Blighted ovum vs normal pregnancy
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic Pregnancy): Causes & Symptoms
Overview
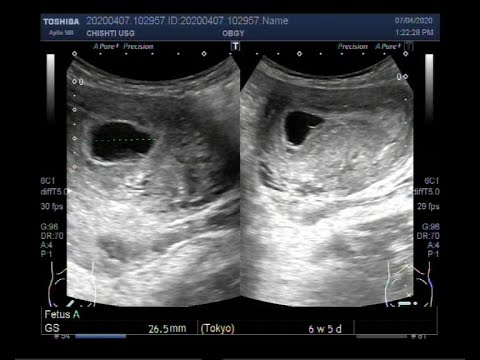
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum (also called an anembryonic pregnancy) is a type of early miscarriage that occurs when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would develop) continues to grow. The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones — even without an embryo present. This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
When does a blighted ovum happen?
A blighted ovum causes an early miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. During fetal development, a fertilized egg turns into a blastocyte. At around four weeks of pregnancy, this blastocyte implants in the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. When you have a blighted ovum, the gestational sac that would hold the embryo continues to grow, even without an embryo present. The following can occur:
- A blighted ovum happens so early in pregnancy, that you never realize you are pregnant.
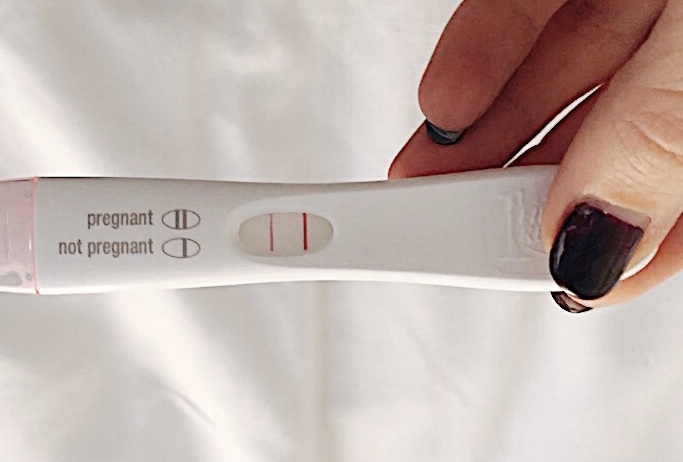
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy only to discover a blighted ovum at your first ultrasound.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy but then experience a miscarriage.
How common is a blighted ovum pregnancy?
A blighted ovum is the number one cause of first trimester miscarriages.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum can occur so early in pregnancy that you never knew you were pregnant. In other cases, you may experience signs of pregnancy such as a missed menstrual period or a positive pregnancy test. You can have symptoms of early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness.
Other times your symptoms will resemble those of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal bleeding: Spotting (light bleeding), bleeding or passing light gray tissue or blood clots.
- Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping in your pelvic and abdominal region.
The only way to confirm a blighted ovum is through an ultrasound. It will show a gestational sac that is missing an embryo inside.
What causes a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is usually caused by chromosomal or genetic problems during cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide shortly after being fertilized by sperm. Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
How does a blighted ovum miscarriage start?
A blighted ovum miscarriage will cause vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. A miscarriage usually feels more intense than your regular menstrual period. You can take an over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen to relieve cramping. Avoid lifting anything heavy or any strenuous exercise as it can increase your bleeding. You may experience spotting for several weeks after a miscarriage.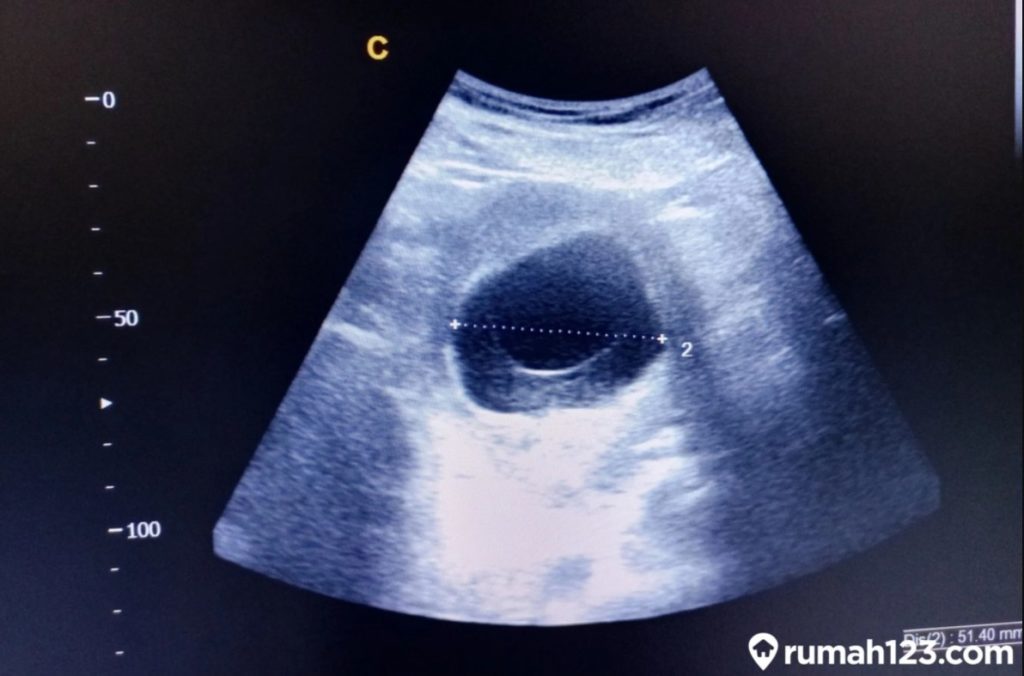
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
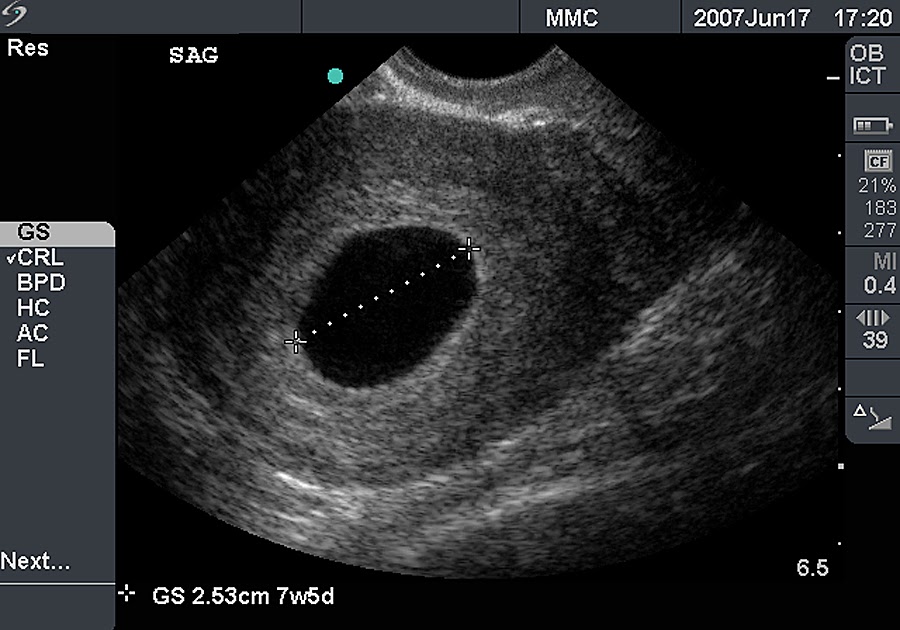
Your healthcare provider will diagnose a blighted ovum using transvaginal ultrasound. This happens in the first trimester, usually between seven and nine weeks of pregnancy. An embryo should be visible at this time in pregnancy. With a blighted ovum, the gestational sac will be empty.
- You will lie back on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups like you do for a pelvic exam. Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus.
- A blighted ovum will appear as an empty sac — almost like a bubble.
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.
People are often unaware that they have a blighted ovum. This is because your placenta continues to give off hormones, making your body think you are pregnant. This is also why you can still have symptoms of pregnancy, including a positive pregnancy test.
If you’ve already experienced bleeding or signs of a miscarriage, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound to look at the contents of your uterus to diagnose a blighted ovum.
Some healthcare providers will collect a series of blood samples that check the levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. HCG is known as the pregnancy hormone because it's only produced if you are pregnant. The level of hCG in your blood increases rapidly in early pregnancy and reaches its peak around weeks eight to ten. If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
Management and Treatment
How is a blighted ovum treated?
For some people, there may be no treatment needed, because your body passes the embryo through your vagina (a miscarriage).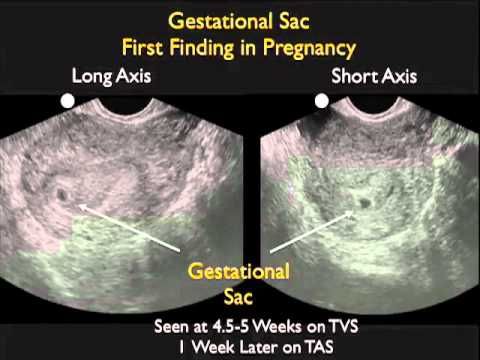 If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): This is a surgical procedure to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will dilate, or open, the cervix and use medical tools and suction to remove the pregnancy tissues from your uterus. This is done under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Natural miscarriage: If it's safe, you may be able to watch and wait to see if your body eventually releases the pregnancy tissues. It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins.
- Medication-induced miscarriage: You may be given a medication called misoprostol to trigger your body to miscarry.
 This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled four to six weeks after a miscarriage or D&C. You may be given another ultrasound to confirm the uterus is empty. Your healthcare provider will check for signs of infection and make sure there were no complications.
What are the complications of a blighted ovum?
Complications of a blighted ovum are uncommon, but the possible complications could include:
- Excessive bleeding or hemorrhage.
- Infection.
- Scarring (from the D&C procedure).
- Tears in the uterus (from the D&C procedure).
How long does it take to recover from a blighted ovum?
Recovering from a blighted ovum miscarriage or D&C can last from one or two weeks to a month. Cramping generally lasts up to a week, but bleeding can last several weeks.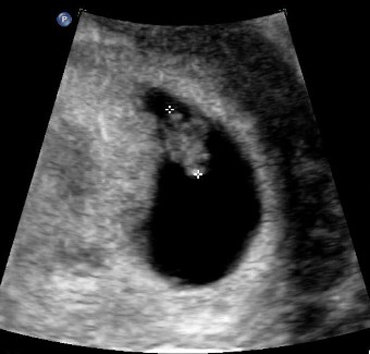 Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
You can resume normal activities when you feel comfortable. Bleeding can increase with strenuous activity or exercise. Hormones may remain in your body and delay your menstrual cycle. Most people will get their period within four to six weeks after a blighted ovum.
It may take longer to recover emotionally from a blighted ovum miscarriage. You may have feelings of sadness, anger or confusion. It’s OK to take time to grieve. Ask your friends and family for support.
Prevention
Can a blighted ovum be prevented?
A blighted ovum can’t be prevented. Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Outlook / Prognosis
How soon after a blighted ovum can I get pregnant again?
Most healthcare providers recommend having one or two regular menstrual cycles before trying to conceive again after any type of miscarriage.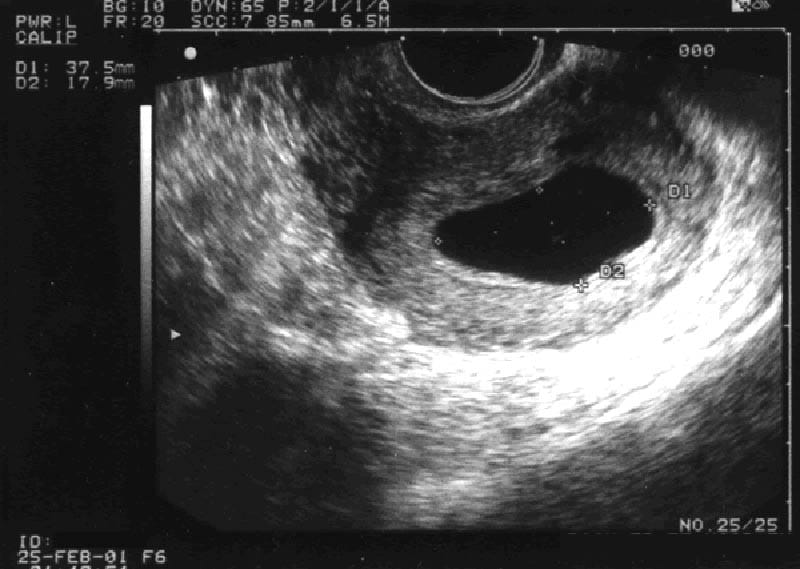
What are my chances of having another blighted ovum?
Your chances of having another blighted ovum are low. Most people go on to have healthy, full-term pregnancies. If you experience more than one blighted ovum, your healthcare provider may suggest testing to determine if there is an underlying cause.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding from your vagina.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Fever that does not go away.
- Symptoms that get worse over time.
- Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest ER If you experience heavy vaginal bleeding — more than two pads per hour for two consecutive hours — or have symptoms of anemia like dizziness, palpitations or paleness.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Losing a pregnancy is upsetting and confusing. Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
- Can I let my body miscarry or should I take medication to induce a miscarriage?
- What are the risks of miscarriage?
- Do I have to have a D&C?
- What are the risks of a D&C?
- How long can I expect to bleed or have cramping?
- Is there any indication this will happen again?
- When can I start trying to conceive?
- Do I need to come back for another ultrasound?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a blighted ovum considered a miscarriage?
Yes, a blighted ovum is a miscarriage. A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
How long can you carry a blighted ovum?
The amount of time you can carry a blighted ovum varies. Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby?
No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo. Your healthcare provider will be able to examine your gestational sac to confirm that no embryo has developed.
Do hCG levels rise with blighted ovum?
Yes, most of the time hCG levels will rise, giving you a positive pregnancy test and symptoms of pregnancy. This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
Is a blighted ovum more common with IVF?
A blighted ovum is not more common with IVF (In Vitro Fertilization). Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Losing a pregnancy is difficult. If you are struggling after a miscarriage, speak with your healthcare provider so they can recommend support groups or counselors. Finding support may help you get through this hard time. Most people who have had a blighted ovum will go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic Pregnancy): Causes & Symptoms
Overview
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum (also called an anembryonic pregnancy) is a type of early miscarriage that occurs when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would develop) continues to grow. The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones — even without an embryo present.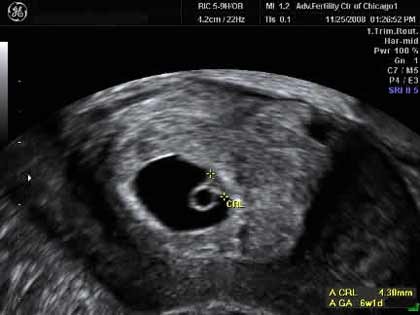 This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
When does a blighted ovum happen?
A blighted ovum causes an early miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. During fetal development, a fertilized egg turns into a blastocyte. At around four weeks of pregnancy, this blastocyte implants in the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. When you have a blighted ovum, the gestational sac that would hold the embryo continues to grow, even without an embryo present. The following can occur:
- A blighted ovum happens so early in pregnancy, that you never realize you are pregnant.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy only to discover a blighted ovum at your first ultrasound.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy but then experience a miscarriage.
How common is a blighted ovum pregnancy?
A blighted ovum is the number one cause of first trimester miscarriages.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum can occur so early in pregnancy that you never knew you were pregnant. In other cases, you may experience signs of pregnancy such as a missed menstrual period or a positive pregnancy test. You can have symptoms of early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness.
Other times your symptoms will resemble those of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal bleeding: Spotting (light bleeding), bleeding or passing light gray tissue or blood clots.
- Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping in your pelvic and abdominal region.
The only way to confirm a blighted ovum is through an ultrasound. It will show a gestational sac that is missing an embryo inside.
What causes a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is usually caused by chromosomal or genetic problems during cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide shortly after being fertilized by sperm. Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
How does a blighted ovum miscarriage start?
A blighted ovum miscarriage will cause vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. A miscarriage usually feels more intense than your regular menstrual period. You can take an over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen to relieve cramping. Avoid lifting anything heavy or any strenuous exercise as it can increase your bleeding. You may experience spotting for several weeks after a miscarriage.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will diagnose a blighted ovum using transvaginal ultrasound. This happens in the first trimester, usually between seven and nine weeks of pregnancy. An embryo should be visible at this time in pregnancy. With a blighted ovum, the gestational sac will be empty.
- You will lie back on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups like you do for a pelvic exam.
 Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus.
Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus. - A blighted ovum will appear as an empty sac — almost like a bubble.
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.
People are often unaware that they have a blighted ovum. This is because your placenta continues to give off hormones, making your body think you are pregnant. This is also why you can still have symptoms of pregnancy, including a positive pregnancy test.
If you’ve already experienced bleeding or signs of a miscarriage, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound to look at the contents of your uterus to diagnose a blighted ovum.
Some healthcare providers will collect a series of blood samples that check the levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. HCG is known as the pregnancy hormone because it's only produced if you are pregnant. The level of hCG in your blood increases rapidly in early pregnancy and reaches its peak around weeks eight to ten. If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
Management and Treatment
How is a blighted ovum treated?
For some people, there may be no treatment needed, because your body passes the embryo through your vagina (a miscarriage). If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): This is a surgical procedure to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will dilate, or open, the cervix and use medical tools and suction to remove the pregnancy tissues from your uterus. This is done under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Natural miscarriage: If it's safe, you may be able to watch and wait to see if your body eventually releases the pregnancy tissues.
 It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins.
It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins. - Medication-induced miscarriage: You may be given a medication called misoprostol to trigger your body to miscarry. This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled four to six weeks after a miscarriage or D&C. You may be given another ultrasound to confirm the uterus is empty. Your healthcare provider will check for signs of infection and make sure there were no complications.
What are the complications of a blighted ovum?
Complications of a blighted ovum are uncommon, but the possible complications could include:
- Excessive bleeding or hemorrhage.

- Infection.
- Scarring (from the D&C procedure).
- Tears in the uterus (from the D&C procedure).
How long does it take to recover from a blighted ovum?
Recovering from a blighted ovum miscarriage or D&C can last from one or two weeks to a month. Cramping generally lasts up to a week, but bleeding can last several weeks. Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
You can resume normal activities when you feel comfortable. Bleeding can increase with strenuous activity or exercise. Hormones may remain in your body and delay your menstrual cycle. Most people will get their period within four to six weeks after a blighted ovum.
It may take longer to recover emotionally from a blighted ovum miscarriage. You may have feelings of sadness, anger or confusion. It’s OK to take time to grieve. Ask your friends and family for support.
Prevention
Can a blighted ovum be prevented?
A blighted ovum can’t be prevented.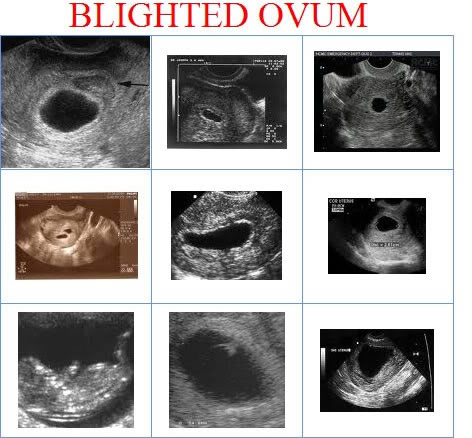 Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Outlook / Prognosis
How soon after a blighted ovum can I get pregnant again?
Most healthcare providers recommend having one or two regular menstrual cycles before trying to conceive again after any type of miscarriage.
What are my chances of having another blighted ovum?
Your chances of having another blighted ovum are low. Most people go on to have healthy, full-term pregnancies. If you experience more than one blighted ovum, your healthcare provider may suggest testing to determine if there is an underlying cause.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding from your vagina.
- Dizziness or fainting.

- Fever that does not go away.
- Symptoms that get worse over time.
- Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest ER If you experience heavy vaginal bleeding — more than two pads per hour for two consecutive hours — or have symptoms of anemia like dizziness, palpitations or paleness.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Losing a pregnancy is upsetting and confusing. Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
- Can I let my body miscarry or should I take medication to induce a miscarriage?
- What are the risks of miscarriage?
- Do I have to have a D&C?
- What are the risks of a D&C?
- How long can I expect to bleed or have cramping?
- Is there any indication this will happen again?
- When can I start trying to conceive?
- Do I need to come back for another ultrasound?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a blighted ovum considered a miscarriage?
Yes, a blighted ovum is a miscarriage.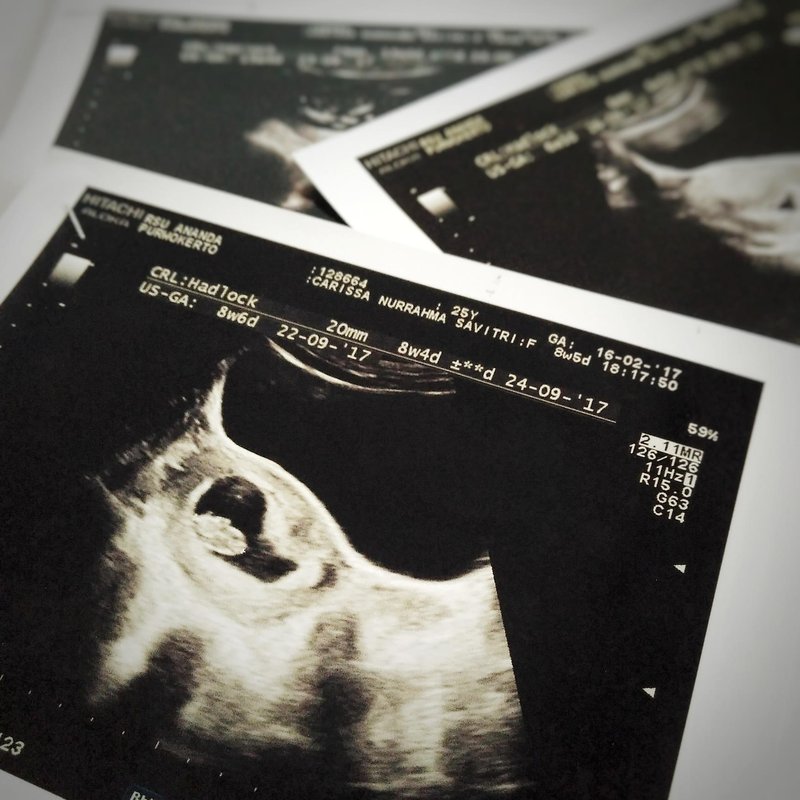 A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
How long can you carry a blighted ovum?
The amount of time you can carry a blighted ovum varies. Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby?
No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo. Your healthcare provider will be able to examine your gestational sac to confirm that no embryo has developed.
Do hCG levels rise with blighted ovum?
Yes, most of the time hCG levels will rise, giving you a positive pregnancy test and symptoms of pregnancy. This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
Is a blighted ovum more common with IVF?
A blighted ovum is not more common with IVF (In Vitro Fertilization). Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Losing a pregnancy is difficult. If you are struggling after a miscarriage, speak with your healthcare provider so they can recommend support groups or counselors. Finding support may help you get through this hard time. Most people who have had a blighted ovum will go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
Female infertility - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Astakhova Elena Stanislavovna
Otorhinolaryngologist (ENT)
MD GROUP Clinical Hospital
Every month, hormonal changes occur in a woman's body.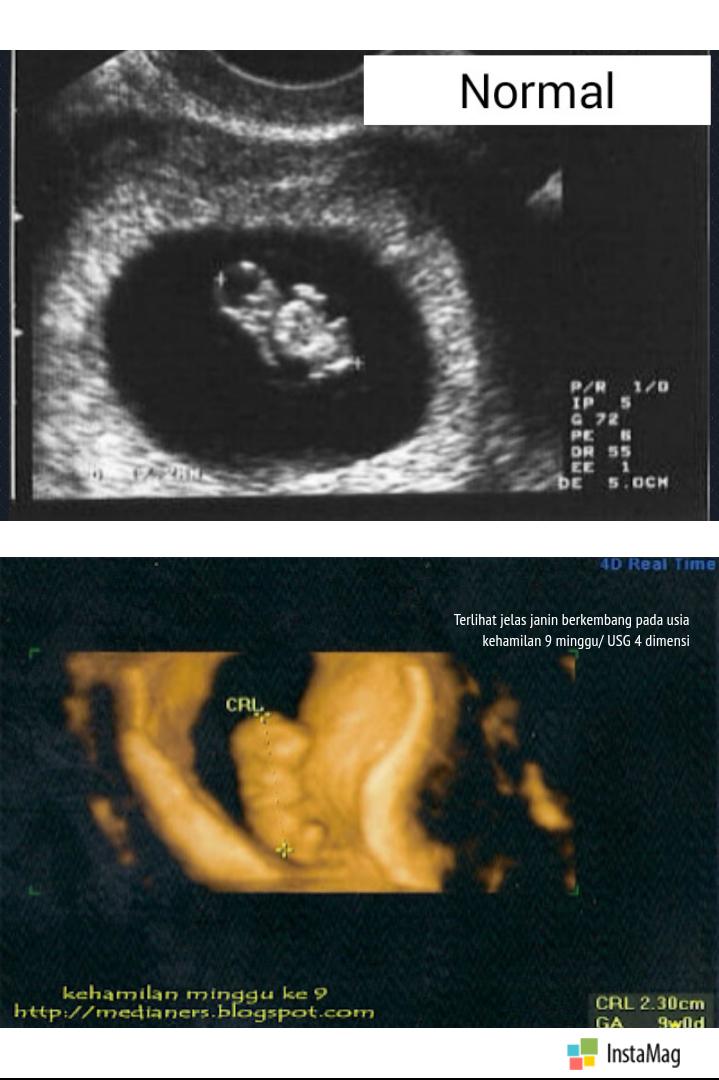 Thanks to them, eggs mature in the structure of the ovaries (in the follicles). In the middle of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs, that is, the follicle ruptures and the egg is released. It enters the fallopian tube, where it is fertilized by spermatozoa. Then the fertilized egg begins to divide and move along the fallopian tube to the uterus, which accepts it and ensures the further course of the pregnancy.
Thanks to them, eggs mature in the structure of the ovaries (in the follicles). In the middle of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs, that is, the follicle ruptures and the egg is released. It enters the fallopian tube, where it is fertilized by spermatozoa. Then the fertilized egg begins to divide and move along the fallopian tube to the uterus, which accepts it and ensures the further course of the pregnancy.
With hormonal disorders, ovulation does not occur. The egg does not mature, which means that pregnancy is impossible. If the fallopian tubes are impassable, then the fertilization process also cannot occur. Violation of ovulation and obstruction of the fallopian tubes are the reasons why a woman cannot become pregnant.
Factors affecting the possibility of conception are also inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, the presence of concomitant extragenital pathology.
In the presence of intrauterine pathology, the difficulty in the onset of pregnancy is associated with the impossibility of attaching the embryo to form a fetal egg and / or further development of the fetus.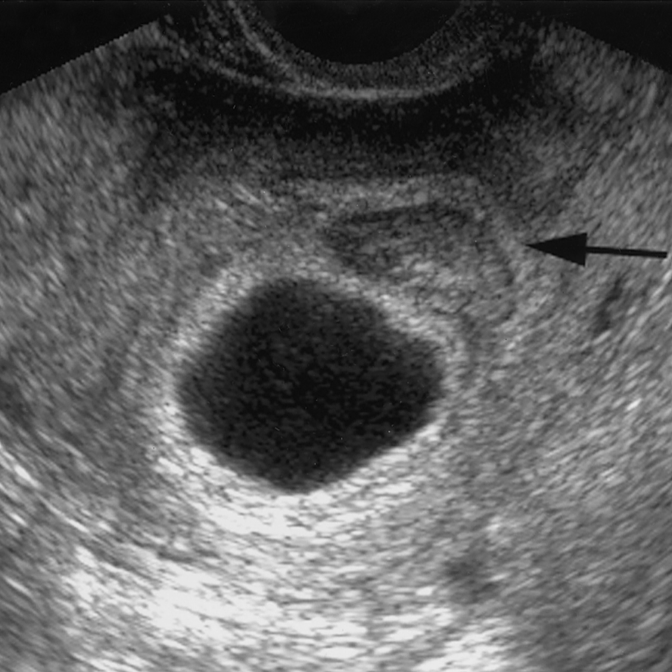
Ovarian endometriosis is an unfavorable factor in infertility that has a negative impact on folliculogenesis, egg quality, and the formation of the corpus luteum, thereby reducing the effectiveness of treatment, including the use of in vitro fertilization. The duration of the presence of endometriosis also has a significant impact on the outcome of treatment, determining the need to start planning pregnancy as soon as possible, avoiding a significant increase in the experience of infertility.
Pathology of the cervix can also be the cause of non-pregnancy. Timely and high-quality treatment of cervical diseases made it possible to obtain pregnancy in vivo in 15% of patients with this pathology and who received treatment at our Centers at the stage of preparation for ART programs. Thus, these women avoided the need for in vitro fertilization.
The causes of female infertility or non-carrying of pregnancy in some cases are violations of individual genes, structure or number of chromosomes.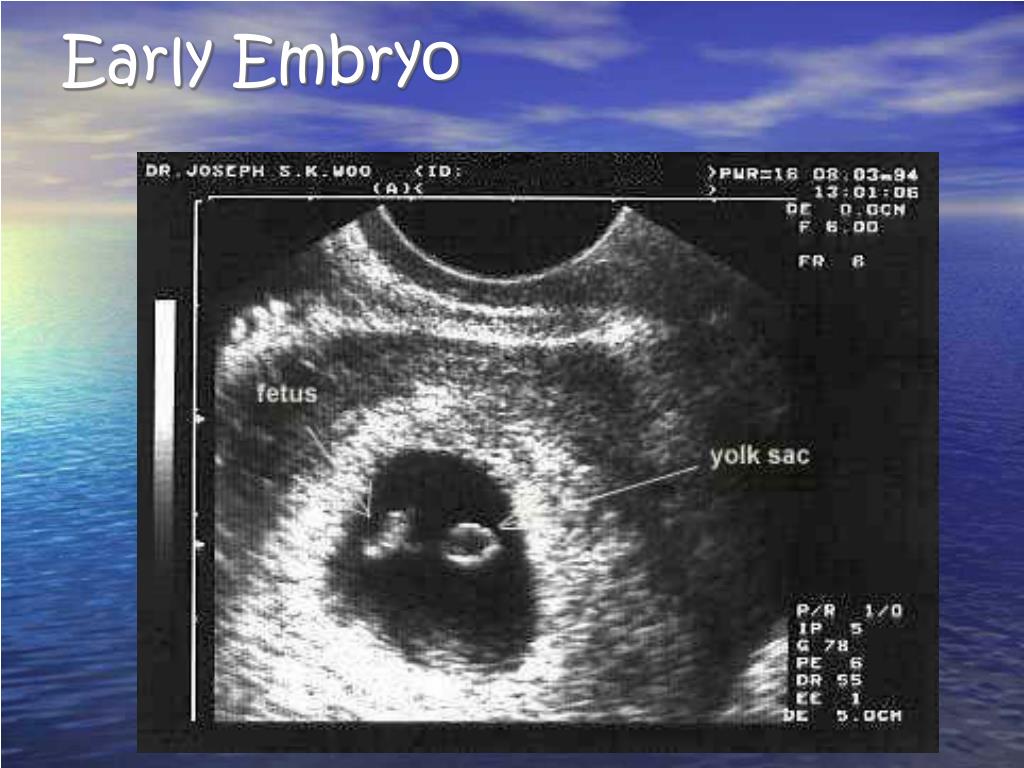 In these cases, conducting a preliminary genetic examination allows you to establish the nature of genetic disorders and choose tactics to overcome reproductive problems.
In these cases, conducting a preliminary genetic examination allows you to establish the nature of genetic disorders and choose tactics to overcome reproductive problems.
Increasingly, women seek to have children after 30 years, which is explained by the desire to sufficiently establish their social positions. However, with age, the cumulative effect of numerous risk factors for infertility increases both due to an increase in the duration of their exposure, and due to the addition of more and more new causes that negatively affect the onset of pregnancy. In addition, the reproductive potential of a woman has significant age restrictions, creating additional difficulties in the treatment of infertility, especially in women over 37 years of age.
Types of infertility
Infertility I - primary infertility. It is installed in a woman who has not had a single pregnancy.
Infertility II - secondary infertility. A condition in which a woman has had pregnancies in the past (regardless of their outcome), but at the present time, conception does not occur without protection for a year.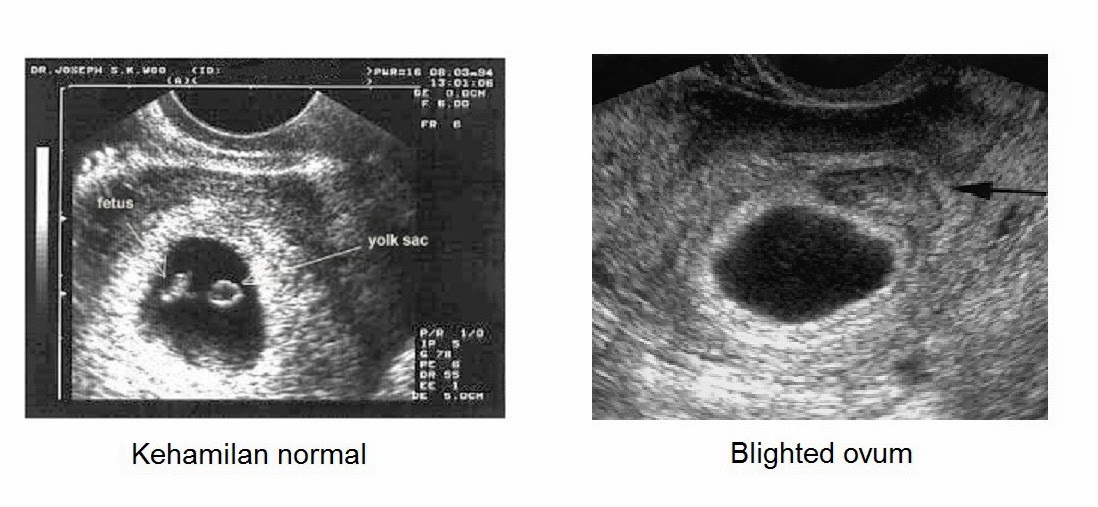
Absolute is infertility, in which the possibility of becoming pregnant is excluded, for example, in the absence of internal genital organs or their surgical removal.
Relative infertility - when a woman and a man are able to have children each separately outside of marriage, but with a long life together their marriage is fruitless.
In addition, female infertility is divided into congenital (malformations, hereditary disorders) and acquired (due to adverse effects of various external and internal causal factors on the reproductive system after birth).
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Astakhova Elena Stanislavovna
MD GROUP Clinical Hospital
Otorhinolaryngology
By clicking on the submit button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Clinic "Mother and Child" Khodynskoye PoleClinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" South-WestClinic "Mother and Child" Lefortovo
All directionsEco DepartmentEco services
01.
IVF department
02.
Eco services
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Ectopic pregnancy - causes, most common symptoms and treatment.
Benefit from the knowledge of our experts
- Home Page
- Knowledge
Return to the list of articles
3 decembris 2021 | 3.5 minutes of reading
SUMMARY An ectopic pregnancy, that is, the implantation and development of an embryo in a pathological site, is quite rare. However, this causes very dangerous complications that endanger the life of the mother, so it is very important to quickly diagnose an ectopic pregnancy and start appropriate treatment.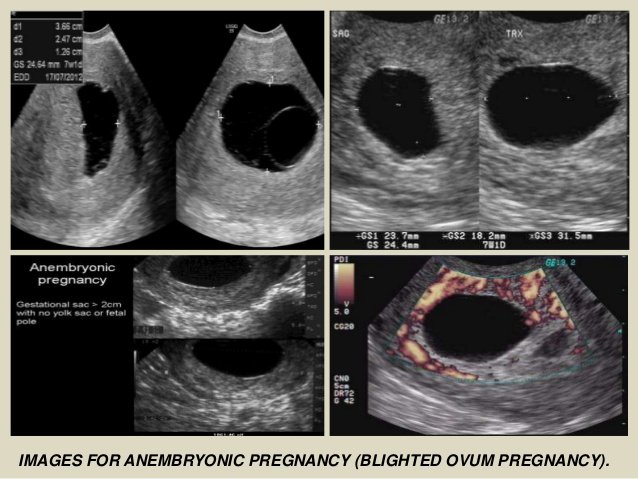
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
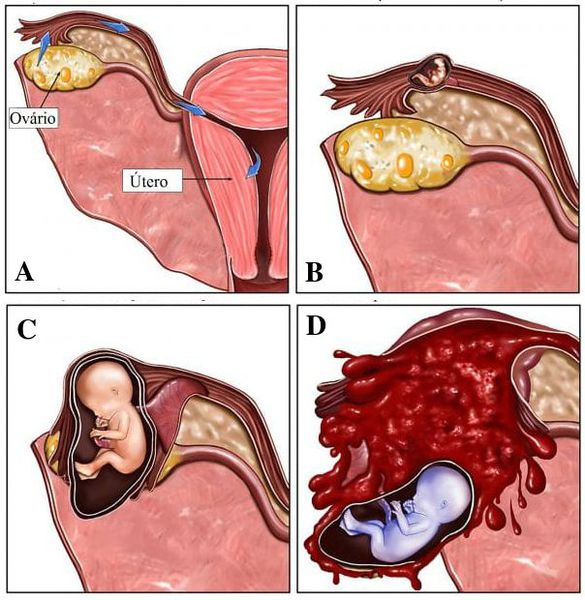
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fetus develops outside the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity . The course of a normal pregnancy is as follows: the egg meets the sperm in the fallopian tube, where fertilization takes place. The fertilized egg then passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus, where the implantation process takes place, that is, the embryo is implanted in the endometrium of the uterus. The situation when the embryo implants outside the endometrium is called an ectopic pregnancy. The most common pathological sites of embryo implantation are the fallopian tubes, but sometimes an ectopic pregnancy develops in the ovaries, cervix, and even the abdominal cavity. In these cases, the development and bearing of pregnancy is impossible, and this endangers not only the health of the woman, but also her life. Usually, the treatment of an ectopic pregnancy requires surgery.
Do you have any questions? Contact us!
Types of ectopic pregnancy
Depending on the place of implantation of the embryo , the following types of ectopic pregnancy are distinguished:

Causes of ectopic pregnancy
Most ectopic pregnancies develop without a specific cause. Factors contributing to the development of an ectopic pregnancy:
- endometriosis,
- narrowing of the fallopian tubes,
- inflammation of the ovaries or fallopian tubes,
- sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea, chlamydia,
- gynecological and other abdominal surgeries,
- fallopian tube defects,
- smoking,
- previous ectopic pregnancy,
- intrauterine device.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Early ectopic pregnancy is asymptomatic. Pregnancy tests show a positive result, just like a normal pregnancy. Signs of an ectopic pregnancy may appear about two months after conception, making early detection difficult. In the case of a progressive ectopic pregnancy, improper implantation of the embryo may be indicated by:
- painful abdomen,
- bleeding from the genitals,
- fainting and dizziness,
- nausea and vomiting,
- pain in the shoulders,
- feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen.
In case of rupture of the fallopian tubes, symptoms of shock may occur - cold sweat, shortness of breath, fainting, "hard stomach", heart palpitations. In this case, immediate medical attention is required.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
Women usually see a doctor immediately after a positive pregnancy test result. Then it is still impossible to distinguish a normal pregnancy from an ectopic pregnancy. During the first visit, the doctor determines the date of the last menstrual period and the duration of the woman's menstrual cycle. If, according to ultrasound, there is no fetal egg in the uterine cavity, a test for beta-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) should be performed as soon as possible and appropriate treatment should be prescribed. The level of the hormone hCG in the blood and the rate of its growth indicate the course of pregnancy - if the level of the hormone increases too slowly, an ectopic pregnancy can be suspected. In some cases, a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed to confirm the diagnosis.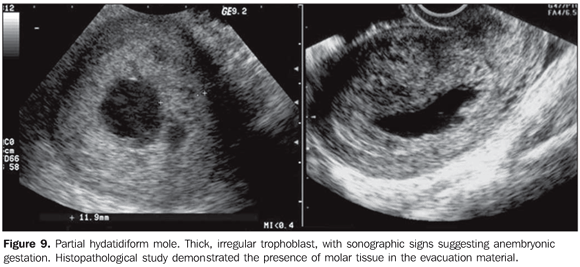
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
The method of treatment depends on the period of development of the fetus, the site of abnormal implantation and the degree of risk to the health of the woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is detected early , the doctor may prescribe pharmacological drugs that inhibit the development of the embryo . This will protect the fallopian tubes from damage. If the diagnosis is made after 8 weeks of gestation, surgery is usually required, and sometimes removal of the fallopian tube, especially for internal bleeding . Currently, this procedure is performed using laparoscopy, after which there are no visible scars, and recovery is much faster. In only a few cases, an incorrectly implanted embryo spontaneously disappears - is absorbed into the tissues. With an ectopic pregnancy, a consultation with a gynecologist is always required.
Re-pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy
Although an ectopic pregnancy is a very unpleasant and sometimes very painful experience, it usually does not prevent a second, healthy pregnancy.