hospitals and birthing centers that offer an optimal level of care for infant feeding and mother-baby bonding.
This designation is given to hospitals and birthing centers that offer an optimal level of care for infant feeding and mother-baby bonding.
Learn more
The First Trimester: Changes to Your Body
During pregnancy, many changes will happen to your body to help nourish and protect your baby. Women experience these changes differently. Some symptoms of pregnancy continue for several weeks or months. Others are only experienced for a short time. Some women experience many symptoms, and other women experience only a few or none at all. The following is a list of changes and symptoms that may happen during the first trimester:
-
The mammary glands enlarge, causing the breasts to swell and become tender in preparation for breast-feeding. This is due to an increased amount of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. A supportive bra should be worn.
-
Your areolas (the pigmented areas around each breast’s nipple) will enlarge and darken.
 They may become covered with small, white bumps called Montgomery’s tubercles (enlarged sweat glands).
They may become covered with small, white bumps called Montgomery’s tubercles (enlarged sweat glands). -
Veins become more noticeable on the surface of your breasts.
-
The uterus is growing and begins to press on your bladder. This causes you to need to urinate more often.
-
Partly due to surges in hormones, you may experience mood swings similar to premenstrual syndrome, a condition experienced by some women that is characterized by mood swings, irritability and other physical symptoms that happen shortly before each menstrual period.
-
Increased levels of hormones to sustain the pregnancy may cause “morning sickness,” which causes nausea and sometimes vomiting. However, morning sickness does not necessarily happen just in the morning and rarely interferes with proper nutrition for the mother and her fetus.
-
Constipation may happen as the growing uterus presses on the rectum and intestines.
-
The muscular contractions in the intestines, which help to move food through the digestive tract, are slowed due to high levels of progesterone. This may, in turn, cause heartburn, indigestion, constipation and gas.
-
Clothes may feel tighter around the breasts and waist, as the size of the stomach begins to increase to accommodate the growing fetus.
-
You may experience extreme tiredness due to the physical and emotional demands of pregnancy.
-
Cardiac volume increases by about 40 to 50 percent from the beginning to the end of the pregnancy. This causes an increased cardiac output. An increased cardiac output may cause an increased pulse rate during pregnancy. The increase in blood volume is needed for extra blood flow to the uterus.
The First Trimester: Fetal Development
The most dramatic changes and development happen during the first trimester. During the first eight weeks, a fetus is called an embryo. The embryo develops rapidly and by the end of the first trimester, it becomes a fetus that is fully formed, weighing approximately 0.5 to 1 ounce and measuring, on average, 3 to 4 inches in length.
During the first eight weeks, a fetus is called an embryo. The embryo develops rapidly and by the end of the first trimester, it becomes a fetus that is fully formed, weighing approximately 0.5 to 1 ounce and measuring, on average, 3 to 4 inches in length.
First Trimester Fetal Growth and Development Benchmarks
The chart below provides benchmarks for most normal pregnancies. However, each fetus develops differently.
| Timing | Development Benchmark |
|---|---|
| By the end of four weeks |
|
| By the end of eight weeks |
|
| From embryo to fetus |
|
| During weeks nine to 12 |
|
The fetus is most vulnerable during the first 12 weeks. During this period of time, all of the major organs and body systems are forming and can be damaged if the fetus is exposed to drugs, infectious agents, radiation, certain medications, tobacco and toxic substances.
Even though the organs and body systems are fully formed by the end of 12 weeks, the fetus cannot survive independently.
1st trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus
1st trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics1st trimester: 1st-12th weeks
The gestational age is calculated from the first day of the last menstruation, since it is difficult to determine the exact day of conception.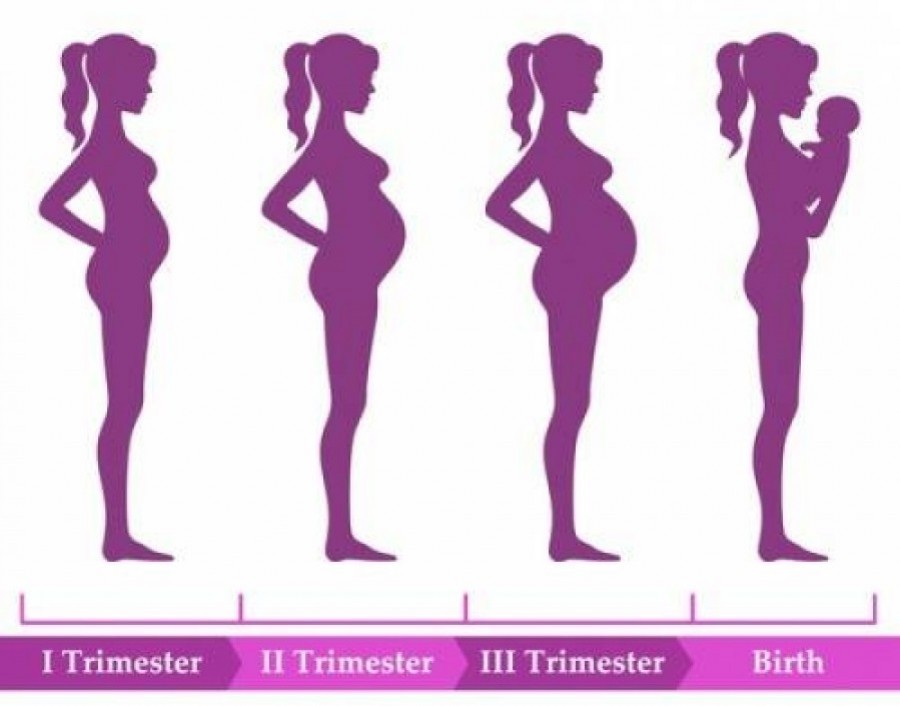 Since conception usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, you are not actually pregnant during the first two weeks, but this period is counted as the beginning of pregnancy.
Since conception usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, you are not actually pregnant during the first two weeks, but this period is counted as the beginning of pregnancy.
As soon as the fertilization of the egg takes place around the 3rd week, the hormones begin to produce changes in your body little by little. As a result, you may experience some of the following symptoms:
- Morning sickness. As a result of rising levels of hormones characteristic of pregnancy, up to 80% of women in the 1st trimester experience morning sickness with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. The idea that such malaise occurs only in the morning is a common misconception. In fact, symptoms can appear at any time of the day or night. Up to 1 in 5 women experience morning sickness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and can sometimes persist throughout pregnancy.
If you experience morning sickness, avoid foods that make you sick, eat little and often, avoid fatty and spicy foods, drink more water.
 If you experience severe symptoms or symptoms that bother you, see your doctor.
If you experience severe symptoms or symptoms that bother you, see your doctor. - Breast changes. The mammary glands will begin to increase in size, soreness may appear. The nipples will increase in size, become darker and more protruding.
- Fatigue. High levels of the hormone progesterone can make you feel tired and sleepy. Rest as often as possible in a horizontal position with your legs up and eat as well as possible, which is not easy if you are experiencing morning sickness!
- Increased emotionality. A higher level of emotionality, manifested as a result of an increase in hormone levels, is normal. Understanding and patience on the part of your partner and loved ones is very important here.
- Food likes and dislikes. You may find yourself intolerant of one food and addicted to another. This is usually not a problem, unless you feel like eating weird foods like chalk.
 If you are concerned about the situation, contact your doctor.
If you are concerned about the situation, contact your doctor. - Frequent urination. As your fluid levels increase and your uterus puts pressure on your bladder, you will become more likely to visit the toilet. Go to the toilet as soon as you feel the need - this minimizes the pressure on the bladder.
- Feeling of dizziness. Sometimes you may feel a little dizzy (this is due to hormonal changes). Try not to stay on your feet for a long time and slowly rise from a sitting or lying position. If you experience severe dizziness, contact your doctor immediately.
- Heartburn and constipation. Your digestive system will slow down to give you more time to digest your food. This can lead to heartburn and constipation. To help manage heartburn, try to eat small meals at regular intervals and avoid fried or spicy foods and carbonated drinks. Constipation is helped by eating a diet rich in fiber, maintaining physical activity and drinking plenty of water.
1st trimester milestones
- Approximately 7 days after fertilization, the embryo implants in the uterine wall. The placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic sac will begin to form to provide nourishment and protection to the embryo.
- By the end of the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the uterus is palpable through the wall of the abdomen, the abdomen will begin to grow.
Child development in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
By the end of the 1st trimester:
- All the main organs of the baby are formed, the circulatory system works.
- The development of the sexual organs has begun.
- Fingers are formed on the hands and feet, nails have appeared.
- Facial features have formed.
- The length of the baby's body is about 6 cm from the head to the lower part of the body, he is already recognizable. The baby moves in the amniotic sac, but you don't feel it move yet.

Clinic mobile app
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more...
Fill out the form to make an appointment or order a call back
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
Sign up for a consultation
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
By continuing to use rd.clinic23.ru, you agree to the use of cookies. How to ban the use of certain cookies can be found in Politics
1st trimester of pregnancy: everything you need to know | Mamovedia
The average gestation period is 40 weeks, counted from the date of the last menstrual period and measured in trimesters, months and weeks
The first trimester of covers the period from the 1st to the 12th week of pregnancy, which is approximately three months of the solar calendar. The second trimester starts at 13 weeks and ends at 27 weeks of pregnancy.
The second trimester starts at 13 weeks and ends at 27 weeks of pregnancy.
Finally, the third trimester covers the period from 28 weeks to the due date.
The first trimester of pregnancy is the most important for the development of your future baby.
During this period, the embryo (as the fetus of the first 8 weeks of life is defined) develops until it weighs from 14 to 28 grams, and growth, on average, from 7.5 to 10.5 centimeters.
Until the 20th week, the length of the embryo (and then the fetus) is usually measured from the head to the end of the spine. After that, its length is measured from head to toe.
The growth of the fetus in length will occur during the third, fourth and fifth months, and the increase in its weight will fall on the last two months of pregnancy.
What are the most common symptoms of pregnancy in the first trimester?
Usually the first symptoms accompanying pregnancy are nausea, vomiting, frequent urination, fatigue, breast tenderness . Many women begin to experience these symptoms even before a missed period or a positive pregnancy test result.
Many women begin to experience these symptoms even before a missed period or a positive pregnancy test result.
As your pregnancy progresses, you may begin to experience other symptoms such as mood swings, headaches, cramps, constipation, indigestion, bloating, food cravings or aversion, and an incredibly strong sense of smell: the latter often makes nausea worse.
Most of these symptoms, including mood swings and emotional outbursts, are believed to be caused by elevated levels of estrogen and progesterone.
If during this period you feel severe pain in the lower back, you have bleeding, severe nausea, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist, as these may be symptoms of a miscarriage.
First trimester weight gain
- Fetus. The weight gain of the fetus in the first trimester is negligible: at the end of the first trimester, it is actually the size of a peach.
- Expectant mother. Although the growth rate of the fetus is very subjective, the weight gain of the expectant mother by the end of the first three months should be about 1-2 kg.
During the first three months of motherhood, you can follow your regular diet and you don't have to eat for two!
Examinations and screenings during this period
As soon as you know you are pregnant, schedule your first appointment with your OB/GYN. The first examination is usually never done before the 8th week of pregnancy unless there is a risk of complications such as a history of abortion or a family history of hereditary genetic diseases. This visit is required for:
- check for any abnormalities in the growing embryo;
Testing for HIV, syphilis, rubella, hepatitis B, as well as asymptomatic bacteriuria, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis is generally recommended for all women.
Ultrasonography as part of prenatal screening for genetic chromosomal risks should be performed between weeks 9 and 12 , along with a biochemical blood test for beta-hCG, PAPP-A and PIGF (optional) with a geneticist's conclusion. The woman must be informed of the abnormalities that may be found in order to have the choice of whether to continue the pregnancy or not.
The woman must be informed of the abnormalities that may be found in order to have the choice of whether to continue the pregnancy or not.
What does the baby look like in the 1st trimester?
At the end of the 1st month the embryo reaches the size from 2 to 5 millimeters . The heart and stomach are being formed in him, the sensory apparatus and the structure from which the nervous system will originate begin to develop. In addition, cavities for the eyes are formed and the very first sketches of future upper limbs appear.
By the end of the second month of embryonic development, the contours of the head and face begin to be drawn; nostrils, mouth, bronchi and lungs begin to form; brain grows; the very first sketches of the lower extremities appear; the upper limbs lengthen, acquiring the shape of a scoop. At this stage, the retina also begins to develop. At the end of the 2nd month, the embryo reaches a size of 2.3 centimeters and a weight of 15 grams . The heart of the embryo makes 110 beats per minute.
The heart of the embryo makes 110 beats per minute.
By the end of the third month, the elbows begin to bend, the eyelids and outer ear are defined, the corpus callosum appears in the brain between the two hemispheres, the formation of bones, nerves, muscles and great vessels continues. The growth of the body is observed.
Formed liver produces red blood cells and bile fluid; sketches of future external genital organs (penis in men; clitoris and labia majora in women) begin to develop, which is why it is possible to predict the future sex of the child at an early stage. Nails appear on the fingers; the intestine passes into the abdominal cavity; teeth are laid; the pancreas begins to produce insulin.
At the end of the 3rd month, the fetus measures 6.5 centimeters and weighs about 73 grams .
Things to remember in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Most of the development of your unborn baby's nervous system occurs during the 1st trimester of pregnancy.