Pregnancy thrush mouth
Thrush When Pregnant - Symptoms & Causes
There is nothing more irritating than vaginal thrush. Unfortunately, it is common for pregnant women to experience the yeast infection, alongside everything else that goes with pregnancy.
The good news is that it is not normally serious, but it can be very uncomfortable.
Here we take a closer look at some of the symptoms of thrush and investigate what exactly can cause it.
What is thrush?
Thrush, also known as candidiasis, is a yeast infection which can affect both men and women.1
Contrary to popular opinion, it is not classed as a sexually transmitted infection.
It is caused by a fungus called candida and thrives in warm, moist conditions.2
What causes thrush?
Candida usually lives in the vagina without causing any symptoms and its growth is kept under control by normal bacteria.
However, if the balance of this bacteria changes, then the candida fungus may grow and result in thrush. 3
Thrush symptoms
Now that we know the causes of thrush, here are some of the symptoms to look out for.
Thrush in women can cause several symptoms, which remain the same in pregnancy.
These include:
- Itchiness and irritation around the vagina and vulva
- A sore feeling around the entrance to the vagina
- A slight swelling of the labia (vaginal lips)4
- A white discharge which is a similar consistency to cottage cheese and is usually odourless
- A stinging or burning feeling during sex or when going to the toilet
- Redness of the vagina5
Sometimes thrush does not cause any symptoms and so you may not even know that you have had it.6
Why is thrush common during pregnancy?
Pregnant women tend to get thrush because of the changes that happen to the body during pregnancy, especially during the third trimester.7
These changes cause a change in the balance of bacteria in the body.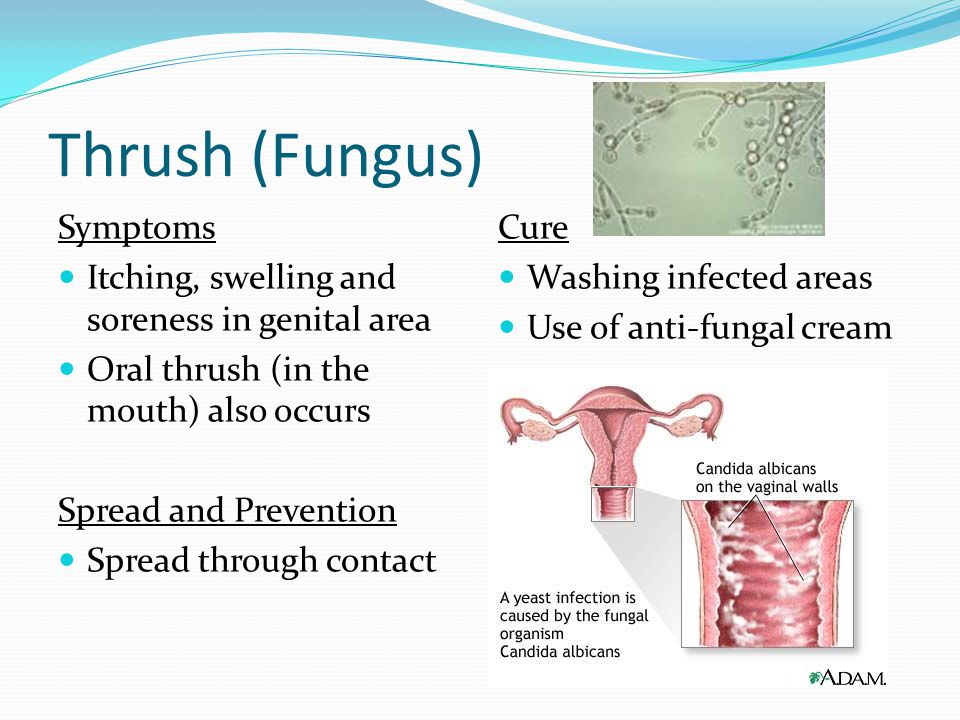
The glucose content in the vaginal wall can increase, which provides good conditions for fungus to grow.
Your immune system is slightly weakened during pregnancy and this means that your body might find it more difficult to fight off vaginal infections.
Thrush is especially common during the latter stages of pregnancy, in the third trimester.9
During pregnancy, you might find that thrush keeps coming back or that the symptoms can take a while to clear completely.10
Why it is normal to have thrush when you are pregnant
Don’t worry, having thrush is no reflection on either you or your partner.
It does not mean that there is anything wrong with your pregnancy or that you have done anything wrong. It is completely normal to experience thrush during your pregnancy.
Oral thrush
Oral thrush can also happen more often during pregnancy. Symptoms of thrush in the mouth include redness inside the mouth, an unpleasant taste or loss of taste and a sore tongue and gums. 11
11
Consult your GP or midwife to discuss a mouth thrush treatment suitable for pregnant women.
Can having thrush harm an unborn baby?
There is no evidence to suggest that a pregnant mother having thrush can harm an unborn baby.
Your baby is tucked safely inside your womb and will not come into contact with the infection during pregnancy.12
If you are suffering from thrush when the baby is born, the baby may catch it during birth. However, this is not anything to worry about and it can easily be treated.13
How can you treat thrush when pregnant?
If you are pregnant, you should consult your GP or your midwife before you take any treatments or medication to treat thrush.14
During pregnancy, thrush can be treated with a cream to use externally or a tablet which is inserted into the vagina. This thrush treatment tablet is called a pessary and contains clotrimazole, which is an antifungal drug. 15
15
If you are pregnant, breast-feeding or trying for a baby then you should steer clear of anti-thrush oral tablets.16
How can I prevent thrush?
You may not be able to completely avoid thrush whilst pregnant, due to the hormonal changes in your body.
However, there are a few things you can do which might help to prevent it.
We know we don’t need to remind you, but always wipe from front to back when going to the toilet. This helps to prevent any bacteria entering the vagina.
Make sure you change your underwear if you go swimming or do a workout.
And speaking of underwear, cotton is best, as it allows the skin to breathe and helps to avoid the warm, moist conditions where candida otherwise thrives.17
To learn more about thrush and how to treat it, read our article on the best natural ways to tackle candida.
Last updated: 1 March 2021
Oral Thrush Treatment During Pregnancy Linked to Malformations
Published June 3, 2020
News and Trends
By staff
Boston—Vulvovaginal candidiasis, commonly known as thrush, often occurs during pregnancy, and expectant mothers usually are prescribed a short course of topical antifungal agents or one dose of oral fluconazole.
Now, a report in The BMJ suggests that pregnant women who use oral thrush treatment might have a higher risk of delivering a baby with muscle and bone malformations. Brigham and Women’s Hospital–led researchers emphasize, however, that the absolute risk is small and that they did not demonstrate any association between the therapy and heart defects or oral clefts in babies, which had been feared.
The researchers note that topical antifungal treatment is available OTC in many countries, but that patients often opt for oral fluconazole because of the convenience of taking one oral dose.
Researchers sought to examine the risk of congenital malformations associated with exposure to oral fluconazole at commonly used doses in the first trimester of pregnancy for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis.
To do that, they focused on a cohort of 1.9 million pregnancies publicly insured in the United States, with data from the nationwide Medicaid Analytic eXtract 2000-14. Participants included pregnant women enrolled in Medicaid from 3 or more months before the last menstrual period to 1 month after delivery, and their infants enrolled for 3 or more months after birth. During the first trimester, 37,650 (1.9%) pregnancies were exposed to oral fluconazole and 82,090 (4.2%) pregnancies were exposed to topical azoles.
Participants included pregnant women enrolled in Medicaid from 3 or more months before the last menstrual period to 1 month after delivery, and their infants enrolled for 3 or more months after birth. During the first trimester, 37,650 (1.9%) pregnancies were exposed to oral fluconazole and 82,090 (4.2%) pregnancies were exposed to topical azoles.
Researchers established use of fluconazole and topical azoles by requiring one or more prescriptions during the first trimester of pregnancy. The study team was looking for increased risk of musculoskeletal malformations, conotruncal malformations, and oral clefts, associated with exposure to oral fluconazole, diagnosed during the first 90 days after delivery.
Results indicate the following:
• The risks of musculoskeletal malformations were 52.1 (95% CI, 44.8 to 59.3) per 10,000 pregnancies exposed to fluconazole versus 37.3 (33.1 to 41.4) per 10,000 pregnancies exposed to topical azoles.
• The risks of conotruncal malformations were 9.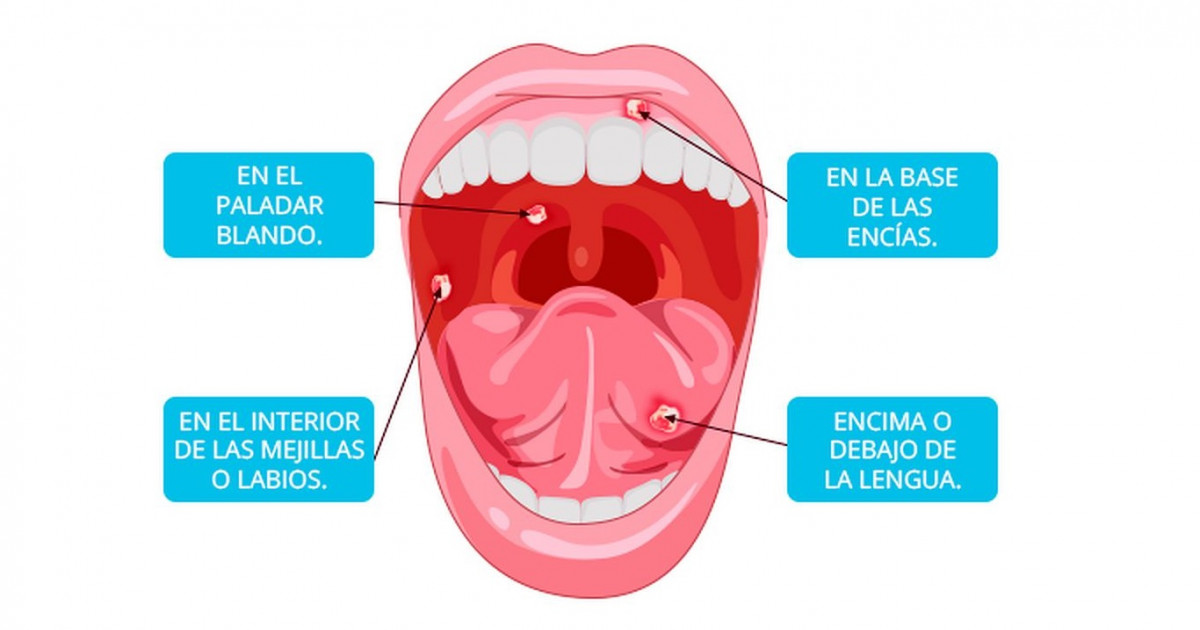 6 (6.4 to 12.7) versus 8.3 (6.3 to 10.3) per 10,000 pregnancies exposed to fluconazole and topical azoles, respectively.
6 (6.4 to 12.7) versus 8.3 (6.3 to 10.3) per 10,000 pregnancies exposed to fluconazole and topical azoles, respectively.
• The risks of oral clefts were 9.3 (6.2 to 12.4) versus 10.6 (8.4 to 12.8) per 10 000 pregnancies, respectively.
The authors calculated the adjusted relative risk after fine stratification of the propensity score at 1.30 (1.09 to 1.56) for musculoskeletal malformations, 1.04 (0.70 to 1.55) for conotruncal malformations, and 0.91 (0.61 to 1.35) for oral clefts overall. Based on cumulative doses of fluconazole, they note, adjusted relative risks for musculoskeletal malformations, conotruncal malformations, and oral clefts overall were 1.29 (1.05 to 1.58), 1.12 (0.71 to 1.77), and 0.88 (0.55 to 1.40) for 150 mg of fluconazole; 1.24 (0.93 to 1.66), 0.61 (0.26 to 1.39), and 1.08 (0.58 to 2.04) for more than 150 mg up to 450 mg of fluconazole; and 1.98 (1.23 to 3.17), 2.30 (0.93 to 5.65), and 0.94 (0.23 to 3.82) for more than 450 mg of fluconazole, respectively.
The risk of musculoskeletal malformations was double in women taking the highest dose in early pregnancy (above 450 mg), but absolute risks were still small (12 incidents per 10,000 exposed pregnancies overall). A 30% increased risk among women who had taken a smaller cumulative dose of 150 mg of oral fluconazole also was identified.
“Oral fluconazole use in the first trimester was not associated with oral clefts or conotruncal malformations, but an association with musculoskeletal malformations was found, corresponding to a small adjusted risk difference of about 12 incidents per 10,000 exposed pregnancies overall,” the researchers conclude.
“Oral fluconazole during the first trimester, especially prolonged treatment at higher than commonly used doses, should be prescribed with caution, and topical azoles should be considered as an alternative treatment,” they add.
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
« Click here to return to Weekly News Update.
Read More On: NEWS AND TRENDS
December 2022
In This Issue Digital Magazine Archives Subscription-
Increased Statin Use for Primary Prevention in Oldest Elderly
-
Who Requires Medication Under New Hypertension Guidelines?
-
Methotrexate Reduces Joint Damage in Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis Patients
-
Older RZV Recipients Have Elevated Risk of Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Thrush in the mouth in adults: symptoms, treatment - ROOTT
Causes Types Danger Treatment Remedial measures Drugs against thrush
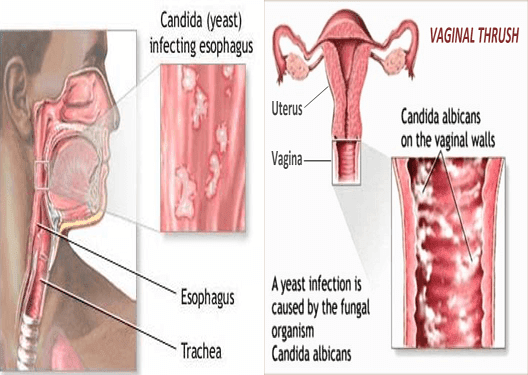
Oral candidiasis (thrush) is an infectious disease of the mucous membranes. It is caused by a fungus of the genus Candida.
It is caused by a fungus of the genus Candida.
Mucous membranes are covered with whitish plaques resembling curd mass. Patients have unpleasant sensations in the mouth, a burning sensation. Eating, sometimes even speaking, becomes painful. Patients complain of dry mouth and bad breath. nine0003
Thrush is very common in infants but is easily tolerated and heals quickly. It often occurs in people with dentures, those taking corticosteroids, or undergoing chemotherapy.
Causes of the disease
Yeast fungi are present in the body of any person. Under the influence of certain factors, they begin to multiply uncontrollably.
Thrush in the mouth is caused by:
- Hormonal changes, e.g. during pregnancy
- Taking certain medications
- Weakening of immunity due to illness
- Inadequate oral hygiene
- Mucosal injuries
- High carbohydrate diet
- Taking contraceptives
- Smoking
- Candidiasis is contagious, it can be transmitted through shared utensils, kissing.
Classification
Symptoms of thrush manifest themselves in different ways, depending on the form of the disease. In dentistry, the following forms of candidiasis are distinguished:
- Acute pseudomembranous - Mild form: the only symptom is the presence of plaque. If you scrape it off, a swollen, reddened mucous membrane is visible. - Moderate: plaque is difficult to remove, there are unpleasant sensations while eating. The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. - Severe form: extensive, off-white plaque. Signs of tissue infiltration. Plaques are removed with difficulty, bleeding mucous membrane is visible under them.
- Acute atrophic Mucosa red, painful to touch, smooth. The plaque is dense, covers the cheeks from the inside, tongue, palate. The mouth is dry. There are teeth marks on the tongue. There may be a bitter, sour, metallic taste in the mouth. The acute course can become chronic, usually in patients with removable dentures.
 Therefore, its second name is prosthetic stomatitis. Under the prosthesis, the mucous membrane is dry, red. There is almost no plaque, but the pain syndrome is pronounced. On the back of the tongue papillae atrophy. This leads to a change in taste sensations. Sometimes atrophic candidiasis is called erythematous ("erythema" - redness). nine0018
Therefore, its second name is prosthetic stomatitis. Under the prosthesis, the mucous membrane is dry, red. There is almost no plaque, but the pain syndrome is pronounced. On the back of the tongue papillae atrophy. This leads to a change in taste sensations. Sometimes atrophic candidiasis is called erythematous ("erythema" - redness). nine0018 - Chronic hyperplastic It occurs only in adults, mainly in smokers. The coating is dirty gray, located in the corners of the lips, on the tongue. It scrapes off badly, has an unpleasant smell. The plaques merge, covering the mucosa almost completely. Saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foams. The most common such thrush in men.
Why is thrush dangerous? But candida is a yeast-like fungus, and, therefore, is capable of rapid reproduction, like any yeast. From the mucous membranes of the mouth, thrush can spread to the throat. This causes changes in the voice, makes it hoarse. Spreading to the esophagus, it provokes inflammation of the esophageal mucosa (esophagitis), making it painful for food to pass through it.
 nine0003
nine0003 Untreated hyperplastic candidiasis develops into malignant neoplasms.
Most importantly, the reproduction of the fungus indicates a malfunction in the body's defenses.
Only a doctor is able to prescribe the necessary examination and, based on its results, prescribe the appropriate treatment for a fungal infection.
How to treat thrush
Successful treatment requires an accurate diagnosis. For this, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. Bacteriological culture is mandatory. He will not only confirm the thrush, but also determine which type of fungus caused it. This is important when prescribing drugs. After a clinical examination, the dentist may recommend blood glucose or HIV testing. nine0003
Recommended consultations with narrow specialists:
- Endocrinologist To make sure there are no endocrine disorders.
- Allergist To detect sensitivity to dentures.
- Therapist To clarify the nature of somatic diseases.
Treatment of thrush in adults and children should be comprehensive and include activities aimed at strengthening general immunity, teaching adequate oral hygiene, and changing the diet. nine0003
Algorithm of therapeutic measures
- For the best result, the intervention begins with the sanitation of the oral cavity. Carious teeth are treated by replacing the affected tissues with filling material. Remove hard plaque and tartar from enamel. Plaque is a hotbed of infection, it is necessary to get rid of it.
- Eliminate the factors provoking candidiasis. Replace dentures if they cause an allergic reaction or do not fit well. Stop the exacerbation of common diseases. Take steps to improve your hormone levels. Conduct activities that increase immunity. nine0018
- Administer antifungals based on culture results. Prescribed antihistamines, restorative agents, immunomodulators.
- Give recommendations on the normalization of the microflora in the oral cavity.

To prevent relapses, it is useful to establish regular hygiene, to exclude foods rich in fast carbohydrates and sugars from the diet. Restorative activities include physical activity and stress-reducing activities (hobbies). It is important not to take medicines uncontrollably, according to recommendations from the Internet or from friends. nine0003
Thrush medicines
- Candidiasis medicines come in various forms:
- Suspensions (Diflucan, Amphotericin B)
- Tablets (Nystatin, Flucanosole, Itriconazole)
- Gels (Mikanozol)
A good effect in candidiasis is brought by rinsing with antiseptic agents: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. This is especially important if the patient wears removable dentures or, for various reasons, cannot maintain adequate hygiene. nine0003
Patients should be advised to regularly disinfect their prostheses.
Physician's opinion: Most drugs for the treatment of thrush are prescription drugs. Their independent use can cause serious complications. Therefore, do not self-medicate, contact your dentist. The doctor will prescribe treatment only after determining the sensitivity of the fungus to certain drugs. This will increase the effectiveness of the intervention and prevent relapses.
Their independent use can cause serious complications. Therefore, do not self-medicate, contact your dentist. The doctor will prescribe treatment only after determining the sensitivity of the fungus to certain drugs. This will increase the effectiveness of the intervention and prevent relapses.
Candidiasis or thrush in the mouth, symptoms and underlying causes
Oral candidiasis: what is it?
A fungus of the genus Candida can settle on the lining of the mouth, which causes a disease called candidiasis, or oral thrush. With this disease, white plaques appear on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks. During tongue cleaning, they can cause soreness and even slight bleeding. Without treatment, candidiasis can spread to other parts of the mouth, such as the back of the throat, tonsils, gums, and palate. nine0003
Although no one is immune from oral candidiasis, it is more common in immunocompromised people, denture wearers, patients taking inhaled corticosteroids, and infants. Oral thrush also occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy, patients with a history of dry mouth syndrome (xerostomia) and smokers.
Oral thrush also occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy, patients with a history of dry mouth syndrome (xerostomia) and smokers.
Causes of oral candidiasis
A number of well-defined factors contribute to the development of oral thrush. The causes of the disease can be both a weakening of the immune system (caused by illness or the use of certain drugs), and the use of antibiotics, which changes the natural microbial balance in the human body. nine0003
The result of failures in the natural defense mechanisms can be a significant imbalance of "beneficial" and "harmful" microbes. Under normal circumstances, the immune system fights viruses and bacteria that are dangerous to humans, but with a weakened immune system, this fight becomes less effective, which allows the fungus that causes oral candidiasis to multiply.
Vaginal fungal infections, diabetes, most forms of cancer, HIV/AIDS all weaken the body and make it more vulnerable to oral thrush. nine0003
nine0003
Oral candidiasis in immunocompromised adults
Oral candidiasis can spread to other organs such as the lungs, liver, and digestive tract. With the penetration of infection into the intestines, a violation of its work and an even greater weakening of the body are possible.
Depending on the severity of your illness, you may be prescribed antifungal medicines that come in the form of tablets, lozenges, and a mouthwash that you swallow. Amphotericin B, which is often used in the treatment of advanced HIV and other antifungal drug-resistant infections, may also be prescribed. nine0003
Because some antifungal drugs can damage the liver, your doctor will likely do regular blood tests and monitor your liver (especially if it has already been infected). This same strategy should be used if you are on long-term treatment or if you have liver disease.
Symptoms of oral thrush in children and adults
In some cases, the symptoms of oral candidiasis may not appear immediately: sometimes they can appear completely unexpectedly. Here are some tell-tale signs that you may have oral thrush:
Here are some tell-tale signs that you may have oral thrush:
- White, cheesy plaques anywhere in the mouth
- Unusual pain with habitual movements of the tongue and jaw
- Bleeding of plaques when rubbed
- Cracks and redness in the corners of the lips (more often when wearing prostheses)
- Dry mouth
- Marked loss of taste in food and drink
Although thrush most often develops in the most visible areas of the mouth, lesions can also occur in the esophagus. This makes swallowing difficult or feels like the food is stuck in the throat. This happens in the most severe cases, and if you have any of these symptoms, you should immediately contact your dentist or GP. nine0003
While waiting for treatment, you can relieve pain yourself if you have any. Eat unsweetened yogurt or take probiotics containing lactobacillus acidophilus. Neither is a cure in the truest sense of the word, but it can help restore normal microflora. If the infection persists, your doctor will likely prescribe you an antifungal medication or antibiotics.
If the infection persists, your doctor will likely prescribe you an antifungal medication or antibiotics.
Symptoms of oral candidiasis in infants and nursing mothers
With oral candidiasis, the baby may have difficulty feeding or become more restless and irritable than before. A manifestation of thrush is most likely to be white plaques in the child's mouth. Mothers should keep a close eye on their baby's oral health because candidiasis is transmitted through breastfeeding, and if this happens and the baby then recovers, the mother may inadvertently infect it again.
As a breastfeeding mother, look out for the following signs and symptoms:
- Itching, tenderness or unusual redness of the nipples
- Shiny or flaky skin around alveoli
- Unusual pain during or between feedings
- Severe, piercing pain in the chest
If white plaques appear in your mouth or in your child's mouth, contact your doctor or dentist immediately. Do not postpone a visit to the doctor if symptoms of candidiasis occur in older children or adolescents, since diabetes may be the main disease against which thrush has developed. nine0003
Do not postpone a visit to the doctor if symptoms of candidiasis occur in older children or adolescents, since diabetes may be the main disease against which thrush has developed. nine0003
Since there are two people to be treated at once, the doctor may use a special strategy, such as starting with two different antifungals: a cream for your breasts and another medicine for your baby.
If you are breastfeeding, use lactation pads to prevent fungus from getting on your clothes. Do not buy liners with plastic membranes, as they only encourage fungus to thrive. Reusable liners (and, of course, the bra itself) should be washed in hot water with bleach to help keep the infection from spreading. nine0003
If you are breastfeeding your baby, but also bottle feeding, and give him a pacifier, wash all objects that come into contact with the baby's mouth daily in a solution of equal parts water and vinegar. After washing, let things air dry to prevent the growth of fungus. In the same way, you need to process all parts of the breast pump, especially its removable parts.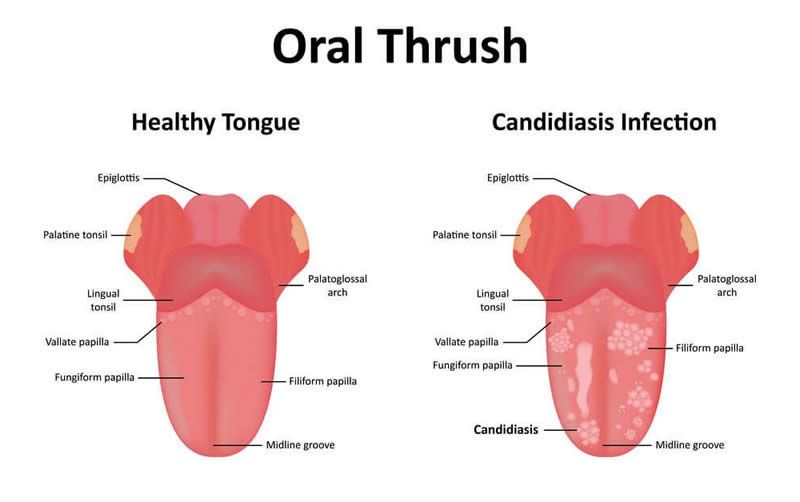
Physician or dentist consultation
If you suspect that you have an oral disease that requires medical attention, make a list of all the symptoms you have, including any that you may think are not related to thrush: the doctor will understand whether they are important or not. Also include non-medical events in this list, such as increased stress levels and causes of anxiety. Indicate if you are in the company of people with a weakened immune system. nine0003
You will also need to have a list of all the medicines you take. Also, write down the questions you want to ask the doctor. This will help you find out all the details you are interested in and get a comprehensive consultation, regardless of whether you have oral candidiasis or not.
Your doctor may ask you follow-up questions that will allow him to narrow down his search for a diagnosis based on the symptoms he has identified and the symptoms you describe. Try to answer as frankly and honestly as possible so that the doctor can quickly diagnose the disease and begin treatment without waiting for complications. nine0003
nine0003
If the examination of the oral cavity does not allow the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis, he will definitely take a small sample and either examine it himself or give it to the laboratory for analysis.
If the infection has already affected not only the oral cavity, but also the esophagus, a couple of studies may be required. First of all, the doctor will take a swab from the back of the throat to determine which bacteria or fungi have become (and have become) the cause of the symptoms. Then you may need to have an endoscopy, in which your doctor uses an endoscope (flexible tube with light) to look at your esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine. This will determine how far the infection has spread. nine0003
Lifestyle and home remedies for oral thrush
At the initial stage of candidiasis, good oral hygiene will help to contain the development of the disease - brushing your teeth twice a day and at least daily flossing will help to timely remove food debris and plaque from the surface of the teeth , from interdental spaces and along the gum line.