Pregnancy and degenerative disc disease
Pregnancy and spinal problems - PubMed
Save citation to file
Format: Summary (text)PubMedPMIDAbstract (text)CSV
Add to Collections
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Name your collection:
Name must be less than 100 characters
Choose a collection:
Unable to load your collection due to an error
Please try again
Add to My Bibliography
- My Bibliography
Unable to load your delegates due to an error
Please try again
Your saved search
Name of saved search:
Search terms:
Test search terms
Email: (change)
Which day? The first SundayThe first MondayThe first TuesdayThe first WednesdayThe first ThursdayThe first FridayThe first SaturdayThe first dayThe first weekday
Which day? SundayMondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFridaySaturday
Report format: SummarySummary (text)AbstractAbstract (text)PubMed
Send at most: 1 item5 items10 items20 items50 items100 items200 items
Send even when there aren't any new results
Optional text in email:
Create a file for external citation management software
Full text links
Wolters Kluwer
Full text links
Review
. 2010 Dec;22(6):477-81.
doi: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e3283404ea1.
In-Ho Han 1
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan, Korea. [email protected]
- PMID: 20930629
- DOI: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e3283404ea1
Review
In-Ho Han. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2010 Dec.
. 2010 Dec;22(6):477-81.
doi: 10.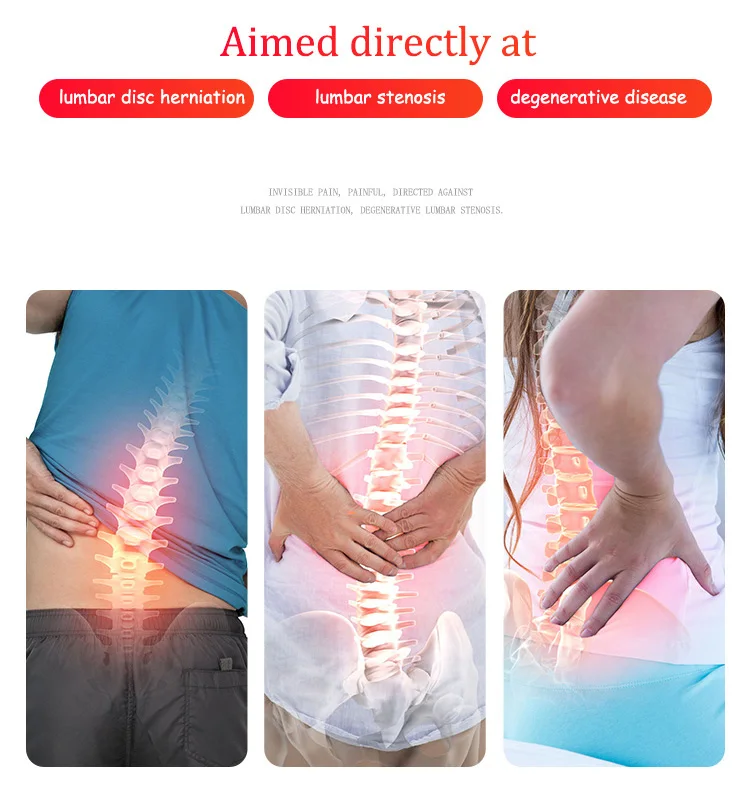 1097/GCO.0b013e3283404ea1.
1097/GCO.0b013e3283404ea1.
Author
In-Ho Han 1
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan, Korea. [email protected]
- PMID: 20930629
- DOI: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e3283404ea1
Abstract
Purpose of review: To review recent publications in spinal problems during pregnancy, diagnosis, and management.
Recent findings: Pregnancy-related low back pain (LBP) is the most common problem which can occur during pregnancy.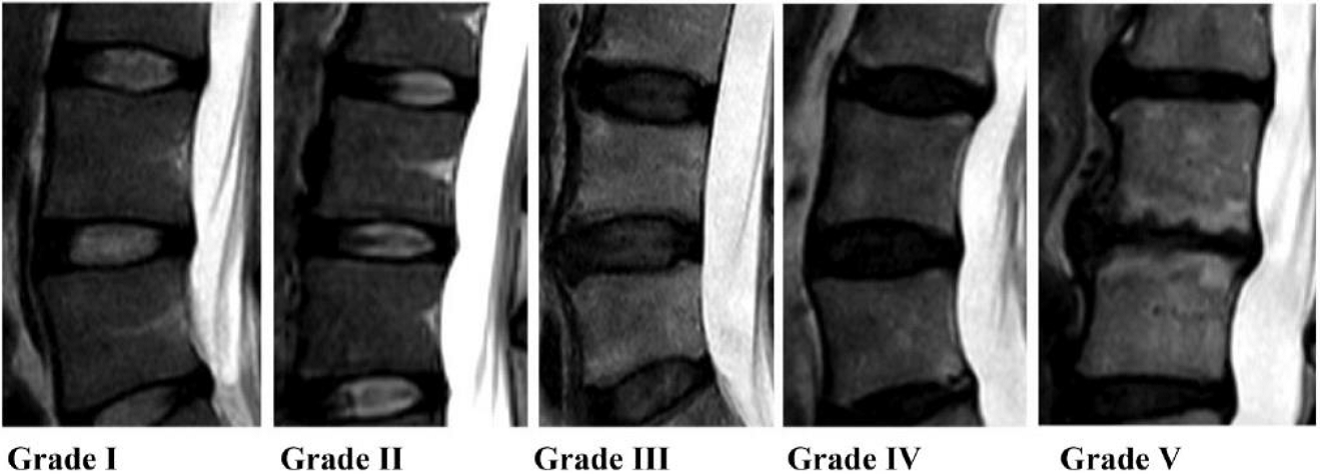 Among the various factors of pregnancy-related LBP, previous LBP and LBP during menstruation seem to be significant risk factors of pregnancy-related LBP. Patient counseling and wearing of a nonelastic pelvic belt are effective for the control of pelvic girdle pain. Lumbar pain can be treated with exercise such as water gymnastics during the second and third trimesters. Although rare, pregnancy can cause osteoporotic compression fractures and symptoms in spinal tumors, especially in vertebral hemangiomas. Lumbar disc herniation is the most common spinal disorder during pregnancy and can cause permanent neurologic deficit in pregnant women. Most cases can be treated by conservative management, but operation can also be safely performed maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
Among the various factors of pregnancy-related LBP, previous LBP and LBP during menstruation seem to be significant risk factors of pregnancy-related LBP. Patient counseling and wearing of a nonelastic pelvic belt are effective for the control of pelvic girdle pain. Lumbar pain can be treated with exercise such as water gymnastics during the second and third trimesters. Although rare, pregnancy can cause osteoporotic compression fractures and symptoms in spinal tumors, especially in vertebral hemangiomas. Lumbar disc herniation is the most common spinal disorder during pregnancy and can cause permanent neurologic deficit in pregnant women. Most cases can be treated by conservative management, but operation can also be safely performed maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
Summary: Recent concern about spinal problems in pregnancy is still pregnancy-related LBP. The further studies about its prevalence, risk factors, and treatment will be expected to continue.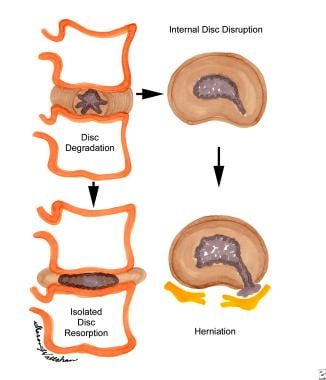 In both general spinal diseases and pregnancy-induced spinal diseases, there is no significant difference in treatment between pregnant women and ordinary people. Therefore, if consideration of possible spinal problems, exact diagnosis and adequate treatment are performed, good prognosis may be enough achieved in pregnant women.
In both general spinal diseases and pregnancy-induced spinal diseases, there is no significant difference in treatment between pregnant women and ordinary people. Therefore, if consideration of possible spinal problems, exact diagnosis and adequate treatment are performed, good prognosis may be enough achieved in pregnant women.
Similar articles
-
Information from your family doctor. Treating low back pain from a disk injury.
American Academy of Family Physicians. American Academy of Family Physicians. Am Fam Physician. 2008 Oct 1;78(7):844. Am Fam Physician. 2008. PMID: 18841732 No abstract available.
-
A case of radiating low back pain.
Antoun J, Saab B. Antoun J, et al. J Med Liban.
 2008 Jan-Mar;56(1):61-2. J Med Liban. 2008. PMID: 19534097 No abstract available.
2008 Jan-Mar;56(1):61-2. J Med Liban. 2008. PMID: 19534097 No abstract available. -
[Lumbago and radicular complaints: not always a herniated disk or degenerative stenosis of the spinal canal. A differential diagnosis of infrequent diseases].
Benini A. Benini A. Orthopade. 1999 Nov;28(11):916-21. Orthopade. 1999. PMID: 10602827 German.
-
Acute lumbar disk pain: navigating evaluation and treatment choices.
Gregory DS, Seto CK, Wortley GC, Shugart CM. Gregory DS, et al. Am Fam Physician. 2008 Oct 1;78(7):835-42. Am Fam Physician. 2008. PMID: 18841731 Review.
-
MR imaging and osseous spinal intervention and intervertebral disk intervention.

Obray RW, Filice RW, Beall DP. Obray RW, et al. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2007 May;15(2):257-71, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2007.05.001. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2007. PMID: 17599643 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Sudden perceived absence of foetal movement - a unique presentation of a vertebral haemangioma in pregnancy.
Devaraj A, Raoof J, Janjua O, Tsang K, Zamir M. Devaraj A, et al. BJR Case Rep. 2021 Oct 20;8(1):20200199. doi: 10.1259/bjrcr.20200199. eCollection 2022 Jan 1. BJR Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 35136631 Free PMC article.
-
MRI in Pregnancy and Precision Medicine: A Review from Literature.
Gatta G, Di Grezia G, Cuccurullo V, Sardu C, Iovino F, Comune R, Ruggiero A, Chirico M, La Forgia D, Fanizzi A, Massafra R, Belfiore MP, Falco G, Reginelli A, Brunese L, Grassi R, Cappabianca S, Viola L.
 Gatta G, et al. J Pers Med. 2021 Dec 23;12(1):9. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010009. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 35055324 Free PMC article. Review.
Gatta G, et al. J Pers Med. 2021 Dec 23;12(1):9. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010009. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 35055324 Free PMC article. Review. -
Methods of Delivery in Pregnant Women with Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Narrative Review of General Management and Case Report.
Paslaru FG, Giovani A, Iancu G, Panaitescu A, Peltecu G, Gorgan RM. Paslaru FG, et al. J Med Life. 2020 Oct-Dec;13(4):517-522. doi: 10.25122/jml-2020-0166. J Med Life. 2020. PMID: 33456600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Management of Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review.
Whiles E, Shafafy R, Valsamis EM, Horton C, Morassi GL, Stokes O, Elsayed S. Whiles E, et al. Global Spine J. 2020 Oct;10(7):908-918.
 doi: 10.1177/2192568219886264. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Global Spine J. 2020. PMID: 32905728 Free PMC article.
doi: 10.1177/2192568219886264. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Global Spine J. 2020. PMID: 32905728 Free PMC article. -
Risk Factors Associated with Low Back Pain among A Group of 1510 Pregnant Women.
Bryndal A, Majchrzycki M, Grochulska A, Glowinski S, Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A. Bryndal A, et al. J Pers Med. 2020 Jun 15;10(2):51. doi: 10.3390/jpm10020051. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32549306 Free PMC article.
See all "Cited by" articles
Publication types
MeSH terms
Full text links
Wolters Kluwer
Cite
Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Send To
Looking after your back during pregnancy
Looking after your back during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Backache during pregnancy is very common, especially in the later stages when your ligaments loosen and the growing baby affects your posture. The stress on your body caused by pregnancy also puts you at greater risk of back injury.
The stress on your body caused by pregnancy also puts you at greater risk of back injury.
One reason why your back is at particular risk of injury is that you gain a lot of weight in your abdomen. This puts extra strain on the arch in your lower back and it can also strain the joints.
The changes to your hormones during pregnancy cause your ligaments to relax, which can aggravate your lower spine and pelvis.
If you are unfit, overweight or if you smoke, you are more likely to experience backache or sciatica during pregnancy. Regular exercise can reduce this risk.
Treatment of back injury during pregnancy
If you injure your back while you are pregnant, simple exercises and using back support are usually enough to fix the injury. In very rare cases, pregnant women can have a serious injury such as a herniated disc. In this case you might need surgery. Back surgery is usually safe, however, both for you and your baby during pregnancy.
Many women have a pre-existing back condition before they become pregnant, such as scoliosis, spondylolisthesis or a lumbar disc condition. Sometimes your back problems get better during pregnancy, but sometimes they get worse. It's important to mention any back problems to the medical team who are looking after you.
Sometimes your back problems get better during pregnancy, but sometimes they get worse. It's important to mention any back problems to the medical team who are looking after you.
Talk to your doctor if you need to take medicine to control back pain. Paracetamol is one of the safest painkillers during pregnancy. Do not take aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatories such as Nurofen while you are pregnant.
Your back injury should not affect labour or pain relief during labour. It is also usually possible to have an epidural if you have a back injury. Tell the hospital about your condition because there are different positions you can use to ease back pain during labour.
How to protect your back
You can protect your back during pregnancy by avoiding or changing the way you do some things. This becomes more important the further along in your pregnancy you are.
- Avoid heavy lifting. If you have to lift something heavy, bend your knees, keep your back straight and tighten your pelvic floor and abdominal muscles.
 Make sure the object you are lifting stays close to your body. Allow toddlers to climb onto your lap or into the car or bath, and squat down next to them rather than picking them up.
Make sure the object you are lifting stays close to your body. Allow toddlers to climb onto your lap or into the car or bath, and squat down next to them rather than picking them up. - Always have a good posture. Try to keep your pelvis symmetrical. Stand with your weight evenly on both legs, your back straight and your pelvis tucked under. Avoid standing for a long time. Sit up straight with your bottom at the back of your chair and your feet on a stool if necessary.
- Avoid activities that might hurt your back. These include bending or twisting, climbing ladders, or walking up steep hills.
- Be careful in bed. Sleep on your side with a pillow between your knees. To get out of bed, roll onto your side with your knees together. Then use your arms for support as you swing your legs onto the floor.
- Wear shoes with low heels (not flats). These have good arch support. Avoid high heels.
- Consider a maternity support belt.
Strengthening your back
Regular physical activity is important when you are pregnant and can protect your back. If your doctor says it's OK, you can do some gentle exercise like walking or water exercise. Talk to a physiotherapist for specific exercises to strengthen your back.
Stretch your lower back by kneeling on all fours with your head in line with your back. Pull in your stomach and round your back. Hold the posture for a few seconds and then relax. Repeat 10 times.
Keep your tummy muscles strong with pelvic tilt exercises. Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the ground. Tilt your pelvis and hips backwards so the curve of your back is flat to the floor. Hold for 3 to 5 seconds. You can also do this exercise standing up or sitting on a gym ball.
Strengthen your tummy muscles and pelvic floor by gently drawing in the lower part of your tummy (bellow the belly button) towards your spine. Keep breathing. Gradually lengthen the time you hold the posture. Brace these muscles whenever you lift, push or pull something heavy.
Brace these muscles whenever you lift, push or pull something heavy.
Complementary therapies such as yoga and pilates can help some women, but always talk to your doctor or midwife first.
When to see a doctor
Talk to your doctor if the back pain is severe or if it lasts for more than 2 weeks.
Sometimes back pain can be a sign of premature labour or a urinary tract infection. See your doctor straight away if you also have bleeding from your vagina, painful urination or any signs of premature labour.
Sources:
The Royal Women's Hospital (Common concerns in early pregnancy), The Royal Women's Hospital (Back care & posture), Women's and Children's Health Network (Caring for your body in pregnancy - physiotherapy advice)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: February 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Yoga and Pilates during pregnancy
- Pelvic floor exercises
- Exercising during pregnancy
- Backache in pregnancy
Need more information?
Backache in pregnancy
There are several things you can do to help prevent backache from happening during your pregnancy, and to help you cope with an aching back if it does occur.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Exercising during pregnancy
Doing regular moderate physical activity has health benefits during pregnancy and also helps to prepare the body for childbirth. Read about getting fit during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Yoga and Pilates during pregnancy
Yoga and Pilates during pregnancy can be beneficial, but you should be careful to avoid some positions. Find out how yoga and Pilates can help you here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Complementary therapy during pregnancy
About half of Australian women consult a complementary therapist while pregnant. Here's what you should know about integrative medicine and pregnancy.
Here's what you should know about integrative medicine and pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health problems & complications | Raising Children Network
Many pregnancy health problems are mild, but always call your doctor if you’re worried about symptoms. A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Multiple pregnancy (triplets or more)
Learning you're pregnant with triplets or more can be a shock, but overall, most parents find having multiple babies to be a positive experience.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 33
Your baby's brain and nervous system are now fully developed, and the baby is continuing to gain weight. You'll probably also be feeling sore and tired.
You'll probably also be feeling sore and tired.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 38
Your baby is now ready to be born and you could go into labour at any time. Make sure you have you plan for getting to the hospital and you have everything packed ready to go.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 30
Your baby's reflexes are developing, and they may even be sucking their thumb or fingers. You might be tired and sore, but try to exercise and get enough sleep.
You might be tired and sore, but try to exercise and get enough sleep.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.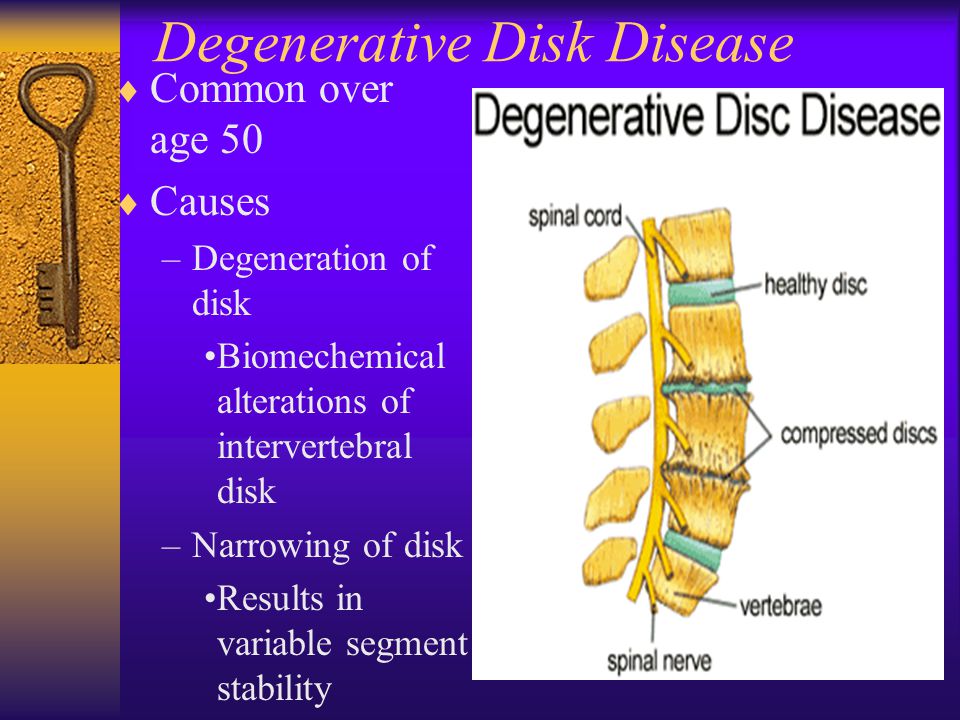
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.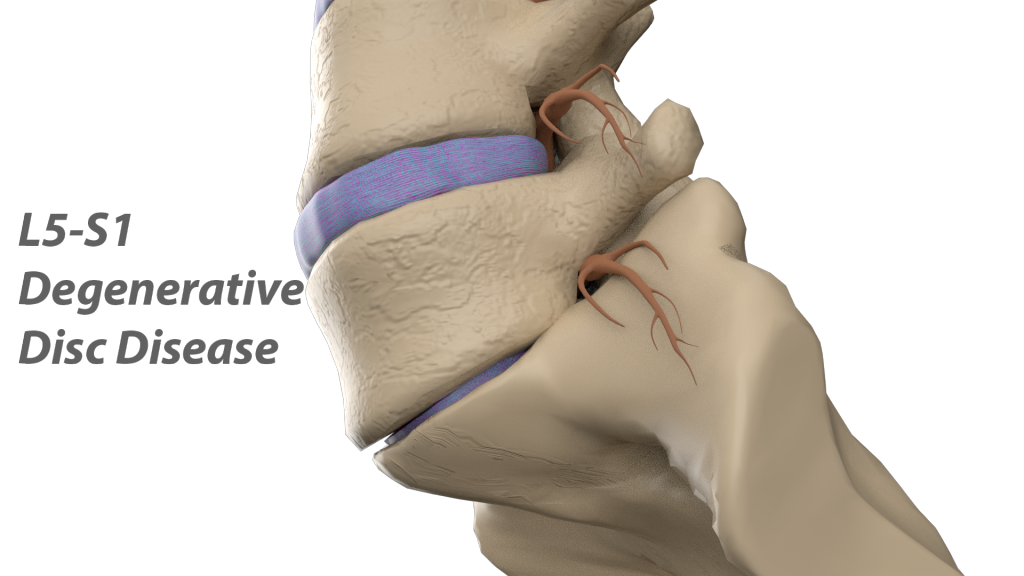
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
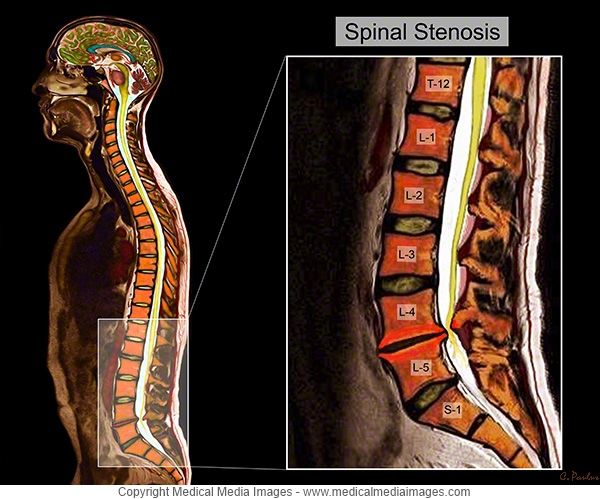
Osteochondrosis during pregnancy
09/14/2021
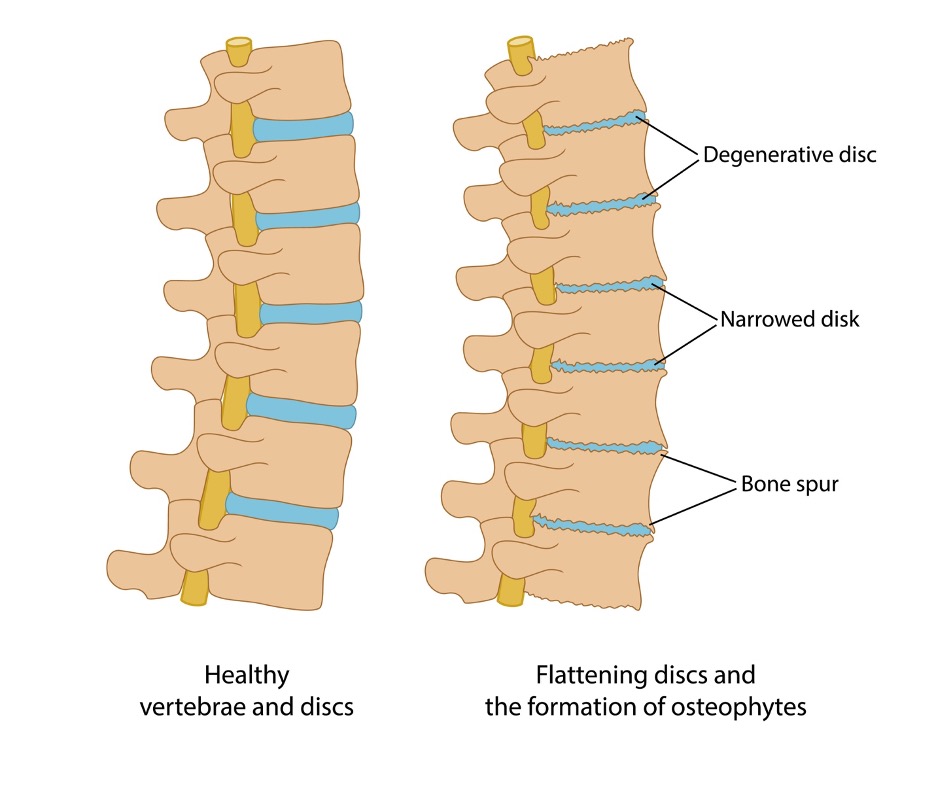
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine , which is characterized by degeneration of the spinal disc and a change in its height.
Treatment of osteochondrosis must be carried out immediately, as soon as it is diagnosed, in no case should you postpone
for later or ignore the recommendations of a doctor . If you are planning pregnancy , then you first need to treat osteochondrosis , since in this case
If you are planning pregnancy , then you first need to treat osteochondrosis , since in this case
there is an additional load on the back and the lower back . And if the disease is accompanied by scoliosis , then all the more need consultation
orthopedist . But what to do if you learned about the disease already during pregnancy ? What means can be used during this period?
The main danger lies in the fact that osteochondrosis can affect not only joints back but the whole body.
The following types of disease are distinguished (taking into account localization):
- cervical,
- lumbar,
- thoracic and so on.
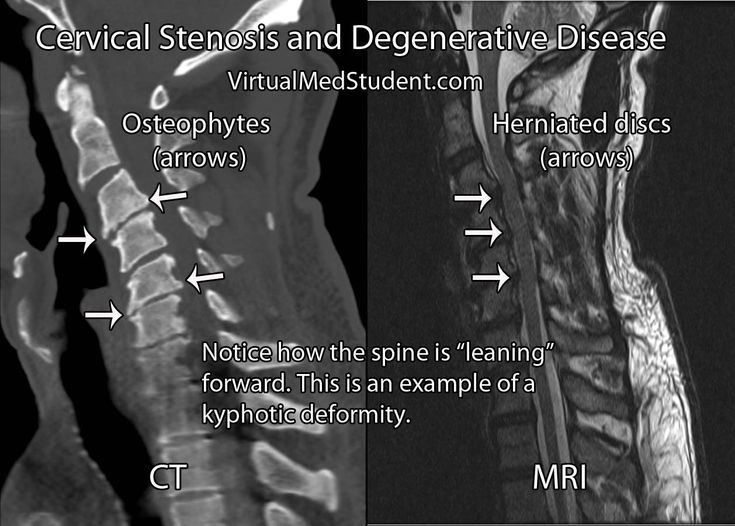
As a result of the disease, nerves can be injured, blood circulation is disturbed, or even the structure of the vertebrae themselves is changed.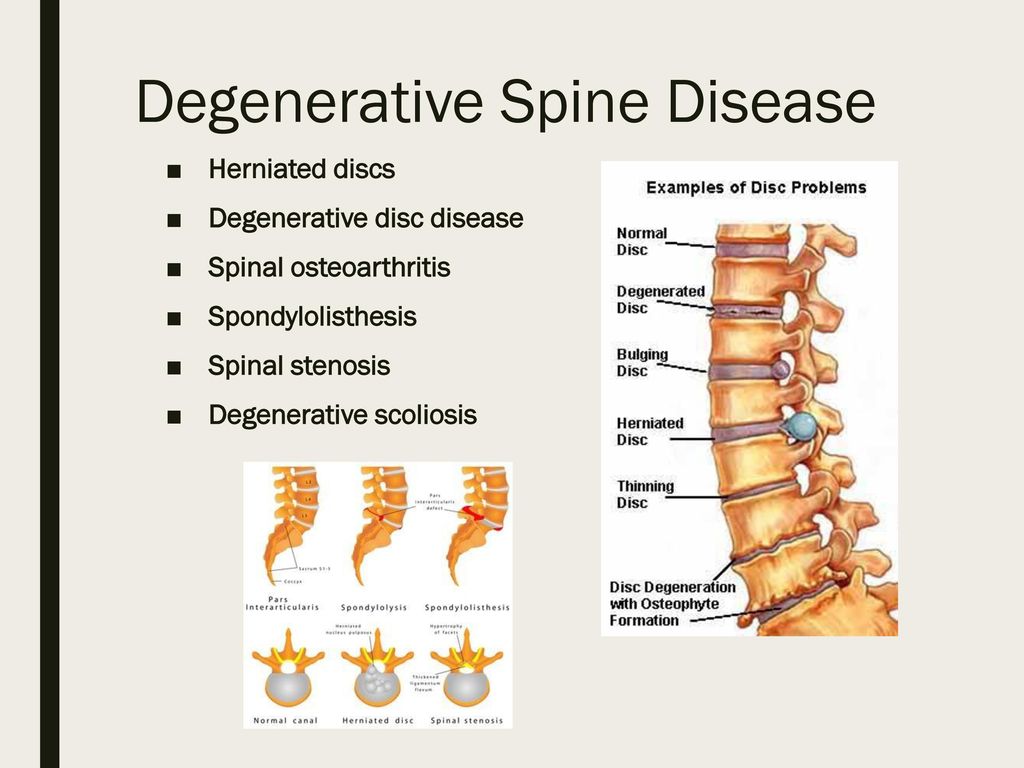
Causes of osteochondrosis :
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders;
- overweight;
- violation of posture ;
- wrong supply;
- spinal injuries ;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overload spine and many other negative factors.
A symptom of cervical osteochondrosis in pregnant women is a dull aching pain in the neck , especially after physical exertion.
Diagnose chest osteochondrosis during pregnancy is much more difficult, because due to its location it is often confused with cardiovascular or
gastrointestinal diseases. This is the reason that this type of osteochondrosis is detected already at more than
later stages, when the treatment becomes more complicated and less effective.
Some drugs, as many people know, are prohibited during pregnancy .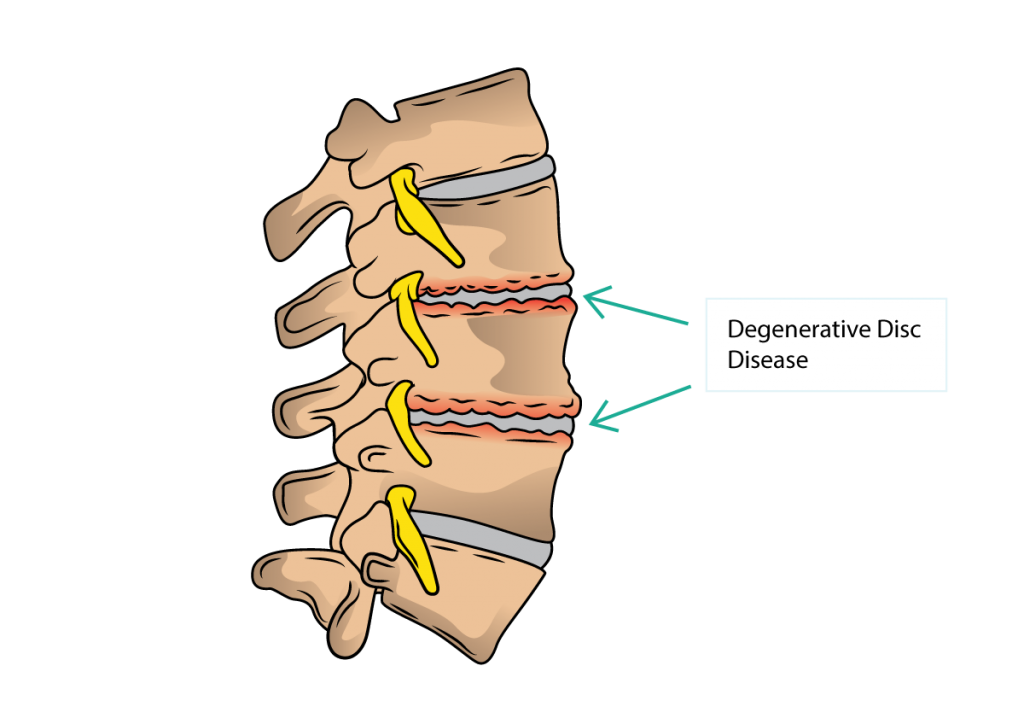 Medicines for 9 were no exception.0005 osteochondrosis .
Medicines for 9 were no exception.0005 osteochondrosis .
Clinically proven harm to fetal development and pregnancy . Then the treatment of osteochondrosis during pregnancy
should be carried out by non-drug methods. Often osteochondrosis is associated with loads on the spine , which is why they should be reduced
. A bandage belt will help with this. In addition to it, special corsets, orthopedic shoes and
physiotherapy exercises .
A well-known method of treating osteochondrosis is manual therapy . However, the opinions of physicians are divided on this issue. Some specialists
categorically exclude its use, since it can cause premature labor . Others argue that the lack of
methods of treatment will affect the health of the mother and the unborn baby even more detrimentally.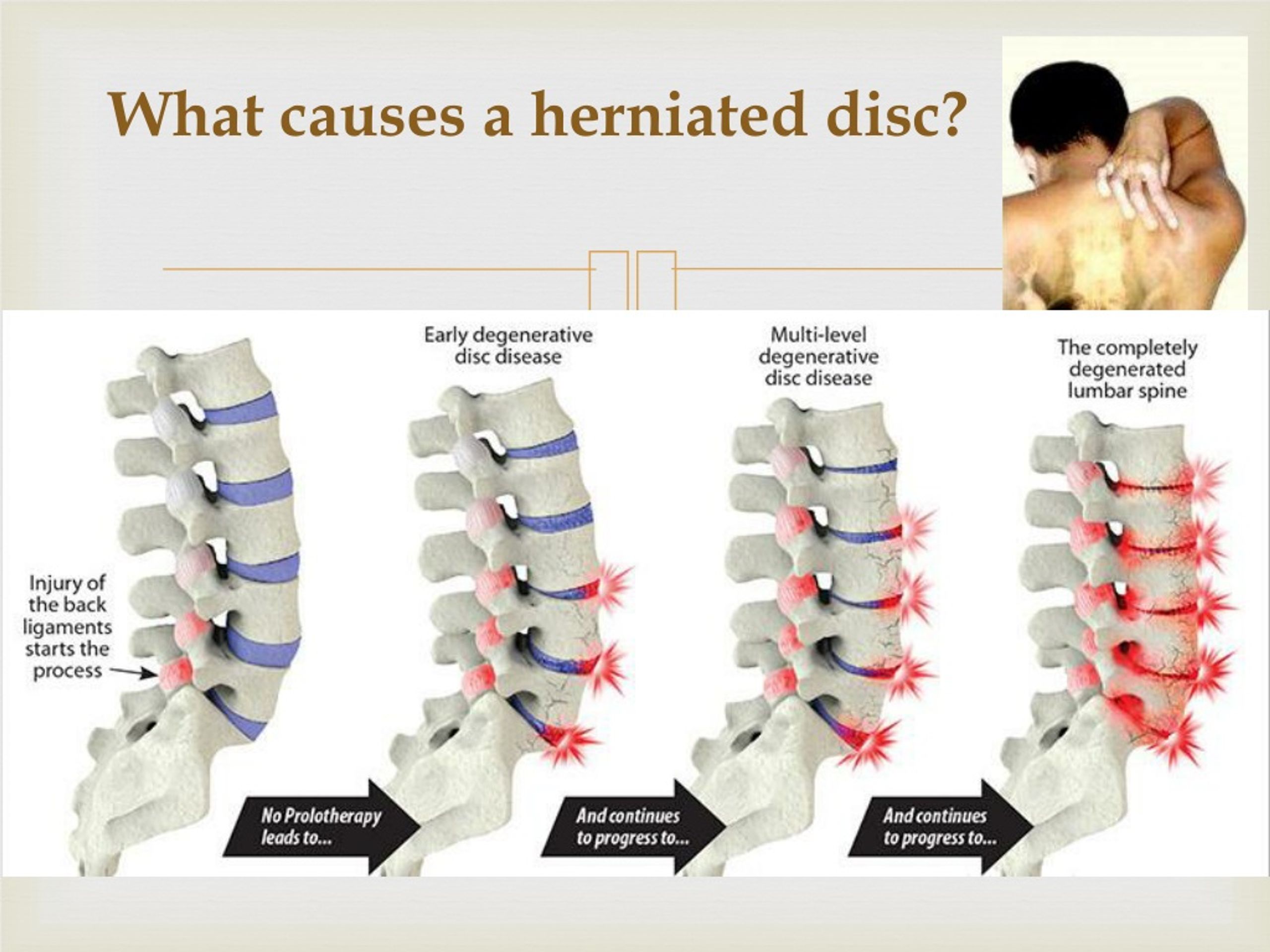 The point is that due to osteochondrosis muscles are in constant
The point is that due to osteochondrosis muscles are in constant
tone, the hormonal background is changing, in this regard, the work of the central nervous and endocrine systems is disturbed. All this affects the tone of the uterus , which
can lead to undesirable consequences. In any case, manual therapy is not safe during pregnancy , before using it
be sure to consult a doctor .
The best thing, of course, is to solve the problem osteochondrosis to pregnancy , since the methods of treatment of the disease during this period may affect the course of pregnancy and subsequent childbirth . In the presence of this disease in most cases doctors recommend caesarean section .
Recipes of traditional medicine
Warming compresses will help against cervical osteochondrosis . It is necessary to prepare a decoction of burdock, St. John's wort, dandelion root and parsley. Dipped in
It is necessary to prepare a decoction of burdock, St. John's wort, dandelion root and parsley. Dipped in
This decoction should be applied to the neck with cotton wool, wrapped with cellophane or a towel. Keep for about 15-20 minutes. In the first stages of the disease
it is allowed to use a bag of hot sand or pepper plaster.
Published in Pregnancy and pregnancy management Premium Clinic
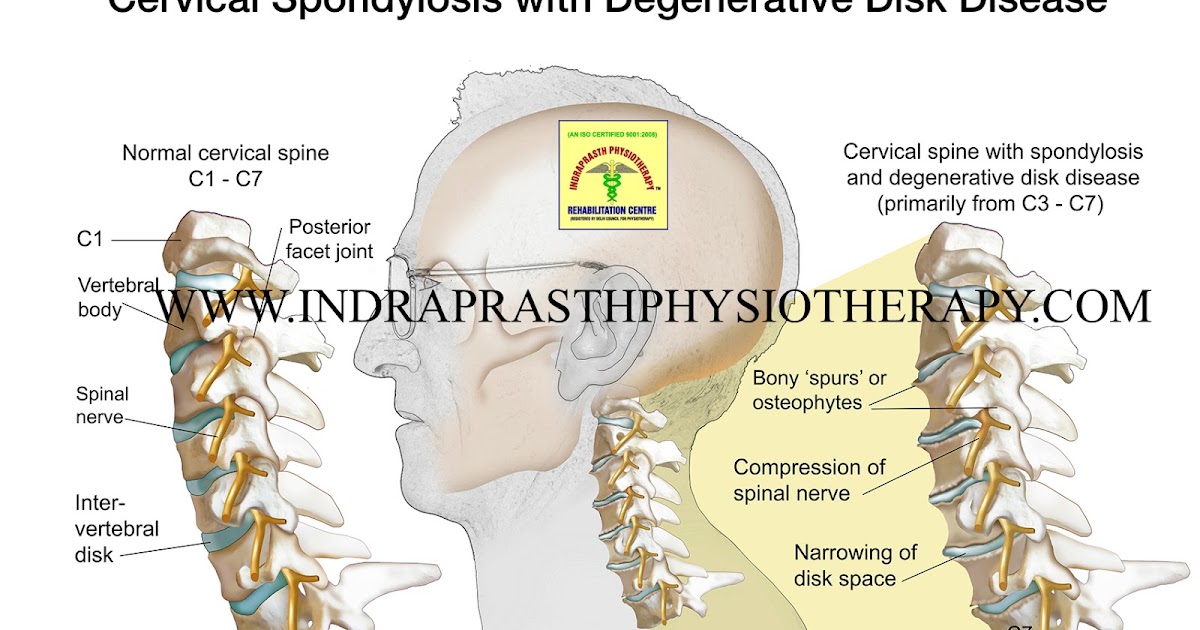
Cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy: symptoms, treatment and prevention
Pregnancy is a difficult period in a woman's life, as the body undergoes major changes. And against the background of ongoing changes, either new health problems appear, or old ones “wake up”. Very often during pregnancy, a large load falls on the spine, and one of the most common diseases is osteochondrosis. The pathology of the lumbar is mainly diagnosed, the second most common is cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy.
What you need to know about cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy
It is important that osteochondrosis brings serious and sometimes painful discomfort, and at the slightest manifestation and discomfort in the neck, you should consult a doctor. Cervical osteochondrosis occurs during the period of bearing a child, either as a result of changes that have occurred, that is, for the first time, or manifest itself after a long "sleep mode". More often at this time, the lumbosacral region suffers, because it has the main burden during pregnancy. The thoracic and cervical regions are affected less frequently and require less attention when choosing a course of treatment.
Cervical osteochondrosis occurs during the period of bearing a child, either as a result of changes that have occurred, that is, for the first time, or manifest itself after a long "sleep mode". More often at this time, the lumbosacral region suffers, because it has the main burden during pregnancy. The thoracic and cervical regions are affected less frequently and require less attention when choosing a course of treatment.
Causes of disease
What provoked the onset of the disease, only the doctor can say for sure after he conducts an examination and receives the results of the patient's diagnosis.
Flat feet
Flat feet is a pathology, the main symptom of which is the absence of a notch on the inner arch of the foot. At the same time, a person’s support goes to the entire foot, which is an unnatural position, and since our body is a single mechanism, the presence of such a pathology can lead to various kinds of ailments. In the presence of osteochondrosis, the main symptom is pain. If this pain was provoked by flat feet, then it will rise from the bottom up - from the knees to the pelvis, lower back and then along the entire spine.
If this pain was provoked by flat feet, then it will rise from the bottom up - from the knees to the pelvis, lower back and then along the entire spine.
Frequent wearing of heels
Despite all the beauty and love of women for high heels, it is not recommended to abuse them for several reasons. Wearing high heels leads to a shift in the center of gravity, an unusual and harmful load on the spine, and this can also lead to a bending of the uterus. For everyday or frequent wearing of such shoes, it is better to choose heels 5-6 cm high. And during pregnancy, it is better to give preference to those shoes that will soften the impact of increased weight on the spine.
Back injuries
Injury to the back, which leads to the appearance or exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy, occurs due to force majeure or due to the unpreparedness of the body, or rather the muscular corset, to increase weight and load on the spine.
Stress and chronic lack of sleep
External factors, internal worries about a change in status, physiological changes - all this can cause stress in pregnant women, and an uncomfortable bed and pain in the neck can cause constant lack of sleep.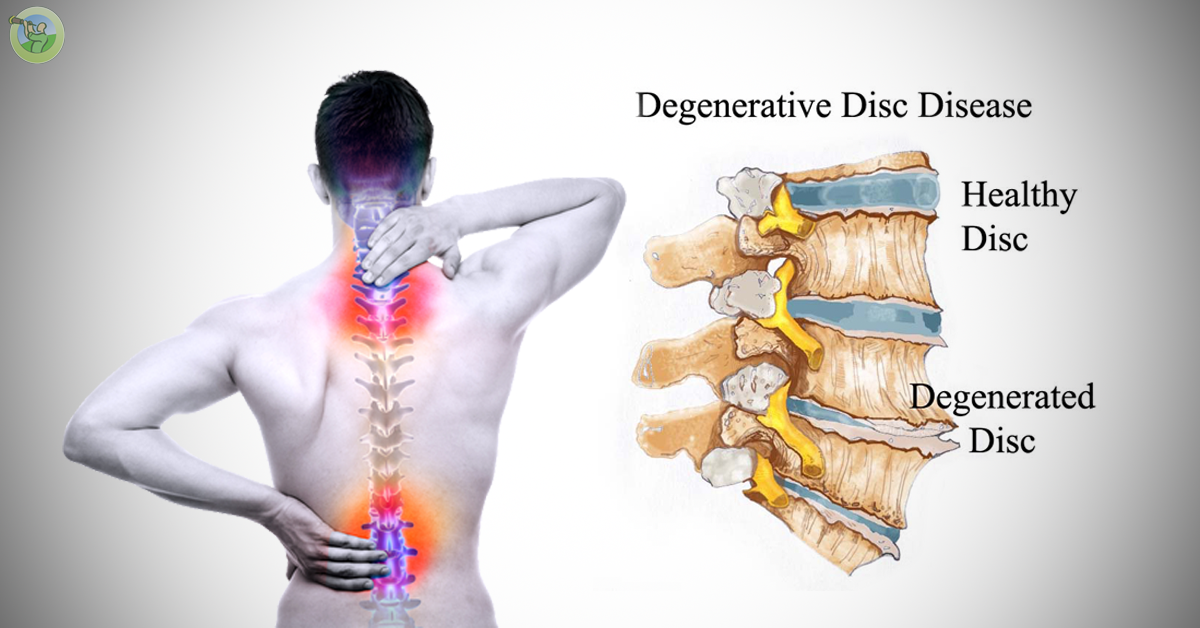 Excitement, stress, inability to sleep and constant fatigue greatly affect the state of the nervous system, which can lead to stiffness of the cervical muscles and a decrease in the mobility of the cervical vertebrae and provoke an attack of osteochondrosis. Also, a genetic predisposition, a sedentary lifestyle, especially in the last stages, changes in hormonal levels, displacement of organs, compression of nerve endings, etc., lead to cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy.
Excitement, stress, inability to sleep and constant fatigue greatly affect the state of the nervous system, which can lead to stiffness of the cervical muscles and a decrease in the mobility of the cervical vertebrae and provoke an attack of osteochondrosis. Also, a genetic predisposition, a sedentary lifestyle, especially in the last stages, changes in hormonal levels, displacement of organs, compression of nerve endings, etc., lead to cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy.
Symptoms
With the occurrence and development of cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy, the symptoms can be pronounced and cause severe discomfort. Women may often have a headache, dizziness, pain and pain in the neck. In especially difficult cases, cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, as well as pressure drops, pallor and numbness of the skin.
Pain in arms and shoulders
Pain in the arms and shoulders, which can sometimes be pulsating, is caused by compression or pinching of the nerve roots. In this case, numbness in the shoulder region and a decrease in the sensitivity of the skin may appear.
In this case, numbness in the shoulder region and a decrease in the sensitivity of the skin may appear.
Aches and numbness in the hands
Decreased sensitivity, numbness of the fingers, as well as a feeling of "goosebumps" in the hands appear due to violations in the structure of the vertebrae of the neck, and also if osteochondrosis has developed to the stage of the appearance of intervertebral hernias.
Difficulty in some movements
Depending on what caused the disease and how it developed, there may be difficulty turning the head (sometimes accompanied by a crunch), as well as swallowing and inhaling. Sometimes patients complain of a lump in the throat and the inability to take a full breath.
Headache
The occurrence of a headache in cervical osteochondrosis is associated with compression of the vertebral artery, which can also lead to constant dizziness and impaired hearing and vision.
How to treat the disease during pregnancy?
If cervical osteochondrosis was diagnosed during pregnancy, treatment should be started immediately, but very carefully.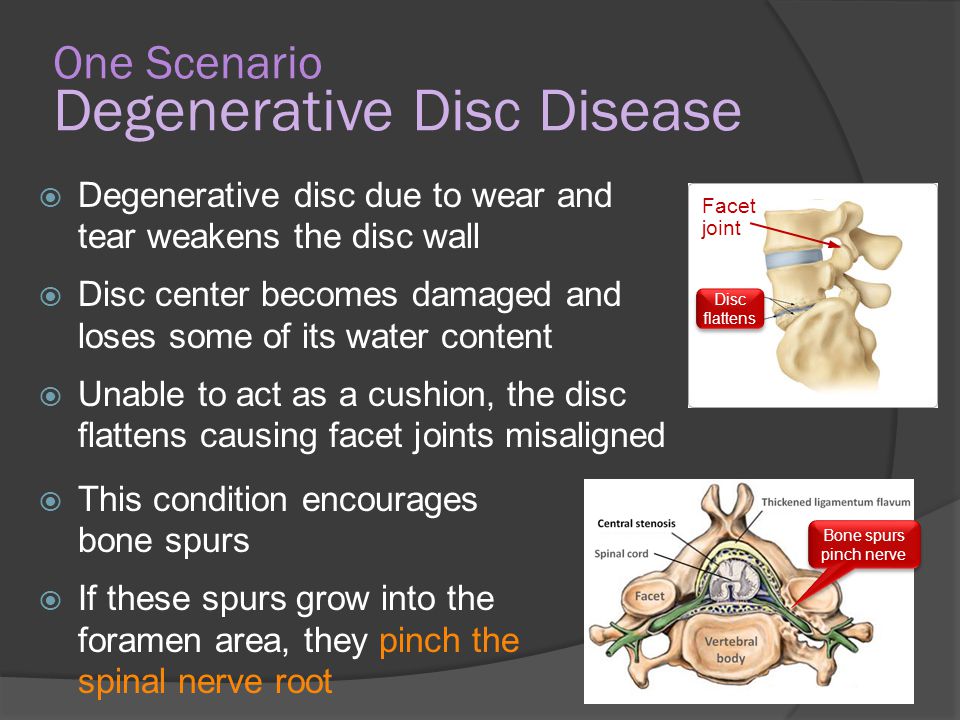 The complexity of treatment lies in the fact that it is impossible to choose medication as one of the methods. Also, many physiotherapy procedures are not recommended. To avoid such a situation as cervical osteochondrosis during childbearing, experts advise to undergo a full examination at the planning stage in order to exclude the disease or treat and take control of the situation. How and how to treat cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy, decides neurologist , based on the clinical picture. The main task of the course of treatment and the doctor is to alleviate the condition without harming the fetus and the health of the expectant mother.
The complexity of treatment lies in the fact that it is impossible to choose medication as one of the methods. Also, many physiotherapy procedures are not recommended. To avoid such a situation as cervical osteochondrosis during childbearing, experts advise to undergo a full examination at the planning stage in order to exclude the disease or treat and take control of the situation. How and how to treat cervical osteochondrosis during pregnancy, decides neurologist , based on the clinical picture. The main task of the course of treatment and the doctor is to alleviate the condition without harming the fetus and the health of the expectant mother.
Traditional medicine
As a method of traditional medicine, you can choose warming compresses with herbs and decoctions, the choice of which is carried out taking into account the absence of allergies to the components. In any case, before using any folk remedy, you should consult a doctor.
Massage
Any physiotherapeutic and manual procedures, including massage, can be prescribed to relieve pain and reduce the manifestation of symptoms, but selection and appointment are possible only if the doctor is completely sure that any procedures will not harm the fetus, the expectant mother and will not cause preterm labor.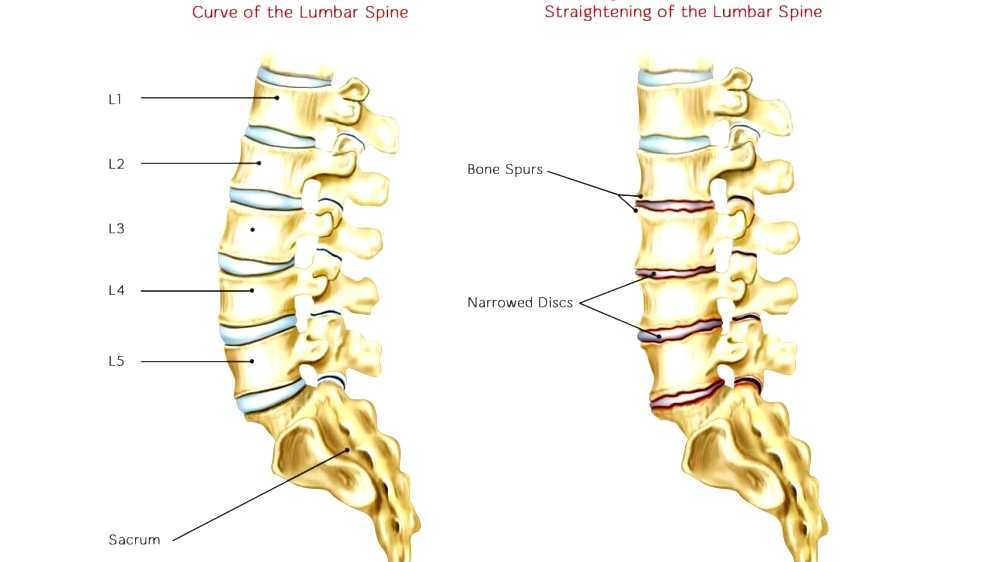 Let's allow light self-massage, but only after consultation with a specialist. Also, in order to alleviate the condition of the expectant mother and relieve tension and pain a little, a special orthopedic collar can be prescribed. They wear such a collar for a short time and infrequently, so as not to lead to a weakening of the muscular corset.
Let's allow light self-massage, but only after consultation with a specialist. Also, in order to alleviate the condition of the expectant mother and relieve tension and pain a little, a special orthopedic collar can be prescribed. They wear such a collar for a short time and infrequently, so as not to lead to a weakening of the muscular corset.
Neck warmer
Any methods of warming the neck (ointments, compresses, etc.) should also be agreed with the doctor. But this method, as a rule, is prescribed to patients with the only condition that only the cervical spine can be warmed up.
Medicines
Most drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle blockades, hormones, etc.) are unacceptable in the treatment of illness during pregnancy, as this can harm the fetus. Any drugs for the relief of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are taken only as directed and under the supervision of a doctor and in the first or second trimester. It is better to start treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical region not during pregnancy, but during its planning, but if the disease happened already in the process of bearing a child, then you should not delay contacting a doctor.