Pregnancy 6 months baby weight
Fetal Chart from Baby My Baby
Free info for you and your baby! Text BABY to 511411
Search
Search for:
(crown to rump measurements)
| Gestational Age | Length (inches) | Weight (oz/lb) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 weeks | 0.63 | 0.04 oz | 1.6 | 1 |
| 9 weeks | .9 | 0.07 oz | 2.3 | 2 |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 | 0.14 oz | 3.1 | 4 |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 | 0.25 oz | 4.1 | 7 |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 | 0.49 oz | 5.4 | 14 |
| 13 weeks | 2.19 | 0.81 oz | 7.4 | 23 |
| 14 weeks | 3.42 | 1.52 oz | 8.7 | 43 |
| 15 weeks | 3.98 | 2.47 oz | 10.1 | 70 |
| 16 weeks | 4. | 3.53 oz | 11.6 | 100 |
| 17 weeks | 5.12 | 4.94 oz | 13 | 140 |
| 18 weeks | 5.59 | 6.70 oz | 14.2 | 190 |
| 19 weeks | 6.02 | 8.47 oz | 15.3 | 240 |
| 20 weeks | 6.46 | 10.58 oz | 16.4 | 300 |
| 21 weeks | 10.51 | 12.70 oz | 26.7 | 360 |
| 22 weeks | 10.94 | 15.17 oz | 27.8 | 430 |
| 23 weeks | 11.38 | 1.10 lb | 28.9 | 501 |
| 24 weeks | 11.81 | 1.32 lb | 30 | 600 |
| 25 weeks | 13.62 | 1.46 lb | 34.6 | 660 |
| 26 weeks | 14.02 | 1.68 lb | 35.6 | 760 |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 | 1.93 lb | 36.6 | 875 |
| 28 weeks | 14. 80 80 | 2.22 lb | 37.6 | 1005 |
| 29 weeks | 15.2 | 2.54 lb | 38.6 | 1153 |
| 30 weeks | 15.71 | 2.91 lb | 39.9 | 1319 |
| 31 weeks | 16.18 | 3.31 lb | 41.1 | 1502 |
| 32 weeks | 16.19 | 3.75 lb | 42.4 | 1702 |
| 33 weeks | 17.20 | 4.23 lb | 43.7 | 1918 |
| 34 weeks | 17.72 | 4.73 lb | 45 | 2146 |
| 35 weeks | 18.19 | 5.25 lb | 46.2 | 2383 |
| 36 weeks | 18.66 | 5.78 lb | 47.4 | 2622 |
| 37 weeks | 19.13 | 6.30 lb | 48.6 | 2859 |
| 38 weeks | 19.61 | 6.80 lb | 49.8 | 3083 |
| 39 weeks | 19.96 | 7.25 lb | 50.7 | 3288 |
| 40 weeks | 20. 16 16 | 7.63 lb | 51.2 | 3462 |
| 41 weeks | 20.35 | 7.93 lb | 51.7 | 3597 |
| 42 weeks | 20.28 | 8.12 lb | 51.5 | 3685 |
| 43 weeks | 20.20 | 8.19 lb | 51.3 | 3717 |
English
Fetus size by week: Your baby's weight throughout pregnancy
Find out how big your baby is during each week of their development with our fetal growth chart. From early in pregnancy, babies grow at different rates, so your baby's actual size by week may vary substantially – but look how they grow! At 20 weeks your baby may be just over 10 inches long and weigh less than 12 ounces, but by 32 weeks they'll reach almost 17 inches and top 4 pounds. At 33 weeks they may be over 17 inches and closer to 5 pounds, and by 37 weeks they'll reach 19 inches and about 6.5 pounds.
How do you determine fetus size by week?
There are different methods for estimating how big a fetus is, which is why you'll find different numbers depending on the source.
Experts have formulas they use to come up with the estimated fetal weight (EFW) and height of a fetus, and the formulas aren't always the same. The measurements that are used in equations to estimate weight usually include biparietal (head) diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC) and femur (thigh bone) length (FL).
Height is a straightforward measurement, but the method of measuring it changes after the first trimester. For the first 13 weeks, the height measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's bottom. After the first 13 weeks, the measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's heel – explaining why, on the chart below, your baby appears to grow 3 inches from week 13 to week 14!
Hadlock, the main source we use in our fetal growth chart, provides one of the most commonly used – and most accurate – equations for estimating fetal height and weight. The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) and the Society for Maternal and Fetal Medicine (SMFM) use Hadlock's figures to diagnose and manage fetal growth conditions, such as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).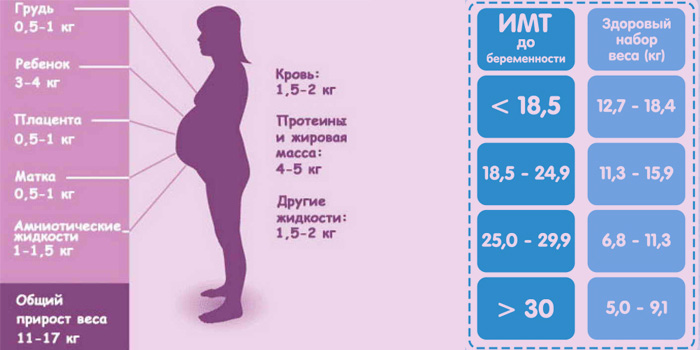
The numbers on our chart should coincide with the numbers your healthcare provider will be checking against when they measure your baby using ultrasound. (Providers don't measure height after 13 weeks, however, so don't expect to get those numbers at your ultrasound appointments.)
Note that the data used by Hadlock was gathered from middle-class Caucasian women with no history of maternal diseases known to affect fetal growth and no evidence of congenital anomalies. Your provider may make adjustments based on your individual circumstances.
Fetal growth chart
Wondering how big your baby is during each week of pregnancy? The numbers in our chart below can give you a sense of your baby's size. Keep in mind that your baby may be much smaller or larger than these averages. That's okay – after all, healthy babies can weigh less than 5 pounds or more than 9 pounds at birth.
Boy's measurements are different than girl's measurements, even this early. For the numbers on our chart, we've taken an average of boys and girls. And remember, the height measurements up to 13 weeks are head-to-bottom estimates, while the height measurements starting at week 14 are head-to-toe estimates.
And remember, the height measurements up to 13 weeks are head-to-bottom estimates, while the height measurements starting at week 14 are head-to-toe estimates.
| Gestational age | Length (US) | Weight (US) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (head to bottom) | (head to bottom) | |||
| 8 weeks | 0.62 inches | 0.71 ounces | 1.57 cm | 20 grams |
| 9 weeks | 0.91 inches | 0.95 ounces | 2.30 cm | 27 grams |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 inch | 1.23 ounces | 3.1 cm | 35 grams |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 inch | 1.59 ounces | 4.1 cm | 45 grams |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 inches | 2.05 ounces | 5.4 cm | 58 grams |
| 13 weeks | 2. 64 inches 64 inches | 2.58 ounces | 6.7 cm | 73 grams |
| (head to toe) | (head to toe) | |||
| 14 weeks | 5.79 inches | (head to toe)3.28 ounces | 14.7cm | 93 grams |
| 15 weeks | 6.57 inches | 4.13 ounces | 16.7 cm | 117 grams |
| 16 weeks | 7.32 inches | 5.15 ounces | 18.6 cm | 146 grams |
| 17 weeks | 8.03 inches | 6.38 ounces | 20.4 cm | 181 grams |
| 18 weeks | 8.74 inches | 7.87 ounces | 22.2 cm | 223 grams |
| 19 weeks | 9.45 inches | 9.63 ounces | 24.0 cm | 273 grams |
| 20 weeks | 10.12 inches | 11.68 ounces | 25.7 cm | 331 grams |
| 21 weeks | 10.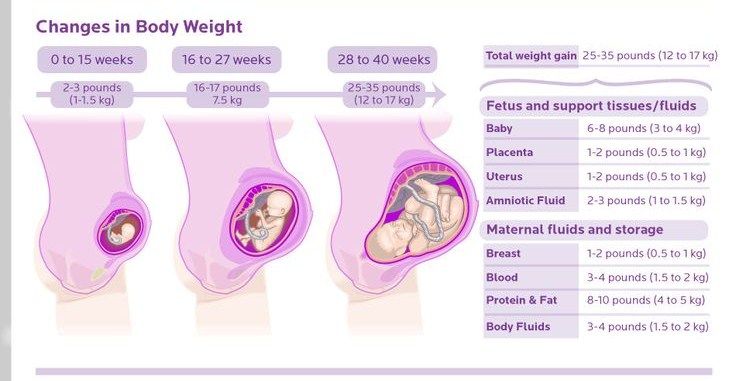 79 inches 79 inches | 14.07 ounces | 27.4 cm | 399 grams |
| 22 weeks | 11.42 inches | 1.05 pounds | 29.0 cm | 478 grams |
| 23 weeks | 12.05 inches | 1.25 pounds | 30.6 cm | 568 grams |
| 24 weeks | 12.68 inches | 1.48 pounds | 32.2 cm | 670 grams |
| 25 weeks | 13.27 inches | 1.73 pounds | 33.7 cm | 785 grams |
| 26 weeks | 13.82 inches | 2.01 pounds | 35.1 cm | 913 grams |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 inches | 2.33 pounds | 36.6 cm | 1055 grams |
| 28 weeks | 14.80 inches | 2.67 pounds | 37.6 cm | 1210 grams |
| 29 weeks | 15.47 inches | 3.04 pounds | 39.3 cm | 1379 grams |
| 30 weeks | 15. 95 inches 95 inches | 3.44 pounds | 40.5 cm | 1559 grams |
| 31 weeks | 16.46 inches | 3.86 pounds | 41.8 cm | 1751 grams |
| 32 weeks | 16.93 inches | 4.30 pounds | 43.0 cm | 1953 grams |
| 33 weeks | 17.36 inches | 4.77 pounds | 44.1 cm | 2162 grams |
| 34 weeks | 17.84 inches | 5.24 pounds | 45.3 cm | 2377 grams |
| 35 weeks | 18.23 inches | 5.72 pounds | 46.3 cm | 2595 grams |
| 36 weeks | 18.62 inches | 6.20 pounds | 47.3 cm | 2813 grams |
| 37 weeks | 19.02 inches | 6.68 pounds | 48.3 cm | 3028 grams |
| 38 weeks | 19.41 inches | 7.13 pounds | 49.3 cm | 3236 grams |
| 39 weeks | 19. 72 inches 72 inches | 7.57 pounds | 50.1 cm | 3435 grams |
| 40 weeks | 20.08 inches | 7.98 pounds | 51.0 cm | 3619 grams |
| 41 weeks | 20.39 inches | 8.35 pounds | 51.8 cm | 3787 grams |
Thanks to Dr. Mark Curran, maternal-fetal medicine specialist, for his help preparing this chart.
Advertisement | page continues below
Fetal weight by week: How it changes
Your baby steadily gains weight over the course of your pregnancy, but it's not always at the same rate. If you're having one baby (not twins or multiples), your baby's rate of growth accelerates until 35 weeks, then decelerates.
Here are some highlights, based on estimations:
- Up until 16 weeks, a fetus grows an average of about 19 grams per week, gradually increasing from 7 grams per week at 8 weeks to 15 grams per week at 12 weeks and 29 grams per week at 16 weeks.
- By 20 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 59 grams per week (just over 2 ounces).
- By 30 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 175 grams each week (more than 6 ounces).
- At 35 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 215 grams each week, or about 7.5 ounces. At this point their growth rate peaks.
- After 35 weeks, growth slows to about 188 grams per week, or 6.6 ounces. (Twins slow earlier, at around 28 weeks, and then average about 170 grams each week.)
- In the last few weeks of pregnancy, the growth rate continues to gradually slow to about 168 grams (a little less than 6 ounces) per week by week 40.
Using a tape measure stretched over your belly, your provider will use a fundal height measurement to check your baby's size at your prenatal visits. Beginning at about 24 weeks, the measurement in centimeters should roughly match the gestational age of your baby. If you're 26 weeks pregnant, for example, your fundal height should be about 26 cm, give or take a centimeter in each direction.
If your provider is concerned that your baby is too small, they'll monitor your baby's size with ultrasound, which is more accurate. Using ultrasound, your practitioner can take various measurements (head circumference and diameter, abdomen circumference, femur length) and use them to estimate your baby's size. They may also use a Doppler ultrasound to look at the blood flow to your placenta.
If your baby's estimated weight is less than the 10th percentile for their gestational age, they may be diagnosed with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), also called fetal growth restriction (FGR). IUGR can happen at any time during pregnancy. Some babies with IUGR just turn out to be small for their age, but sometimes there's a problem that's preventing the baby from growing properly.
At birth, a baby with IUGR is called "small for gestational age." While most SGA babies who are otherwise healthy grow just fine, some (especially those born prematurely) are at higher risk of problems such as c-section, jaundice, low blood sugar, and even long-term developmental and health problems.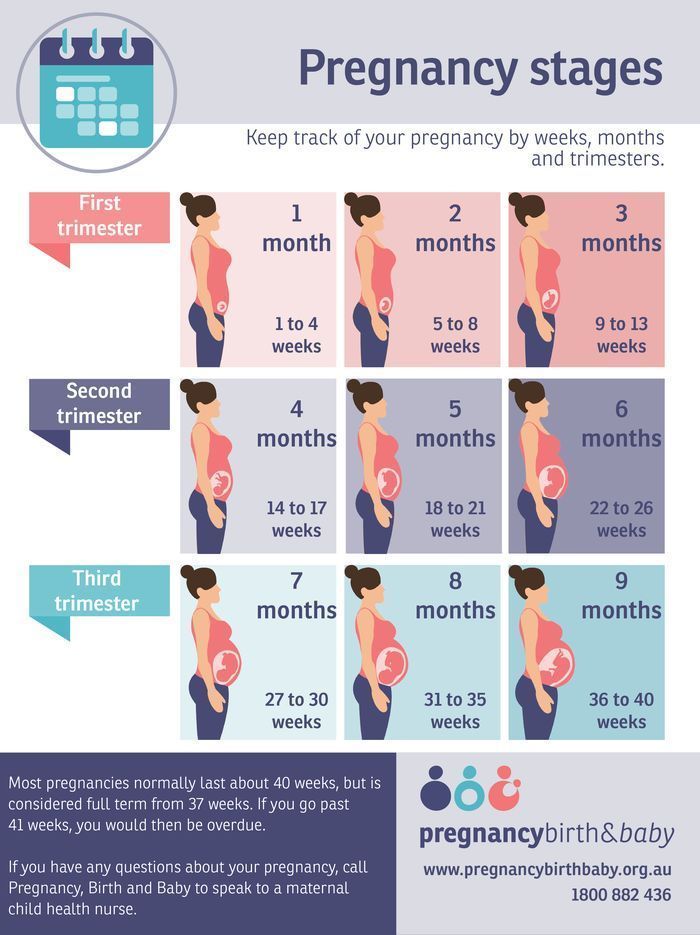
Your baby's size by week
Here are some highlights of your baby's growth during pregnancy:
At 20 weeks, about the midpoint in your pregnancy, your baby is transmitting taste signals to their brain. And you may feel them hiccupping. Your baby's weight at 20 weeks is about 11.68 ounces, and they're about the length of a (10.12-inch) banana.
At 32 weeks, your baby's lungs are developing fast, and your baby's storing minerals like iron for their first 6 months of life. Your baby's weight at 32 weeks is 4.30 pounds, and their length is 16.93 inches, about the size of a jicama.
At 33 weeks, things are getting snug in there! Your baby's skin is becoming less wrinkled as they fill in – your baby's weight at 33 weeks is about 4.77 pounds. At 17.36 inches, your baby is now about the size of a pineapple.
At 37 weeks, your baby's brain and lungs are still maturing, and they're still moving a lot, despite the close quarters. Your baby's weight at 37 weeks is about 6. 68 pounds, and they're about the length of a bunch of Swiss chard, 19.02 inches.
68 pounds, and they're about the length of a bunch of Swiss chard, 19.02 inches.
Once your baby is born, they'll be weighed and measured, and your provider will continue to monitor their growth. While the average newborn weight is a little over 7 pounds, most newborns lose about 5 to 10 percent of their weight in the first days. No worries – they gain it back by the time they're about 2 weeks old, and by 4 months they usually double their birth weight.
Learn more:
- To-do lists for the first, second, and third trimesters
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- How to understand pregnancy weeks, months, and trimesters
6 month pregnant { 21 - 24 weeks }
The sixth month of pregnancy is the month of movement. It is one of the most calm and pleasant periods of waiting for a baby. The tummy is rounded and you are already moving smoother and slower. What changes await mom and baby in each of the weeks?
A baby at 21 weeks pregnant is already half its height at birth. His weight reached 600 g, and his height was 28-30 cm. In comparison, the baby is already the size of a carrot.
His weight reached 600 g, and his height was 28-30 cm. In comparison, the baby is already the size of a carrot.
21 weeks pregnant: what happens to the baby?
The baby's muscles and skeleton are rapidly developing, subcutaneous fat is just beginning to form in a thin layer, the skin has become flesh-colored.
Movements become more frequent at 21 weeks of pregnancy. The kid moves all the time, he can unbend and bend his limbs, change his position several times a day, make turns and somersaults. Since the child is not yet strong enough, he cannot be in motion for a long time and sleeps about 20 hours a day.
21 weeks of pregnancy: the physical and emotional state of the mother
The belly of the expectant mother at 21 weeks of pregnancy noticeably increases and continues to grow. Due to such changes, stretch marks may appear. Of course, it all depends on individual characteristics, but the formation of stretch marks is inevitable due to a sharp increase in volume.
Since the fetus is growing rapidly, there is pressure on the internal organs and bones of the pelvis, because of which the woman's lower back aches and pulls her lower abdomen. Perhaps this is the most unpleasant moment of the 21st week.
The emotional state of a woman during this period improves, headaches are less and less painful. The focus of attention from career, friends and even family is shifting towards the baby. The most important thing is what happens inside - the development of the baby.
Expectant mother is looking forward to the birth of her baby and is even more nervous, because of this emotional stress and anxiety grows.
21 weeks of pregnancy: tests and ultrasound
Scheduled ultrasound at this time allows you to assess the condition of the mother and the development of the child, track his activity and exclude all sorts of abnormalities and diseases.
Doctors measure chest, abdomen, head, limb length and body proportions at the second screening. More precisely, you can view the baby's organs, body structure and parts of the heart. Also, during an ultrasound scan, the woman's uterus is examined for possible deviations.
More precisely, you can view the baby's organs, body structure and parts of the heart. Also, during an ultrasound scan, the woman's uterus is examined for possible deviations.
Nowadays, ultrasound has become more than just an examination. In the Ivimed Medical Center, fathers are allowed to be present, observe the movements of the baby and even get a picture and video of an ultrasound scan. It is during the screening for 21 weeks that you can find out the sex of the baby, if desired. Moreover, we can already see in the outlines of the face of the fetus a resemblance to one of the parents.
21 weeks of pregnancy: tips
Experts give some tips for expectant mothers at 21 weeks of pregnancy to improve well-being, pregnancy and baby development:
- Talk to your child, read books or tell him stories.
- Avoid overexertion, do not carry heavy.
- Walk and do relaxation exercises.
- Attend courses for expectant mothers.
The fetus becomes an exact copy of a newborn baby, at the twenty-second week. By this time, the child will reach 31 centimeters in height and 730 grams in weight, which can be compared to the size of a zucchini.
By this time, the child will reach 31 centimeters in height and 730 grams in weight, which can be compared to the size of a zucchini.
22 weeks of pregnancy: fetal development
The baby's brain at this time has an absolute set of neurons, the number of which does not change throughout life. The vestibular apparatus and fetal coordination develop.
The child can already suck his thumb, move his head to the right and left. Increasingly, he unbends his arms and legs, feels the position of his own body in space.
22nd week of pregnancy: sensations of the expectant mother
22nd week of pregnancy, movements are the main sensations. Mom's belly is getting rounder every week. The uterus creates pressure on the bladder, as a result of which you often want to go to the ladies' room.
The expectant mother's breast becomes more sensitive, which causes some discomfort. Another of the less pleasant changes of the 22nd week of pregnancy is swelling. Most of all, excess fluid accumulates in the arms and legs.
Most of all, excess fluid accumulates in the arms and legs.
The feeling of a woman at this time is really special, because the baby can make about 200 movements per day, thanks to the free space in the uterus.
22nd week of pregnancy: examinations of mother and child
Ultrasound at 22nd week of pregnancy may be scheduled by a gynecologist. As before, this procedure allows you to examine the condition of the mother and fetus for the occurrence of various pathologies and evaluate the work of the internal organs formed by this period.
A very important procedure for the 22nd week is a scheduled visit to the gynecologist. At the appointment, the doctor measures the stomach and pressure, listens to the baby's heart. In this way, the health of mother and child can be better assessed.
Required tests to be done:
- hCG test (human chorionic gonadotropin)
- estriol hormone test
- alpha-fetoprotein test
- blood sugar test
22nd week of pregnancy: mom's nutrition
During pregnancy, every woman has faced quirks of food preferences.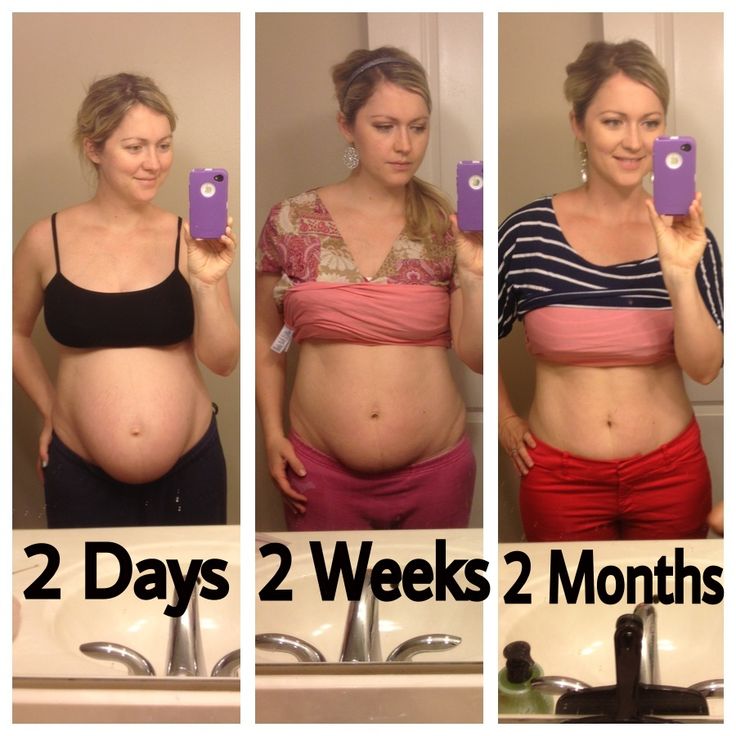
Nutrition at the 22nd week of pregnancy must necessarily include lean meat and fish. Every day, the expectant mother should eat dairy products with probiotics that help beneficial microflora.
The child's skeletal system is strengthened and he takes calcium from the mother's body intensively. Therefore, it is important to include the following foods in your diet:
- almonds
- beans
- spinach
You should also eat foods with folic acid:
- egg white
- pork
- cabbage
- linseed oil
Of course, you really want something harmful, starchy and sweet, but you should give it up, as this can lead to weight gain.
It is recommended that you consult your doctor about prenatal vitamins to ensure that your baby is getting enough nutrition.
22nd week of pregnancy: doctor's advice
Twenty-second week of pregnancy, you can already be called an "experienced pregnant", because you know all the manifestations and all the features of this wonderful period.
Doctors recommend the following:
- Talk to your baby. The child can already hear and respond to your voice.
- Get enough sleep. It is advisable to use a pregnancy pillow and sleep on a hard surface.
- Wear comfortable shoes and clothing.
- Monitor your own weight and blood pressure. Eat a healthy diet and get outdoors more.
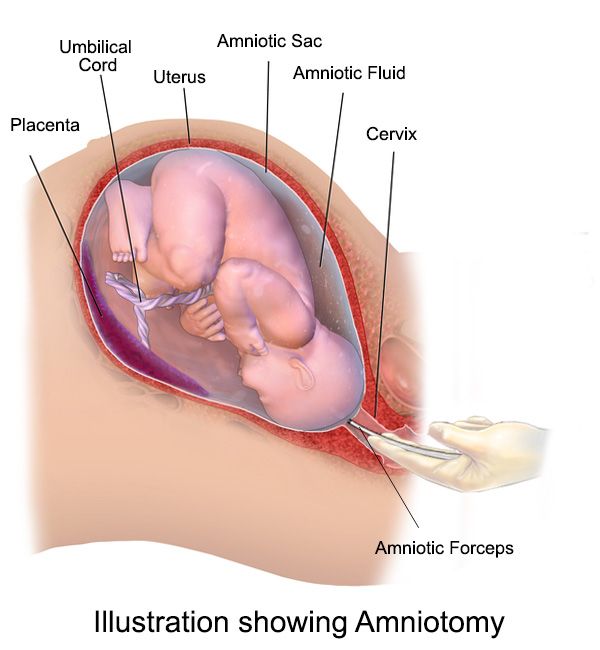
23rd week of pregnancy - week of dreams. Scientists have proven that the fetus can already dream. Also, the baby is developing rapidly, pulling the umbilical cord, feeling his face and body, and even sometimes swallowing amniotic fluid.
23rd week of pregnancy: what happens to the baby?
The baby has already grown so much that on ultrasound you can see how the main features of the face have formed, the contours of the nose and chin are clearly outlined, it is clearly visible which of the parents is more similar.
By this period, the baby reaches 32.4 cm in height and 840 g in weight. which can be compared with the size of an eggplant.
which can be compared with the size of an eggplant.
23rd week of pregnancy: changes in the mother's body
The week of well-being and calmness is the twenty-third week of pregnancy. Toxicosis is already behind, now the new sensations of the mother are frequent and pronounced movements of the child.
The belly at 23 weeks pregnant is not yet big enough to cause discomfort. But at this time, not entirely pleasant sensations may occur, such as: heartburn, fatigue and headaches. Varicose veins in the legs and increased swelling are also possible.
23rd week of pregnancy: fetal movement
The baby can already push off the walls of the uterus and often kicks.
Due to the ingestion of amniotic fluid, the baby may experience hiccups, from which the woman will feel rhythmic shudders inside.
At the 23rd week of pregnancy, the baby still has enough space in the mother's womb to turn over, so he constantly changes his position. A woman pregnant with twins can only be envied, since the children at this time are very active and both kick their mother diligently.
Doctors offer the expectant mother to count the number of movements of the baby, normally 10-15 times a day.
23 weeks of pregnancy: possible problems
The uterus increases in size at 23 weeks of gestation. As a result, it begins to put pressure on all nearby organs, which can cause digestive problems, heartburn, constipation, sometimes nausea and even vomiting. Also, due to the enlargement of the uterus, a woman wants to go to the toilet more often, as it has had an effect on the bladder.
Stretch marks on the skin may continue to appear as the belly grows rapidly. They occur due to the fact that the skin loses elasticity due to a decrease in the amount of collagen and elastin.
Another possible problem at week 23 may be pain in the lumbar region, in the legs and headache.
23rd week of pregnancy: ultrasound diagnostics
At the 23rd week of pregnancy, ultrasound is not planned. The doctor may prescribe it as needed or if you have not had it for some reason before.
Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics at the above time, it is possible to determine the weight and size of the fetus, the condition of the placenta, the location of the baby and its development.
If the baby is positioned with the legs towards your pelvis, don't worry, because the baby takes the correct position only by 33 weeks.
23rd week of pregnancy: tips
Each week, such a wonderful period for a woman, passes in a special way.
Specialists highlight useful tips for week 23:
- Watch your diet, eat less flour and fried foods, as weight gain is inevitable at the 23rd week of pregnancy.
- Visit a doctor in a timely manner, take all tests and undergo diagnostics.
- Try to stretch regularly before bed.
- Sleep is the key to good health. If you feel tired and want to sleep, sleep.
Twenty-fourth week of pregnancy - the weight of the child is already 735 g, height -30-32 cm. Now the baby is the size of a corn.
24th week of pregnancy: Your baby's size
At this time, the baby's skin remains wrinkled, and the arms and legs are still thin. The number of muscle fibers is already noticeably increased. Now the child is an exact copy of a newborn, with clear outlines. He already even has fluff, soft nails and cilia.
The movements of the child become distinct, not as impulsive as before, due to the fact that he already occupies the entire uterine cavity.
24 weeks pregnant: how does a woman feel?
Your belly at 24 weeks of pregnancy continues to grow, you become less and less agile at night. It's getting harder for you to bend over and breathe.
The expectant mother may notice an increase in weight of 6-7 kilograms, which is the norm at this time. But this affects your well-being - feelings of fatigue and drowsiness, and also pulls the lower back.
The baby still sleeps most of the time, but you definitely won't miss his activity. Somersaults, flips, kicks - this is what the baby loves.
24th week of pregnancy: examination
The expectant mother can take a break from constant tests and examinations at the twenty-fourth week. All you have to do is complete a urinalysis and a glucose tolerance test.
Discharge at 24 weeks pregnant should be colorless and scanty. If you notice a brown or scarlet tint, an unpleasant odor, a watery discharge and painful sensations, contact your doctor immediately!
In any case, if you are concerned about any pain, discharge and unknown sensations, consult a specialist, this is important for you and your baby.
24 weeks pregnant: diet
You may suffer from heartburn and occasionally nausea. Therefore, fried, fatty and spicy should be excluded from the diet.
During the period when a child develops vision and hearing, it is important for a woman to eat foods containing vitamin A, such as:
- carrots
- cabbage
- yellow pepper
Remember to eat often, but in small portions. The baby is growing and requires more nutrients. The diet of the expectant mother should be healthy and balanced.
The baby is growing and requires more nutrients. The diet of the expectant mother should be healthy and balanced.
24 weeks pregnant: what is important to know?
- Do not sleep on your back. The fetus is no longer small and presses on the internal organs, which leads to heartburn, fainting, and increased heart rate. Your sleeping position is now on your side.
- The development of the child is rapidly gaining momentum, it is very important to eat right, get enough vitamins.
- Don't forget about skin care. Use special creams, drink enough water and take contrast showers to avoid stretch marks.
- At 24 weeks, you can start wearing a brace that distributes the load on the spine.
- You may feel contractions. Do not be afraid and worry, these are the so-called “training contractions”, they prepare the body for childbirth. You should consult a doctor if the contractions become regular and painful.
Would you like to book an appointment for
?
what is happening, development of pregnancy and fetus
Week by week
25 - 28 weeks pregnant
Elena Gevorkova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
25th week
BABY
The weight of the fetus at this time is 700-750 g, and the body length is 30-32 cm. cheeks, eyelids, eyebrows, nose. The auricles are pressed to the head, the cartilages are thin and soft, capillaries shine through them. The skin becomes more elastic due to the accumulation of subcutaneous fat, folds and wrinkles are gradually smoothed out.
cheeks, eyelids, eyebrows, nose. The auricles are pressed to the head, the cartilages are thin and soft, capillaries shine through them. The skin becomes more elastic due to the accumulation of subcutaneous fat, folds and wrinkles are gradually smoothed out.
Fetal movements distinct, rhythmic. At this time, periods of sleep and wakefulness of the baby are already being formed. Moreover, sleep has a fast and slow phase - like in adults. The intensive development of the fetal osteoarticular system continues. There is a strengthening of bones due to the accumulation of compounds of calcium, fluorine, magnesium, etc. - inorganic salts that provide strength to bone tissue.
Future MOM
The general condition of the expectant mother does not undergo significant changes compared to previous weeks. Perhaps the growing uterus somewhat restricts movement, limits the duration of walks and physical exercises. Properly selected clothes, shoes and, if necessary, a bandage can significantly change the situation and provide a woman with comfort.
If there are signs of rapid fatigue, shortness of breath, drowsiness, palpitations, then this is a reason to pay attention to the level of hemoglobin in the clinical blood test. These symptoms may indicate anemia in pregnancy. In this condition, which in everyday life is called anemia, there is a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. During pregnancy, in the vast majority of cases, we are talking about iron deficiency anemia. Iron is part of hemoglobin, a special complex protein found inside the red blood cell. Thanks to iron, hemoglobin binds oxygen and transports it from the lungs to the tissues. Oxygen is needed by every cell in the body for energy. Thus, iron deficiency leads to oxygen starvation of tissues.
Expectant mothers consume iron intensively due to the fact that the development of fetal tissues requires a large amount of energy, and therefore iron. Anemia in pregnant women can become an additional risk factor for the development of many complications: late toxicosis - gestosis, premature birth, impaired fetal development, etc.
Anemia during pregnancy is not an independent disease and is called physiological anemia, or anemia of pregnancy. But if the hemoglobin level drops to low values, then the appointment of iron supplements is quite justified. Anemia in pregnancy can be completely asymptomatic, so it is extremely important to take all tests in a timely manner to keep the situation under control.
26th week
BABY
The height of the fetus at this period is 32-34 cm, and the weight reaches 850-900 g. there is an opportunity to survive. Of course, it is worth noting that such chances are small and the viability of the child, which is determined by his individual adaptive capabilities and the availability of special equipment, is of great importance.
At this time, maturation of lung tissue occurs - the most important process in the formation of the respiratory system. The smallest vesicles of the lung tissue - the alveoli in the prenatal period are in a collapsed state. The first breath after birth expands the lung tissue. When air enters the lungs, it is extremely important that the alveoli straighten out and retain just such a rounded shape - like bubbles in a sponge. The inner surface of each alveolus is lined with a special substance - a surfactant. It is he who does not allow the alveolar bubbles to stick together when exhaling. If the content of surfactant is not enough, then a severe pathology occurs in a born premature baby - respiratory failure. The chances of survival in premature babies are largely determined by the quality and quantity of this most important substance - surfactant. It is worth noting that today there are drugs - analogues of surfactant, which significantly increase the chances of premature babies to recover.
The first breath after birth expands the lung tissue. When air enters the lungs, it is extremely important that the alveoli straighten out and retain just such a rounded shape - like bubbles in a sponge. The inner surface of each alveolus is lined with a special substance - a surfactant. It is he who does not allow the alveolar bubbles to stick together when exhaling. If the content of surfactant is not enough, then a severe pathology occurs in a born premature baby - respiratory failure. The chances of survival in premature babies are largely determined by the quality and quantity of this most important substance - surfactant. It is worth noting that today there are drugs - analogues of surfactant, which significantly increase the chances of premature babies to recover.
The fetal reproductive system also undergoes important developmental milestones. At this time, in boys, the testicles begin to descend into the scrotum. This process takes several weeks, and by the time of birth, the testicles should take their final place in the scrotum: this is one of the signs of a full-term baby. In girls, by the time of 26 weeks, the formation of the external genitalia and vagina is completely completed.
In girls, by the time of 26 weeks, the formation of the external genitalia and vagina is completely completed.
Future MOM
At the 26th week, the fundus of the uterus reaches 6 cm above the navel. The growth of the uterus, as a rule, is 1 cm per week. Most often, the height of the uterus corresponds to the gestational age in weeks. So, for a period of 26 weeks, the bottom of the uterus rises above the pubis - the so-called pubic symphysis - by 26 cm.
Fetal movements at this time are very active, a sufficient amount of amniotic fluid allows the baby to make a variety of movements. Sometimes they are perceived by a pregnant woman as sensitive and even painful. Internal organs: the bladder, intestines, stomach, liver - are under pressure from the growing uterus, and the additional load in the form of active tremors of the fetus can aggravate sensitivity. At such moments, you need to change your posture, lie down, choose a comfortable position. Most often, it is a change in body position that leads to relief. If such pain occurs frequently, several times a day and does not go away within an hour, then you need to tell your doctor about it.
If such pain occurs frequently, several times a day and does not go away within an hour, then you need to tell your doctor about it.
27th week
BABY
The weight of the fetus at the 27th week is about 900-1000 g, and the height reaches 34 cm. This happens due to an increase in muscle mass and daily training: all this helps the fetus prepare for childbirth, because the movements of the limbs, in particular the straightening of the legs, play a big role when passing through the mother's birth canal.
At this time, important events take place in the organs of the endocrine system of the fetus: in his brain, namely in a small gland - the pituitary gland, growth hormone - somatotropin begins to be produced. This hormone regulates metabolic processes in cells, stimulates the growth of the body, and the baby noticeably stretches in length.
Most of the endocrine glands of the fetus are already formed, but from 27 weeks there is a significant increase in the activity of the endocrine system. So, the thyroid gland begins to produce three main hormones - thyroxine, triiodothyronine and calcitonin, which are involved in all the most important metabolic processes. These hormones regulate the activity of the brain, cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and much more. Before this period, all these hormones functioned, but the main function was performed by the mother's hormones. Now the baby's hormones provide their own needs.
So, the thyroid gland begins to produce three main hormones - thyroxine, triiodothyronine and calcitonin, which are involved in all the most important metabolic processes. These hormones regulate the activity of the brain, cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and much more. Before this period, all these hormones functioned, but the main function was performed by the mother's hormones. Now the baby's hormones provide their own needs.
All this determines the most important stage in the formation of the fetus's own type of metabolism. Features of the immune system, the constitution, reactions to stress, adaptability - all these specific individual reactions are laid precisely at this stage of pregnancy and are closely related to the beginning of the "independent" life of the organs of the endocrine system of the fetus.
Future MOM
Pregnant women often notice an improvement in their well-being at this time, and this is also due to the peculiarities of the endocrine system of the fetus. The mother's thyroid gland stops working "for two", which significantly improves the mother's condition if before this period there were problems with hormonal regulation.
The mother's thyroid gland stops working "for two", which significantly improves the mother's condition if before this period there were problems with hormonal regulation.
Around 27-28 weeks, many pregnant women begin to experience unusual sensations that were not there before, such as tingling in the arms and legs, a feeling of “goosebumps”, changes in sensitivity. The most common manifestations of this kind also include spasms in the muscles of the legs - cramps. Painful spasms most often occur in the calf muscles in the evening or at night and last for several minutes. These ailments are associated with a change in the metabolism of magnesium and potassium in the muscles, as well as with the peculiarity of blood circulation during pregnancy. The blood flow in the small vessels of peripheral organs - in the arms and legs - often suffers in expectant mothers. These phenomena are not a pathology, most often do not require serious treatment and disappear after childbirth.
In addition to the peculiarities of blood circulation, convulsions can be provoked by a number of other reasons - varicose veins of the legs, lack of electrolytes in the blood - calcium or magnesium, pressure of large veins in the uterus, etc. When such symptoms appear, it is necessary to change the position of the body, slowly bend the leg at the knee, lifting it up. You can rub the painful area of the skin or apply a towel dipped in cold water to it.
When such symptoms appear, it is necessary to change the position of the body, slowly bend the leg at the knee, lifting it up. You can rub the painful area of the skin or apply a towel dipped in cold water to it.
During the visit to the doctor, it is necessary to tell him about such problems: this may require additional examination or treatment.
28th week
BABY
By the end of 28 weeks, the baby has a height of 35 cm, and its weight reaches 1100-1200 g. The body of the fetus becomes more and more rounded, subcutaneous tissue accumulates. The fluffy hairs covering the entire body of the baby begin to fall out slowly and remain in small quantities in the area of the shoulders, back and lower back. Hair on the head, eyebrows and cilia darken, which gives the fetus a more "adult" appearance. From 28 weeks, the baby often opens his eyes, blinks his eyelids. His auditory organs are actively improved.
Expectant MOM
The height of the uterine fundus by this time reaches 28 cm above the level of the pubic articulation. Weight gain can be 7-10 kg, depending on the initial body weight.
Weight gain can be 7-10 kg, depending on the initial body weight.
In the case of a multiple pregnancy from 28 weeks, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued - maternity leave.
A period of 28 weeks is significant for pregnant women with Rh-negative blood. Rh-conflict is a pathological condition that occurs when a combination of an Rh-negative mother and an Rh-positive fetus. The Rh factor is a protein located on the surface of the red blood cell. In its presence, people belong to the Rh-positive group, in its absence - to the Rh-negative group. If the blood of a Rh-positive person enters the blood of an Rh-negative, then the body perceives these same Rh proteins as foreign and develops a “weapon” against them - antibodies.
Damage to fetal tissues in Rhesus conflict occurs due to the fact that mother's antibodies destroy fetal red blood cells. However, for the development of the Rh conflict, a significant accumulation of antibodies in the mother's blood is necessary, which occurs only during pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus. Thus, in the first pregnancy, the risk of developing a conflict is negligible.
Thus, in the first pregnancy, the risk of developing a conflict is negligible.
It is at 28 weeks that the first administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is recommended. This is a special "vaccination" against the development of the Rhesus conflict in the future. Anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin binds fetal red blood cells and "does not allow" the mother's body to produce antibodies. Thus, the formation of the immune response is inhibited.
The second injection of immunoglobulin is carried out in the maternity hospital, in the first 72 hours after birth. A necessary condition for this vaccination is the absence of Rh antibodies in the blood of a pregnant woman: this is considered proof that there is no Rh conflict. The introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin pursues a preventive goal, i.e. prevents the occurrence of Rh-conflict in subsequent pregnancies.
If Rh antibodies are detected, then their value must be carefully monitored. An increase in antibody titers over time indicates the development of an Rhesus conflict.