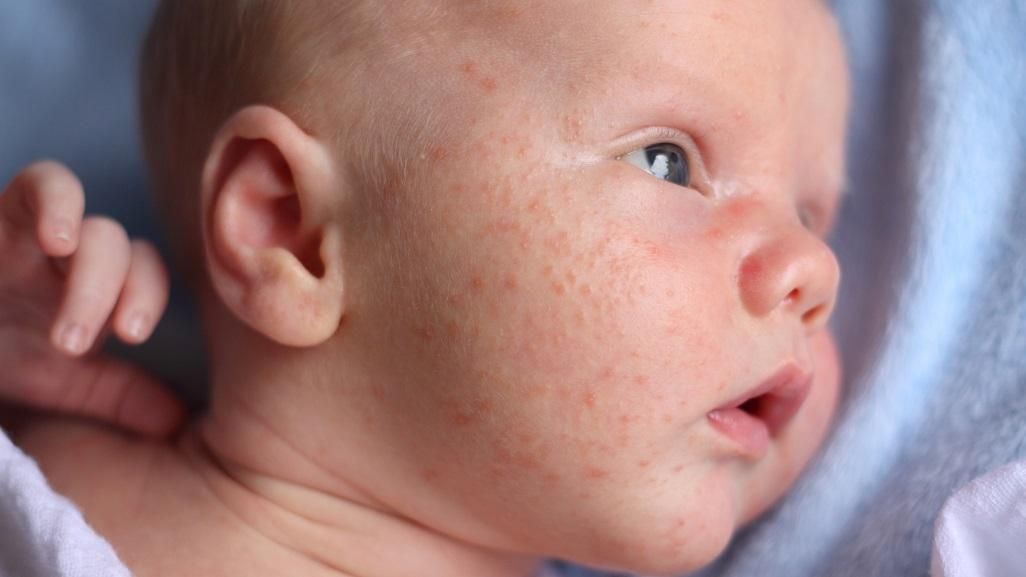
Baby getting rashes on face
Rash on a baby's face: Pictures, causes, and treatments
In babies, most facial rashes are harmless and tend to clear up without treatment. Causes can include eczema, acne, and infection.
Sometimes, however, a rash on a baby’s face can indicate a more serious condition.
Being able to distinguish between different rashes can help a parent or caregiver know when to seek professional advice.
In this article, we describe common facial rashes in babies, treatments, and when to see a doctor.
Eczema refers to a group of conditions that cause the skin to become rough, irritated, itchy, and inflamed.
These conditions are common in young children, often appearing between the ages of 6 months and 5 years. Many children grow out of their eczema.
According to the National Eczema Association in the United States, if eczema develops within the first 6 months of life, it tends to appear on the cheeks, chin, forehead, or scalp. The rash will be dry, red, and itchy.
Between the ages of 6 and 12 months, eczema may develop in other parts of the body. The elbows and knees are particularly susceptible when babies start to crawl.
Treatment
Although the exact cause of eczema is unknown, experts believe that both genetic and environmental factors can play a role.
Certain environmental triggers may over-activate the immune system, causing inflammation and skin irritation.
When trying to establish the cause of a child’s eczema, it may help to keep a diary of symptoms and potential triggers. By avoiding these triggers, it may be possible to prevent flare-ups of symptoms.
Below are some common triggers of eczema in babies:
- heat and sweating
- dry skin
- irritants, such as soaps, washing detergents, and cigarette smoke
- allergens, such as dust mites, pollen, and pet dander
- certain fabrics, such as wool and nylon
Treatments for eczema include:
- over-the-counter (OTC) moisturizers
- prescription creams and ointments, such as steroid creams
- immunosuppressant drugs
- phototherapy
A doctor can consult with a pediatric dermatologist and recommend a course of treatment.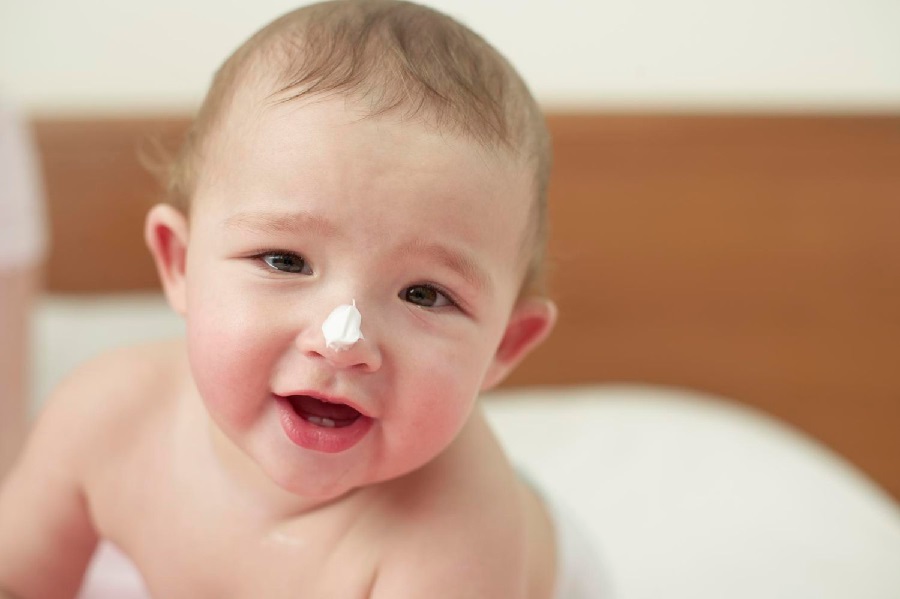 They can also advise about triggers and how to avoid them.
They can also advise about triggers and how to avoid them.
Check that over-the-counter treatments are suitable for infants.
Seborrheic dermatitis causes a rash to develop on areas of skin that contain many oil-producing glands.
In babies, the rash mainly appears on the scalp, and people commonly refer to it as cradle cap. However, cradle cap can also affect the cheeks, particularly around the eyes and nose.
The rash may have the following characteristics:
- redness and inflammation
- an oily or greasy appearance
- white or yellow scaly or crusty patches
Treatment
Cradle cap is generally harmless and usually disappears between 6 and 12 months of age.
If the child is not experiencing any discomfort, treatment may not be necessary.
For mild symptoms, OTC medications, such as antifungal creams and medicated shampoos, may help to relieve discomfort and speed healing. However, talk to a doctor before using these products on an infant.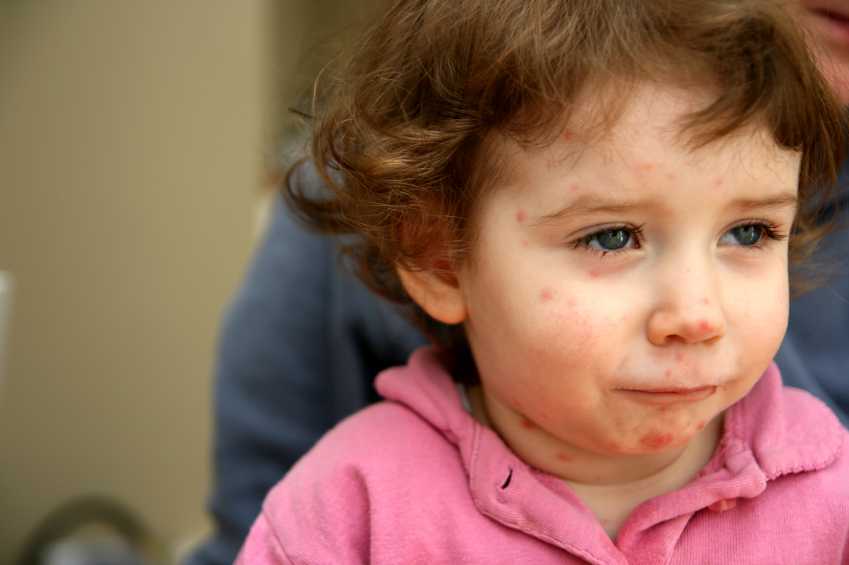
If the rash is scaly, applying mineral oil or petroleum jelly to the baby’s scalp 1 hour before using an anti-dandruff shampoo can help loosen and remove the scales.
For babies with more severe symptoms, a doctor may prescribe topical steroids to reduce inflammation.
Particularly severe cradle cap can increase the risk of infection. See a doctor immediately, if the baby’s skin:
- feels hot
- oozes fluid
- gives off an unpleasant odor
Around 40–50 percent of healthy newborns develop milia, which are tiny white or yellow bumps about 1–3 mm in size.
Milia result from blocked pores and typically develop on the face, often around the eye and nose. The bumps can appear in large numbers, and usually a roughly equal number form on each side of the face.
In babies, milia can also develop in the mouth. In this case, the medical name is Epstein pearls.
Treatment
Milia tends to clear up on their own within a few weeks, once the pores open up.
No treatment is usually necessary. Avoid using creams and ointments on the baby’s skin, as these can further clog the pores and lead to more milia.
Newborn, or neonatal, acne causes small, red pimples to develop, usually around 2–6 weeks of age. However, some babies are born with them.
The medical term for acne that develops between 6 weeks and 6 months of age infantile acne, and we discuss this below.
Neonatal acne affects around 20 percent of newborns, according to the American Academy of Dermatology.
The pimples tend to develop on the baby’s cheeks and nose, but breakouts can also appear on the:
- forehead
- chin
- scalp
- neck
- chest
- upper back
Treatment
Generally, newborn acne is not a cause for concern. It is unlikely to cause scarring and tends to clear up without treatment after a few weeks or months.
Parents and caregivers should:
- gently wash the baby’s skin with lukewarm water
- avoid scrubbing affected areas
- avoid oily or greasy skincare products
- seek advice from the child’s doctor before using acne medicines or cleansing products
Infantile acne develops in babies older than 6 weeks.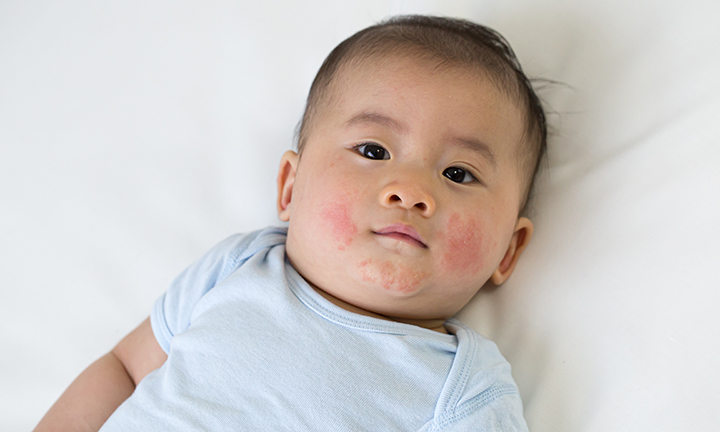 It typically appears between 3 and 6 months of age.
It typically appears between 3 and 6 months of age.
Infantile acne is less common than newborn acne. Symptoms can be more severe and may require treatment.
Before treating infantile acne, it is important to rule out other conditions, such as such as eczema and infections, which are more common in this age group.
Treatment
Infantile acne usually clears up within 6–12 months after it first appears.
After diagnosis, a dermatologist can advise about treating the acne and preventing scarring. If they suspect that the acne results from an underlying medical condition, they may consult a specialist.
A doctor can diagnose the cause of a rash.
Slapped cheek syndrome is a viral infection. Anyone can get it, but it most commonly develops in school-aged children.
Other names for the syndrome include fifth disease and erythema infectiosum. It results from infection with the B19 parvovirus.
The defining characteristic is a bright red rash on one or both cheeks.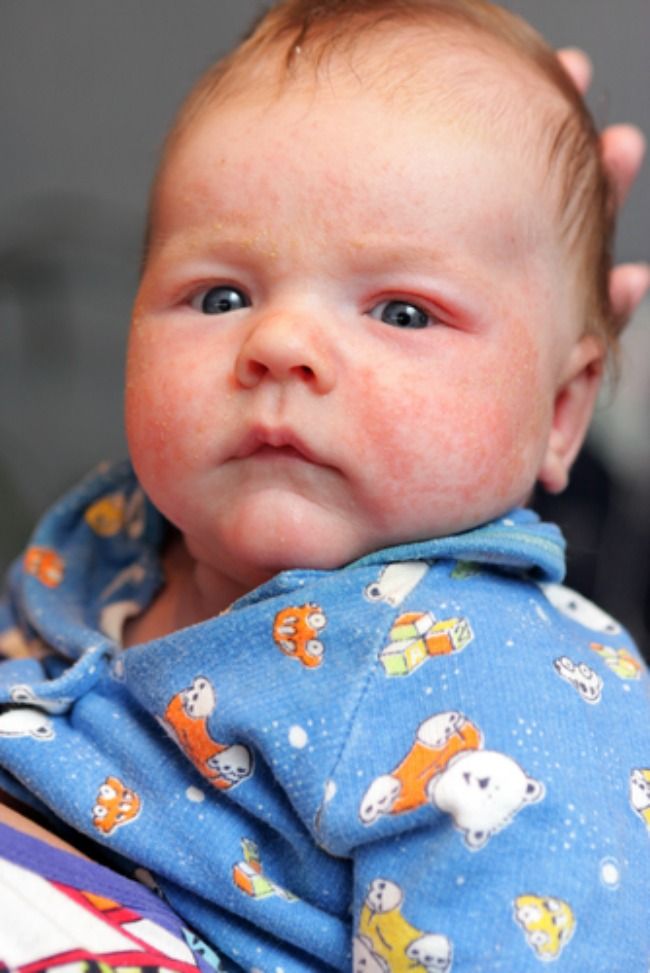 The rash is not usually painful. It typically appears within 4–14 days of infection.
The rash is not usually painful. It typically appears within 4–14 days of infection.
The cheek rash often disappears in a few days, but another rash may develop on areas such as the chest, arms, and legs. This rash usually lasts for 7–10 days, but it may come and go.
The rash on the body is usually blotchy and light in color. It can be itchy, but it is not typically painful.
Slapped cheek syndrome can also cause the following symptoms:
- a fever of 38°C or higher
- a headache
- a runny nose
- a sore throat
Children can initially pass the infection to other children, but it usually stops being contagious once the rash appears.
Treatment
The symptoms of slapped cheek syndrome are usually mild, and the underlying infection typically clears up without treatment.
OTC medications, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, can help relieve any discomfort. However, speak to a doctor before giving these drugs to babies or young children.
Never give a child aspirin, as it may increase the risk of a serious condition called Reye’s syndrome.
Most rashes on babies’ faces are harmless. They usually clear up on their own.
However, a rash in this area can indicate an infection or an underlying health condition.
See a doctor if the rash is severe, or if the baby has:
- fluid-filled blisters
- a fever
- a loss of appetite
- red streaks extending from the rash
- tiny red or purple spots that do not fade when someone applies pressure
- swollen lymph nodes
- lethargy
- a cough
Facial rashes are common in babies and young children. The many possible causes include eczema, acne, and infection.
Most rashes clear up without treatment. However, see a doctor if a rash is severe or persistent, or if it accompanies other symptoms.
Read the article in Spanish.
Nappy rash - NHS
Around 1 in 4 babies and toddlers in nappies have nappy rash at any one time. It doesn't usually develop in newborns, but all babies can get nappy rash.
It doesn't usually develop in newborns, but all babies can get nappy rash.
Nappy rash can be caused by:
- your baby's skin being in contact with wee or poo for a long time
- the nappy rubbing against your baby's skin
- not cleaning the nappy area or changing the nappy often enough
- soap, detergent or bubble bath
- alcohol-based baby wipes
- some types of medicines, such as antibiotics or laxatives (used to make a baby poo more often)
There may be red patches on your baby's bottom, or the whole area may be red. Their skin may look sore and feel hot to touch, and there may be spots, pimples or blisters.
Most babies with mild nappy rash don't feel sore, but if the rash is severe your baby may feel uncomfortable and be distressed.
If your baby gets nappy rash, you can usually treat their skin yourself.
If the rash isn't upsetting your baby, at each nappy change apply a thin layer of a barrier cream to protect their skin. Ask your health visitor or pharmacist to recommend one.
Follow this advice to help look after your baby's skin.
- Change wet or dirty nappies as soon as possible.
- Clean the whole nappy area gently but thoroughly, wiping from front to back. Use water or fragrance-free and alcohol-free baby wipes. Read more about how to clean your baby and change your baby's nappy.
- Bath your baby daily – but avoid bathing them more than twice a day as that may dry out their skin.
- Dry your baby gently after washing them – avoid vigorous rubbing.
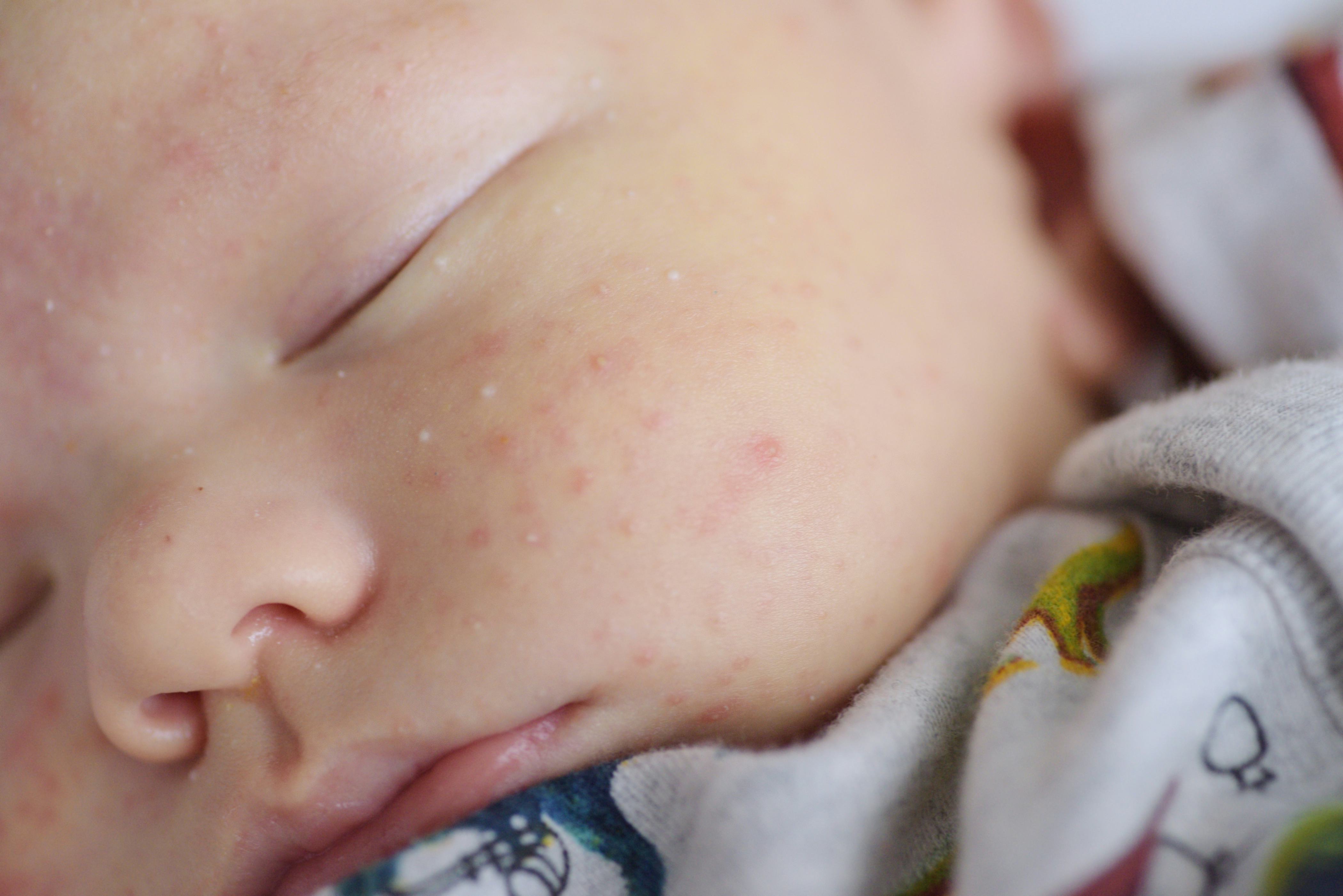
- Lie your baby on a towel and leave their nappy off for as long and as often as you can to let fresh air get to their skin.
- Do not use soap, bubble bath, or lotions.
- Do not use talcum powder as it contains ingredients that could irritate your baby's skin.
- Make sure your baby’s nappy fits properly. If it is too tight then it can irritate the skin and if it is too loose, then the nappy will not be able to soak up pee properly.
Nappy rash usually clears up after about 3 days if you follow this advice. You should keep following this advice as this will help prevent nappy rash from coming back.
If the rash is causing your baby discomfort, your health visitor or pharmacist can recommend a nappy rash cream to treat it.
You should apply the cream first and wait a few minutes before you apply the barrier cream.
If the rash doesn't go away or your baby develops a persistent bright red, moist rash with white or red pimples that spreads into the folds of their skin, they may have an infection.
Ask a pharmacist or health visitor for advice. The pharmacist may recommend a cream for you to use.
If the rash is severe, take your baby to the GP who may prescribe cream or medicine. Follow a GP's instructions on whether and when to apply barrier cream as well as the prescribed cream.
It's normal for babies to develop skin rashes, but it's important to know the difference between a minor irritation and a condition that requires attention.
Read more about rashes in babies and children.
Page last reviewed: 17 September 2021
Next review due: 17 September 2024
Red pimples on the face of a newborn: symptoms, causes and treatment
Allergic rash in a newborn
An allergy in a baby is an unfavorable immune response of a child's body to a potentially dangerous substance.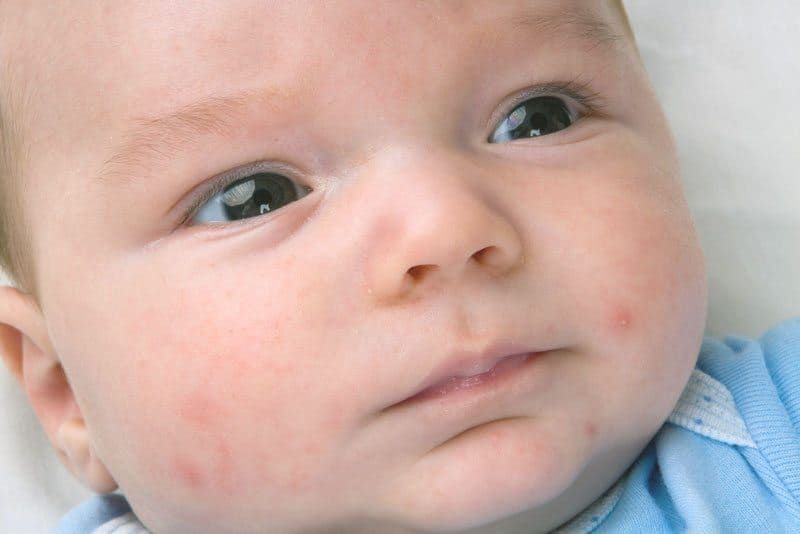 Most often, an allergic rash occurs against the background of the use by a nursing mother of products that can act as an irritant. This group includes:
Most often, an allergic rash occurs against the background of the use by a nursing mother of products that can act as an irritant. This group includes:
- cow's milk;
- soy [1] and egg white;
- fish;
- strawberry;
- nuts.
The first sign of developing allergic rash is peeling. Pathological foci with dry skin on the face of a newborn are formed symmetrically, localized on the cheeks and on the forehead.
It is necessary to consult a doctor if the appearance of rashes affects the general condition of the baby. Irritability, restless sleep, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, fever and vomiting are dangerous symptoms that should be stopped immediately under the supervision of a pediatrician.
Neonatal acne
Neonatal acne may appear in the first weeks of a child's life on the forehead, nose and cheeks. In appearance, they resemble acne with purulent heads, characteristic of a teenage rash.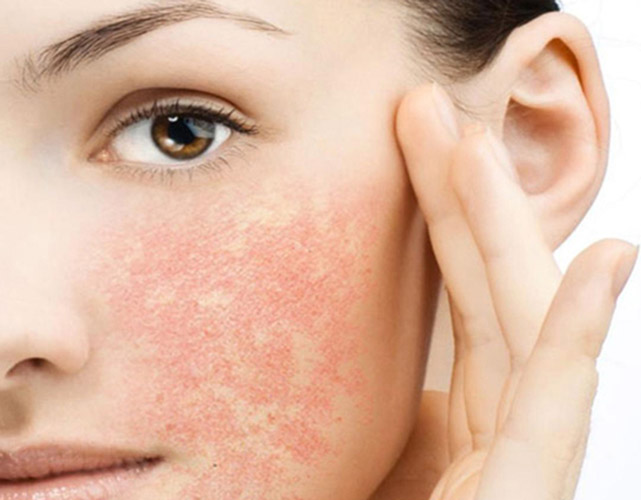 It is assumed that the cause of the appearance of acne is increased production of sebum , which clogs the ducts of the sebaceous glands and provokes an inflammatory reaction.
It is assumed that the cause of the appearance of acne is increased production of sebum , which clogs the ducts of the sebaceous glands and provokes an inflammatory reaction.
The pathogenesis of the appearance of small pimples in newborns is also associated with the processes of the formation of the hormonal system. The body gets rid of the transplacental influence of maternal androgens [2], adrenal hormones begin to be produced more intensively, which affect the condition of the skin.
Neonatal acne does not require treatment [9] - standard daily care using delicate soap or baby cosmetics is sufficient. In most cases, pimples that appear on the face go away on their own by 4 months of age.
Miliaria
Miliaria is a skin lesion that is associated with hyperfunction of the sweat glands and irritation of the excretory ducts . The disease can develop due to improper skin care newborn, with a long stay in hot rooms and the wrong choice of clothing (the child is heavily wrapped up).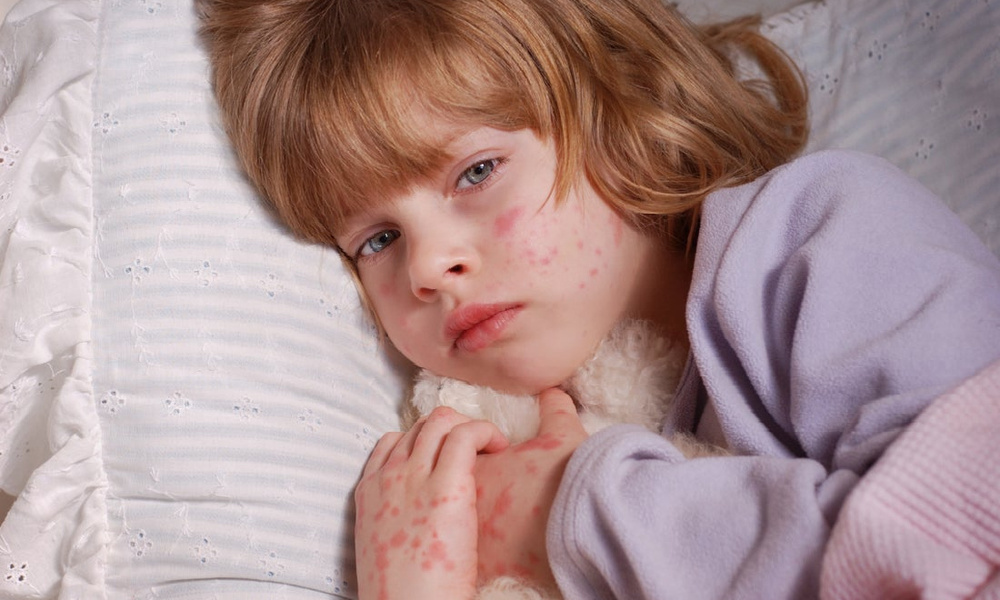
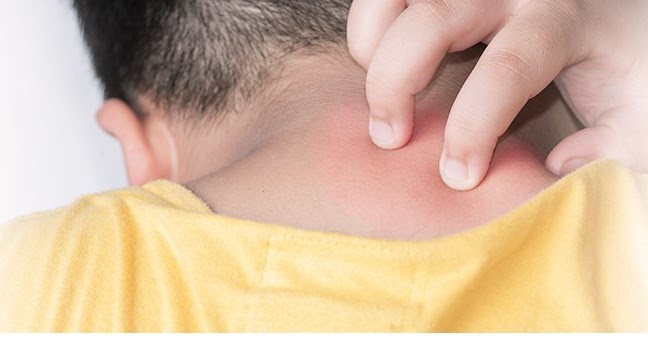
Miliaria resembles an allergic rash, but differs from it in localization. Signs of allergy most often appear on the skin of the child's face, and with miliaria, rashes form throughout the body - most often in natural folds, on the neck, lower abdomen and upper chest.
What prickly heat looks like:
- small blisters with clear contents, prone to burning and itching;
- in difficult cases, reddish nodules with an inflamed rim;
- with extensive skin lesions - weeping areas.
Miliaria itself is not dangerous to the health of the child. But damage to the skin is fraught with the addition of a bacterial or fungal infection. In this case, purulent processes develop, the skin becomes edematous, a putrid odor appears. Red pimples with prickly heat cause discomfort in the child - he becomes capricious and irritable, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly.
Seborrheic dermatitis
In addition to red pimples, yellowish scales may appear on the skin of a newborn.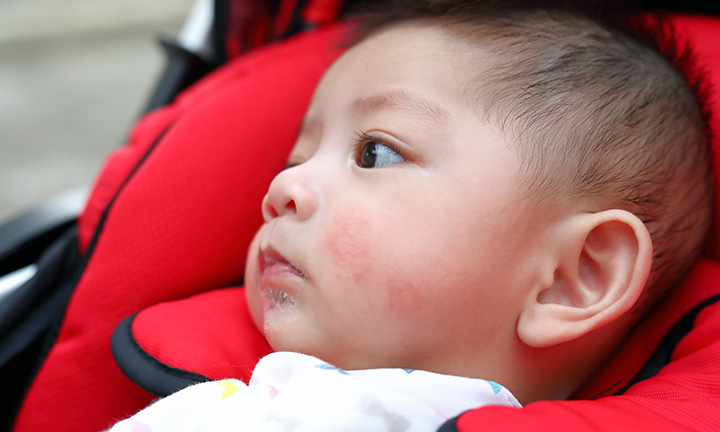 These are signs of seborrheic dermatitis, a disease associated with increased secretion of sebum. Scales are formed in the first month of life in areas of the body with a large accumulation of sebaceous glands - on the scalp, upper third of the back, on the face, chest and in the area of the auricles. Seborrheic dermatitis is sometimes called "milky crusts", which may be associated with the use of unsuitable cosmetic products for baby skin care.
These are signs of seborrheic dermatitis, a disease associated with increased secretion of sebum. Scales are formed in the first month of life in areas of the body with a large accumulation of sebaceous glands - on the scalp, upper third of the back, on the face, chest and in the area of the auricles. Seborrheic dermatitis is sometimes called "milky crusts", which may be associated with the use of unsuitable cosmetic products for baby skin care.
In fact, the disease is caused by a high content of maternal hormones in the blood or a change in the biochemical composition of lipids on the surface of the skin [4].
Most childhood seborrheic dermatitis resolves on its own. Parents need only take care of proper care , but diligently remove the crusts is not recommended - you risk damaging delicate skin and causing infection. It is better to use specially designed products - such as Shampoo-foam from "milk crusts" for newborns.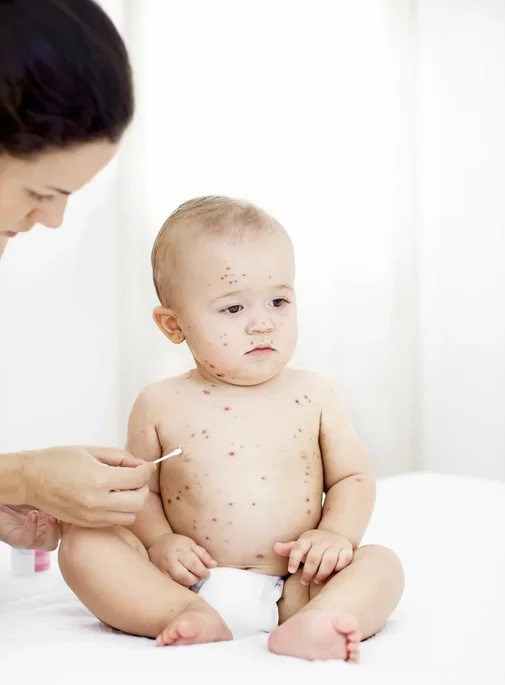 He facilitates the removal of scales in 90% of cases and soothes the scalp in 95% of babies [5.2]. The product contains 99% ingredients of natural origin. The shampoo is fragrance-free and has a tear-free formula.
He facilitates the removal of scales in 90% of cases and soothes the scalp in 95% of babies [5.2]. The product contains 99% ingredients of natural origin. The shampoo is fragrance-free and has a tear-free formula.
In the presence of thick, dense scales, which are located not only on the scalp, but also in other areas, a good helper will be Cream for "milk crusts" which helps to completely remove "milk crusts" in an average of 7 days [5.3].
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is an allergic disease that is accompanied by chronic inflammation of the skin. Causes of an uncontrolled allergic reaction in infants are:
- food allergens - animal protein, soy products, certain types of vegetables;
- airborne allergens - household dust, pollen, pet hair, tobacco smoke, etc.;
- pathogenic microflora - fungi, viruses, bacteria.
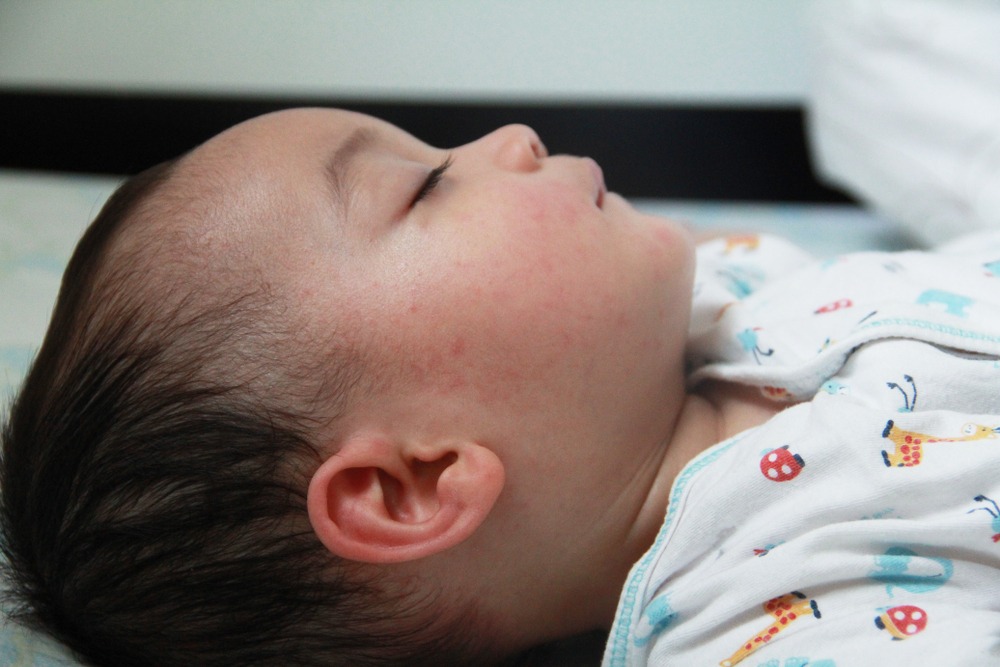
Newborns are most often diagnosed with erythematous-squamous form of atopic dermatitis with signs of an acute inflammatory reaction:
- hyperemia of the skin;
- peeling;
- flat small papules.
Red spots are localized on the arms and legs in the area of the folds , on the sides of the neck, on the back of the hands and on the cheeks.
Children with atopic dermatitis are advised to regularly cleanse and moisturize their skin [6]. Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed only for extensive skin lesions that impair the quality of life of the baby - in this case, you should contact your pediatrician.
For daily care it is recommended to use STELATOPIA Emollient Cream . Studies [5.1] have shown that emollient:
- In 90% of cases reduces increased dryness of the skin [5.1] and reduces the likelihood of clinical signs of AD by 51% [10]
- Soothes itching in 91% of cases [5.
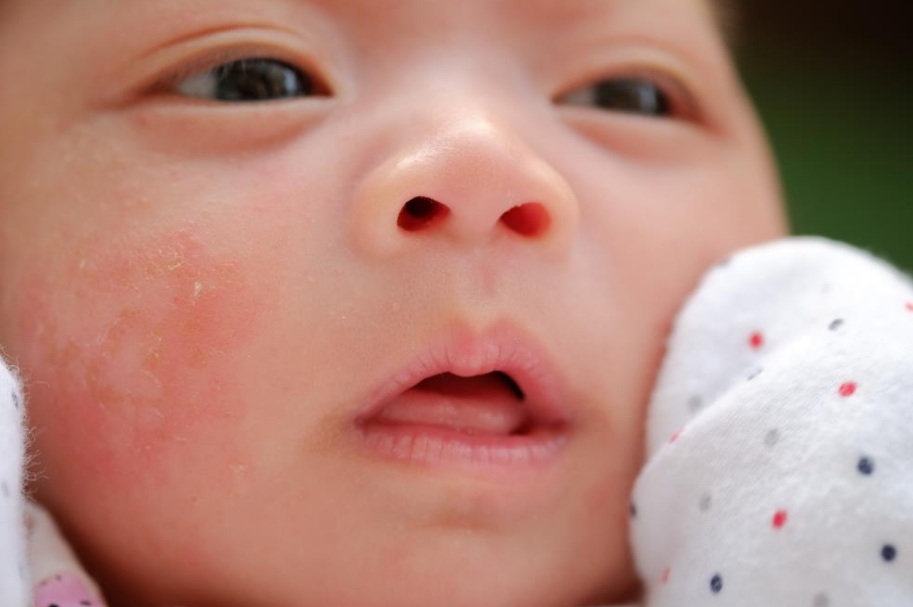 1]
1] - Reduces inflammation after 32 hours [11]
Diaper dermatitis
This disease is better known as diaper rash and is accompanied by inflammation of the skin in the diaper zone in infants. Rash appears as a result of prolonged body contact with wet diapers - the skin becomes excessively moist and defenseless against damaging factors (chemical, physical, infectious). The situation is aggravated by the simultaneous effect on the skin of children's feces that remain in a diaper or diaper.
Diaper dermatitis is not localized on the face - pimples in newborns appear on the lower abdomen, on the convex surfaces of the thighs and buttocks.
9 indicated for non-drug treatment of pathology0006 air baths [7], bathing in decoction of string and celandine [8] and meticulous hygiene procedures. For the prevention of diaper dermatitis and redness, it is recommended to use Diaper Cream 1 2 3.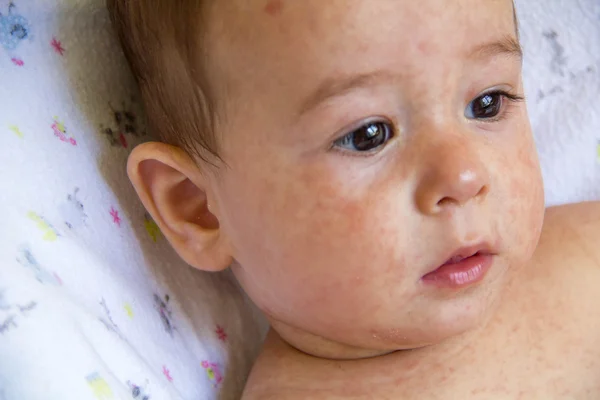
Useful properties of the product:
- reduces redness and irritation by 80% from the first application [5];
- does not interfere with skin breathing;
- reduces the risk of exacerbations by 74% [5];
- protects, restores and soothes inflamed skin.
A number of dermatological diseases of newborns develop as a result of improper care, so parents should pay special attention to children's hygiene, and if the baby's condition worsens, immediately consult a doctor.
______________________________________________________________________________________
References:
1. Bhatia J, Greer F, for the Committee on Nutrition of the American Academy of Pediatrics. The use of mixtures based on soy protein in infant feeding.// Pediatrics, 2008; 121:1062–1068.
2. Herani M.I., Ando I. Acne in infancy and acne genetics // Dermatology 2003. Volume 206. Number 1. pp. 24-28. DOI: 10.1159/000067819
3. Zanko NI Efficiency of new technologies for skin care in young children: Ph.D. dis. ... cand. honey. Sciences, M., 2000
Zanko NI Efficiency of new technologies for skin care in young children: Ph.D. dis. ... cand. honey. Sciences, M., 2000
4. Naldi L., Rebora A. Clinical practice. Seborrheic dermatitis.
N Engle Gee Med. 360(4):387-96 (2009 January).
5. Results of the study 1035 F4.
5.1 Test results 1016F10.01.02
5.2 Test results 1008F4.01.16
5.3 Results of the study 1042F3.01.24
6. Thompson M., Hanifin J. Effective treatment of atopic dermatitis in children alleviates problems associated with food allergies
// GM Akad Dermatol.2005; 53: S214-S219.
7. Galliamova Yu.A. Diaper dermatitis and skin trauma in children. Attending doctor. – 2013; 9:42-6.
8. Zverkova F.A. Skin diseases in young children. SPb.: Sotis, 1994.
9. Tamrazova OB, Zaslavsky DV Diseases of the sebaceous glands in infants. Medical advice. 2019; 2:152-160.
10. Atopic-prone skin: latest discoveries (Laboratoire Expansion Center for Development and Research)
11. Inhibits the synthesis of inflammatory mediators. “A study of the activity of sunflower oil distillate on inflammatory mediators. June 2010»
“A study of the activity of sunflower oil distillate on inflammatory mediators. June 2010»
Causes of a rash in children
Naturally, only a pediatrician, dermatologist or allergist can correctly determine the cause of the rash , diagnose and prescribe treatment for a child. But provide initial assistance, take down itching and the parents themselves can help the baby, knowing the main signs and causes of the rash . At the first stage, it is important to determine the nature of the rash - infectious , allergic or none of the above.
Causes of rashes in children:
1. Newborn acne . For the first time may occur in newborns at the age of 1 - 2 months. As a rule, such rashes are hormonal in nature, are not contagious and are not allergic . A rash in the form of pimples, sometimes with a white dot in the middle, appears on the head, body of the baby. If there are no purulent compartments, then the rash goes away on its own and does not require treatment. Acne can also occur in teenagers. They most often appear on the face in the form of black dots and are associated with hormonal changes in the body of a teenager and increased work of the sebaceous glands. To prevent acne, there are cosmetic lotions, washing gels and other products. In case of inflammation, it is better to seek advice from a pediatric dermatologist or cosmetologist, because. antibiotic treatment may be needed;
If there are no purulent compartments, then the rash goes away on its own and does not require treatment. Acne can also occur in teenagers. They most often appear on the face in the form of black dots and are associated with hormonal changes in the body of a teenager and increased work of the sebaceous glands. To prevent acne, there are cosmetic lotions, washing gels and other products. In case of inflammation, it is better to seek advice from a pediatric dermatologist or cosmetologist, because. antibiotic treatment may be needed;
2. Urticaria is an allergic reaction on the child's skin, accompanied by itching and the appearance of blisters on various parts of the body, in some cases the temperature may rise and the child's stool is disturbed. The blisters appear suddenly and can disappear just as quickly, but sometimes they disappear only after a few days. The causes of urticaria can be various factors: hormonal disorders, malfunctions of the liver, kidneys, consumption of foods that caused an allergic reaction (fish, eggs, citrus fruits, etc.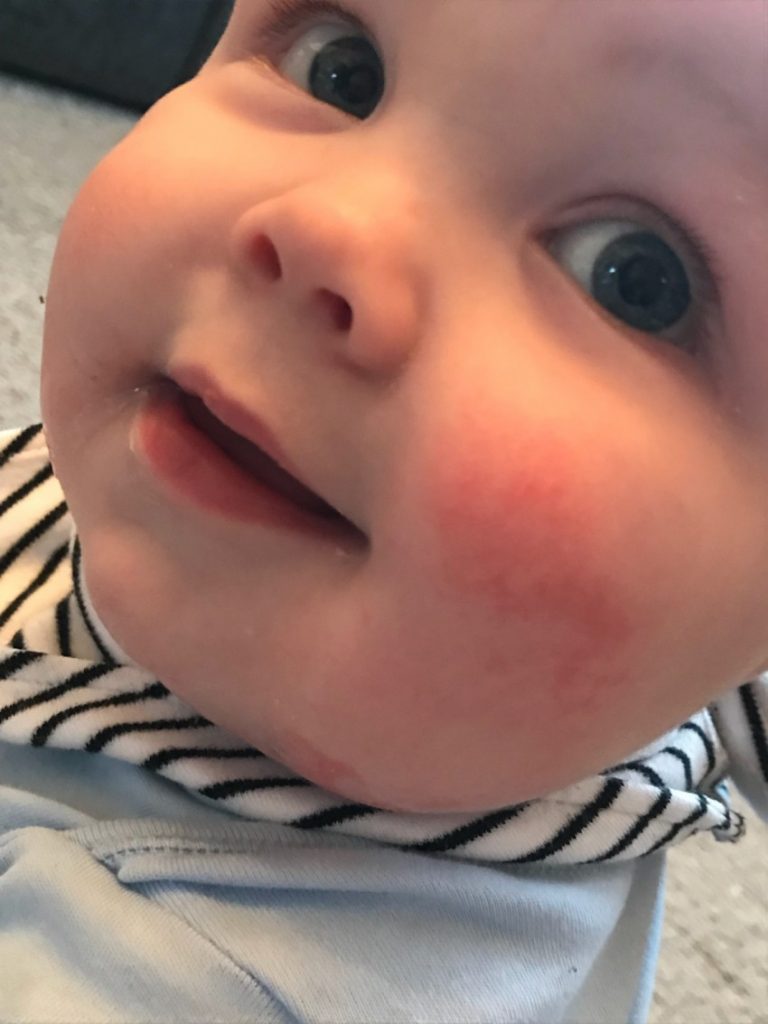 ), insect bites, reaction to sunlight, temperature changes, emotional stress etc. Urticaria can be chronic and does not go away for a long time, and acute - disappearing after a few hours. For the treatment of urticaria, it is important to identify the underlying cause that caused it;
), insect bites, reaction to sunlight, temperature changes, emotional stress etc. Urticaria can be chronic and does not go away for a long time, and acute - disappearing after a few hours. For the treatment of urticaria, it is important to identify the underlying cause that caused it;
3. Food allergy manifests itself as spots pinkish red. It is slightly convex, edematous in places of scratching and is accompanied by itching. It is localized, as a rule, on the baby's cheeks, but can also appear on other parts of the body. It can occur in both infants and adolescents. If the baby is breastfed, then the allergy that has arisen is associated with the products consumed by the mother. If the newborn is artificially fed, then an allergic reaction may appear on the mixture. In older children, food allergies can be caused by fish, eggs, nuts, chocolate, strawberries, and other foods;
Allergy, as a rule, is accompanied by edema, which, in turn, in case of improper treatment and untimely assistance, cause suffocation . If an allergy of any nature occurs, a pediatrician's consultation is required to help in choosing the optimal mixture for the baby, or a pediatric dermatologist - allergist to refer older children to laboratory tests ;
If an allergy of any nature occurs, a pediatrician's consultation is required to help in choosing the optimal mixture for the baby, or a pediatric dermatologist - allergist to refer older children to laboratory tests ;
4. Household allergies . It can occur in both newborns and older children. It usually appears as pimples all over the body and is accompanied by lachrymation, sneezing. The causes of such a reaction of the body can be washing powder and other detergents, dust, plants, animal hair, etc. An allergic rash differs from an infectious rash in that the child does not have a temperature with it, he does not have general ailments, there is no loss of appetite, drowsiness;
5. Prickly heat . It occurs mainly in infants. It manifests itself in the form of red pimples all over the body, especially in the inguinal zone. The affected areas must be smeared with a special baby cream, air baths more often for the baby and a diaper change;
6. Roseola (erythema infectiosum) is an acute childhood viral disease affecting only children under 2 years of age. Very often, roseola is confused with SARS or rubella . At the beginning of the illness, the baby's temperature rises sharply, which lasts 3-5 days, and after that the child becomes covered with a red-pink rash that disappears in 5-7 days. This is not a dangerous disease, it does not require treatment, and if it occurs, the child should be given only antipyretic drugs;
Roseola (erythema infectiosum) is an acute childhood viral disease affecting only children under 2 years of age. Very often, roseola is confused with SARS or rubella . At the beginning of the illness, the baby's temperature rises sharply, which lasts 3-5 days, and after that the child becomes covered with a red-pink rash that disappears in 5-7 days. This is not a dangerous disease, it does not require treatment, and if it occurs, the child should be given only antipyretic drugs;
7. Windmill . This is a common childhood infectious disease that requires treatment. The incubation period of this disease can last from 11 to 21 days. Occurs at any age. It is accompanied by a rash on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of red spots, in the center of which blisters with a yellowish liquid are localized. Accompanied by itching. As the disease progresses, the blisters burst, crusts form, leaving scars if the child has scratched the blister and brought the infection. The disease can also cause fever and headache;
The disease can also cause fever and headache;
8. Measles is an acute infectious disease that is quite rare due to the use of vaccinations. In addition, this virus is rarely activated in babies under 8 months old, because. they are protected by their mother's immunity. The disease begins with symptoms of a common cold - coughing, lacrimation, sneezing and fever up to 40 C. Then the child develops white spots on the mucous surface of the cheeks, nasal discharge, severe headache, photophobia. Then, within a few days, red spots of various shapes appear on the face, neck, near the head and further throughout the body. The disease is contagious within a week of the onset of the first symptoms. The virus is dangerous with complications such as: meningitis pneumonia development of deafness, brain damage and even death;
9. Scarlet fever is an acute infectious streptococcal disease. Begins with sore throat, high fever, enlarged tonsils , in some cases with plaque.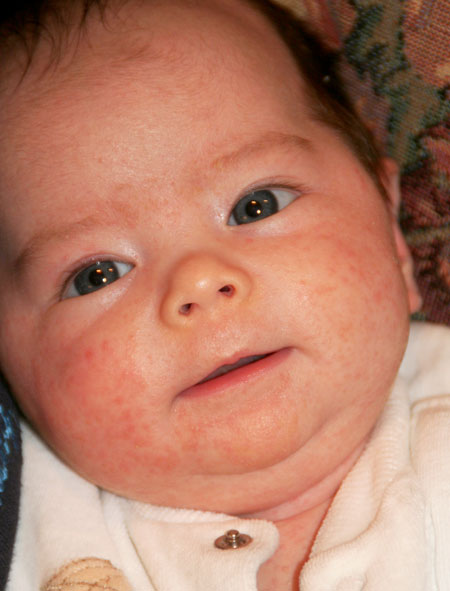 Then a small dotted rash appears on the back, chest, knees, armpits, groin and quickly spreads throughout the body and face. Only the area around the mouth remains white. Throat and tongue become very red. By the end of the disease, peeling of the skin on the toes and hands begins;
Then a small dotted rash appears on the back, chest, knees, armpits, groin and quickly spreads throughout the body and face. Only the area around the mouth remains white. Throat and tongue become very red. By the end of the disease, peeling of the skin on the toes and hands begins;
10. Rubella is an acute infectious disease . The disease begins with a slight increase in temperature and enlargement of the lymph nodes in the parotid and cervical region. A small rash also appears on the face and behind the ears, and then all over the body. Rubella is very dangerous for pregnant women, and complications can occur in older children and adolescents. In children, the disease proceeds in a fairly mild form;
11. Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. Rash in meningitis is not the main symptom. However, with this disease, rashes appear on the back of the throat, as well as on the hips, back, buttocks in the form of a red rash of various shapes.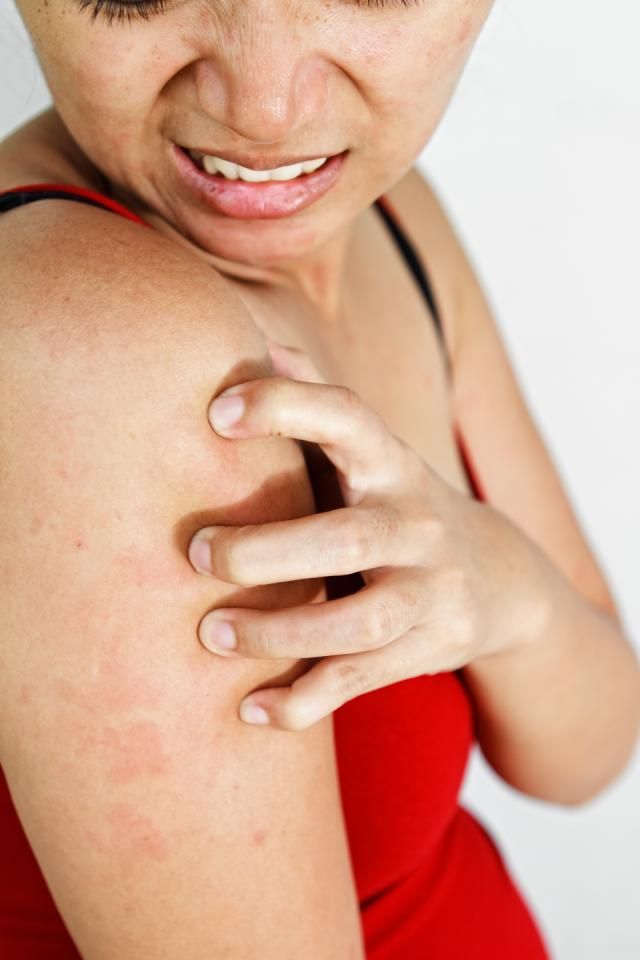 Symptoms of meningitis include very high fever, severe headache, vomiting, photophobia, and neck muscle tension. At the slightest suspicion of meningitis, parents should immediately consult a doctor. Timely help with this disease will save the child's life;
Symptoms of meningitis include very high fever, severe headache, vomiting, photophobia, and neck muscle tension. At the slightest suspicion of meningitis, parents should immediately consult a doctor. Timely help with this disease will save the child's life;
12. Streptoderma is a skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus. The disease affects, as a rule, the paranasal and perioral region. In the beginning, redness appears around the nose and mouth, then small bubbles with liquid. When they burst, yellow crusts remain. The disease may be accompanied by fever;
13. Herpes is an infectious disease accompanied by the appearance of blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, in children it is most often located on the lips. This disease is extremely rare in newborns, because. they are given maternal immunity. It affects children from 3 to 4 years of age. In addition to a rash, the disease may be accompanied by a sore throat, fever.
There are a lot of skin rashes and diseases in children, they can be very similar, but some are completely harmless to your child's health, while others pose a threat not only to the general condition, but also to the child's life! Do not take risks, and if you have any doubts, if any spots, rashes and other symptoms appear, contact your pediatrician, who, if necessary, will refer you and your child to a pediatric dermatologist, allergist, neurologist or other highly specialized specialist, depending on the nature of the rash and the severity of the skin disease.