Pregnancy beta hcg
HCG blood test - quantitative Information | Mount Sinai
Serial beta HCG; Repeat quantitative beta HCG; Human chorionic gonadotropin blood test - quantitative; Beta-HCG blood test - quantitative; Pregnancy test - blood - quantitative
A quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. HCG is a hormone produced in the body during pregnancy.
Other HCG tests include:
- HCG urine test
- HCG blood test -- qualitative
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This is most often taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
HCG appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception.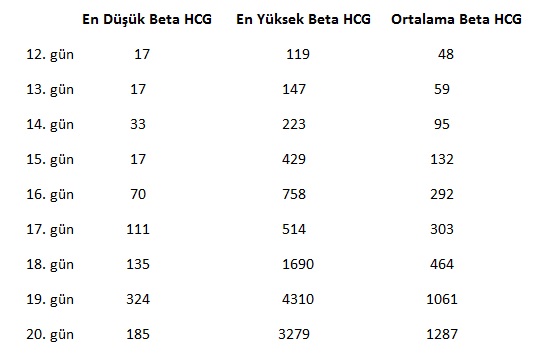 Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
This test is also done to diagnose abnormal conditions not related to pregnancy that can raise HCG level.
Normal Results
Results are given in milli-international units per milliliter (mUI/mL).
Normal levels are found in:
- Non-pregnant women: less than 5 mIU/mL
- Healthy men: less than 2 mIU/mL
In pregnancy, HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester and then declines slightly. The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
- 3 weeks: 5 - 72 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 10 -708 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 217 - 8,245 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 152 - 32,177 mIU/mL
- 7 weeks: 4,059 - 153,767 mIU/mL
- 8 weeks: 31,366 - 149,094 mIU/mL
- 9 weeks: 59,109 - 135,901 mIU/mL
- 10 weeks: 44,186 - 170,409 mIU/mL
- 12 weeks: 27,107 - 201,165 mIU/mL
- 14 weeks: 24,302 - 93,646 mIU/mL
- 15 weeks: 12,540 - 69,747 mIU/mL
- 16 weeks: 8,904 - 55,332 mIU/mL
- 17 weeks: 8,240 - 51,793 mIU/mL
- 18 weeks: 9,649 - 55,271 mIU/mL
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal level may indicate:
- More than one fetus, for example, twins or triplets
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus
- Hydatidiform mole of the uterus
- Ovarian cancer
- Testicular cancer (in men)
During pregnancy, lower than normal levels based on the gestational age may indicate:
- Fetal death
- Incomplete miscarriage
- Threatened spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Risks
Risks of having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Blood accumulating under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Jain S, Pincus MR, Bluth MH, McPherson RA, Bowne WB, Lee P. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 25.
University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories. Test directory: HCG - serum, quantitative. www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/path_handbook/rhandbook/test446.html. Updated February 10, 2022. Accessed March 11, 2022.
Yarbrough ML, Stout M, Gronowski AM. Pregnancy and its disorders. In: Rifai N, ed. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
Last reviewed on: 12/3/2020
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA.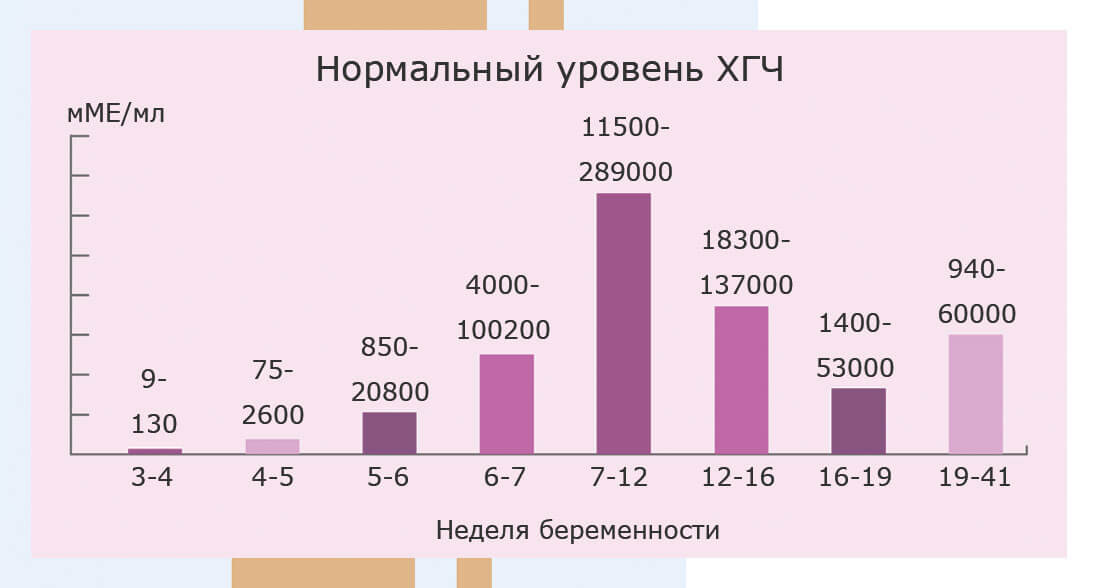 Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
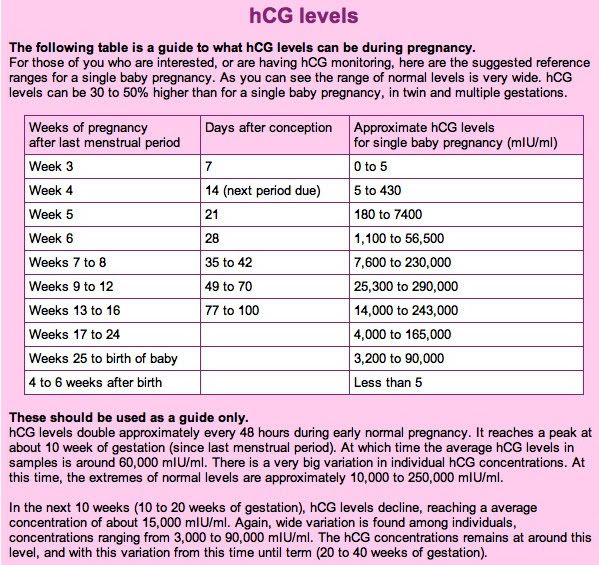
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
- 3 weeks: 6 – 70 IU/L
- 4 weeks: 10 - 750 IU/L
- 5 weeks: 200 - 7,100 IU/L
- 6 weeks: 160 - 32,000 IU/L
- 7 weeks: 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L
- 8 weeks: 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L
- 9 weeks: 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L
- 10 weeks: 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L
- 12 weeks: 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L
- 14 weeks: 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L
- 15 weeks: 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L
- 16 weeks: 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L
- 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester): 1,400 - 53,000 IUL
- 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester): 940 - 60,000 IU/L
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet), Lab Tests Online (Human chorionic gonadotropin), UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.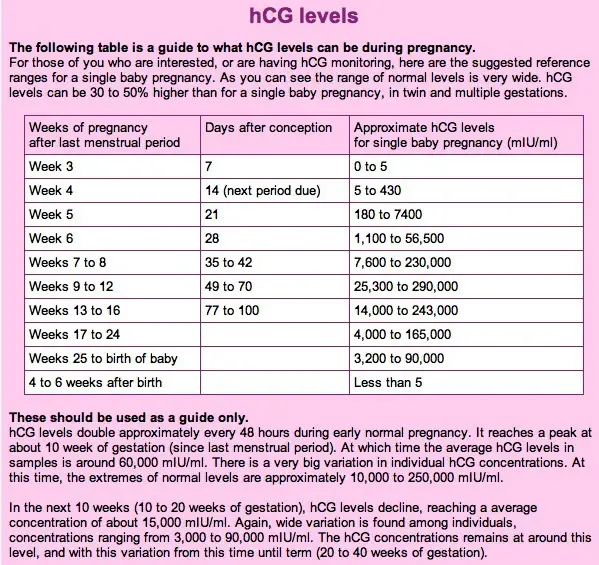
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
betterhealth.vic.gov.au
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness. Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
Read more on Parenthub website
Support for Girls - Brave Foundation
Yes, it sounds like in the movies, but food cravings sometimes can be a sign of pregnancy
Read more on Brave Foundation website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG)
Beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin is one of the subunits of a specific hormone molecule - chorionic gonadotropin, which is formed in the shell of the human embryo. The analysis is carried out for the purpose of early diagnosis of pregnancy, detection of its complications and diagnosis of diseases associated with impaired hCG secretion.
Synonyms Russian
Beta subunit of hCG.
Synonyms English
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, hCG, b-HCG, Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG, Total hCG, Total beta hCG.
Test method
Electrochemiluminescent immunoassay (ECLIA).
Detection range: 0.1 - 1,000,000 IU/L.
Units
IU/l (international unit per litre).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for an examination?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
Study Overview
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced in the fetal membrane of the human embryo. It is an important indicator of the development of pregnancy and its deviations. It is produced by the cells of the chorion (the shell of the embryo) immediately after it is attached to the wall of the uterus (this happens only a few days after fertilization). The embryo at this stage of pregnancy is a microscopic vesicle filled with fluid, the walls of which are made up of rapidly multiplying cells. From one part of these cells, the unborn child (embryoblast) develops, while from the cells outside the embryo, a trophoblast is formed - that part of the fetal egg, with which it is attached to the wall of the uterus. Later, the chorion is formed from the trophoblast.
The embryo at this stage of pregnancy is a microscopic vesicle filled with fluid, the walls of which are made up of rapidly multiplying cells. From one part of these cells, the unborn child (embryoblast) develops, while from the cells outside the embryo, a trophoblast is formed - that part of the fetal egg, with which it is attached to the wall of the uterus. Later, the chorion is formed from the trophoblast.
Chorion performs the function of nourishing the embryo, being an intermediary between the body of the mother and the child. In addition, it produces chorionic gonadotropin, which, on the one hand, affects the formation of the child, on the other hand, it specifically affects the mother's body, ensuring a successful pregnancy. The appearance of this hormone in the body of a future mother at the initial stage of pregnancy explains the importance of the test for early diagnosis of pregnancy.
Chorionic gonadotropin stimulates the secretory function of the corpus luteum of the ovaries, which should produce the hormone progesterone, which maintains the normal state of the inner lining of the uterine wall - the endometrium.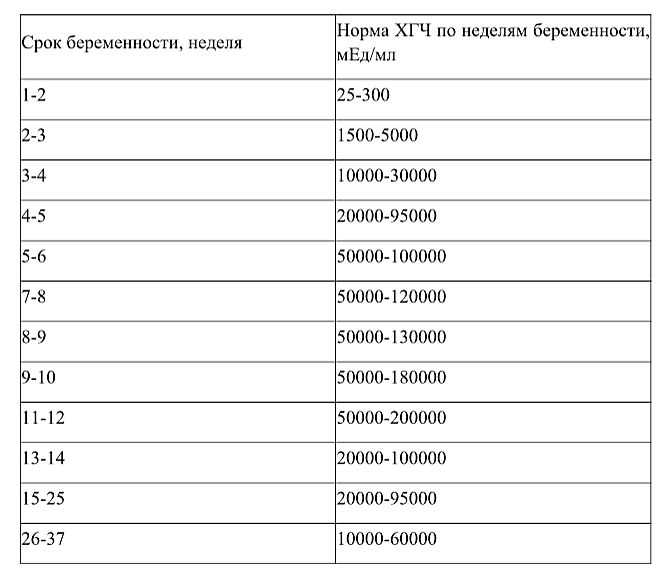 The endometrium provides reliable attachment of the fetal egg to the mother's body and its nutrition with all the necessary substances.
The endometrium provides reliable attachment of the fetal egg to the mother's body and its nutrition with all the necessary substances.
Due to a sufficient amount of human chorionic gonadotropin, the corpus luteum, which normally exists for only about 2 weeks during each menstrual cycle, does not undergo resorption after successful conception and remains functionally active throughout the entire period of pregnancy. Moreover, it is in pregnant women under the influence of chorionic gonadotropin that it produces very large amounts of progesterone. In addition, CG stimulates the production of estrogens and weak androgens by ovarian cells and promotes the development of the functional activity of the chorion itself, and later the placenta, which is formed as a result of the maturation and growth of the chorionic tissue, improving its own nutrition and increasing the number of chorionic villi.
Thus, the role of human chorionic gonadotropin lies in the specific and multifaceted effect on the body of a woman and the fetus in order to ensure a successful pregnancy. Based on the analysis for chorionic gonadotropin, the presence of chorionic tissue in the woman's body is determined, and hence pregnancy.
Based on the analysis for chorionic gonadotropin, the presence of chorionic tissue in the woman's body is determined, and hence pregnancy.
According to its chemical structure, chorionic gonadotropin is a combination of protein and complex carbohydrates, consisting of two parts (subunits): alpha and beta. The alpha subunit of chorionic gonadotropin is completely identical to the alpha subunits of the luteinizing, follicle-stimulating and thyroid-stimulating hormones of the pituitary gland, which perform functions that are largely similar to the function of chorionic gonadotropin, but not during pregnancy. The beta subunit of chorionic gonadotropin is unique, which, on the one hand, determines the specificity of its action, and, on the other hand, allows it to be identified in biological media. In this regard, this test is called "beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG)".
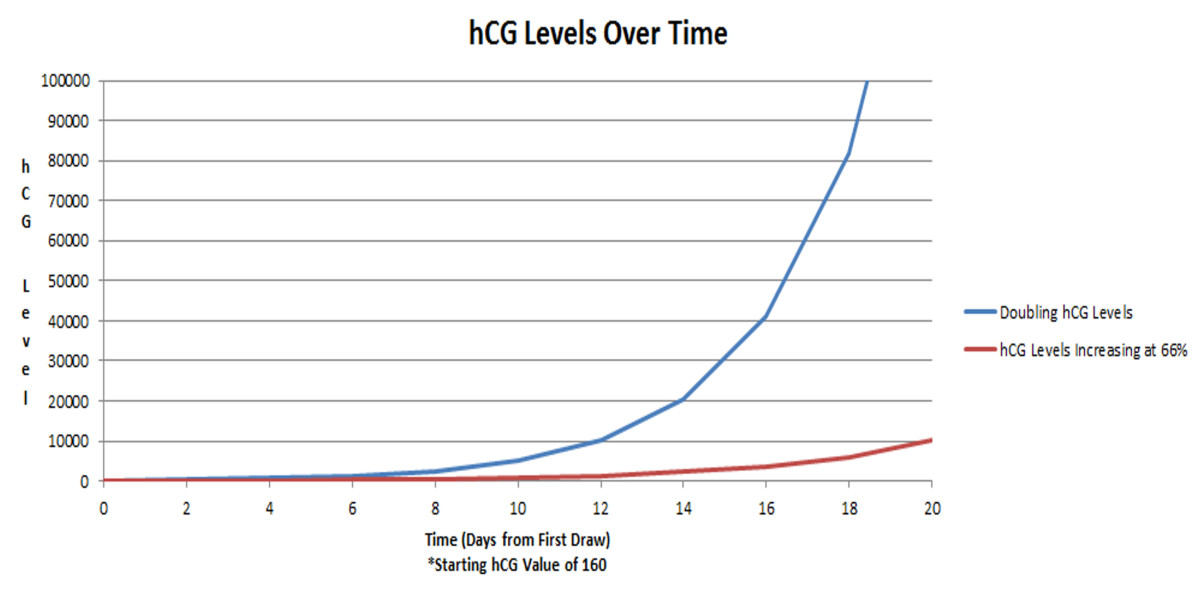
Knowing the level of beta-hCG in the blood, it is possible to diagnose pregnancy already on the 6-8th day after conception (in the urine, the concentration of beta-hCG reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later).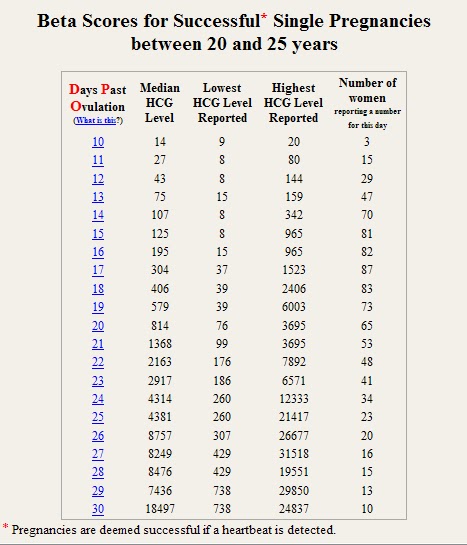 Normally, during pregnancy between the 2nd and 5th weeks, the amount of beta-hCG doubles every 1.5 days. With multiple pregnancy, it increases in proportion to the number of fetuses. The maximum level of hCG reaches the 10-11th week, and then gradually decreases. This is due to the fact that from the beginning of the 2nd third of pregnancy, the placenta is able to independently produce enough estrogens and progesterone, with the participation of which the endometrium functions normally, regardless of the secretion of hormones in the ovarian corpus luteum. At the same time, the concentration of CG in the blood of a pregnant woman gradually decreases, and the corpus luteum can function without the effects of CG. During this period, the role of the hormone is to stimulate the production of testosterone in the fetus, which is necessary for the normal development of the external genital organs of the embryo.
Normally, during pregnancy between the 2nd and 5th weeks, the amount of beta-hCG doubles every 1.5 days. With multiple pregnancy, it increases in proportion to the number of fetuses. The maximum level of hCG reaches the 10-11th week, and then gradually decreases. This is due to the fact that from the beginning of the 2nd third of pregnancy, the placenta is able to independently produce enough estrogens and progesterone, with the participation of which the endometrium functions normally, regardless of the secretion of hormones in the ovarian corpus luteum. At the same time, the concentration of CG in the blood of a pregnant woman gradually decreases, and the corpus luteum can function without the effects of CG. During this period, the role of the hormone is to stimulate the production of testosterone in the fetus, which is necessary for the normal development of the external genital organs of the embryo.
Thus, during pregnancy, the level of beta-hCG in the blood first increases and then decreases.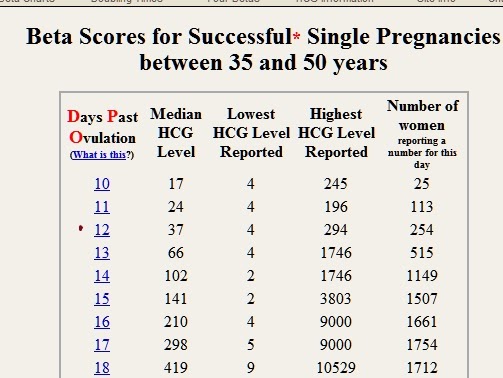 According to this indicator, one can judge the successful course of pregnancy and identify violations of the development of the fetus. The test for hCG in the blood is the most reliable method for determining pregnancy in the early stages. HCG appears in the body of a woman from 6-8 days after fertilization. A common rapid pregnancy test that every woman can use at home is also based on measuring hCG in the urine.
According to this indicator, one can judge the successful course of pregnancy and identify violations of the development of the fetus. The test for hCG in the blood is the most reliable method for determining pregnancy in the early stages. HCG appears in the body of a woman from 6-8 days after fertilization. A common rapid pregnancy test that every woman can use at home is also based on measuring hCG in the urine.
Below normal hormone levels at various stages of fetal development suggest ectopic pregnancy, fetal growth retardation, threatened miscarriage, non-progressive pregnancy, or placental insufficiency. The reason for the increased content of beta-hCG may be toxicosis, diabetes mellitus, or an incorrectly set gestational age. A high level of the hormone after a mini-abortion indicates a progressing pregnancy.
Determining the level of hCG is included in the triple test study, the results of which can be used to judge some anomalies in the development of the fetus, but an accurate diagnosis cannot be made.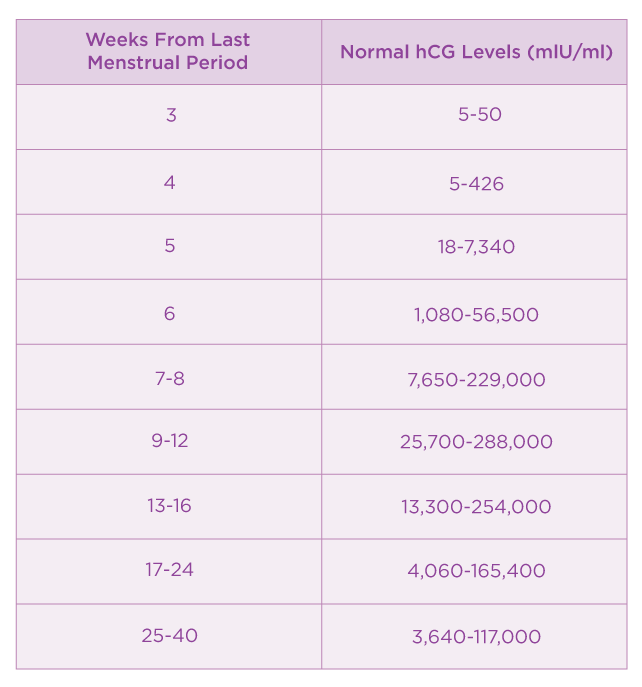 The study only allows you to classify a woman as a risk group for this pathology. In this case, further investigation is necessary. In non-pregnant women, CG is normally absent, but it can be secreted by some abnormal chorion-derived tissues (hydatidiform mole, chorionepithelioma) and some other tumors.
The study only allows you to classify a woman as a risk group for this pathology. In this case, further investigation is necessary. In non-pregnant women, CG is normally absent, but it can be secreted by some abnormal chorion-derived tissues (hydatidiform mole, chorionepithelioma) and some other tumors.
What is research used for?
- For the diagnosis of pregnancy, including multiple, ectopic and non-developing.
- To monitor the progress of pregnancy.
- To detect fetal growth retardation, threatened miscarriage, placental insufficiency.
- For the diagnosis of amenorrhea.
- To monitor the effectiveness of induced abortion.
- As part of a comprehensive examination to identify fetal malformations.
- For the diagnosis of CG-producing tumors.
When is the test ordered?
- If pregnancy is suspected, in particular multiple pregnancy.
- When monitoring the progress of pregnancy.

- When there is an assumption about a complication during pregnancy: fetal growth retardation, the threat of spontaneous abortion, non-developing or ectopic pregnancy, chronic placental insufficiency.
- Confirm successful induced abortion if necessary.
- With a comprehensive examination to identify fetal malformations.
- When finding out the reason for the absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- When is the diagnosis of tumors producing hCG.
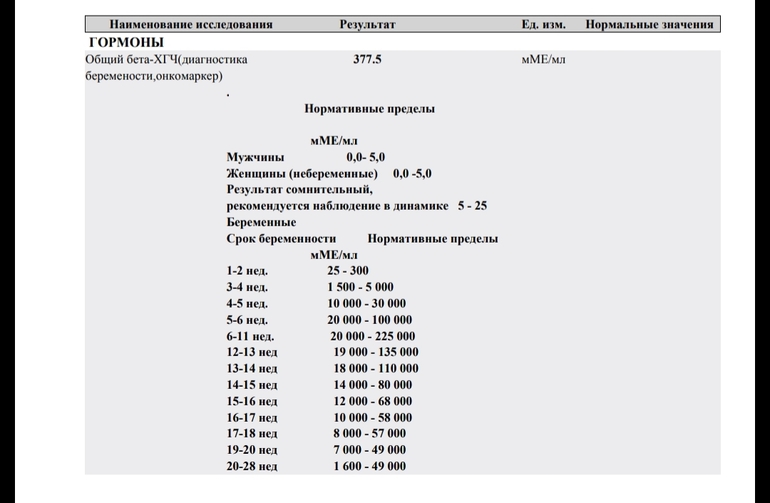
What do the results mean?
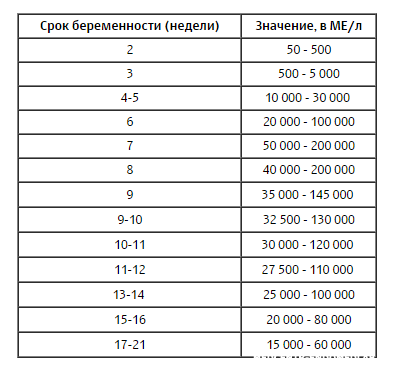
Reference values
| Floor | Week of pregnancy (from conception) | Reference values |
|
Female | Not pregnant | Less than 5 IU/L |
| 3 weeks | 5. | |
| 4 weeks | 9.5 - 750 IU/L | |
| 5 weeks | 217 - 7138 IU/L | |
| 6 weeks | 158 - 31795 IU/l | |
| 7 weeks | 3697 - 163563 IU/L | |
| 8 weeks | 32065 - 149571 IU/l | |
| 9 weeks | 63803 - 151410 IU/L | |
| 10 weeks | 46509 - 186977 IU/l | |
| 11-12 weeks | 27832 - 210612 IU/L | |
| 13-14 weeks | 13950 - 62530 IU/L | |
| 15 weeks | 12039 - 70971 IU/L | |
| 16 weeks | 9040 - 56451 IU/L | |
| 17 weeks | 8175 - 55868 IU/L | |
| 18 weeks | 8099 - 58176 IU/L | |
| Male |
| Less than 5 IU/L |
Causes of high beta-hCG levels
In the absence of pregnancy, the result of the beta-hCG test should be negative.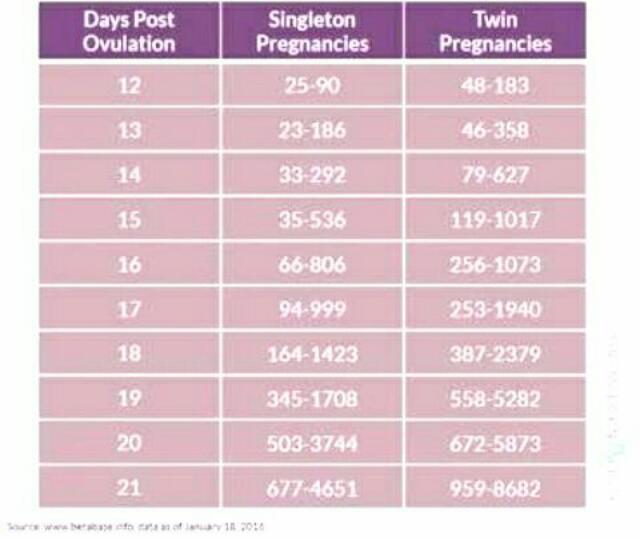 The detection of beta-hCG suggests that at least 5-6 days have passed since fertilization. Between the 2nd and 5th weeks of pregnancy, during its normal course, the level of beta-hCG doubles every 1.5 days and soon reaches its maximum. Then it starts to slowly decline. The results of the analysis are compared with the normal values for each gestational age. For a correct interpretation of the results, it is necessary to know exactly when the conception occurred.
The detection of beta-hCG suggests that at least 5-6 days have passed since fertilization. Between the 2nd and 5th weeks of pregnancy, during its normal course, the level of beta-hCG doubles every 1.5 days and soon reaches its maximum. Then it starts to slowly decline. The results of the analysis are compared with the normal values for each gestational age. For a correct interpretation of the results, it is necessary to know exactly when the conception occurred.
In pregnant women:
- multiple pregnancies (the rate increases in proportion to the number of fetuses),
- toxicosis,
- prolonged pregnancy,
- maternal diabetes mellitus,
- fetal malformations,
- taking synthetic hormones.
Not pregnant:
- hCG-producing tumors,
- surgical abortion (first 4-5 days after the procedure),
- taking hCG preparations.
Causes of low beta-hCG levels (during pregnancy):
- ectopic or non-developing pregnancy,
- fetal growth retardation,
- threatened miscarriage,
- chronic placental insufficiency,
- fetal death (in the 2nd-3rd trimester of pregnancy).
What can influence the result?
- When diagnosing pregnancy, taking the test too early - when less than 5 days have passed since conception - can lead to a false negative result.
Also recommended
- Alpha-fetoprotein (alpha-FP)
- Antiphospholipid antibodies IgG
- Antiphospholipid antibodies IgM
- Placental lactogen
- Free estriol
- Pregnancy - Prenatal screening for trisomies of the first trimester of pregnancy (Down syndrome), PRISCA
- Plasma pregnancy-associated protein A (PAPP-A)
- Pregnancy - Prenatal screening for trisomies of the second trimester of pregnancy, PRISCA
- Antibodies to steroid-producing cells of the placenta
Who orders the examination?
General practitioner, obstetrician-gynecologist, oncologist.
Literature
- Handbook of Clinical Laboratory Testing During Pregnancy, edited by Ann M.
 Gronowski. Springer-Verlag LLC, New York, 2004
Gronowski. Springer-Verlag LLC, New York, 2004 - Prenatal Diagnosis in Obstetric Practice. M. J. J. Whittle, Blackwell Publishers 1995
- Endocrinology of Pregnancy. Fuller W. Bazer, Humana Press 1998
- Blood Biochemistry. N J Russell, G M Powell, J G Jones, P J, Winterburn and J M Basford, Croom Helm, London and Canberra, 1982
- Blood Chemistry and CBC analysis-Clinical Laboratory Testing from a Functional Perspective. Rychard Weatherby N.D and Scott Fergusson, N.D., Bear Mounting Publishing, 2002.
- Tietz Clinical Guide to Laboratory Tests. Alan H. B. Wu, Saunders/Elsevier, 2006
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests. Joyce LeFever Kee - Pearson, Prentice Hall, 8th Edition 2010
- District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries. Monica Cheesbrough, Cambridge University Press, second edition, 2005.
- Clinical Chemistry. A Laboratory Perspective. Wendy L. Arneson, Jean M. Brickell, F.A. Davis Company, 2007
- Clinical Chemistry.
 Michael L. Bishop, Edward P. Fody, Larry E. Schoef, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005
Michael L. Bishop, Edward P. Fody, Larry E. Schoef, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005
HCG test - Donate blood for pregnancy in Moscow (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin)
Beta hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is a subunit of a specific hormone molecule that is formed in the shell of the human embryo. Determining the level of total beta-hCG is necessary for diagnosing pregnancy, monitoring its course, and this hormone also serves as a marker for certain oncological diseases.
Why is it important to test hCG during pregnancy
HCG begins to be produced in the chorion of the embryo shortly after implantation of the embryo. Already on the 6th day, its level becomes sufficient for testing in the blood, later, on average for a week, in the urine. That is, after a few days from the moment of the delay of menstruation, according to the indicators of this hormone, pregnancy is diagnosed. By the 7-11th week, the production of chorionic gonadotropin increases many times, then gradually decreases. For each period of bearing a child, there are hCG norms. Normal values of the hormone indicate the successful course of pregnancy processes, deviations indicate the presence of pathologies.
For each period of bearing a child, there are hCG norms. Normal values of the hormone indicate the successful course of pregnancy processes, deviations indicate the presence of pathologies.
"HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy"
| Week | Reference values, mIU/ml |
| 1–2 | 25-300 |
| 2–3 | 350-5000 |
| 3-4 | 1500-30000 |
| 4-5 | 20000–100000 |
| 6-11 | 20000–234000 |
| 12 | 19000–135000 |
| 13 | 18000–110000 |
| 14 | 14000–80000 |
| 15 | 12000–68000 |
| 16 | 10000–58000 |
| 17-18 | 8000–57000 |
| 19 | 7000-49000 |
| 20–28 | 1600-49000 |
| No pregnancy | <5 |
| Pregnancy doubtful | 5–25 |
“HCG norms by days of pregnancy”
| Day (from conception, ovulation) | hCG: minimum, average, maximum, mIU / ml | ||
| 7 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| 8 | 3 | 7 | 18 |
| 9 | 5 | 11 | 21 |
| 10 | 8 | 18 | 26 |
| 11 | 11 | 28 | 45 |
| 12 | 17 | 45 | 65 |
| 13 | 22 | 73 | 105 |
| 14 | 29 | 105 | 170 |
| 15 | 39 | 160 | 270 |
| 16 | 8 | 260 | 400 |
| 17 | 120 | 410 | 580 |
| 18 | 220 | 650 | 840 |
| 19 | 370 | 980 | 1300 |
| 20 | 520 | 1380 | 2000 |
| 21 | 750 | 1960 | 3100 |
| 22 | 1050 | 2680 | 4900 |
| 23 | 1400 | 3550 | 6200 |
| 24 | 1830 | 4650 | 7800 |
| 25 | 2400 | 6150 | 9800 |
| 26 | 4200 | 8160 | 15600 |
| 27 | 5400 | 10200 | 19500 |
| 28 | 7100 | 11300 | 27300 |
| 29 | 8800 | 13600 | 33000 |
| 30 | 10500 | 16500 | 40000 |
| 31 | 11500 | 19500 | 60000 |
| 32 | 12800 | 22600 | 63000 |
| 33 | 14000 | 24000 | 68000 |
| 34 | 15500 | 27200 | 70000 |
| 35 | 17000 | 31000 | 74000 |
| 36 | 19000 | 36000 | 78000 |
| 37 | 20500 | 39500 | 83000 |
| 38 | 22000 | 45000 | 87000 |
| 39 | 23000 | 51000 | 93000 |
| 40 | 25000 | 58000 | 108000 |
| 41 | 26500 | 62000 | 117000 |
| 42 | 28000 | 65000 | 128000 |
The effect of human chorionic gonadotropin on the course of pregnancy
HCG has a direct effect on the suppression of the menstrual cycle and the maintenance of pregnancy.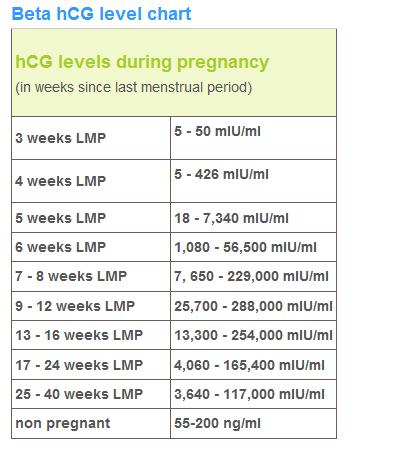 Thanks to hCG, the corpus luteum in the ovary does not dissolve, but continues to produce until the 12th week, while the placenta builds up, estrogens and progesterone, which prevents uterine contractions and reduces its tone. Chorionic gonadotropin also has a beneficial effect on the development and functioning of the placenta. In addition to acting on the ovaries, gonadotropin stimulates temporary hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex of a pregnant woman. Increased secretion of glucocorticoids helps to reduce the level of stress, including that caused by the immune response to the growth of the embryo, and increase the adaptive properties of the woman's body.
Thanks to hCG, the corpus luteum in the ovary does not dissolve, but continues to produce until the 12th week, while the placenta builds up, estrogens and progesterone, which prevents uterine contractions and reduces its tone. Chorionic gonadotropin also has a beneficial effect on the development and functioning of the placenta. In addition to acting on the ovaries, gonadotropin stimulates temporary hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex of a pregnant woman. Increased secretion of glucocorticoids helps to reduce the level of stress, including that caused by the immune response to the growth of the embryo, and increase the adaptive properties of the woman's body.
If there is a threat or presence of disorders during pregnancy, hCG analysis is carried out in dynamics by weeks. The assessment of the deviation of indicators from normal values is carried out in conjunction with other studies, ultrasound data.
Pathologies can be the reason for the decrease in hCG:
- non-developing pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- fetal developmental delay;
- threatened miscarriage, spontaneous abortion;
- insufficiency of functioning or aging of the placenta.
An excess of CG from normal values is often not a sign of pathology, but requires a more thorough examination of the body of a pregnant woman, clarification of the gestation period.
The level of human chorionic gonadotropin increases in the following conditions:
- early and late toxicosis, in particular preeclampsia;
- multiple pregnancy;
- prediabetic;
- abnormalities in fetal chromosomes;
- the use of gestagens of synthetic origin.
The content of chorionic gonadotropin in the blood increases many times over normal values for pregnancy in case of a serious pathology - hydatidiform mole. In this disease, the chorionic villi are converted into blisters filled with fluid. The tissues of the hydatidiform mole produce hCG intensively, which provokes the appearance of cysts in the ovaries. In some cases, up to 20% of the total, the drift degenerates into a malignant neoplasm, chorionepithelioma.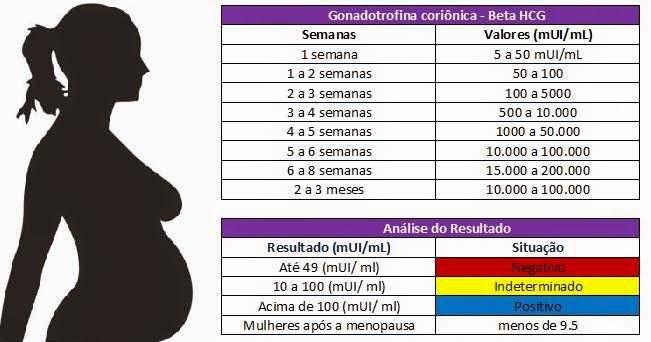
HCG test in the diagnosis of pathologies in non-pregnant women
A small amount of human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the pituitary gland of healthy people, both men and women. Normally, its indicators in non-pregnant women are close to zero. An increase in CG outside of pregnancy occurs when hormonally active tumors form in the body, with the following pathologies:
- tapeworm infestations;
- choriocarcinoma;
- malignant neoplasms of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, uterus in women, testicles in men.
General recommendations
The level of human chorionic gonadotropin is determined in blood serum. Biomaterial is taken from a vein on an empty stomach. To obtain accurate results of the analysis, it is necessary to follow the recommendations:
- Eating should be excluded for 4 hours.
- In the days preceding the analysis, refrain from physical activity, sexual intercourse.
 8 - 71.2 IU/L
8 - 71.2 IU/L