What is toxic pregnancy
Toxic household products to avoid during pregnancy
Toxic household products to avoid during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Almost every pregnant woman will come into contact with chemicals that could possibly harm her or her baby. Usually it’s such a small amount that you don’t need to worry, but it’s still a good idea to avoid some toxic products while you're pregnant.
What are 'toxic' household products?
We are surrounded by chemicals and toxins (poisons). They include pesticides in the garden, flame retardants on furniture, lead, mercury and some cleaning products.
Most chemicals you come across in your daily life won’t harm your baby. But if you are exposed to large quantities of chemicals for a long time, it’s possible your child will be at an increased risk of congenital disorders or future health problems.
If you breathe or swallow some chemicals, they can enter your bloodstream and pass to your baby via the placenta. Your baby can also be exposed to chemicals after they are born through your breastmilk or if they put their fingers in their mouth.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, these tips will help you minimise your exposure.
Chemicals to avoid when you’re pregnant or breastfeeding
Pesticides and herbicides
Some pesticides (bug killers) and herbicides (weed killers) are known to affect developing and newborn babies. Usually pesticides used in the home and for professional pest treatments are safe. But it’s a good idea to avoid them as much as possible while you are pregnant. Ask someone else, like a licensed pest control professional, to do the treatment for you.
Cleaning products
Although most cleaning products are safe, there have been reports of some household chemicals causing wheezing in early childhood. To be on the safe side, wear gloves and avoid breathing in fumes from products such as oven and tile cleaners.
Paint
Most paint fumes are safe while you’re pregnant, but there is a slightly increased risk if you use solvent-based paints or strip old paintwork as these may contain traces of lead. Choose a water-based paint and a paint brush or roller rather than spray (which contains solvents). Make sure the room is well ventilated if you paint — or have someone else do it for you.
Mosquito repellent
All mosquito repellents in Australia have been tested and are safe to use. However, a small amount of the chemicals DEET or picaridin will enter the skin, and it’s best to take care during the first 3 months of pregnancy Choose a repellent with a low to moderate concentration of the chemical — between 5% and 20% — and consider other ways to avoid mosquitos, such as fly screens and long sleeves.
Mercury
Being exposed to high levels of mercury can damage your health and increase the likelihood of brain damage, and hearing and vision problems in a developing baby. Some fish contain mercury, including shark (flake), broadbill, marlin and swordfish. To be on the safe side, pregnant women should limit eating these species of fish to no more than once a fortnight. If you need a dental filling, talk to your dentist about options that don’t contain mercury.
Some fish contain mercury, including shark (flake), broadbill, marlin and swordfish. To be on the safe side, pregnant women should limit eating these species of fish to no more than once a fortnight. If you need a dental filling, talk to your dentist about options that don’t contain mercury.
Arsenic-treated timber
Outdoor wood is often treated with copper, chromium or arsenic to protect it from dry rot, fungi, mould and termites. This treatment has been linked to some cancers, diabetes, miscarriage and stillbirth. It gives the wood a greenish tinge, which fades over time. You can protect yourself and your baby by not putting food on arsenic-treated timber and washing your (and your child’s) hands after they play on it.
Nail polish
Formaldehyde is a chemical used in nail polish, some cosmetics and hair-straightening products. The amount of formaldehyde in nail polish is very small and quickly broken down by the body, however adverse effects on the baby cannot be ruled out. So it’s best to use nail polishes that don’t have formaldehyde.
So it’s best to use nail polishes that don’t have formaldehyde.
Paint and lead-based products
High levels of lead in the body can affect the health of unborn babies and children. Very high levels can lead to premature birth, low birth weight, or even miscarriage or stillbirth. It's important to keep your exposure to lead as low as possible.
Paint containing lead was used in many Australian houses before 1970, so avoid stripping old paint while you’re pregnant. Consuming a small flake of paint the size of a 5-cent piece can raise levels in your blood for several weeks, and some of this will remain in the body for life. It's important to keep young children away from old paint, too.
Flame retardants
Chemicals used to make household furniture less flammable have been linked to learning disabilities in children. To avoid exposure, wash your hands frequently, use a vacuum fitted with a HEPA filter and mop the floor regularly. Also, avoid coming into contact any foam inside the furniture.
Dry cleaning chemicals
It’s safe to have your clothes dry cleaned when you’re pregnant. If you come into contact with a lot of the chemicals – if, for example, you work at a dry cleaners — you may be at a slightly increased risk of miscarriage. Talk to your employer about working safely while you are pregnant.
Asbestos
Asbestos was used in many building materials in Australia and is linked to several lung diseases such as lung cancer and mesothelioma. While there is no evidence that asbestos can affect your pregnancy or result in a congenital disorder, you should avoid contact with asbestos — or suspected sources of asbestos — at any time.
BPA
The chemical bisphenol A (BPA) is found in most plastics, and can pass from a mother to her baby in the womb. It has been suggested that it can cause brain and behaviour problems in some children. However, Food Standards Australia New Zealand says BPA used in food packaging poses no health risks to people of any age, including unborn children and infants.
Mothballs (naphthalene)
Mothballs contain the chemical naphthalene, which has been known to give people headaches, nausea, dizziness and vomiting. It can also lead to serious health problems in small children because they are more likely to put mothballs in their mouths. Don’t use mothballs around children under 3 years and make sure they’re stored safely.
How to avoid exposure to chemicals
To reduce your exposure to chemicals:
- Store all chemicals safely — out of the reach of children and with safety caps screwed on correctly.
- Always read and follow the instructions on any packaging.
- Find alternatives, if you can — for example, use products that contain low levels of chemicals, or baking soda and vinegar for cleaning.
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Consider not renovating while you’re pregnant or breastfeeding.
- If you have a task that involves chemicals (such as some types of cleaning), ask someone else to do it.
- Keep your home well ventilated.
Working with chemicals during pregnancy
If your work involves exposure to chemicals, talk to your employer. They must carry out a risk assessment and find ways to reduce your exposure. By law, employers must make work safe for you and your baby when you are pregnant.
For more information, contact Safe Work Australia.
Where to seek help
If you are exposed to a toxic product while you are pregnant, don’t panic. Remember, it’s only long-term exposure to large quantities of chemicals that could potentially harm your baby. A one-off exposure is very unlikely to cause any harm.
If you are worried, call the Poisons Information Hotline on 13 11 26.
For more information and advice, call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak to a maternal child health nurse.
Sources:
Babycenter Australia (What chemicals should I avoid during pregnancy), California Childcare Health Program (Minimizing Exposure to Toxic Flame-Retardants), Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (Lead), Food Standards Australia New Zealand (Mercury in fish), Food Standards Australia New Zealand (Bisphenol A (BPA)), Healthy WA (Pregnancy and pesticides), Healthy WA (Stay safe around copper chrome arsenate treated wood), NSW Health (Lead exposure in children), NSW Health (Naphthalene in moth balls and toilet deodorant cakes), NSW Health (Asbestos and health risks), Safe Work Australia (Managing risks of exposure to solvents in the workplace), Thorax (Frequent use of chemical household products is associated with persistent wheezing in pre-school age children), RANZCOG (Common questions in pregnancy), UK Teratology Information Service (Exposure to formaldehyde in pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
- Keeping baby safe
- Allergies: controlling your environment
- Protecting your child from lead poisoning
- Medicine and poisons safety in the home
- Working during pregnancy
Need more information?
Chemicals in the home - Better Health Channel
Learn how to safely store and dispose of household chemicals, and how to respond when a person is poisoned.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
How to avoid chemicals that can reduce fertility
In our modern everyday life we come into contact with many different chemicals through the products we use, the food we eat, and the air we breathe.
Read more on Your Fertility website
Household poisons: keeping children safe | Raising Children Network
Young children put everything in their mouths, including household poisons, chemicals and medicines. Keep all household poisons up high in locked cupboards.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Chemicals in our environment | Your Fertility
It’s impossible to completely avoid EDCs
Read more on Your Fertility website
Medicine and poisons safety in the home
Learn more about the importance of child-resistant packaging, how to reduce the risk of poisoning and what to do if your child swallows a poison.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Poisoning prevention for children | Raising Children Network
Prevent poisoning in children by storing medicines, chemicals and cleaners up high in a locked cupboard. Call the Poisons Information Centre on 131 126.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Things to avoid during pregnancy
From hair dye to house paints, there are a few products or lifestyle habits pregnant women and their partners should be cautious of during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Accidental poisoning - MyDr.com.au
Children's curiosity can lead to danger, such as unintentional poisoning.
Read more on myDr website
Poisons | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Poisoning is one of the most common childhood injuries
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Tick removal: First aid and prevention - MyDr.com.au
Freeze it; Don't squeeze it! That's the latest advice from experts to Australians who have an attached adult tick. Tick removal: First aid and prevention
Read more on myDr website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
6 in-home toxins to avoid during pregnancy | Your Pregnancy Matters
While you can't avoid all in-home pollutants, you can reduce exposure during pregnancy.Every day, it seems as if there's a new thing expecting moms should worry about.
Don't eat that! Avoid those products!
The latest news is a 2019 study out of Sweden, which analyzed the effects of first-trimester exposure to 26 endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDQs) on children's brain development by age 7. Research has shown that certain chemicals can absorb into a mother's skin, interfere with hormone activity, and potentially cause altered brain development in the baby.
The study of 718 child-mother pairs found that, particularly in boys, maternal exposure to EDQs resulted in lower IQ scores. The study found that bisphenol F (BPF) was the most concerning chemical. BPF is found in plastics, varnishes, and dental sealants and has been touted as a safer alternative to bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is present in many commercial products, such as plastic cups, food containers, and even cash register receipt paper. The differences weren’t huge but are still concerning.
"Chemicals are in almost everything around us, from the dishes to pet care products to the air we breathe.
Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.While pregnant patients can and should avoid certain toxins, such as the chemicals and bacteria in deli meat and unpasteurized milk, it's impossible to avoid every potential exposure to toxins."
This type of report can be scary. Chemicals are in almost everything around us, from the dishes to pet care products to the air we breathe. While pregnant patients can and should avoid certain toxins, such as the chemicals and bacteria in deli meat and unpasteurized milk, it's impossible to avoid every potential exposure to toxins.
Pregnant women can limit exposure to certain day-to-day toxins, though. We've identified six common in-home pollutants and ways to reduce the risks to your baby.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has called for Ob/Gyn providers and patients to discuss toxin exposure prevention since 2013. Following is a list of chemicals to avoid during pregnancy.
Following is a list of chemicals to avoid during pregnancy.
1. Pet medications and waste. Avoid handling flea and tick medication and other pet chemicals during pregnancy. Not only will you reduce exposure, you can also avoid the risk of being scratched or bitten by an annoyed furry friend. Also hand off cat litter duty during pregnancy to avoid toxoplasmosis – a parasitic infection from handling feline waste. Toxoplasmosis can cause liver and eye complications in the developing baby and flu-like symptoms in the mother.
2. Smoking and vaping. Don't allow either in your home or vehicle. A few of the potentially harmful chemicals found in both cigarette smoke and vape smoke include benzene and nickel.
If you currently smoke or vape, now is a good time to quit. UT Southwestern offers a free nicotine cessation program; call 214-761-3139 or email us at [email protected] to enroll.
3. Lead. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cautions pregnant women to avoid eating spices and candy imported from outside the U. S. due to potential lead contamination. Some pottery uses a lead glaze, which can leach lead into food that is prepared or served in it. Also, if your home was built in the 1970s or earlier, its paint and plumbing might contain lead. Talk to your doctor about screening for lead exposure if you have risk factors.
S. due to potential lead contamination. Some pottery uses a lead glaze, which can leach lead into food that is prepared or served in it. Also, if your home was built in the 1970s or earlier, its paint and plumbing might contain lead. Talk to your doctor about screening for lead exposure if you have risk factors.
4. Pesticides. Pesticide toxicity has received ample press in recent years. For example, beginning in 2021, California will prohibit the use of chlorpyrifos, a commonly used pesticide that has been linked to brain damage in children. During pregnancy, avoid handling lawn chemicals. If your yard is recently treated, don't go barefoot on the grass. Wash fruits and vegetables prior to slicing or eating them to remove pesticides, dirt, and bacteria. You don't need a special produce-wash product – running the food under water and toweling it off is sufficient.
5. Cleaning products. When used as directed, most cleaning products shouldn’t pose a health hazard. However, it's still smart to limit exposure. Consider wearing rubber gloves when you clean to reduce absorption through your skin. Also, be sure to crack a window to reduce the amount of chemicals you inhale.
However, it's still smart to limit exposure. Consider wearing rubber gloves when you clean to reduce absorption through your skin. Also, be sure to crack a window to reduce the amount of chemicals you inhale.
6. BPA. Research has associated this chemical with altered brain development and behavior. In recent years, organizations have taken steps to raise awareness of BPA. Many children's products now come "BPA-free," though the U.S. Food and Drug Administration maintains that BPA is safe in food packaging products. Interestingly, the Swedish study listed BPA among the lowest risk of the top 10 chemicals analyzed.
Remember, it's impossible to avoid all potentially harmful chemicals at home and in our daily lives. If you are concerned, consult this Environmental Exposure History Form for tips to limit exposure. Still worried? Talk with your doctor about how to reduce risks at home.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
Treatment of toxicosis of pregnant women in the clinic
In this section you will learn:
- What is toxicosis
- Types of toxicosis of pregnancy
- Causes of toxicosis
- Symptoms of toxicosis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of toxemia of pregnancy
- Possible consequences and prevention
Toxicosis is not just a habitual companion of pregnancy, but a common name for pathological conditions that negatively affect the course and outcome of pregnancy. nine0005
nine0005
What is toxicosis
Toxicosis of pregnant women appears at the stage of gestation as a pathological condition of the body. This is a whole complex of gestational complications resulting from the formation of the fetal egg. Manifestations of toxicosis are a consequence of a violation of the body's adaptation to pregnancy.
Types of toxicosis of pregnant women
Each pregnant woman manifests toxicosis in her own way. Despite this, gynecology classifies toxicosis of pregnant women according to the period of occurrence as follows:
- Early
This form of gestational complications is characteristic of pregnancy up to 22-23 weeks and is the most common. Early toxicosis is characterized by nausea and vomiting of varying degrees, as well as ptyalism - increased salivation.
- Late
It is called preeclampsia. Preeclampsia begins development from 26–27 weeks and is manifested by dropsy of pregnant women, nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia. Uncontrolled late toxicosis poses a serious danger to pregnancy and a woman's health. nine0005
Uncontrolled late toxicosis poses a serious danger to pregnancy and a woman's health. nine0005
- Rare forms
These are jaundice, dermatosis, tetany, osteomalacia and bronchial asthma - they can manifest themselves at any time during pregnancy, so there is no certain period of occurrence in rare types of toxicosis.
Early toxicosis: causes
The body reacts with early toxicosis to the formation of an embryo in the uterine cavity, and there are a lot of theoretical justifications for this process. Each theory has the right to exist and gives quite reasonable explanations for the appearance of toxicosis:
- Toxic
This theory explains the development of toxicosis of pregnant women with toxic substances that can be formed as a result of the vital activity of the fetus or metabolic disorders.
- Neuroreflex
The developing fetus serves as an irritant for the endometrium, which increases the sensitivity of the subcortical structures of the brain. The vomiting and olfactory centers, the zones of control of digestion, secretion and other functions of the body are located precisely in the subcortical regions, therefore they immediately respond to stimuli with known symptoms: nausea, vomiting, etc. By the third trimester, the body adapts to pregnancy, and toxicosis stops. nine0005
The vomiting and olfactory centers, the zones of control of digestion, secretion and other functions of the body are located precisely in the subcortical regions, therefore they immediately respond to stimuli with known symptoms: nausea, vomiting, etc. By the third trimester, the body adapts to pregnancy, and toxicosis stops. nine0005
- Hormonal
This theory positions the main cause of toxicosis as a high level of hCG in the blood, which is caused by the development of the corpus luteum of pregnancy in the ovaries. And it is provoked by the growth of the chorionic villi due to the active reproduction of the hormone chorionic gonadotropin.
- Psychogenic
The theory is based on the fact that toxicosis of pregnancy occurs in women with mental disorders who cannot fully control their emotions. As a rule, these are very sensitive and vulnerable women; under the pressure of stress and experiences, they develop toxicosis. nine0005
nine0005
- Immunological
This theory considers the embryo as a foreign body, which differs in type of antigens from the body of a pregnant woman. As a result, the active production of antibodies that cause toxicosis begins.
The above theories complement each other and can be used in combination to determine the causes of toxicosis. Also, medical statistics reveals the following reasons for the complex course of toxicosis of pregnant women:
- burdened somatics;
- psychological trauma;
- overwork;
- malnutrition;
- bad habits;
- past abortions and inflammation of the reproductive organs;
- problems of the digestive system.
With the above factors, the violation of the body's adaptation is observed long before pregnancy, and with its onset it intensifies.
Symptoms of early toxicosis
Toxicosis is detected in more than half of pregnant women and more often manifests itself at 5-6 weeks. Medicine distinguishes between mild, moderate and excessive toxicosis. Signs are very diverse and appear in different combinations:
Medicine distinguishes between mild, moderate and excessive toxicosis. Signs are very diverse and appear in different combinations:
- Nausea and vomiting
The intensity of these symptoms becomes the main parameter for differentiating toxicosis. With a neurotic mild stage, vomiting is possible up to five times a day. In the moderate stage, it occurs up to ten times a day, while in the severe excessive stage, which is called dystrophic, vomiting is indomitable and can be repeated more than twenty times a day. If food and liquids are not retained in the body for the necessary time for digestion, nausea and vomiting can cause problems with pregnancy and exhaustion of the body. nine0005
- Increased salivation
It is both an independent manifestation of toxicosis and a companion of vomiting. In itself, increased salivation is fraught with the loss of up to 1 liter of water per day by the body, so it must be controlled with the help of the right treatment.
- Change in taste and smell, loss of appetite
A certain degree of change in taste and smell is observed with each form of toxicosis, including intolerance to certain smells and foods. Loss of appetite is typical only for serious types of toxicosis. With moderate toxicosis, food and liquids are retained in a small amount in the stomach, excessive toxicosis makes digestion almost impossible. nine0005
- Lethargy, drowsiness
These signs are observed in varying degrees in moderate and severe forms. Deterioration of general well-being and sleep disorders are characteristic symptoms for these types of toxicosis of pregnant women and become the cause of an apathetic state.
- Weight loss
With mild toxicosis, weight loss is up to 2 kg per week, which does not cause significant damage to health. With a moderate form of toxicosis, weight loss is from 3 to 5 kg. Severe toxicosis provokes a rapid loss of body weight, 7–15 kg per week, and becomes a threat not only to pregnancy, but also to the health of a woman. nine0005
Severe toxicosis provokes a rapid loss of body weight, 7–15 kg per week, and becomes a threat not only to pregnancy, but also to the health of a woman. nine0005
- Hypotension, tachycardia
Also characteristic to varying degrees of all types of toxicosis. With a mild degree of toxicosis, hypotension is insignificant (100–100/60 mm Hg), and tachycardia does not exceed 90 bpm. With moderate toxicosis, these figures are 100–90/60–50 mm Hg. and tachycardia 90–100 bpm. In severe toxicosis, instead of tachycardia, arrhythmia is observed, and the level of blood pressure reaches 80/40 mm Hg.
- Failed tests
Blood and urine parameters with mild toxicosis remain normal. With moderate toxicosis, acetone is found in the urine. Excessive toxicosis differs from others in extensive deviations in the composition of urine, as well as a high concentration of bilirubin, urea, and creatinine in the blood.
- Dehydration
It develops against the background of excessive toxicosis due to a large loss of body fluid. Dehydration manifests itself as yellowness and dryness of the skin in combination with a decrease in tissue turgor. There are hemorrhages in the conjunctiva and petichia on the skin. Blood clotting is impaired. nine0005
Dehydration manifests itself as yellowness and dryness of the skin in combination with a decrease in tissue turgor. There are hemorrhages in the conjunctiva and petichia on the skin. Blood clotting is impaired. nine0005
- Dermatoses
They are a rare manifestation of early toxicosis and provoke pruritus, which can be localized in the genital area or spread to the whole body. Usually, the symptoms are limited to this, but it is possible to develop dermatosis in the form of eczema, herpes, herpetiform impetigo. Dermatoses cause insomnia and irritability, as their manifestations are aggravated at night. To confirm dermatosis, it is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms - for example, diabetes mellitus, trichomoniasis, helminths, allergic reactions. nine0005
- Tetanya
This unusual type of early toxicosis is also rare and has no restrictions on the duration of pregnancy. Occurs in the presence of hypoparathyroidism and disorders of calcium metabolism. Tetany makes itself felt with muscle cramps.
Tetany makes itself felt with muscle cramps.
Diagnosis
The clinical picture of early toxicosis is compiled in accordance with the patient's complaints and the results of studies that are used in the complex:
- Medical examination
This is the first thing you need to diagnose toxicosis and differentiate its form. An examination on the chair confirms the presence of a fetus in the uterus and indicates to the doctor the direction for further examination.
- Ultrasound
Ultrasound determines the gestational age and the degree of development of the fetus in accordance with it.
- Tests
This is a general blood test, as well as its biochemical studies, which allow to determine the level of total protein, liver enzymes, fibrinogen, electrolytes and CBS. A general urine test is also required. nine0005
- Body measurements
A pregnant woman is able to independently assess the frequency of vomiting and calculate the total diuresis - this will help the doctor to differentiate toxicosis. Measurements of blood pressure and pulse rate, ECG are shown.
Measurements of blood pressure and pulse rate, ECG are shown.
All these diagnostic methods allow you to get a complete clinical picture of toxicosis of pregnant women and choose the right treatment.
Treatment of toxicosis of pregnancy
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor and requires strict adherence to his instructions. The approach to treatment is multilateral and depends on the form of pathology:
- Light
It is sufficient to observe this form of pathology on an outpatient basis. A pregnant woman with a mild form of toxicosis is treated in such a way as to ensure that the situation remains under control and improves. To do this, it is enough to provide the pregnant woman with physical and psychological comfort, if necessary, the doctor will prescribe sedatives for this - for example, valerian or motherwort. Antiemetics and fractional meals with easily digestible food will help to avoid the urge to vomit. Take it in small portions and often. Tanning herbal solutions of chamomile, sage and mint help reduce salivation. nine0005
Tanning herbal solutions of chamomile, sage and mint help reduce salivation. nine0005
- Moderate
Moderate toxicosis requires hospital conditions, where a pregnant woman is shown parenteral administration of saline solutions, proteins, glucose and other nutrients that the body lacks. To reduce vomiting, antipsychotics are prescribed - for example, droperidol. The positive effect of physiotherapy has been proven. Acupuncture, aromatherapy, herbal medicine, electrosleep, galvanization, endonasal electrophoresis show high efficiency.
- Expressed
Excessive toxicosis requires serious intensive care. Treatment methods are reduced to the introduction of the necessary nutrients into the body of a pregnant woman with the help of enemas and infusions. Drug therapy is used: predominantly antiemetic and neuroleptic drugs are administered. A severe form requires close attention to the condition of the pregnant woman, since untimely or incorrectly chosen treatment threatens to end in coma and even death.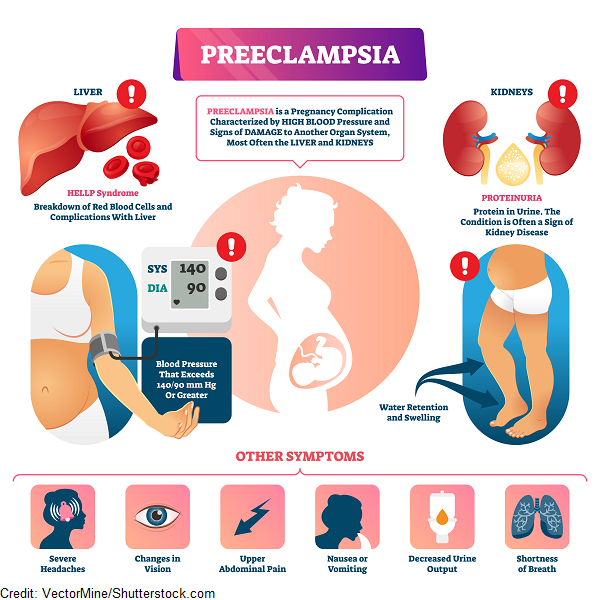 In severe cases, a woman may be advised to terminate the pregnancy to save her life. nine0005
In severe cases, a woman may be advised to terminate the pregnancy to save her life. nine0005
Consequences and prevention
Most often, the end of early toxicosis occurs at 12-13 weeks of pregnancy, and the well-being of a pregnant woman improves. But with toxicosis, there is a high risk of developing the following pathologies:
- dehydration: dehydration of the body;
- multiple organ failure: impaired functioning of the heart, liver, kidneys;
- yellow atrophy of the liver: this is a deadly consequence of toxicosis;
- spontaneous abortion. nine0008
If toxicosis is observed for too long, it will be necessary to exclude a number of pathologies: pancreatitis and hepatitis. The cause of prolonged toxicosis is often obstetric pathologies - for example, cystic drift or hepatosis.
Prevention of toxicosis should be carried out well before pregnancy. Women who do not have abortions and lead a healthy lifestyle minimize the risk of developing toxicosis of any severity, up to its complete absence.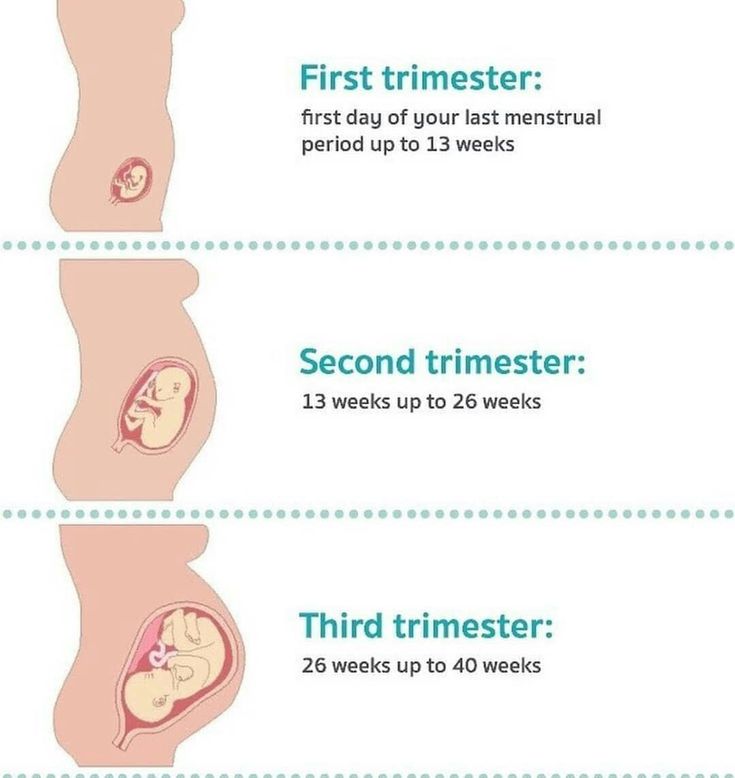 It is also necessary to take a responsible attitude to the upcoming pregnancy: when planning it, it is necessary to identify and cure diseases that provoke toxicosis. nine0005
It is also necessary to take a responsible attitude to the upcoming pregnancy: when planning it, it is necessary to identify and cure diseases that provoke toxicosis. nine0005
Toxicosis during pregnancy at different periods
Valentina
Almetyevsk
Toxicosis is a painful condition that develops during pregnancy. Toxicosis is early (usually occurs in the first trimester) and late (appears in the second or third trimester). In severe cases, toxicosis can pose a danger to the mother and child.
Toxicosis during early pregnancy: symptoms
- Heightened sense of smell. Tobacco smoke, cosmetics, the scent of flowers, or any other odor is irritating. nine0008
- Changing gastronomic tastes. "Classics of the genre" - pickles, herring, oranges. By the way, contrary to the existing misconception, the gender of the unborn child does not affect the food preferences of a woman. Toxicosis during pregnancy as a girl is no different from toxicosis during pregnancy as a boy.
 A woman's eating habits depend on the needs of the body.
A woman's eating habits depend on the needs of the body. - Nausea, vomiting, salivation. Usually these symptoms make themselves felt in the morning hours, but sometimes they haunt a woman around the clock. nine0006
- A mild form of toxicosis is accompanied by vomiting no more than 5 times a day and does not require the intervention of specialists.
- The average form of toxicosis is characterized by vomiting up to 10 times a day, and it is a reason for mandatory consultation with a doctor.
- Severe toxicosis during pregnancy occurs in 1 out of 500 cases. If a woman vomits more than 10 times a day, suffers from salivation, she needs urgent hospitalization.
- Deficiency of fluid and nutrients can lead to dehydration and metabolic disorders, as a result of which toxins will only accumulate. The expectant mother is waiting for great weight loss and exhaustion. During severe toxicosis, there is a risk of tachycardia, toxic liver dystrophy, arterial hypotension.
 nine0008
nine0008
Toxicosis during early pregnancy: causes
There are many hypotheses explaining the causes of early toxicosis. The most famous among them:
- Immunological theory. A cell, consisting of foreign genes and proteins, is perceived by the body as a foreign body that needs to be disposed of.
- Hormonal theory. Already on the 6th - 8th day after fertilization, the embryo actively produces the pregnancy hormone - human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Its concentration is growing rapidly, but by the 12th week it begins to fall, then toxicosis usually disappears.
 One of the arguments in favor of this theory is the coincidence of peak hCG values with the onset of vomiting. nine0008
One of the arguments in favor of this theory is the coincidence of peak hCG values with the onset of vomiting. nine0008 - Toxic theory. The development of the fetal egg is accompanied by the formation of toxins that poison the mother's body.
- Neuro-reflex theory. The fetal egg irritates the nerve receptors of the uterus and provokes disturbances in the interaction of the central nervous system, the autonomic nervous system and internal organs. A failure occurs in the work of the subcortical nuclei of the central nervous system, which leads to the appearance of zones of pathological excitation at the most vulnerable points - in the vomiting center and the center of salivation. nine0008
- Psychogenic theory. Toxicosis develops against the background of experiences associated with pregnancy.
All these hypotheses complement each other, but the most convincing, according to experts, is the neuro-reflex theory.
Factors contributing to the development of toxicosis
In most women, toxicosis lasts from 6 to 12-13 weeks.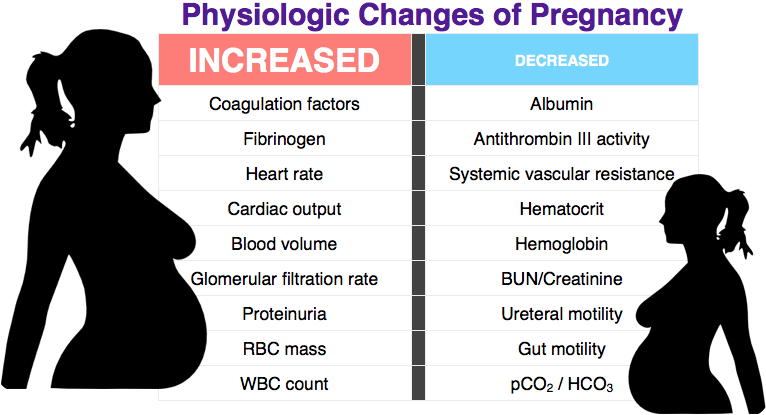 But this is not an axiom. Someone has a pregnancy without toxicosis, and someone is sick all 9 months. It is very difficult to predict the reaction of the body. However, factors are known that increase the risk of development and severity of toxicosis during pregnancy. Among them: nine0005
But this is not an axiom. Someone has a pregnancy without toxicosis, and someone is sick all 9 months. It is very difficult to predict the reaction of the body. However, factors are known that increase the risk of development and severity of toxicosis during pregnancy. Among them: nine0005
- multiple pregnancy,
- heredity,
- too young or, on the contrary, mature age,
- underweight,
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver,
- termination of pregnancy,
- malnutrition,
- bad habits,
- stress.
Early toxicosis: what to do?
There is no universal remedy for toxicosis: everything is very individual. However, in any case, in order to alleviate the symptoms of malaise, it is necessary to reconsider the usual lifestyle and diet. nine0005
- Get more rest. Sleep at least 8 hours a day and walk outdoors for at least 1.5 hours.
- Eat small meals 6 to 7 times a day.
- Eliminate hot, spicy and fatty foods from your diet.
- Introduce foods rich in pyridoxine (vitamin B6) into your diet. Its lack can exacerbate toxicosis during pregnancy. There is not so much vitamin B6 in animal food, so focus on plant products: rice, barley and buckwheat, millet, beans, soy. nine0008
- Include foods rich in complex carbohydrates in the evening menu. Cereals, potatoes, pasta made from durum wheat will help maintain a stable level of glucose in the blood and avoid its sharp drop in the morning.
- Before going to bed, leave a glass of water, a lemon, some biscuits or crackers on your bedside table. After waking up, without getting up, add lemon to the water, drink it and eat cookies or crackers.
- Stay in bed after breakfast. Lie down for a bit and only then slowly get up. nine0008
- If gagging occurs while brushing teeth, change toothpaste or limit mouthwash.
- Consult your doctor about herbal teas. Chamomile, calendula, lemon balm and valerian can alleviate your condition.
- Ask your doctor about taking ginger. In American literature, it is known as one of the most effective remedies for toxicosis.
Toxicosis in late pregnancy: causes
Late toxicosis during pregnancy is better known as "preeclampsia". This is a serious complication, which is accompanied by disruption of the functioning of vital organs. Most often, toxicosis in late pregnancy occurs in women younger than 19 and older than 30. Risk factors:
- multiple pregnancy,
- early toxicosis,
- fetal malnutrition,
- Rhesus conflict,
- heredity, nine0007 anemia,
- obesity,
- hypertension,
- kidney disease,
- endocrine diseases,
- malnutrition,
- preeclampsia during previous pregnancies.
The cause of late toxicosis is a violation of blood microcirculation and water-salt metabolism. Spasm of small vessels provokes a decrease in blood flow velocity and the formation of blood clots. The volume of circulating blood decreases, and the permeability of the walls of blood vessels increases. As a result, blood circulation is disturbed, and tissue nutrition deteriorates. Changes occur in organs that can lead to necrosis (death of cells and tissues). nine0005
The volume of circulating blood decreases, and the permeability of the walls of blood vessels increases. As a result, blood circulation is disturbed, and tissue nutrition deteriorates. Changes occur in organs that can lead to necrosis (death of cells and tissues). nine0005
Toxicosis in late pregnancy: stages and symptoms
There are 4 stages of late toxicosis: dropsy, nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia.
- dropsy. This is the mildest form of gestosis. It is characterized by a sharp increase in weight and swelling.
- Nephropathy. In addition to edema, other symptoms of late toxicosis appear: protein in the urine and high blood pressure. Its sudden changes are especially dangerous for the fetus. Possible premature detachment of the placenta, bleeding, premature birth. nine0008
- Preeclampsia. The woman's condition is deteriorating. Against the background of high pressure, headaches occur, rippling in the eyes, nausea, vomiting, sometimes drowsiness, lethargy, forgetfulness.