Pregnancy and bulging disc
Does Pregnancy Cause Herniated Disc?
Pregnancy is both an exciting and challenging time for women. While it’s a blessing to be carrying another life, their bodies are also put under a great amount of stress due to the changes that occur throughout their childbearing journey. One of the bodily issues that they experience is lumbar pain which can sometimes happen due to spinal problems.
So how often does lumbar disc herniation occur during pregnancy? A herniated disc isn’t a risk during pregnancy. However, women who have a pre-existing lumbar spine disorder or disc condition before getting pregnant may experience significant pain, particularly in their second and third trimesters. Herniated discs shouldn’t pose a direct threat to your health and the baby’s safety, and there are treatments that can help provide pain relief.
How Common Is Lumbar Disc Herniation During Pregnancy?
From weight gain, morning sickness, and frequent headaches, women experience a lot of discomfort within the first few months of their pregnancy. Once the fifth to seventh month period of their pregnancy journey arrives, that’s when lower back pain symptoms become more constant and debilitating.
According to related studies, pregnancy-related low back pain can happen to up to 80% of women. However, a herniated disc is rarely an issue during gestation, and may only occur in less than 1% of pregnancies. In these cases, the majority of pregnant women diagnosed with herniated lumbar disc can recover without surgery and their symptoms can improve once they give birth.
There are some risk factors that may increase your chances of having lumbar disk herniation during pregnancy. Here are some of the possible causes of herniated discs during childbearing:
- Being of older age: The risk for lumbar disc herniation is higher in pregnant women who are older than 30 years old. Herniated discs are associated with age since they’re usually a result of disc degeneration and natural wear and tear of the spinal structures.

- Being overweight: Women who have a higher body mass index and have excess weight may be at a greater risk for a herniated disc during pregnancy.
- Having a spinal cord or disc injury: Pregnant women are always advised to take it easy to avoid any accident that may cause their spinal discs to bulge or rupture.
- Being diagnosed with an underlying medical condition: Women who have spinal stenosis and other low back problems may experience disc herniation during pregnancy.
Signs of Herniated Disc in a Pregnant Patient
Even though lumbar disc herniation is uncommon in pregnancies, it’s still important to be aware of its symptoms so you can get immediate proper treatment. To better understand what disc herniation is and what it feels like, let’s have a quick look at the anatomy of the spine:
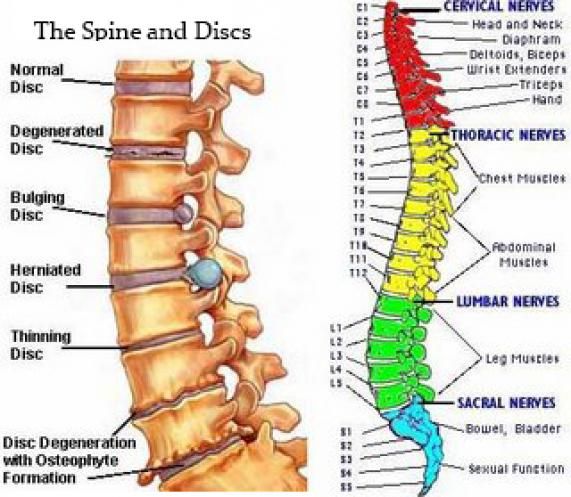
- The spine is divided into five sections: the cervical spine or neck, thoracic spine (middle back), lumbar spine (lower back), sacrum, and coccyx (tailbone).
- During pregnancy, the most affected segment is the lumbar spine since the additional weight and the growing uterus may cause pressure on the surrounding nerves.
- Located between the vertebrae, there are soft discs that cushion and protect the spinal nerve.
- Lumbar disc herniation can happen when an intervertebral disc gets damaged or torn, causing the inner nucleus to leak out and compress or irritate the nerves.
The signs of a ruptured disc can vary depending on which part of the spine is injured. Here are some of the usual symptoms of a pregnancy-related lumbar herniated disc:
- Persistent lower back pain that may get worse with certain movements
- Frequent muscle spasms
- Difficulty moving or reduced flexibility and range of motion
- Sleep disturbances because of severe pain
- Weakness or numbness in the lower extremities
How Exactly Does Pregnancy Affect Your Spine?
When you’re pregnant, your body undergoes a lot of changes to accommodate the developing uterus.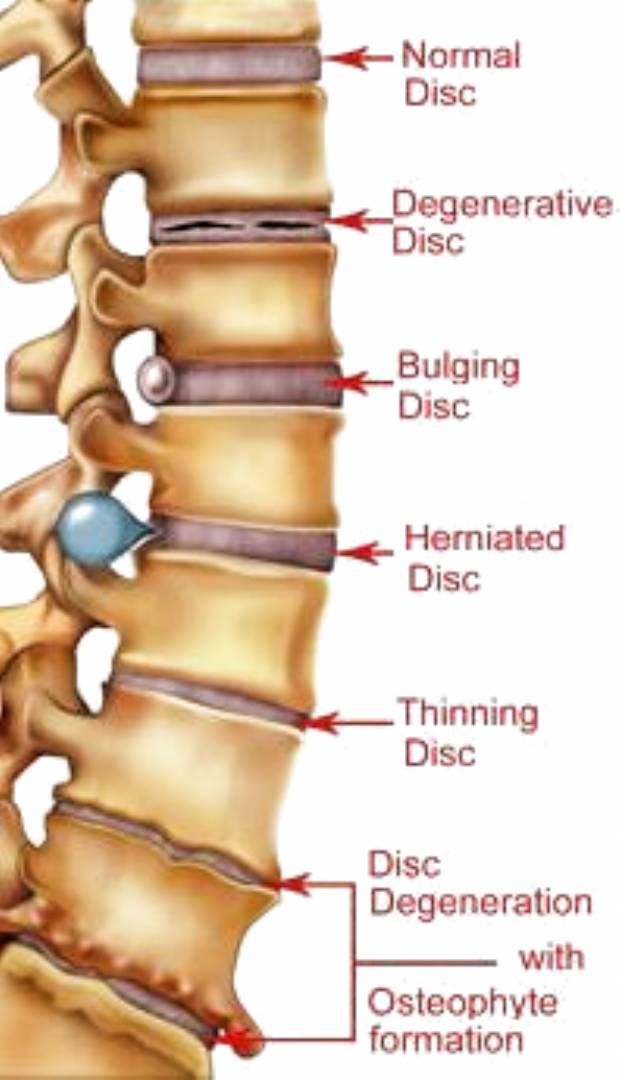 Aside from the hormonal shifts, there are other reasons why you notice chronic low back pain during pregnancy:
Aside from the hormonal shifts, there are other reasons why you notice chronic low back pain during pregnancy:
1) Excess pressure on the spinal discs
It’s normal to experience some weight gain as the uterus grows throughout childbearing. However, this means that your spine has to work twice as hard to support that added weight. As the spinal discs and nerves bear most of the increased pressure, you’ll notice more frequent discomfort and lower back pain.
2) Instability of the sacroiliac joints
The changes in hormones during pregnancy can also contribute to lower back pain. During your first trimester, the body produces relaxing hormones which are responsible for relaxing the sacroiliac joints and ligaments in the pelvic area to prepare your body for birth. This hormone can also affect the structures that support the spine, which can lead to joint instability and lumbar pain.
3) Changes in spinal posture
You’ll also notice that you have a more inward curve in your lower back which happens to help you maintain balance as you show more of the baby bump. But of course, note that this can also trigger low back pain and muscle tension since the lordotic curve restricts your spine’s movement. It also increases pressure on the vertebrae which may lead to a herniated or bulging disc.
But of course, note that this can also trigger low back pain and muscle tension since the lordotic curve restricts your spine’s movement. It also increases pressure on the vertebrae which may lead to a herniated or bulging disc.
4) Added stress on the pelvic joints
Your pelvic joints also experience alignment changes as you need more support for your upper body weight during pregnancy. It’s common to experience lumbar and pelvic pain because of the posture changes and additional pressure that’s put on the ligaments and joints of your lower body.
Possible Complications From Disc Herniation During Pregnancy
Most cases of lumbar disc herniation can heal on their own and get better without surgical intervention. However, if your symptoms worsen and you don’t get immediate medical attention, there’s a slight risk that it may lead to serious complications. Here are some possible conditions that may happen if you have untreated herniated disc:
1) Cauda Equina Syndrome
In rare cases, a severe bulging or slipped disc can affect the cauda equina nerves which are found at the end of the spinal cord.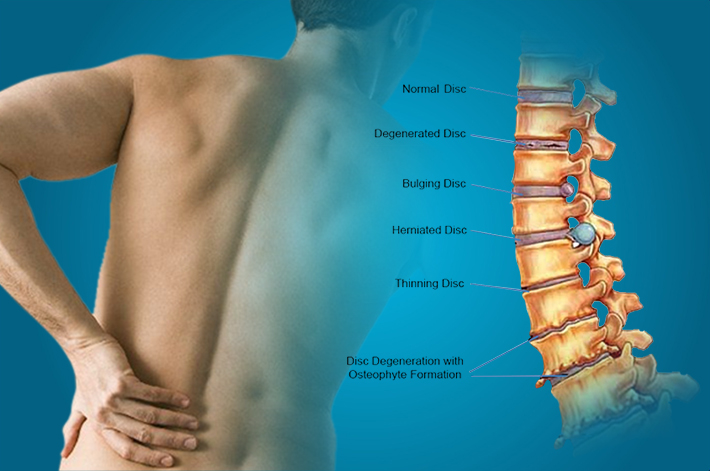 When this happens, it may cause debilitating symptoms such as bowel dysfunction or urinary incontinence. It may also affect the function of the nerves and lead to leg weakness or numbness of the lower extremities.
When this happens, it may cause debilitating symptoms such as bowel dysfunction or urinary incontinence. It may also affect the function of the nerves and lead to leg weakness or numbness of the lower extremities.
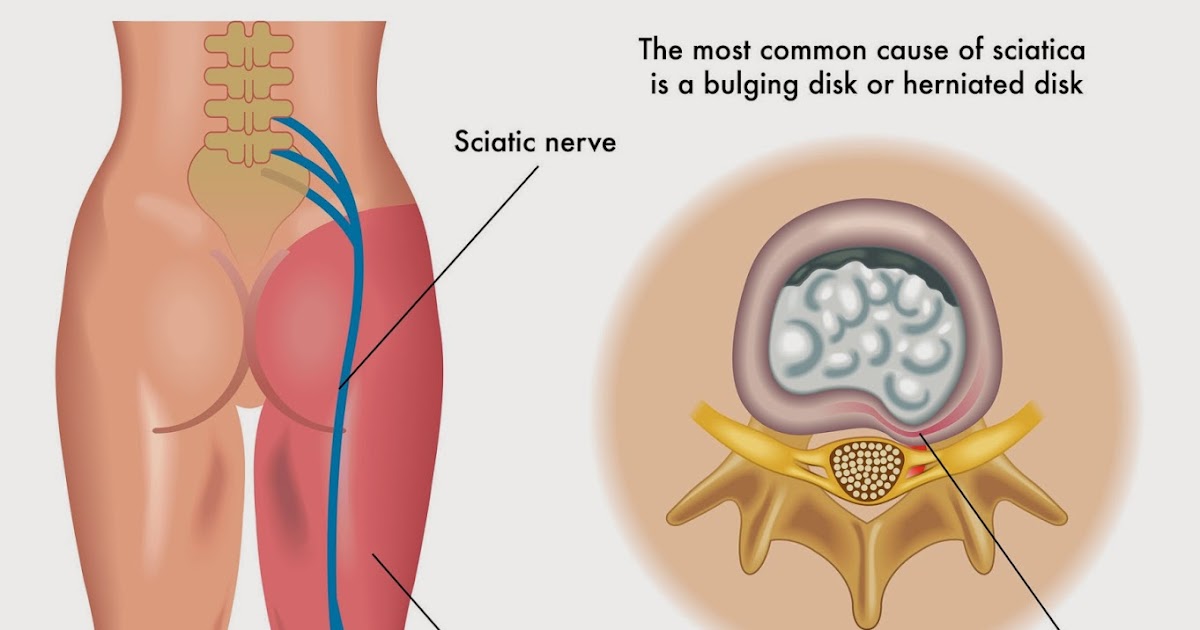
2) Sciatica
Also known as lumbar radiculopathy, this condition can occur when a herniated disc compresses the sciatic nerve root. This can cause symptoms of tingling or radiating leg pain that can also be felt on the buttocks and thighs. Typically, sciatica pain only affects one side of the body at a time.
Some patients may confuse the symptoms of sciatica with posterior pelvic pain or pelvic girdle pain. Similar to sciatic pain, it can cause a stabbing or dull ache but it’s commonly felt in the posterior pelvic region and can extend to the groin. It’s important to get an accurate diagnosis from your physician so you can receive the appropriate treatment.
3) Nerve Damage
One of the most serious but rare complications of lumbar disc herniation is permanent nerve damage.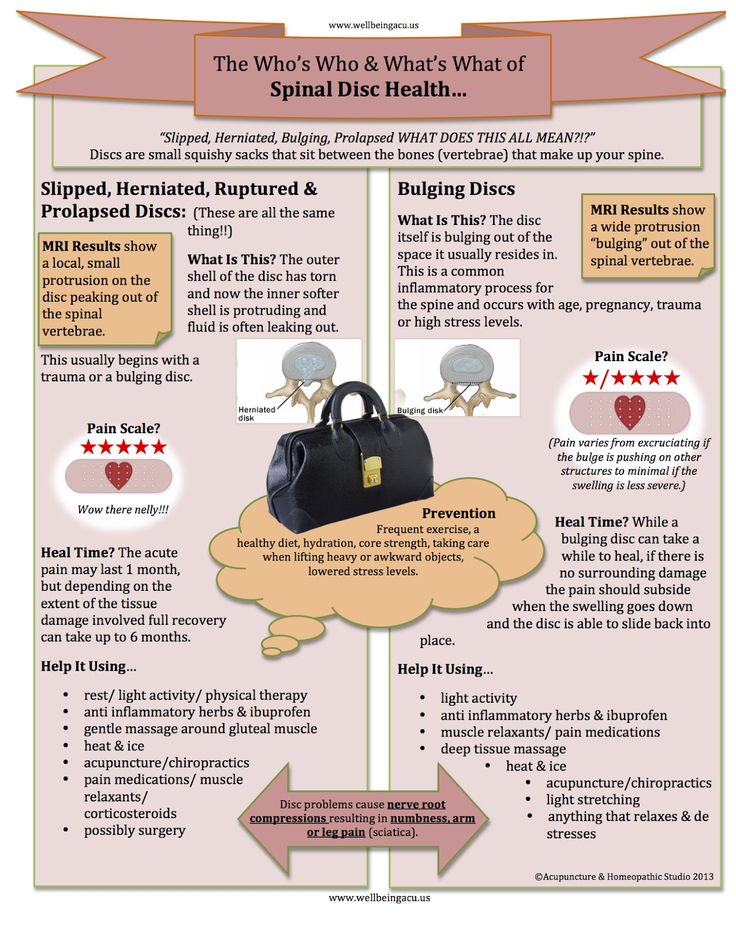 This happens when a large, untreated ruptured disc compresses and interrupts the nerve impulses which can lead to loss of sensation in the lower body and difficulty controlling bowel or bladder movements.
This happens when a large, untreated ruptured disc compresses and interrupts the nerve impulses which can lead to loss of sensation in the lower body and difficulty controlling bowel or bladder movements.
When Should You See A Doctor For Your Pregnancy Back Pain?
Although low back pain is a usual phenomenon during pregnancies, it doesn’t mean that you can just ignore its symptoms. It’s still necessary to receive a proper diagnosis to see if your pain is related to a spinal disc injury or damage. Here are some signs that you should consult your doctor for your pregnancy discomfort:
- You experience recurrent lower back pain that lasts for several weeks during pregnancy
- You experience vaginal bleeding or severe pain in the abdominal muscles
- You have a fever accompanied by a dull ache in your lower back
How to Treat a Herniated Disc While Pregnant
Most pregnant women find relief in knowing that their lower back pain and disc herniation usually gets better once they give birth. However, it’s still necessary to receive specialized care to ensure your comfort and the baby’s safety. Here are some treatment options for lumbar pain and herniated discs during pregnancy:
However, it’s still necessary to receive specialized care to ensure your comfort and the baby’s safety. Here are some treatment options for lumbar pain and herniated discs during pregnancy:
1) Physical therapy
You can consult with a physical therapist for exercises that can help strengthen your muscles, stretch your lumbar spine, and maintain optimal mobility during pregnancy. A specialist may recommend specialized low-impact activities such as pelvic tilts, leg raises, and Kegel exercises.
2) Prenatal massage therapy
Gentle massage treatments can also reduce your low back pain and promote relaxation during pregnancy. A trained massage therapist can help alleviate pressure from the nerves and relieve muscle tightness to minimize the severity and prevent the recurrence of sciatica and herniated disc pain.
3) Acupuncture
Pregnant women can also find low back and herniated disc pain relief with acupuncture treatments. As long as it’s performed by a trained specialist, acupuncture should be a safe alternative therapy that can help manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.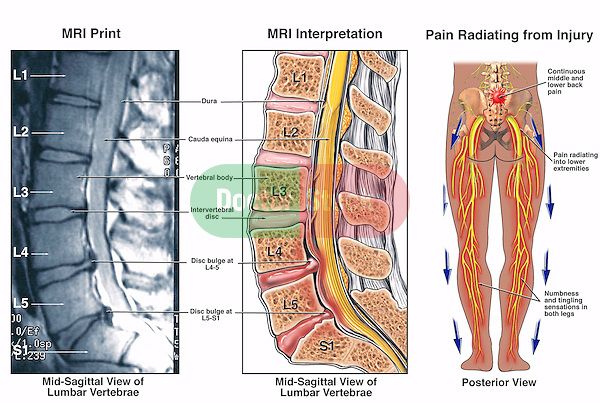
4) Medication
Doctors may also recommend certain pregnancy-safe painkillers which can help relieve herniated disc pain. Over-the-counter medications like paracetamol, are typically safe for expecting mothers and they can also help improve other pregnancy-related symptoms like headaches and muscle aches.
5) Spinal surgery
Your doctor may only recommend lumbar spine surgery or discectomy as the last option when the other pain management methods and conservative treatments are ineffective. A study suggests that the best time to perform the surgical treatment is during the second trimester when there’s a low risk of early labor.
Take Care of Your Body During Pregnancy With New York Pain Care
Your comfort should always come first during pregnancy. If you feel any unusual signs of discomfort aside from low back pain, you should immediately visit your doctor to get the right treatment. Find a trusted provider of safe and effective non-invasive treatments that provide lasting pain relief like New York Pain Care.
We have a team of specialists that are trained in the best techniques that can help alleviate your symptoms so you can have peace of mind throughout your pregnancy journey. Request a consultation today to discuss your pregnancy-related concerns and receive a personalized treatment plan.
Call to book 212.389.9918
Page Updated on Mar 6, 2023 by Dr. Hosny (Interventional Spine Specialist) of New York Pain CarePregnancy With A Herniated Disc - DiscSeel
About half of pregnant women experience low back pain. True disc herniation can be rare and most patients recover without the need for surgery. Herniated discs can be very painful. Pregnancy can make herniated discs even more painful. This condition is quite common in pregnant women, due to increased pressure on the spine and weight gain. Sometimes, a herniated disc will not cause symptoms in women. A herniated disc can cause severe pain during pregnancy, which may get worse as the baby grows.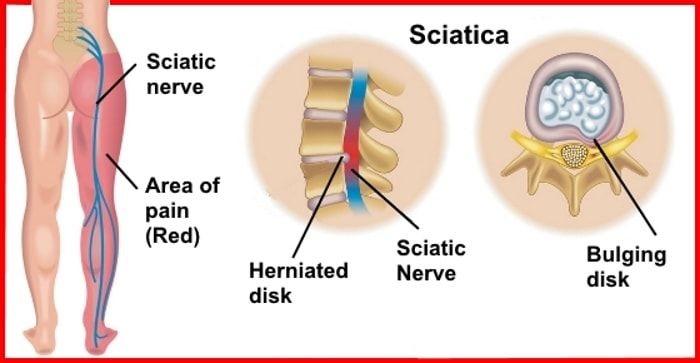
Introduction
LBP is very common in pregnancy, with approximately half the women suffering from it. According to some authors, the hormonal changes that affect the pelvic joints may also cause changes in the intervertebral discs and posterior longitudinal ligament. This could lead to lumbar disc protrusion which can result in LBP. True disc herniation in pregnant women is only 1 in 10,000 cases of LBP. According to available data, only 15% of lumbar disc hernias cause severe neurologic deficits. This is the reason why patients need emergency surgery. Radiculopathy due to lumbar disc herniation is a condition that most patients are able to heal without the need for surgery. The health of a pregnant woman must be considered when treating her. Multidisciplinary teams are required for patient patients. They must include specialists in obstetrics and maternal-foetal medicine as well as neurosurgery, anesthesiology, and anesthesiology.
Conservative management has been shown to be very effective and remains the first choice for patients with herniated discs.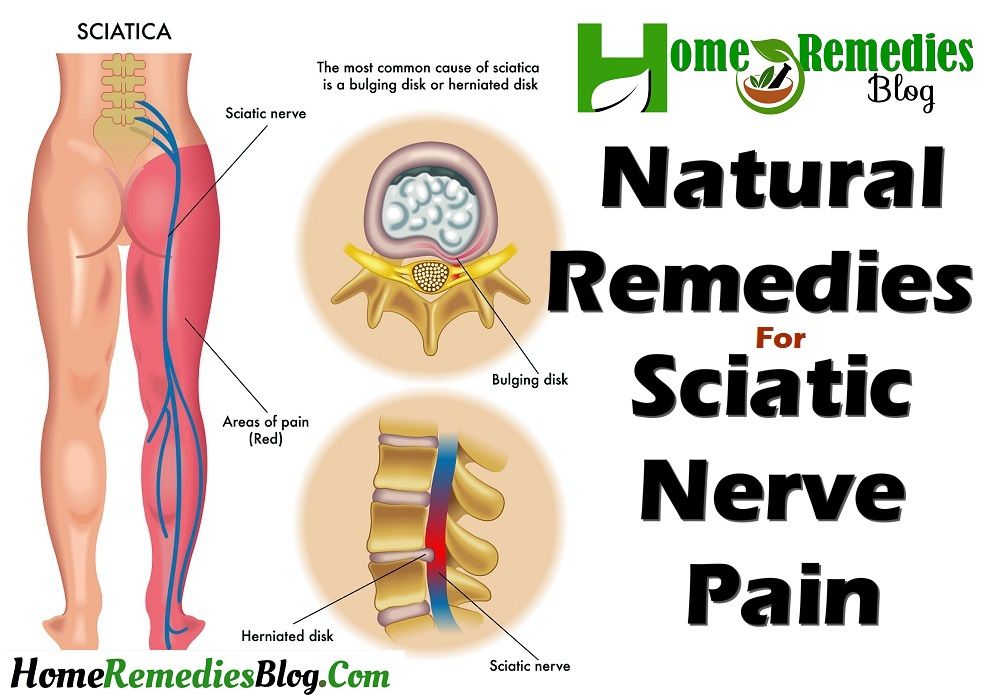 If the patient does not have any neurologic deficits, there is very little need for neurosurgical intervention. These patients are likely to have a normal pregnancy that leads to childbirth.
If the patient does not have any neurologic deficits, there is very little need for neurosurgical intervention. These patients are likely to have a normal pregnancy that leads to childbirth.
It is not clear which method of delivery is best for women with lumbar disc herniation. This paper will provide further insight by examining the literature and performing a narrative review.
A herniated disc is usually not caused by pregnancy. It is unlikely that a herniated disc developed during pregnancy unless the patient has osteoporosis and/or suffered a traumatic injury to their lower back. A herniated disc can also be caused by an underlying condition, injury, or injury. However, women are more likely to feel general back pains and aches that result from changes in the body and around their spine.
For perspective, herniated discs are most common in men between the ages 30 and 50. This doesn’t necessarily mean that women are immune to this condition. Herniated discs can also be developed by women, and can occur at any age.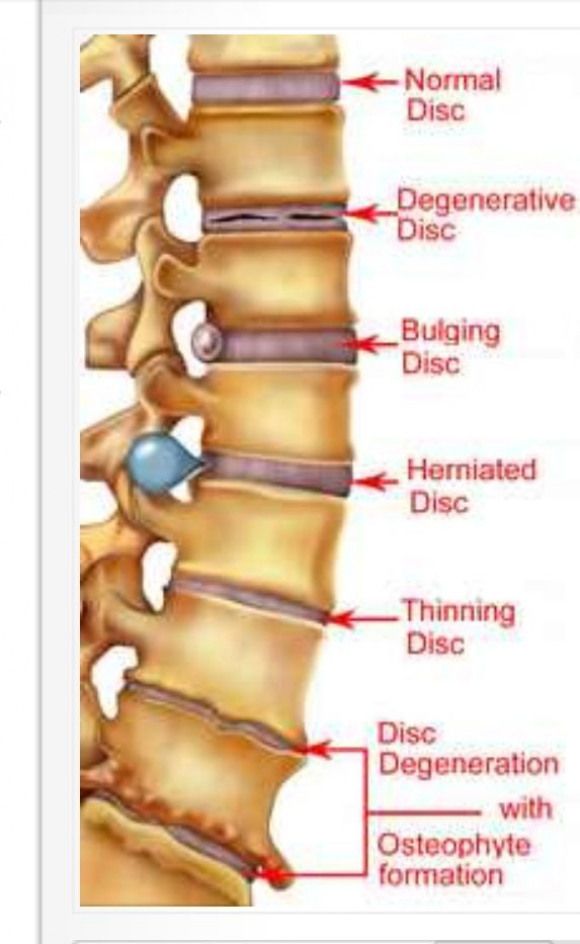 The majority of herniated discs in people between 25 and 55 years old develop in the lower lumbar region. People over 55 years old are more likely to have herniated discs above the L4/5 or L5/S1 levels.
The majority of herniated discs in people between 25 and 55 years old develop in the lower lumbar region. People over 55 years old are more likely to have herniated discs above the L4/5 or L5/S1 levels.
Simple exercises and support can usually fix a back injury that occurs during pregnancy. A herniated disc, which is a severe injury that can occur in pregnant women, is possible in very rare instances. If this happens, you may need surgery. However, back surgery is generally safe for both you and your baby during pregnancy.
Pre-existing back conditions can be a problem for many women before they get pregnant. Sometimes back problems improve during pregnancy. Other times they can get worse. It is important that you mention any back problems to your medical team.
If you feel the need to take medication to manage your pain, talk to your doctor. Paracetamol is one the most effective painkillers for pregnant women. While you’re pregnant, do not take aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like Nurofen.
A back injury should not interfere with labor or pain relief during labor. If you have a back injury, an epidural is usually possible. You can tell the hospital about your situation so they can help you with back pain.
How to protect your backPreventing or changing certain actions can help protect your back in pregnancy. This is more important as you get further along in your pregnancy.
- Do not lift heavy objects. Do not lift anything heavy. Instead, bend your knees and straighten your back. Keep the object you are lifting close to your body. Let toddlers climb on your lap, into the car or bathtub, and then squat next to them instead of picking them up.
- Good posture is essential. Keep your pelvis aligned. Your weight should be evenly distributed on both your legs. Keep your back straight, your pelvis down and your spine straight. Do not stand for too long. If necessary, sit straight up with your back against the chair.

- Avoid activities that could cause injury to your back. Avoid bending, twisting, climbing ladders or walking up steep hills.
- Be cautious when you’re in bed. With a pillow between you knees, sleep on your back. Roll onto your back, bringing your knees together. Next, support your arms with your arms as you lift your legs off the ground.
- Shoes with low heels are best (not flats). These shoes provide good arch support. Avoid wearing high heels.
- You might consider a maternity support band.
Being active during pregnancy is good for your back and health. You can walk or do water exercises if your doctor allows it. For specific exercises that will strengthen your back, talk to a physiotherapist.
Your lower back can be stretched by kneeling on your stomach with your head aligned with your back. Bring your stomach in and wrap your back.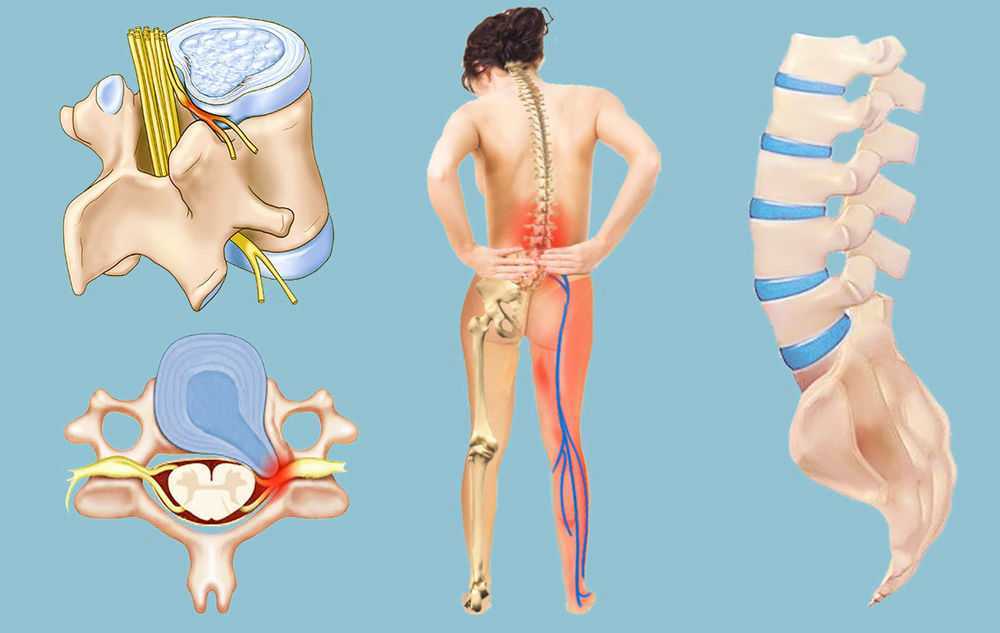 For a few seconds, hold the position and then release. Repeat the process 10 times. With pelvic tilt exercises, you can strengthen your stomach muscles. Place your hands on the ground and lie on your back. Your pelvis and hips should be tilted backwards to ensure your back is flat on the ground. For 3 to 5 seconds, hold the position. This exercise can be done standing up, or on a stationary bike.
For a few seconds, hold the position and then release. Repeat the process 10 times. With pelvic tilt exercises, you can strengthen your stomach muscles. Place your hands on the ground and lie on your back. Your pelvis and hips should be tilted backwards to ensure your back is flat on the ground. For 3 to 5 seconds, hold the position. This exercise can be done standing up, or on a stationary bike.
You can strengthen your pelvic floor and tummy muscles by gently drawing your lower tummy (below your belly button) towards the spine. Continue to breathe. Gradually increase the length of your posture. These muscles should be braced whenever you lift, push, or pull something heavy. Some women may find that complementary therapies like yoga or pilates are helpful, but it is important to talk with your doctor first.
What can you do to treat a herniated disc during pregnancy?Women who experience severe to moderate herniated disc pain in pregnancy should remain positive and see a spine specialist.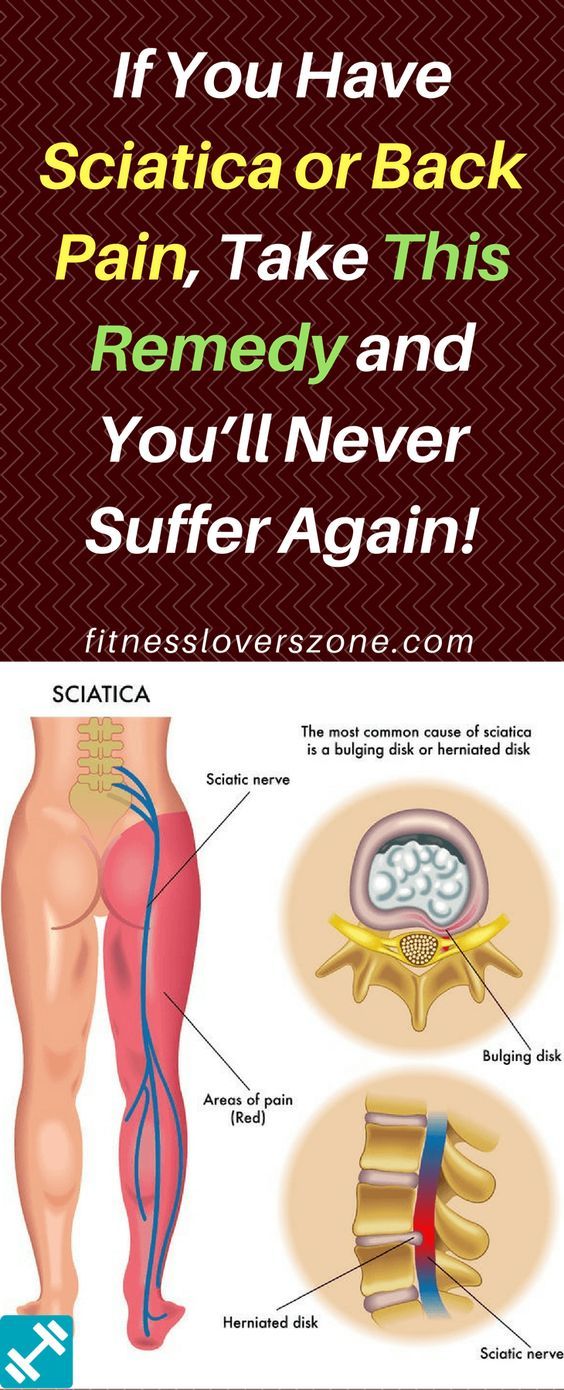 Herniated discs that are mild to moderately severe do not pose a danger to the baby’s health or safety. However, severe cases may need to be treated or rehabilitated.
Herniated discs that are mild to moderately severe do not pose a danger to the baby’s health or safety. However, severe cases may need to be treated or rehabilitated.
Lower back pain and pelvic discomfort are common in pregnancy, particularly during the third trimester. To have a smooth and trouble-free pregnancy, it is important to keep a positive outlook and educate yourself about herniated discs. Talk to your OB/GYN if you are experiencing pain. NSAIDs, bed rest, safe exercises, etc.) To prevent injury or pain from occurring again.
The doctor may suggest that you coordinate care with a spine surgeon in order to discuss minimally invasive treatments or spine surgery after giving birth. These conservative and interventional options may be able to relieve your herniated disc pain temporarily. Please consult your doctor before you try any of these options.
- Stretches and exercises that are safe for pregnant women can be used in physical therapy
- Acupuncture
- Ice and heat therapy
- Prenatal massage
- TENS units
To prevent any further complications, your OBGYN might recommend bed rest for the time that the baby is born. To ensure your child’s safety and health, it is important that you follow the instructions of your OBGYN.
To ensure your child’s safety and health, it is important that you follow the instructions of your OBGYN.
When should you see a doctor?
If the pain persists or is severe, consult your doctor. Sometimes, back pain may be an indication of premature labor or a urinary tract infection. If you have bleeding from the vagina, pain in your urination, or other signs of premature labor, see your doctor immediately.
Discussion
While symptomatic lumbar disc herniation is the most common spinal condition during pregnancy, it is much less common than pregnancy-related LBP. It is estimated that 1 in 10,000 pregnant women will experience this condition. A rise in the incidence of lumbar disc hernia among pregnant women can be expected due to the recent increase in the average age at which women become pregnant.
According to reports, the percentage of children born to women over 35 years old increased from 4% in 1990 to 21% in 2015. Nineteen of the 10 cases were older than 30, and four were over 35.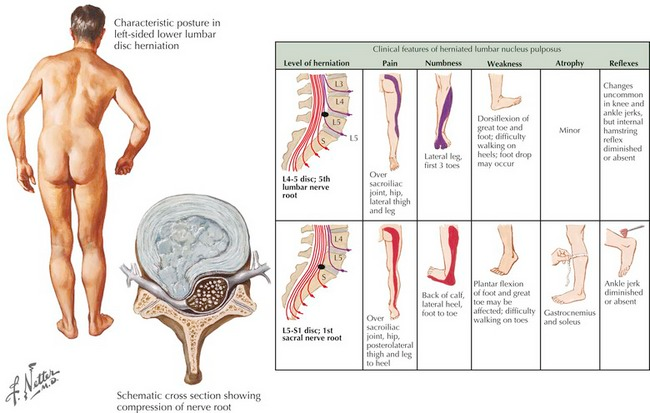 LBP may be caused by hormonal changes, particularly a rise in serum relaxation.
LBP may be caused by hormonal changes, particularly a rise in serum relaxation.
Radicular pain is the most common symptom associated with lumbar disc herniation. Two of the 10 cases in this article presented with LBP. The other eight presented with either urinary problems, radicular discomfort, decreased sensation in one spinal nerve’s sensory distribution, or weakness in the muscles that are innervated through the motor root of a spinal nerve. Cauda Equina Syndrome, which is a criteria for emergency neurosurgical treatment, refers to radiating pain, numbness, and bilateral muscle weakness that affects both the lower extremities, bladder, and bowel dysfunction.
According to literature, only 15% of patients with lumbar disc hernias experience severe neurologic deficits. We reviewed a case with CES. The patient had laminectomy right after the caesarean section (CS). There were no neurological sequelae. Although MRI in pregnancy is now more accepted, the exact risk to the foetus remains unknown.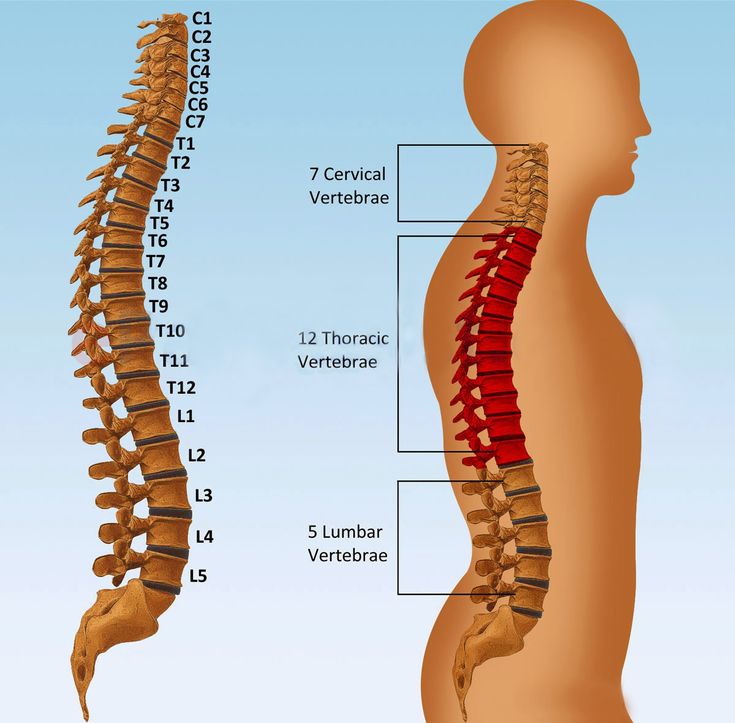 Research needs to continue in this area. The MRI scans revealed lumbar disc hernia at the L5/S1 or L4/L5 levels in all cases. The majority of patients with lumbar disc hernia are able to heal themselves without the need for surgery, according to therapeutic management. Six of the 10 patients received conservative treatment. They had no neurological deficits or residual pain after delivery.
Research needs to continue in this area. The MRI scans revealed lumbar disc hernia at the L5/S1 or L4/L5 levels in all cases. The majority of patients with lumbar disc hernia are able to heal themselves without the need for surgery, according to therapeutic management. Six of the 10 patients received conservative treatment. They had no neurological deficits or residual pain after delivery.
One patient presented with radicular pain at 33 weeks and then developed motor weakness the week after. The patient was delivered via cesarean section and underwent discectomy within minutes. She was discharged with no neurological deficit. Another patient had an epidural steroid injection. Her symptoms improved and she was discharged without any neurological sequelae.
The delivery method is still controversial. There is no published data on lumbar disc hernias in pregnancy. Based on MRI data, the decision to treat conservatively (“wait-and-see”) or surgically appears to be influenced largely by the cooperation between the obstetrician (or neurosurgeon).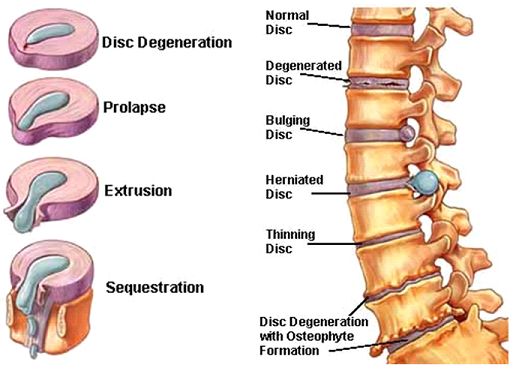
Postpartum evolution was unpredictable. Cesarean section was offered to pregnant women suffering from lumbar disc hernia. This was followed by remission and no neurological deficit. Antepartum epidural steroid injection, vaginal birth and no neurological deficit during the postpartum period. Cesarean section for failed labor inducement at term. CES followed by immediate microdiscectomy. CES followed by operative vaginal extraction. CES followed by spontaneous vaginal deliveries.
These cases suggest that labor could increase the risk of neurological symptoms worsening in the postpartum period or CES development. CS may be a safer option for pregnant women suffering from symptomatic lumbar disc hernia.
Conclusion
It is unclear which method of delivery is best for women who have lumbar disc hernia. This is due to a lack of experience and a small number of cases. Collaboration between obstetricians, neurosurgeons, and MRI data seems to lead to the best decisions and results.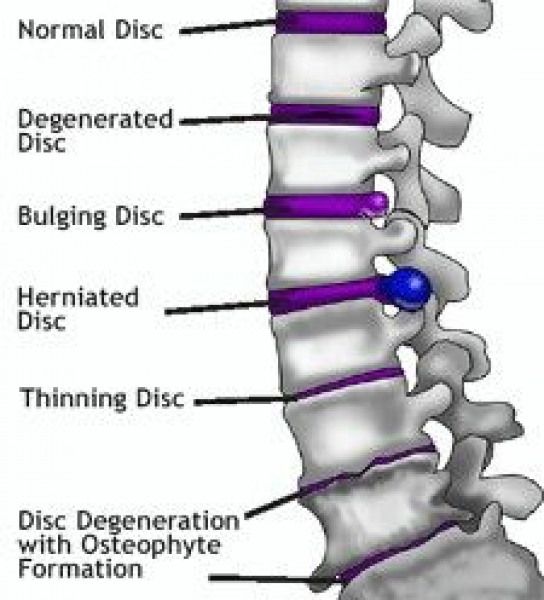 Although limited data suggests that CS is preferred to vaginal delivery for avoiding symptom progression and avoiding symptom worsening, further research is needed.
Although limited data suggests that CS is preferred to vaginal delivery for avoiding symptom progression and avoiding symptom worsening, further research is needed.
Pain in the lower back and abdomen during pregnancy, causes, types, treatment in Moscow
13 July 2020
85886
3.9 of 5
Table of contents
- 1 Physiological causes of back pain during pregnancy
- 2 Diseases that can cause back pain during pregnancy
- 2.1 Osteochondrosis
- 2.2 Protrusions and intervertebral hernia 9012
0012 - 2.4 Kidney disease
- 5.1 Conservative treatment
- 12
Pregnancy is a happy and at the same time rather difficult period in the life of most women.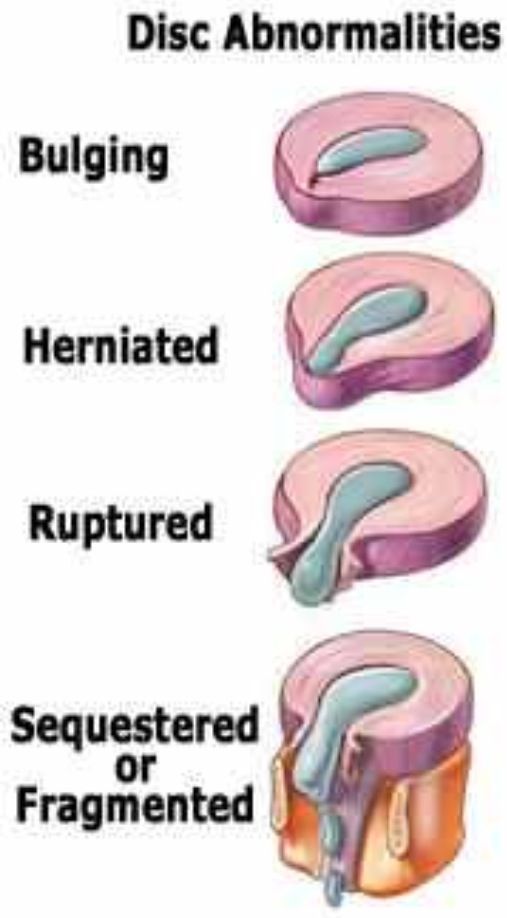 In 40 weeks, both the psyche and the body of a woman undergoes many changes. And if the awakening of the maternal instinct and trying on a new role as a mother is exclusively positive, then physical changes are not always desirable and equally positive.
In 40 weeks, both the psyche and the body of a woman undergoes many changes. And if the awakening of the maternal instinct and trying on a new role as a mother is exclusively positive, then physical changes are not always desirable and equally positive.
One of the most common problems for expectant mothers is back pain, especially in the lower back. In some cases, it is physiological in nature, that is, it is regarded as the norm, but in other situations it is a sign of pathological changes and requires medical attention. It is because of the changes taking place in the body during pregnancy that chronic diseases become aggravated and sluggish ones appear. The difficulty lies in recognizing harmless lower back pain during pregnancy from a symptom of the disease, because many medical procedures are contraindicated for expectant mothers. Therefore, if discomfort appears in the back, it is imperative to talk about it to the doctor and, if necessary, contact narrow specialists, for example, a neurologist or vertebrologist.
Physiological causes of back pain during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a lot of new processes and transformations take place in a woman's body. In the earliest stages, hormonal changes come to the fore. The body prepares for the bearing of the fetus and future childbirth, the hormones produced affect the ligaments and joints. They gradually stretch, which can lead to pulling pains in the lower back. Their presence up to 10 weeks is a variant of the norm, but only if there is no bloody, brownish discharge from the vagina, since this combination of symptoms indicates the possibility of spontaneous miscarriage.
In addition to the fact that the hormonal background is changing, the uterus is gradually increasing and the center of gravity is shifting. For this reason, a woman has to lean back while walking, abduct her shoulders and bend in the lower back. As a result, the spine acquires a more pronounced lordosis, i.e., the natural lumbar curve increases, and the muscles are in constant tension. This cannot go unnoticed and provokes the appearance of back pain. They will especially disturb women with weak muscles, carrying twins or with multiple pregnancies. Pain tends to appear or worsen after prolonged standing, sitting, walking, or physical exertion.
This cannot go unnoticed and provokes the appearance of back pain. They will especially disturb women with weak muscles, carrying twins or with multiple pregnancies. Pain tends to appear or worsen after prolonged standing, sitting, walking, or physical exertion.
Acute pain is always a sign of abnormalities. Therefore, in such situations, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
In the third trimester, so-called training contractions often occur, which, in some women, cause back pain. This is due to the beginning of the preparation of the body for childbirth and does not pose a threat to the woman herself and the fetus. In addition, at this time, the configuration of the pelvic bones changes, the fetus moves downward, and its head exerts more pressure on them and the cervix. It can also cause aching pain in the back.
The appearance of cramping pains with decreasing intervals between attacks can act as a sign of the onset of labor.
Diseases that can cause back pain during pregnancy
Since immunity decreases during pregnancy and the shape of the spine changes, this contributes to the manifestation of all latent diseases and exacerbation of chronic pathologies. Therefore, often during pregnancy, diseases of the urinary, reproductive system and, last but not least, the spine occur.
Therefore, often during pregnancy, diseases of the urinary, reproductive system and, last but not least, the spine occur.
The fact is that the increasing load on the spine leads to a sharp creation of unfavorable conditions. Therefore, if a woman already had any disorders before conception, even if she does not know about them, during pregnancy they will progress rapidly, which will result in back pain. The main reasons for their appearance are:
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusions and herniated discs;
- scoliosis.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common causes of back pain during pregnancy. For this disease, the development of a degenerative-dystrophic process in the intervertebral discs with a decrease in their thickness is typical. The disease is widespread even among young people and is most often provoked by a sedentary lifestyle, excessive physical activity and the presence of excess weight.
When it pains in the lower back are of a chronic aching nature and are aggravated after prolonged standing, sitting, physical work. It is osteochondrosis that becomes a prerequisite for the occurrence of more severe pathologies of the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine - protrusions and hernias.
It is osteochondrosis that becomes a prerequisite for the occurrence of more severe pathologies of the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine - protrusions and hernias.
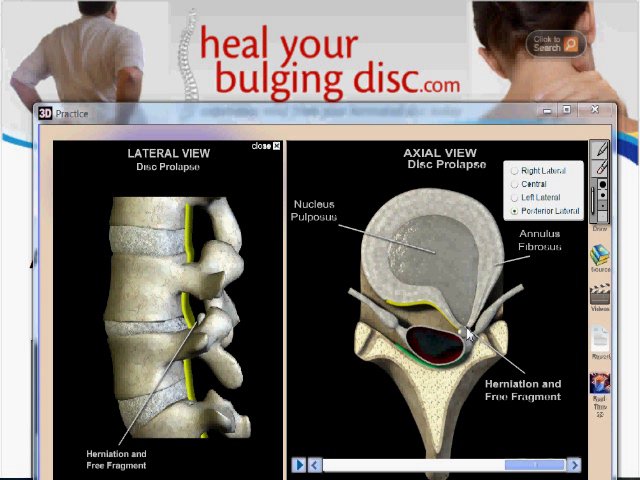
Protrusions and herniated discs
Protrusions are the deformation of the intervertebral disc, in which it protrudes into the spinal canal and can compress the spinal roots and nerves of the so-called cauda equina passing right there. This is accompanied by severe pain in the lower back, which radiate to the legs in accordance with the areas of innervation of the compressed nerves, and sensory disturbances. This is called radicular syndrome.
If the orthopedic regimen is not observed, the outer shell of the intervertebral disc, called the annulus fibrosus, will rupture and its inner contents (nucleus pulposus) will be able to partially leak into the spinal canal. This is fraught with compression of the spinal cord and pinching of its nerve roots, which will provoke severe pain along the nerves and in the lower back. A large hernia and a pronounced radicular syndrome are an indication for surgical treatment.
A large hernia and a pronounced radicular syndrome are an indication for surgical treatment.
The formation of protrusions and hernias of the intervertebral discs against the background of weight gain due to the growth of the fetus is one of the most common causes of back pain during pregnancy.
Scoliosis
The presence of scoliotic deformity in a woman before pregnancy is a serious prerequisite for the appearance of back pain after conception. The increasing weight and size of the uterus will provoke an increase in the scoliotic arc. This will lead not only to severe pain in the lower back, but can also contribute to the occurrence of disorders in the functioning of internal organs. Additional signs of scoliosis are the asymmetry of the position of the pelvic bones and shoulder blades, the difference in the position of the legs and the visible deformity of the back when leaning forward.
Diseases of the kidneys
Often back pain during pregnancy is due to the development of kidney disease, in particular pyelonephritis. It is characterized by an inflammatory process, one of the triggers for which is hypothermia or infection. It is possible to differentiate violations in the work of the kidneys by the presence of additional symptoms:
It is characterized by an inflammatory process, one of the triggers for which is hypothermia or infection. It is possible to differentiate violations in the work of the kidneys by the presence of additional symptoms:
- fever;
- chills;
- soreness and frequent urination;
- discoloration of urine;
- swelling of the legs.
Also, low back pain during pregnancy is often caused by urolithiasis or nephrolithiasis. With it, stones of different composition and degree of density are formed in the kidneys. Under the influence of physical exertion, vibration when moving in shaky vehicles, or other factors, they can move from their places and begin to move along the ureters. This is accompanied by severe pain in the back, radiating to the groin, lower abdomen and thighs. Often, the movement of stones along the ureters is accompanied by the appearance of blood impurities in the urine, due to injury to their mucous membranes with sharp edges of stones. Over time, the stone descends into the bladder and the pain subsides. Then it can start moving again, causing pain in the urethra and blood in the urine.
Over time, the stone descends into the bladder and the pain subsides. Then it can start moving again, causing pain in the urethra and blood in the urine.
Danger symptoms
Although low back pain is often physiological, carelessness can be tragic for a young family. Therefore, if the pain is acute and severe, it is important to consult a gynecologist, neurologist and urologist as soon as possible, as well as undergo the necessary examinations.
But if back pain is accompanied by the following symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help:
- bloody, brownish discharge from the vagina;
- persistent or worsening low back pain not relieved by rest;
- pains radiate to legs, groin;
- lower abdominal pain;
- fever.
These symptoms may indicate a threatened miscarriage or a serious exacerbation of an existing disease.
Diagnosis of causes of back pain during pregnancy
In order to determine the causes of discomfort in the lumbar region, a woman should first contact a gynecologist leading the pregnancy. The doctor will listen to the patient's complaints and, if there are suspicions about the presence of deviations from the norm, will conduct an examination for the presence of gynecological diseases. If no violations are detected or there are clear signs of pathologies of the spine or kidneys, he will refer the woman for a consultation with a urologist, neurologist or vertebrologist.
The doctor will listen to the patient's complaints and, if there are suspicions about the presence of deviations from the norm, will conduct an examination for the presence of gynecological diseases. If no violations are detected or there are clear signs of pathologies of the spine or kidneys, he will refer the woman for a consultation with a urologist, neurologist or vertebrologist.
These specialists will conduct a thorough examination and interview of the patient, use special tests to diagnose pinched spinal roots, and functional tests. If there is a suspicion of pathology of the kidneys or spine, the pregnant woman will be recommended to take blood and urine tests, as well as undergo instrumental diagnostics.
Since x-rays and CT scans are contraindicated during pregnancy, the only methods that can be used to determine the causes of low back pain are:
- Ultrasound - used to diagnose diseases of the genital organs and kidneys;
- MRI - allows you to assess the condition of the intervertebral discs, ligaments, spinal cord and other soft tissue structures.
The most informative and at the same time completely safe method of examination of pregnant women is MRI without contrast.
Treatment of back pain during pregnancy
The main difficulty in the development of tactics for the treatment of various diseases manifested by back pain is that many drugs and physiotherapeutic procedures are contraindicated during pregnancy. Therefore, doctors often have to assess the risks and choose the lesser evil in order to preserve the health of the mother and child.
As a result of a very gentle treatment, at best, it is possible to slow down the development of pathology, especially when it comes to diseases of the spine. But the ever-increasing weight and changes in the load on the intervertebral discs lead to the rapid progression of degenerative-dystrophic processes and deformities. Therefore, often patients with protrusions and hernias after childbirth require surgery. In particularly difficult cases, very rarely, for example, when part of the nucleus pulposus is separated from the disc (sequestered herniated disc), surgery can be performed even during pregnancy with the utmost care. This is due to the fact that the risks of non-intervention in such situations are much higher than during the operation.
This is due to the fact that the risks of non-intervention in such situations are much higher than during the operation.
Conservative treatment
Treatment is initially conservative. It may include:
- massage;
- manual therapy;
- exercise therapy.
When diagnosing kidney pathologies, as well as the threat of miscarriage or premature birth, treatment is carried out mainly in stationary conditions under constant medical supervision, since violations in their work are fraught with serious consequences for the mother and fetus.
The nature of the treatment of back pain during pregnancy depends entirely on what caused them, and for each woman is selected individually. But in all cases, it is very important to monitor your lifestyle and nutrition. Recommended for back pain:
- avoid prolonged standing and sitting;
- wear comfortable shoes with low heels or sneakers;
- sleep on an orthopedic mattress, for comfort, you can use a special pillow for pregnant women;
- completely avoid carrying heavy loads;
- use a prenatal bandage that will help reduce stress on the spine and back muscles;
- enrich your daily diet with fresh vegetables, fruits and foods rich in calcium;
- visit the pool if there are no contraindications.
If back pain is caused by diseases of the spine, a woman should have more rest. Depending on the severity of the existing violations and their nature, treatment is selected. Of the medicines, local remedies are most often used in the form of ointments, gels and creams. Their main components are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which also have analgesic properties. Their application helps to improve well-being, and relieve pain without harming the child.
If the woman's condition allows, she is recommended to engage in physiotherapy exercises. For each pregnant woman, the complex is developed individually, taking into account the diagnosis, the presence of a threat of miscarriage and the level of physical development. Classes are recommended to be carried out under the supervision of a specialist in order to perfectly master the methodology for performing each proposed exercise. During gymnastics, any sudden movements are completely excluded, and the exercises are more focused on stretching and relaxing the back muscles.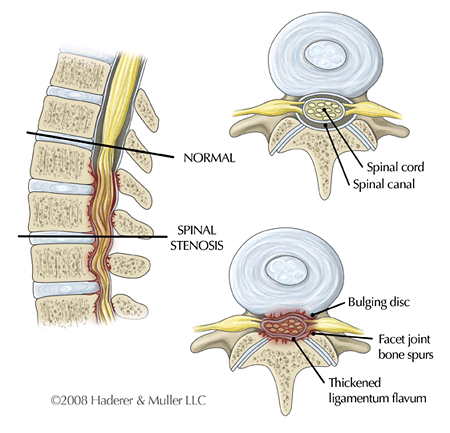
It is good to help reduce the severity of back pain during pregnancy and even slow down the progression of diseases of the spine can manual therapy. But the choice of a specialist should be treated with the greatest possible care, otherwise special massage sessions can cause irreparable harm to the health of the mother and child. With the use of a number of manual therapy techniques, it is possible to reduce the load on the intervertebral discs and improve the position of the vertebrae relative to the central axis. This will not only lead to a reduction in pain, and sometimes the release of pinched nerves, but will also help to avoid serious changes in the spine before childbirth.
Surgical treatment
Indications for operations is the development of radicular syndrome (pain in the lower back, radiating to the legs) with protrusions and hernias of the intervertebral discs, as well as other severe pathologies of the spine.
But during pregnancy, surgical interventions are carried out only in very complex, life-threatening and health-threatening conditions.
Often, in the event of large protrusions and intervertebral hernias, surgery is prescribed for the next postpartum period.
It may consist of carrying out:
- Nucleoplasty is a percutaneous surgical technique that involves the destruction of a portion of the nucleus pulposus by laser, radio waves or cold plasma under local anesthesia, as a result of which the hernia is reduced in size. Surgical instruments are inserted under the control of an image intensifier tube through a thin skin puncture in the projection of the affected disc, which ensures minimal intraoperative risks and the absence of a postoperative scar.
- Hydroplasty - a method similar to nucleoplasty, differing only in the use of liquid pressure to destroy the required volume of the nucleus pulposus and aspiration of the spent material through a special outlet. Like nucleoplasty, hydroplasty allows you to solve the problem of lower back pain in one day and does not require a complex and lengthy recovery.
 The woman can leave the clinic on the day of the operation.
The woman can leave the clinic on the day of the operation. - Microdiscectomy is an operation indicated for large sizes of the intervertebral hernia, which implies its resection through an incision up to 3 cm. It allows you to revise the affected spinal motion segment, release the pinched nerves and blood vessels, and radically solve the hernia problem. The method allows, if necessary, to completely remove the disk if it is too badly damaged and can no longer perform the functions assigned to it.
- Endoscopic surgery - in some cases considered as an alternative to microdiscectomy. It consists in removing a hernia with special endoscopic equipment with a camera, which is inserted into the patient's body through several punctures up to 1 cm in diameter.
If the disc is so damaged that it needs to be removed completely, patients are offered the installation of interbody endoprostheses or special implants. The former are preferable, since in terms of their functionality they practically do not differ from natural intervertebral discs. By design, they are their exact copies and in the same way have an analogue of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus. With their help, it is possible not only to maintain the flexibility of the spine in the operated spinal motion segment, but also to ensure its normal biomechanics. As a result, patients after the end of the rehabilitation period do not even notice the difference.
By design, they are their exact copies and in the same way have an analogue of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus. With their help, it is possible not only to maintain the flexibility of the spine in the operated spinal motion segment, but also to ensure its normal biomechanics. As a result, patients after the end of the rehabilitation period do not even notice the difference.
Thus, pain in the back and lower back during pregnancy can be both natural and evidence of the development of the disease. But future mothers do not have the right to risk their own health and the child growing in their womb and hope that the discomfort in the lower back is harmless. Therefore, when pain occurs, especially if it occurs frequently, in the early stages of pregnancy or intensifies, it is better to play it safe and consult a doctor. This will prevent the development of complications, at the earliest stages of the onset of the pathological process, take measures to stop it, give birth to a healthy baby, and ultimately undergo a full treatment of existing diseases. Easy childbirth!
Easy childbirth!
9 months
Pregnancy / Health
Unfortunately, nowadays few people can boast of an absolutely healthy spine. Often even young people complain of back pain. It also happens that by pregnancy women already have protrusions or hernias, and of course, in this case, one cannot but worry about how the back will behave while waiting for the baby.
Throughout life, the human spine experiences serious stress. Injuries, static overload (for example, carrying heavy bags), a sedentary lifestyle over the years can cause spinal diseases.
The spine can be compared to a train, in which the individual cars (vertebrae) are connected to each other by means of joints. Between the vertebrae are elastic pads (intervertebral discs) that act as shock absorbers that prevent the vertebrae from rubbing against each other. Inside each such disc is a gel-like center (nucleus pulposus), surrounded by a fibrous outer shell (annulus fibrosus).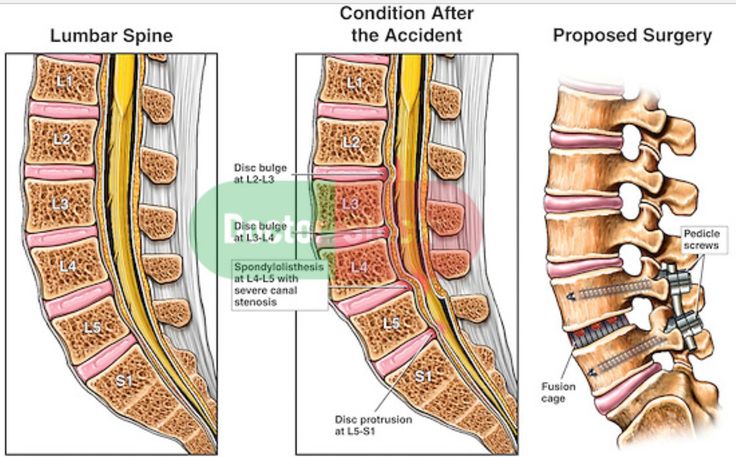 With loads on the spinal column, displacement and compression of the intervertebral discs occurs. If the integrity of the disc is maintained and it does not go beyond the spinal column, then this does not lead to the development of the disease.
With loads on the spinal column, displacement and compression of the intervertebral discs occurs. If the integrity of the disc is maintained and it does not go beyond the spinal column, then this does not lead to the development of the disease.
Protrusion and hernia: what's the difference?
The intervertebral disc does not have its own blood vessels, but is nourished by the penetration of nutrients from the surrounding tissues of the spine. Malnutrition of the discs is at the heart of the development of osteochondrosis. When the metabolism inside the disc is disturbed, it dries out, the height of the disc decreases, the fibrous capsule exfoliates, due to which it loses its strength. With excessive loads, the bodies of neighboring vertebrae approach each other, they exert great pressure on the damaged disc, which leads to the “squeezing” of its contents outside the spinal column. If at the same time the fibrous ring retains its integrity, then such a protrusion of the disc is called protrusion.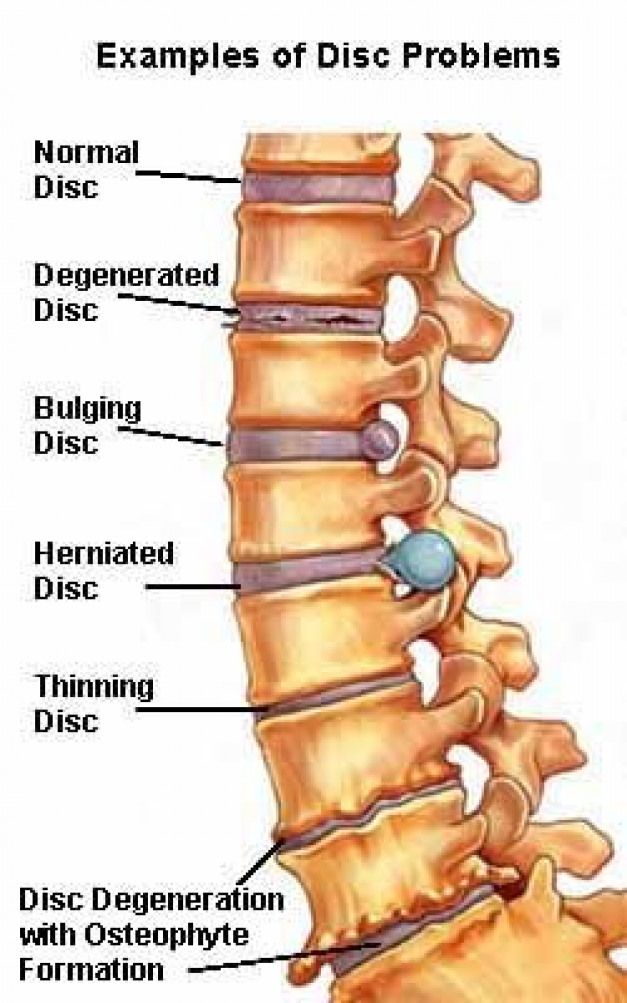 This is the first stage of the formation of an intervertebral hernia. This stage is reversible, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, full recovery of health occurs.
This is the first stage of the formation of an intervertebral hernia. This stage is reversible, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, full recovery of health occurs.
If the pathological effect on the intervertebral disc persists, then at some point it leads to a rupture of the altered fibrous ring and extrusion of a part of the nucleus pulposus beyond the intervertebral disc. This is how a herniated disc is formed. Once in the spinal canal, the nucleus pulposus compresses the nerves located next to the disc, which leads to pain. First of all, those intervertebral discs that experience the greatest load are prone to herniation. As a rule, these are discs of the cervical and lumbar vertebrae. The thoracic spine suffers the least.
How does disc protrusion and herniation manifest?
The main symptom of a herniated disc is severe back or neck pain with any movement. Also, signs of the disease can be loss of sensitivity (numbness) of the skin of the neck, arms, legs, the appearance of "goosebumps" in the toes or hands, pain in the joints of the extremities.












