Most common complication of pregnancy
Complications of Pregnancy | Johns Hopkins Medicine
What are some of the more common complications of pregnancy?
Although the majority of pregnancies are uneventful, sometimes complications do happen. The following are some of the more common pregnancy complications.
Amniotic fluid complications
Too much or too little amniotic fluid in the sac around the fetus may be a sign of a problem with the pregnancy. Too much fluid can put too much pressure on the mother's uterus, leading to preterm labor. It also can cause pressure on the mother's diaphragm. This can lead to breathing difficulties. Fluids tend to build up in cases of uncontrolled diabetes, a multiple pregnancy, incompatible blood types, or birth defects. Too little fluid may be a sign of birth defects, growth retardation, or stillbirth.
Bleeding
Bleeding in late pregnancy may be a sign of placental complications, a vaginal or cervical infection, or preterm labor. Women who bleed in late pregnancy may be at greater risk of losing the fetus and bleeding excessively. Bleeding at any time during the pregnancy should be reported to your healthcare provider right away.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is the development of the fetus outside of the uterus. This can happen in the fallopian tubes, cervical canal, or the pelvic or belly. The cause of an ectopic pregnancy is usually scar tissue in the fallopian tube from infection or disease. The risk of ectopic pregnancy is increased in women who have had tubal sterilization procedures, especially women who were younger than age 30 at the time of sterilization.
Ectopic pregnancies happen in about 1 out of 50 pregnancies and can be very dangerous to the mother. Symptoms may include spotting and cramping. The longer an ectopic pregnancy goes on, the greater the chance that a fallopian tube will rupture. An ultrasound and blood tests may confirm the diagnosis. Treatment of an ectopic pregnancy may include medicine or surgical removal of the fetus.
Miscarriage or fetal loss
A miscarriage is pregnancy loss that happens up to 20 weeks of gestation.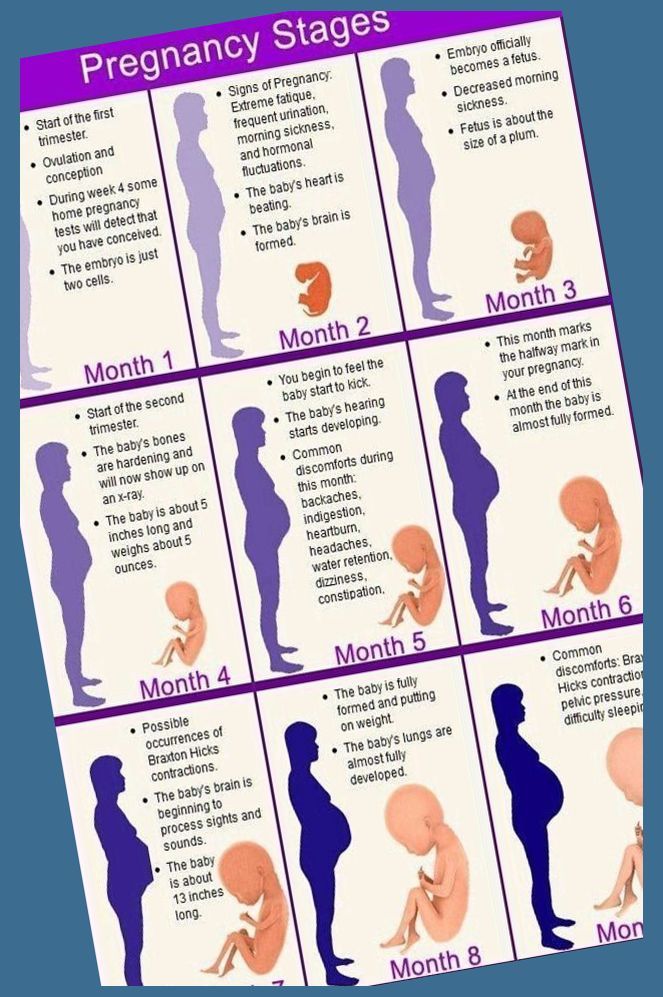 Most miscarriages happen before 12 weeks. Miscarriages happen in about 15% of all pregnancies and are usually due to genetic or chromosomal abnormalities.
Most miscarriages happen before 12 weeks. Miscarriages happen in about 15% of all pregnancies and are usually due to genetic or chromosomal abnormalities.
Miscarriages are usually preceded by spotting and intense cramping. To confirm a miscarriage, an ultrasound and blood tests may be done. The fetus and contents of the uterus are often naturally expelled. If this does not happen, a procedure called a dilation and curettage (D & C) may be necessary. This procedure uses special instruments to remove the abnormal pregnancy.
Fetal loss in the second trimester may happen if the cervix is weak and opens too early. This is called incompetent cervix. In some cases of incompetent cervix, a healthcare provider can help prevent pregnancy loss by stitching the cervix closed until delivery.
Placental complications
Under normal circumstances, the placenta attaches to the uterine wall. However, two types of placental complications may happen, including:
Placental abruption is more common in women who smoke, have high blood pressure, and/or have a multiple pregnancy. It also happens in women who have had previous children or a history of placental abruption. Symptoms and treatment of placental abruption depend on the degree of detachment. Symptoms may include bleeding, cramping, and belly tenderness. Diagnosis is usually confirmed by doing a complete physical exam and an ultrasound. Women are usually put in the hospital for this condition. They may have to deliver the baby early.
It also happens in women who have had previous children or a history of placental abruption. Symptoms and treatment of placental abruption depend on the degree of detachment. Symptoms may include bleeding, cramping, and belly tenderness. Diagnosis is usually confirmed by doing a complete physical exam and an ultrasound. Women are usually put in the hospital for this condition. They may have to deliver the baby early.
Placenta previa. Normally, the placenta is located in the upper part of the uterus. Placenta previa is a condition in which the placenta is attached close to or covering the cervix (the opening into the uterus). This type of placental complication happens in about 1 in every 200 deliveries and happens more often in women who have scarring of the uterus from previous pregnancies. It also happens in women who have fibroids or other problems in the uterus, or in women who have had previous uterine surgeries.
Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding that is bright red and not associated with belly tenderness or pain.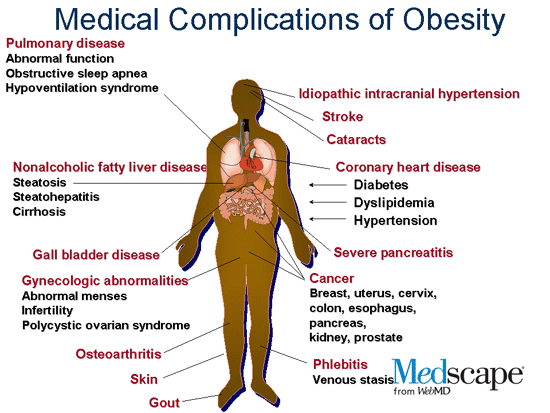 Diagnosis is confirmed by doing a physical exam and an ultrasound. Depending on how bad the problem is and the stage of pregnancy, a change in activities or bed rest may be ordered. The baby usually has to be delivered by cesarean section to keep the placenta from detaching early and depriving the baby of oxygen during delivery.
Diagnosis is confirmed by doing a physical exam and an ultrasound. Depending on how bad the problem is and the stage of pregnancy, a change in activities or bed rest may be ordered. The baby usually has to be delivered by cesarean section to keep the placenta from detaching early and depriving the baby of oxygen during delivery.
Preeclampsia or eclampsia
Preeclampsia, formerly called toxemia, is characterized by pregnancy-induced high blood pressure. It is accompanied by protein in the urine. Sometimes swelling due to fluid retention is also present. Eclampsia is the more severe form of this problem. This can lead to seizures, coma, or even death.
The cause of preeclampsia is unknown, but it is more common in first pregnancies. It affects about 5% to 8% of all pregnant women. Other risk factors for preeclampsia include:
A woman carrying multiple fetuses
A teenage mother
A woman older than 40
A woman with high blood pressure, diabetes, and/or kidney disease before she became pregnant
A woman who is obese with a BMI greater than 30
Symptoms may include severe swelling of the hands and face, high blood pressure, headache, dizziness, irritability, decreased urine output, belly pain, and blurred vision. Treatment will vary according to the severity of the condition and the stage of the pregnancy. Treatment may include hospitalization, bed rest, medicine to lower blood pressure, and close monitoring of both the fetus and the mother.
Treatment will vary according to the severity of the condition and the stage of the pregnancy. Treatment may include hospitalization, bed rest, medicine to lower blood pressure, and close monitoring of both the fetus and the mother.
Pregnancy Complications | Maternal and Infant Health
Complications of pregnancy are health problems that occur during pregnancy. They can involve the mother’s health, the baby’s health, or both. Some women have health problems that arise during pregnancy, and other women have health problems before they become pregnant that could lead to complications. It is very important for women to receive health care before and during pregnancy to decrease the risk of pregnancy complications.
Before Pregnancy
Make sure to talk to your doctor about health problems you have now or have had in the past. If you are receiving treatment for a health problem, your health care provider might want to change the way your health problem is managed.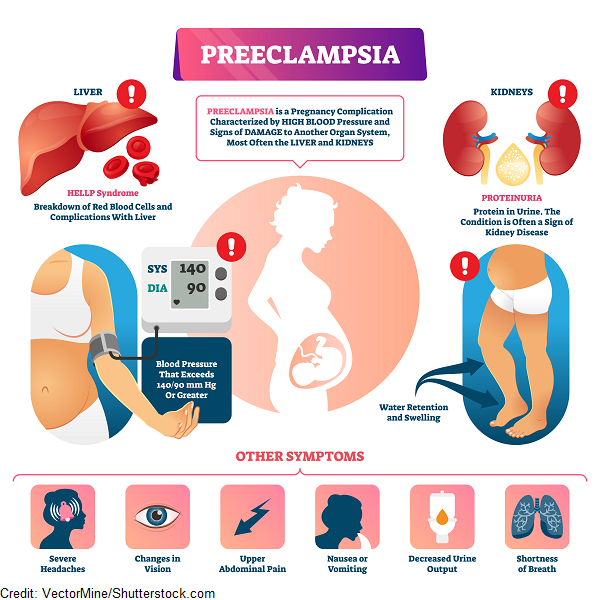 For example, some medicines used to treat health problems could be harmful if taken during pregnancy. At the same time, stopping medicines that you need could be more harmful than the risks posed should you become pregnant. In addition, be sure to discuss any problems you had in any previous pregnancy. If health problems are under control and you get good prenatal care, you are likely to have a normal, healthy baby.
For example, some medicines used to treat health problems could be harmful if taken during pregnancy. At the same time, stopping medicines that you need could be more harmful than the risks posed should you become pregnant. In addition, be sure to discuss any problems you had in any previous pregnancy. If health problems are under control and you get good prenatal care, you are likely to have a normal, healthy baby.
- Before Pregnancy
- During Pregnancy
- Research
- Obesity
- Severe maternal morbidity in the United States
During Pregnancy
Pregnancy symptoms and complications can range from mild and annoying discomforts to severe, sometimes life-threatening, illnesses. Sometimes it can be difficult for a woman to determine which symptoms are normal and which are not. Problems during pregnancy may include physical and mental conditions that affect the health of the mother or the baby. These problems can be caused by or can be made worse by being pregnant. Many problems are mild and do not progress; however, when they do, they may harm the mother or her baby. Keep in mind that there are ways to manage problems that come up during pregnancy. Always contact your prenatal care provider if you have any concerns during your pregnancy.
Many problems are mild and do not progress; however, when they do, they may harm the mother or her baby. Keep in mind that there are ways to manage problems that come up during pregnancy. Always contact your prenatal care provider if you have any concerns during your pregnancy.
The following are some common maternal health conditions or problems a woman may experience during pregnancy—
Anemiaexternal icon
Anemia is having lower than the normal number of healthy red blood cells. Treating the underlying cause of the anemia will help restore the number of healthy red blood cells. Women with pregnancy related anemia may feel tired and weak. This can be helped by taking iron and folic acid supplements. Your health care provider will check your iron levels throughout pregnancy.
The Hear Her campaign supports CDC’s efforts to prevent pregnancy-related deaths by sharing potentially life-saving messages about urgent warning signs.
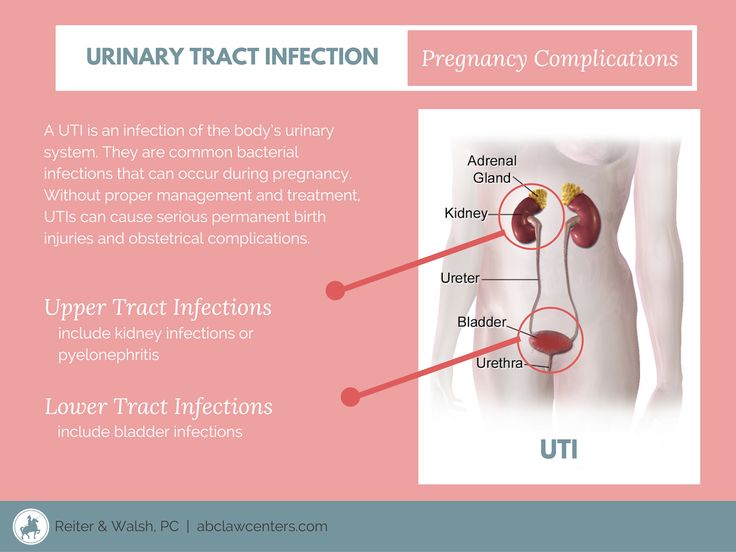
Urinary Tract Infectionsexternal icon (UTI)
A UTI is a bacterial infection in the urinary tract. You may have a UTI if you have—
You may have a UTI if you have—
- Pain or burning when you use the bathroom.
- Fever, tiredness, or shakiness.
- An urge to use the bathroom often.
- Pressure in your lower belly.
- Urine that smells bad or looks cloudy or reddish.
- Nausea or back pain.
If you think you have a UTI, it is important to see your health care provider. He/she can tell if you have a UTI by testing a sample of your urine. Treatment with antibiotics to kill the infection will make it better, often in one or two days. Some women carry bacteria in their bladder without having symptoms. Your health care provider will likely test your urine in early pregnancy to see if this is the case and treat you with antibiotics if necessary.
Mental Health Conditions
Some women experience depression during or after pregnancy. Symptoms of depression are:
- A low or sad mood.
- Loss of interest in fun activities.
- Changes in appetite, sleep, and energy.
- Problems thinking, concentrating, and making decisions.
- Feelings of worthlessness, shame, or guilt.
- Thoughts that life is not worth living.
When many of these symptoms occur together and last for more than a week or two at a time, this is probably depression. Depression that persists during pregnancy can make it hard for a woman to care for herself and her baby. Having depression before pregnancy also is a risk factor for postpartum depression. Getting treatment is important for both mother and baby. If you have a history of depression, it is important to discuss this with your health care provider early in pregnancy so that a plan for management can be made.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Chronic poorly-controlled high blood pressure before and during pregnancy puts a pregnant woman and her baby at risk for problems. It is associated with an increased risk for maternal complications such as preeclampsiaexternal icon, placental abruption (when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus), and gestational diabetes. These women also face a higher risk for poor birth outcomes such as preterm delivery, having an infant small for his/her gestational age, and infant death. The most important thing to do is to discuss blood pressure problems with your provider before you become pregnant so that appropriate treatment and control of your blood pressure occurs before pregnancy. Getting treatment for high blood pressure is important before, during, and after pregnancy.
These women also face a higher risk for poor birth outcomes such as preterm delivery, having an infant small for his/her gestational age, and infant death. The most important thing to do is to discuss blood pressure problems with your provider before you become pregnant so that appropriate treatment and control of your blood pressure occurs before pregnancy. Getting treatment for high blood pressure is important before, during, and after pregnancy.
Diabetes During Pregnancy
Learn about types of diabetes during pregnancy, the percentage of women affected, and what CDC is doing to address this important health topic. Managing diabetes can help women have healthy pregnancies and healthy babies.
Obesity and Weight Gain
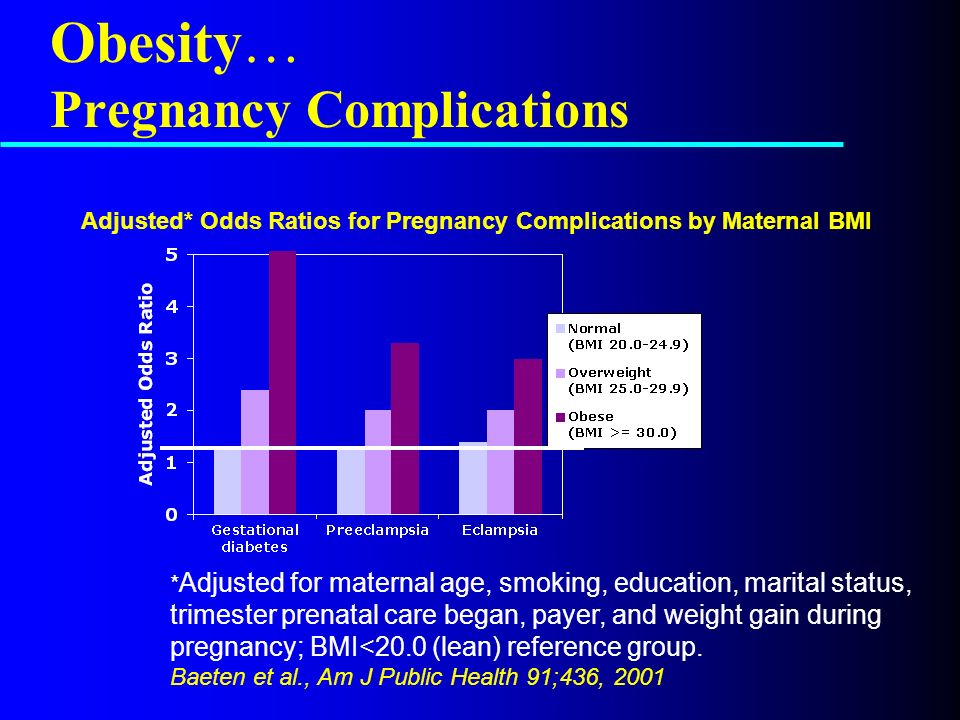
Recent studies suggest that the heavier a woman is before she becomes pregnant, the greater her risk of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, GDM, stillbirth and cesarean delivery. Also, CDC research has shown that obesity during pregnancy is associated with increased use of health care and physician services, and longer hospital stays for delivery. Overweight and obese women who lose weight before pregnancy are likely to have healthier pregnancies. Learn more about ways to reach and maintain a healthy weight before you get pregnant.
Overweight and obese women who lose weight before pregnancy are likely to have healthier pregnancies. Learn more about ways to reach and maintain a healthy weight before you get pregnant.
Infectionsexternal icon
During pregnancy, your baby is protected from many illnesses, like the common cold or a passing stomach bug. But some infections can be harmful to you, your baby, or both. Easy steps, such as hand washing, and avoiding certain foods, can help protect you from some infections. You won’t always know if you have an infection—sometimes you won’t even feel sick. If you think you might have an infection or think you are at risk, see your health care provider.
Infections with HIV, viral hepatitis, STDs, and TB can complicate pregnancy and may have serious consequences for a woman, her pregnancy outcomes, and her baby. Screening and treatment for these infections, and vaccinations against viruses, such as hepatitis B and human papillomavirus, can prevent many bad outcomes.
Hyperemesis Gravidarumexternal icon
Many women have some nausea or vomiting, or “morning sickness,” particularly during the first 3 months of pregnancy. The cause of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy is believed to be rapidly rising blood levels of a hormone called HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which is released by the placenta. However, hyperemesis gravidarum occurs when there is severe, persistent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy—more extreme than “morning sickness.” This can lead to weight loss and dehydration and may require intensive treatment.
Learn more about pregnancy complications from womenshealth.gov.external icon
Top of Page
Research
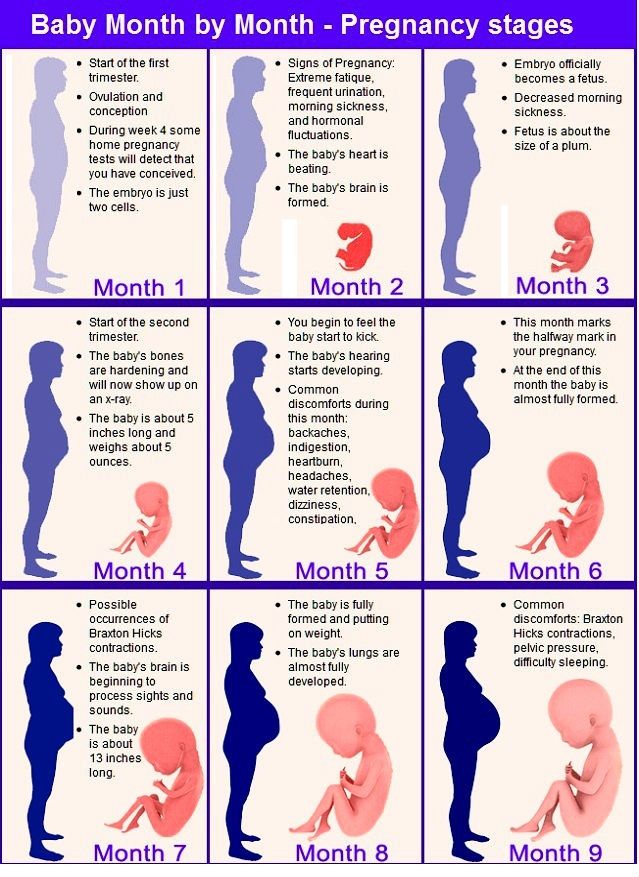
CDC’s Division of Reproductive Health conducts research to better understand pregnancy-related problems, with the aims of making pregnancy healthier, preventing or managing complications, and reducing poor pregnancy outcomes, including death—the most extreme adverse outcome. There are approximately 6 million pregnancies each year in the United States.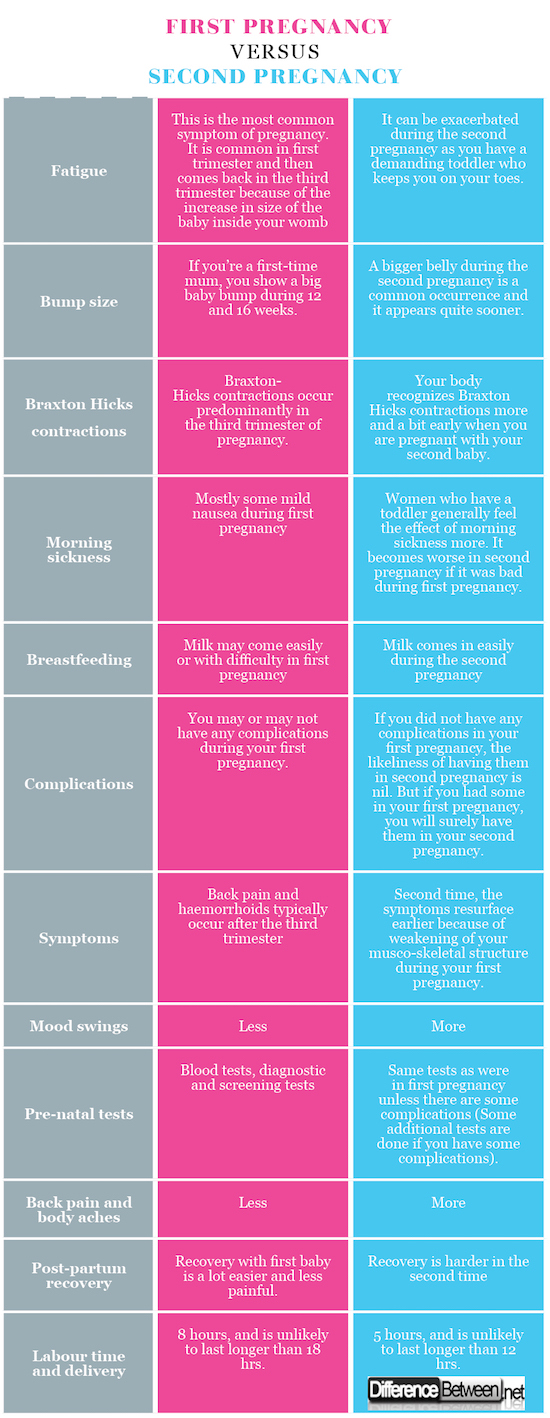 Small advances in preventing pregnancy-related complications can improve the quality of life for thousands of pregnant women. We can further the development of evidence-based public health prevention with improved sources of maternal health data, and methods for measuring and studying the data. Highlights of some of our research follow
Small advances in preventing pregnancy-related complications can improve the quality of life for thousands of pregnant women. We can further the development of evidence-based public health prevention with improved sources of maternal health data, and methods for measuring and studying the data. Highlights of some of our research follow
Obesity
In the United States, obesity during pregnancy is common and it increases obstetrical risks. In collaboration with Kaiser Permanente Northwest, CDC conducted a study to assess associations between indicators of use of health care services and body-mass index before pregnancy or in early pregnancy and found that obesity during pregnancy is associated with increased use of health care services. A higher-than-normal BMI was associated with significantly more prenatal fetal tests, obstetrical ultrasonographic examinations, medications dispensed from the outpatient pharmacy, telephone calls to the department of obstetrics and gynecology, and prenatal visits with physicians. It was also associated with significantly fewer prenatal visits with nurse practitioners and physician assistants. Most of the increase in length of stay associated with higher BMI was related to increased rates of cesarean delivery and obesity-related high-risk conditions. (Association between obesity during pregnancy and increased use of health careexternal icon. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1444–53.)
It was also associated with significantly fewer prenatal visits with nurse practitioners and physician assistants. Most of the increase in length of stay associated with higher BMI was related to increased rates of cesarean delivery and obesity-related high-risk conditions. (Association between obesity during pregnancy and increased use of health careexternal icon. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1444–53.)
CDC has supported university investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital to develop Balance after Baby, a lifestyle intervention program tailored specifically to meet the needs of postpartum women. The primary aim of this study was to assist women with a new baby to return to a normal weight through an Internet-based program of healthy eating and physical activity, which they could participate in at their convenience.
Severe maternal morbidity in the United States
Maternal morbidity includes physical and psychologic conditions that result from or are aggravated by pregnancy and have an adverse effect on a woman’s health. The most severe complications of pregnancy, generally referred to as severe maternal morbidity (SMM), affect more than 50,000 women in the United States every year. Based on recent trends, this burden has been steadily increasing.
The most severe complications of pregnancy, generally referred to as severe maternal morbidity (SMM), affect more than 50,000 women in the United States every year. Based on recent trends, this burden has been steadily increasing.
Rises in SMM are likely driven by a combination of factors, including increases in maternal age, pre-pregnancy obesity, pre-existing chronic medical conditions, and cesarean delivery. The consequences of the increasing SMM prevalence are wide-ranging and include higher health service use, higher direct medical costs, extended hospitalization stays, and long-term rehabilitation. The review of SMM cases provides an opportunity to identify points of intervention for quality improvements in maternal care. Tracking SMM will help monitor the effectiveness of such interventions.
Top of Page
Multiple pregnancy
49. Suspicion for early multiple pregnancy timing based on:
a) compliance increase in the size of the uterus delay period menstruation
b) mismatch increase in the size of the uterus delay period menstruation
c) data family history
d) more expressed signs of Piskachek, Snegirev
e) no correct answer
50. Diagnostic criteria for multiple pregnancy include:
Diagnostic criteria for multiple pregnancy include:
a) sensation of fetal movement in different places
b) definition external methods of three or more large parts of the fetus
c) distinct fetal heartbeat in different places uterus
d) high standing of the fundus of the uterus, not corresponding gestational age
e) large head sizes with significant uterus dimensions
51. Partition, separating each fetus with an identical double, contains:
a) one amnion and one chorion
b) two amnions
c) two chorion
d) two amnion and two chorions
e) no correct answer
52. Partition, dividing each fetus with a dizygotic double, contains:
a) one amnion and one chorion
b) two amnions
c) two chorion
d) two amnion and two chorions
e) no correct answer
53. For multiple pregnancy are characterized by:
For multiple pregnancy are characterized by:
a) large uterine size and large presenting head
b) large uterine size and small presenting head
c) large size of uterus and presenting head normal sizes
d) small uterus size and small size heads
e) no correct answer
54. Most common complication of pregnancy multiple pregnancy:
a) delay fruit development
b) premature detachment is normal located placenta
c) postmaturity pregnancy
d) premature discharge of amniotic fluid
e) no correct answer
55. Most frequent complication in childbirth with multiple pregnancies:
a) weakness labor activity
b) belated discharge of amniotic fluid
c) premature detachment of normally located placenta
d) rupture uterus
e) no correct answer
56. The most formidable complication in the second period of childbirth with multiple pregnancy:
The most formidable complication in the second period of childbirth with multiple pregnancy:
a) weakness labor activity
b) intrauterine fetal hypoxia
c) premature detachment of normally located placenta
d) collision twins
e) no correct answer
57. After birth of the first fetus with longitudinal the position of the second is shown:
a) expectant self birth tactics fetus
b) intravenous administration of oxytocin
c) caesarean section section
d) amniotomy
e) no correct answer
58. In second stage of labor with pelvic presentation of the second fetus, the doctor must:
a) open amniotic sac and give birth natural flow
b) open fetal bladder and remove the fetus behind the pelvic end
c) open fetal bladder and provide assistance for Tsovyanov
d) perform caesarean section
e) no correct answer
59. In second stage of labor with transverse position of the second fetus, the doctor must:
In second stage of labor with transverse position of the second fetus, the doctor must:
a) open amniotic sac and give birth natural flow
b) open fetal bladder and rotate fetus per stalk
c) open amniotic sac and caesarean section section
d) execute fruit-destroying operation
e) no correct answer
60. The most accurate diagnostic method multiple pregnancy is:
a) external obstetric examination
b) phonoelectrocardiography
in) amnioscopy
d) Ultrasound examination
e) no correct answer
61. After the birth of a fetus weighing 2800.0 in the uterus a second fetus was found in the transverse position. Head left, pelvic end turned to the right. Fetal heartbeat clear, rhythmic up to 140 beats / min. Your tactics:
a) cesarean section
b) outer turn
c) external-internal rotation of the fetus on leg
G) fruit-destroying operation
e) no correct answer
62. The course of pregnancy with multiple pregnancy most frequently complicated:
The course of pregnancy with multiple pregnancy most frequently complicated:
a) preterm pregnancy
b) late preeclampsia
in) overwearing
d) all answers are wrong
e) no correct answer
63. During auscultation of a pregnant woman with multiple pregnancy is characteristic:
a) the presence of two points with clear listening fetal heart sounds
b) there is a zone between points of clear sound muting
in) heart rate in different points differ by 10 - 15 beats
d) all answers are correct
e) no correct answer
64. Multiple pregnancy must be differentiated from:
a) large fruit
b) polyhydramnios
in) obese
d) all answers are correct
e) no correct answer
65. The most accessible method in the clinic diagnosis of multiple pregnancy:
The most accessible method in the clinic diagnosis of multiple pregnancy:
a) ultrasound procedure;
b) x-ray examination;
in) radioisotope scintigraphy;
G) all of the above;
e) no correct answer
66. Complications arising from multiple pregnancy pregnancy:
a) premature birth;
b) premature and early effusion amniotic fluid;
in) weakness of tribal forces;
d) all listed.
e) no correct answer
67. Clinical symptoms of multiple pregnancy:
a) discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the term pregnancy;
b) numerous fetal movements;
in) three or more large parts of the fetus with palpation of the uterus;
d) all listed.
e) no correct answer
Topic 19 Initial test - Page 2
6. Outions in pregnant women with hypertension
Outions in pregnant women with hypertension
1) Premature birth
2) Development of gestosis
3) Premature detachment of a normally located placenta
4) Hemormanding in the brain
5) all these complications
7. HYPERTENSION CRISIS DURING PREGNANCY NOT CHARACTERISTIC
1) the development of a crisis at any stage of pregnancy
2) the development of a crisis only in the second half of pregnancy
3) the absence of edema, proteinuria and cylindruria
4) The appearance of parestesia, hyperemia of the face, increased sweating
5) headache, nausea, vomiting
8. The most likely cause of blood pressure after 28 weeks of pregnancy
1) hypertension
2) development of preeclampsia
3 ) chronic glomerulonephritis
4) chronic pyelonephritis
5) urolithiasis
0003
1) hypertension
2) preeclampsia
3) chronic glomerulonephritis
4) chronic pyelonephritis
5) urolithiasis
10. Upon conducting the first period of birth in women in childbirth with hypertension, maximum 1) labor pain relief
Upon conducting the first period of birth in women in childbirth with hypertension, maximum 1) labor pain relief
2) antihypertensive therapy
3) early amniotomy
4) administration of magnesium sulfate
5) prevention of fetal hypoxia
0003
1) increase in circulating blood volume
2) constantly decreasing peripheral vascular resistance
3) increase in cardiac output and increased heart rate
4) increase in renal blood flow
5) all of the above changes OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARRIED OUT AT THE TERM OF PREGNANCY
| 1) | 6-12 weeks | 4) 29–35 weeks |
| 2) | 13–25 weeks | 5) 36–38 weeks |
3) 26–28 weeks
13. The main task when examining a pregnant woman with heart defect
1) Diagnostics of a defect form
2) Identification of circulatory disorders during pregnancy
3) Diagnostics of rheumatism and degree of its activity
4) detection of concomitant complications
14. PROSENT OF heart failure in pregnant women
PROSENT OF heart failure in pregnant women
1) Increase in the BCC and Minute of the heart
2) development of gestosis
3) Exacerbation of rheumatism
4) Acute infection of the upper respiratory tract and exacerbation of chronic infection
15. Diagnostic criteria 15. EVALUATION OF THE ACTIVITY OF THE RHEUMATIC PROCESS DURING PREGNANCY
1) the number of leukocytes exceeding 11.0 109/l, and ESR more than 35 mm/h, a pronounced shift of the leukocyte formula to the left
2) circulatory failure during active treatment
3) decrease in the number of reticulocytes
4) increase in the titer of anti-O-streptolysin and anti-hyaluronidase
A set of tests of the initial level of knowledge to topic No. 19 in the discipline "outpatient therapy"
5Choose one correct answer
1. ANTIBACTERIAL DRUGS FOR THE TREATMENT OF PYELONEPHRITIS IN THE FIRST TRIMESTER OF PREGNANCY
| 1) | aminoglycosides | 4) penicillin antibiotics |
| 2) | nitrofurans | series |
| 3) | cephalosporins | 5) sulfonamides |
2 BEST DELIVERY METHOD FOR PYELONEPHRITIS
1) planned caesarean section
2) caesarean section in childbirth
3) vaginal delivery without shortening the period of expulsion
4) childbirth through the natural birth canal with shortening of the period of expulsion by perineotomy
3 THE MOST COMMON FORM OF CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
| IN PREGNANT WOMEN |
|
| |
| 1) | latent | 4) | mixed |
| 2) | hypertonic | 5) | with pronounced |
| 3) | nephrotic |
| symptomatic |
4. The most frequent complication of pregnancy with glomerulonephritis
The most frequent complication of pregnancy with glomerulonephritis
1) development of gestosis
2) acute renal failure
3) premature detachment of a normally located placenta
4) 9000 .DATE OF PREGNANCY AT WHICH THE PAIN SYNDROME IS MOST COMMONLY OCCURRED IN URINAL STONE DISEASE
| 1) 38–40 weeks | nine0346 20–27 weeks | |
| 2) 32–36 weeks | 5) | 8–12 weeks |
3) 28–32 weeks
6. The most frequent liver disease associated with
1) Virus hepatosis
| 2) Holecystitis | 5) viral hepatitis B |
3) cholestatic hepatosis
7. Clinic and laboratory criteria for diagnosis of viral hepatitis during pregnancy
1) vomiting and nausea at any time of the day
2) increase in body temperature, often with a chills of
3) the appearance of jaundice, dark urine
4) hyperbilirubinemia and hyperbilirubinum and increase in ALT and AST levels in the blood
8. A FEATURE OF THE COURSE OF VIRAL HEPATITIS B DURING PREGNANCY IS
A FEATURE OF THE COURSE OF VIRAL HEPATITIS B DURING PREGNANCY IS
1) a longer incubation period
2) severe intoxication
3) joint pain and urticar rashes
4) Significant increase in AST and ALT
9. The deposition of pregnancy and childbirth with viral hepatitis is
1) Development of liver failure
2) intrauterine infection of the fetus
3)) fetal death
4) bleeding in the third stage of labor and early postpartum period with development
5) DIC
10
100003
1) Symptomatic treatment
2) planned cesarean section
3) Emergency cesarean section
4) Giving birth through natural birth canal after symptomatic treatment
5) immediate delivery of
11. When conducting the expulsion of the exile in the ranges of HYPERTENSION IS NECESSARY
1) to exclude the period of exile
2) to shorten the period of exile by perineotomy or the application of obstetric forceps
3) to perform an epidural. anesthesia
anesthesia
4) Introduce magnesium sulfate
5) End the birth with Caesarean section
12. For controlled normotonia in the second period of birth, it is necessary to apply
1) Intravenous administration of magnesium
2) Introduction of beta-adrenordicars
3) Investigation
4) administration of glucose-novocaine mixture
5) epidural anesthesia
0003
2) Changing the hormonal balance
3) uterine pressure on the ureters
4) Bubble-ware reflux
14. Pyelonephritis during pregnancy
1) anemia
2) Fruit development syndrome
3) development of combined preeclampsia
4) infection of the mother and fetus
5) all these complications
0003
| 2) | hydronephrosis | 5) kidney tumors |
| 3) | pyelonephritis |
|
Sample answers to test tasks to control the initial level of knowledge on topic No.