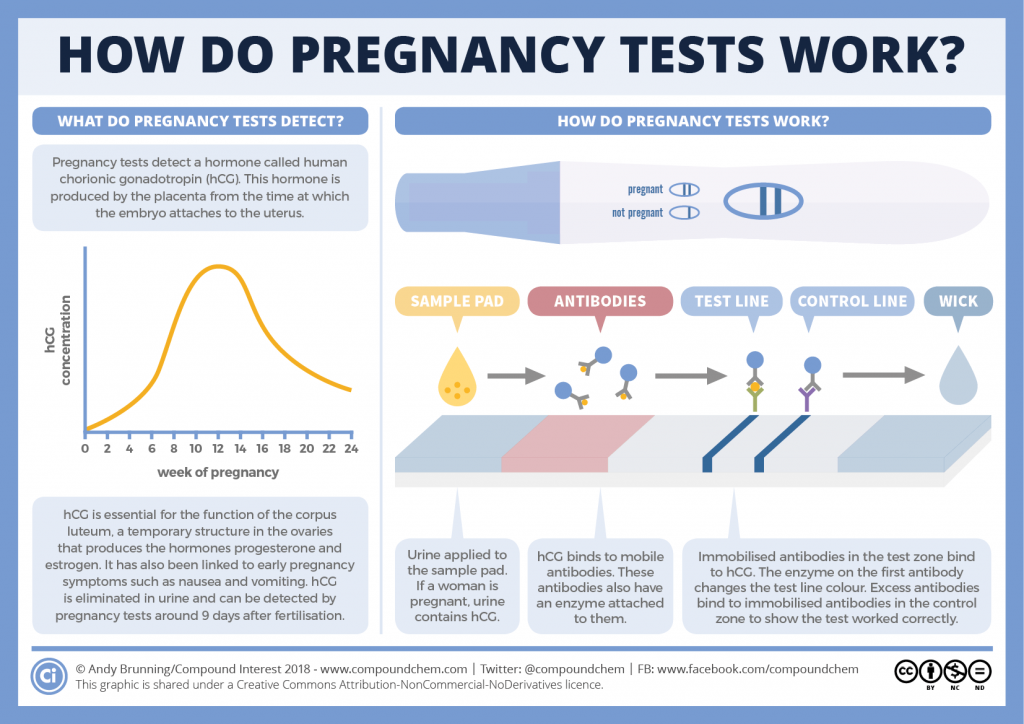
What is the hcg
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
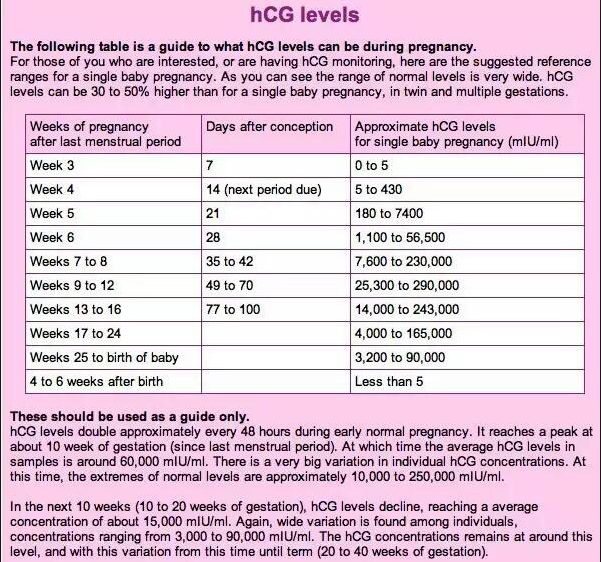
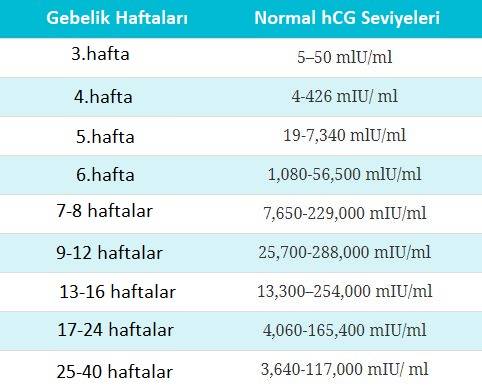
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
| 3 weeks | 6 – 70 IU/L |
| 4 weeks | 10 - 750 IU/L |
| 5 weeks | 200 - 7,100 IU/L |
| 6 weeks | 160 - 32,000 IU/L |
| 7 weeks | 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L |
| 8 weeks | 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 9 weeks | 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 10 weeks | 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L |
| 12 weeks | 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L |
| 14 weeks | 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L |
| 15 weeks | 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L |
| 16 weeks | 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L |
| 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester) | 1,400 - 53,000 IU/L |
| 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester) | 940 - 60,000 IU/L |
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin), Pathology Tests Explained (Human chorionic gonadotropin), NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy testing - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Pregnancy testing can be done from around the time that your period is due, and involves testing your urine for the pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Read more on myDr website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
Sometimes, a home pregnancy test may be positive when a woman isn’t pregnant.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.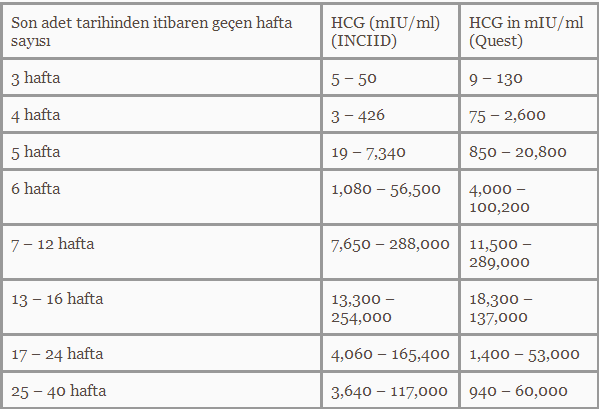
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness.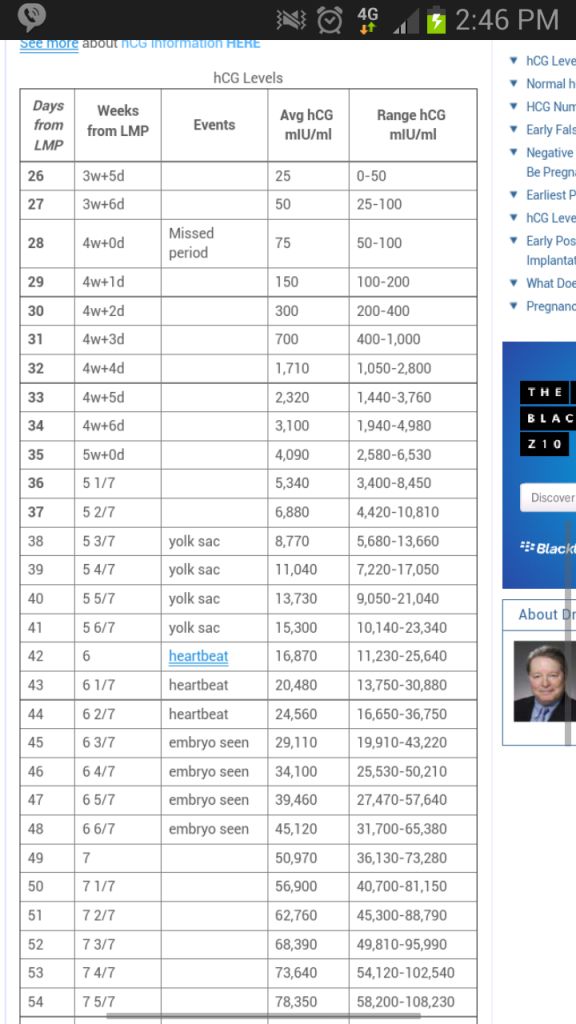 Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.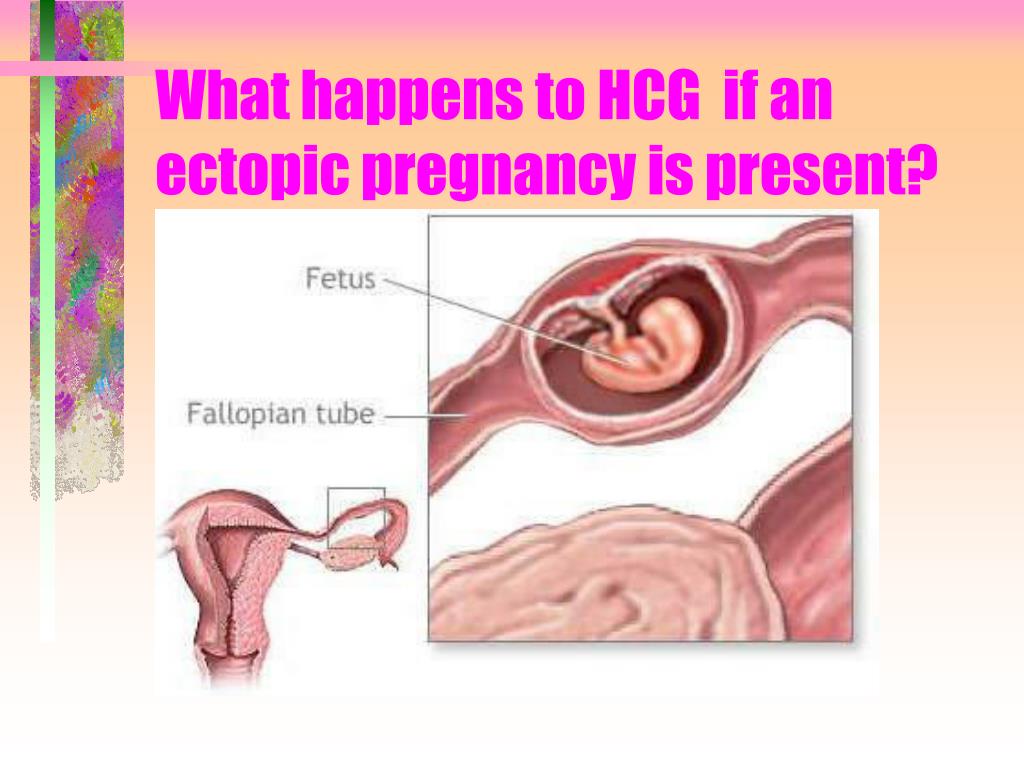
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin - StatPearls
Introduction
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a chemical created by trophoblast tissue, tissue typically found in early embryos and which will eventually be part of the placenta. Measuring hCG levels can be helpful in identifying a normal pregnancy, pathologic pregnancy, and can also be useful following an aborted pregnancy.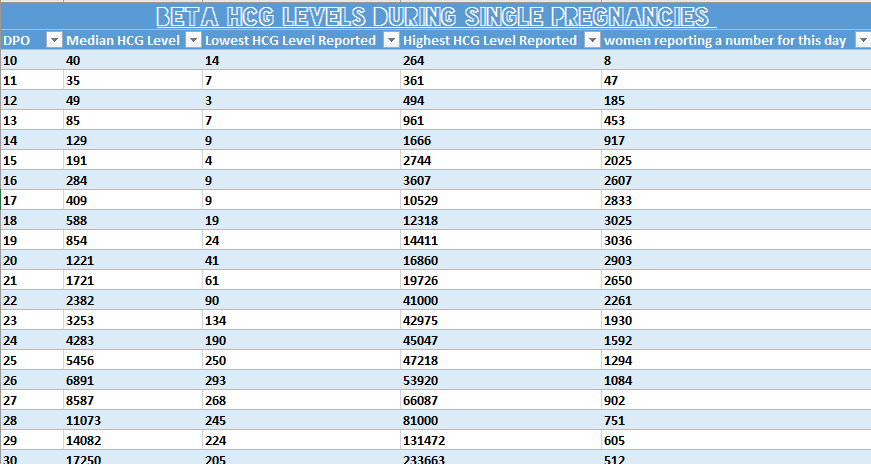 There is also a benefit in measuring hCG in a variety of cancers including choriocarcinoma and extra-uterine malignancies.
There is also a benefit in measuring hCG in a variety of cancers including choriocarcinoma and extra-uterine malignancies.
Etiology and Epidemiology
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced primarily by syncytiotrophoblastic cells of the placenta during pregnancy. The hormone stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone to maintain the pregnancy. Smaller amounts of hCG are also produced in the pituitary gland, the liver, and the colon.[1] As previously mentioned, certain malignancies can also produce either hCG or hCG-related hormone. Trophoblastic cancers (hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma, and germ cell tumors) are associated with high serum levels of hCG-related molecules.
The hormone itself is a glycoprotein composed of two subunits, the alpha and beta subunits.[1] There are multiple forms found in the serum and urine during pregnancy including the intact hormone and each of the free subunits. HCG is primarily catabolized by the liver, although about 20% is excreted in the urine. The beta subunit is degraded in the kidney to make a core fragment which is measured by urine hCG tests.
The beta subunit is degraded in the kidney to make a core fragment which is measured by urine hCG tests.
Specimen Requirements and Procedure
Urine Testing
Urine should not be collected after the patient has been drinking a large amount of fluid, as a dilute specimen may result in a falsely negative test.[2]
Blood in the urine may cause a false positive test result.
Serum Testing
Diagnostic Tests
Serum tests for hCG are immunometric assays. This means that they use 2two antibodies that bind to the hCG molecule, a fixed antibody and a radiolabeled antibody which adhere to different sites on the molecule, sandwiching and immobilize the molecule to make it detectable.[3] Assays involve washing away the excess serum components and measuring the amount of remaining labeled hCG to give a quantitative result. There are more than 100 different assays commercially available which results in significant variability in reported values.
Urine assays are similar, although many detect total hCG levels greater than 20 mIU/mL.[4] Many over-the-counter urine pregnancy tests do not detect hyperglycosylated hCG, which accounts for most of the hCG in early pregnancy, resulting in a wide range of sensitivities of these tests.
Serum testing is much more sensitive and specific than urine testing. Urine testing, however, is more convenient, affordable, comfortable for patients, has a fast turnaround (5 to 10 minutes), and does not require a medical prescription.
Testing Procedures
Urine Testing
Urine is placed in or on a designated receptacle (most commercially available and medical point of care tests)
An indicator (typically a colored line or symbol), along with a control, will appear if the test is positive
An isolated control line/symbol will be evident if the test is negative
Serum Testing
Serum hCG testing is performed in a laboratory equipped with the proper machinery and uses a peripheral blood sample
If a hook effect/gestational trophoblastic disease is suspected, the lab should perform a dilution prior to testing
Interfering Factors
There are multiple reasons why an hCG test (serum or urine) may have a false report. While uncommon, false positive hCG tests can result in unnecessary medical care and/or irreversible surgical procedures. False negatives may be equally concerning and result in a delay in care or diagnostic evaluation. Potential causes of false results are listed and briefly discussed.
Serum False Positives (1/1000 to 1/10,000) [5]
Ectopic production of hCG (hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma, and germ cell tumors,[6], in addition to multiple myeloma, stomach, liver, lung, bladder, pancreatic, breast, colon, cervical, and endometrial cancers)[7][8][9][10][11]
Heterophile antibodies (autoantibodies and antibodies formed after exposure to animal products that interact with the assay antibodies)[12][13]
Rheumatoid factors (can bind the antibodies in the assay as well)
IgA deficiency[14]
Chronic renal failure or ESRD on hemodialysis (rare)[15]
Red blood cell or plasma transfusion of blood with hCG in it have been reported
Exogenous hCG preparations for weight loss, assisted reproduction, doping[16]
Serum False Negatives
Early measurement after conception
"Hook effect" can occur when hCG levels are about 500,000 mIU/mL.
 [17] This is because there are so many hCG molecules that they saturate both the tracer and the antibodies separately, which doesn't allow for the sandwiching of the tracer-hCG-antibody required for the measurement. This means that all of the complexes are washed away, giving a false-negative result. If gestational trophoblastic disease is suspected, the lab should perform a dilution prior to testing.
[17] This is because there are so many hCG molecules that they saturate both the tracer and the antibodies separately, which doesn't allow for the sandwiching of the tracer-hCG-antibody required for the measurement. This means that all of the complexes are washed away, giving a false-negative result. If gestational trophoblastic disease is suspected, the lab should perform a dilution prior to testing.
Urine False Positives
Blood or protein in the urine
Human error in result interpretation
Ectopic production of hCG
Exogenous hCG
Drugs (aspirin, carbamazepine, methadone, high urinary pH and seminal fluid)[18]
Urine False Negatives
Early measurement after conception
Dilute urine specimen[2]
"Hook effect" as discussed above
Results, Reporting, Critical Findings
HCG levels are reported in milli-international units of hCG hormone per milliliter of blood, or mIU/mL.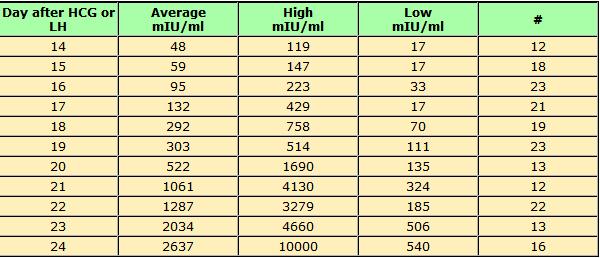 International unit per liter (IU/L) may also be used.
International unit per liter (IU/L) may also be used.
Urine hCG testing is qualitative, reporting a positive or negative result. The assays detect hCG levels typically starting at 20 to 50 (reportedly as low as 6.3 to 12.5)[19] mIU/mL, corresponding to levels at approximately 4 weeks post-conception.
Serum assays can measure beta-hCG as low as 1 to 2 mIU/mL.
Clinical Significance
Pregnancy
HCG is an important hormone in pregnancy, and its clinical utility is primarily centered around its detection in early pregnancy, along with serial measurement during pregnancy and pregnancy-related complications.
Levels of hCG can vary widely between women with normal pregnancies. Typically, serum and urine concentrations of hCG rise exponentially in the first trimester of pregnancy, doubling about every 24 hours during the first 8 weeks. The peak is usually around 10 weeks of gestation and then levels decrease until about the 16th week of gestation where they remain fairly constant until term. [3]
[3]
Patients who have hCG levels that plateau prior to 8 weeks or that fail to double commonly have a nonviable pregnancy, whether intra-uterine or extra-uterine. Extra-uterine (ectopic) pregnancies usually have a rate-of-rise that is low without the typical doubling. However, given the large range of normal hCG levels and inconsistent rates-of-rise of this hormone, checking serum levels is typically paired with ultrasound evaluation to improve sensitivity and specificity.[20]
Return of hCG to zero following delivery or termination of pregnancy ranges from 7 to 60 days.[21] Trending the fall of hCG levels can be important in termination of molar pregnancies and also following the termination of normal or ectopic pregnancies to be assured that the therapy has been successful.
It notable that there are many different combinations of antibodies used in commercial assays. This results in heterogeneous results with as much as a 50-fold difference in immunoassay results.[3] This is clinically relevant, particularly when comparing results from different laboratories in different facilities/hospitals when examining low values following pregnancy termination or trophoblastic disease.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Detection of hCG is also useful in the evaluation of trophoblastic disease, including complete and partial hydatidiform mole, postmolar tumor, gestational choriocarcinoma, testicular choriocarcinoma, and placental site trophoblastic disease. All of these entities produce hCG, varying levels of which are reported on commercial assays. A total hCG level of greater than 100,000 mIU/mL in early pregnancy, for example, is highly suggestive of a complete hydatidiform mole,[22] although many normal pregnancies may reach this level at their peak around weeks 8 to 11 of gestation. Precise hCG measurements are important to assess the tumor mass, the successful treatment of malignancy, and to test for recurrence or persistence of disease.[6]
Non-Pregnant Patients
HCG in the serum increases with age in nonpregnant women. A cut off of 14 mIU/mL has been suggested for use in interpreting results in women over the age of 55. In all nonpregnant patients, testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, or other malignancy should be evaluated as a source of persistently positive hCG testing.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Knowing the utility and variability of different hCG assays is clinically relevant to a wide range of medical providers. False positive and false negative testing has a large impact on patient care. All providers in a patient care team should be aware of common limitations in testing, for example, urine assay false positives with hematuria, false negatives with dilute urine, along with more obscure but still very relevant causes of inaccurate testing. Interpreting results that may be false should be undergone with care to help prevent unnecessary testing and treatment.[23] (Level V) Collaboration, shared decision making, and communication are critical elements in good patient care.
Review Questions
Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
Comment on this article.
References
- 1.
Montagnana M, Trenti T, Aloe R, Cervellin G, Lippi G. Human chorionic gonadotropin in pregnancy diagnostics.
 Clin Chim Acta. 2011 Aug 17;412(17-18):1515-20. [PubMed: 21635878]
Clin Chim Acta. 2011 Aug 17;412(17-18):1515-20. [PubMed: 21635878]- 2.
Ong S, Beebeejaun H. The effect of physiological urine dilution on pregnancy test results in complicated early pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999 Jan;106(1):87-8. [PubMed: 10426268]
- 3.
Cole LA. Immunoassay of human chorionic gonadotropin, its free subunits, and metabolites. Clin Chem. 1997 Dec;43(12):2233-43. [PubMed: 9439438]
- 4.
Greene DN, Schmidt RL, Kamer SM, Grenache DG, Hoke C, Lorey TS. Limitations in qualitative point of care hCG tests for detecting early pregnancy. Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Jan 16;415:317-21. [PubMed: 23159297]
- 5.
Braunstein GD. False-positive serum human chorionic gonadotropin results: causes, characteristics, and recognition. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Jul;187(1):217-24. [PubMed: 12114913]
- 6.
Cole LA, Shahabi S, Butler SA, Mitchell H, Newlands ES, Behrman HR, Verrill HL. Utility of commonly used commercial human chorionic gonadotropin immunoassays in the diagnosis and management of trophoblastic diseases.
 Clin Chem. 2001 Feb;47(2):308-15. [PubMed: 11159780]
Clin Chem. 2001 Feb;47(2):308-15. [PubMed: 11159780]- 7.
Marcillac I, Troalen F, Bidart JM, Ghillani P, Ribrag V, Escudier B, Malassagne B, Droz JP, Lhommé C, Rougier P. Free human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit in gonadal and nongonadal neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 15;52(14):3901-7. [PubMed: 1377600]
- 8.
Alfthan H, Haglund C, Roberts P, Stenman UH. Elevation of free beta subunit of human choriogonadotropin and core beta fragment of human choriogonadotropin in the serum and urine of patients with malignant pancreatic and biliary disease. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 01;52(17):4628-33. [PubMed: 1324787]
- 9.
Sheaff MT, Martin JE, Badenoch DF, Baithun SI. beta hCG as a prognostic marker in adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Apr;49(4):329-32. [PMC free article: PMC500461] [PubMed: 8655711]
- 10.
Lundin M, Nordling S, Carpelan-Holmstrom M, Louhimo J, Alfthan H, Stenman UH, Haglund C. A comparison of serum and tissue hCG beta as prognostic markers in colorectal cancer.
 Anticancer Res. 2000 Nov-Dec;20(6D):4949-51. [PubMed: 11326644]
Anticancer Res. 2000 Nov-Dec;20(6D):4949-51. [PubMed: 11326644]- 11.
Reisenbichler ES, Krontiras H, Hameed O. Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin production associated with phyllodes tumor of the breast: an unusual paraneoplastic phenomenon. Breast J. 2009 Sep-Oct;15(5):527-30. [PubMed: 19624411]
- 12.
Kricka LJ. Human anti-animal antibody interferences in immunological assays. Clin Chem. 1999 Jul;45(7):942-56. [PubMed: 10388468]
- 13.
Check JH, Nowroozi K, Chase JS, Lauer C, Elkins B, Wu CH. False-positive human chorionic gonadotropin levels caused by a heterophile antibody with the immunoradiometric assay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;158(1):99-100. [PubMed: 2447778]
- 14.
Knight AK, Bingemann T, Cole L, Cunningham-Rundles C. Frequent false positive beta human chorionic gonadotropin tests in immunoglobulin A deficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Aug;141(2):333-7. [PMC free article: PMC1809437] [PubMed: 15996198]
- 15.

Fahy BG, Gouzd VA, Atallah JN. Pregnancy tests with end-stage renal disease. J Clin Anesth. 2008 Dec;20(8):609-13. [PubMed: 19100935]
- 16.
Delbeke FT, Van Eenoo P, De Backer P. Detection of human chorionic gonadotrophin misuse in sports. Int J Sports Med. 1998 May;19(4):287-90. [PubMed: 9657371]
- 17.
Griffey RT, Trent CJ, Bavolek RA, Keeperman JB, Sampson C, Poirier RF. "Hook-like effect" causes false-negative point-of-care urine pregnancy testing in emergency patients. J Emerg Med. 2013 Jan;44(1):155-60. [PubMed: 21835572]
- 18.
Chard T. Pregnancy tests: a review. Hum Reprod. 1992 May;7(5):701-10. [PubMed: 1639991]
- 19.
Cervinski MA, Lockwood CM, Ferguson AM, Odem RR, Stenman UH, Alfthan H, Grenache DG, Gronowski AM. Qualitative point-of-care and over-the-counter urine hCG devices differentially detect the hCG variants of early pregnancy. Clin Chim Acta. 2009 Aug;406(1-2):81-5. [PubMed: 19477170]
- 20.

Davies S, Byrn F, Cole LA. Human chorionic gonadotropin testing for early pregnancy viability and complications. Clin Lab Med. 2003 Jun;23(2):257-64, vii. [PubMed: 12848444]
- 21.
Butts SF, Guo W, Cary MS, Chung K, Takacs P, Sammel MD, Barnhart KT. Predicting the decline in human chorionic gonadotropin in a resolving pregnancy of unknown location. Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Aug;122(2 Pt 1):337-343. [PMC free article: PMC3752097] [PubMed: 23969803]
- 22.
Menczer J, Modan M, Serr DM. Prospective follow-up of patients with hydatidiform mole. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Mar;55(3):346-9. [PubMed: 7360433]
- 23.
Cole LA. Phantom hCG and phantom choriocarcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1998 Nov;71(2):325-9. [PubMed: 9826481]
hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin, indications for the appointment, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
I confirm More
- INVITRO
- Library
- Laboratory...
- HCG, Chorionic...
Miscarriage
Pregnancy
6415 July 29
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.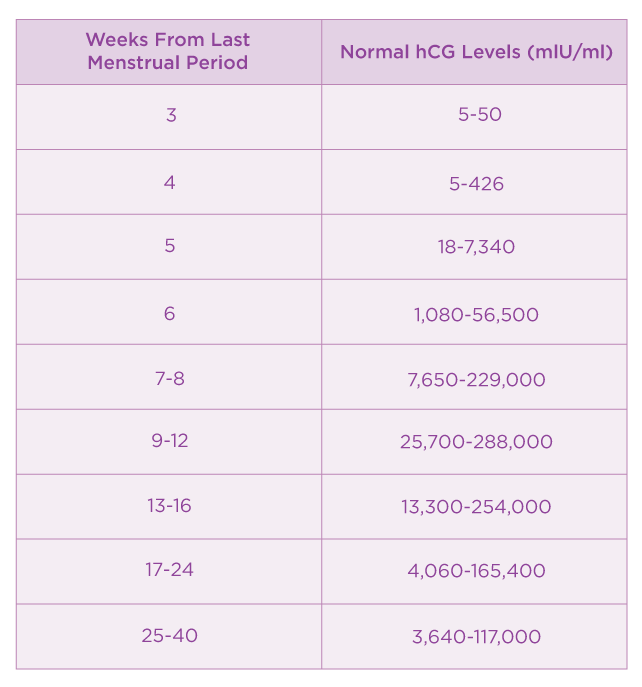
We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, β-hCG, beta-hCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators. nine0031
Chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by the outer shell of the embryo, and is normally determined in the blood and urine of a woman only when pregnancy occurs.
Chorionic gonadotropin consists of two subunits - alpha and beta. The beta subunit (β-hCG) used for the immunometric determination of the hormone is unique. To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum). nine0003
nine0003
HCG has a multifaceted effect on the body of a pregnant woman: it affects the development of the embryo and fetus, stimulates the synthesis of estrogens and androgens by ovarian cells, promotes the functional activity of the chorion and placenta, and ensures the successful course of pregnancy.
The introduction of hCG into the body of non-pregnant women stimulates ovulation and the synthesis of sex hormones necessary for conception. In men, this hormone enhances the formation of seminal fluid, activates the production of gonadosteroids. nine0003
In early pregnancy and up to the 2nd trimester, β-hCG supports the production of hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy, and in male fetuses it stimulates cells responsible for the formation and development of the male reproductive system.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic)
Synonyms: Beta-hCG general.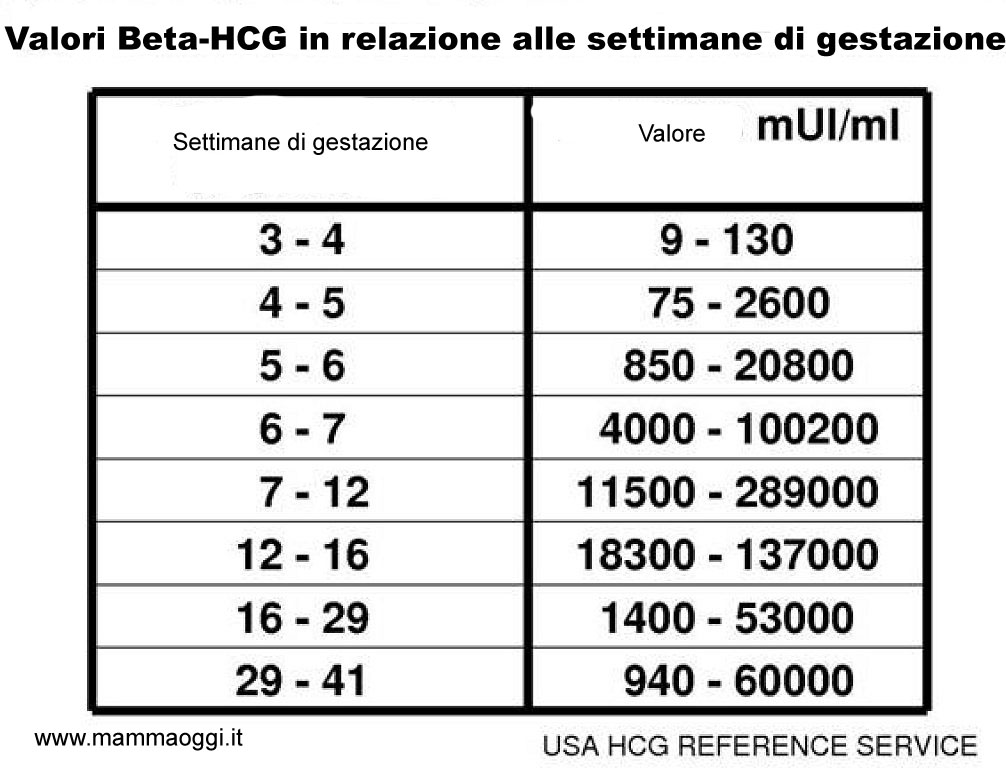 Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
RUB 685
Add to cart
Indications for determining the level of hCG in women
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Exclusion/confirmation of pregnancy, including ectopic (ectopic). nine0006
- Diagnosis of the state of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy.
- Assessment of the state of the placenta at different stages of pregnancy.
- Dynamic monitoring of fetal development during pregnancy, including in the diagnosis of malformations.

- Suspicion of the presence of neoplastic diseases of the reproductive system, such as hydatidiform mole (a rare pathology of the fetal egg, in which instead of developing the embryo, chorionic villi grow), chorionepithelioma (a malignant tumor that develops from the epithelium of the villi of the fetal egg). nine0006
- Performing artificial termination of pregnancy.
Indications for determining the level of hCG in men:
The presence of suspicion of tumors of the testicles.
Deadline for this test is 1 working day, excluding the day of taking the biomaterial.
Rules for preparing for a blood test to determine the level of hCG
non-specific: it is enough to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol on the eve of the procedure, limit stress and intense physical activity for a week; blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach. nine0003
nine0003
The determination of hCG in the blood is possible already on the 6-8th day after conception. The use of urinary test systems (rapid pregnancy tests) will be informative starting from the 7th day after the fertilization of the egg. To confirm the result, it is recommended to re-determine the level of the hormone a few days after the first analysis.
You can take a blood test for hCG (thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin, Thyroid StimulatingHormone, TSH) at the nearest INVITRO medical office. The list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory testing is presented in the "Addresses" section. nine0003
Reasons leading to high levels of β-hCG
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Incorrect timing of pregnancy.
- Pathological pregnancy: the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine (preeclampsia), convulsions (eclampsia), toxicosis.
- The presence of a pregnant woman with chronic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus). nine0006
- Multiple fetal malformations (in such a situation, the determination of the level of β-hCG is used together with other indicators, the so-called "triple test". This study is used as a screening, and not for diagnosis.).
Reasons for fixing a decrease in the level of β-hCG
- Incorrectly established terms of pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy. nine0006
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Fetal or placental disorders (including placental insufficiency).
- Intrauterine fetal death (in this case, it is informative to determine the level of the hormone in the first and second trimesters).
During abortions, the level of β-hCG is also monitored, the dynamics of growth / fall of which can be used to judge the completeness of the manipulation.
Determining the level of hCG, in addition to establishing the fact of pregnancy in the early stages, is part of the screening examination of pregnant women in the first trimester, along with ultrasound. nine0003
1st trimester prenatal screening for trisomies, PRISCA-1 (1st trimester biochemical screening - 1st trimester “double test”, risk calculation using PRISCA software)
Synonyms: Prenatal Screening Markers for Down Syndrome; PRISCA-1. Brief description of the study "Prenatal screening for trisomies of the 1st trimester of pregnancy, PRISCA-1)" Test run...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
2 040 RUB
Add to cart
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.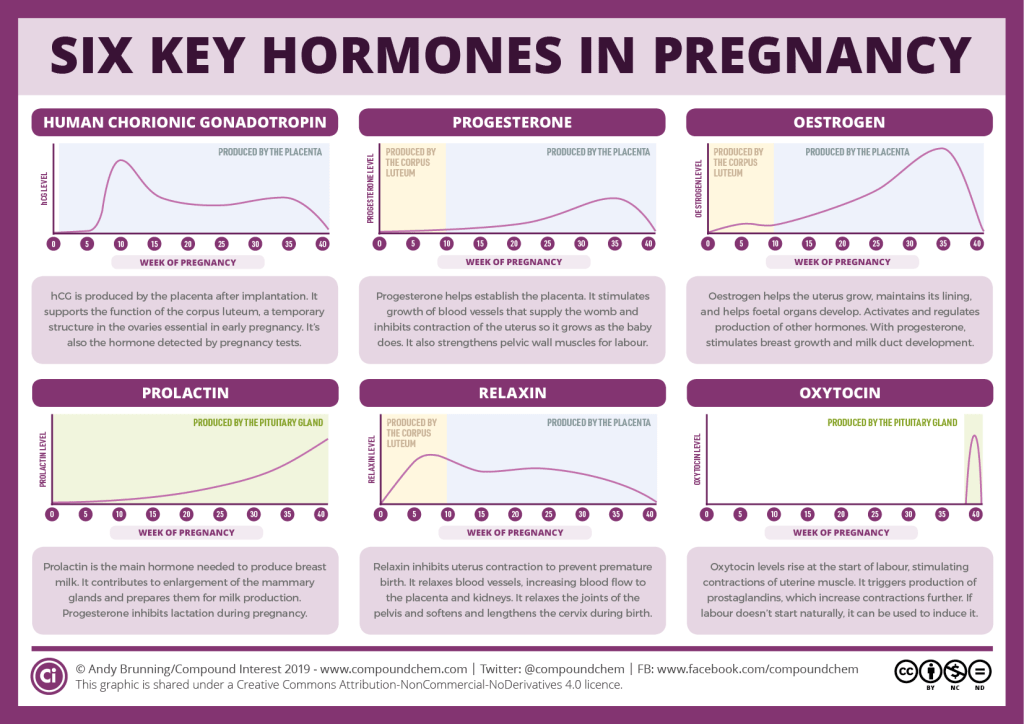
RUB 2,790 Sign up nine0003
In gynecological practice, human chorionic gonadotropin is used to treat infertility, stimulate ovulation, and synthesize sex steroids. In urology, it is used in the treatment of cryptorchidism (undescended testicles) and infertility associated with impaired spermatogenesis.
Quantitatively, β-hCG is determined in the blood, for a qualitative determination, special test systems (pregnancy tests) are used, and in this case, urine serves as a biomaterial.
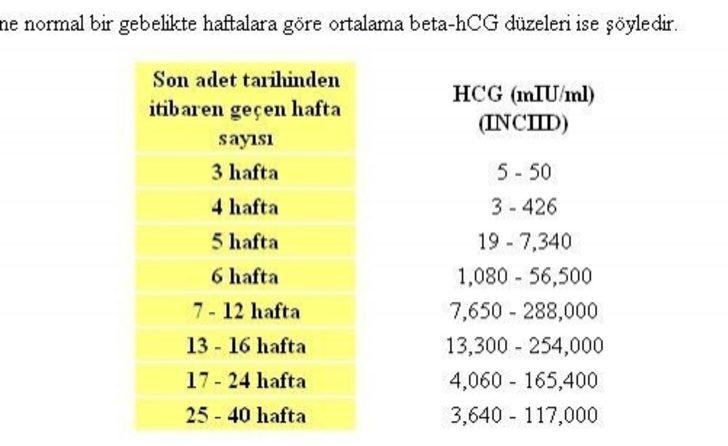
Quantitative determination of the level of hCG allows you to monitor the course of pregnancy in dynamics. To do this, obstetrician-gynecologists have developed tables for increasing the level of hCG, depending on the duration of pregnancy in weeks. The sensitivity of the determination is in the range of 1.2-1125000 mU/ml. nine0025
Reference values of hCG levels in dynamics by gestational age
| Pregnancy (weeks from conception) | HCG level (mU / ml) |
| 2 | 25–300 |
| 3 | 1500–5000 | nine0195
| four | 10000–30000 |
| five | 20000–100000 |
| 6–11 | 20000–>225000 |
| 12 | 19000–135000 |
| 13 | 18000–110000 | nine0195
| fourteen | 14000–80000 |
| 15 | 12000–68000 |
| sixteen | 10000–58000 |
| 17–18 | 8000–57000 |
| nineteen | 7000–49000 | nine0195
| 20–28 | 1600–49000 |
| Men and non-pregnant women | 0–<5 mU/ml |
Values ranging from 5 to 25 mU / ml do not allow unambiguous confirmation or denial of pregnancy, therefore, a second study is required after two days.
Since the hormone is produced by the placenta, during normal pregnancy, with placental pathology (for example, with fetoplacental insufficiency - a violation of the development of the fetus and placenta), with multiple pregnancies, the values of β-hCG will differ. With a normal pregnancy until the fifth week, the level of the hormone rises exponentially: every two days its concentration doubles, reaching a peak by the 11th week of gestation. Accordingly, in a multiple pregnancy, the level of β-hCG will be even higher than in a single pregnancy. nine0003
If the indicator deviates from the norm, additional ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, appendages) is required.
US examination of pelvic organs (uterus, adnexa)
Ultrasound scanning of the organs of the female reproductive system to assess the shape and size, as well as exclude pathology.
RUB 2,390 Sign up nine0003
However, with a normal hCG value, additional examinations may also be needed:
- Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy (required to confirm pregnancy, clarify the term).
Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy
Examination to confirm pregnancy and determine the place of attachment of the ovum (to exclude ectopic pregnancy).
RUB 2,290 Sign up nine0003
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to assess the characteristics and confirm the normal development of the fetus.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 2,790 Sign up nine0003
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to confirm the presence of several fetuses, determine their characteristics; It is necessary for planning the subsequent actions of the doctor and the management of pregnancy.

Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
A study that allows you to assess the growth and development of fetuses, their position in the uterus, and make a plan for further pregnancy management. nine0003
RUB 3,840 Sign up
- Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week) - performed in case of suspected ectopic pregnancy.
Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week)
Additional ultrasound, which is prescribed in the presence of concomitant pathologies to monitor the condition of the fetus.
RUB 2,540 Sign up nine0003
- Lab tests to be performed in the first trimester are collected in the Pregnancy: 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) profile.

For professional assistance in interpreting the results, contact
obstetrician-gynecologist
.
Sources:
- www.invitro.ru
- Clinical guidelines "Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2021.
- Clinical guidelines "Premature birth". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2020.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.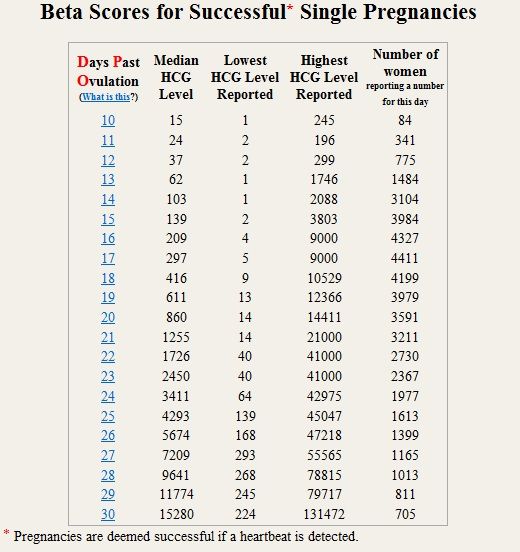
Recommendations
-
PSA (prostate specific antigen) test
10998 may 13 nine0003
-
Human papillomavirus
15405 04 May
-
Alkaline phosphatase
5570 16 April
Similar articles
ECO
Blood transfusion
Pregnancy
Rh-affiliation (Rh-factor, Rh)
Rh-affiliation: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the analysis, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.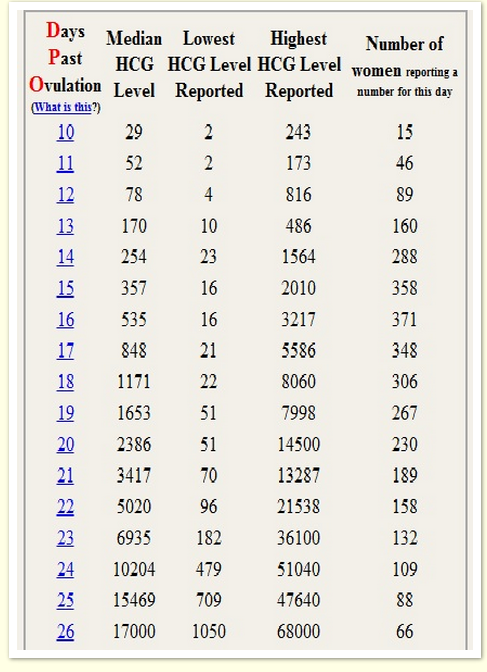 nine0003
nine0003
More
Heredity
Pregnancy
ECO
Research to determine biological relationship in the family: paternity and motherhood
You can perform molecular genetic studies that reveal a predisposition to various diseases, and now also undergo research to establish biological relationship in the family: paternity and motherhood. nine0003
More
Pregnancy
ECO
Physiological changes in blood parameters during pregnancy
Changes in the coagulogram of a pregnant woman is a physiological process associated with the appearance of the uteroplacental circulation.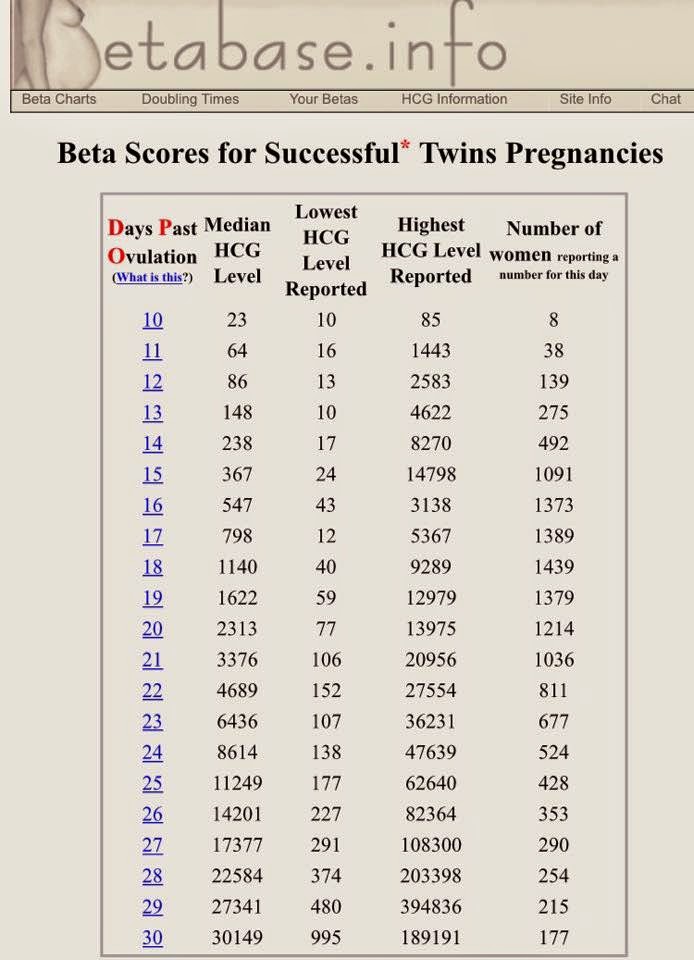 This process is associated with the evolutionary, adaptive reactions of the body of a pregnant woman. The body of a woman prepares for the costs during gestation and possible blood loss during childbirth. During the physiological course of pregnancy, the activity of the procoagulant link increases. Already at the 3rd month of pregnancy, fibrinogen rises (this is the factor I (first) of the plasma coagulation system) and reaches maximum values on the eve of childbirth. Therefore, gynecologists reasonably recommend monitoring this indicator during pregnancy (1 time per trimester, if there are deviations of these indicators more often, 1 time per week). nine0003
This process is associated with the evolutionary, adaptive reactions of the body of a pregnant woman. The body of a woman prepares for the costs during gestation and possible blood loss during childbirth. During the physiological course of pregnancy, the activity of the procoagulant link increases. Already at the 3rd month of pregnancy, fibrinogen rises (this is the factor I (first) of the plasma coagulation system) and reaches maximum values on the eve of childbirth. Therefore, gynecologists reasonably recommend monitoring this indicator during pregnancy (1 time per trimester, if there are deviations of these indicators more often, 1 time per week). nine0003
More
ECO
Thrombophilia
Pregnancy
Thrombosis: extended panel 114GP
Thrombosis, extended panel: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the analysis, interpretation of the results and norm indicators. nine0003
nine0003
More
Hypogonadism
ECO
Menopause
Climax
Estradiol
Estradiol
More
Nothing found
Try changing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from the list
Medical office not found
Try changing your request or select medical office from list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
Nothing found
Please try editing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Subscribe to our newsletters
nine0481Enter e-mail
I consent to processing of personal data
Subscribe
what shows, the norm during pregnancy, how and when to take, decoding
June 2, 2020
608232
0
share
Contents
What is HCG?
The role of the hormone in the diagnosis of pregnancy
When should I donate blood for hCG?
How to prepare for the analysis?
HCG test interpretation
How accurate is the hCG test? nine0003
An hCG blood test is one of the most important tools for monitoring a developing pregnancy.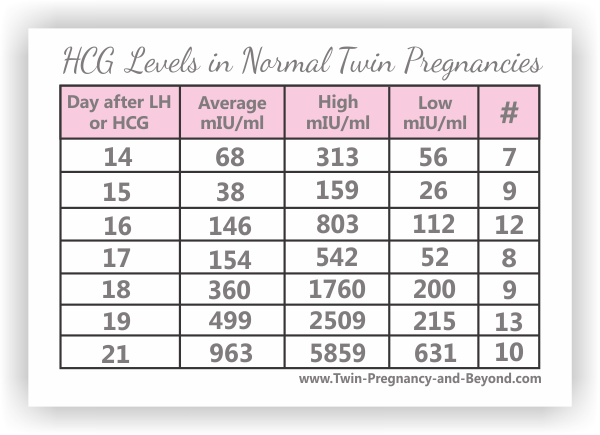
What is HCG?
An hCG blood test is a reliable way to determine pregnancy in the early stages. HCG is a protein consisting of two units. Alpha particles of the hormone are similar to biologically active substances secreted by the pituitary gland. Beta particles are unique. The mass of the CG molecule is approximately 46 kDa. During pregnancy, glycoprotein is synthesized in the placenta. The biological properties of CG are in many ways similar to the properties of other hormones: luteinizing and follicle-stimulating. In some malignant diseases, hCG begins to produce tumor cells. In a non-pregnant woman and a healthy man, the hormone is practically absent in blood tests. nine0003
In obstetrics and gynecology, the test for b hCG, along with ultrasound, is used to monitor pregnancy throughout the entire period. Deviations in the readings of the analysis are the basis for further examination and require the consultation of a geneticist. An artificial increase in the level of hCG is used in the IVF process. As a result of injections of hCG in women, the maturation and release of the egg is stimulated, the production of estrogen and progesterone increases. In men, the introduction of exogenous hCG activates the growth of the number of spermatozoa. nine0003
As a result of injections of hCG in women, the maturation and release of the egg is stimulated, the production of estrogen and progesterone increases. In men, the introduction of exogenous hCG activates the growth of the number of spermatozoa. nine0003
It is proved that the substance also has the properties of corticotropic hormone. HCG has an effect on the adrenal glands, stimulating the synthesis of steroids in their cortex. Thus, he is involved in preparing the body of a pregnant woman for the upcoming physiological stress. Since the fetus is perceived as foreign by the mother's body, some immunosuppressive influence of hormones, including hCG, is required for its normal development.
HCG promotes the maturation of placental tissues. Thanks to him and other hormones, its functional activity increases and the number of chorionic villi increases. nine0003
Without the hormone, the normal development of the embryo is not possible. HCG ensures the production of estrogens and progesterone, and also maintains their balance in the body of the expectant mother. Therefore, any pregnancy support program always contains regular tests for hCG levels.
Therefore, any pregnancy support program always contains regular tests for hCG levels.
Urinalysis for hCG (beta particles)
Compared to blood, expectant mother's urine contains less of the hormone. Therefore, determining the concentration of a substance in the urine can diagnose pregnancy only from a period of 8-10 days. Like a laboratory study, pharmacy tests are also based on the determination of hCG in the urine. Home tests have a lower threshold of sensitivity than laboratory tests, and, accordingly, a lower degree of reliability. Their positive result requires a visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist to confirm a normal pregnancy. nine0003
Free hCG assay (beta-hCG subunit)
The range of application of this test is quite wide. In oncology, it is in demand as a marker of malignant tumors. Measurement of the number of independent particles of hCG in the blood is informative in relation to testicular cancer in men. In addition, this indicator is important in the diagnosis of trophoblastic tumors in women. It is included in 1 and 2 pregnancy screenings. The study helps to assess the risk of such congenital fetal pathologies as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. nine0003
It is included in 1 and 2 pregnancy screenings. The study helps to assess the risk of such congenital fetal pathologies as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. nine0003
The role of the hormone in the diagnosis of pregnancy
An analysis of the amount of total hCG occupies a special place in confirming pregnancy in the early stages. This is due to the fact that the hormone begins to be actively released already a few days after the attachment of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. With the normal development of the embryo, the level of the substance doubles every 1.5-2 days. By the tenth week, the amount of hCG in a woman's tests can reach maximum values - up to 225,000 mU / ml. nine0003
Simultaneously with the blood for total hCG, other examinations are prescribed for the pregnant woman. So the patient should visit the ultrasound scanning room at least three times. Within nine months, several studies may be required. Comprehensive screenings of the 1st and 2nd trimesters also include an hCG test.
When to donate blood for hCG
A blood test for the hormone is given as needed. The hCG test is prescribed for the first time directly during the diagnosis of pregnancy itself. The second is as part of screening with ultrasound and other tests. Screening is designed to identify a risk group for congenital fetal pathologies among pregnant women. nine0003
Approximate dates of studies on hCG:
- confirmation of pregnancy - from the 6th day after conception;
- first - from 11 to 13 weeks;
- second from 19 to 23 weeks;
- 3rd trimester screening is done after 28 weeks of gestation.
How to prepare for a blood test
Preparing for an hCG test involves a number of standard requirements for hormone testing. The analysis is given on an empty stomach, after an overnight fast in the morning or afternoon. You should come to the treatment room in good health. In order for the results of the hCG test to be as reliable as possible, it is recommended in 2-3 days: nine0003
- stop drinking alcohol;
- exclude spicy and fatty foods from the diet;
- cancel strength training;
- Avoid smoking a couple of hours before donating blood.