What does it mean when you bleed and your pregnant
Vaginal bleeding - NHS
Bleeding during pregnancy is relatively common and does not always mean there's a problem – but it can be a dangerous sign.
Urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP immediately if:
- you have any bleeding from your vagina
Coronavirus (COVID-19) update
If you're well, it's really important you go to all your appointments and scans for the health of you and your baby.
If you're pregnant, hospitals and clinics are making sure it's safe for you to go to appointments.
If you get symptoms of COVID-19, or you're unwell with something other than COVID-19, speak to your midwife or maternity team. They will advise you what to do.
Find out more about pregnancy and COVID-19
Causes of bleeding in early pregnancy
Implantation bleeding
In early pregnancy, you might get some harmless light bleeding, called "spotting". This is when the developing embryo plants itself in the wall of your womb. This type of bleeding often happens around the time your period would have been due.
Cervical changes
Pregnancy can cause changes to the cervix, and this may sometimes cause bleeding – after sex, for example.
Miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
During the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, vaginal bleeding can be a sign of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
However, if you bleed at this stage of pregnancy it's likely you will go on to have normal and successful pregnancies.
Miscarriage
If a pregnancy ends before the 24th week, it's called a miscarriage. Around 1 in 5 pregnancies ends this way.
Many early miscarriages (before 14 weeks) happen because there is something wrong with the baby. There can also be other causes of miscarriage, such as hormone or blood clotting problems.
There can also be other causes of miscarriage, such as hormone or blood clotting problems.
Most miscarriages occur during the first 12 weeks (3 months) of pregnancy and, sadly, most cannot be prevented. Other symptoms of miscarriage include:
- cramping and pain in your lower abdomen
- a discharge or fluid from your vagina
- a discharge of tissue from your vagina
- no longer experiencing the symptoms of pregnancy, such as feeling sick
If you have bleeding or any of the symptoms above, contact your midwife or GP straightaway.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants outside the womb – for example, in the fallopian tube.
It can cause bleeding and is dangerous because the fertilised egg cannot develop properly outside the womb. The egg has to be removed, which can be done through an operation or with medicines.
The egg has to be removed, which can be done through an operation or with medicines.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy tend to develop in the 6th week of pregnancy but can happen later.
Other signs of ectopic pregnancy can include:
- tummy pain low down which may be on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown, watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
Call 111 if you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
Causes of bleeding in later pregnancy
Cervical changes
These can lead to bleeding, particularly after sex.
Vaginal infections
Your midwife or doctor can discuss tests and treatment with you.
A 'show'
This is when the plug of mucus that has been in the cervix during pregnancy comes away, signalling that the cervix is getting ready for labour to start. It may happen a few days before contractions start or during labour itself.
Find out about the signs of labour and what happens in labour.
Placental abruption
This is a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the womb wall. Placental abruption usually causes stomach pain, and this may occur even if there is no bleeding.
Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)
This is when the placenta is attached in the lower part of the womb, near to or covering the cervix. Bleeding from a low-lying placenta can be very heavy, and put you and your baby at risk.
You may be advised to go into hospital for emergency treatment, and a caesarean section will usually be recommended. The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists has more information on placenta praevia.
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists has more information on placenta praevia.
Vasa praevia
This is a rare condition where the baby's blood vessels run through the membranes covering the cervix.
When your waters break, these vessels may be torn and cause vaginal bleeding. The baby can lose a life-threatening amount of blood.
Finding out the cause of bleeding in pregnancy
To work out what is causing the bleeding, you may need to have a vaginal or pelvic examination, an ultrasound scan or blood tests to check your hormone levels.
Your doctor will also ask you about other symptoms, such as cramp, pain and dizziness. Sometimes it might not be possible to find out what caused the bleeding.
If your symptoms are not severe and your baby is not due for a while, you'll be monitored and, in some cases, kept in hospital for observation.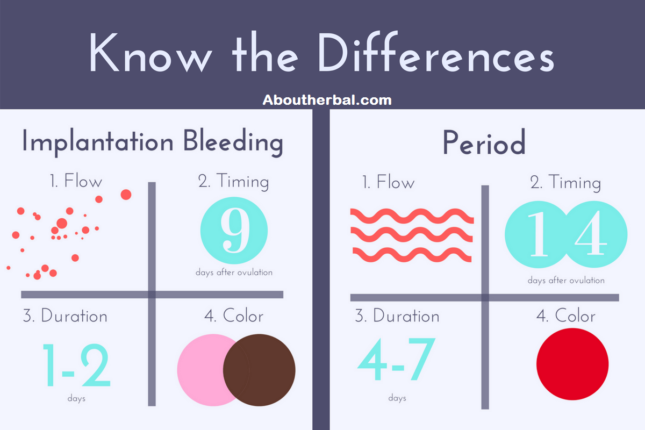
How long you need to stay in hospital depends on the cause of the bleeding and how many weeks pregnant you are.
Being in hospital allows staff to keep an eye on you and your baby, so they can act quickly if there are further problems.
Find the answers to common health problems in pregnancy
Video: What should I do if I start bleeding during early pregnancy?
In this video, a midwife tells you what to do if you start to bleed during early pregnancy.
Media last reviewed: 20 March 2020
Media review due: 20 March 2023
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy
Topics
In This Topic
KEY POINTS
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common
If you bleed or spot during pregnancy, it doesn’t always mean there’s a problem but in some cases they may be signs of a problem for you or your baby’s health
If you have heavy bleeding, call your health care provider right away
Tell your provider about any bleeding or spotting you have during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common. Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
Bleeding and spotting in pregnancy don’t always mean there’s a problem, but they can be a sign of miscarriage or other serious complications. Miscarriage is when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you have any bleeding or spotting, even if it stops. It may not be caused by anything serious, but your provider needs to find out what’s causing it.
What’s the difference between bleeding and spotting?
Bleeding or spotting can happen anytime, from the time you get pregnant to right before you give birth. Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldn’t cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
What should you do if you have bleeding or spotting during pregnancy?
Call your health care provider if you have any kind of bleeding during pregnancy and do these things:
- Keep track of how heavy your bleeding is, if it gets heavier or lighter, and how many pads you are using.
- Check the color of the blood. Your provider may want to know. It can be different colors, like brown, dark or bright red.
- Don’t use a tampon, douche or have sex when you’re bleeding.
Call your health care provider right away at any time during pregnancy or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?
It’s normal to have some spotting or bleeding early in pregnancy. Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester may not be a problem. It can be caused by:
- Having sex
- An infection
- Implantation. When a fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the lining of the uterus (womb) and begins to grow.
- Hormone changes. Hormones are chemicals made by the body.
- Changes in your cervix. The cervix is opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina.

- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These are tests that are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby. Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
- Problems related to smoking. If you smoke, it’s best to stop before pregnancy or as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Sometimes bleeding or spotting in the first trimester is a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry have bleeding or spotting before the miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus and begins to grow. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of a baby. It can cause serious, dangerous problems for the pregnant woman.
- Molar pregnancy. This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby.
 Molar pregnancy is rare.
Molar pregnancy is rare.
What causes bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy?
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be caused by:
- Labor
- Having sex
- An internal exam by your health care provider
- Problems with the cervix, like an infection, growths, inflammation or cervical insufficiency. This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta previa. This is when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
- Placenta accreta. This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply.
- Placental abruption. This is when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before birth.

- Uterine rupture. This is when the uterus tears during labor. This happens very rarely. It can happen if you have a scar in the uterus from a prior cesarean birth (also called c-section) or another kind of surgery on the uterus. A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
How are bleeding and spotting treated?
Your treatment depends on what caused your bleeding. You may need a medical exam and tests.
Most of the time, treatment for bleeding or spotting is rest. Your provider may also suggest treatments like:
- Take time off from work and stay off your feet for a little while
- You may need medicine to help protect your baby from Rh disease. Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby.
- Don’t have sex, douche or use tampons
- If you have heavy bleeding, you may need a hospital stay or surgery
Last reviewed: April 2020
') document.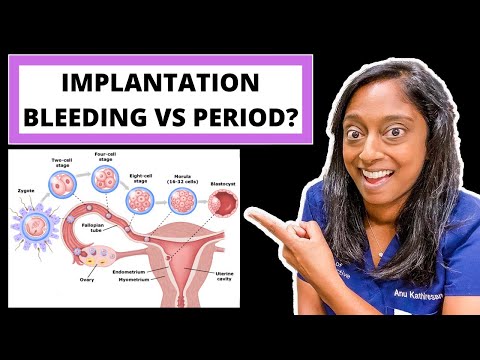 write('
write('
Preterm labor & premature birth
') document.write('') }
') document.write('') }
Bloody discharge during pregnancy ᐈ Blood during early pregnancy
Seeing bloody discharge, a pregnant woman is always frightened. They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
In early pregnancy, bloody discharge occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation. If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said Elena Petrovna Domnich, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS medical center.
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?
- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although bleeding may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?
- Bloody discharge is not common in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has atypical discharge, should she take a pregnancy test?
– Yes, but it is better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?
- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but a previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?
- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management. Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Bleeding may occur with:
- threatened miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- cysts;
- myomas;
- cervical erosion;
- placental abruption;
- threatened preterm birth.

You can watch the video version of Elena Petrovna Domnich's interview here. More helpful videos on our YouTube channel.
What is implantation bleeding? - IVF center Generation NEXT
How our body functions and what changes occur in it every month is always interesting. Especially during the period when we are pregnant or hope to become pregnant. Almost certainly never do we monitor our condition so carefully and closely as during the period when we hope to become pregnant. From feeling tired to feeling slightly nauseous, the smallest signs are examined and tested for their significance. In this article, we will look at some of the most common implant bleeding problems. This problem is frightening and confusing if the desired pregnancy has already occurred.
Thus, we will try to figure out what are the symptoms and signs of implantation bleeding, how to recognize the earliest signs of implantation and pregnancy? Such self-control in people undergoing assisted fertility treatment can be much stronger, which is understandable. In this context, we will consider whether any other symptoms of implantation should be expected during pregnancy, and if so, how.
In this context, we will consider whether any other symptoms of implantation should be expected during pregnancy, and if so, how.
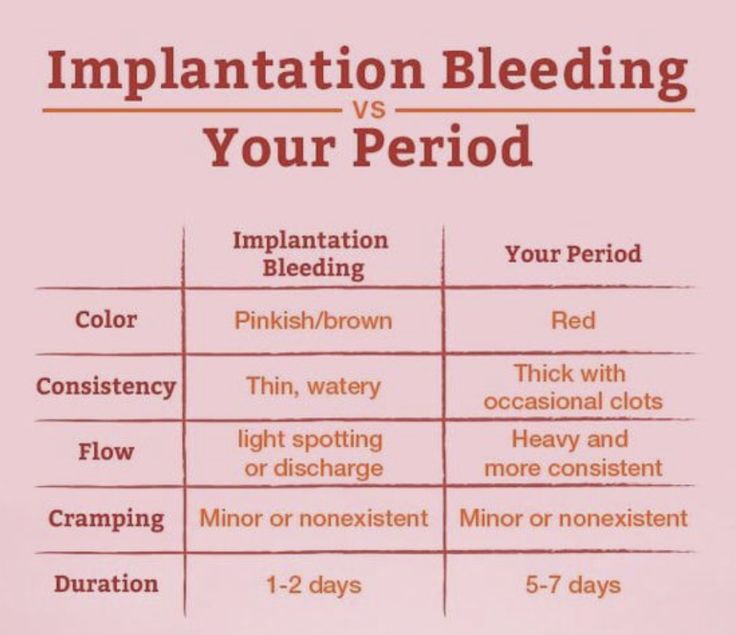
What is implantation bleeding?
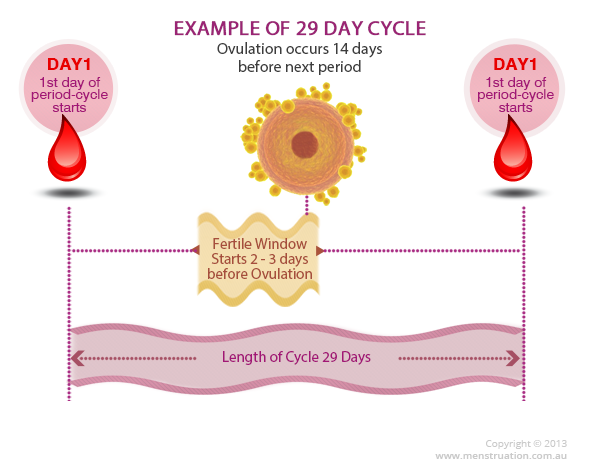
About 30-40% of women experience a slight loss of blood after the embryo is implanted in the uterus. This phenomenon is known as implantation bleeding. Since this happens at the beginning of the cycle, it may even be the first sign of realizing that you are pregnant. Bleeding usually occurs in the first weeks of pregnancy, as the uterus is an organ rich in blood vessels that can easily "damage". When the embryo sticks to the inner wall of the uterus, the small veins and arteries that normally connect to the endometrium rupture, and this can cause bleeding. If this occurs, usually 6-10 days after fertilization, then it usually coincides with the theoretical date of menstruation, and therefore can be confused with its onset. There is no set pattern, and implantation bleeding may occur in one or all of a particular individual's pregnancies.
How to recognize implantation bleeding?
The first question for many people is how to recognize that this is implantation bleeding and not just the start of a cycle, in other words, how do these types of bleeding differ? The most common reason for confusion here is that bleeding occurs 10-14 days after conception, around the time that menstruation would have occurred if conception had not occurred. However, vaginal bleeding can occur anytime during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. Blood loss may last 1-3 days, and the amount of discharge is usually less than during menstruation, although the color may be darker. It may look like a light spot or light continuous bleeding, and blood may or may not be mixed with mucus. The color may vary depending on how long it took to leave the body. Fresh bleeding looks red, it may look pink or orange if mixed with other vaginal discharge, and old blood may look brown due to oxidation.
How bad can implantation bleeding be? Can implantation bleeding have clots?
Usually, the bleeding that occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo in the uterus is manifested by a spot or light bleeding. Usually it is not strong and does not have clots, as in a normal cycle. If you suspect you may be pregnant and are bleeding heavily with clots, you should see your doctor as this could signal problems or even the onset of a premature miscarriage. On the other hand, if you have no other reason to suspect that you are pregnant, this type of bleeding is more likely to just be the start of your cycle.
Usually it is not strong and does not have clots, as in a normal cycle. If you suspect you may be pregnant and are bleeding heavily with clots, you should see your doctor as this could signal problems or even the onset of a premature miscarriage. On the other hand, if you have no other reason to suspect that you are pregnant, this type of bleeding is more likely to just be the start of your cycle.
What are other symptoms of implantation in early pregnancy?
Since implantation bleeding only occurs in about a third of pregnancies, you are likely to be among the majority who do not experience it. However, your vigilance for the signs and symptoms of successful implantation is probably still massively high! So what are other early signs that you might be pregnant? They may include:
Morning sickness
This can start as early as 4 weeks after conception (10-14 days after embryo transfer), although more often it happens after about 6 weeks. Luckily for those who go through this, morning sickness is usually temporary and usually improves by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy.
Luckily for those who go through this, morning sickness is usually temporary and usually improves by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy.
Sensitivity to smells and tastes
Sudden sensitivity to smell and taste can be a sign of early pregnancy and no doubt contributes to the long tales of pregnancy “cravings” for certain foods. Both heightened sensitivity and morning sickness are the result of hormonal changes taking place in your body.
Frequent urination
It seems strange when your baby is still very young, but the need to urinate more often in early pregnancy is one of the most common symptoms. It is also the result of hormonal changes that cause faster blood flow through the liver and kidneys to remove waste as efficiently as possible. In addition, the uterus rapidly increases in size even at this early stage of pregnancy and therefore puts more pressure on the bladder, especially at night.
Breast tenderness
The well-known symptom of breast tenderness is another sign of early pregnancy. This is the result of an increase in blood flow and fluid retention in the mammary glands against the background of a sharp increase in the level of female sex hormones in the blood serum.
This is the result of an increase in blood flow and fluid retention in the mammary glands against the background of a sharp increase in the level of female sex hormones in the blood serum.
Stomach cramps
Spasms may occur on their own or be accompanied by slight bleeding, which may be a signal of implantation. You might think that all these possible early signs and symptoms of pregnancy will help to be easily confident in its onset. But the fact is that some symptoms are also present in some people as a harbinger of their normal monthly cycle in premenstrual syndrome. Thus, despite all the possible clues, the only way to be sure of pregnancy is to take a pregnancy test, and with it, confirm the pregnancy with your doctor.
Is implantation bleeding the same when you are undergoing IVF treatment?
People undergoing IVF or any other assisted fertility treatment often wonder if pregnancy symptoms will be the same if embryo transfer and implantation is successful.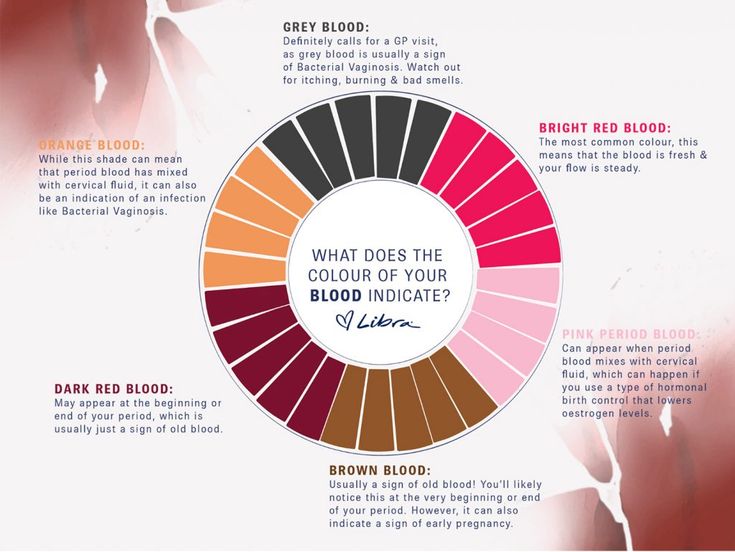 In a word, yes. While some stages of IVF are drug-driven, and even though the actual pairing of the egg and sperm takes place in the laboratory, the end result is identical.
In a word, yes. While some stages of IVF are drug-driven, and even though the actual pairing of the egg and sperm takes place in the laboratory, the end result is identical.
Let's look at a summary of the steps that led to the implantation of the embryos. The first step is ovarian stimulation, which causes the ovaries to produce a number of oocytes. Then, when the oocytes have reached a suitable stage of maturity, they are retrieved during ovarian puncture in order to be fertilized with prepared sperm in the embryology laboratory. This is the point at which fertilization occurs and embryos are formed. They are cultivated - "grow" in special incubators and pass the necessary tests (if a genetic study of the embryos is performed). The healthiest and most viable embryo is then transferred into the woman's uterus. This is, in a nutshell, the final stage of the process. The implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall after it has been transferred is not part of the assisted reproduction process; it is something that happens naturally in the same way as in normal conception.