Perineum itch female
Itchy Perineum: Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Itching or burning sensations in the perineal area can cause extreme discomfort that make sitting and sleeping difficult.
Potential causes range from infections to nerve damage, and sometimes the cause is unknown. Fortunately, there are many preventive and treatment approaches that can help you reduce perineal itching.
Learn what might cause an itchy perineum and how to treat it.
When should I seek medical care?
While we provide some general at-home remedies, don’t hesitate to seek medical care. A doctor can diagnose the cause, and provide targeted treatment that will clear up underlying conditions and reduce discomfort.
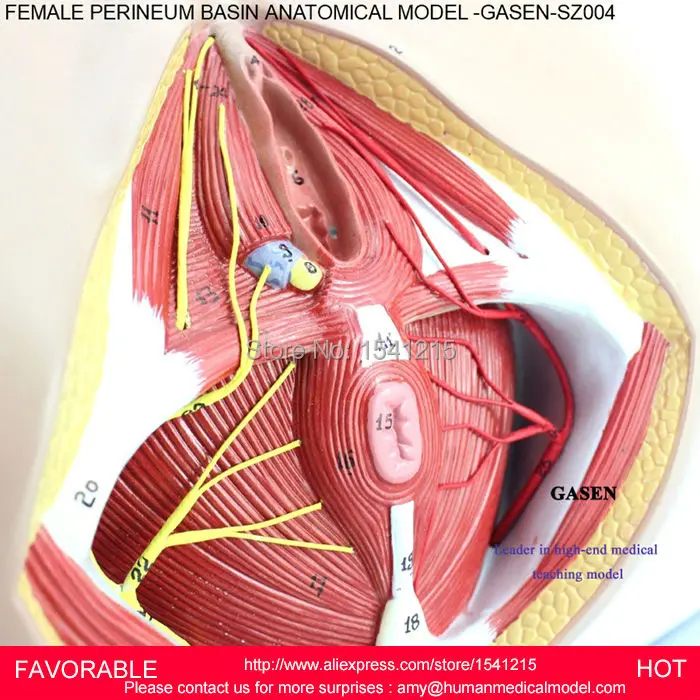
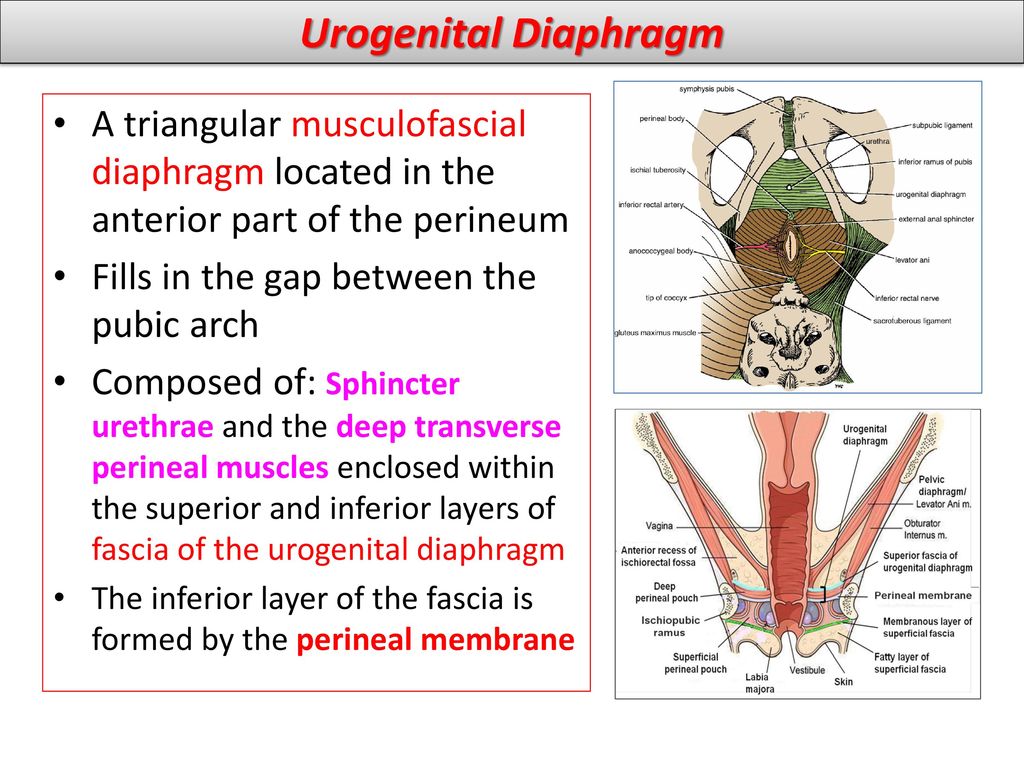
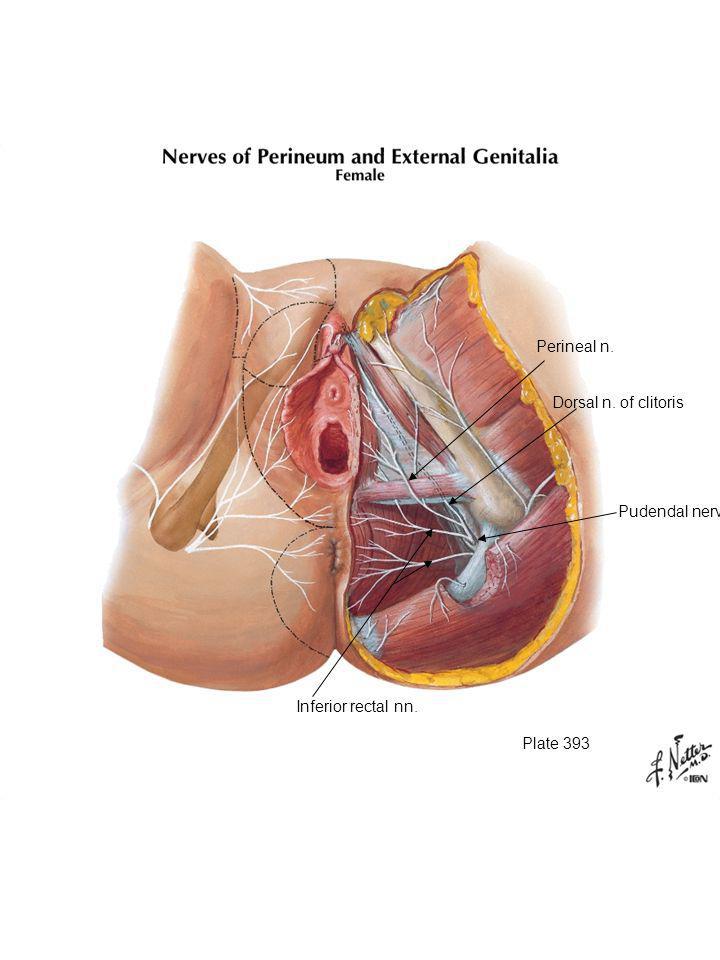
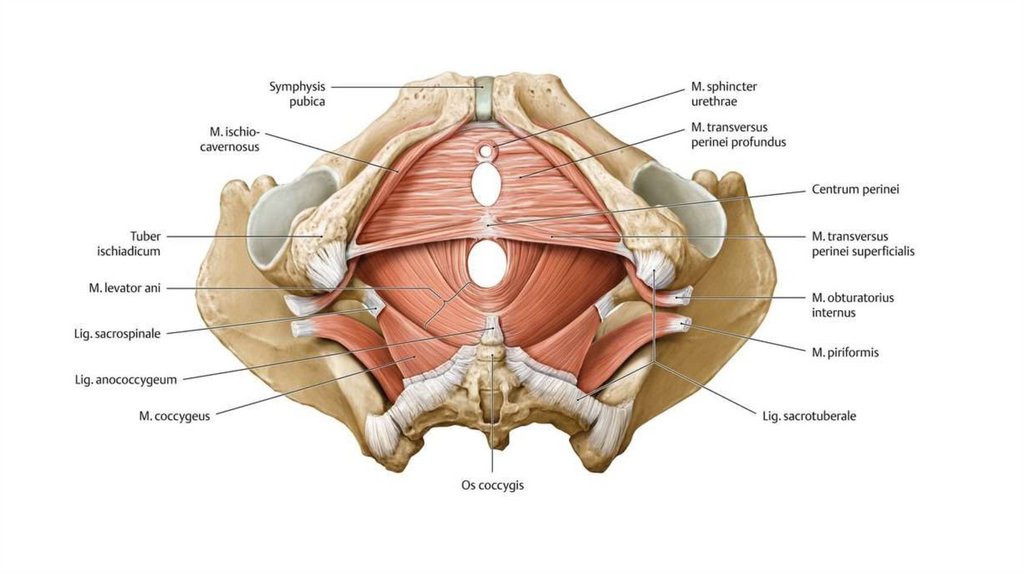
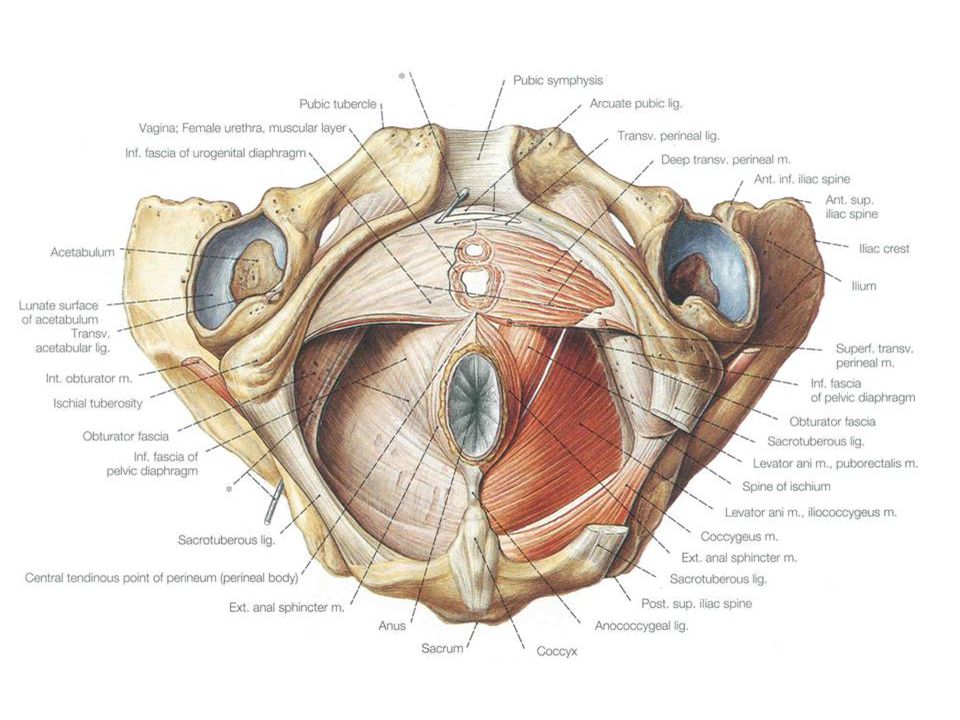
The perineum is the area of skin between the vagina and anus in women and the scrotum and anus in men.
In women, the perineum is the protective covering for the perineal muscles that work with other key muscles and ligaments to hold the pelvic organs in place. The pelvic organs include the bladder, rectum, vagina, and uterus. There are also blood vessels underneath the perineum.
In men, the perineum protects the underlying pelvic floor muscles and blood vessels as well. The perineum is also responsible for covering nerves a man’s body uses in order urinate or achieve an erection.
This area is a common source of itching and discomfort in both genders for a variety of reasons, ranging from skin irritation to underlying medical conditions.
Here are the common causes of burning or itching in the perineum.
Pruritus ani
Pruritus ani is a condition that can occur in both genders, but is most common in men. The condition causes an itching sensation in the anal area that can be an acute or chronic occurrence.
Acute pruritus (itching) may be due to contact dermatitis, such as from a new laundry detergent or soap, or from fungal or bacterial infections. Waxing burns and shaving injuries can also cause the condition.
Chronic pruritus ani in men can have many causes. These include atopic dermatitis, diabetes, basal cell carcinomas, and other causes.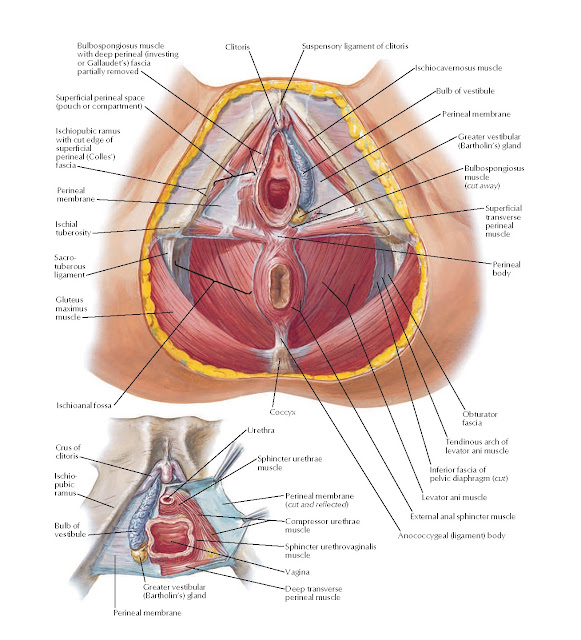 Sometimes, the cause is idiopathic, meaning a doctor can’t identify the underlying cause.
Sometimes, the cause is idiopathic, meaning a doctor can’t identify the underlying cause.
Sexually transmitted infection
Itching around the anal and perineal area can be a sexually transmitted infection (STI) symptom. Conditions that can cause this symptom include:
- anal herpes
- anal warts
- gonorrhea
- pubic lice
These conditions don’t always cause symptoms you can easily see. For this reason, it’s a good idea to see a doctor.
A doctor can perform a physical examination and testing to determine the most likely cause. Treatment is available for each condition that can reduce your symptoms and the likelihood of passing the condition on to a partner.
Straddle injuries
Straddle injuries are those that occur from experiencing trauma to areas between the thighs, including the perineum. This may occur from falling on a bicycle crossbar, fence, gym equipment, or bathtub’s edge.
This injury type can cause burning in the perineum due to nerve damage or swelling in the area that affects nerves.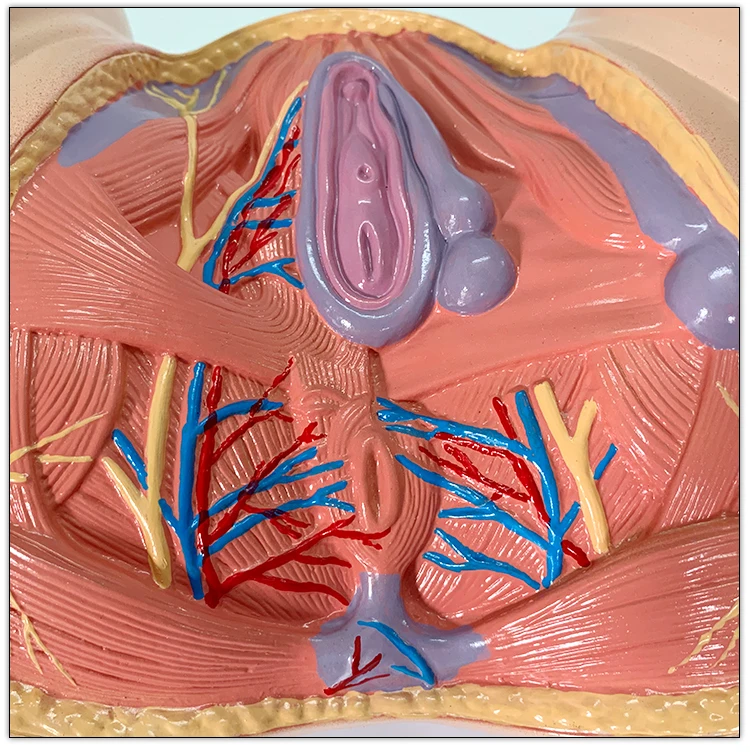 Ideally, this injury and its symptoms will resolve with 2 to 3 days of rest, cold compresses to the affected areas, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers.
Ideally, this injury and its symptoms will resolve with 2 to 3 days of rest, cold compresses to the affected areas, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers.
Causes affecting women
Some perineal itching and pain may specifically affect women. Examples of these include:
- Post-episiotomy/tear pain. An episiotomy is a surgical cut made to facilitate childbirth if the vaginal opening is not large enough. Some women who undergo an episiotomy or tear after childbirth can experience nerve damage, pelvic floor disorders, and problems passing stool, especially immediately after giving birth. These can affect the perineum, leading to itching or burning during the healing process.
- Yeast infections. Women are especially vulnerable to yeast infections, which is an overgrowth of the fungus Candida. Symptoms include vaginal itching that can extend to the perineal area, pain during sex, and pain upon urination. Doctors can treat yeast infections through prescribing oral or topical anti-fungal medications.

- Hormone-related tissue thinning. As a woman enters menopause, the natural estrogen decline can lead to thinning tissue in the vagina and perineal area. This may make the area more vulnerable to itching.
These are just some examples of common perineal itching or burning causes affecting women. If you’re concerned you may have another related condition, contact your doctor.
Causes affecting men
Some causes of perineal burning and itching may affect men specifically. These include:
- Surgical history. If a man has had surgery, such as to remove the prostate or repair a urethral stricture, his surgeon may have cut the perineum to access key areas. This can lead to itching and burning if the surgery damaged nerves in the process.
- Fournier’s gangrene. Although a rare occurrence, this serious infection occurs in the male genital region, including the perineum. The condition can result from trauma, surgical history, or as an after-effect of another infection (such as a urinary tract infection).
Chronic bicycle, motorcycle, or horseback riding can also cause chronic damage to the perineal nerves.
If doctors can identify the underlying cause of itching in the perineum, they’ll direct their treatments accordingly. However, sometimes a doctor can’t determine a specific underlying cause. When this is the case, some of the general treatments include:
- Take an over-the-counter antihistamine (such as Benadryl), especially at night when itching tends to worsen.
- Apply cool compresses to the perineal area to soothe burning sensations.
- Apply emollient or barrier creams to the anal area to protect against irritation from stool or urine. Examples include petroleum ointments or a zinc oxide ointment.
- Wear clean, breathable underwear washed in a gentle, nonirritating soap.
Sometimes, a doctor will prescribe medications in addition to recommending antihistamines as a way to break the itch-and-scratch cycle that can keep a person up at night.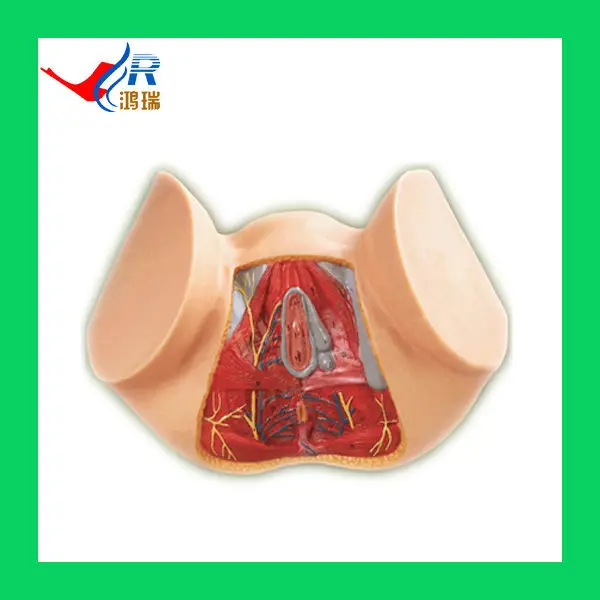 Examples of these medications may include gabapentin and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Examples of these medications may include gabapentin and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
A note about topical steroids
When you have an itchy perineum, it’s natural to contemplate treating the itch with topical corticosteroids. These anti-itch creams can work well on other parts of the body, but applying them to the perineum isn’t the best choice. Steroid itch creams can have a skin-thinning effect, which could worsen symptoms or create new ones.
For this reason, don’t apply steroid creams to the perineal area unless your doctor recommends it.
While it’s not always possible to prevent itching in the perineum, there are some steps you can take to reduce the likelihood that itching will occur. These include:
- Avoid vigorous rubbing when cleansing the anal area after having a bowel movement.
- Change underwear immediately after exercising to reduce sweat irritation of the perineal area.
- Eat a high-fiber diet and drink plenty of water to reduce the incidences of constipation.

- Refrain from using hot water when taking a bath or shower.
- Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to clean the genital area.
Ask your doctor if there are specific preventive approaches you can take given the underlying cause of your perineal discomfort.
Perineal itching may be an uncomfortable topic to talk about, but it’s often more uncomfortable to experience.
If preventive methods or at-home treatments haven’t helped (or you’re worried you have an infection), talk to a doctor. They can help determine potential causes and help you feel more comfortable.
Itchy Perineum: Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Itching or burning sensations in the perineal area can cause extreme discomfort that make sitting and sleeping difficult.
Potential causes range from infections to nerve damage, and sometimes the cause is unknown. Fortunately, there are many preventive and treatment approaches that can help you reduce perineal itching.
Learn what might cause an itchy perineum and how to treat it.
When should I seek medical care?
While we provide some general at-home remedies, don’t hesitate to seek medical care. A doctor can diagnose the cause, and provide targeted treatment that will clear up underlying conditions and reduce discomfort.
The perineum is the area of skin between the vagina and anus in women and the scrotum and anus in men.
In women, the perineum is the protective covering for the perineal muscles that work with other key muscles and ligaments to hold the pelvic organs in place. The pelvic organs include the bladder, rectum, vagina, and uterus. There are also blood vessels underneath the perineum.
In men, the perineum protects the underlying pelvic floor muscles and blood vessels as well. The perineum is also responsible for covering nerves a man’s body uses in order urinate or achieve an erection.
This area is a common source of itching and discomfort in both genders for a variety of reasons, ranging from skin irritation to underlying medical conditions.
Here are the common causes of burning or itching in the perineum.
Pruritus ani
Pruritus ani is a condition that can occur in both genders, but is most common in men. The condition causes an itching sensation in the anal area that can be an acute or chronic occurrence.
Acute pruritus (itching) may be due to contact dermatitis, such as from a new laundry detergent or soap, or from fungal or bacterial infections. Waxing burns and shaving injuries can also cause the condition.
Chronic pruritus ani in men can have many causes. These include atopic dermatitis, diabetes, basal cell carcinomas, and other causes. Sometimes, the cause is idiopathic, meaning a doctor can’t identify the underlying cause.
Sexually transmitted infection
Itching around the anal and perineal area can be a sexually transmitted infection (STI) symptom. Conditions that can cause this symptom include:
- anal herpes
- anal warts
- gonorrhea
- pubic lice
These conditions don’t always cause symptoms you can easily see. For this reason, it’s a good idea to see a doctor.
For this reason, it’s a good idea to see a doctor.
A doctor can perform a physical examination and testing to determine the most likely cause. Treatment is available for each condition that can reduce your symptoms and the likelihood of passing the condition on to a partner.
Straddle injuries
Straddle injuries are those that occur from experiencing trauma to areas between the thighs, including the perineum. This may occur from falling on a bicycle crossbar, fence, gym equipment, or bathtub’s edge.
This injury type can cause burning in the perineum due to nerve damage or swelling in the area that affects nerves. Ideally, this injury and its symptoms will resolve with 2 to 3 days of rest, cold compresses to the affected areas, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers.
Causes affecting women
Some perineal itching and pain may specifically affect women. Examples of these include:
- Post-episiotomy/tear pain. An episiotomy is a surgical cut made to facilitate childbirth if the vaginal opening is not large enough.
 Some women who undergo an episiotomy or tear after childbirth can experience nerve damage, pelvic floor disorders, and problems passing stool, especially immediately after giving birth. These can affect the perineum, leading to itching or burning during the healing process.
Some women who undergo an episiotomy or tear after childbirth can experience nerve damage, pelvic floor disorders, and problems passing stool, especially immediately after giving birth. These can affect the perineum, leading to itching or burning during the healing process. - Yeast infections. Women are especially vulnerable to yeast infections, which is an overgrowth of the fungus Candida. Symptoms include vaginal itching that can extend to the perineal area, pain during sex, and pain upon urination. Doctors can treat yeast infections through prescribing oral or topical anti-fungal medications.
- Hormone-related tissue thinning. As a woman enters menopause, the natural estrogen decline can lead to thinning tissue in the vagina and perineal area. This may make the area more vulnerable to itching.
These are just some examples of common perineal itching or burning causes affecting women. If you’re concerned you may have another related condition, contact your doctor.
Causes affecting men
Some causes of perineal burning and itching may affect men specifically. These include:
- Surgical history. If a man has had surgery, such as to remove the prostate or repair a urethral stricture, his surgeon may have cut the perineum to access key areas. This can lead to itching and burning if the surgery damaged nerves in the process.
- Fournier’s gangrene. Although a rare occurrence, this serious infection occurs in the male genital region, including the perineum. The condition can result from trauma, surgical history, or as an after-effect of another infection (such as a urinary tract infection).
Chronic bicycle, motorcycle, or horseback riding can also cause chronic damage to the perineal nerves.
If doctors can identify the underlying cause of itching in the perineum, they’ll direct their treatments accordingly. However, sometimes a doctor can’t determine a specific underlying cause. When this is the case, some of the general treatments include:
- Take an over-the-counter antihistamine (such as Benadryl), especially at night when itching tends to worsen.
- Apply cool compresses to the perineal area to soothe burning sensations.
- Apply emollient or barrier creams to the anal area to protect against irritation from stool or urine. Examples include petroleum ointments or a zinc oxide ointment.
- Wear clean, breathable underwear washed in a gentle, nonirritating soap.
Sometimes, a doctor will prescribe medications in addition to recommending antihistamines as a way to break the itch-and-scratch cycle that can keep a person up at night. Examples of these medications may include gabapentin and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
A note about topical steroids
When you have an itchy perineum, it’s natural to contemplate treating the itch with topical corticosteroids. These anti-itch creams can work well on other parts of the body, but applying them to the perineum isn’t the best choice. Steroid itch creams can have a skin-thinning effect, which could worsen symptoms or create new ones.
Steroid itch creams can have a skin-thinning effect, which could worsen symptoms or create new ones.
For this reason, don’t apply steroid creams to the perineal area unless your doctor recommends it.
While it’s not always possible to prevent itching in the perineum, there are some steps you can take to reduce the likelihood that itching will occur. These include:
- Avoid vigorous rubbing when cleansing the anal area after having a bowel movement.
- Change underwear immediately after exercising to reduce sweat irritation of the perineal area.
- Eat a high-fiber diet and drink plenty of water to reduce the incidences of constipation.
- Refrain from using hot water when taking a bath or shower.
- Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to clean the genital area.
Ask your doctor if there are specific preventive approaches you can take given the underlying cause of your perineal discomfort.
Perineal itching may be an uncomfortable topic to talk about, but it’s often more uncomfortable to experience.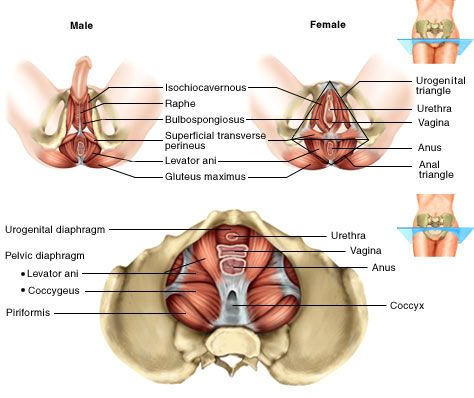
If preventive methods or at-home treatments haven’t helped (or you’re worried you have an infection), talk to a doctor. They can help determine potential causes and help you feel more comfortable.
Itching in the vagina - causes, what to do and how to treat
2020-12-17
Gynecological pathologies are an extensive group of diseases of infectious or non-infectious origin, which a doctor can diagnose based on the results of examinations. Diseases of the female genital area have characteristic symptoms that significantly impair the quality of life. Common symptoms include itching in the vagina, which should not be ignored, as it can be a sign of quite serious diseases.
Causes of vaginal itching
Itching in the vagina is not a disease, but only a symptom that indicates a particular disorder in a woman's body. There are a lot of reasons for its development, therefore, before starting treatment, the doctor will prescribe a comprehensive examination to the patient, which will help identify the etiology of the disease and select the most effective treatment.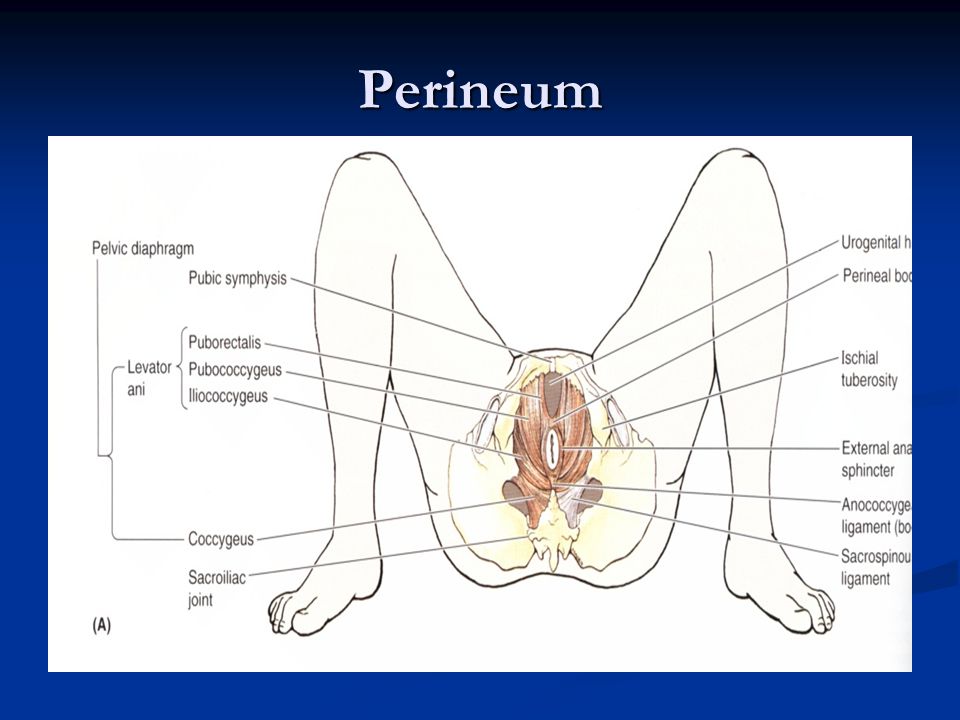 Vaginal itching may be present in the following cases:
Vaginal itching may be present in the following cases:
- Bacterial infections: candidiasis, vaginosis.
- Sexually transmitted infections: trichomoniasis, chlamydia, genital herpes.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs: cervicitis, adnexitis, endometritis, cervical erosion.
- Allergy to underwear, hygiene products, birth control pills, food.
- Poor hygiene of the genitals.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- External factors: wearing low-quality or tight underwear, stress, nervous strain.
In addition to the underlying causes, vaginal itching is often present in women who have diabetes or problems with the endocrine system. Such a symptom is not an indicator for making a diagnosis or prescribing therapy, so the doctor also pays attention to other manifestations, as well as the results of studies that the woman will appoint at the initial consultation after a gynecological examination and anamnesis.
Concomitant symptoms
Itching in the vagina is not the only symptom that can bother a woman. Clinical signs directly depend on the etiology of the disease, the stage of development, and the characteristics of the female body. As practice shows, vaginal itching is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms:
Clinical signs directly depend on the etiology of the disease, the stage of development, and the characteristics of the female body. As practice shows, vaginal itching is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms:
- increased vaginal dryness, burning;
- skin rash;
- discharge of a different nature: from cheesy white to brown and bloody;
- bad smell;
- pain, discomfort in the lower abdomen or in the lumbar region;
- elevated body temperature;
- extreme mood swings;
- weakness, increased fatigue.
If you ignore itching, constant scratching increases the risk of a secondary infection, which will only worsen the prognosis for a quick recovery. Many diseases of the female genital area have similar symptoms, so when it appears, you do not need to hesitate to visit a gynecologist. The sooner the cause is identified and treated, the sooner a woman can get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
What treatment can be prescribed by a doctor
A gynecologist or venereologist deals with the treatment of itching in the vaginal area, but consultation of related specialists, in particular a dermatologist, allergist, neurologist, may be required.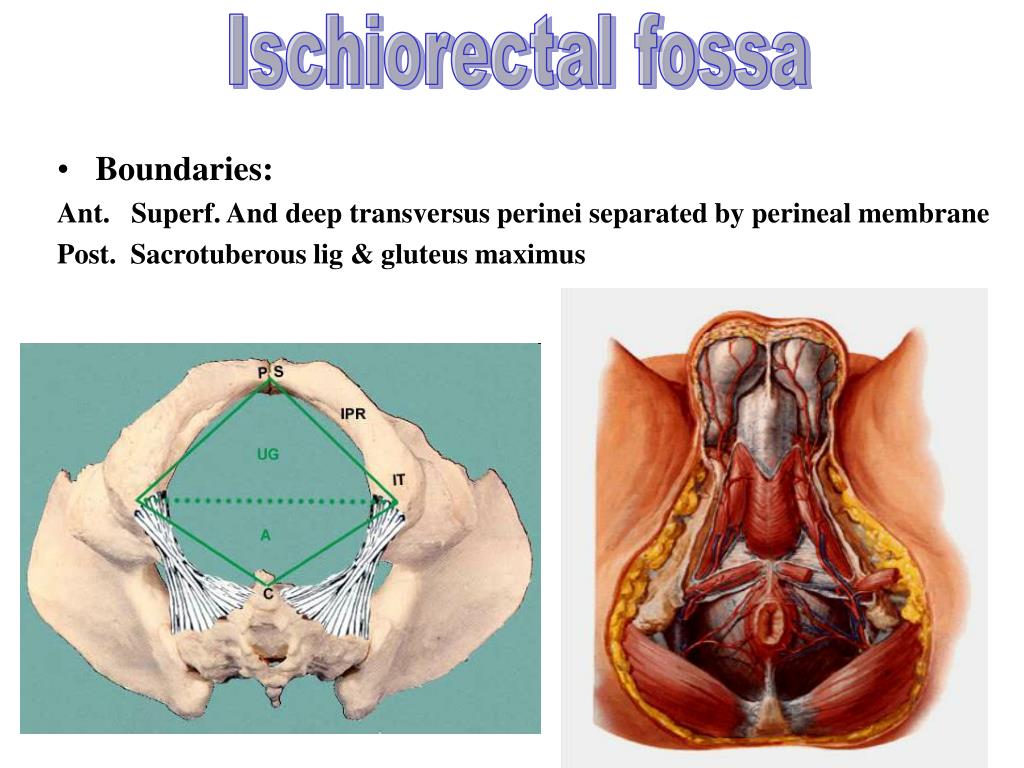 Therapy is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination, directly depends on the underlying cause, may include the following medications:
Therapy is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination, directly depends on the underlying cause, may include the following medications:
- Antibacterial and antimicrobial. They are prescribed if the source of the disease is the bacterial flora. Taking antibiotics will help to destroy the pathogenic pathogen, to exclude its reproduction and spread. The doctor chooses the medicine: it can be both tablets and injections, as well as topical preparations in the form of vaginal suppositories.
- Antifungals. Shown in diseases that are caused by fungal pathogens, often of the genus Candida.
- Antihistamines. Eliminate itching, suppress an allergic reaction, relieve tissue swelling.
- Hormonal. Appointed by an endocrinologist strictly according to indications.
- Sedatives.
- Vitamins.
Medications are prescribed by a doctor individually for each woman, based on the diagnosis, stage of the disease, and characteristics of the organism.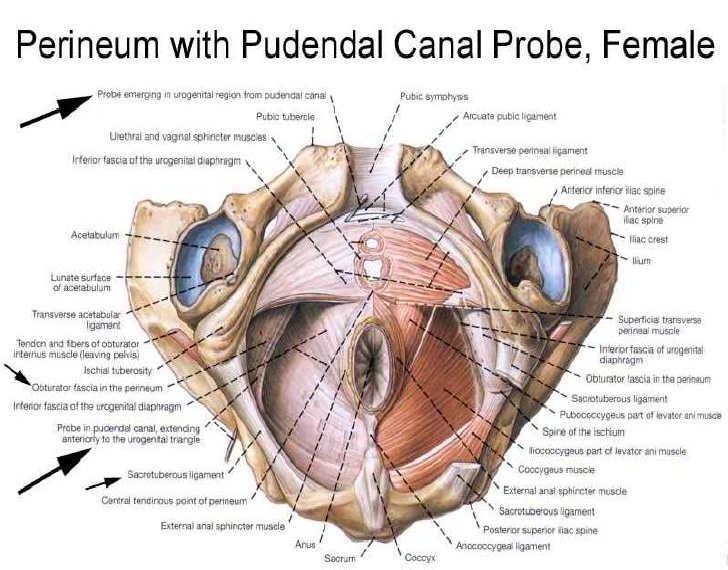 The duration of therapy can take from a couple of days to several weeks. The doctor also gives valuable advice on nutrition and lifestyle. As an adjunct therapy, various baths based on medicinal plants can be prescribed, which relieve itching, inflammation and irritation.
The duration of therapy can take from a couple of days to several weeks. The doctor also gives valuable advice on nutrition and lifestyle. As an adjunct therapy, various baths based on medicinal plants can be prescribed, which relieve itching, inflammation and irritation.
If itching is caused by fungal or bacterial flora, sexually transmitted diseases, treatment is prescribed not only for the woman, but also for her sexual partner.
Prevention
Itching in the vagina as a sign of illness is very common, causing not only physical but also mental discomfort. To reduce the risk of its development, women need to follow some rules:
- regular hygiene;
- preventive examinations at the gynecologist 2 times a year;
- avoid unprotected intercourse;
- take contraceptives as prescribed by a doctor;
- healthy and proper nutrition;
- wearing quality underwear;
- Use hypoallergenic intimate care products.
The main rule that women must adhere to when itching in the vagina is to refuse self-medication, to consult a doctor. It is important to understand that such a symptom may be a sign of a banal skin irritation or a symptom of a serious illness. Therefore, the sooner a woman turns to a specialist, the sooner she will get rid of discomfort and a possible disease.
Also read
Breast cancer diagnostics
The best way to prevent breast cancer is early diagnosis, including self-examination.
Myths and facts about varicose veins
Myths and facts about varicose veins. Varicose veins are a disease accompanied by thinning of the venous wall, an increase in the lumen of the veins and the formation of aneurysm-like nodular dilatations.
Blood in stool
Blood in the stool is a characteristic symptom of various diseases of the stomach and intestines, which can appear both constantly and periodically.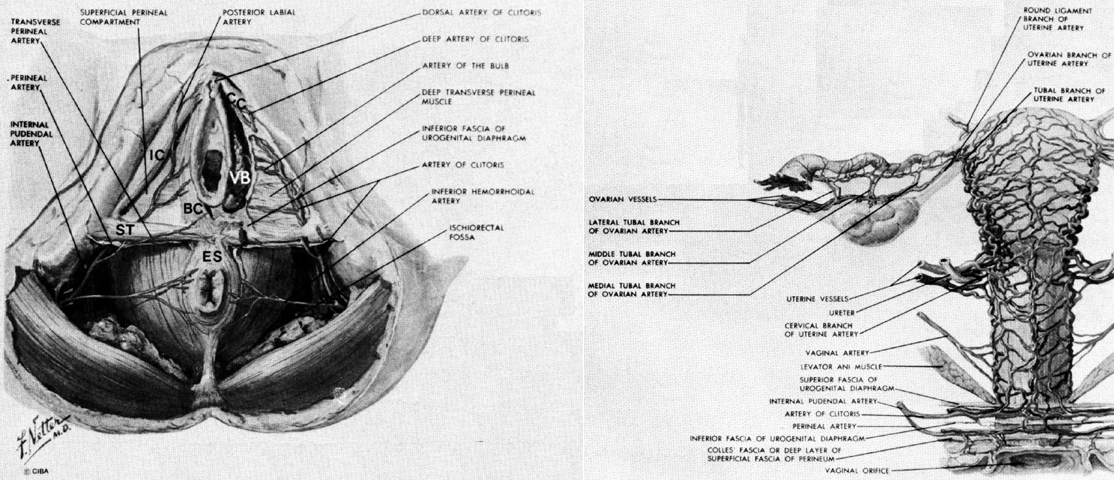 Blood can be in the form of streaks, stain the feces completely or lie on its surface.
Blood can be in the form of streaks, stain the feces completely or lie on its surface.
or
+7 495 223 30 88
NEWSLETTER
Subscribe to Newsletter
Follow our news and special offers
By clicking on the "Subscribe" button, you agree to the processing of personal data.
Thank you! Your application has been accepted.
Consent to the processing of personal data
Thank you! Your application has been accepted.
Itching and burning in the vagina: causes, symptoms, treatment
Itching in the vagina can occur in any woman due to a number of diseases of varying severity or simply insufficient attention to hygiene in the intimate area. Clinically, this deviation is manifested by inflammation of the vagina and vulva, and often by concomitant secretions.
Why does itching appear in the intimate area?
Let's take a closer look at the factors that cause this symptom, because it is the identification of the root cause that determines the correct diagnosis and the appointment of effective therapy.
Non-medical factors
Itching in the perineum may be due to:
- mechanical trauma from shaving or intense intercourse;
- the use of synthetic underwear that violates the natural moisture and heat exchange, rubs and irritates the skin;
- lack of proper hygienic care of the perineum at least once a day;
- ovulation, during which an abundance of secretions from the genitals often leads to discomfort, which normally disappears after 2-3 days.
Non-medical factors can be easily eliminated on your own, without seeking help from a doctor.
Inflammations and infections
Possible causes of burning and tingling in the perineum:
- a disease called kraurosis, affecting women of reproductive age, caused by degeneration of mucous tissues - in the absence of proper treatment, the genitals are deformed;
- vulvar leukoplakia - symptoms are similar to the previously described disease, but are characterized by pathological proliferation of epithelial tissues;
- vulvovaginal candidiasis, also called thrush, caused by a violation of the vaginal microflora and characterized, in addition to itching, pain in the lower abdomen and cheesy discharge - drugs that suppress the fungus minimize the severity of symptoms, but a 3-time or more frequent return of the disease per year is an indication for undergoing a semi-annual special therapy;
- eczema characterized by redness and painful sores in the intimate area;
- fungal infection with rash, swelling and pain in the perineum;
- infectious inflammation of the Bartholin's gland in the vagina, the large gland of the vestibule - uncomfortable sensations are aggravated by tight underwear and after intercourse;
- inflammation of the urethra or bladder mucosa, also characterized by painful urination and sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
Burning and tingling in the groin can be caused by STDs, the most common of which are:
- Trichomoniasis, caused by an aggressive tissue-destroying bacterium, acquired from an infected sexual partner through unprotected sex or through neglect of hygiene procedures. It is characterized by itching, painful urination, foul-smelling discharge. Trichomoniasis can lead to menstrual irregularities and other complications that affect a woman's reproductive function.
- Genital herpes, caused by herpes simplex virus type I and II, often occurring for the time being without any symptoms, and therefore can actively spread. It is acquired through contact with infected people at home or during unprotected sex, as well as during spontaneous immunization of the body.
- Papillomavirus infection due to immunosuppression or certain medications. This infection has about a hundred varieties, in the first stages it develops most often without symptoms and can only be detected by a PCR test.
Developing, the virus is expressed in the appearance of skin neoplasms and damage to the mucous tissues of the perineum.
Pathologies manifesting as a woman grows up
Various hormonal changes can be accompanied by thinning of mucous tissues, dryness in the perineum. Against the background of these deviations from the norm, other diseases of the female organs develop.
Risks for the pregnant woman
Groin discomfort during pregnancy is often due to hormonal changes. Possible exacerbation of vulvovaginal candidiasis, which also causes discomfort.
Risks for allergy sufferers
Discomfort in the genital area, swelling, redness and rash are often caused by an individual allergic reaction of the body.
Attention!
For STDs, both partners need to be treated. Doctors usually prescribe antifungal medications and antibiotics.
How does the pathology develop?
Itching in the perineum is caused by inflammation and irritation of the vaginal walls, or rather the reactions of nerve endings to these phenomena.
In addition to physical factors, discomfort can be triggered by problems of the female psycho-emotional state: prolonged psychological stress, neurotic disorder.
Symptoms
Itching in the intimate area, in addition to an intense restless desire to scratch, is associated with the following manifestations in the female body:
- bloody and bloodless discharge;
- rashes, edema, excessive blood supply to the vessels in the tissues of the intimate zone;
- occurrence of bad smell;
- pain in lower abdomen;
- drying out of the mucous tissues of the vagina;
- feeling of a foreign object in the perineum.
Itching may worsen and worsen. Sometimes the pathology does not bother during the day, but manifests itself in the evening before going to bed.
Unpleasant symptoms are aggravated by the systematic wearing of tight, synthetic clothing and panty liners.
Attention!
At the first sign of itching in the perineum, go for an examination by a gynecologist, as well as additional examinations if prescribed by a general practitioner. Proper diagnosis will help reduce unpleasant symptoms and deal with the root cause in the future.
Proper diagnosis will help reduce unpleasant symptoms and deal with the root cause in the future.
How is a pathology diagnosed?
A gynecologist during the first appointment determines the main and concomitant symptoms, signs of diseases of the endocrine system.
To find the root cause of itching in the groin and prescribe the correct course of therapy, the specialist prescribes the following examinations:
- Advanced or conventional colposcopy. Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Additionally, examinations with a hysteroscope and a laparoscope are sometimes prescribed.
- Taking a swab to assess the microflora of the vagina and the presence of pathogens in it.
- Microbiological analysis aimed at determining the microbe that provoked inflammation and determining its resistance to drugs.
- Serological testing aimed at detecting STDs and identifying the pathogen with high accuracy.
- Other laboratory tests: urine, estrogen, blood, depending on the patient's history.
How is itching in the perineum treated?
Conservative methods:
- Group B antimicrobials, antibiotics, drugs for fungi and protozoal infections are prescribed to reduce disturbing symptoms. Other types of STDs cause the simultaneous use of two or more drugs.
- Estrogen replacement therapy prescribed for colpitis and other pathologies characterized by a deficiency of female hormones. The preparations are released in the form of suppositories, tablets and ointments.
- Therapeutic methods to combat inflammation and tissue atrophy: douching, special creams, suppositories. The number and regularity of application varies depending on the overall clinical picture.
- Restoration of the vaginal microflora through local exposure to lactic acid bacteria that counteract the development of pathogens. It is indicated for vaginosis, atrophy of the mucous membranes of the vagina and after a course of taking antifungal agents.
- Taking antidepressants in cases where vaginal itching is due to the woman's psycho-emotional depression.

- A hygienic preparation in the form of a cream helps relieve itching for pregnant patients and allergy sufferers.
Surgery
The operation is performed only in cases of severe pathology. Growths on the skin and mucous membranes are removed by minimally invasive, bloodless methods of laser treatment and cryodestruction.
Attention!
Only a specialist in the field of gynecology can correctly prescribe therapy. Without direct instructions from a doctor, one or another treatment should not be used in order to avoid a deterioration in health.
How to prevent the development of itching in the intimate area?
The risk of inflammation and irritation is significantly reduced in women with the following healthy habits:
- Pay due attention to hygiene in the intimate area: wash the genitals daily with clean warm water, use a special cleanser in the form of a gel 2-3 times a week .
- Do not wear tight synthetic underwear for a long time, give preference to natural materials and loose fit.