Pale green poop in baby
Stools - Unusual Color
Is this your child's symptom?
- Stool color that is strange or different than normal
- Normal stool colors are any shade of brown, tan, yellow or green
- The only colors that may be caused by a disease are red, black and white
- Dark green may look like black, but dark green is a normal color
Causes of Unusual Stool Color
- Almost always due to food coloring or food additives.
- Stool color relates more to what is eaten than to any disease.
- In children with diarrhea, the gastrointestinal (GI) passage time is very rapid. Stools often come out the same color as the fluid that went in. Examples are Kool-Aid or Jell-O.
- The only colors we worry about are red, black (not dark green) and white.
Clues to Unusual Stool Colors
Red:
- "Bloody stools": 90% of red stools are not caused by blood
- Blood from lower GI tract bleeding
- Medicines.
Red medicines (like Amoxicillin). Sometimes, other medicines that turn red in the GI tract (such as Omnicef)
- Foods. See list below.
Foods That Can Cause
Red Stools:- Red Jell-O, red or grape Kool-Aid
- Red candy, red licorice
- Red cereals
- Red frosting
- Red food coloring
- Beets
- Cranberries
- Fire Cheetos
- Paprika
- Red peppers
- Rhubarb
- Tomato juice or soup, tomato skin
- Blood from stomach bleeding (stomach acid turns blood to a dark, tar-like color)
- Foods. Licorice, Oreo cookies, grape juice
- Medicines. Iron, bismuth (Pepto-Bismol)
- Other. Cigarette ashes, charcoal
- Bile. Dark green stools from bile may look black under poor lighting. Smear a piece of stool on white paper. Look at it under a bright light. This often confirms that the color is really dark green.
- Green stools are always normal, but they can be mistaken for black stools.

- Bile. Most dark green stools are caused by bile.
- Green stools are more common in formula fed than breastfed infants. It can be normal with both.
- Green stools are more common with diarrhea. This is due to a fast transit time through the gut. However, formed stools can also be green.
- Dark green stools may look black under poor lighting. Eating spinach can cause dark green stools.
- Medicines. Iron (such as in formula)
- Foods. See list below.
Foods That Can Cause
Green Stools:- Green Jell-O
- Grape-flavored Pedialyte (turns bright green)
- Green fruit snacks
- Spinach or other leafy vegetables
- Foods. Milk-only diet
- Medicines. Aluminum hydroxide (antacids), barium sulfate from barium enema
- Liver disease. Babies with blocked bile ducts have stools that are light gray or pale yellow.
When to Call for Stools - Unusual Color
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Stool is light gray or white and occurs 2 or more times
- Strange color without a cause lasts more than 24 hours.
 Exception: green stools.
Exception: green stools. - Suspected food is stopped and strange color lasts more than 48 hours
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Strange stool color most likely from food or medicine
- Green stools
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Stools - Unusual Color
- What You Should Know About Unusual Stool Color:
- Strange colors of the stool are almost always due to food coloring.

- The only colors that may relate to disease are red, black and white.
- All other colors are not due to a medical problem.
- Normal stools are not always dark brown. Sometimes they are light brown, tan or yellow.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Strange colors of the stool are almost always due to food coloring.
- Green Stools:
- Green color of the stools is always normal. Most often, green stools are caused by bile.
- Green stools are more common in formula fed than breastfed infants. But, they can be normal with both.
- Green stools are more common with diarrhea. This is due to a fast transit time through the gut. However, formed stools may also be green. This is normal and nothing to worry about.
- If your child takes iron, be sure your child is not taking too much.
- Avoid Suspected Food or Drink:
- Don't eat the suspected food.
- Don't drink the suspected drink.
- The strange stool color should go away within 48 hours.

- Save a Sample:
- If the strange stool color doesn't go away, bring in a sample.
- Keep it in the refrigerator until you leave.
- What to Expect:
- Remove the cause of the unusual color from the diet.
- Then the stool should change back to normal color.
- This should happen within 48 hours or 2 stools later.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Strange color without a cause lasts more than 24 hours
- Suspected food is stopped and strange color lasts more than 48 hours
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 12/30/2022
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
What does baby poop color mean? Chart and guide
An infant’s poop changes color and consistency during their first few days, weeks, and months of life, and a wide range of colors is normal. Below, learn what changes to expect as a baby grows and how to recognize unhealthy baby poop.
In infants, the main reasons for changes in stool color are age, diet, and health. The poop of newborns is almost black, while older infants tend to have yellow or brown poop.
Breast milk and formula can also influence the color of a baby’s stools.
Red or white poop can indicate a health problem. Otherwise, a wide range of colors is normal. Anyone who suspects that a baby has diarrhea or constipation should seek medical advice.
Various factors can cause changes in the color of a baby’s stools. Common colors and their causes include:
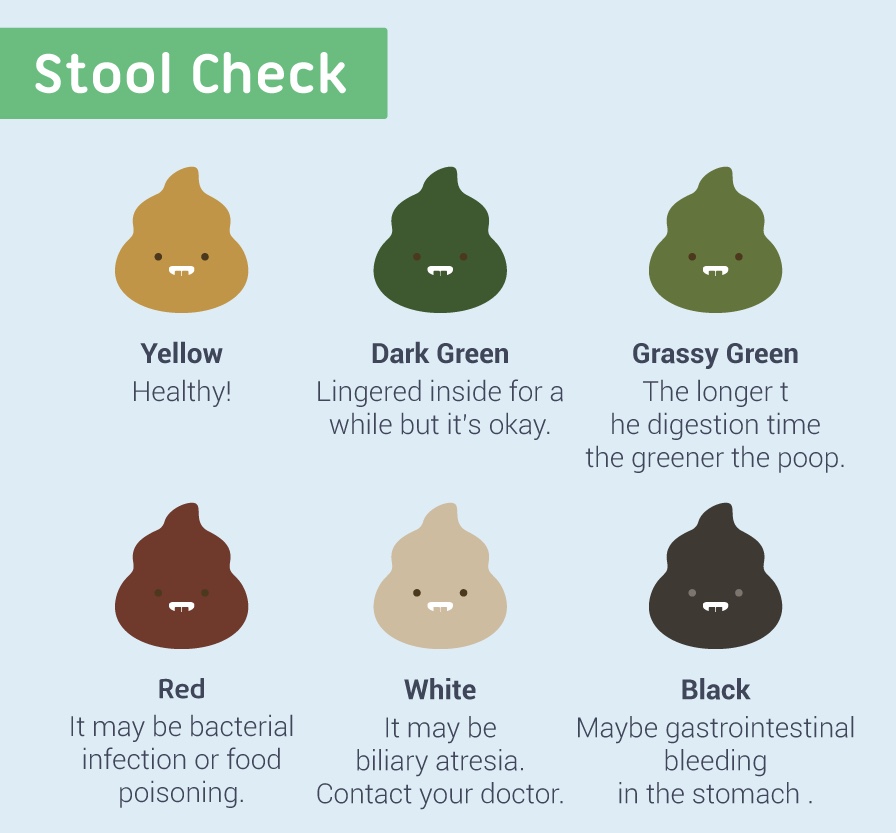
Black
In newborns younger than 1 week, black is a healthy color for stool. After this time, however, it could indicate a health problem.
During the first 24 hours of life, a newborn will pass meconium. This is thick, black stool. It comprises cells, amniotic fluid, bile, and mucus that the baby ingested while in the womb. Meconium is sterile, so it usually does not smell.
Over the first few days of life, a newborn will continue to pass meconium. The color should gradually change from black to dark green, then yellow.
After 1 week of life, stool should no longer be black. If a black color persists, it is important to seek medical advice. This color could mean that there is some bleeding in the digestive system.
Yellow
This is a normal color of poop from a baby who drinks breast milk. Their poop tends to be dark yellow, and it may have small flecks in it.
These flecks come from breast milk and are harmless. People often describe this poop as “seedy.” The so-called seeds may resemble curds in cottage cheese, but they are yellow.
Brown or orange
This is a normal color of poop from a formula-fed baby.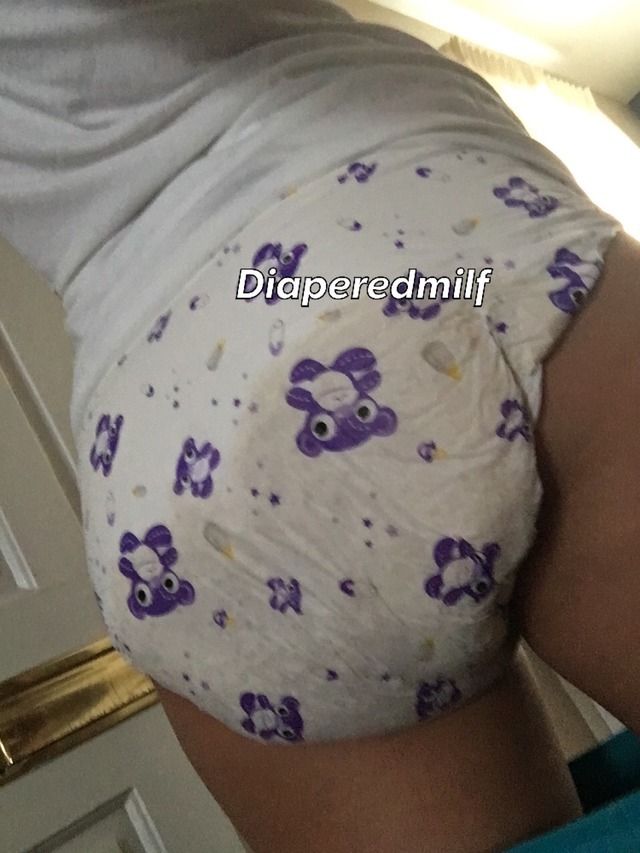
When a baby drinks formula, their poop tends to be light brown or orange. It may be slightly darker and firmer than stool from a baby who drinks breast milk.
Green
Many babies occasionally have green poop. Possible causes include:
- slow digestion, usually because the baby has eaten more than usual
- green foods in the diet of the person producing breast milk
- a cold or stomach bug
- a food allergy or intolerance
- antibiotics, either in the baby or in the person producing breast milk
- treatment for jaundice
Some infants’ poop is naturally slightly green. If the baby is putting on weight and seems content, green poop is not necessarily a cause for concern.
Learn more about green poop in children.
Red
Red is not a healthy poop color.
Poop is usually red because there is blood in it. Parents or caregivers should seek medical advice as soon as possible.
The baby may have a health problem, or they may have swallowed a small amount of blood. This could happen if the person breastfeeding them has cracked or bleeding nipples. Another cause of red poop is bleeding from the baby’s bottom.
This could happen if the person breastfeeding them has cracked or bleeding nipples. Another cause of red poop is bleeding from the baby’s bottom.
White
White poop is uncommon, but white is not a healthy color for stool. It could indicate a liver problem.
Jaundice, for example, is highly common in newborns, affecting about 60% of full-term babies in their first few days of life. It usually goes away within the first 2 weeks.
Anyone who suspects that their baby still has jaundice after 14 days should check the color of their poop. Pale or white poop may suggest liver disease. Another sign to look for is urine that is very dark yellow or brown.
If the baby has white or pale stool, the doctor may test their bilirubin levels. Bilirubin is a compound that helps the body get rid of waste. There are two types of bilirubin, and if the levels of one type are too high, this can cause health problems.
Baby poop can also have a variety of textures and other features. Before an infant starts eating solid food, their poop is usually very soft.
Before an infant starts eating solid food, their poop is usually very soft.
Babies who drink breast milk may have quite runny or stringy poop, while formula-fed babies tend to have firmer, but not solid, poop.
Mucus in a baby’s stool is also common and rarely a sign of any health issue. However, if the baby shows other signs of unusual behavior or illness, it is important to speak with a doctor.
Dry or hard poop can mean that a baby is not drinking enough fluids or that they are ill.
After an infant starts to eat solid foods, hard poop can also be a sign of constipation. Babies commonly become constipated when they eat foods that their body cannot yet digest properly.
Very watery stool can result from diarrhea. A baby with diarrhea may also poop more often than usual or have a high temperature. Diarrhea can cause dehydration, which is potentially serious for infants.
Every baby is different, and some poop more often than others. Many newborns poop after each feeding, though they tend to pass stool less frequently once they reach 6 weeks of age. Babies who drink breast milk may only poop once a week. A healthy frequency for formula-fed babies is once per day.
Babies who drink breast milk may only poop once a week. A healthy frequency for formula-fed babies is once per day.
Learn more about constipation in babies.
As a baby grows, their poop often changes color. For example, as an infant starts to eat solid foods, what they eat may affect the color of their poop. Undigested food in stool can also cause a change in color.
Unusual colors, such as green, may not signal a health issue. Stool color may vary for a short time and then return to its regular shade.
White, red, or black are the exceptions — these colors can indicate a health problem.
Also, if a lot of mucus is present or it appears in stool on an ongoing basis, this could signal an illness.
Parents or caregivers should contact a doctor if they have any concerns regarding an infant’s health.
Newborns generally poop frequently, sometimes after every feed. Infants older than 3 weeks may poop anywhere between 8–12 times a day to less than once a day.
Healthy poop can be shades of yellow, orange, brown, or green, and the texture may be runny to fairly firm. It should not be hard or watery.
Babies often strain a little as they pass stool and may make noises or scrunch up their faces. This is normal. However, too much straining or discomfort when pooping could be a sign of constipation.
Poop color can be one way to keep track of a baby’s health.
Stool that is quite soft and earthy in color is generally healthy. However, red or white poop often signals a health issue that requires attention. Black stool from babies older than 1 week may also be a cause for concern.
Overall, as long as an infant is gaining weight and feeding as often as they need, a broad range of poop colors is healthy. Parents or caregivers should discuss any concerns with a doctor.
Green feces - causes, what diseases it occurs in, diagnosis and treatment
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. nine0003
Green feces: causes of occurrence, in which diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
Definition
Greenish stool in people of any age can be both a normal variant and evidence of serious changes in the body.
Feces is a waste product of the body, formed in the large intestine, consists of 80% water and 20% solids. The dry residue includes undigested food (40%), almost completely non-viable intestinal microflora (30%), secretions of the glands of the intestinal wall (mucus) and dead cells of the intestinal mucosa (30%). nine0003
nine0003
The composition and nature of feces are determined by nutrition, the state of the digestive system, intestinal microflora, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The composition of the normal intestinal microflora includes a large number of bifido- and lactobacilli, E. coli, bacteroids. They are useful because they perform a protective function and inhibit the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. Enterobacteria, enterococci, clostridia, staphylococci, streptococci, fungi of the genus Candida are present in a smaller amount in the intestine. With uncontrolled reproduction, they can cause unpleasant symptoms. nine0003
Varieties of green stool
Green stool occurs in normal and pathological conditions. With the pathological nature of the stool, the general well-being of the patient changes, the frequency of defecation, the consistency of the stool, its smell, impurities of mucus, pus, and blood may appear.
Possible causes of green stools
The most common cause of green stools without changing its other characteristics is the consumption of green plant foods - spinach, sorrel, lettuce, etc., as well as foods containing green food coloring. In this case, the color of feces normalizes on its own within one to two days after stopping the use of these products. nine0003
Another normal variant is meconium, the first feces of a newborn. It is viscous, sticky, dark green in color, consists of dead cells of the intestinal wall, mucus, amniotic fluid, bile.
The intestines of a newborn baby are gradually colonized by microorganisms. At the same time, the composition of the microflora of a breastfed baby, despite the predominance of lacto- and bifidobacteria, is more variable than that of a formula-fed baby.
Some bacteria can affect the color of stool and turn it green. With good health, appetite and the absence of other symptoms, these phenomena are considered a variant of the norm. nine0003
nine0003
Persistent disturbance of the composition of the intestinal microflora (dysbacteriosis) is considered a pathological condition that affects the color of feces.
When taking tableted and encapsulated iron preparations, excess iron is excreted naturally, the feces acquire a dark, greenish, up to black tint.
Kal completely restores its characteristics after the end of the course of medication.
Possible causes of green stools include infectious and inflammatory diseases of the stomach, small and large intestines. nine0003
Diseases that cause feces to turn green
Lactase deficiency is a congenital or acquired condition in which the activity of the lactase enzyme and the ability to digest lactose are absent or reduced. Congenital lactase deficiency begins in early childhood and persists throughout life; transient deficiency develops against the background of immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of a newborn (occurs at 3-6 weeks of life and decreases as the child grows and develops). Secondary lactase deficiency is a consequence of a previous disease, accompanied by damage to the cells of the intestinal wall. nine0003
Secondary lactase deficiency is a consequence of a previous disease, accompanied by damage to the cells of the intestinal wall. nine0003
The main symptoms of lactase deficiency are severe bloating, intestinal colic, loose frothy stools after drinking breast or whole cow's milk.
With insufficient processing of lactose in the gastrointestinal tract, the processes of fermentation and decay begin, which cannot but affect the composition of the microflora. With a pronounced imbalance of microorganisms, green stools may appear.
Violation of the ratio of normal and pathogenic intestinal microflora is called dysbacteriosis . This condition can occur against the background of a sharp change in nutrition, with insufficient consumption of plant foods and dairy products, due to inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, gastric and duodenal ulcers, infectious lesions of the small or large intestine, after taking a course of antibacterial drugs, against the background of a decrease in immunity .
Symptoms of dysbacteriosis include constipation or unstable stools, impaired processing and absorption of beneficial nutrients, bloating and pain in the abdomen. nine0003
Among intestinal infections, which are characterized by the appearance of green stools, dysentery, giardiasis, salmonellosis, and rotavirus are distinguished.
Dysentery is caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella, which are excreted in the stool by an ill person or carrier. Shigella enter the body through dirty hands, and after 2-3 days, the development of the disease begins. Bacteria multiply in the large intestine, irritating and damaging its wall.
Symptoms of dysentery are false painful urge to defecate, as well as frequent, scanty liquid stools of dark green color with impurities of blood, mucus, and pus. nine0003
The patient's general health worsens, he is worried about weakness, body temperature rises. At the same time, due to light stools, the risk of dehydration remains low, but perforation of the intestinal wall is possible.
At the same time, due to light stools, the risk of dehydration remains low, but perforation of the intestinal wall is possible.
Giardiasis is caused by protozoa - Giardia. The transmission mechanism is fecal-oral, infection is possible through direct contact with a sick person or through contaminated water and food. It takes up to four weeks from the moment of infection to the onset of symptoms. More often sick children and adults with low acidity of gastric juice. nine0003
The simplest cause symptoms of inflammation of the small intestine: nausea, bloating, pain in its upper and middle thirds, around the navel, frequent (up to 5 times a day) liquid, profuse, frothy, foul-smelling green stools.
Extraintestinal manifestations are also possible - skin rashes, pronounced allergic reactions.
Giardia
Salmonellosis is caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. They enter the human body through poorly thermally processed eggs, dairy products and meat. The period from infection to the onset of the disease lasts up to two days. The symptoms of salmonellosis include spasmodic pain in the upper abdomen and near the navel, nausea, vomiting (up to 3 times a day), as well as frequent (up to 15 times a day) plentiful, liquid, frothy, fetid stools of the color of marsh mud. nine0003
The period from infection to the onset of the disease lasts up to two days. The symptoms of salmonellosis include spasmodic pain in the upper abdomen and near the navel, nausea, vomiting (up to 3 times a day), as well as frequent (up to 15 times a day) plentiful, liquid, frothy, fetid stools of the color of marsh mud. nine0003
The disease is dangerously severe intoxication, dehydration, possible entry of salmonella into the blood and dysfunction of many organs and systems (sepsis).
Rotavirus is spread by food, water, airborne droplets, household. Perfectly preserved in the external environment, resistant to most disinfectants. For the development of the disease, it is enough for just a few viral particles to enter the mouth. It begins with symptoms of an acute respiratory viral infection - fever, redness and sore throat. Then frequent profuse vomiting and frequent (5-15 times a day) loose stools, which can be of different shades, including yellow-green, join. Against this background, dehydration quickly develops. nine0003
Against this background, dehydration quickly develops. nine0003
Which doctors to contact
If there are signs of an intestinal infection, especially in a child, it is best to call an ambulance team, which, if necessary, will take the patient to the infectious diseases hospital.
Otherwise, please contact therapist general practitioner, pediatrician gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics and examinations in case of green stool
To determine the causes of green stool, the doctor conducts a thorough survey and examination of the patient, clarifies the regimen and nature of nutrition, finds out concomitant diseases and conditions. nine0003
For a more complete understanding of the picture, a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods may be required:
- complete blood count with an expanded leukocyte formula;
What to do if green stool appears
You need to see a doctor, undergo an examination and follow the recommendations of a specialist.
To prevent the occurrence of green stools, you should eat a balanced diet, observe personal hygiene, take care of the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. nine0003
Treatment for green stools
Treatment is not required only in one case - when the green color of the stool is associated with dietary errors.
Adults with lactase deficiency are advised to follow a diet low in whole and powdered milk. Breastfed children are prescribed lactase preparations, and artificially fed children are prescribed low-lactose or lactose-free mixtures.
With established dysbacteriosis, diet and medications that normalize the intestinal microflora are required. In rare cases, drugs are prescribed that inhibit the growth and development of a certain type of microbe. nine0003
In intestinal infections, the main task is to maintain water balance (if necessary, fluid is administered intravenously) and to remove intoxication.
If there is a drug that specifically affects the causative agent of a particular disease (antibiotic, bacteriophage, etc. ), it is recommended to be taken. At the same time, measures are taken to restore the intestinal microflora.
), it is recommended to be taken. At the same time, measures are taken to restore the intestinal microflora.
Sources:
- Clinical guidelines "Salmonellosis in adults". Developed by: National Scientific Society of Infectious Diseases. – 2021.
- Belmer S.V. Lactose insufficiency: origin and ways of correction // The attending physician. - No. 2. - 2018. - S. 41-46.
- Clinical guidelines "Salmonellosis in children". Developed by: Euro-Asian Society for Infectious Diseases, Association of Infectious Disease Doctors of St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region. – 2021.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0005 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes over time, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Child's stool color - what does light, green or black stool indicate?
The characteristics of the baby chair are influenced by such indicators as age, type of feeding, and developmental features of the baby. At the same time, a change in the shade, consistency of the stool, the appearance of an unpleasant odor may indicate the presence of a particular pathology. Let's talk about which stool changes are a variant of the norm, and which are a cause for concern. nine0003
Peculiarities of the child's nutrition
Having noticed an unusual color of feces in a child, parents should also pay attention to the color of the urine and the general well-being of the baby. If the urine has not become more saturated, and the child is active and cheerful, then the changes are most likely associated with the food eaten the day before.
If we are talking about a baby who feeds on mother's milk, then it is the mother herself who should analyze the diet. In formula-fed babies, stool changes may be due to the fact that the parents decided to introduce a new mixture. nine0003
nine0003
In older children who eat at the same table with adult family members, unusual stools are also most often associated with eating certain foods. Calcium-rich food contributes to the staining of feces in a light color, increasing its viscosity. For example, many kids love cottage cheese with sour cream. Eaten the day before, such a snack helps to lighten and increase the viscosity of feces - it becomes like clay.
The cause of green stool in a child may be eating a large amount of green vegetables, as well as lettuce leaves. Brick-red staining is often due to the fact that the child went too far with red berries or tomatoes. Blackcurrants and blueberries can cause very dark stools. nine0003
Other causes
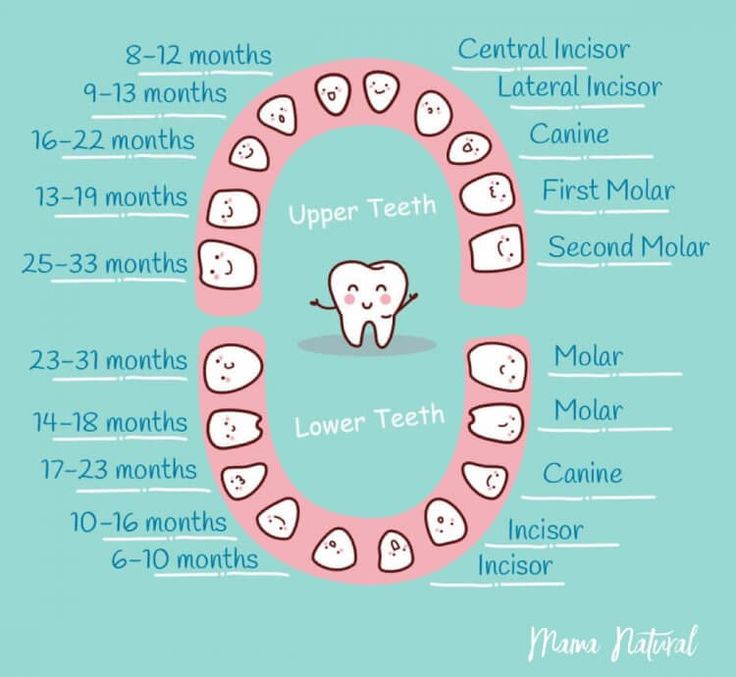
Pediatricians say that the appearance of light-colored feces in a child may be due to the eruption of milk teeth. The exact causes of this process remain not fully understood, but the fact remains. Young mothers should remember about this feature of the child's body. However, if you are in doubt about a change in stool color, it is best to consult your pediatrician. Remember that the period of teething is often accompanied by an increase in susceptibility to various infections, including enteroviruses. nine0003
However, if you are in doubt about a change in stool color, it is best to consult your pediatrician. Remember that the period of teething is often accompanied by an increase in susceptibility to various infections, including enteroviruses. nine0003
Also, if the color of the child's feces changes, parents should remember whether they gave him any medications the day before. Some drugs stain the stool: for example, the use of iron-containing products is associated with the appearance of greenish-black stool.
Finally, healthy children's feces can darken and lighten periodically. If the baby’s well-being does not suffer at the same time and the color of the feces returns to normal within a couple of days, then you should not sound the alarm.
The child's stool color has changed - maybe something is wrong? nine0163
Features of feces often indicate certain pathological processes. And sometimes a change in color, smell and other characteristics are the only symptoms that prompt a pediatrician to think about the correct diagnosis.
Dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of the intestinal microflora. The shift in the species ratio of bacteria towards symbionts, which are normally present in small quantities, cannot but affect the properties of feces. In children suffering from dysbacteriosis, the stool becomes watery, with an admixture of a mucous character, lighter than normal. In severe cases, the feces can become frothy, acquire a sharp unpleasant odor. nine0003
These symptoms are often accompanied by pain in the abdomen, increased gas formation - the general condition of the child suffers. To solve the problem as soon as possible, you need to see a doctor.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis in children and adults may present with characteristic grayish discolored stools. In order to exclude the presence of hepatitis in a child, when light stool appears, parents should pay attention to the color of the urine. Discolored stools, caused by a malfunction of the liver cells, are always accompanied by the release of saturated urine (the so-called "beer-colored" urine). nine0003
nine0003
If warning symptoms appear, you should not panic - only a specialist can make a diagnosis of hepatitis. But there is no need to delay visiting the pediatrician. The doctor will prescribe a diagnostic plan and give the necessary recommendations.
Pancreatitis
Many people think that only adults suffer from pancreatitis. But, unfortunately, inflammation of the pancreas can occur at any age. Cal at the same time acquires a grayish tint, an unpleasant odor. In chronic pancreatitis, the total amount of excreted feces is increased, and it itself acquires a kind of oiliness, it is poorly washed off. nine0003
In a classic attack of pancreatitis, abdominal pains of girdle nature (or localized in the navel) are also observed. There are also symptoms of dyspepsia:
- loss of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased gas formation.
Children may also experience mild fever, pale skin, and dry mouth. An attack of pancreatitis can be triggered by excessive consumption of chocolate, cocoa, carbonated drinks, fresh vegetables.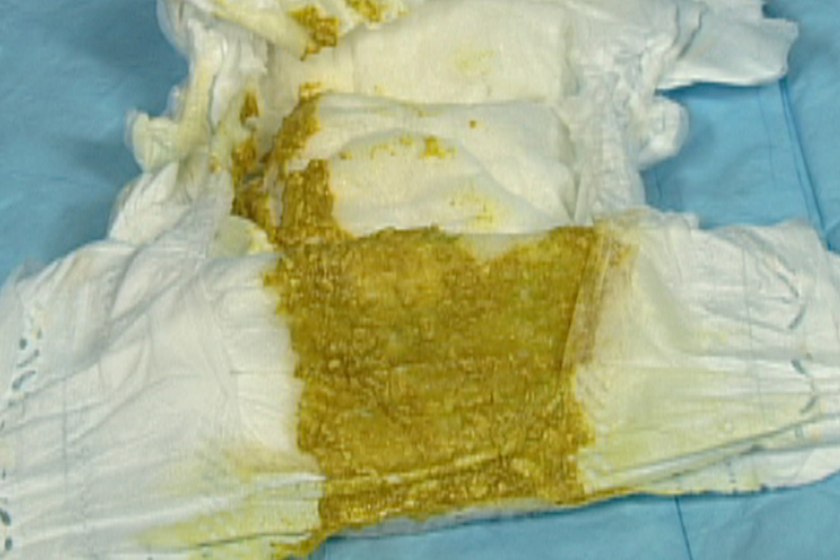 nine0003
nine0003
Bent gallbladder
Bent gallbladder is a fairly common congenital anomaly. The bend of the gallbladder may be asymptomatic. Manifestations of pathology can appear after heavy consumption of food, especially fatty. Children are worried about vomiting with an admixture of bile, pain in the right side.
The bending of the gallbladder is characterized by alternating periods of constipation and diarrhea. With a pronounced inflection, the feces may become lighter than normal.
Rotavirus infection
This viral infectious disease is accompanied by intoxication (its signs are weakness, fever, general malaise) and symptoms of gastrointestinal lesions. The latter include pain, nausea, repeated vomiting, rumbling in the abdomen. At the same time, the child's stool is plentiful, it becomes watery, frothy, has a greenish-yellow color and a pungent odor. As a rule, pathological impurities are absent or there is a small amount of mucous inclusions.
Vomiting and diarrhea in children can cause severe dehydration very quickly.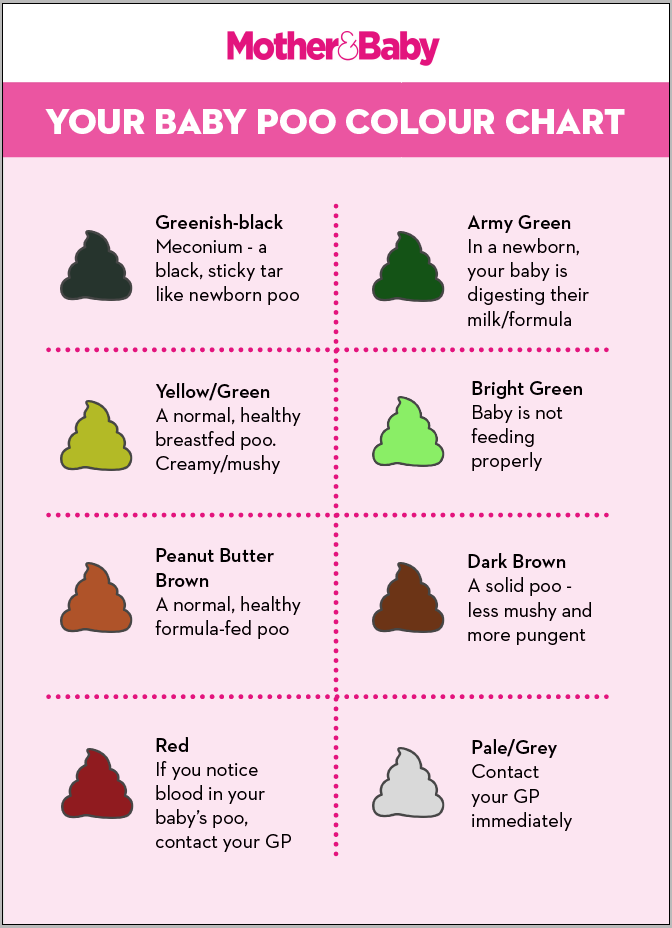 This condition is extremely dangerous for children, therefore, if the above symptoms appear, seek medical help immediately. nine0003
This condition is extremely dangerous for children, therefore, if the above symptoms appear, seek medical help immediately. nine0003
Whipple's disease
This rare infectious disease is accompanied by damage to the lymphatic system of the small intestine and articular syndrome. Whipple's disease occurs with marked fever, abdominal pain, flatulence, nausea, and vomiting. The stool is liquid, defecation occurs up to 10 times a day, the stool has a grayish tint and a pungent odor.
Is it necessary to go to the doctor if there is a change in the color of feces in children?
Since a change in the characteristics of the stool in a child can often be a variant of the norm, parents should act depending on the circumstances of the particular case. Attentive mothers and fathers can easily notice the connection between a change in stool and a previously eaten product or medication the day before. Even if the nature of the feces has changed for no apparent reason, but the child feels normal, it is worth observing him for 1-2 days. Perhaps the stool will normalize on its own. nine0003
Perhaps the stool will normalize on its own. nine0003
In all other cases, when a change in the color and other properties of feces is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, fever, nausea, pallor of the skin and any other pathological signs, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician as soon as possible. Acute diseases in children can progress at a very high rate, so refusing to consult a specialist can be deadly.
Foamy stool in an infant
Foamy stool in an infant is a sign of a deficiency in the normal intestinal microflora. Without the right amount of beneficial bacteria, the physiological process of digestion becomes impossible, and the consistency of the stool changes. nine0003
Microflora imbalance may be temporary, transient. In this case, the condition is normalized without special treatment. In more serious cases, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of pro- and prebiotics. Finally, dysbacteriosis in combination with foamy stools is often one of the symptoms of an intestinal infection, especially if the child complains of abdominal pain, fever, and deterioration in the general well-being of the baby.
Diarrhea in infants
Newborns have loose stools due to infectious and non-infectious causes. nine0003
Diarrhea of an infectious nature has the following features:
- pronounced unpleasant odor;
- foaminess;
- increasing up to 8-10 times a day;
- combination with nausea and vomiting, fever.
Causes of non-infectious diarrhea in an infant include:
- lactose intolerance;
- violations of the diet by a nursing mother;
- reaction to unusual complementary foods. nine0116
Constipation in infants
Normally, a baby's stool is soft, but constipation can occur as early as the first month. If a child of the first year of life (and especially the first four weeks) has difficulty passing feces, parents should consult a pediatrician. Constipation in an infant may be a sign of one of the pathologies:
- Hirschsprung's disease. In this disease, there is a violation of the innervation of the rectum.
 The main symptoms of the disease are increased gas formation and recurrent constipation, the appearance of which is not associated with a change in the nature of nutrition. nine0116
The main symptoms of the disease are increased gas formation and recurrent constipation, the appearance of which is not associated with a change in the nature of nutrition. nine0116 - Anal fissure, irritation of the perianal zone. In this case, each act of defecation gives the child severe discomfort, therefore, at the psychological level, the baby can be restrained - constipation forms.
In addition, excessive use of microenemas and the gas tube can lead to constipation. Sometimes parents, sincerely caring about the child, trying to relieve him of constipation, use special assistive devices almost every day. However, such actions can irritate the delicate skin of children in the anus, which indirectly can further aggravate the problem of constipation. nine0003
Occult blood in the stool
The presence of a significant amount of blood in the stool is not so difficult to recognize. Bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (with anal fissure, ulcerative colitis) is manifested by bright red streaks. If the source of bleeding is higher (esophagus, stomach), the stool turns black.
If the source of bleeding is higher (esophagus, stomach), the stool turns black.
Occasionally, stool may be normal in color and consistency, but may contain microstreaks of blood. This condition must be identified and treated, as the child regularly loses blood (even in microscopic amounts), which can provoke the development of iron deficiency anemia. nine0003
A pediatrician orders a fecal occult blood test, mainly due to a suspected gastrointestinal food allergy. The intestinal mucosa in young children is very delicate, so it is easily damaged by allergens. Especially frequent appearance of blood microveins in the feces is associated with the action of such generally recognized allergens as soy, chicken egg, wheat, seafood, cow's milk protein, peanuts.
Stools with mucus and strong odor
Mucus is a lingering secretion produced by the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall. With the help of mucus, the intestines are protected from the aggressive effects of the external environment, the pH of which differs from the norm in the acid or alkaline direction.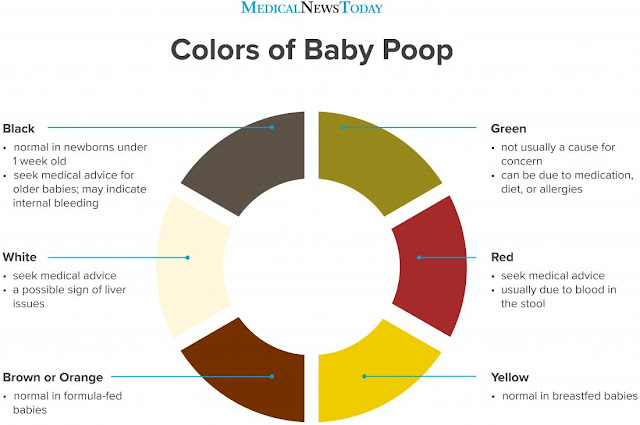 nine0003
nine0003
Few people know that reduced mucus content in feces can also lead to problems - cause constipation. However, parents are more concerned about the high content of mucus in the feces of the child.
The appearance of a mucous admixture may be one of the signs:
- Acute respiratory infection. Young children, who are not yet able to blow their nose and cough, swallow nasal mucus and phlegm. This mucus is excreted along with the stool.
- Teeth eruption. At the same time, saliva is actively secreted, which can also contribute to the appearance of mucous secretions. nine0116
Mucus in a child's stool should not be of great concern to parents, since most often this sign does not indicate serious health problems.
Pieces of undigested food in the stool
Pieces of food in the stool of a child also often cause anxiety in parents. The logic of mothers and fathers is simple: if the baby could not digest the food to the end, then perhaps he has problems with the work of the stomach and he does not receive enough nutrients. However, such judgments are not entirely correct. nine0003
However, such judgments are not entirely correct. nine0003
The causes of the appearance of undigested food particles can be:
- Physiological (age-related) deficiency of enzymes. Some periods of a child's development are accompanied by a temporary deficiency of enzymes. But this does not mean that the child does not receive enough proteins, fats and carbohydrates. As you get older, your enzyme levels will normalize and your stools will become smooth.
- Eating foods that, in principle, cannot be completely broken down in the human body. So, individual elements of fiber, which are rich in many vegetables and corn, are always excreted unchanged with feces. Small seeds of berries and some fruits (such as bananas) are also not digested in the gastrointestinal tract of children. nine0116
Bad smell
A child's feces may acquire an uncharacteristic smell in the following cases:
- intestinal infection - the stool has a sharp, fetid odor;
- enzyme deficiency - putrid odor in combination with a change in the consistency of feces;
- constipation: stool that passes after a stool may have a different smell and texture.

What can I do to get my baby's stool normal? nine0163
Let's summarize. Treatment of stool disorders in babies depends on the causes of their occurrence.
If the mother clearly sees the connection of the changes that have occurred with too early complementary foods or the use of certain foods, it is only necessary to normalize the diet. With a high degree of probability, after 1-2 days, the child's stool will return to normal.
Do not require treatment and changes in feces caused by teething, taking the necessary medications. The exception to the rule is antibiotics: they cause dysbacteriosis. Prevention of this condition with the help of pre- and probiotics should begin from the first day of taking antibacterial drugs. nine0003
In all other cases, it is best to consult a doctor. Especially "dangerous" options for staining feces in a child are grayish-white, black and with bright red streaks of fresh blood. Also, babies with any changes in the stool in combination with signs of an infectious disease need an urgent visit to the doctor: fever, weakness, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.