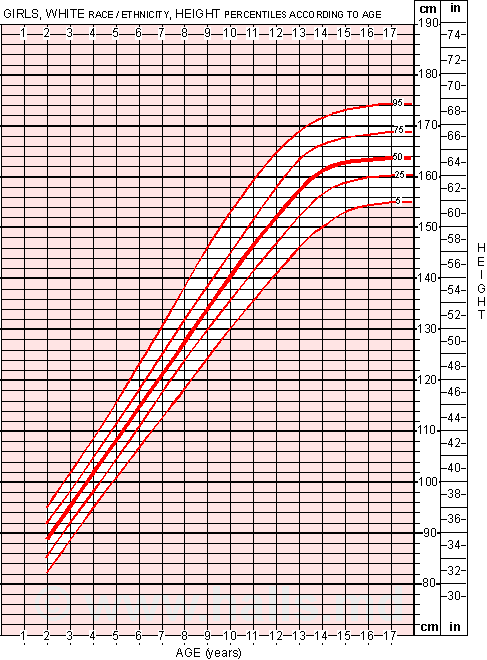
Infant height charts
Growth Charts - Clinical Growth Charts
The clinical growth charts reflect modifications in the format of the individual charts, whereby two individual charts appear on a single page, and data entry tables have been added. The clinical charts have the grids scaled to metric units (kg, cm), with English units (lb, in) as the secondary scale. Clinical charts are available for boys and for girls. The available clinical charts include the following:
Infants, birth to 36 months:
- Length-for-age and Weight-for-age
- Head circumference-for-age and Weight-for-length
Children and adolescents, 2 to 20 years
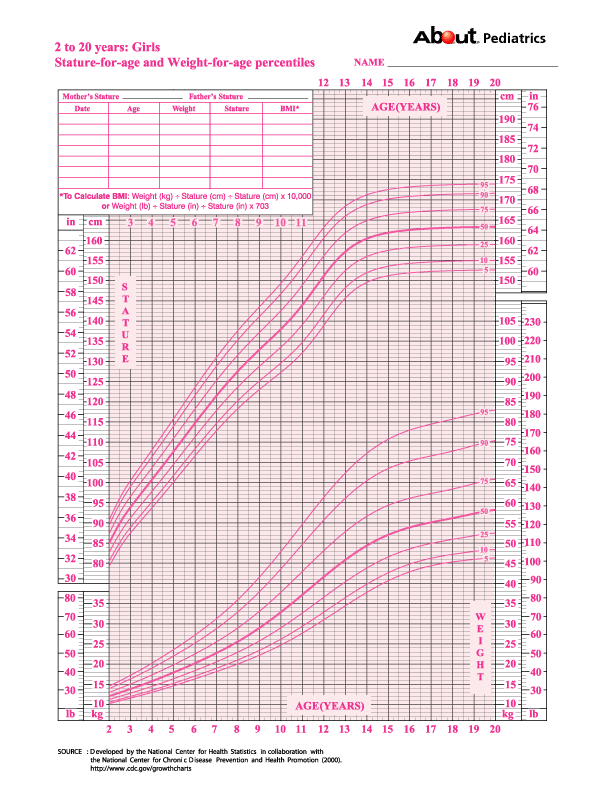
- Stature-for-age and Weight-for-age
- BMI-for-age
Preschoolers, 2 to 5 years
- Weight-for-stature
The clinical charts for infants and older children were published in two sets.
- Set 1 contains 10 charts (5 for boys and 5 for girls), with the 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th smoothed percentile lines for all charts, and the 85th percentile for BMI-for-age and weight-for-stature.
- Set 2 contains 10 charts (5 for boys and 5 for girls), with the 3rd, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 97th smoothed percentile lines for all charts, and the 85th percentile for BMI-for-age and weight-for-stature.
Set 1 has the outer limits of the curves at the 5th and 95th percentiles. These are the charts that most users in the United States will find useful for the majority of routine clinical assessments. Set 2 has the outer limits of the curves at the 3rd and 97th percentiles for selected applications. Pediatric endocrinologists and others who assess the growth of children with special health care requirements may wish to use the format in set 2 for selected applications.
Two summary files, each with all 10 clinical charts in set 1 or set 2 are also available. These summary files contain the clinical charts from either set 1 or set 2 as described above.
Infants (birth to 24 months) must be measured for length, and the sex appropriate length-for-age or weight-for-length charts for infants, birth to 36 months must be used to plot the measurements. At age 24 months and older, if children can stand unassisted and follow directions, stature should be measured and plotted on the stature-for-age chart for children (2 to 20 years). Otherwise, between 24 and 36 months, length can be used in place of stature.
At age 24 months and older, if children can stand unassisted and follow directions, stature should be measured and plotted on the stature-for-age chart for children (2 to 20 years). Otherwise, between 24 and 36 months, length can be used in place of stature.
BMI-for-age charts are recommended to assess weight in relation to stature for children ages 2 to 20 years. The weight-for-stature charts are available as an alternative to accommodate children ages 2-5 years who are not evaluated beyond the preschool years. However, all health care providers should consider using the BMI-for-age charts to be consistent with current recommendations.
All individual 2000 CDC growth charts have an initial publication date of May 30, 2000. For various reasons, modifications were made to charts after the initial publication date. For example, the individual charts were modified to create the clinical charts, which were made available on October 16, 2000. Subsequent modifications were made to selected clinical charts to correct or enhance particular aspects of the scales on the graphs. In all cases, the data points in the corresponding data file for each modified chart remain unchanged from the initial release on May 30, 2000. Where applicable, when selected clinical charts were further modified, the date is indicated on each chart. The clinical growth charts for stature-for-age were modified because the scale for inches was not correctly aligned with the metric scale. The clinical growth charts for infant length-for-age and infant weight-for-age were revised to improve the appearance of the scale for inches on the length charts by extending the indicators at ½ inch increments, and enhancing alignment of the English with the metric scales on both the length and weight scales.
In all cases, the data points in the corresponding data file for each modified chart remain unchanged from the initial release on May 30, 2000. Where applicable, when selected clinical charts were further modified, the date is indicated on each chart. The clinical growth charts for stature-for-age were modified because the scale for inches was not correctly aligned with the metric scale. The clinical growth charts for infant length-for-age and infant weight-for-age were revised to improve the appearance of the scale for inches on the length charts by extending the indicators at ½ inch increments, and enhancing alignment of the English with the metric scales on both the length and weight scales.
Users should use the most recent version of each chart, as available on the growth charts web site.
To view, print, and reproduce clinical growth charts
All clinical growth charts may be viewed, downloaded, and printed in Adobe Acrobat. For routine viewing on a computer monitor and printing on a laser printer, the individual charts are available as PDF files (Black and White).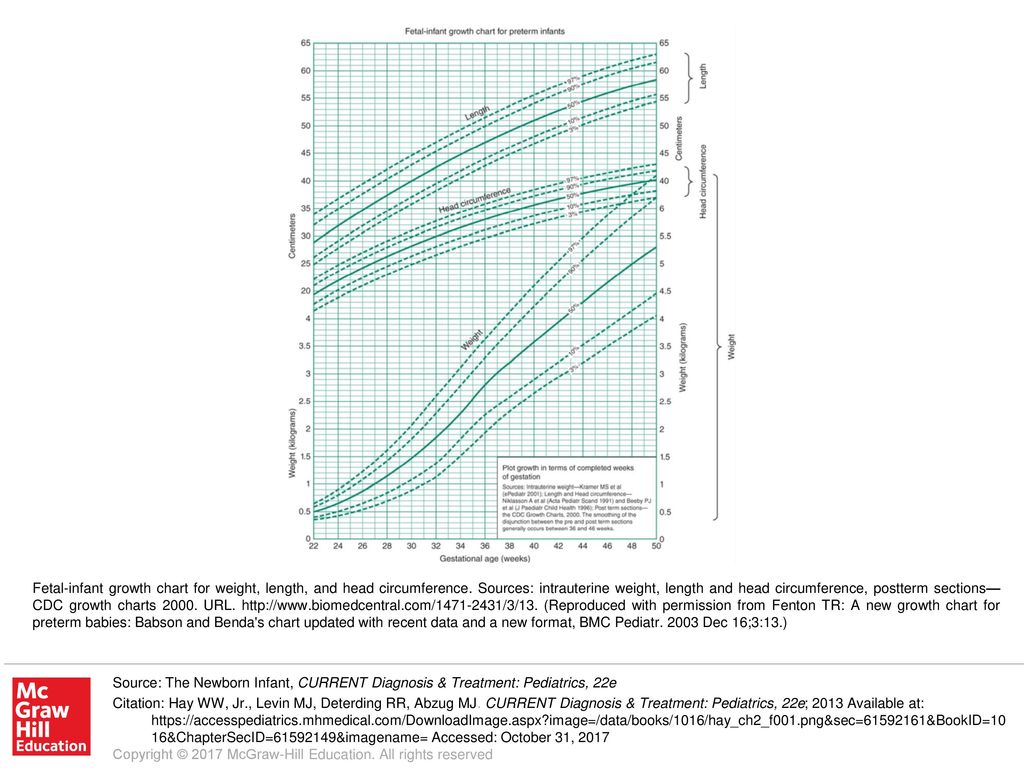 All clinical charts have been colorized for viewing and printing. When routed to a color printer, the clinical charts for boys will print in blue and the clinical charts for girls will print in red. Otherwise, these same charts can be routed to a black-and-white printer, and will print in black-and-white. Higher resolution PDF files (Color) are available to provide the highest resolution and are intended to be used as a high quality print master for quantity production when using the services of a commercial printing facility. The recommended ink colors for printing are Pantone 206 red (for girls) and Pantone 286 blue (for boys). The recommended paper weight is 80#. Charts should be printed as two-sided copies, in the following combinations for each sex:
All clinical charts have been colorized for viewing and printing. When routed to a color printer, the clinical charts for boys will print in blue and the clinical charts for girls will print in red. Otherwise, these same charts can be routed to a black-and-white printer, and will print in black-and-white. Higher resolution PDF files (Color) are available to provide the highest resolution and are intended to be used as a high quality print master for quantity production when using the services of a commercial printing facility. The recommended ink colors for printing are Pantone 206 red (for girls) and Pantone 286 blue (for boys). The recommended paper weight is 80#. Charts should be printed as two-sided copies, in the following combinations for each sex:
Infants, birth to 36 months:
- Side 1: Length for age + Weight-for-age
- Side 2: Head circumference-for-age + Weight-for-length
Children and adolescents, 2 to 20 years:
- Side 1: Stature-for-age + Weight-for-length
- Side 2: BMI-for-age or
- Weight-for-stature (age 2 to 5 years only)
Set 1: Clinical charts with 5th and 95th percentiles
Birth to 36 months (5th-95th percentile)
Boys Length-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 41 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Color [PDF – 44 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 44 KB] Modified 4/20/01
French Version, Color [PDF – 44 KB] Modified 4/20/01
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 186 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 200 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Length-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Boys Head circumference-for-age and Weight-for-length
B&W [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version Color [PDF – 52 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version Color [PDF – 56 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 206 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 236 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Head circumference-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-length charts
Girls Length-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 40 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Color [PDF – 40 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 50 KB] Modified 4/20/01
French Version, Color [PDF – 44 KB] Modified 4/20/01
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 186 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 401 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Length-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Girls Head circumference-for-age and Weight-for-length
B&W [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 55 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 60 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 55 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 206 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 440 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Head circumference-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-length charts
Children 2 to 20 years (5th-95th percentile)
Boys Stature-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 77 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Color [PDF – 77 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 63 KB] Modified 11/21/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 78 KB] Modified 11/21/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 208 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 260 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Stature-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Boys BMI-for-age
B&W [PDF – 61 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 61 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 50 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 64 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 141 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 183 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of BMI-for-age charts
Girls Stature-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 77 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Color [PDF – 77 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 62 KB] Modified 11/21/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 79 KB] Modified 11/21/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 208 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 499 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Stature-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Girls BMI-for-age
B&W [PDF – 67 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 61 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 51 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 64 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 142 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 339 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of BMI-for-age charts
Optional Chart (5th-95th percentile)
Boys Weight-for-stature
B&W [PDF – 40 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 41 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 148 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 180 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Weight-for-stature charts
Girls Weight-for-stature
B&W [PDF – 40 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 41 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 147 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 334 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Weight-for-stature charts
Set 2: Clinical charts with 3rd and 97th percentiles
Birth to 36 months (3rd -97th percentile)
Boys Length-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 41 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Color [PDF – 47 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 47 KB] Modified 4/20/01
French Version, Color [PDF – 44 KB] Modified 4/20/01
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 186 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 201 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Length-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Boys Head circumference-for-age and Weight-for-length
B&W [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 52 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 53 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 51 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 207 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 223 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Head circumference-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-length charts
Girls Length-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 41 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Color [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 4/20/01
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 4/20/01
French Version, Color [PDF – 45 KB] Modified 4/20/01
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 186 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 390 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Length-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Girls Head circumference-for-age and Weight-for-length
B&W [PDF – 48 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 53 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 54 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 52 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 206 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 434 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Head circumference-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-length charts
Children 2 to 20 years (3rd-97th percentile)
Boys Stature-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 79 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Color [PDF – 83 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 61 KB] Modified 11/21/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 79 KB] Modified 11/21/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 208 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-ready [PDF – 250 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Stature-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Boys BMI-for-age
B&W [PDF – 64 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 68 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 52 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 66 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 153 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 173 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of BMI-for-age charts
Girls Stature-for-age and Weight-for-age
B&W [PDF – 79 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Color [PDF – 84 KB] Modified 11/21/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 62 KB] Modified 11/21/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 81 KB] Modified 11/21/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 218 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 488 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Stature-for-age charts
Data table of Weight-for-age charts
Girls BMI-for-age
B&W [PDF – 54 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 58 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Spanish Version, Color [PDF – 52 KB] Modified 10/16/00
French Version, Color [PDF – 67 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 152 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 334 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of BMI-for-age charts
Optional Chart (3rd-97th percentile)
Boys Weight-for-stature
B&W [PDF – 31 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 34 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 158 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 168 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Weight-for-stature charts
Girls Weight-for-stature
B&W [PDF – 40 KB] Modified 10/16/00
Color [PDF – 46 KB] Modified 10/16/00
B&W Press-Ready [PDF – 157 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Color Press-Ready [PDF – 323 KB] Modified 9/15/05
Data table of Weight-for-stature charts
Summary files
Set 1 summary file; 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, 95th percentiles
Download all 10 charts in Set 1
B&W [PDF – 409K]
Color [PDF – 418 KB]
Set 2 summary file; 3rd, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, 97th percentiles
Download all 10 charts in Set 2
B&W [PDF – 408K]
Color [PDF – 423 KB]
Growth Charts - Background
Introduction
The growth charts consist of a series of percentile curves that illustrate the distribution of selected body measurements in U.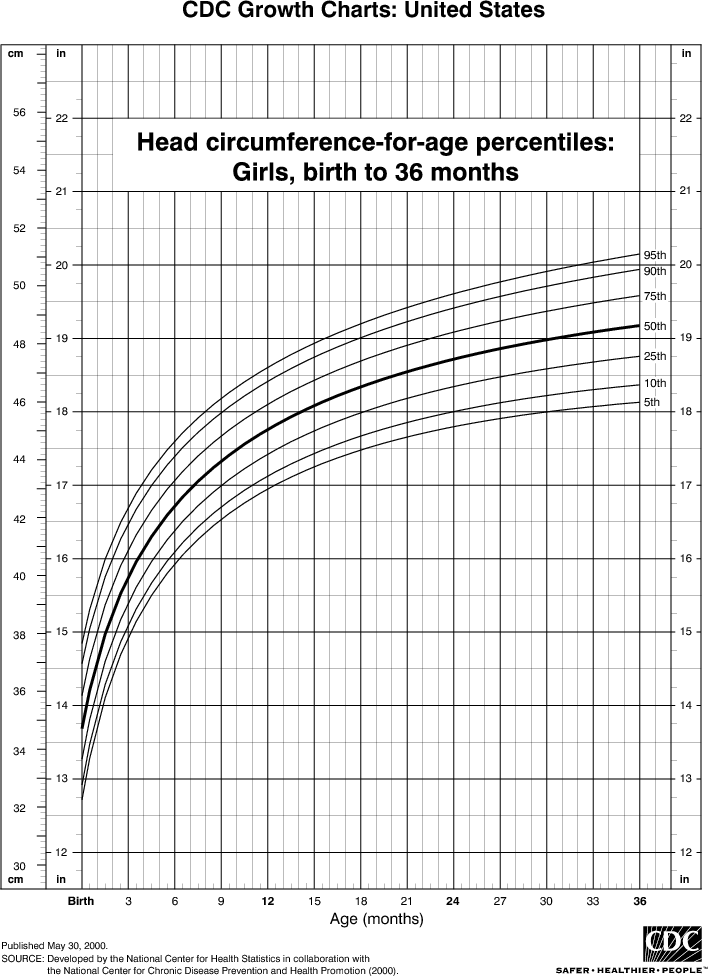 S. children. Pediatric growth charts have been used by pediatricians, nurses, and parents to track the growth of infants, children, and adolescents in the United States since 1977. The 1977 growth charts were developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) as a clinical tool for health professionals to determine if the growth of a child is adequate. The 1977 charts were also adopted by the World Health Organization for international use.
S. children. Pediatric growth charts have been used by pediatricians, nurses, and parents to track the growth of infants, children, and adolescents in the United States since 1977. The 1977 growth charts were developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) as a clinical tool for health professionals to determine if the growth of a child is adequate. The 1977 charts were also adopted by the World Health Organization for international use.
When the 1977 NCHS growth charts were first developed, NCHS recommended that they be revised periodically as necessary. With more recent and comprehensive national data now available, along with improved statistical procedures, the 1977 growth charts were revised and updated to make them a more valuable clinical tool for health professionals. The 2000 CDC growth charts represent the revised version of the 1977 NCHS growth charts. Most of the data used to construct these charts come from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which has periodically collected height and weight and other health information on the American population since the early 1960’s.
Growth charts are not intended to be used as a sole diagnostic instrument. Instead, growth charts are tools that contribute to forming an overall clinical impression for the child being measured. The revised growth charts provide an improved tool for evaluating the growth of children in clinical and research settings.
The 2000 CDC Growth Charts and the New BMI-For-Age Charts
The revised growth charts consist of 16 charts (8 for boys and 8 for girls). These charts represent revisions to the 14 previous charts, as well as the introduction of two new body mass index-for-age (BMI-for-age) charts for boys and for girls, ages 2 to 20 years.
Most of the specific differences between the revised charts and the original charts occur in the charts for infants, where national data were previously lacking. The revised head circumference charts also show some noticeable differences when compared to the earlier charts. Compared to the original infant charts that were based on primarily formula-fed infants, the revised growth charts for infants contain a better mix of both breast- and formula-fed infants in the U.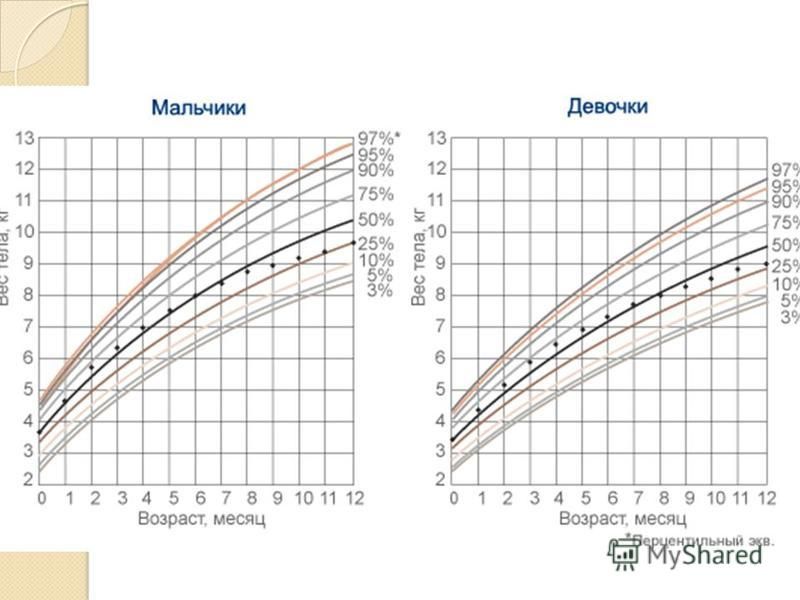 S. population. (On average, since 1970 approximately one-half of children born in the United States are reported to have been breast fed at some point, and about one-third have been breast fed for 3 months or more.) The addition of the BMI charts is probably the single most significant new feature of the revised growth charts.
S. population. (On average, since 1970 approximately one-half of children born in the United States are reported to have been breast fed at some point, and about one-third have been breast fed for 3 months or more.) The addition of the BMI charts is probably the single most significant new feature of the revised growth charts.
These BMI-for-age charts were created for use in place of the 1977 weight-for-stature charts. BMI (wt/ht2) is calculated from weight and height measurements and is used to judge whether an individual’s weight is appropriate for their height. BMI is the most commonly used approach to determine if adults are overweight or obese and is also the recommended measure to determine if children are overweight. The new BMI growth charts can be used clinically beginning at 2 years of age, when an accurate stature can be obtained.
In recent years, BMI has received increased attention for pediatric use. In 1994, an expert committee charged with developing guidelines for overweight in adolescent preventive services (ages 11-21 years) recommended that BMI be used routinely to screen for overweight adolescents. In addition, in 1997 an expert committee on the assessment and treatment of childhood obesity concluded that BMI should be used to screen for overweight children, ages 2 years and older, using the BMI curves from the revised growth charts. BMI can also be used to characterize underweight (though no expert guidelines exist for the classification of underweight based on BMI).
In addition, in 1997 an expert committee on the assessment and treatment of childhood obesity concluded that BMI should be used to screen for overweight children, ages 2 years and older, using the BMI curves from the revised growth charts. BMI can also be used to characterize underweight (though no expert guidelines exist for the classification of underweight based on BMI).
Methods and Development
For more information about the methods and development of the CDC Growth Charts, please see the 2000 CDC Growth Charts for the United States: Methods and Development [PDF – 5M] report.
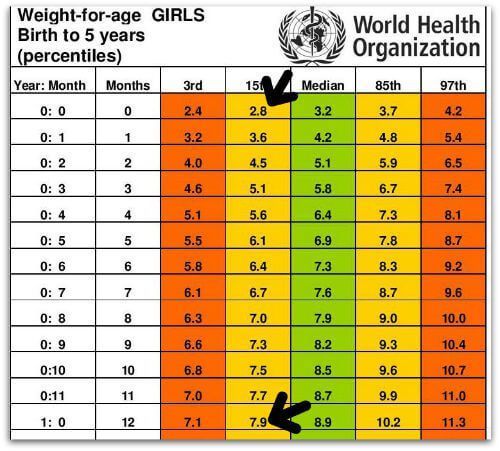
Tables of weight and height of the child by months and by years. For boys and for girls.
The height and weight of a child are the main indicators of his physical development. That is why immediately after the birth of the baby, it is imperative to measure the weight of his body and the length of the body and continue to weigh himself daily at the same time until discharge from the hospital.
There are many factors that affect the physical development of a child, for example:0010
How to understand what is the norm? nine0004
The All-Russian Health Organization recommended special tables for matching the height and weight of children, or as they are called, centile tables. At each examination, the pediatrician measures the height and weight of the child, compares the obtained values \u200b\u200bwith the standard indicators. Such tables allow you to identify obvious pathologies, for a more accurate analysis, the doctor calculates additional indicators using special formulas.
Monthly infant weight and height chart (up to 1 year)
The table shows the average height and weight of infants (under 1 year of age) by month for boys and girls.
| Age | Girls | Boys | ||||||
| , kg | 9000 9000, KG, KG | 9000 9000, KG, KG 9000 9000, KG, KG 9,000|||||||
| Newborns | 3.33 ± 0.44 | 49.50 ± 1.63 | 3.53 ± 0.45 | 50.43 ± 1.89 | 1 month | 4.15 ± 0.54 | 53.51 ± 2.13 | 4.32 ± 0.64 | 54.53 ± 2.32 |
| 2 months | 5.01 ± 0.56 | 56.95 ± 2.18 | 5 .29 ± 0.76 | 57.71 ± 2.48 | ||||
| 3 months | 6.07 ± 0.58 | 60.29 ± 2.08 903 nine0038 | 61.30 ± 2.41 | |||||
| 4 months | 6. 55 ± 0.79 55 ± 0.79 | 62.15 ± 2.49 | 6.87 ± 0.74 | 63.79 ± 2.68 | ||||
| 9000 3 months | 7.38 ± 0.96 | 63.98 ± 2.49 | 7.82 ± 0.80 | 66.92 ± 1.99 | ||||
| 6 months | 7.97 ± 0.92 | 66.60 ± 2.44 | 8.77 ± 0.78 | 67.995 ± 2.24 80049 7 months | 8.25 ± 0.95 | 67.44 ± 2.64 | 8.92 ± 1.11 | 69.56 ± 2.61 |
| 9000 3 months 9000 | 8.35 ± 1.10 | 69.84 ± 2.07 | 9.46 ± 0.98 | 71.17 ± 2.24 | ||||
| 9000 9 months | 9.28 ± 1 .01 | 70.69 ± 2.21 | 9.89 ± 1.18 | 72.84 ± 2.71 | ||||
| 10 months | 9.52 ± 1.3572.11 ± 2.86 | 10.35 ± 1.12 | 73.91 ± 2.65 | |||||
| 11 months | 9.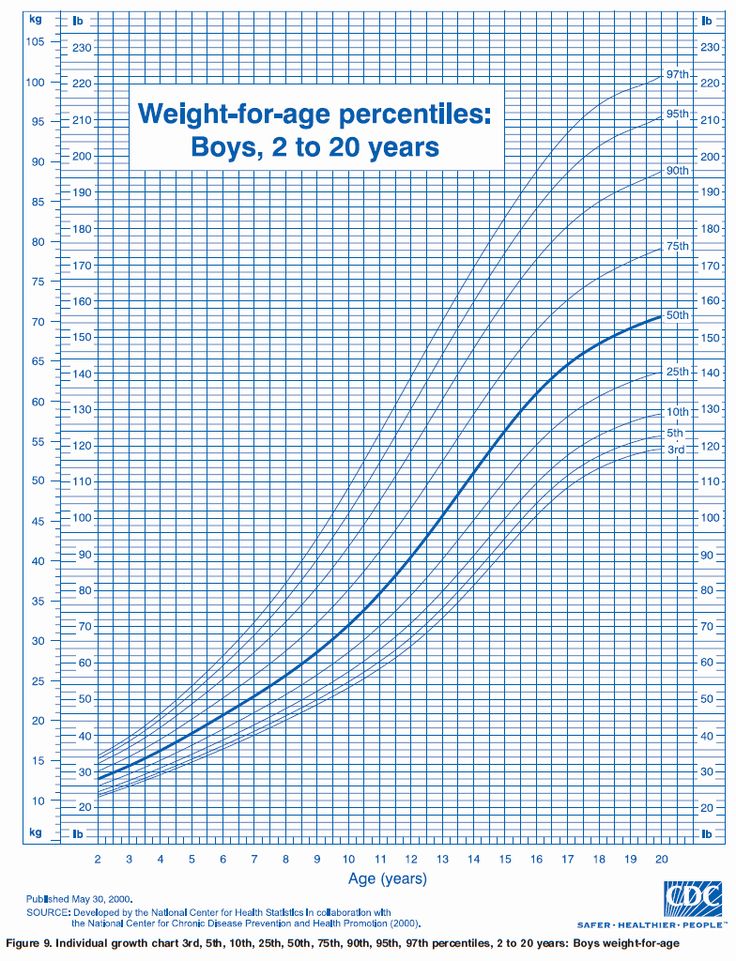 80 ± 0, 0, 80 80 ± 0, 0, 80 | 73.60 ± 2.73 | 10.47 ± 0.98 | 74.90 ± 2.55 | ||||
| 10.0.04 ± 1.16 | 74.78 ± 2.54 | 10.66 ± 1.21 | 75.78 ± 2.79 | |||||
Table of weight and height of the child by years (from 1 to 18 years)
weight of the child by years aged 1 to 18 years for boys and girls. nine0005
| Age | Girls | Boys | |||||
| , kg | 9000 9000, KG, KG | 9000 9000, KG, KG 9000 9000, KG, KG||||||
| 1 year 3 months | 10.52 ± 1.27 | 76.97 ± 3.00 | 11.40 ± 1.30 | 79.45 ± 3.56 | |||
| 1 year 6 months | 11.40 ± 1.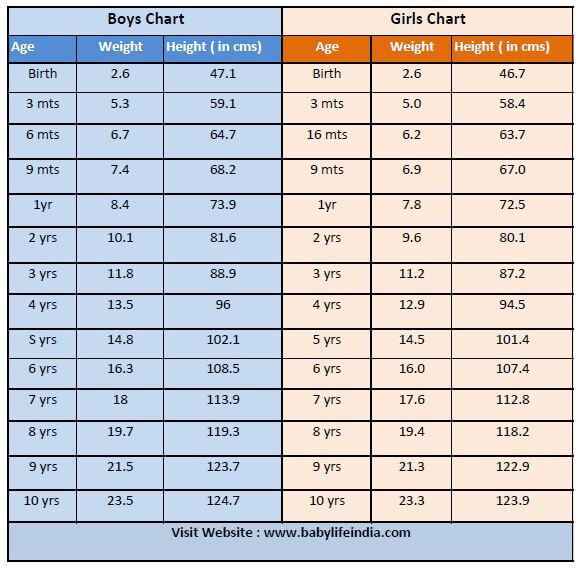 12 12 | 80.80 ± 2.98 | 11.80 ± 1.18 | 81.73 ± 3.34 | |||
| 9000. 1 year | 12.27 ± 1.37 | 83.75 ± 3.57 | 12.67 ± 1.41 | 84.51 ± 2.85 | |||
| 12.6.63 ± 1.76 | 86.13 ± 3.87 | 13.04 ± 1.23 | 88.27 ± 3.70 | ||||
| 2 years 6 months | 13.93 ± 1.60 | 91.20 ± 4,28 | 13.96 ± 1.27 | 81.85 ± 3.78 | |||
| 3 years old | 14.85 ± 1.53 | 97.27 ± 3 , 78 | 14.95 ± 1.68 | 95.72 ± 3.68 | |||
| 4 years | 16.02 ± 2.30 | 100.56 ± 5.76 | 17, 14 ± 2.18 | 102.44 ± 4.74 | |||
| 5 years | 18.48 ± 2.44 | 109.00 ± 4.72 038 | 110.40 ± 5.14 | | ||||
| 6 years | 21.34 ± 3.14 | 115.70 ± 4. 32 32 | 21.20 | 115.98 ± 5.51 | |||
| 7 years old | 24.66 ± 4.08 | 123.60 ± 5.50 | 24.92 ± 4.44 | 123.88 ± 5.40 | |||
| 8 years | 27.48 ± 4.92 | 129.00 ± 5.48 | 27.86 ± 4.72 | 129.94 ± 5.70 | 0049 9 years old31.02 ± 5,92 | 136.96 ± 6.10 | 30.60 ± 5.86 | 9004.64 ± 6.12
| 10 years 10 years old | 888888888834.32 ± 6.40 | 140.30 ± 6.30 | 33.76 ± 5.26 | 140.33 ± 5.60 | |||
| years 11 years | 37.40 ± 7 06 | 144.58 ± 7.08 | 35.44 ± 6.64 | 143.38 ± 5.72 | |||
| 12 years 9004 038 | 152.81 ± 7.01 | 41.25 ± 7.40 | 150.05 ± 6.40 | ||||
| 48.70 ± 9.16 | 156.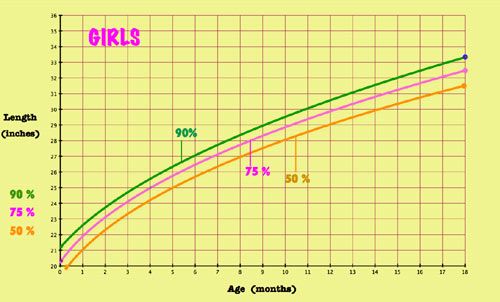 85 ± 6.20 85 ± 6.20 | 45.85 ± 8.26 | 156.65 ± 8.00 | ||||
| 14 years old | 51.32 ± 7.30 | 160.86 ± 6.36 | 51 , 18 ± 7.34 | 162.62 ± 7.34 | |||
| 15 years old | 56.65 ± 9.85 | 161.80 ± 7.40 | 56.50 ± 13.50 ± 13.50 nine0038 | 168.10 ± 9.50 | |||
| 16 years old | 58.00 ± 9.60 | 162.70 ± 7.50 | 62.40 ± 14.10 | 172.60 ± 9.40 | |||
| 17 years old | 58.60 ± 9.40 | 163.10 ± 7.30 | 67.35 ± 12.75 | 176.30 | |||
Deviations of weight or height from tabular values
There is no need to panic if there is a minimal discrepancy with the indicated values in the table, and here's why:
- First of all, the child's height and weight charts contain reference indicators , what should ideally be the weight and height of the child, without taking into account many other factors .
 Sometimes parents of premature babies mistakenly use a standard table for comparison, while there are special tables for assessing the development of children born prematurely.
Sometimes parents of premature babies mistakenly use a standard table for comparison, while there are special tables for assessing the development of children born prematurely. - The rate of growth and weight gain for each child is unique . In the first year of life, babies develop in leaps and bounds. For example, during the period of introducing complementary foods, the weight of the baby may not reach the “norm” due to adaptation to a new type of food, and not because of pathology. nine0010
This does not mean that deviations from the norm should be ignored , but it is better to regard them as an occasion to pay attention and consult a specialist in order to identify possible health problems, or to make sure that they are not present.
What can cause obvious deviations from the norm?
Earlier we talked about minor deviations from the norm and that there is no need to be scared if your child is not growing and gaining weight strictly according to the chart.![]() But what to do if the values of the essential have gone beyond the limits of the permissible parameters , or are they at the intersection of norm and pathology?
But what to do if the values of the essential have gone beyond the limits of the permissible parameters , or are they at the intersection of norm and pathology?
Reasons for possible deviations can be divided into two groups:
1. Non-endocrine:
- Constitutional growth retardation . Or in another way, the syndrome of late puberty. One of the variants of the norm, when the puberty jump occurs later than in other children.
- Family stunting . It has a hereditary predisposition, in the family of such children there are relatives with short stature. Growth retardation manifests itself from early childhood. nine0010
- Prematurity, intrauterine and postnatal injuries.
- Genetic syndromes . As a rule, they have many clinical manifestations, one of which is growth retardation.
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular, bronchopulmonary systems, gastrointestinal tract, as well as anemia.

- Fasting .
- Taking certain medications .
2. Endocrine:
- Growth hormone deficiency . Biologically active substance, which is the main regulator of the growth process after 2 years.
- Deficiency of thyroid hormones . More often of a congenital nature, it is clinically characterized by a delay in physical and intellectual development from birth.
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus . A disease in which, due to insulin deficiency, the flow of glucose into the cells of the body is impaired, the so-called. "starvation" of cells, as a result, growth rates slow down. nine0010
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease (or syndrome) . At the same time, the production of hormones of the adrenal cortex, glucocorticoids, is increased, which in large doses leads to a violation of the secretion of growth hormone.
- Rickets .
 A lack of vitamin D leads to bone destruction and skeletal deformities, which in turn is manifested, among other things, by a decrease in growth.
A lack of vitamin D leads to bone destruction and skeletal deformities, which in turn is manifested, among other things, by a decrease in growth. - Other rare disorders of the endocrine system.
As you can see, there are a lot of reasons.
If the child's growth is stunted, parents should consult a doctor to identify the causes of short stature and correct it in a timely manner.
Which specialist should I contact? First, you should make an appointment with a pediatrician. Also, in most cases, consultation with a pediatric endocrinologist is required.
Remember that for the normal growth of the child you need a complete, balanced diet with enough vitamins and minerals, as well as dosed physical activity. nine0004
Height and weight gain for children in their first year of life. Tables
Dear parents, your baby is growing and you are worried about whether he is gaining enough weight and height. For control, there are centile tables for assessing the physical development of children, weight and height indicators. At the same time, you must remember that each baby is individual, he cannot grow according to the textbook. These weight and height recommendations are based on an average number of children and 10% deviation is normal. In addition, the centile corridor from 25% to 75% is an average physical indicator. That is why they say: Physical development is mesosomatic, macrosomatic, microsomatic. nine0005
For control, there are centile tables for assessing the physical development of children, weight and height indicators. At the same time, you must remember that each baby is individual, he cannot grow according to the textbook. These weight and height recommendations are based on an average number of children and 10% deviation is normal. In addition, the centile corridor from 25% to 75% is an average physical indicator. That is why they say: Physical development is mesosomatic, macrosomatic, microsomatic. nine0005
It is important that the weight and height indicators are in the same centile corridor, but no more than two adjacent ones. Then we can talk about harmonious development. If the gap is more than two centile corridors, the development is disharmonious. Then we can think either about an unbalanced diet or about a pathology associated with obesity (paratrophy), or protein-energy deficiency (hypotrophy). In addition, one should not forget about the constitutional characteristics of the child, about genetic predisposition. Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7.8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions. nine0005
Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7.8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions. nine0005
We'll talk about weight and height gain for term babies. In preterm infants, rates of weight gain and height differ according to the degree of prematurity. In addition, children can be born with intrauterine malnutrition.
The tables for girls and boys are different in terms of numerical indicators, but at 1 year of age, these differences are quite minimal.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of girls from 0 to 12 months. nine0005
nine0005
| Body length (height), cm. Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg. Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | nine0002 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 nine0005 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| nine0002 45.8 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 50.7 | 52.0 | 53.1 | 53.9 nine0038 | 0 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3. | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| 48.5 | 50.3 | 52.1 | 53.5 | 55.0 | nine0049 57.3 | 1 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.2 nine0005 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 5.1 | |
| 51.2 | 53.3 | 55.2 | nine0049 58.0 | 59.3 | 60.6 | 2 | 3.8 | 4.2 nine0005 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5. | |
| 54.0 | 56.2 | 57.6 | 59.3 | 67.7 | 61.8 | 63.6 | 3 nine0005 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 | nine0002 6.7 |
| 56.7 | 58.4 | 60.0 | 61.2 | 62.8 | 64.0 nine0005 | 65.7 | four | 5.0 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.2 | nine0002 6.6 | 7.0 | 7.5 |
| 59.1 | 60.8 | 62. | 63.8 nine0005 | 65.1 | 66.0 | 68.0 | five | 5.5 | 5.9 | nine0002 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.1 |
| 60.8 | 62.5 nine0005 | 64.1 | 65.5 | 67.1 | 68.8 | 70.0 | 6 | nine0002 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.7 nine0038 |
| 62.7 | 64.1 | 65.9 | 67.5 | 69.2 | 70. | nine0002 71.9 | 7 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.4 | nine0049 9.3 | |
| 64.5 | 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.5 nine0005 | 72.5 | 73.7 | 8 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.6 | nine0002 8.2 | 8.8 | 9.3 | 9.7 |
| 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.1 nine0005 | 70.2 | 72.0 | 74.1 | 75.5 | nine | 7. | nine0002 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.1 |
| 67.5 nine0005 | 69.0 | 70.3 | 71.9 | 73.2 | 75.3 | 76.8 | nine0002 10 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.1 nine0038 | 10.5 |
| 68.9 | 70.1 | 71.5 | 73.0 | 74.7 | nine0002 76.5 | 78.1 | eleven | 7.7 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 9. | 9.9 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| 70.1 | 71.4 | 72.8 | nine0002 74.1 | 75.8 | 78.0 | 79.6 | 12 | 8.0 | 8.5 nine0038 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 11.3 |
At the same time, until the age of three months, the child adds 20-30 grams per day daily, respectively, from 140 to 200 per week. If we talk about the average weight gain by months, then it is only 600 g per month, since the child after birth has physiological weight loss (with urine, feces, transition from intrauterine feeding to breastfeeding during the adaptation period), approximately 10% of the weight, which is 200-300 grams. nine0005
nine0005
More often, by 3-4 days, the child restores its original weight, and then there is an increase. But I had a case in practice when the child began to gain weight from the 20th day of life, while the girl was active, reflexes were alive, her appetite was good, she could withstand the night interval, stool 4-5 times a day, urination was sufficient, developed according to age. Therefore, do not worry. Our indicator is the well-being of the child. If the baby is active, eats with appetite, sleep is calm, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed, be calm, your baby is healthy and not hungry. You see from the table the range of weight per year is from 8 to 13 kg. This is the norm. There is no reason to run to the endocrinologist, genetics, to examine the child. nine0005
Or the opposite situation: in the first months of life, a child gains 1-1.5 kg while breastfeeding. If the baby does not have colic, he does not spit up, there are no gastrointestinal manifestations, he is active, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed - this is also the norm. Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them. nine0005
Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them. nine0005
| Month | Weight gain in grams |
| 1 | 600.0 |
| 2 | 800.0 nine0005 |
| 3 | 800.0 |
| four | 750.0 |
| five | 700.0 nine0038 |
| 6 | 650.0 |
| 7 | 600.0 |
| 8 | 550. | nine0047
| nine | 500.0 |
| 10 | 450.0 |
| eleven | 400.0 |
| 12 | 350.0 |
It is believed that by 4-4.5 months the child should double the weight, and triple by the end of the year.
It happens that the increase in height and weight goes in leaps, seasonality, unevenness, and sometimes asymmetry of growth are noted. Pediatricians are concerned about the circumference of the head and chest, by 2-3 months they should be equal. Further, the breast grows faster. This is important so as not to miss the pathology. nine0005
The younger the child, the faster his growth. In the first 3 months of life, body length increases by 3 cm monthly, in the second quarter by 2.5-2 cm monthly. In the third - 1.5-2 cm, in the fourth - 1 cm monthly.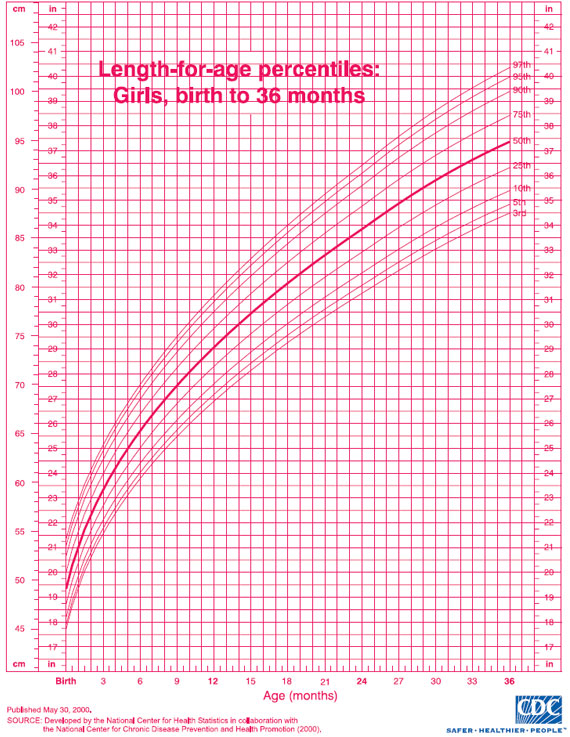 The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of boys from 0 to 12 months.
| Body length (height), cm. nine0005 Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | 10 | 25 nine0005 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 | 10 nine0038 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 46.5 | 48.0 nine0005 | 49.8 | 51.3 | 52.3 | 53. | 55.0 | 0 | nine0002 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.4 nine0038 |
| 49.5 | 51.2 | 52.7 | 54.5 | 55.6 | 56.5 | nine0002 57.3 | 1 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.7 | nine0049 5.4 | |
| 53.6 | 53.8 | 55.3 | 57.3 | 58.2 nine0005 | 59.4 | 60.9 | 2 | 3. | 4.2 | 4.6 | nine0002 5.1 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.4 |
| 55.3 | 56.5 | 58.1 nine0005 | 60.0 | 60.9 | 62.0 | 63.8 | 3 | 4.5 | nine0002 4.9 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 7.3 |
| 57.5 nine0038 | 58.7 | 60.6 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 64.5 | 66.3 | four nine0005 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6. | 7.2 | 7.6 | nine0002 8.1 |
| 59.9 | 61.1 | 62.3 | 64.3 | 65.6 | 67.0 nine0005 | 68.9 | five | 5.6 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.1 | nine0002 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.8 |
| 61.7 | 63.0 | 64.8 | 66.1 nine0005 | 67.7 | 69.0 | 71.2 | 6 | 6.1 | 6.6 | nine0002 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9. |
| 63.8 | 65.1 nine0005 | 66.3 | 68.0 | 69.8 | 71.1 | 73.5 | 7 | nine0002 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 9.9 nine0038 |
| 65.5 | 66.8 | 68.1 | 70.0 | 71.3 | 73.1 | nine0002 75.3 | 8 | 7.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.4 | nine0049 10.5 | |
| 67.3 | 68.2 | 69. | 71.3 | 73.2 nine0005 | 75.1 | 75.5 | nine | 7.5 | 7.9 | 8.4 | nine0002 9.1 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 |
| 68.8 | 69.1 | 71.2 nine0005 | 73.0 | 75.1 | 76.9 | 78.8 | 10 | 7.9 | nine0002 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.4 |
| 70.1 nine0005 | 71.3 | 72.6 | 74.3 | 76.2 | 78. | |||||||||
 3
3 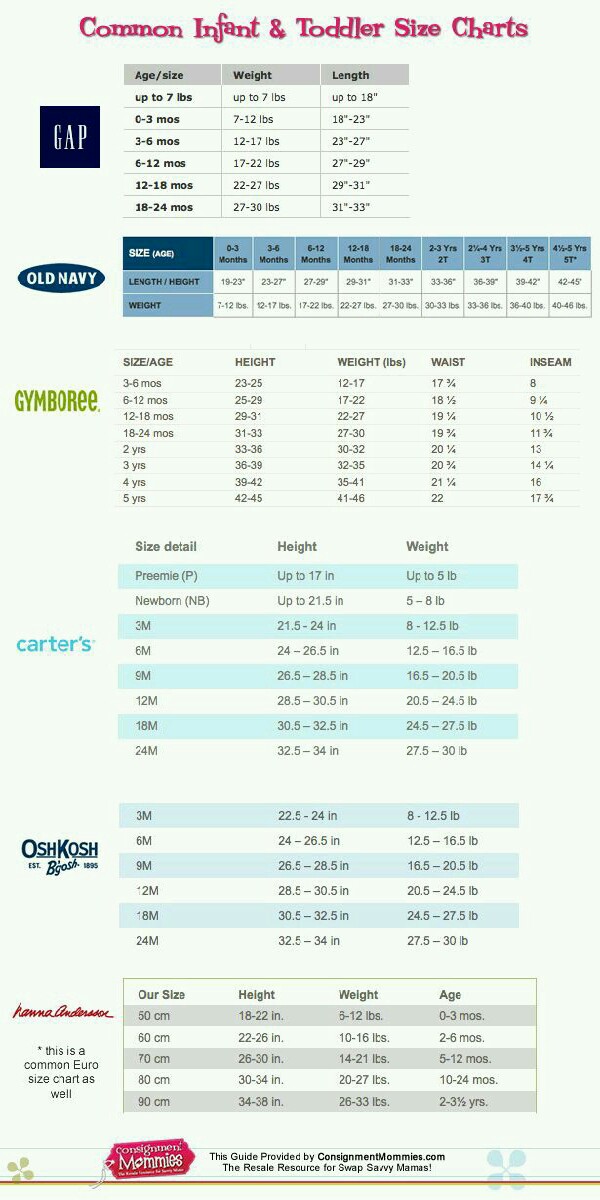 9
9 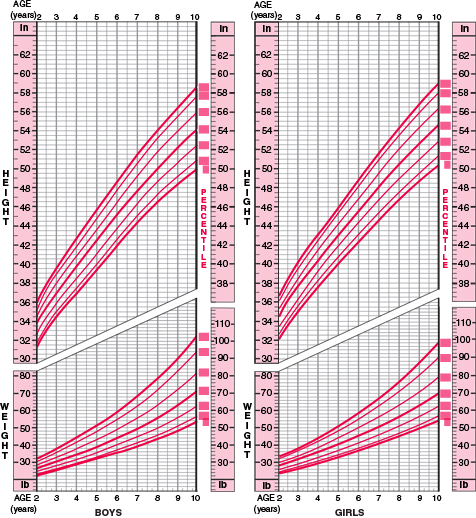 0
0  4
4 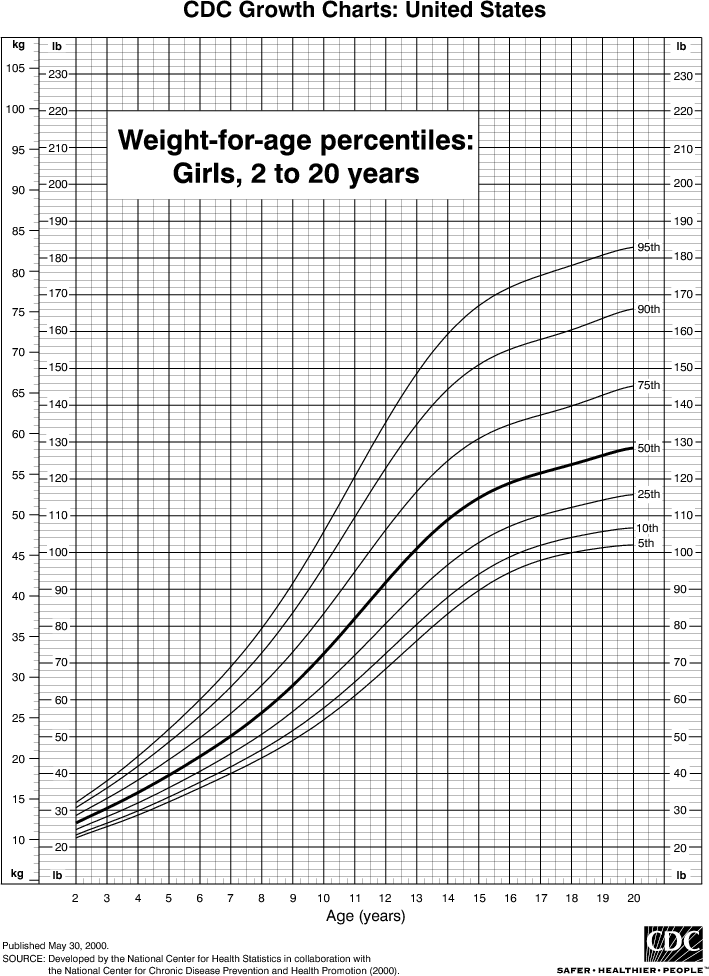 1
1  3
3 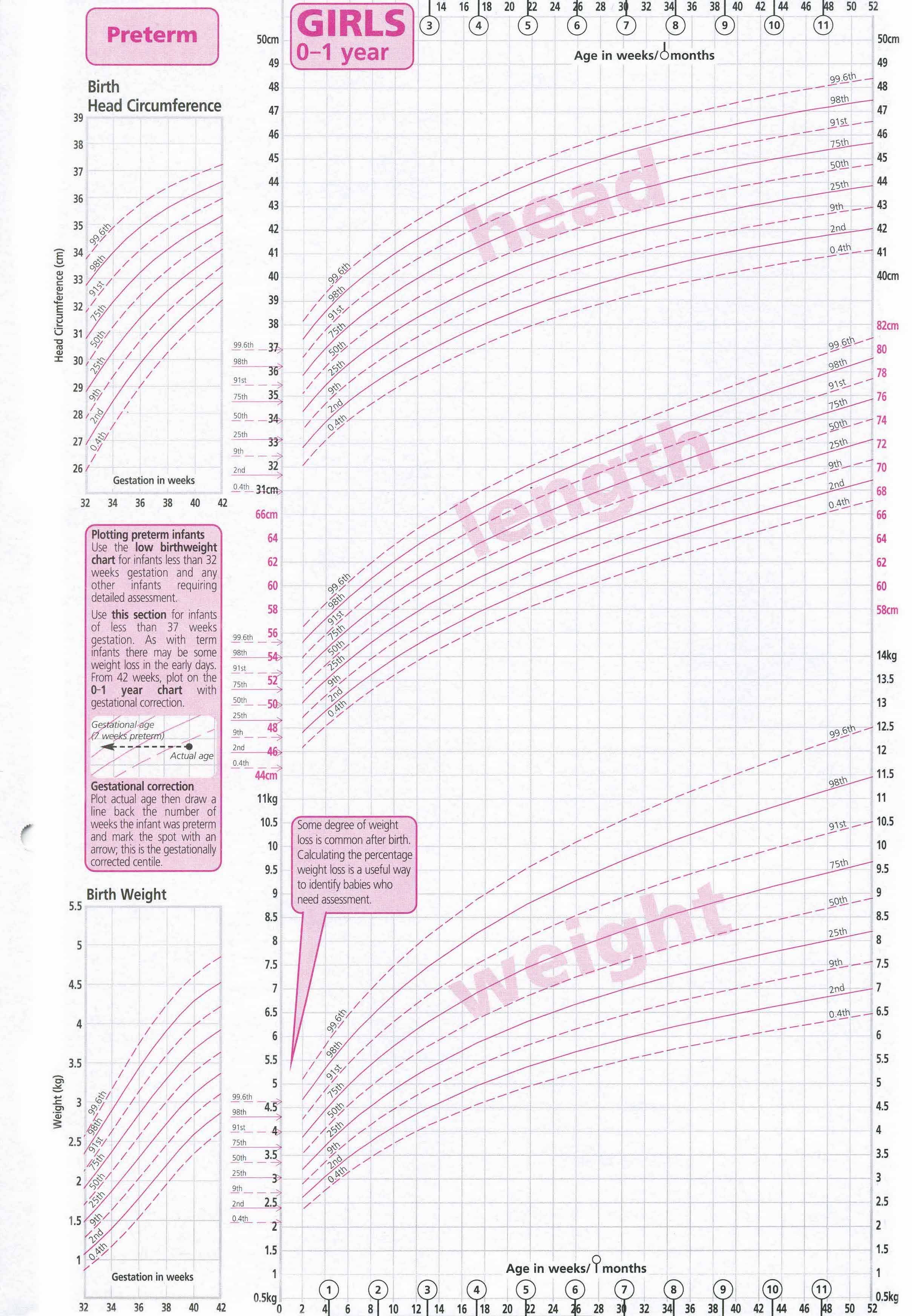 0
0  5
5 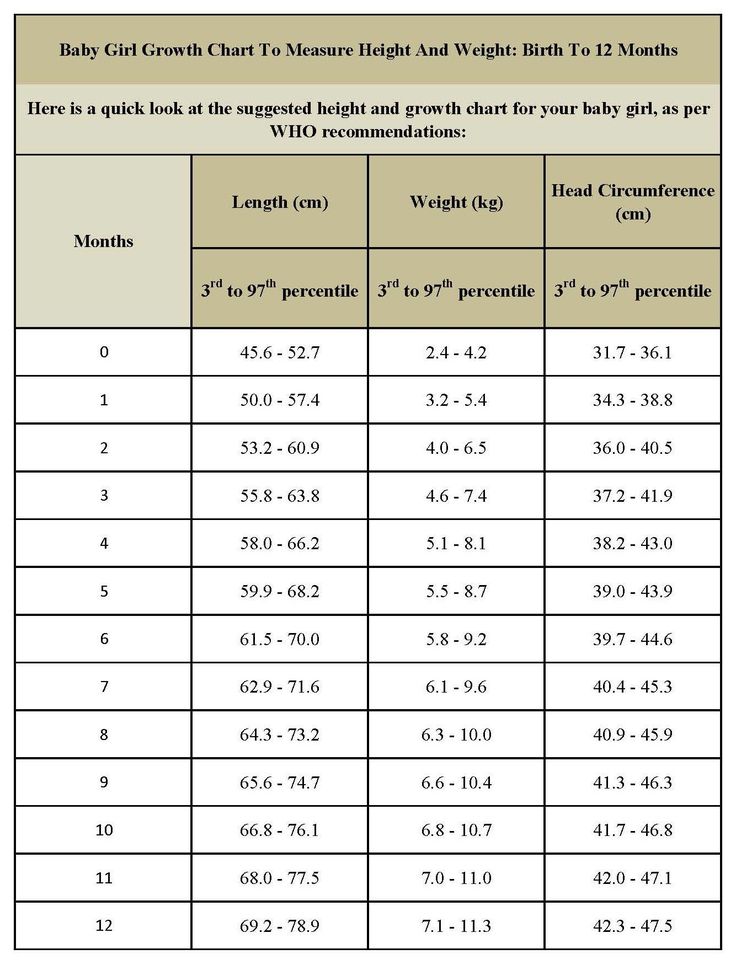 9
9 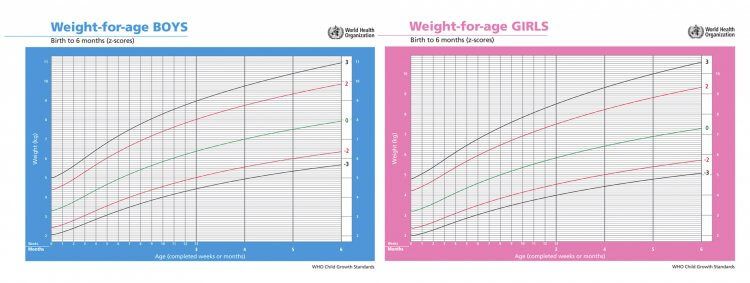 5
5 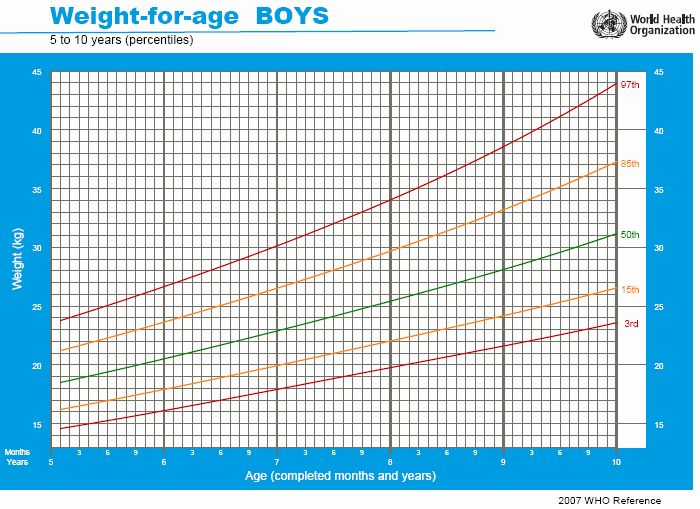 4
4 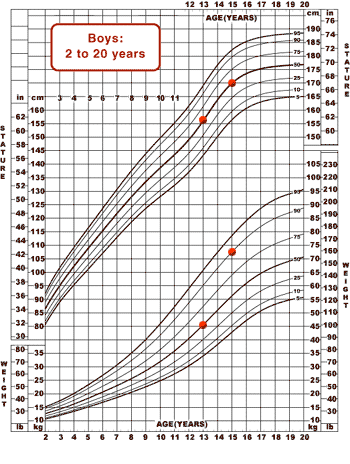 8
8