Pcos and natural pregnancy
Getting pregnant with PCOS: A guide to conceiving naturally
Back to Top
Now Reading:
Getting pregnant with PCOS: A guide to conceiving naturally
Share fbsharetwsharepinshareComments (0)
TIMESOFINDIA.COM | Last updated on -Nov 22, 2020, 15:00 ISTShare fbsharetwsharepinshare
Comments (0)- close
01/6Getting pregnant with PCOS: Here are a few tips you should know
PCOS is a lifestyle problem which affects 1 in 7 women, according to gynecologists and infertility specialists.
A problem that's typically associated with irregular or scanty periods, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) can have a huge impact on fertility, ovulation and hormonal functioning. It remains to be one of the leading causes of infertility and many struggle conceiving because of their unpleasant diagnosis. What's rather scarier is bleak awareness. Many women only learn of the problem when they face trouble getting pregnant naturally, and have to seek additional help.
Even though PCOS can make it difficult for ovulation to happen, the big question remains, can a woman conceive with PCOD or PCOS? Is natural conception possible?
If you have been diagnosed with PCOS and have been facing trouble conceiving, here is a handy guide which could answer your questions.
readmore
02/6How does PCOS impact your fertility?
PCOS is a condition which causes excess production of male hormones (androgens) in the body, which can pose problems.
While women with PCOS can conceive, they face more problems than other women. One of the prime reasons being, irregular menstruation, which reduces the chances of ovulation.
Another factor which can trigger problems is obesity. Since women with PCOS tend to be put on weight, excess weight can make it difficult for a woman to conceive.
Apart from this, women with PCOS are also at a higher risk for problems like
-Type 2 and gestational diabetes
-Taking a longer while to conceive
-Health risks during pregnancy
readmore
03/6What can women with PCOS do to boost their chances of conception?
Even though a little difficult, women with PCOS actually go on to have the same number of children as other women. However, the journey to getting pregnant can be a little lengthier, or often requires assistance.
That being said, there are ways women struggling with PCOS can boost their chances of getting pregnant, naturally.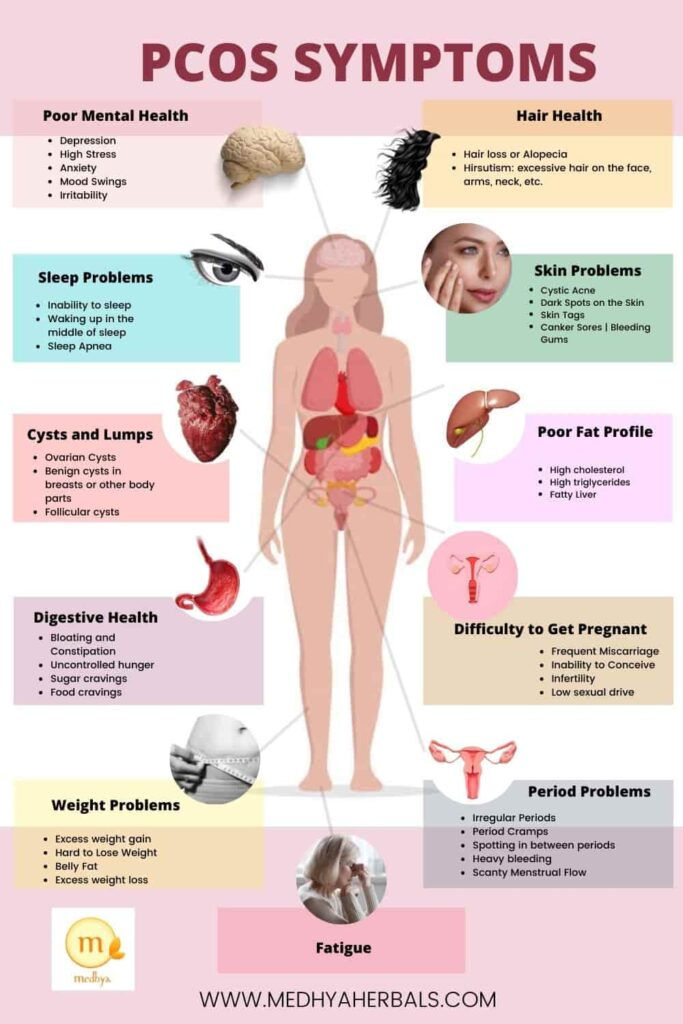
Managing weight gain: Weight loss is one of the ways to increase chances of conception. Since extra weight can lead to inflammation and induce stress on the body, managing your weight and BMI (Body Mass Index) can regularize menstruation and help you have a baby. Seeking advice from a medical professional, or maintaining vitals as per your age can help you get started. Studies suggest that even a 5-10% reduction in weight can promote ovulation and make it easier for the body. However, it's not a permanent solution for fertility issues.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can beat the ill-effects of a sedentary lifestyle and manage weight gain. It can also counter stress, which can be bad for conception. Simple activities like walking regularly, weight training or cardio can promote fat loss and muscle gain.
Eating healthy is important too: Diet is also said to have a beautiful impact for those struggling to conceive with PCOS. Even though there isn't something like the 'best diet' for reversing PCOS, following a low-carb diet with heavy proteins can help. Food groups like nuts and seeds, vitamins like B12, D, folate, iron, omega-3 (which is a natural fertility booster) should be had plenty. Quitting dairy, which is said to impact gut sensitivity may also prove helpful.
Food groups like nuts and seeds, vitamins like B12, D, folate, iron, omega-3 (which is a natural fertility booster) should be had plenty. Quitting dairy, which is said to impact gut sensitivity may also prove helpful.
Controlling blood sugar levels: PCOS is linked to insulin resistance and can trigger diabetes, which again, is a risk factor for conception. Controlling and managing blood sugar levels may bring a change in your health.
Some women also benefit from trying out natural therapies like yoga, meditation, acupuncture.
readmore
04/6Is natural conception possible?
PCOS is one of the most common contributing factors responsible for infertility. However, natural conception is possible. Making changes to your diet and lifestyle are some of the simplest ways to boost your odds. Women with PCOS who have a healthy weight are more likely to get pregnant than those who aren't. If you control your lifestyle problems, getting pregnant won't be a struggle for long.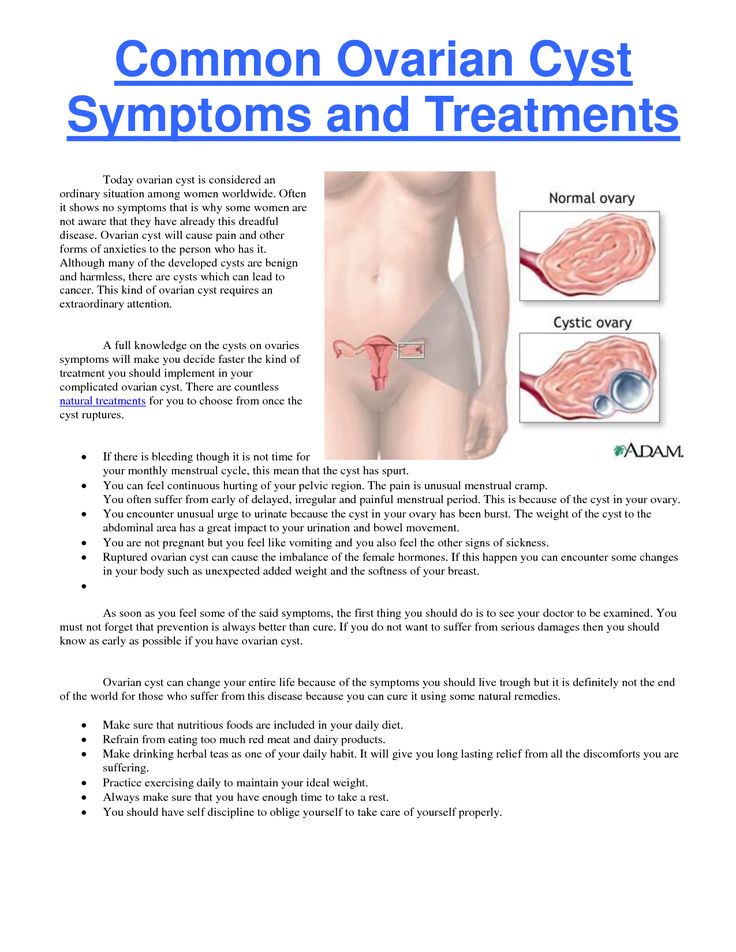 Expert guidance can help you make the right decisions and get your health on the right track.
Expert guidance can help you make the right decisions and get your health on the right track.
readmore
05/6Do fertility drugs and treatments help?
Women with PCOS are often put on drugs. Medical studies have shown that 80% of women with PCOS who are treated with various fertility assisting drugs and treatments conceive within six to twelve-period cycles. However, age and pre-existing health complications can have a role to play here.
The type of drugs you are being put on can help manage the root problem which is making it difficult for you to conceive. For example, metformin, a common medicine used to treat PCOS regulates blood sugar and hormonal functioning. Birth control pills and patches can help regularize conception. They may also reduce the chances of miscarriages for high-risk women.
Some women with severe complications are also advised to go for therapies and fertility treatments. IVF (In-Vitro Fertilization) can help. However, do remember that it's an expensive and lengthy procedure. For some, it can take repeated cycles and years of IVF treatment to help conceive naturally.
IVF (In-Vitro Fertilization) can help. However, do remember that it's an expensive and lengthy procedure. For some, it can take repeated cycles and years of IVF treatment to help conceive naturally.
Women also undergo ovulation procedures. Less-expensive and easier alternative, intrauterine insemination (IUI) is where high concentrates of sperm are inseminated inside the body to fuse with the egg. In more complex cases of PCOS, making use of egg donors, or opting for surrogacy or adoption may also be recommended. It also depends on an individual's choice.
readmore
06/6When is the right time to seek help?
Like any medical problem, the earliest intervention makes way for timely help and treatment. Having a baby with PCOS is tricky, but not impossible. A little help from a guiding doctor, making lifestyle changes and controlling weight can go a long way in promoting fertility and good health.
Frequent intercourse, managing stress levels and last of all, being optimistic will help you conceive and have a baby of your own.
Consider seeking help if you face conceiving naturally six months after trying naturally. If you get very few periods in a year or have heavy bleeding, or are over 30, consulting a doctor can prevent problems.
readmore
How to Get Pregnant with PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is a hormonal condition that tampers with more than just your fertility, but you might first receive a diagnosis when you’re trying to get pregnant. This is because it’s a common — and treatable — cause of infertility in women.
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), up to 12 percent of women in the United States have difficulty getting pregnant because of untreated PCOS. In reality, this number might be bigger because almost 50 percent of women with this syndrome don’t know they have it or are not diagnosed correctly.
Having PCOS doesn’t mean you can’t get pregnant. It just might be a bit trickier and you may need extra help. There is plenty that you can do at home and with medical treatment to keep PCOS symptoms at bay and raise your chances for a healthy pregnancy.
Getting pregnant with PCOS involves some of the same steps that women without PCOS should take for a healthy pregnancy.
- Have your weight and body mass index (BMI) measured by your doctor. Your BMI shows whether you have a healthy body weight and how much of your body composition is fat. If you are carrying extra weight, talk to your doctor about how much weight you need to lose before you get pregnant.
- Start a healthy diet and exercise plan. Get into the habit of choosing healthier food choices and being more active.
- Use an ovulation calendar or app to track when you have your period. This helps you make a better guess about which days of the month you are more likely to get pregnant.

- Check your blood sugar levels. See your doctor to make sure your blood sugar levels are balanced. Your blood sugar levels are important in getting pregnant, having a healthy pregnancy, and even in your baby’s future health.
Being overweight has been linked to PCOS, but many women who have this condition are not overweight at all. Still, if you are carrying extra weight, you may improve your fertility and reduce other PCOS symptoms by losing just 5 percent of your weight.
Exercise daily by going for a walk and getting in your steps. Use a standing desk rather than sitting down while you’re working. Lift light weights while watching TV as building more muscle helps bring down PCOS symptoms and improves your health.
Any woman who is trying to get pregnant needs to have the right levels of nutrients. Switch out sugary foods, simple carbs, and unhealthy fats for healthier choices, including:
- fresh and cooked fruit and vegetables
- whole grains like brown rice, oats, and barley
- beans and lentils
- chicken
- fish
Certain vitamins and minerals are important for a healthy pregnancy and a growing baby.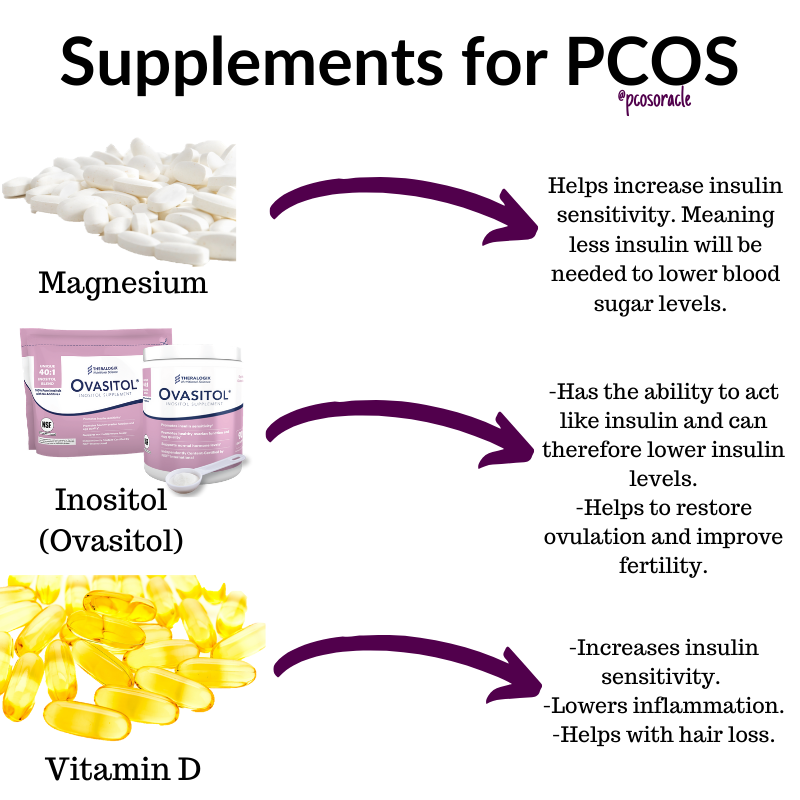 Ask your doctor about the best supplements for you. Supplements that may help fertility include:
Ask your doctor about the best supplements for you. Supplements that may help fertility include:
- folic acid (vitamin B9)
- vitamin B6
- vitamin B12
- vitamin C
- vitamin D
- vitamin E
- coenzyme Q10
Your doctor will test your blood sugar levels if you’re having trouble getting pregnant. PCOS sometimes leads to high blood sugar levels or type 2 diabetes. This may cause fertility problems.
This happens because PCOS may change how your body uses insulin. This important hormone moves sugar (glucose) out of the blood and into the muscles and cells where it is burned for energy. PCOS makes your body less sensitive to insulin — making it harder for it to do its job.
Balancing your blood sugar levels may help you get pregnant. Eat a healthy diet with more fiber, protein, and healthy fats. Getting plenty of daily exercise and strength training can also help your body use insulin better.
In some cases, your doctor might recommend medications to help balance your blood sugar levels. A common type 2 diabetes drug called metformin (or Glucophage) makes your body use insulin better to help lower high blood sugar. This can also help you get pregnant with PCOS.
A common type 2 diabetes drug called metformin (or Glucophage) makes your body use insulin better to help lower high blood sugar. This can also help you get pregnant with PCOS.
You might need to take metformin in low doses and only temporarily, depending on your blood sugar levels. For best results, eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly along with taking any prescribed medications to help you get pregnant.
If you have high blood sugar levels or type 2 diabetes, it’s important to check your blood sugar levels with a home monitor every day.
Your doctor will check your blood sugar levels with tests, including:
- random blood sugar test
- overnight fasting blood sugar test
- oral glucose tolerance tests (after fasting and drinking a sugary drink)
- hemoglobin A1C test (checks your blood sugar levels for the last two to three months)
If you have PCOS your body might make more of both the male hormone testosterone and the female hormone estrogen. Too much (or too little) of these hormones can make it tricky to get pregnant. Your doctor might recommend prescription medications to help balance your hormones.
Too much (or too little) of these hormones can make it tricky to get pregnant. Your doctor might recommend prescription medications to help balance your hormones.
Medications to help you get pregnant with PCOS include:
- metformin to balance insulin levels
- clomiphene citrate (or Clomid) to help balance estrogen levels
- birth control pills to balance estrogen and testosterone levels (before beginning fertility treatment)
- fertility medications to jump-start the ovaries to send out more eggs
You may need in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment to help you get pregnant with PCOS. Your fertility doctor will give you a checkup that may include more blood tests, ultrasounds scans, and a physical exam.
IVF is a process that can take months or even years whether you have PCOS or not. However, medical research shows that women with PCOS have a high success rate of getting pregnant with IVF treatment.
Some clinical studies found that women with PCOS who took birth control pills before the IVF treatment had better results.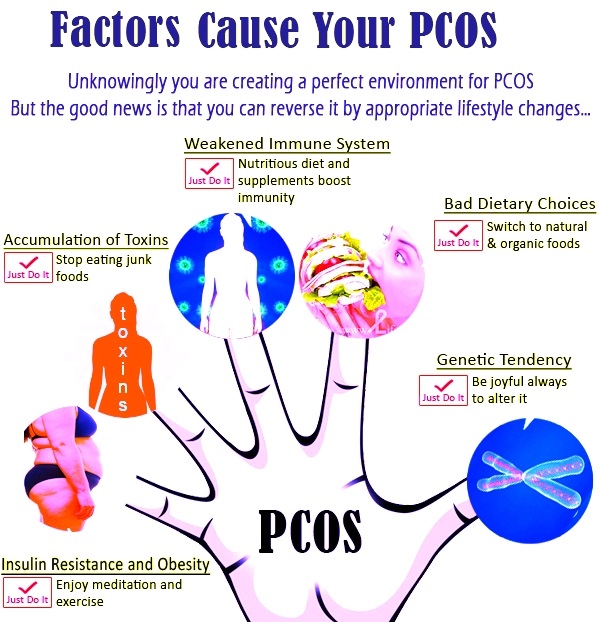 You may also need other mediations to help balance hormones and get your body ready for the IVF treatment.
You may also need other mediations to help balance hormones and get your body ready for the IVF treatment.
For all women, the first step in IVF treatment is to eat a balanced diet and get plenty of exercise to reach a healthy weight. Women with PCOS who are a healthy weight are twice as likely to get pregnant with IVF than women with PCOS who are obese.
Before exploring IVF, your doctor might suggest a less-costly alternative called intrauterine insemination (IUI). This process increases the chance of pregnancy because it directly injects a high concentration of sperm closer to the egg.
PCOS may make it harder to get pregnant because it can impact your menstruation cycle (your monthly period). Symptoms include:
- too few menstrual periods
- having your period for longer than usual
- not getting your period
- very heavy periods
- higher levels of male hormones like testosterone
- acne breakouts
- getting facial hair and extra hair in other places
- small cysts or bundles of fluid in the ovaries
- fewer eggs released from the ovaries
If you don’t get treated for PCOS, it also raises your risk for other health conditions, like:
- type 2 diabetes
- sleep apnea (snoring)
- heart disease
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- stroke
No one knows why some women get PCOS.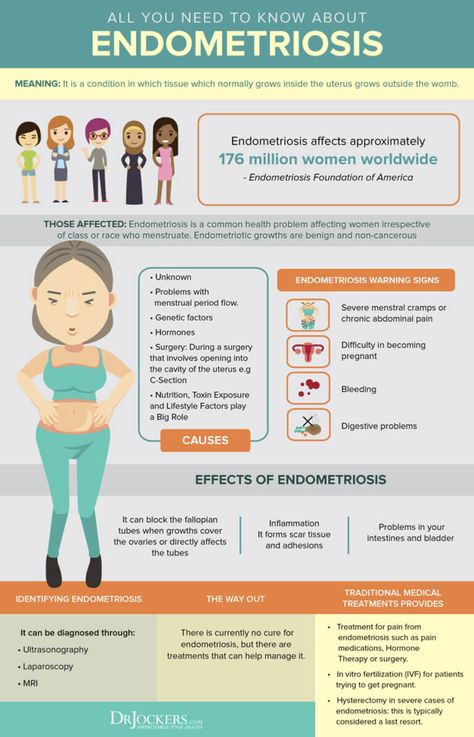 Nothing you did — or didn’t do— caused you to have this condition. But getting an early diagnosis and treatment along with making other lifestyle changes may help you get pregnant and prevent health complications from PCOS.
Nothing you did — or didn’t do— caused you to have this condition. But getting an early diagnosis and treatment along with making other lifestyle changes may help you get pregnant and prevent health complications from PCOS.
If you are trying to get pregnant with PCOS, you may only need treatment with medications. A medical study found that almost 80 percent of women with PCOS treated with the drug clomiphene citrate successfully ovulated. Out of these, half of the women got pregnant naturally within six period cycles.
If medications don’t help you get pregnant, your doctor may recommend IVF treatments. Most women with PCOS have a 20 to 40 percent chance of getting pregnant with IVF treatment. Women who are 35 years old and older or who are overweight have a lower chance of getting pregnant.
You can get pregnant with PCOS. You will likely need to have moderate weight, balance your blood sugar levels, and treat other PCOS symptoms with healthy lifestyle changes and medications.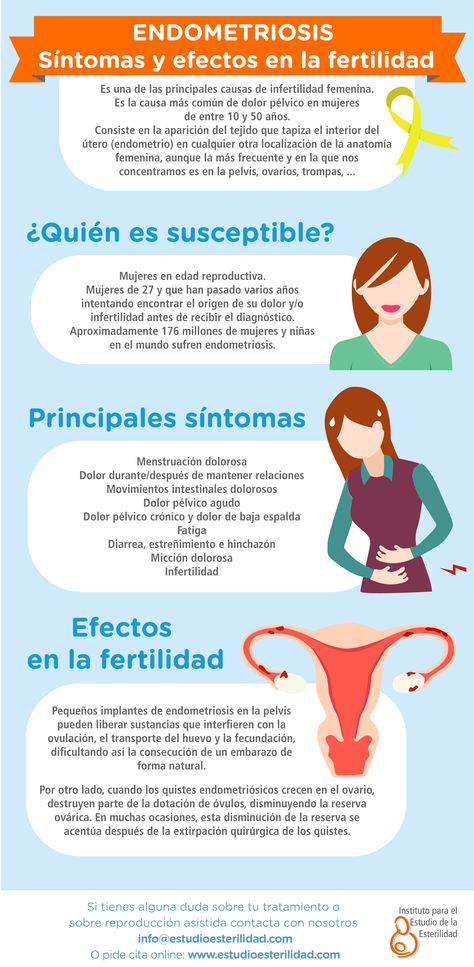
In some cases, fertility medications alone will help you get pregnant. If that doesn’t work, you may need IVF treatment.
But regardless of what treatment you explore, don’t lose hope. Success rates are optimistic. In time you may be smiling, positive pregnancy test in hand.
How to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries?
Polycystic disease is a common hormonal disease that affects the functioning of a woman's ovaries. The dangers of PCOS include irregular menstrual periods, excessive hair growth, acne, weight gain, and other problems. Left untreated, PCOS can even lead to infertility. In this article, we will tell you more about causes of polycystic , polycystic ovaries and pregnancy , and also give an answer to the question: “ Is it possible to give birth with polycystic ovaries? ".
What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have menstrual irregularities and elevated levels of male hormones (androgens). Numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) may form in the ovaries, and an egg may not be released regularly. This condition should not be confused with multifollicular ovaries, because with multifollicular ovaries, ovulation and a normal menstrual cycle can persist, unlike polycystic disease.
Women with PCOS may have menstrual irregularities and elevated levels of male hormones (androgens). Numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) may form in the ovaries, and an egg may not be released regularly. This condition should not be confused with multifollicular ovaries, because with multifollicular ovaries, ovulation and a normal menstrual cycle can persist, unlike polycystic disease.
50-75% of cases of endocrine infertility. 20-22% of marital infertility. It is detected in 5-16% of women of reproductive age. These are the figures for the diagnosis of "Polycystic Ovary".
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, upon noticing which it is necessary to seek advice from an endocrinologist or gynecologist. For some women, symptoms begin around the time of their first menstrual period. Others discover symptoms of PCOS only after they have gained a lot of weight or have trouble getting pregnant. In some cases, PCOS may be asymptomatic.
In some cases, PCOS may be asymptomatic.
The most common symptoms of PCOS:
- Irregular periods. Lack of ovulation prevents the lining of the uterus from falling off every month. Some women with PCOS have fewer than eight periods a year, or none at all.
- Severe bleeding. The lining of the uterus builds up over a longer period of time, so menstruation may be heavier than usual.
- Hair growth . More than 70 percent of women with this condition grow hair on their face and body, including on their back, abdomen, and chest. Excess hair growth is called hirsutism.
- Acne . Male hormones can make the skin more oily than normal and cause breakouts on areas such as the face, chest, and upper back.
- Weight gain. Up to 80 percent of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
- Male pattern baldness. The hair on the scalp becomes thinner and may fall out.

- Darkening of the skin. Dark patches of skin may develop in body folds, such as the neck, groin area, and under the breasts.
- Headaches. Hormonal changes may cause headaches in some women.
Irregular periods
Infrequent, irregular periods, long or no periods are the most common symptom of PCOS. For example, with PCOS, you may have fewer than nine periods a year, more than 35 days between periods, and abnormally heavy periods.
Hyperandrogenism
Hyperandrogenism is a disease characterized by high levels of androgens. It is more common in women than in men. Symptoms of hyperandrogenism may include acne, seborrhea (inflammation of the skin), hair loss on the scalp, increased body or facial hair, and infrequent or absent periods.
Hyperandrogenism is a defining feature of women and young girls with PCOS. Polycystic disease causes a malfunction of the ovaries or adrenal glands, which leads to the production of excess androgens (male sex hormones).
Anovulation
Anovulation occurs when an egg is not released from the ovary during the menstrual cycle. The egg is essential for pregnancy. Since several hormones are involved in ovulation, there are many causes of anovulation, one of which is PCOS. Chronic anovulation is a common cause of infertility.
Diagnosis
There is no test to definitively diagnose polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The doctor will likely begin by discussing your medical history, including menstrual periods and weight changes. A physical exam will include checking for signs of excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain.
Your doctor may recommend:
- Gynecological examination. A physician visually and manually examines the reproductive organs for growths or other abnormalities.
- Blood tests. A blood test is given to determine the level of hormones. This will help rule out possible causes of menstrual irregularities or excess androgens that mimic PCOS.
 An additional blood test may also be needed to measure insulin resistance as well as fasting cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
An additional blood test may also be needed to measure insulin resistance as well as fasting cholesterol and triglyceride levels. - Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). The doctor will check the appearance of the ovaries and the thickness of the lining of the uterus. A rod-shaped device (sensor) (transvaginal ultrasound) is inserted into the vagina, which emits sound waves and converts them into images on a computer screen.
Is it possible to get pregnant with PCOS
How to get pregnant with PCOS? Getting pregnant with PCOS can be difficult, but that doesn't mean it's impossible. While PCOS can affect your hormones and therefore your fertility, there are medical treatments and lifestyle changes you can make to improve your chances of pregnancy.
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries? To get pregnant, you must ovulate, which PCOS most often prevents. Women who do not ovulate regularly with PCOS do not release enough eggs for fertilization.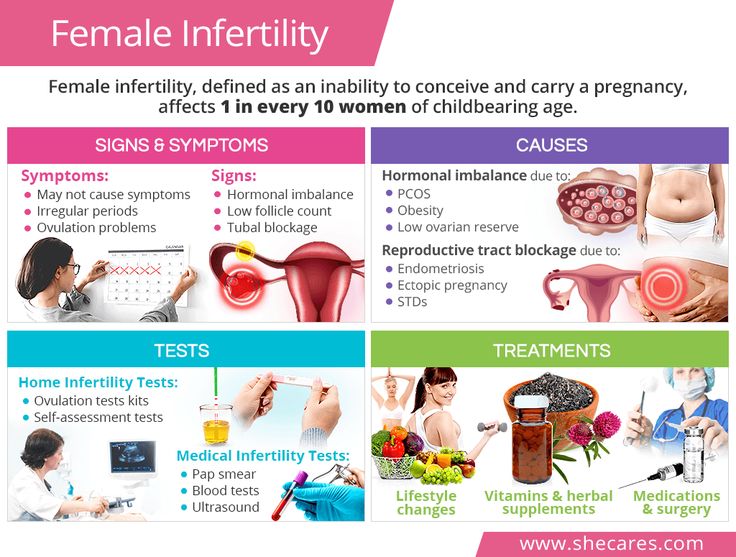 Pregnancy with PCOS is further complicated by the fact that PCOS causes a hormonal imbalance that changes the quality of cervical fluid, making it difficult for sperm to survive.
Pregnancy with PCOS is further complicated by the fact that PCOS causes a hormonal imbalance that changes the quality of cervical fluid, making it difficult for sperm to survive.
It is impossible to say categorically that PCOS is infertility, but PCOS is one of the main causes of infertility in women.
Is it possible to get pregnant with PCOS? And although there are no exact statistics on the chances of pregnancy, 70 to 80 percent of women with PCOS have fertility problems. PCOS disrupts the normal menstrual cycle and makes it difficult to conceive.
Is it possible to get pregnant with PCOS? Polycystic ovary syndrome is not a sentence and it is possible to get pregnant, albeit problematic. However, if PCOS is left untreated, the chances of getting pregnant decrease with age.
It is possible to get pregnant with polycystic disease, but most often pregnancy with polycystic disease is difficult. This condition can increase the risk of pregnancy complications. Women with PCOS are twice as likely to have a preterm birth than women without. They are also at greater risk of miscarriage, high blood pressure, and gestational diabetes. However, by managing the symptoms, many women with PCOS can become pregnant and have a healthy baby.
Women with PCOS are twice as likely to have a preterm birth than women without. They are also at greater risk of miscarriage, high blood pressure, and gestational diabetes. However, by managing the symptoms, many women with PCOS can become pregnant and have a healthy baby.
How to get pregnant with PCOS? Women with PCOS can become pregnant using fertility treatments that improve ovulation. Losing weight and lowering your blood sugar can increase your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Pregnancy planning for PCOS
How to get pregnant with PCOS? While your chances of getting pregnant with PCOS may be lower, there are a few things you can do to increase those chances.
- Call your doctor. How to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries? Normalization of hormones and menstruation is the first step. Your doctor may prescribe medications to help your body deal with insulin better and regulate your menstrual cycle.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
 Is it possible to get pregnant with PCOS? Weight loss can lower insulin levels, androgen levels, and restore ovulation. Ask your doctor about a weight management program and meet with a nutritionist regularly for help with your weight loss goals.
Is it possible to get pregnant with PCOS? Weight loss can lower insulin levels, androgen levels, and restore ovulation. Ask your doctor about a weight management program and meet with a nutritionist regularly for help with your weight loss goals. - Eat right. Polycystic Ovarian Diet includes sugary foods, simple carbohydrates and unhealthy fats. Add to your menu: fresh and cooked fruits and vegetables, whole grains such as brown rice, oats and barley, beans and lentils, chicken, fish.
- Be active. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels. How to get pregnant with insulin resistance? If you have PCOS, increasing daily activity such as walking, exercising, walking can help treat or even prevent insulin resistance, control your weight, and avoid developing diabetes.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. Follow a healthy lifestyle with PCOS, give up bad habits, unhealthy diet, lack of sports and irregular sleep.

Treatment for PCOS
Treatment for PCOS focuses on your individual problems such as infertility, acne or obesity. Also, the direction of PCOS treatment largely depends on whether a woman is planning a pregnancy or not. Specific treatment may include lifestyle changes or medications.
How to treat PCOS?
Lifestyle changes
Your doctor may recommend weight loss through a low-calorie diet combined with moderate exercise. Even small weight loss - like losing 5 percent of your body weight - can improve your condition. Can you get pregnant with PCOS? Losing weight can also increase the effectiveness of medications your doctor recommends to treat PCOS and help with infertility.
Treatment with drugs for polycystic ovaries
To regulate the menstrual cycle, the doctor may recommend:
Combination birth control pills. Estrogen and progestin tablets reduce androgen production and regulate estrogen. Hormone regulation can reduce the risk of endometrial cancer and correct abnormal bleeding, excess hair growth, and acne. Instead of pills, you can use a skin patch or vaginal ring containing a combination of estrogen and progestin.
Hormone regulation can reduce the risk of endometrial cancer and correct abnormal bleeding, excess hair growth, and acne. Instead of pills, you can use a skin patch or vaginal ring containing a combination of estrogen and progestin.
Progestin therapy. Daily progestin may: restore normal hormonal balance, regulate ovulation, stop excessive hair growth, protect against endometrial cancer, and help get pregnant with sleep deprivation.
How to induce ovulation in PCOS? To help induce ovulation in PCOS, your doctor may recommend:
Clomiphene is a fertility medication that can help women with PCOS get pregnant.
Metformin is a drug used to treat type 2 diabetes. It also treats PCOS by increasing insulin levels.
Operation
How to get pregnant with PCOS? Surgery may be an option to improve fertility if other treatments don't work. Ovarian drilling is a procedure in which tiny holes are made in the ovary using a laser or a thin, heated needle to restore normal ovulation and the possibility of pregnancy with PCOS.
Important! To determine the right treatment and choose the right drug, you need to consult a doctor!
Help Doc.ua: you can make an appointment with a gynecologist-endocrinologist on the website.
Pregnancy and childbirth with polycystic ovaries
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most insidious diseases. Until now, doctors have not revealed the secret of his development. With polycystic disease, the ovaries suffer - ovulation is disturbed in them: the eggs do not mature, and pregnancy does not occur. The paradox is that the supply of eggs in PCOS does not deplete for a long time. There are eggs, but the body cannot “use” them.
Pregnancy and childbirth against the background of polycystic ovaries do not always proceed safely. With this disease, it is difficult to conceive, endure and give birth to a child. But difficult does not mean impossible. Comprehensive work with the body and mind helps to overcome the disease, restore the functioning of the ovaries and restore fertility.
Conception
In PCOS, the ovaries “sleep”. They have follicles - and they are enough for a woman to conceive a child. But ovulation does not happen - and the excess of male sex hormones is to blame. Hyperandrogenism does not allow the egg to mature - and pregnancy does not occur.
Infertility with polycystic ovaries is not a sentence. Many women manage to conceive a child on their own - without drug therapy and assisted reproductive technologies (IVF with ovulation stimulation). But about half of the cases require treatment - and here modern medical technologies come to the rescue. The practice of restorative medicine and work with the psychosomatic causes of the disease help to increase the effectiveness of therapy.
It is not enough to “wake up” the ovaries – the cause of the disease must be found and eliminated, both on the psychological and physical levels. It is necessary to help the body to be healthy and start the natural processes of self-healing.

The sooner the problem is identified and the therapy is started, the easier it will be to cope with infertility. Any treatment is most effective in women under 30 years of age. But even at a later age, you should not despair - you can cope with the disease, it just takes more time and effort.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy with polycystic ovaries is often accompanied by complications:
- spontaneous miscarriage in early pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- placental insufficiency;
- gestational diabetes mellitus;
- preeclampsia and preeclampsia.
Clinical studies have shown that the use of hormonal drugs and metabolic correction agents does not improve the course of pregnancy. Therefore, priority is given to other methods.
Particular attention is paid to the emotional state of the woman. You need to come to pregnancy, leaving negative experiences, unlived grievances, fears and unresolved conflicts in the past.

Also recommended:
- Vitamin Therapy . It is recommended to start taking folic acid three months before conception.
- Rational nutrition. In the diet of the expectant mother should be foods rich in calcium, magnesium and B vitamins. It is recommended to abandon easily digestible carbohydrates.
- Physical activity. It has been proven that weight loss of at least 5-10% significantly increases the chances of successful conception and childbearing. The best tactic for weight management: exercise + diet.
- Quit bad habits . It is recommended to stop smoking - addiction to nicotine negatively affects the metabolism and disrupts the functioning of the ovaries.
Childbirth
Polycystic ovaries usually do not interfere with the birth of a child through the birth canal. If the pregnancy is full-term, the fetus develops safely, the woman's condition is satisfactory - there are no obstacles to this. A caesarean section is recommended for the development of complications, its goal is to preserve the health and life of a woman and a child.
A caesarean section is recommended for the development of complications, its goal is to preserve the health and life of a woman and a child.
Many women experience PCOS symptoms after childbirth. The menstrual cycle normalizes, excess hairiness disappears, pain in the lower abdomen subsides. But other problems appear, primarily related to metabolism - the risk of developing diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity increases.
In the postpartum period, it is recommended:
- Breastfeed. Lactation is the natural defense of the ovaries. As long as a woman is breastfeeding, the disease does not progress.
- Watch your weight. BMI must remain within 30 km/m 2 , waist circumference - no more than 88 mm. Being overweight increases the risk of complications, worsens the work of the ovaries.
- Visit an osteopath. Postpartum correction is recommended for all women, both after vaginal delivery and after caesarean section.