What causes indigestion and heartburn
Symptoms, Causes, Diet, and Treatments
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Are the Symptoms of Indigestion?
- Who Is at Risk for Indigestion?
- What Causes Indigestion?
- How Is Indigestion Diagnosed?
- What Is the Treatment for Indigestion?
- How Can I Prevent Indigestion?
- When Should I Call the Doctor About Indigestion?
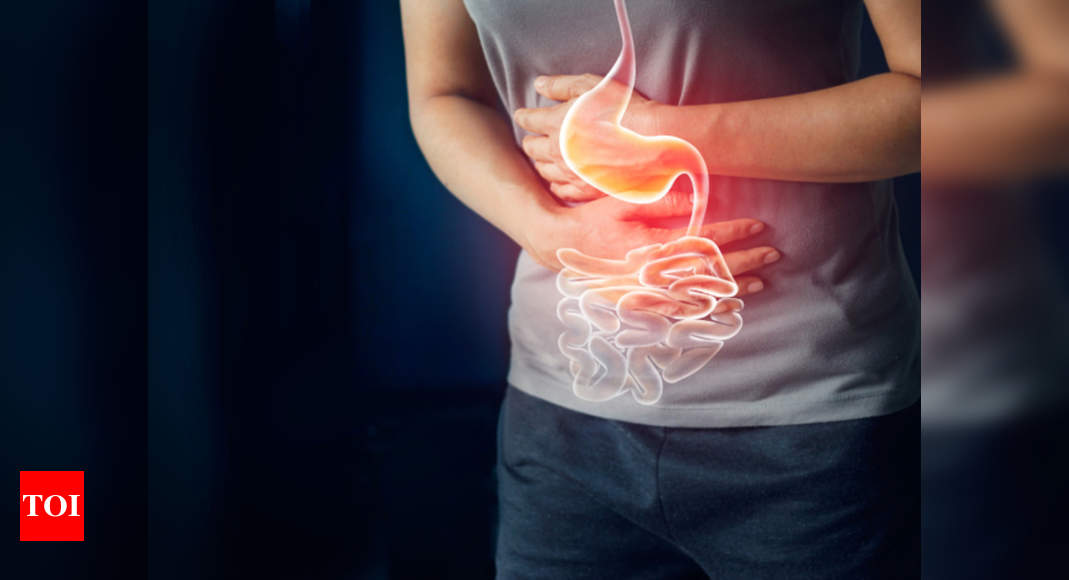
Indigestion is often a sign of an underlying problem, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), ulcers, or gallbladder disease, rather than a condition of its own.
Also called dyspepsia, it is defined as a persistent or recurrent pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen.
What Are the Symptoms of Indigestion?
The symptoms of indigestion can include:
- Burning in the stomach or upper abdomen
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating (full feeling)
- Belching and gas
- Nausea and vomiting
- Acidic taste
- Growling stomach
These symptoms may increase in times of stress.
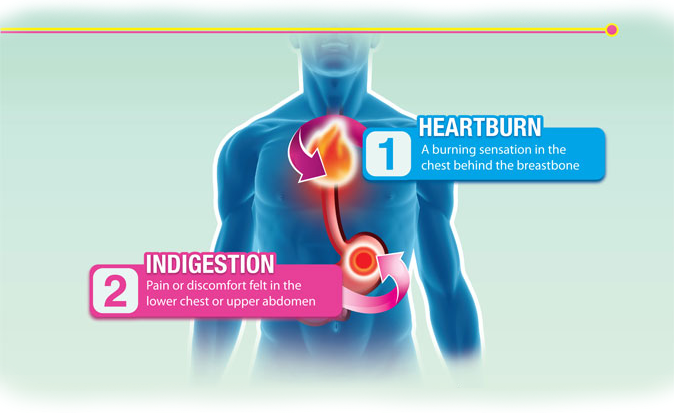
People often have heartburn (a burning sensation deep in the chest) along with indigestion. But heartburn itself is a different symptom that may indicate another problem.
Who Is at Risk for Indigestion?
People of all ages and of both sexes are affected by indigestion. It's extremely common. An individual's risk increases with:
- Excess alcohol consumption
- Use of drugs that may irritate the stomach, such as aspirin and other pain relievers
- Conditions where there is an abnormality in the digestive tract, such as an ulcer
- Emotional problems, such as anxiety or depression
- Obesity
- Smoking
What Causes Indigestion?
Indigestion has many causes, including:
Diseases:
- Ulcers
- GERD
- Stomach cancer (rare)
- Gastroparesis (a condition where the stomach doesn't empty properly; this often occurs in people with diabetes)
- Stomach infections
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Thyroid disease
- Pregnancy
Medications:
- Aspirin and other painkillers, such as NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil), and naproxen (Naprosyn)
- Estrogen and oral contraceptives
- Steroid medications
- Certain antibiotics
- Thyroid medicines
Lifestyle:
- Eating too much, eating too fast, eating high-fat foods, or eating during stressful situations
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Cigarette smoking
- Stress and fatigue
Indigestion is not caused by excess stomach acid.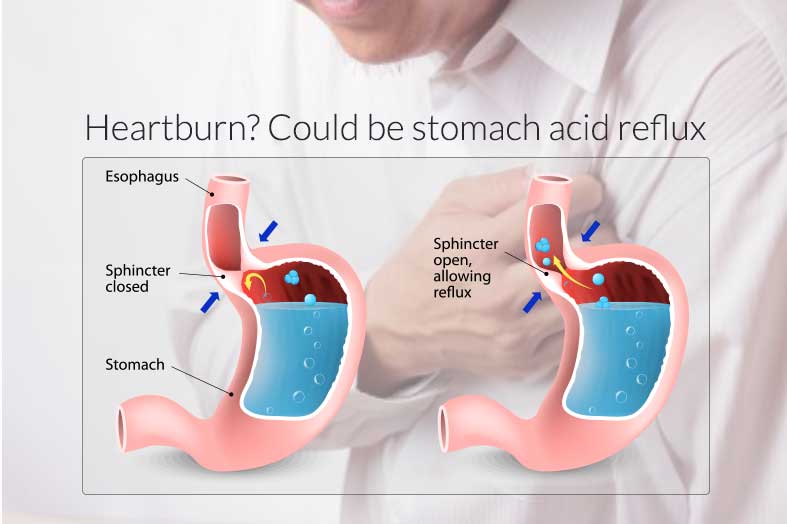
Swallowing excessive air when eating may increase the symptoms of belching and bloating, which are often associated with indigestion.
Sometimes people have persistent indigestion that is not related to any of these factors. This type of indigestion is called functional, or non-ulcer dyspepsia.
How Is Indigestion Diagnosed?
If you are experiencing symptoms of indigestion, make an appointment to see your doctor. Because indigestion is such a broad term, it is helpful to provide your doctor with a precise description of the discomfort you are experiencing. In describing the symptoms, try to define where in the abdomen the discomfort usually occurs.
Your doctor will rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing your symptoms. Your doctor may perform several blood tests and you may have X-rays of the stomach or small intestine. Your doctor may also suggest you have an upper endoscopy to look closely at the inside of the stomach. During the procedure, an endoscope -- a flexible tube that contains a light and a camera to produce images from inside the body -- is used to look inside your stomach.
What Is the Treatment for Indigestion?
Because indigestion is a symptom rather than a disease, treatment usually depends upon the underlying condition causing the indigestion.
How Can I Prevent Indigestion?
The best way to prevent indigestion is to avoid the foods and situations that seem to cause it. Keeping a food diary is helpful in identifying foods that cause indigestion. Here are some other suggestions:
- Eat small meals so the stomach does not have to work as hard or as long.
- Eat slowly.
- Avoid foods that contain high amounts of acids, such as citrus fruits and tomatoes.
- Reduce or avoid foods and beverages that contain caffeine.
- If stress is a trigger for your indigestion, learn new methods for managing stress, such as relaxation and biofeedback techniques.
- If you smoke, quit. Smoking can irritate the lining of the stomach.
- Cut back on alcohol consumption, because alcohol can also irritate the stomach lining.

- Avoid wearing tight-fitting garments, because they tend to compress the stomach, which can cause its contents to enter the esophagus.
- Don't exercise with a full stomach. Rather, exercise before a meal or at least one hour after eating a meal.
- Don't lie down right after eating.
- Wait at least three hours after your last meal of the day before going to bed.
- Sleep with your head elevated (at least 6 inches) above your feet and use pillows to prop yourself up. This will help allow digestive juices to flow into the intestines rather than to the esophagus.
When Should I Call the Doctor About Indigestion?
Because indigestion can be a sign of a more serious health problem, call your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Vomiting or blood in vomit (the vomit may look like coffee grounds)
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Black, tarry stools or visible blood in stools
- Severe pain in the abdomen
- Discomfort unrelated to eating
Symptoms similar to indigestion may be caused by heart attacks.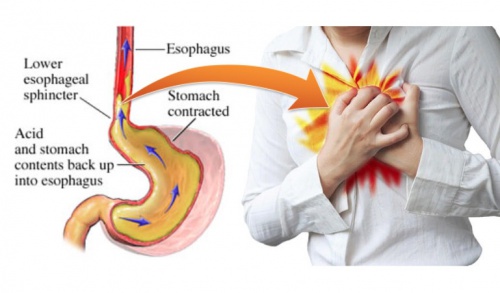 If indigestion is unusual, accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain, or pain radiating to the jaw, neck, or arm, seek medical attention immediately.
If indigestion is unusual, accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain, or pain radiating to the jaw, neck, or arm, seek medical attention immediately.
Symptoms, Causes, Diet, and Treatments
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Are the Symptoms of Indigestion?
- Who Is at Risk for Indigestion?
- What Causes Indigestion?
- How Is Indigestion Diagnosed?
- What Is the Treatment for Indigestion?
- How Can I Prevent Indigestion?
- When Should I Call the Doctor About Indigestion?
Indigestion is often a sign of an underlying problem, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), ulcers, or gallbladder disease, rather than a condition of its own.
Also called dyspepsia, it is defined as a persistent or recurrent pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen.
What Are the Symptoms of Indigestion?
The symptoms of indigestion can include:
- Burning in the stomach or upper abdomen
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating (full feeling)
- Belching and gas
- Nausea and vomiting
- Acidic taste
- Growling stomach
These symptoms may increase in times of stress.
People often have heartburn (a burning sensation deep in the chest) along with indigestion. But heartburn itself is a different symptom that may indicate another problem.
Who Is at Risk for Indigestion?
People of all ages and of both sexes are affected by indigestion. It's extremely common. An individual's risk increases with:
- Excess alcohol consumption
- Use of drugs that may irritate the stomach, such as aspirin and other pain relievers
- Conditions where there is an abnormality in the digestive tract, such as an ulcer
- Emotional problems, such as anxiety or depression
- Obesity
- Smoking
What Causes Indigestion?
Indigestion has many causes, including:
Diseases:
- Ulcers
- GERD
- Stomach cancer (rare)
- Gastroparesis (a condition where the stomach doesn't empty properly; this often occurs in people with diabetes)
- Stomach infections
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Thyroid disease
- Pregnancy
Medications:
- Aspirin and other painkillers, such as NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil), and naproxen (Naprosyn)
- Estrogen and oral contraceptives
- Steroid medications
- Certain antibiotics
- Thyroid medicines
Lifestyle:
- Eating too much, eating too fast, eating high-fat foods, or eating during stressful situations
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Cigarette smoking
- Stress and fatigue
Indigestion is not caused by excess stomach acid.
Swallowing excessive air when eating may increase the symptoms of belching and bloating, which are often associated with indigestion.
Sometimes people have persistent indigestion that is not related to any of these factors. This type of indigestion is called functional, or non-ulcer dyspepsia.
How Is Indigestion Diagnosed?
If you are experiencing symptoms of indigestion, make an appointment to see your doctor. Because indigestion is such a broad term, it is helpful to provide your doctor with a precise description of the discomfort you are experiencing. In describing the symptoms, try to define where in the abdomen the discomfort usually occurs.
Your doctor will rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing your symptoms. Your doctor may perform several blood tests and you may have X-rays of the stomach or small intestine. Your doctor may also suggest you have an upper endoscopy to look closely at the inside of the stomach. During the procedure, an endoscope -- a flexible tube that contains a light and a camera to produce images from inside the body -- is used to look inside your stomach.
What Is the Treatment for Indigestion?
Because indigestion is a symptom rather than a disease, treatment usually depends upon the underlying condition causing the indigestion.
How Can I Prevent Indigestion?
The best way to prevent indigestion is to avoid the foods and situations that seem to cause it. Keeping a food diary is helpful in identifying foods that cause indigestion. Here are some other suggestions:
- Eat small meals so the stomach does not have to work as hard or as long.
- Eat slowly.
- Avoid foods that contain high amounts of acids, such as citrus fruits and tomatoes.
- Reduce or avoid foods and beverages that contain caffeine.
- If stress is a trigger for your indigestion, learn new methods for managing stress, such as relaxation and biofeedback techniques.
- If you smoke, quit. Smoking can irritate the lining of the stomach.
- Cut back on alcohol consumption, because alcohol can also irritate the stomach lining.
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting garments, because they tend to compress the stomach, which can cause its contents to enter the esophagus.
- Don't exercise with a full stomach. Rather, exercise before a meal or at least one hour after eating a meal.
- Don't lie down right after eating.
- Wait at least three hours after your last meal of the day before going to bed.
- Sleep with your head elevated (at least 6 inches) above your feet and use pillows to prop yourself up. This will help allow digestive juices to flow into the intestines rather than to the esophagus.
When Should I Call the Doctor About Indigestion?
Because indigestion can be a sign of a more serious health problem, call your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Vomiting or blood in vomit (the vomit may look like coffee grounds)
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Black, tarry stools or visible blood in stools
- Severe pain in the abdomen
- Discomfort unrelated to eating
Symptoms similar to indigestion may be caused by heart attacks.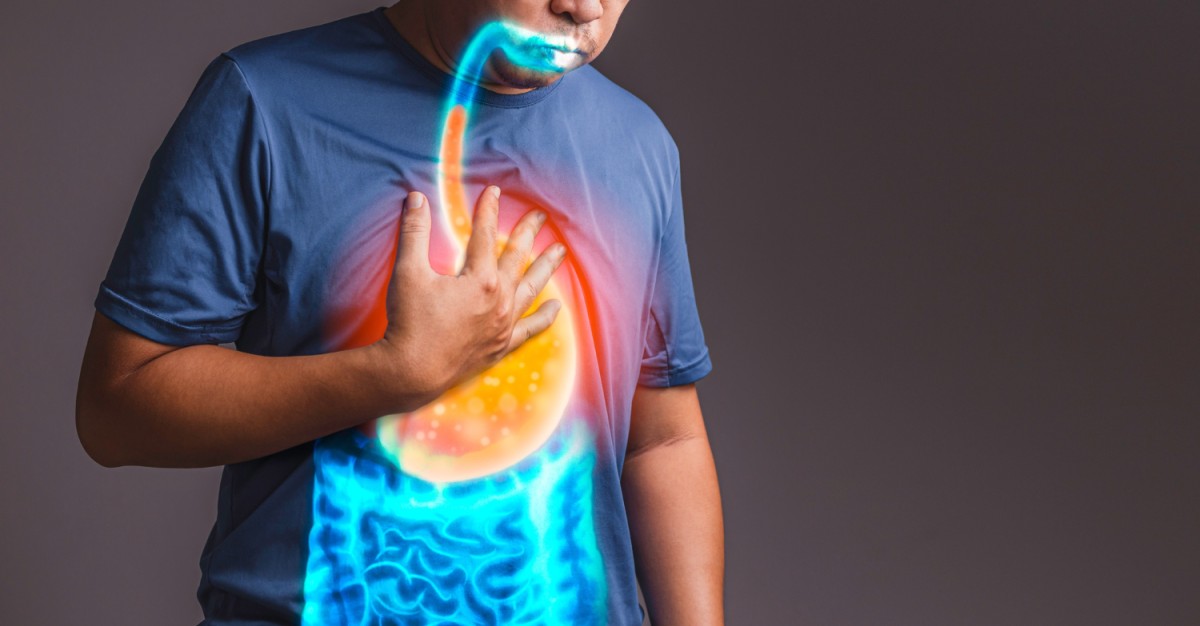 If indigestion is unusual, accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain, or pain radiating to the jaw, neck, or arm, seek medical attention immediately.
If indigestion is unusual, accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain, or pain radiating to the jaw, neck, or arm, seek medical attention immediately.
what are the reasons and what to do?
Indigestion is more correctly called an intestinal disorder, because most of the food is digested there. We will figure out what disrupts digestion and how to deal with burning, bloating, diarrhea, constipation and colic.
With this article we open a series of publications about the most common problems with the stomach and intestines. In the following articles, we will analyze in more detail each of the problems mentioned and tell you what genetics affects and what lifestyle affects.
This and other articles on the Internet will help you learn more about unpleasant symptoms but will not replace your doctor's visit!
Contents
- 1. Heartburn
- 2. Bloating
- 3. Constipation
- 4. Diarrhea
- 5.
 Abdominal pains
Abdominal pains
Heartburn
Symptoms
Heartburn is an unpleasant burning sensation in the chest area, sometimes accompanied by a sour taste in the mouth and belching. It is normal to experience heartburn after a hearty dinner, but with a constant burning sensation in the esophagus, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Why does it occur
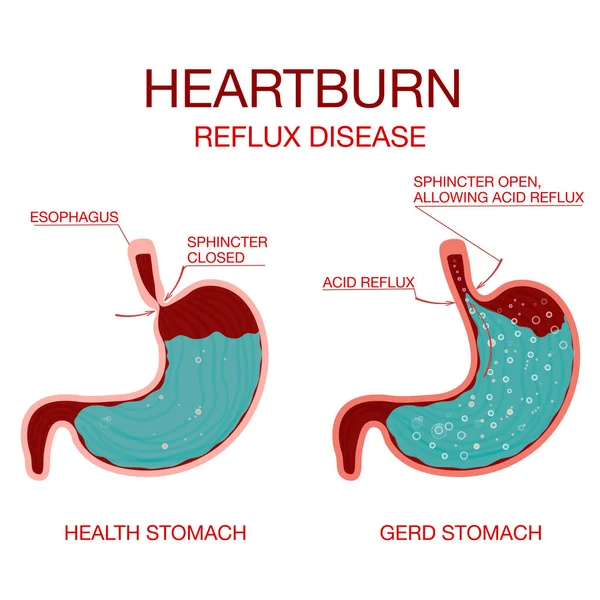
In case of heartburn, the contents of the stomach are partially thrown back into the esophagus. Persistent heartburn is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It can accompany gastritis, gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer, dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome, dysbacteriosis and other pathologies.
Don't rush into making diagnoses. Burning may also occur after:
- a cup of coffee;
- cigarettes;
- sodas;
- alcohol;
- fatty meat food;
- dry snacks;
- coarse food;
- spicy dishes;
- fruit juice.
Being overweight and pregnant can also cause heartburn.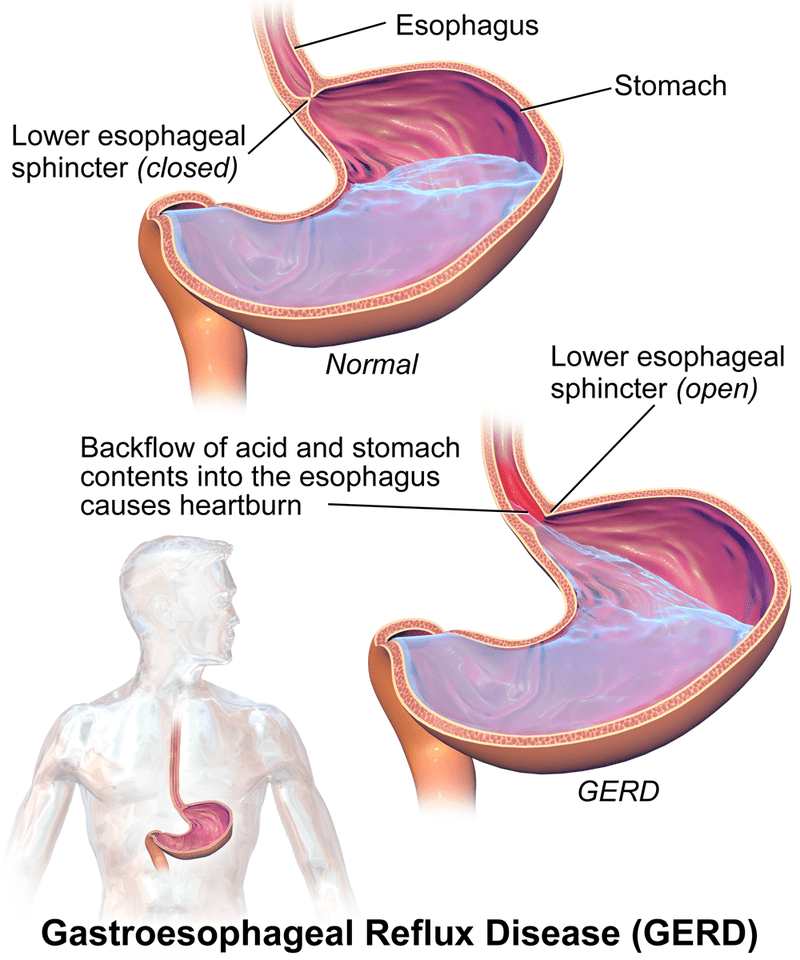
How to solve the problem
To avoid reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, it is better not to lie down, jump or bend over for a couple of hours after eating. It is also important to improve nutrition in order to support your microbiome, not overeat and not lean on spicy food.
You don't need to drink soda or milk for heartburn. You can get rid of heartburn at home with the help of antacids - they instantly and safely "extinguish" the attack.
For persistent heartburn, a gastroenterologist may prescribe proton pump inhibitors or h3-histamine receptor blockers. They slow down the production of hydrochloric acid by the cells of the stomach.
If heartburn torments you all the time, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and do an endoscopy of the stomach (EGD) - this procedure will accurately show whether the mucosa is inflamed.
Bloating
Symptoms
Bloating is flatulence. With it, the stomach bursts, it increases in volume, becomes hard. Sometimes you can feel the movement of gases in the intestines, seething and rumbling. When there is a lot of gas in the intestines, it is difficult and even painful to draw in the stomach.
Sometimes you can feel the movement of gases in the intestines, seething and rumbling. When there is a lot of gas in the intestines, it is difficult and even painful to draw in the stomach.
Why it occurs
A small amount of gas in the intestines is normal. If bloating is noticeable to you and others, interferes with sports and causes discomfort, then this is already excessive gas formation.
A common cause of bloating is eating a lot of fast food and avoiding whole foods, plant foods. A burger, fries, and soda combo can cause stomach heaviness, fermentation, and constipation because there aren't enough enzymes and fiber to digest it all and get it out of the body.
There is another reason for bloating - food intolerance. Many plant and dairy products contain FODMAP carbohydrates, which feed colon bacteria and lead to increased gas production, especially in people with irritable bowel syndrome.
How to solve the problem
If you have severe bloating, it's best to get up and move around to help the gas to leave the intestines. A sitting posture will only worsen the condition - the intestines are pinched in it. During this period, it is better to choose loose clothing.
A sitting posture will only worsen the condition - the intestines are pinched in it. During this period, it is better to choose loose clothing.
Preparations with simethicone, which "collapses" gas bubbles in the intestines, will help to make you feel better. Peppermint tea and other warm drinks can also relieve discomfort.
If you eat healthy but still suffer from bloating, try identifying your trigger foods with the FODMAP diet and cutting them out.
Constipation
Symptoms
Retention of feces for more than two days is constipation. It is usually accompanied by a feeling of incomplete emptying and heaviness in the abdomen. The stool becomes more dense, you have to push hard and for a long time. Constipation can be temporary or chronic.
Causes
Lack of fiber and water in the diet makes feces hard, making going to the toilet more difficult. The situation is complicated by a sedentary lifestyle, in which peristalsis slows down.
Stress, depression, side effects of certain medications, and comorbidities can also cause constipation. Other reasons are haste and reluctance to use public toilets, which makes it necessary to restrain the urge.
How to solve the problem
Prunes, flax seeds, psyllium (psyllium husk) and prebiotics (inulin, lactulose) are considered natural laxatives. Caffeine also stimulates peristalsis.
Preparations with senna extract and other folk recipes are best avoided - they act harshly, irritating the intestinal receptors and causing it to "evacuate" the contents. As a result, constipation turns into diarrhea with bubbling and pain.
Sodium picosulfate or bisacodyl-based preparations work more gently, but they work on the same principle. Options with a more gentle mechanism of work are macrogol and prucalopride. But any laxatives should be used according to the doctor's recommendations.
Constipation is best prevented by eating a variety of fiber (fruits, vegetables, herbs, legumes and mushrooms), eating regularly and around the same time, drinking more water.
Fiber absorbs water - feces pass through the digestive tract more easily. It is also important to move more during the day and not put off going to the toilet.
Diarrhea
Symptoms
Diarrhea requires going to the toilet more than three times a day, and the stool becomes loose, unformed, often with undigested food particles. In this case, the body loses water and electrolytes. Distinguish between acute and chronic diarrhea.
Causes
The main causes of diarrhea are food poisoning and intestinal infections. There is also traveler's diarrhea - it is caused by the ingestion of new species of E. coli for the body.
Loose stools may be due to dysbacteriosis. When pathogenic bacteria take precedence over beneficial ones, the intestinal mucosa and its ability to digest food and synthesize vitamins suffer. Also, a lot of gases are formed that interfere with the normal formation of feces.
Chronic diarrhea often affects people with irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis, folate deficiency anemia, or lactose intolerance.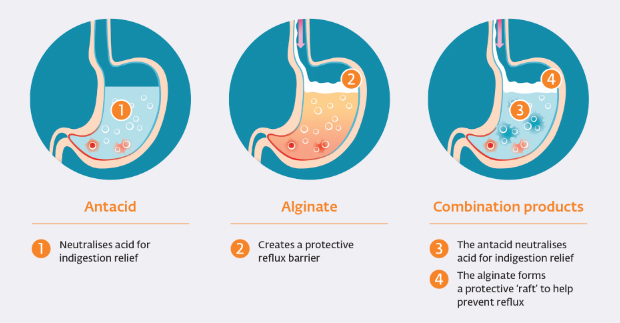 Also, the cause of regular diarrhea can be a violation of the intestinal microflora.
Also, the cause of regular diarrhea can be a violation of the intestinal microflora.
How to solve the problem
You need to drink plenty of water and take gel-like sorbents — they bind and remove toxic substances from the body more efficiently than activated charcoal. Medications like loperamide inhibit peristalsis, but do not solve the problem, so they can be relied on only in emergency cases. If diarrhea lasts a day or longer, you need to restore the water-salt balance with rehydration agents.
If a rotavirus infection is suspected, antibiotics should not be taken on their own - sorbents will be enough. If diarrhea does not go away after 4-5 days, you need to call a doctor. The same should be done if the diarrhea is accompanied by fever, vomiting, or blood in the stool.
Abdominal pain
Symptoms
When they say that the stomach hurts, they usually mean colic and spasms. They can be barely perceptible, or they can literally twist the stomach. In this case, the abdomen is usually swollen or tense. It is from such colic that babies often wake up and cry.
In this case, the abdomen is usually swollen or tense. It is from such colic that babies often wake up and cry.
Causes
One of the possible causes is flatulence. Excess gas stretches the walls of the intestine and thus causes pain when moving along the tract. People with sensitive bowels are especially susceptible to this pain.
Also, the stomach can hurt due to stress or a disturbed daily routine, in which you have to chaotically snack or endure hunger, and then eat up late in the evening.
Another cause is inflammation of the intestinal mucosa caused by intestinal flu or another infection. Colic and spasms can also be the result of a chronic illness such as gastroparesis, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, or liver damage.
Babies can have several causes of colic: emerging microflora, lack of enzymes, increased intestinal sensitivity, intolerance to formula for feeding, swallowing air.
How to solve the problem
Pain is relieved by antispasmodics that completely or selectively relax the smooth muscles of the intestine.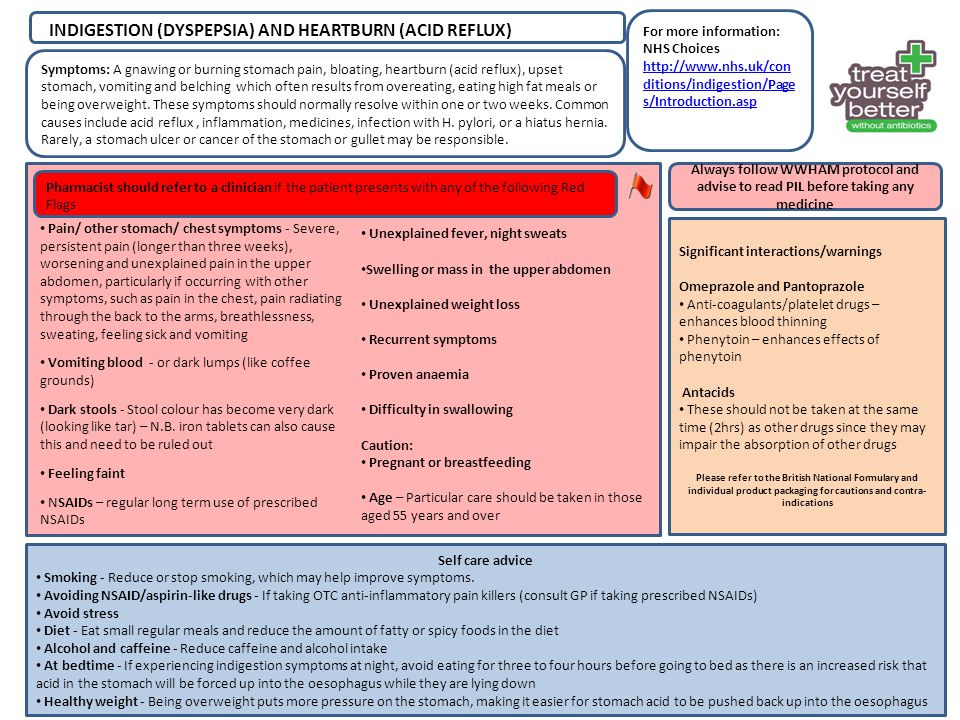 A warm heating pad on the abdomen may help, but only if the cause of the abdominal pain is known and not inflammation. With colic in a baby, parents should keep a diary of colic and baby's nutrition in order to establish the cause.
A warm heating pad on the abdomen may help, but only if the cause of the abdominal pain is known and not inflammation. With colic in a baby, parents should keep a diary of colic and baby's nutrition in order to establish the cause.
If the pain is accompanied by other symptoms of indigestion, do not drown it out - immediately contact a gastroenterologist.
These digestive problems can be solved by changing the contents of your plate. The right products will help improve the composition of the microflora and get rid of discomfort. What exactly needs to be added to the diet in your case, the personal Atlas microbiota test will tell you.
More articles on the causes of digestive problems on the blog:
- Leaky intestines0014
- Chronic constipation diagnosis and treatment evaluation: the “CHRO.CO.DI.T.E.” study
- Bharucha, A. and Wald, A. Chronic Constipation
- Badillo, R.
 and Francis, D. Diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
and Francis, D. Diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease - Mechanisms, Evaluation, and Management of Chronic Constipation
- Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Infectious Diarrhea
- Monash University
What foods cause heartburn ⛑ causes, symptoms |rennie.ua
Burning "in the pit of the stomach" and discomfort in the stomach after eating indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). These unpleasant sensations are intensified if the diet is unbalanced, heavy and aggressive for the stomach. Products that cause heartburn, you need to “know by sight” in order to stop in time and protect the stomach from unpleasant consequences.
Heartburn - what is it?
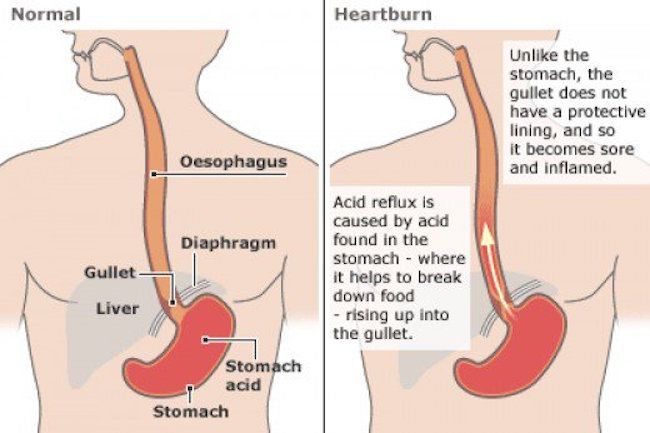
Heartburn is a condition of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the aggressive environment in the stomach begins to irritate its mucosa. In some cases, heartburn is accompanied by reflux disease (GERD) - the reverse reflux of food from the stomach into the esophagus.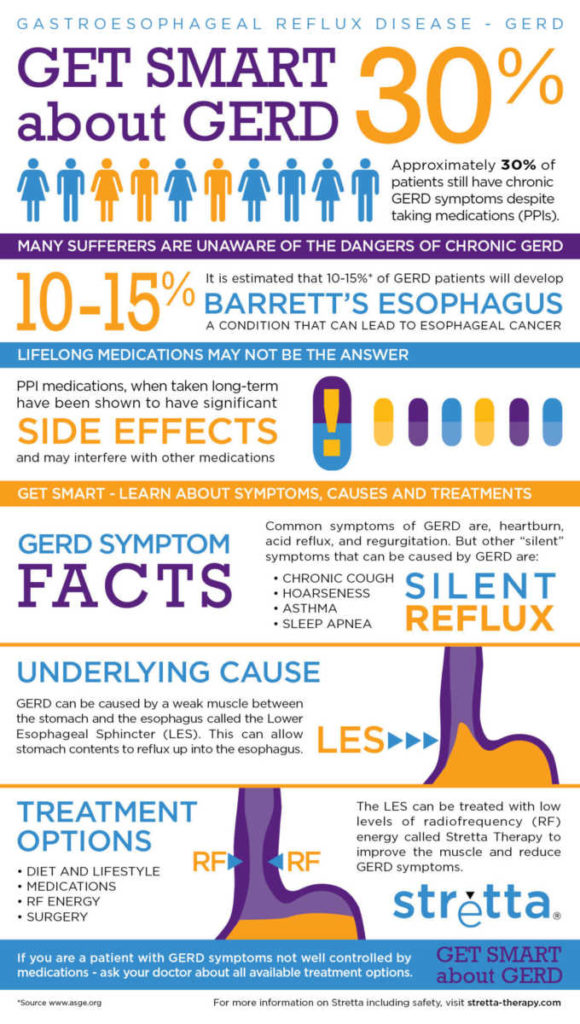 If there is a predisposition to this disease, you need to know which foods cause heartburn.
If there is a predisposition to this disease, you need to know which foods cause heartburn.
Reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter is not working well. This organ is a set of folds that open and close like a valve:
- food got into the esophagus - the valve opened to pass it into the stomach;
- food in stomach - valve closed.
If the sphincter does not work, part of the food is thrown back along with impurities of gastric juice. Among other components, it contains hydrochloric acid, which is aggressive for the walls of the esophagus. A feeling of heat begins, it bakes in the throat. Reflux is not the only cause of burning. Very often, people harm themselves by eating foods that cause heartburn. They are aggressive and irritate the gastric mucosa by themselves.
Heartburn is caused by food
We are what we eat. The physiological causes of heartburn have been elucidated. Concomitant factors remain:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs - ulcers, gastritis, sometimes pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, anatomical disorders of the larynx;
- products that provoke heartburn.
If the first causes must be dealt with in a complex manner, then the second can be easily eliminated. It is enough to remove aggressive food from the diet, and the condition of the body improves. If the causes of heartburn in foods, pay attention to whether there are in your diet:
- Sour vegetables and fruits. These are oranges, lemons, all citrus fruits, pineapples and tomatoes - they contain a lot of acids. If the stomach produces juice in large quantities, acids from vegetables and fruits only increase the effect of hydrochloric acid.
- Sweet, especially in large quantities. Various desserts relax the lower esophageal sphincter with all the ensuing consequences.
- Chocolate and coffee. In increased quantities, they have the same effect as desserts.
- Fat is hard to digest and takes a long time. Therefore, you should not abuse food rich in fats - cheeses, nuts, sausages and sausages. Trans fats are bad for the stomach. Particular attention should be paid to the composition when choosing fast food and semi-finished products.
- Soda - accumulation of gas can bulge the stomach and put pressure on the sphincter.
- Spicy foods such as horseradish and garlic irritate mucous membranes, causing discomfort.
- Alcohol. Alcohol increases the production of gastric juice, especially red wines and beer.
Overweight people are prone to heartburn, as they have increased intra-abdominal pressure, the walls of the stomach and diaphragm are compressed, causing reflux. The same applies to pregnant women.
The first signs of heartburn
Heartburn appears almost immediately after eating. When the aggressor product enters the stomach, it begins to be broken down by enzymes and gastric acids. For the digestion of spicy, fatty and combined carbohydrates, juice is needed more, so the body releases it in an increased amount. A burning sensation begins in the abdomen, which reaches the chest and throat. Pain in the right hypochondrium or side in parallel with heartburn can indicate dangerous diseases or an inflamed appendix.
A sour or bitter taste in the mouth is added to the burning sensation. This suggests that the food has affected the liver and gallbladder, so it is worth examining these organs as well.
If non-specific signs are added: cough, hoarseness, shortness of breath and inflammation of the bronchi, you need to visit narrow specialists. Perhaps the causes of heartburn are associated with pathological processes in the lungs, bronchi or other organs.
The symptoms of heartburn can be divided according to the time of onset and duration. This is an indirect factor for determining the disease:
- heartburn appeared 15-20 minutes after eating - most likely it is GERD (reflux disease), an additional symptom is belching;
- bloating and burning immediately after eating - a sign of gastritis, ulcers, or normal overeating;
- with duodenal ulcer, burning may appear 1-2 hours after eating;
- stones in the gallbladder - after taking drugs for heartburn, it does not go away, acute pain appears.
It is not necessary to self-diagnose the disease, this is done by a doctor during a consultation. If you experience the following dangerous symptoms, you should visit him immediately:
- blood in stool;
- anemia;
- weight loss;
- vomiting;
- a quick feeling of satiety is the first sign of precancerous conditions [1].
If heartburn occurs behind the sternum, does not decrease, but only intensifies, call an ambulance. This may indicate a heart attack.
Heartburn: diagnosis
If the patient complains of regular heartburn, look for the underlying disease. In 70% of cases, burning causes GERD [2]. To diagnose it, they conduct a test with antacids: taking these drugs should quickly eliminate heartburn, which indicates reflux disease.
Additionally, laboratory tests of blood and feces are performed to detect an ulcer or gastritis. Examination with a probe is required, and in some cases endoscopy with contrast [3]. They also determine the acidity of the stomach and take an analysis to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori .
They also determine the acidity of the stomach and take an analysis to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori .
Heartburn associated with eating disorders is eliminated quickly, but gastrointestinal diseases require additional treatment.
Heartburn: treatment and quick help
If the symptom is not caused by severe pathologies of the esophagus, it is easy to get rid of it. It is necessary to maintain a balanced diet, the Ministry of Health of Ukraine recommends removing aggressive foods from the diet [4]. They can be replaced with those that suppress heartburn:
- bananas and melons correct pH;
- green vegetables also normalize the pH in the stomach;
- yoghurts, but only natural and reduced or medium fat content;
- oatmeal “calms” the stomach, but it should be boiled in water;
- Ginger drink can help with mucosal inflammation.
Diet is not the only treatment for heartburn, because sometimes drugs are indispensable.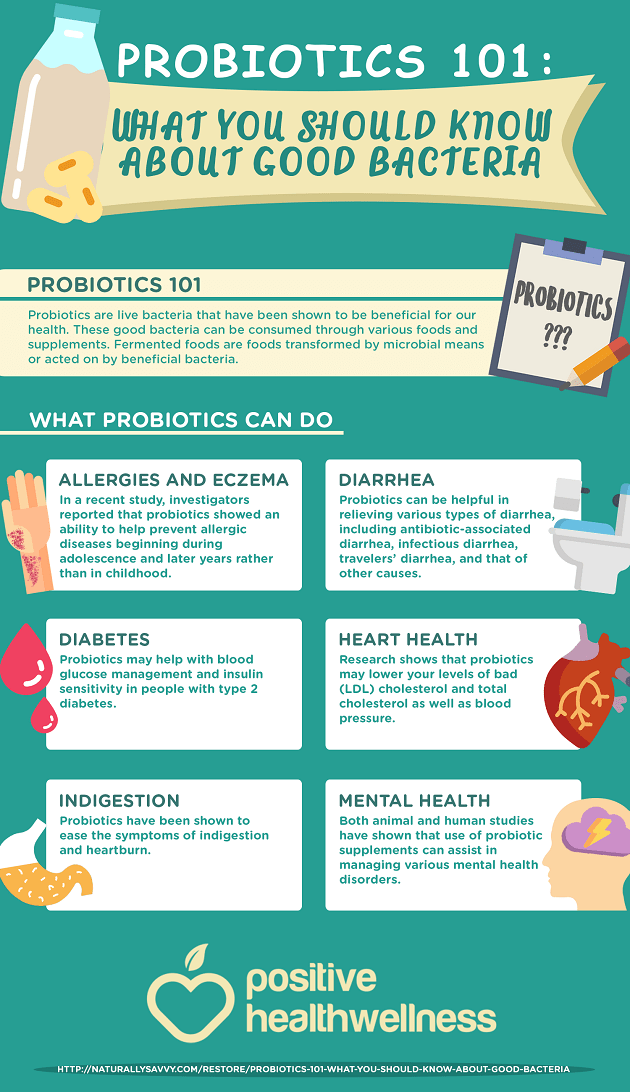 The World Organization of Gastroenterology recommends taking antacids for reflux disease [5]. They quickly eliminate the symptom, so they are prescribed in the complex treatment of diseases accompanied by heartburn. Rennie ® not only starts working after 2 minutes, but also has a favorable safety profile. This means that it can be used during pregnancy.
The World Organization of Gastroenterology recommends taking antacids for reflux disease [5]. They quickly eliminate the symptom, so they are prescribed in the complex treatment of diseases accompanied by heartburn. Rennie ® not only starts working after 2 minutes, but also has a favorable safety profile. This means that it can be used during pregnancy.
Rennie ® mint and orange flavored tablets. They are convenient due to the chewable form. The drug contains two antacids at once - calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate - these substances have proven their ability to increase pH in just a few minutes [6]. They neutralize hydrochloric acid in the stomach and esophagus, so they can quickly relieve heartburn.
Consult your doctor before taking any medication and to calculate the dosage.
[1] UMHS GERD Guideline, September, 2013. Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory, University of Michigan Medical.
[2] A guide to heartburn.