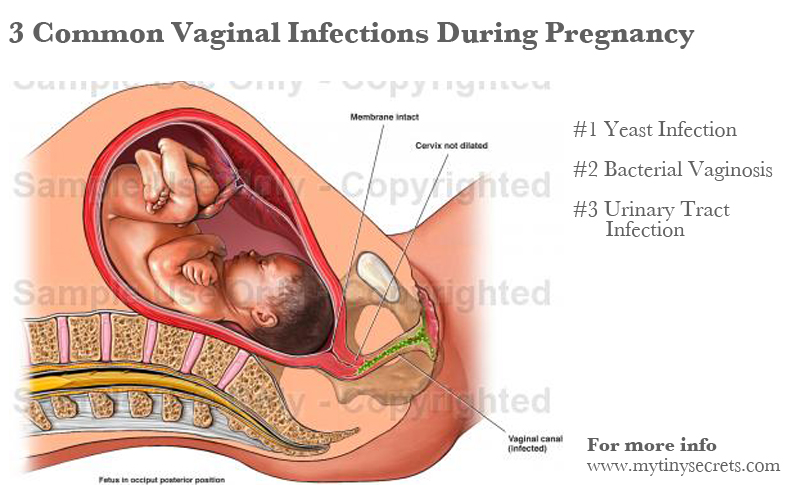
Vaginal discomfort during pregnancy
Vaginal pressure during pregnancy: Causes and relief
During pregnancy, many women feel pressure, or heaviness, around the vagina. This is normal and can happen in the first, second, or third trimester.
A pregnant woman’s uterus will expand from the size of an orange to the size of a watermelon or larger. Her body will not only need to provide space and nutrients for a new person to develop but will have to produce an entirely new organ in the form of a placenta.
With so many changes happening, it is not surprising that many women notice sudden and unusual shifts in how their bodies feel. Vaginal, pelvic, or lower abdomen pressure is common in all three trimesters of pregnancy.
Read on to learn about the causes and symptoms of vaginal pressure during each stage of pregnancy, as well as treatment options and possible complications.
Women will have different experiences of vaginal pressure during pregnancy.
Some may feel an intense pressure in the vagina, while others will have a dull ache throughout the pelvis, or feel like a weight is bearing down on their entire lower body.
Late in pregnancy, this pressure is often due to the baby’s weight pressing down on the pelvic floor, but many other factors can cause pelvic pressure during pregnancy.
Below, we discuss the different causes of vaginal pressure according to the trimester a woman is in:
First trimester
For most women, the first trimester is too early in pregnancy for weight gain to cause vaginal pressure.
Instead, the hormone relaxin is often responsible. This hormone helps relax the muscles, making it easier for the baby to pass through the pelvic area during birth. However, relaxin levels are at their highest in early pregnancy. High levels of this hormone may help the fertilized egg to implant in the lining of the uterus.
For some women, relaxin can cause muscle pain or tension, including in or around the vagina.
According to studies in animal models, relaxin may also weaken the ligaments that support the pelvis. This can lead to a feeling of pressure, as though something is pushing down on the vagina.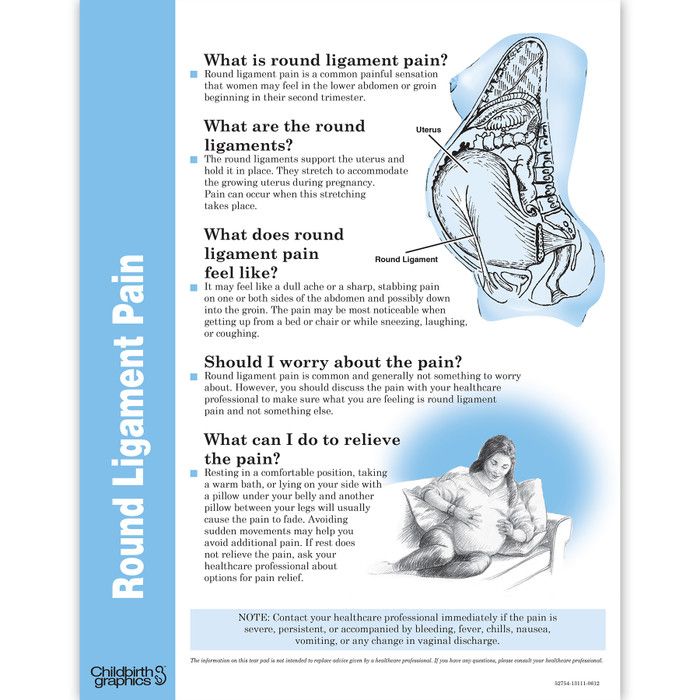
Second and third trimesters
In the second and third trimesters, the combination of a weakening pelvic floor and increased weight putting pressure on the pelvis can cause vaginal pressure.
The pelvic floor resembles a sling made of muscle. It supports the organs of the pelvis, including the uterus, vagina, urethra, and bladder. Pregnancy can weaken the pelvic floor.
Women who have given birth previously may have damage to their pelvic floor, which could cause it to weaken further with a subsequent pregnancy.
The extra weight of pregnancy often becomes more noticeable in the second trimester. As pregnancy progresses, the uterus puts more and more pressure on the lower body.
As the pelvic floor weakens, this pressure can cause a feeling of fullness in the vagina or generalized pain and pressure in the hips and pelvis.
For some women in the later stages of pregnancy, a pressure in the pelvis may be an early sign of labor. If cramping in the stomach also occurs or they feel a sensation of something pressing down on the uterus, it could mean that they are about to give birth.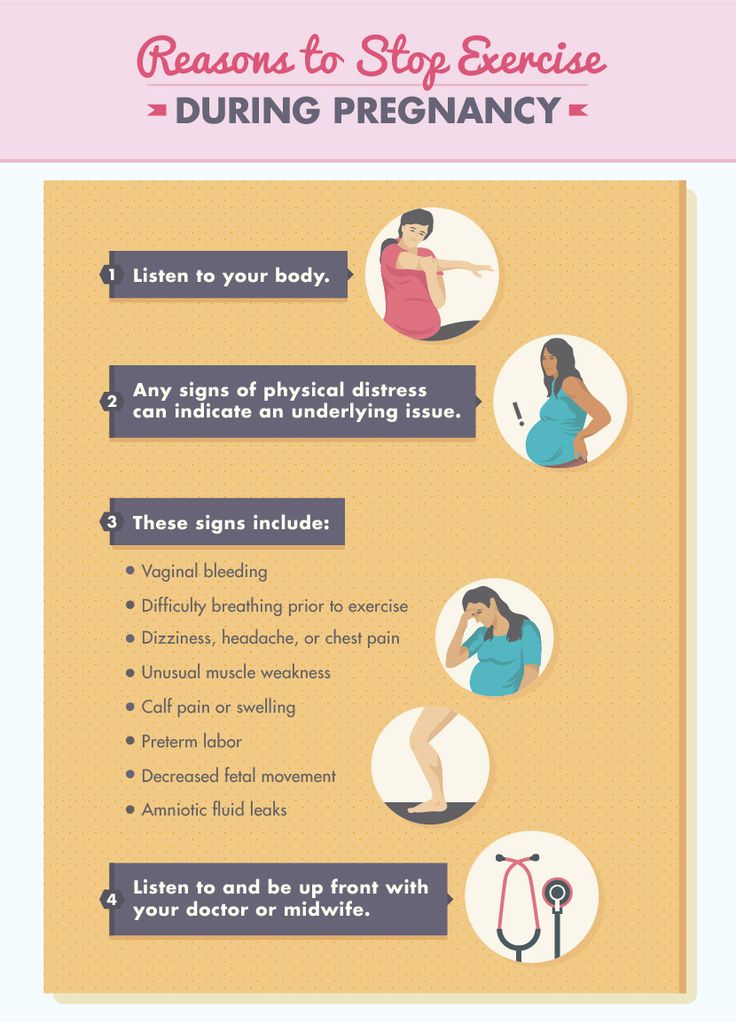
Common problems in all trimesters
Some factors can cause a feeling of vaginal or pelvic pressure in all stages of pregnancy. These include:
Constipation
Many women struggle with constipation throughout their pregnancy. Constipation can cause a feeling of fullness or pressure in the vagina, especially when the stool is hard or several days have passed since a bowel movement.
Drinking plenty of water and eating fruit and other high-fiber foods may help with constipation.
Bladder infections
For some women, pressure or pain can signify a bladder infection. Women are more likely to develop a bladder infection during pregnancy.
If the vaginal or pelvic pressure occurs alongside difficulty going to the bathroom, pain when urinating, or fever, it is essential to see a doctor.
Bladder infections are easy to treat, but, without treatment, they can worsen and increase the risk of health issues during pregnancy.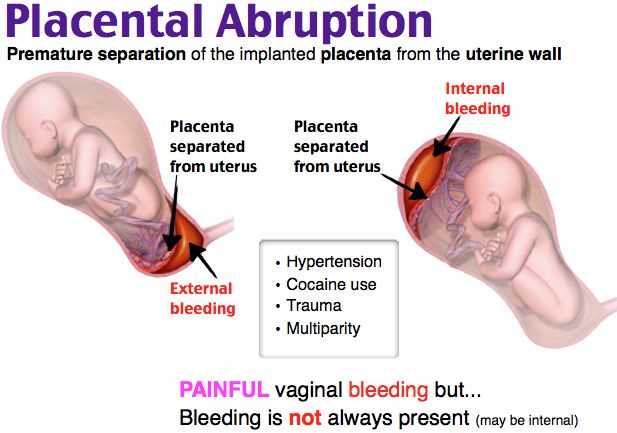
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP)
When vaginal pressure is intense, it could be a sign of POP. POP happens when organs in or near the pelvis move down, sometimes into the vagina or rectum.
POP is treatable but can cause incontinence, intense pain, and severe complications.
Women who suddenly feel intense pressure, have difficulty controlling their bowel or bladder, or notice that something seems to be pushing down into their vagina, should consult a doctor.
A weak cervix
Some women have a weak cervix, which is sometimes called cervical incompetence or cervical insufficiency.
Some women with this condition may have a miscarriage or go into premature labor because the cervix is not strong enough to support the uterus. In most cases, a weak cervix is treatable with early intervention.
Women who feel unexplained vaginal pressure, especially early in pregnancy, could ask a doctor to check their cervix. A previous cervical procedure or injury, including those resulting from childbirth, may increase the risk of a weak cervix.
As vaginal pressure is often due to weak muscles and pressure on the pelvis, gentle stretches may help. Try stretching the back and hips to relieve pain and pressure.
A pregnancy yoga or gentle stretching class can help with finding comfortable and safe stretches.
Using a foam roller can help loosen tense muscles. If the pain is intense, applying a heating pad to the sore area may help. Keep the heat low, and remove the pad after a maximum of 10 minutes.
Other strategies may not offer immediate relief, but can reduce the risk of certain conditions that cause vaginal pressure. These strategies include:
- Doing Kegel pelvic floor exercises. Tense the pelvic floor muscles as though trying to avoid urinating, hold for 10 seconds, then release. Repeat 10 times at least twice a day. This can also strengthen the muscles that the body uses to push out the baby.
- Remaining active during pregnancy. Even low-intensity exercises such as walking can help strengthen the muscles and promote good posture.
 This may relieve pain and pressure and keep the pelvic muscles strong.
This may relieve pain and pressure and keep the pelvic muscles strong. - Drinking plenty of water. Stay hydrated, especially after exercising and in hot weather. This can help prevent constipation, which could otherwise lead to pressure.
Share on PinterestA doctor will prescribe treatment if an infection is causing the vaginal pressure.
In most cases, vaginal pressure is just an unpleasant pregnancy side effect resulting from weakened pelvic muscles and weight gain.
However, sometimes a more severe cause will need treating so that it does not harm the woman and baby. An untreated infection, for example, can spread throughout the body and put the baby in danger. It might even cause premature labor.
Very weak pelvic muscles can lead to POP. This painful condition can cause incontinence, pain during sex, and changes in the appearance of the genitals.
Some women experience muscle injuries during pregnancy or when giving birth. The hormone relaxin may increase the risk of muscle injuries. So it is important to remain physically active to keep the muscles strong. Always lift with the legs rather than the back, and see a doctor for unexplained muscle pain.
So it is important to remain physically active to keep the muscles strong. Always lift with the legs rather than the back, and see a doctor for unexplained muscle pain.
Any injury that a woman experiences during pregnancy can make childbirth more difficult. Pregnancy-related complications may also make the postpartum period more difficult, slowing recovery and potentially harming mental health.
Women should see their doctors or midwives routinely during pregnancy. It is vital to use these visits to discuss all symptoms, even if they seem minor.
Early in pregnancy, women may only see a doctor every few weeks. If they are experiencing intense pressure or pain or have other symptoms, such as fever, painful urination, bleeding, or a change in the baby’s movements, it is important that they seek medical care immediately.
If it is after hours, they should go to the emergency room. Prompt treatment of pregnancy conditions can save both the woman and the baby.
Vaginal pressure during pregnancy is just one of the many symptoms women may experience while pregnant. It should not usually be cause for concern and can be a good sign that the body is releasing the right hormones, and the uterus is growing as expected.
It should not usually be cause for concern and can be a good sign that the body is releasing the right hormones, and the uterus is growing as expected.
A bit of caution in pregnancy can help to detect problems before they become emergencies. Never hesitate to see a doctor, even if the issue seems minor. It is unlikely that there is a severe problem, but reassurance can make pregnancy easier. If something is wrong, it is best to catch the issue as early on as possible.
Read the article in Spanish.
Vaginal Pain During Pregnancy: 8 Causes & What To Do
Vaginal pain is a common symptom during pregnancy. It is usually a result of the baby's development, which can cause pressure on vaginal tissue and decrease blood flow to the region.
However, vaginal pain can also be a sign of a more serious problem like a urinary tract infection, sexually-transmitted infection, or vaginismus, especially if pain emerges with other symptoms.
If you have other symptoms besides vaginal pain, such as bleeding, vaginal discharge, itchiness, or burning, it's important that you visit your doctor or obstetrician, to identify the cause of the vaginal pain and start the adequate treatment.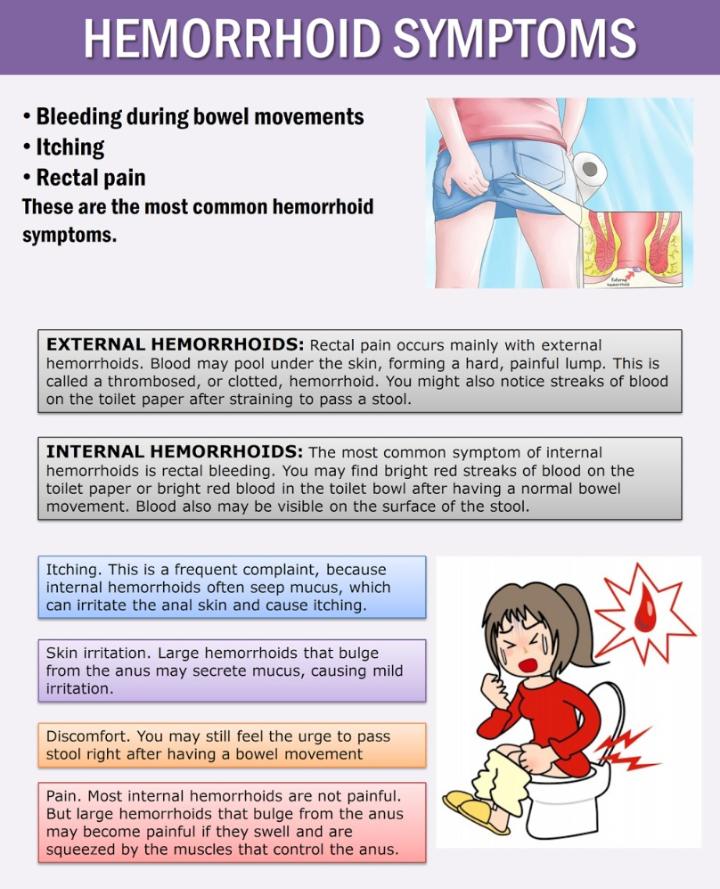
The main causes of vaginal pain during pregnancy are:
1. Normal development of the baby
While the baby grows and gains weight inside the uterus, it also increases pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, which are muscles that support the uterus and the vagina. This can cause intense discomfort or pain in the vagina, which is more common during the third trimester of pregnancy.
In addition, because of the pressure caused by the growing baby, there may be a decrease in blood flow to the pelvic area, which can cause the vagina to become swollen and more painful.
What to do: There are some ways that you can relieve pressure and reduce pain, like avoiding standing for prolonged periods, placing a cold compress on the pelvic area, and resting after activity. Even though discomfort is more common at the end of pregnancy, it's important to see your obstetrician if the pain is too intense and stops you from walking or doing normal day-to-day activities.
2. Vaginal dryness
Vaginal dryness is also very common during pregnancy. It occurs due to the increase in progesterone, although the expectant mother's natural anxiety can also contribute to dryness. As a result, women can experience pain during sexual intercourse.
What to do: it's important to identify the cause of dryness, and to see your obstetrician. He or she may suggest use of a lubricant, changes in diet and/or exercise or routines that may help decrease anxiety.
3. Intense vaginal sex
Vaginal pain during pregnancy can also happen after intense vaginal sex which, due to the friction caused by penetration or lack of lubrication, may lead to vaginal irritation, swelling, and pain.
What to do: it's essential to ensure adequate lubrication before penetration in order to avoid lesions in the walls of the vagina and pain during sexual intercourse. If this is the case, it may also be advised for you and your partner to decrease the frequency and intensity of sexual intercourse, so that the vagina tissue is able to recover more quickly. If there is bleeding during sexual intercourse, you should advise your doctor or obstetrician.
If there is bleeding during sexual intercourse, you should advise your doctor or obstetrician.
4. Vaginismus
Vaginismus is a condition where the vaginal muscles contract and cannot relax naturally, causing pain in the vagina and difficulty with penetration. This situation may appear during pregnancy, but may be present before pregnancy.
What to do: Consult your doctor or a pelvic floor therapist. They will assess the pelvic muscles to identify the cause of the vaginismus and from there they will indicate suitable treatment.
5. Rash
Sometimes expectant mothers can get a rash in the genital area when they use certain products that contain irritant ingredients (e.g. soap, condoms, vaginal creams, or lubricants). This can cause swelling, itchiness, redness, and pain in the vagina.
What to do: It's important to identify the product that may be triggering symptoms and discontinue it immediately. To relieve symptoms, you can place a cold compress on the external genital area. However, in cases in which symptoms do not improve or if they become more intense, consult your doctor for assessment and treatment
However, in cases in which symptoms do not improve or if they become more intense, consult your doctor for assessment and treatment
6. Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common condition during pregnancy. It happens due to changes in the body that encourage overgrowth of naturally-occurring vaginal flora. Vaginal pain is a frequently-occurring symptom of a UTI, as well as itchiness, burning sensation when peeing, and cloudy urine.
What to do: You should consult your doctor if you suspect a UTI, especially if you experience discomfort. Treatment may involve antibiotics or antifungal medication. It's also important that you drink plenty of water every day, follow a diet that is low in sugar, and wear comfortable clothes and cotton panties.
7. Sexually-transmitted infections
Sexually-transmitted infections, known as STIs, can cause vaginal pain in pregnancy. This is particularly the case wuth chlamydia and genital herpes. Other symptoms include itchiness and burning.
Other symptoms include itchiness and burning.
What to do: if you have any symptoms that may indicate an STI, you should see your doctor for assessment. If confirmed, the doctor will initiate treatment, which will likely be done with medication. You should avoid having sex during treatment and ensure that your sexual partner is aware to seek assessment and possible treatment.
8. Bartholin's Cyst
Vaginal pain during pregnancy may also occur when there are cysts in the Bartholin's glands, which happen due to an obstruction of the gland. This can cause swelling and vaginal pain, especially when there is inflammation in the glands.
What to do: If you feel a palpable lump in the vagina or have any other symptoms mentioned above, see your doctor for assessment. Treatment may involve pain medicaition and antibiotics if the cyst is infected.
why does it occur and how to solve the problem?
Pregnancy is one of the important and responsible stages in a woman's life. In most cases, this is 9 months of anxious waiting to meet your baby. However, during pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes major hormonal changes and pleasant emotions can go hand in hand with painful and uncomfortable sensations in different areas of the body. Including unpleasant symptoms may appear in the intimate area. nine0003
In most cases, this is 9 months of anxious waiting to meet your baby. However, during pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes major hormonal changes and pleasant emotions can go hand in hand with painful and uncomfortable sensations in different areas of the body. Including unpleasant symptoms may appear in the intimate area. nine0003
Discomfort in the vagina often manifests itself in the form of itching, burning, irritation and swelling. The main thing, when these symptoms appear, is to understand that it is necessary to establish their cause and eliminate it as soon as possible, because there are risks of harming the health of the fetus.
Various sexual infections can affect the appearance of discomfort in the perineum. Unfortunately, during pregnancy, a woman is prone to various infectious diseases. As mentioned above, bearing a baby causes a restructuring of the hormonal background in a woman's body: the level of the hormone progesterone rises and the activity of the immune system naturally decreases, which creates favorable conditions for the exacerbation of chronic infections and the emergence of new ones. nine0003
nine0003
How dangerous is the development of infectious diseases of the vagina and vulva during the bearing of a baby? Normally, during pregnancy, the amniotic bladder and water, as well as the mucous plug of the cervix, protect the fetus from various infections and bacteria, so your unborn baby is safe.
The presence in the body of a woman in an interesting position of an infectious disease and the lack of necessary therapy can adversely affect the course of pregnancy. For example, an untreated infection can lead to damage to the membranes, the fluid in which the unborn child is located, and the fetus itself. nine0003
There is also a high probability of physical contact of the child with the infection during passage through the birth canal. Therefore, in case of any discomfort in the intimate area during pregnancy, you should consult a specialist.
You can suspect the appearance of an infection of the vagina and vulva by a series of symptoms: cramps, itching, burning.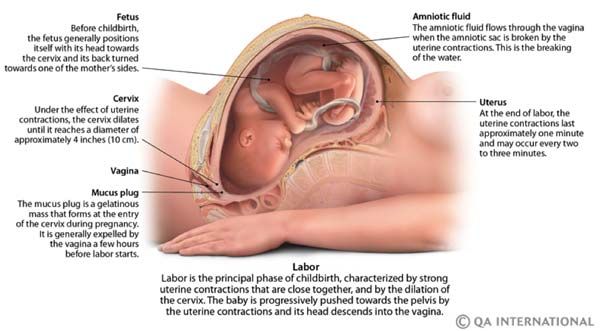 Often, sexual infections provoke colpitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. By itself, colpitis often causes discomfort in the groin of pregnant women. It can be provoked not only by sexual infections, but also by endocrine or chronic diseases, stress, lack of hygiene. nine0003
Often, sexual infections provoke colpitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. By itself, colpitis often causes discomfort in the groin of pregnant women. It can be provoked not only by sexual infections, but also by endocrine or chronic diseases, stress, lack of hygiene. nine0003
Bacterial vaginosis can also cause discomfort. This pathology, caused by a decrease in the number of lactobacilli in the vagina, as a result, their place is taken by other microorganisms that are always present in the vagina, but in excess lead to the development of dysbiosis. Bacterial vaginosis can occur without symptoms, but sometimes it occurs with clinical manifestations. It is usually accompanied by discomfort, as well as vaginal discharge that is white, gray, or yellow-green in color with an unpleasant "fishy" odor. nine0003
Bacterial vaginosis also adversely affects the course of pregnancy, can provoke inflammation of the pelvic organs, premature birth, chorioamnionitis - inflammation of the amniotic membranes and infection of the amniotic fluid.
Itching in the intimate area during pregnancy can appear with vulvovaginal candidiasis - infection of the mucous membranes of the vulva and vagina with yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It should be noted that the first episode of the incidence of vulvovaginal candidiasis is observed during pregnancy. This is due to changes in hormonal levels, reduced immunity. This disease, in addition to discomfort in the groin area, itching and burning, is characterized by: moderate hyperemia, white and thick discharge like cottage cheese, sour smell from the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse and urination. nine0003
However, itching and burning are not always symptoms of serious pathologies. Occasionally, discomfort can occur with the use of poorly fitting underwear or aggressive pH soaps.
Feeling discomfort in the groin, you should consult with a specialist. The specialist can conduct an examination, collect an anamnesis and prescribe, if necessary, laboratory and / or other diagnostic tests. All this will help to establish a diagnosis and choose an individual treatment regimen. nine0003
All this will help to establish a diagnosis and choose an individual treatment regimen. nine0003
In order to prevent the appearance of discomfort in the intimate area and not spoil the pleasant waiting time for the addition, it is necessary to follow preventive recommendations.
- It is necessary to carry out external hygiene of the intimate area. Normally 2 times a day - no more and no less. Frequent washing can lead to “overdrying” of the skin and mucous membranes of the intimate area, and a lack of hygiene can lead to the development of various inflammations. You should not self-douche or vaginal lavage unless recommended by a specialist in your particular case. nine0031
- Choose a quality cleanser. Ideally, this should be a hypoallergenic product that is dermatologically tested, contains lactic acid and components that care for the skin of the genital organs. Epigen Intim Gel is ideal for daily hygiene of the inguinal zone during pregnancy and after childbirth.
 Epigen Intim gel contains activated glycyrrhizic and lactic acids in its composition. Its pH is slightly acidic, which corresponds to the normal acid-base balance of the skin of the intimate area. The tool helps to eliminate discomfort (irritation) due to wearing panty liners or not very comfortable underwear. It has a very pleasant aroma and helps to neutralize unpleasant odors in the intimate area with constant use. nine0031
Epigen Intim gel contains activated glycyrrhizic and lactic acids in its composition. Its pH is slightly acidic, which corresponds to the normal acid-base balance of the skin of the intimate area. The tool helps to eliminate discomfort (irritation) due to wearing panty liners or not very comfortable underwear. It has a very pleasant aroma and helps to neutralize unpleasant odors in the intimate area with constant use. nine0031 - Abandon synthetic underwear in favor of natural fabrics. Cotton panties do not create a "greenhouse effect", especially in the heat.
Treatment of discomfort in the intimate area will be different. The diagnosed disease will influence the choice of therapy. Spray Epigen Intim can be included in the complex treatment of diseases accompanied by discomfort - nonspecific colpitis (vaginitis), bacterial vaginosis, thrush, herpes. nine0003
Spray Epigen Intim
More
Buy
Epigen Intim Spray
The drug has antipruritic and anti-inflammatory action. Thanks to the active ingredient - activated glycyrrhizic acid, Epigen Intim spray helps to eliminate itching and irritation. It also helps to eliminate inflammation, swelling and redness of tissues. The drug is also able to increase the local immunity of the vagina, by stimulating the production of its own interferons. Spray Epigen Intim promotes healing and restoration of the integrity of the damaged mucosa, due to which the protective function of the mucosa will be restored and the number of lactobacilli will increase. nine0003
Thanks to the active ingredient - activated glycyrrhizic acid, Epigen Intim spray helps to eliminate itching and irritation. It also helps to eliminate inflammation, swelling and redness of tissues. The drug is also able to increase the local immunity of the vagina, by stimulating the production of its own interferons. Spray Epigen Intim promotes healing and restoration of the integrity of the damaged mucosa, due to which the protective function of the mucosa will be restored and the number of lactobacilli will increase. nine0003
The drug is successfully used to treat viral infections (caused by the human papillomavirus, genital herpes), diseases associated with a decrease in local immunity (nonspecific vaginitis, thrush, bacterial vaginosis), etc. It can be used to treat exacerbations in conjunction with antiviral, antifungal and antimicrobial drugs, and for the prevention of these vaginal infections.
more nine0003
By the way, while carrying a baby, the use of many drugs sold in pharmacies is limited or prohibited.
But Epigen Intim spray is approved for use in pregnant and lactating women and is dispensed without a doctor's prescription. The drug is applied both externally and intravaginally, depending on the disease.
In the presence of itching, burning, irritation and swelling in the groin area, a woman feels as uncomfortable as possible. Intimate discomfort can bring especially many experiences to women during pregnancy. To minimize the risks of discomfort, try to follow the simple rules indicated in the article. When discomfort appears in the perineum, the most correct thing is to visit a specialist and not self-medicate, since now you are responsible not only for yourself, but also for the unborn baby. nine0003
COLPITIS DURING PREGNANCY
During pregnancy, a woman, as a rule, takes special care of her health and reacts anxiously to every unusual symptom.
Unusual discharge and discomfort in the genital area are often the cause of the expectant mother's panic. Such a complex of symptoms most likely indicates the development of a pathological process, which in medicine is called vaginitis or colpitis. In pregnant women, this condition is noted especially often against the background of a decrease in immunity, hormonal changes in the body and high loads on all organs and systems of a woman. nine0003
Such a complex of symptoms most likely indicates the development of a pathological process, which in medicine is called vaginitis or colpitis. In pregnant women, this condition is noted especially often against the background of a decrease in immunity, hormonal changes in the body and high loads on all organs and systems of a woman. nine0003
Vaginitis during pregnancy is a good reason to immediately contact a gynecologist and start treating this dangerous pathology. Diagnose the disease and determine how to treat colpitis during pregnancy without harming the mother and baby, qualified gynecologists will prompt.
Symptoms of colpitis during pregnancy
First of all, it should be determined that vaginitis or colpitis is an inflammatory disease that involves the mucous membranes of the vagina. The inflamed walls of the vagina swell and undergo hyperemia. Also, single hemorrhages are noted on the surface of the vaginal tissues. If the inflammation does not spread beyond the vagina, the woman does not notice visual manifestations of the disease, while in some cases the pathological process affects the external genitalia. In this case, inflammation can be seen with the naked eye. nine0003
In this case, inflammation can be seen with the naked eye. nine0003
The characteristic signs of colpitis during pregnancy do not differ from the symptoms of a non-pregnant woman:
- itching and burning in the vaginal area - the inflammatory process irritates the delicate mucous membranes, which causes discomfort and sometimes pain in the vaginal walls;
- pain in the lower abdomen - this symptom is especially frightening for pregnant women, but it is not associated with uterine tone, as many assume, but with tissue inflammation; nine0003
- the appearance of specific discharge - the discharge during colpitis during pregnancy is very abundant and may have a different color and consistency. Most often, a woman visually notes a white curdled discharge, resembling a characteristic sign of thrush, but sometimes the vaginal discharge acquires a putrid odor and is greenish-yellow in color. This indicates the specific nature of the pathogen and requires immediate medical advice;
- swelling and redness of the genital organs - patients often notice hyperemia and swelling of the labia and clitoris, which become more sensitive and cause discomfort to the woman.
Acute vaginitis during pregnancy is accompanied by severe symptoms, which should make the patient seek professional help. This will help protect the child from possible negative consequences.
Causes and types of vaginitis during pregnancy
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the vagina is usually of an infectious nature. This becomes possible due to vaginal dysbacteriosis, which often accompanies the period of pregnancy. Hormonal changes and high loads on all organs of the expectant mother cause a decrease in the body's defenses, which provokes an infectious and inflammatory process. In this case, the causative agent of the pathology can act as a bacterial flora that has penetrated into the body from the outside during sexual intercourse or in the household way, and that makes up the normal microflora of the vagina. The most likely infectious agents of colpitis in pregnant women include streptococci, fungi of the genus Candida, E. coli, trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, etc.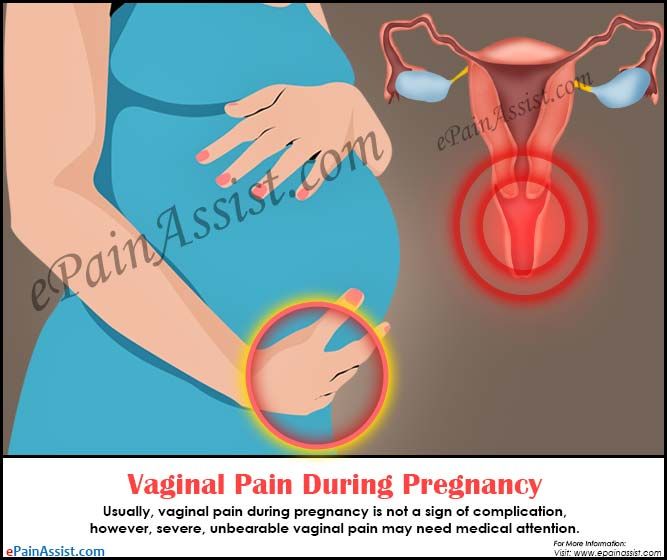
It is interesting that depending on the cause of the development of the disease, its symptoms and manifestations may differ:
- candidal colpitis - accompanied by abundant cheesy discharge and severe itching of the genital organs, which manifests itself even at rest;
- emphysematous colpitis - a very common type of vaginitis in pregnant women. Pathology is accompanied by the formation of small watery vesicles on the surface of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. This form of colpitis resolves on its own in 2-3 weeks after childbirth; nine0003
- Trichomonas colpitis - a very dangerous form of pathology that develops when Trichomonas enters the vaginal environment. Infection occurs during intercourse or when using personal hygiene items shared with the carrier (towel, washcloth, etc.). It is manifested by characteristic putrefactive secretions with a sharp unpleasant odor.
Concomitant conditions for the development of colpitis in a pregnant woman, in addition to a decrease in immunity, may be allergic reactions, microtrauma of the vagina, non-observance of personal hygiene, the presence of chronic diseases. nine0003
nine0003
Colpitis during pregnancy: consequences for the child
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the vagina poses a threat not only to the health of the expectant mother, but also to the baby. The ascending route of infection can lead to pregnancy abnormalities such as polyhydramnios, premature birth, and infection of the amniotic fluid. Vaginitis is especially dangerous during childbirth, when the baby passes through an infected maternal birth canal. At at this moment there is a high probability of infection newborn.
Interestingly, colpitis after pregnancy can go away on its own, but this happens relatively rarely. The development of colpitis after childbirth is most often provoked by trauma to the vaginal membranes during delivery. In connection with this fact, doctors recommend abstaining from sexual activity for the first weeks after childbirth. Violating this prohibition, a woman increases the risk of developing colpitis after childbirth.