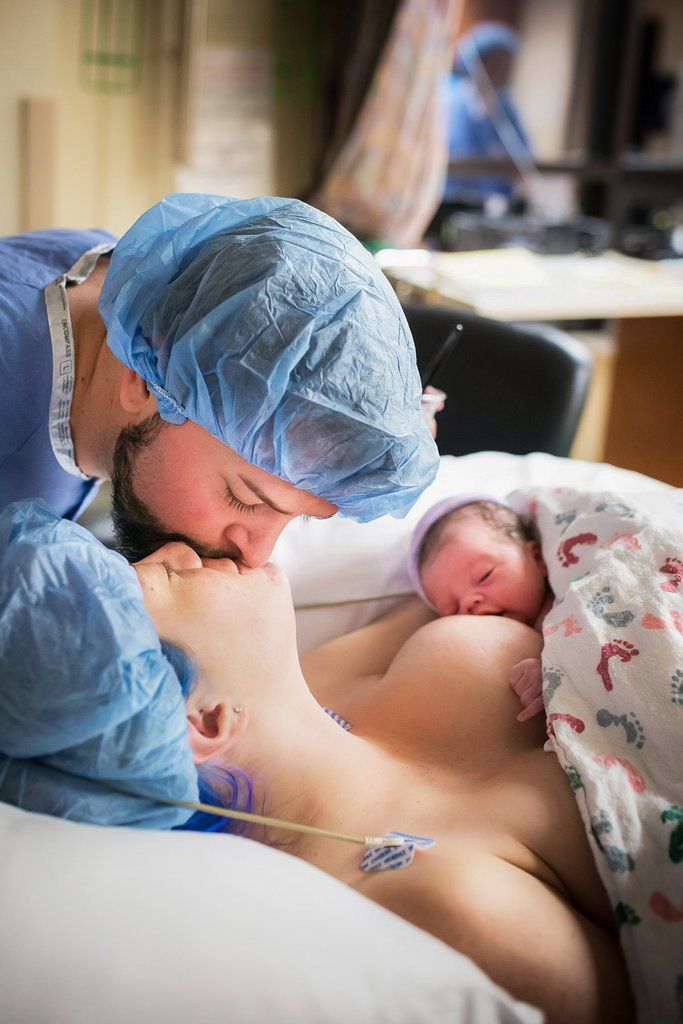
Giving birth humans
Scientists Have Figured Out Why Childbirth Became So Complex and Dangerous
The World Health Organization estimates that nearly 300,000 people die every year due to pregnancy-related causes.
A study finds that complex human childbirth and cognitive abilities are a result of walking upright.
Childbirth in humans is much more complex and painful than in great apes. It was long believed that this was a result of humans’ larger brains and the narrow dimensions of the mother’s pelvis. Researchers at the University of Zurich have now used 3D simulations to show that childbirth was also a highly complex process in early hominin species that gave birth to relatively small-brained newborns – with important implications for their cognitive development.
Complications are common for women during and following pregnancy and childbirth. The majority of these issues arise during pregnancy and are either avoidable or curable. However, childbirth is still dangerous. The World Health Organization estimates that 830 people die every day due to causes related to childbirth and pregnancy. Furthermore, for every woman that dies due to childbirth, another 20-30 encounter injury, infection, or disabilities.
Four major complications are responsible for 75% of maternal deaths: severe bleeding (typically after birth), infections, high blood pressure during pregnancy, and complications from delivery. Other common issues include unsafe abortions and chronic conditions such as cardiac diseases and diabetes.
All of this shows how human birthing is much more difficult and painful than that of large apes. This was long believed to be due to humans’ bigger brains and the limited dimensions of the mother’s pelvis. Researchers at the University of Zurich have now shown, using 3D simulations, that birthing was likewise a highly complicated procedure in early hominin species that gave birth to relatively small-brained newborns – with significant consequences for their cognitive development.
The fetus normally navigates a narrow, convoluted birth canal by bending and turning its head at different phases during human delivery. This complicated procedure has a significant risk of birth complications, which may range from extended labor to stillbirth or maternal death. These issues were long thought to be the outcome of a conflict between humans adjusting to upright walking and our larger brains.
The dilemma between walking upright and larger brains
Bipedalism developed around seven million years ago and dramatically reshaped the hominin pelvis into a real birth canal. Larger brains, however, didn’t start to develop until two million years ago, when the earliest species of the genus Homo emerged. The evolutionary solution to the dilemma brought about by these two conflicting evolutionary forces was to give birth to neurologically immature and helpless newborns with relatively small brains – a condition known as secondary altriciality.
A research group led by Martin Häusler from the Institute of Evolutionary Medicine at the University of Zurich (UZH) and a team headed up by Pierre Frémondière from Aix-Marseille University have now found that australopithecines, who lived about four to two million years ago, had a complex birth pattern compared to great apes. “Because australopithecines such as Lucy had relatively small brain sizes but already displayed morphological adaptations to bipedalism, they are ideal to investigate the effects of these two conflicting evolutionary forces,” Häusler says.
“Because australopithecines such as Lucy had relatively small brain sizes but already displayed morphological adaptations to bipedalism, they are ideal to investigate the effects of these two conflicting evolutionary forces,” Häusler says.
Birth simulation of Lucy (Australopithecus afarensis) with three different fetal head sizes. Only a brain size of maximum 30 percent of the adult size (right) fits through the birth canal. Credit: Martin Häusler, UZH
The typical ratio of fetal and adult head size
The researchers used three-dimensional computer simulations to develop their findings. Since no fossils of newborn australopithecines are known to exist, they simulated the birth process using different fetal head sizes to take into account the possible range of estimates. Every species has a typical ratio between the brain sizes of its newborns and adults. Based on the ratio of non-human primates and the average brain size of an adult Australopithecus, the researchers calculated a mean neonatal brain size of 180 g. This would correspond to a size of 110 g in humans.
This would correspond to a size of 110 g in humans.
For their 3D simulations, the researchers also took into account the increased pelvic joint mobility during pregnancy and determined a realistic soft tissue thickness. They found that only the 110 g fetal head sizes passed through the pelvic inlet and midplane without difficulty, unlike the 180 g and 145 g sizes. “This means that Australopithecus newborns were neurologically immature and dependent on help, similar to human babies today,” Häusler explains.
Prolonged learning is key to cognitive and cultural abilities
The findings indicate that australopithecines are likely to have practiced a form of cooperative breeding, even before the genus Homo appeared. Compared to great apes, the brains developed for longer outside the uterus, enabling infants to learn from other members of the group. “This prolonged period of learning is generally considered crucial for the cognitive and cultural development of humans,” Häusler says. This conclusion is also supported by the earliest documented stone tools, which date back to 3.3 million years ago – long before the genus Homo appeared.
This conclusion is also supported by the earliest documented stone tools, which date back to 3.3 million years ago – long before the genus Homo appeared.
Reference: “Dynamic finite-element simulations reveal early origin of complex human birth pattern” by Pierre Frémondière, Lionel Thollon, François Marchal, Cinzia Fornai, Nicole M. Webb, and Martin Haeusler, 19 April 2022, Communications Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03321-z
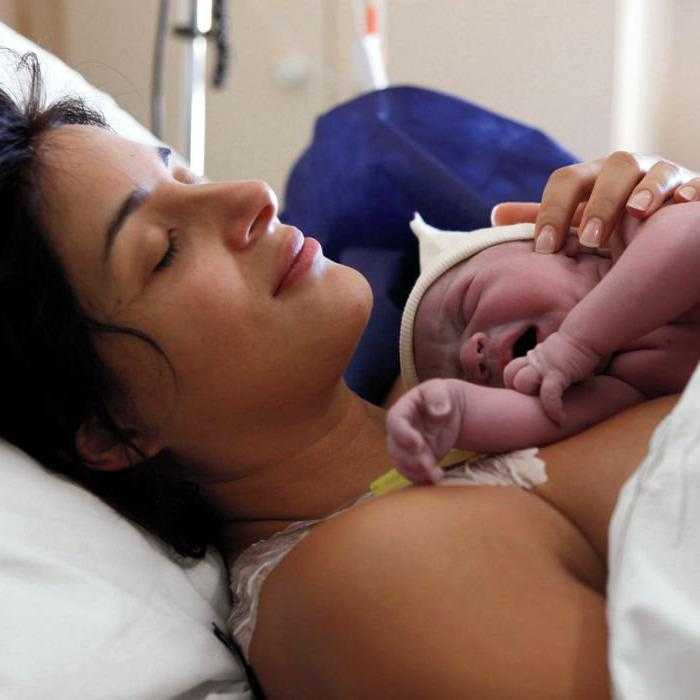
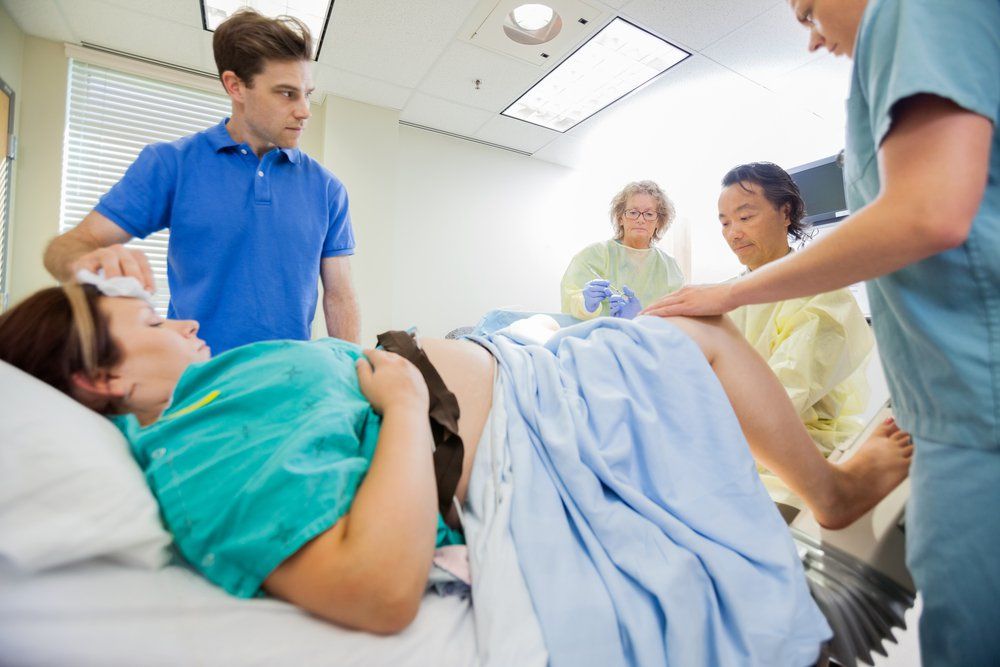
What happens to your body during childbirth
Childbirth is challenging and complications occur, but women's bodies are designed to give birth. The shape of the pelvis, hormones, powerful muscles and more all work together to help you bring your baby into the world - before, during and after childbirth.
How your body prepares for labour
Here are some of the ways your body will prepare both you and your baby for the birth ahead.
Braxton Hicks contractions
In the weeks or days before you start having proper contractions, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions. This is your uterus tightening then relaxing. These contractions don't usually hurt and are thought to help your uterus and cervix get ready for labour.
This is your uterus tightening then relaxing. These contractions don't usually hurt and are thought to help your uterus and cervix get ready for labour.
Braxton Hicks contractions may become more regular as you get closer to the time of birth, but unlike labour contractions, they don't change the shape of the cervix and are sometimes referred to as 'false labour'. Your midwife can tell you if you're experiencing Braxton Hicks contractions or if you are in labour by doing a vaginal examination to look at your cervix.
Changes to the cervix
As labour gets closer, your cervix softens and becomes thinner, getting ready for the dilation (widening) that will allow the baby to enter the vagina. You may also see a 'show', which is a pinkish plug of mucus, stained with blood.
Engagement
Your baby may move further down your pelvis as the head engages, or sits in place over your cervix, ready for the birth. Some women feel they have more room to breathe after the baby has moved down. This is called 'lightening'.
This is called 'lightening'.
Rupture of the membranes, or 'waters breaking'
Some women find the sac of amniotic fluid containing the baby breaks before labour, contractions start and the fluid runs (or gushes) out of the vagina. This is referred to as rupture of the membranes, or 'waters breaking'.
Let your maternity team know when your waters have broken and take notice of the colour of the fluid. It is usually light yellow. If it is green or red, tell your maternity team since this could mean the baby is having problems.
If your waters have broken but you have not started having regular contractions within 24 hours, you may need your labour to be induced because there is a risk of infection. Your midwife or doctor will talk to you about this.
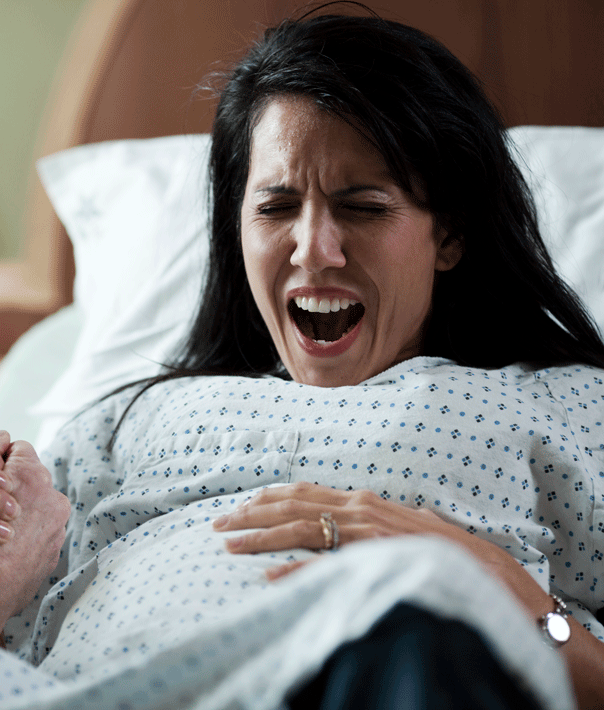
How will you know when labour has started?
Movies often show women suddenly being struck by painful contractions and rushing to hospital. In real life, many women are not sure if they have actually started their labour.
You may feel restless, have back pain or period-like pain, or stomach disturbances such as diarrhoea.
Labour officially begins with contractions, which start working to open up the cervix. You should phone your midwife when your contractions start, although you probably won't be encouraged to come to the hospital or birthing centre until your contractions are closer together.
In preparation for labour, your baby may move further down your pelvis as the head engages, or sits in place over your cervix.How the pelvis is designed for childbirth
Your pelvis is located between your hip bones. Women typically have wider, flatter pelvises than men, as well as a wider pelvic cavity (hole) to allow a baby to pass through.
The organs sitting in a woman's pelvis include the uterus, cervix and vagina, which are held together by a group of muscles. During childbirth, the muscles at the top of your uterus press down on the baby's bottom. Your baby's head then presses on your cervix which, along with the release of the hormone oxytocin (see 'How hormones help you give birth', below), brings on contractions. Your cervix should dilate so your baby can pass through it.
Your cervix should dilate so your baby can pass through it.
Your pelvis has bones and ligaments that move or stretch as the baby travels into the vagina. Your baby also has spaces between the skull bones called 'sutures', and the gaps where the sutures meet on the skull are called fontanelles. This allows for the baby's head to mould as the skull bones meet or overlap, allowing it to fit more easily as it travels through your pelvis.
How hormones help you give birth
Your body produces hormones that trigger changes in your body before, during and after childbirth. Here's how they work to help you deliver your baby.
- Prostaglandin Before childbirth, a higher level of prostaglandin will help open the cervix and make your body more receptive to another important hormone, oxytocin.
- Oxytocin This hormone causes contractions during labour, as well as the contractions that deliver the placenta after the baby is born.
 These post-birth contractions, including more that can occur during breastfeeding, help your uterus shrink back to its normal size. Oxytocin and prolactin are the two main hormones that produce and let down breast milk for your baby. Skin-to-skin contact between a mother and baby helps to release more of these hormones.
These post-birth contractions, including more that can occur during breastfeeding, help your uterus shrink back to its normal size. Oxytocin and prolactin are the two main hormones that produce and let down breast milk for your baby. Skin-to-skin contact between a mother and baby helps to release more of these hormones.
- Relaxin The hormone relaxin helps soften and stretch the cervix for birth, while helping your waters break and stretching the ligaments in your pelvis to allow the baby to come through.
- Beta-endorphins During childbirth, this type of endorphin helps with pain relief and can cause you to feel joyful or euphoric.
- 'Baby blues' After birth, your hormone balance can change again, and this is believed to cause the ‘baby blues’ in some women. You may feel teary, anxious and irritable and your mood can go up and down.
When childbirth doesn’t go to plan
Sometimes, complications can occur before or during childbirth that mean things don’t go as expected.
Sometimes, labour needs to be induced or started. There are a few ways to induce labour, including the mother being offered synthetic prostaglandin. This is inserted into the vagina to soften the cervix and start contractions.
If contractions slow down or stop during labour, the mother may be offered synthetic oxytocin from a drip to increase the contractions. In both these cases contractions can come on strongly and more pain relief may be needed. Your maternity team should explain the benefits and risks of this with you before you agree to it.
The baby could be in a posterior or breech position, not ideally placed above the cervix before the birth. Your maternity team may need to use forceps or a vacuum to help turn the baby or help the baby travel out of the vagina. Sometimes a caesarean is needed.
In rare cases, a mother may experience cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD), which is when the baby’s head is too big to fit through the pelvis. A diagnosis of CPD is usually made when labour hasn’t progressed and synthetic oxytocin has not helped. A caesarean is usually the next step.
A caesarean is usually the next step.
More information
If you have any questions about childbirth or pregnancy, you can call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7 days a week, to speak to a maternal health nurse.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
real-time worldwide statistics
World population
Sources:
- World Population Prospect: the 2019 Revision - United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (June 2019)
- International Programs Center at the U.S. More info:
- World Population (Worldometer)
trends & more >
This Year = January 1st (00:00) to now
Today = from the beginning of the current day to now
Population Growth = Births - Dieds
Government and Economy
quick facts:
- Total global healthcare expenditure represent around 10% of world GDP
- Government portion of healthcare expenditure is around 60%
0009 Global Health Expenditure Database - World Health Organization (WHO)
- World Health Statistics - World Health Organization (WHO)
- World Economic Outlook (WEO) - International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- World Development Indicators (WDI) - World Bank
quick facts:
- Public spending on education in the world is around 5% of global GDP0009 Human Development Report - United Nations
- Global Education Digest - Unesco Institute for Statistics (UIS)
- World Bank Public Expenditure Database - edstats - World Bank
more information >
sources and information:
- military expenditure data - SIPRI
more information >
sources and information:
- Car Production Statistics - International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA)
- Global Auto Report [Pdf file] - ScotiaBank
- Light Vehicle Production Forecasts - IHS
more info >
quick facts:
- at nearly 20 million each per year, but as of 2003 bike production had climbed to over 100 million per year compared with around 50 million cars produced that year.

sources and information: more information > sources and information: more information > sources and information:
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification
sources and information:
- Toxic Release Inventory (TRI) Program - U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- United Nations Environment Program
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
more information >
Food
sources and information:
- The State of Food Insecurity in the World - FAO
More information>
Sources and information:
- Obsity and Overweeight - World Health Organization (WHO)
Sources and information:
- 000 OBESTYS Organization (WHO)
- Hunger Stats - United Nations World Food Program
- World Health Report - World Health Organization (WHO)
- The State of the World's Children - United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
- Featured Page
- Annual Medical Spending Attributable To Obesity: Payer-And Service-Specific Estimates
by:
RTI International
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality - US Dept of Health and Human Services
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - America's Health Rankings (report by the United Health Foundation, the American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention)
- The U.
 S. Weight Loss & Diet Control Market - MarketData Enterprises, Inc., May 1, 2011
S. Weight Loss & Diet Control Market - MarketData Enterprises, Inc., May 1, 2011 - America's Health Rankings (report by the United Health Foundation, the American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention)
- Global Water Outlook to 2025 - International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) and the International Water Management Institute (IWMI)
- Water Sanitation and Health (WSH) - World Health Organization (WHO)
- Water Sanitation and Health (WSH) - World Health Organization (WHO)
- World Proved Reserves of Oil and Natural Gas, Most Recent Estimates - Energy Information Administration (EIA) - Data from BP Statistical Review, Oil & Gas Journal, World Oil, BP Statistical Review, CEDIGAZ, and Oil & Gas Journal.

- Maintaining current consumption rates
- World Proved Reserves of Oil and Natural Gas, Most Recent Estimates - Energy Information Administration (EIA) - Data from BP Statistical Review, Oil & Gas Journal, World Oil, BP Statistical Review, CEDIGAZ, and Oil & Gas Journal.
- boe = barrel of oil equivalent
- "gas" = natural gas
- World Proved Reserves of Oil and Natural Gas, Most Recent Estimates - Energy Information Administration (EIA) - Data from BP Statistical Review, Oil & Gas Journal, World Oil, BP Statistical Review, CEDIGAZ, and Oil & Gas Journal.
- Global Burden of Disease (GBD) - World Health Organization (WHO)
- Young child survival and development - UNICEF
- Child Mortality - Childinfo (UNICEF)
more information >
sources and information:
sources and information:
more information >
sources and information:
more info >
Water
sources and information:
sources and information:
sources and information:
Countdown to oil depletion:
...
guess:
sources and information:
quick facts:
sources and information:
...Days to exhaustion
natural gas
Health
sources and information:
sources and information:
sources and information: 9000 Health Organization )
 ; Ahman, E. (December 2009). "Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges" (Pdf). Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology Canada 31 (12): 1149-58. PMID 20085681
; Ahman, E. (December 2009). "Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges" (Pdf). Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology Canada 31 (12): 1149-58. PMID 20085681 more information >
sources and information:
- Why do so many women still die in pregnancy or childbirth? - World Health Organization (WHO)
- Maternal mortality for 181 countries, 1980-2008: a systematic analysis of progress towards Millennium Development Goal 5
sources and information:
- HIV/AIDS Statistics - World Health Organization
- Global Hiv and Aids Estimates - Avert
More information>
Sources and information:
- Unaids
more information>
more information > sources and information: sources and information: sources and information:
- Global Information System on Alcohol and Health (GISAH) - World Health Organization (WHO)
more information >
sources and information:
- Suicide prevention (SUPRE) - World Health Organization (WHO)
sources and information:
- The illegal drugs business global - Frontline, PBS special report
more information >
info:
- Global launch of the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2011-2020 - World Health Organization (WHO)
share!
Demographics
Rosstat in social networks
Subscribe and follow the activities of the Federal State Statistics Service in social networks
call_made WEB
Total resident population growth
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
The share of the urban population in the total population as of January 1
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Annual average resident population
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Resident population as of January 1
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Population change in radioactive contamination zones
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Migration population growth by sex, age and movement flows
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Number of dropouts by gender, age and movement flows
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Number of arrivals by sex, age and movement flows
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Migration population growth by cities with a population of 100,000 or more
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Population dropped out by cities with a population of 100 thousand people and more
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Population arrived by cities with a population of 100 thousand people and more
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Migration increase by sex, age and directions of movement in the Far North and areas equated to them
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Population withdrew by sex, age and directions of movement in the regions of the Far North and areas equated to them
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Arrival of the population by sex, age and directions of movement in the regions of the Far North and areas equated to them
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Migration increase in population by regions of the Far North and areas equivalent to them
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Population withdrew by regions of the Far North and areas equated to them
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Population income by regions of the Far North and areas equated to them
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Distribution of migrants by age groups (migration gain/loss)
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Distribution of migrants by age groups (number of those who left)
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Distribution of migrants by age groups (number of arrivals)
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Migration gain per 10,000 population
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Interregional (internal) migration rate per 10,000 population
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Migration increase (decrease) in population, absolute data
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Number of dropouts
06/18/2019
call_made WEB
Number of arrivals
06/18/2019
Rosstat Order No.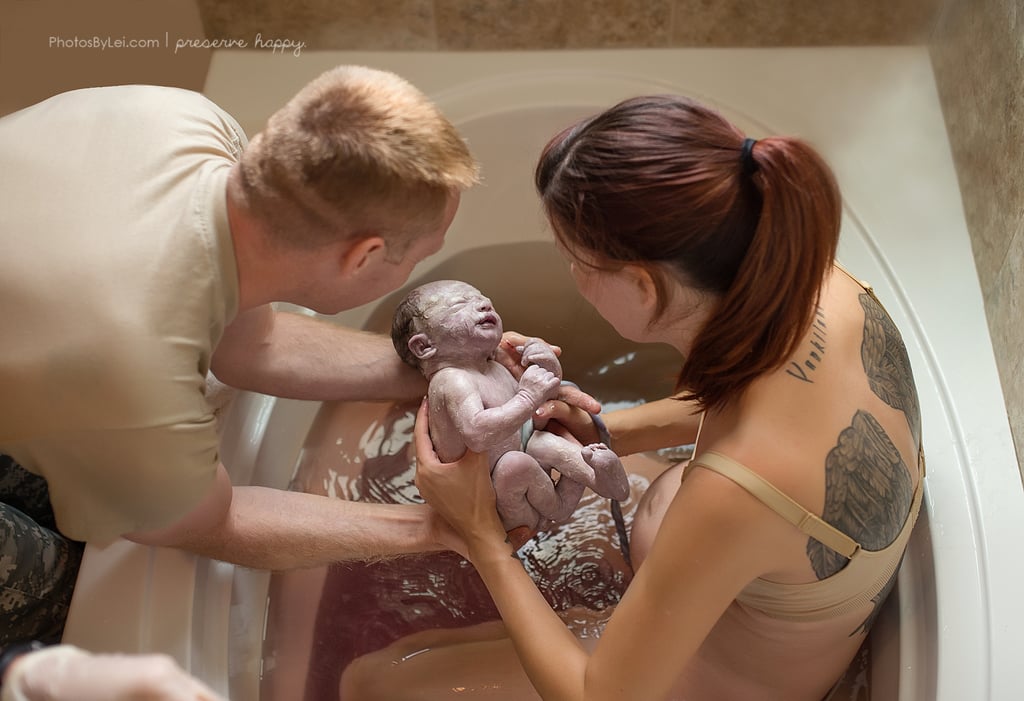 409 dated July 17, 2019 “On approval of the methodology for determining the age groups of the population”
409 dated July 17, 2019 “On approval of the methodology for determining the age groups of the population”
57.87 Kb, 06/23/2020
HTM
Population size and composition, methodology
5.96 Kb, 03.08.2021
XLS
Population
39 Kb, 07/27/2022
call_made WEB
Population density of constituent entities of the Russian Federation
09/11/2018
Components of population change in the Russian Federation
XLS
Number of men and women
33.5 Kb, 06/17/2022
XLS
Distribution of the population by age groups
49.5 Kb, 17.06.2022
XLS
Number of women per 1000 men of the corresponding age group
45 Kb, 06/17/2022
HTM
Vital movement of the population, methodology
11. 9 Kb, 07.10.2021
9 Kb, 07.10.2021
RAR
Vital economic description with annexes
1.01 Mb, 04/10/2020
DOCX
Brief nomenclature of causes of death
58.56 Kb, 10.04.2020
Fertility, mortality and natural increase
Infant mortality
Maternal mortality
Number of deaths by main cause of death
XLSX
Number of deaths by causes of death
34.79 Kb, 06/20/2022
Mortality rates by main classes of causes of death
Life expectancy at birth
call_made WEB
Life expectancy at birth in the Russian Federation
09/11/2018
XLSX
Life expectancy at birth by constituent entities of the Russian Federation for 2021
19.48 Kb, 04.07.2022
Total fertility rate
HTM
Marriages and divorces, methodology XLS
Marriages by age of bride and groom
31 Kb, 06/20/2022
HTML
Migration, methodology
25. 24 Kb, 04.08.2021
24 Kb, 04.08.2021
General results of population migration (by movement flows)
International migration
XLS
Internal Russian migration by territories of arrival and departure (“checkerboard” by federal districts)
167 Kb, 27.07.2022
HTM
Number of internally displaced persons, refugees and persons granted temporary asylum
5.38 Kb, 29.07.2022
call_made WEB
Monthly operational data on population migration: number of arrivals, number of departures, migration growth
09/11/2018
DOC
Demographic forecast up to 2035, methodology
25 Kb, 09/11/2018
DOCX
Forecast technique
542.38 Kb, 04/10/2020
XLS
Population change by forecast options
35 Kb, 03/26/2020
XLS
Number of men and women
32. 5 Kb, 03/26/2020
5 Kb, 03/26/2020
XLS
Population by individual age groups
38.5 Kb, 26.03.2020
XLS
Estimated population of the Russian Federation
183 Kb, 03/26/2020
XLS
Dependency ratio
34.5 Kb, 03/26/2020
XLS
Births, deaths and natural population growth
30.5 Kb, 03/26/2020
XLS
TFR
26 Kb, 03/26/2020
XLS
Life expectancy at birth
27.5 Kb, 03/26/2020
Information
HTM
Methodological notes
22.07 Kb, 11.09.2020
Principles and Recommendations for a Vital Statistics System
2.06 Mb, 11.09.2018
Recommendations on International Migration Statistics
17. 1 Mb, 09/11/2018
XLS
Estimated resident population as of January 1, 2022 and average for 2021 and components of its change
99 Kb, 04/25/2022
XLSX
Permanent population of the Russian Federation by municipalities as of January 1, 2022
1.3 Mb, 04/29/2022
HTM
Vitality (September 2022)
7.09 Kb, 11/11/2022
XLSX
Life expectancy at birth for 2021
19.44 Kb, 03/21/2022
XLSX
Fertility, mortality and natural population growth by constituent entities of the Russian Federation for 2020
18.25 Kb, 08/11/2021
XLSX
The number of deaths at working age and older than working age for 2019-2020
20.75 Kb, 08.10.2021
XLS
Mortality of the population of working age for January-December 2019
150 Kb, 04. 03.2020
03.2020
HTML
Summary of Sample Survey "Family and Fertility"
91.77 Kb, 09/11/2018
XLS
Distribution of the population of the Russian Federation by sex and age groups (as of January 1, 2019)
38 Kb, 08/30/2019
XLSX
Estimated population in places of traditional residence of indigenous peoples of the Russian Federation
120.37 Kb, 29.04.2022
DOC
Analytical report on the results of sample observation of population reproductive plans in 2012 (published on 01/24/2013)
1.16 Mb, 09/11/2018
MP4
Results of sample observation of reproductive plans of the population (video presentation; mp4 format)
409.99 Mb, 11.09.2018
XLSX
Permanent population as of January 1 of the current year for single-industry municipalities
61. 09 Kb, 06.05.2022
09 Kb, 06.05.2022
XLSX
Working-age population of single-industry municipalities as of January 1 of the current year
66.03 Kb, 11/22/2021
call_made WEB
Demographic Yearbook of Russia
09/11/2018
Youth in Russia. 2010
6.18 Mb, 09/11/2018
Children in Russia. 2009
4.43 Mb, 09/11/2018
call_made WEB
Bulletin "Vital movement of the population of the Russian Federation"
06/21/2022
call_made WEB
Bulletin "Population and Migration of the Russian Federation"
07/29/2022
call_made WEB
Bulletin "Population of the Russian Federation by sex and age"
29.07.2022
call_made WEB
Bulletin "Population of the Russian Federation by municipalities"
07/29/2022
call_made WEB
Bulletin "Estimated population of the Russian Federation"
12/26/2018
call_made WEB
Russian Statistical Yearbook
01/28/2019
call_made WEB
Regions of Russia. Socio-economic indicators
Socio-economic indicators
01.02.2019
call_made WEB
Report "Social and economic situation in Russia" (monthly)
07/27/2022
Responsible for section
| Demographics |
| Department of Population and Health Statistics | ||||||
| All-Russian population census | Voronin Vladimir Mikhailovich |
| ||||||
| Population and migration | Vologirova Lyana Aronovna | |||||||