Flu like symptoms during pregnancy
Influenza (flu) and pregnancy | March of Dimes
It’s safe to get the flu shot. It protects you and your baby from serious health problems during and after pregnancy.
Pregnant women who get the flu are more likely than women who don’t get it to have problems, like preterm labor and premature birth.
If you think you have the flu, call your health care provider right away. Quick treatment can help prevent serious flu complications.
What is the flu?
Influenza (also called flu) is a virus that can cause serious illness. It’s more than just a runny nose and sore throat. The flu can make you very sick, and it can be especially harmful if you get it during or right after pregnancy.
How does the flu spread?
The flu spreads easily from person to person. When someone with the flu coughs, sneezes or speaks, the virus spreads through the air. You can get infected with the flu if you breathe it in or if you touch something (like a door handle or a phone) that has the flu virus on it and then touch your nose, eyes or mouth.
People with the flu may be able to infect others from 1 day before they get sick up to 5 to 7 days after. People who are very sick with the flu or young children may be able to spread the flu longer, especially if they still have symptoms.
How can the flu harm your pregnancy?
Health complications from the flu, like a lung infection called pneumonia, can be serious and even deadly, especially if you’re pregnant. If you get the flu during pregnancy, you’re more likely than other adults to have serious complications. It’s best to get a flu shot before you get pregnant. Getting a flu shot can help reduce your risk of getting the flu, having serious flu complications and needing treatment in a hospital.
Pregnant women who get the flu are more likely than women who don’t get it to have preterm labor (labor that happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy) and preterm birth (birth that happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Fever from the flu may be linked to birth defects, like neural tube defects, and other problems in your baby.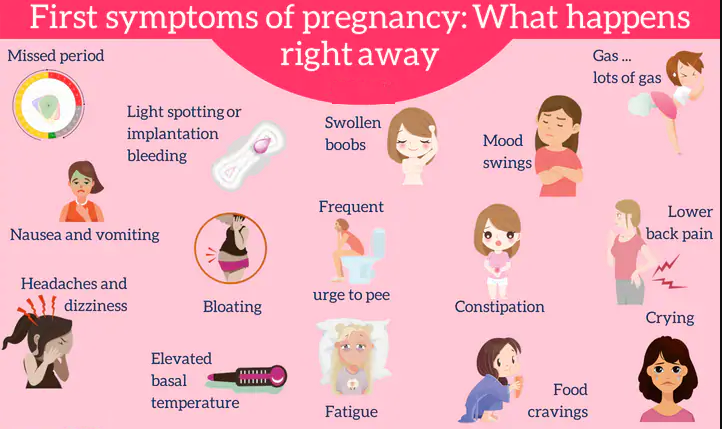 A birth defect is a health condition that is present at birth. Birth defects change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. They can cause problems in overall health, how the body develops, or in how the body works. Neural tube defects are birth defects of the brain and spinal cord.
A birth defect is a health condition that is present at birth. Birth defects change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. They can cause problems in overall health, how the body develops, or in how the body works. Neural tube defects are birth defects of the brain and spinal cord.
How does the flu shot help protect you from flu?
The flu shot contains a vaccine that helps prevent you from getting the flu. The flu shot can’t cause the flu. It’s safe to get a flu shot any time during pregnancy, but it’s best to get it before flu season (October through May). Even though you’re more likely to get the flu during flu season, you can get it any time of year.
There are many different flu viruses, and they’re always changing. Each year a new flu vaccine is made to protect against three or four flu viruses that are likely to make people sick during the upcoming flu season. Protection from a flu shot only lasts about a year, so it’s important to get a flu shot every year. You can get the shot from your health care provider, and many pharmacies and work places offer it each fall. Use the HealthMap Vaccine Finder to find out where you can get the flu vaccine.
You can get the shot from your health care provider, and many pharmacies and work places offer it each fall. Use the HealthMap Vaccine Finder to find out where you can get the flu vaccine.
Is it safe to get a flu shot during pregnancy?
It’s safe for most pregnant women to get the flu shot. Tell your health care provider if you have any severe allergies or if you’ve ever had a severe allergic reaction to a flu shot. Severe allergic reactions to flu shots are rare. If you’re worried about being allergic to the flu shot, talk to your provider to make sure it’s safe for you.
Some flu vaccines are made with eggs. Most women with egg allergies can get the flu shot. But if you have severe egg allergies, get the shot in a medical setting (like a doctor’s office, hospital or clinic) from a provider who knows how to treat severe allergies and allergic reactions.
Pregnant women should not get the flu nasal spray. This is a spray that’s put in your nose.
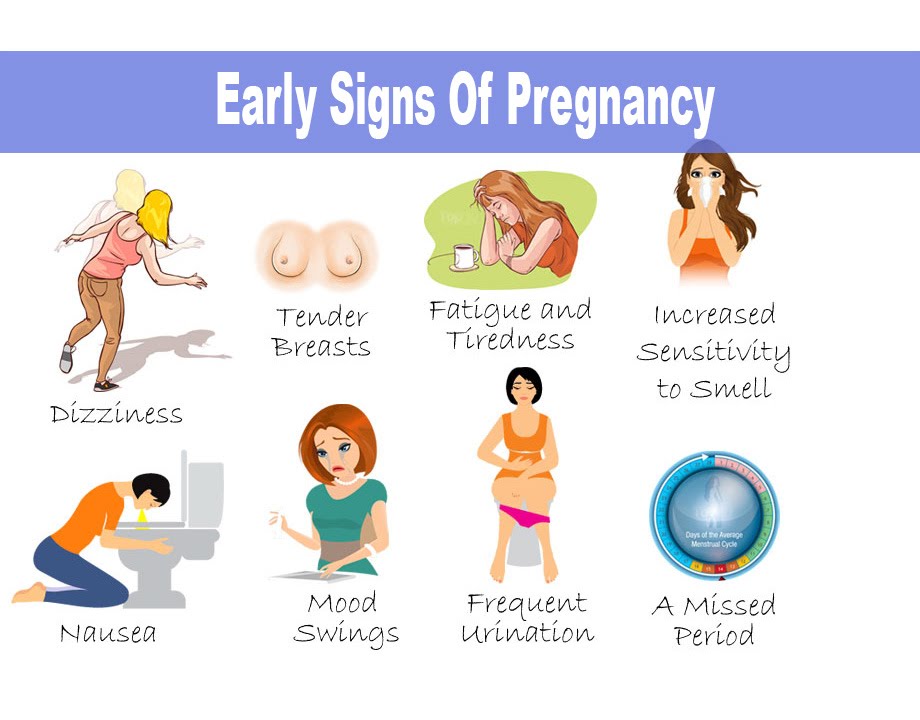
What are signs and symptoms of the flu?
Signs of a condition are things someone else can see or know about you, like you have a rash or you’re coughing. Symptoms are things you feel yourself that others can’t see, like having a sore throat or feeling dizzy. Common signs and symptoms of the flu include:
Symptoms are things you feel yourself that others can’t see, like having a sore throat or feeling dizzy. Common signs and symptoms of the flu include:
- Being very tired or sleepy (also called fatigue)
- Cough
- Fever (100 F or above), chills or body shakes. Not everyone who has the flu has a fever.
- Headache, or muscle or body aches
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Vomiting (throwing up) or diarrhea (more common in children)
The flu often comes on quickly. Fever and most other symptoms can last a week or longer. But some people can be sick from the flu for a long time, including children, people older than 65, pregnant women and women who have recently had a baby.
Call 911 and get medical care right away if you have any of these signs or symptoms:
- Feeling your baby move less or not at all
- High fever that doesn’t go down after taking acetaminophen (Tylenol®). Don’t take any medicine without checking with your provider first.

- Pain or pressure in the chest or belly
- Sudden dizziness or confusion
- Trouble breathing or shortness of breath
- Vomiting that’s severe or doesn’t stop
- Flu signs or symptoms that get better but then come back with fever and a worse cough
How is the flu treated during pregnancy?
If you think you have the flu even if you’ve been vaccinated, call your health care provider right away. Your provider may prescribe an antiviral medicine to help prevent or treat the flu. Antivirals kill infections caused by viruses. They can make your flu milder and help you feel better faster. Antivirals also can help prevent serious flu complications, like pneumonia. For flu, antivirals work best if you take them within 2 days of having symptoms. Quick treatment with antiviral medicine can help prevent serious flu complications.
If you’ve had close contact with someone who has the flu during your pregnancy or in the 2 weeks after giving birth, tell your health care provider.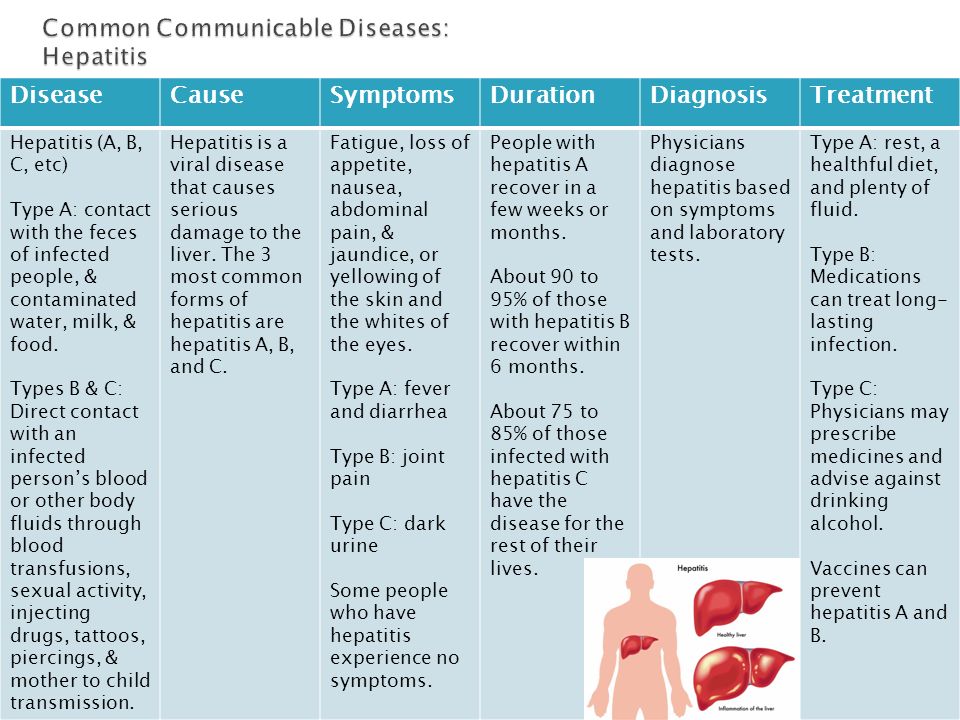 Even if you don’t have signs or symptoms of flu, your provider may want to treat you with an antiviral medicine to help prevent you from getting the flu and having serious complications.
Even if you don’t have signs or symptoms of flu, your provider may want to treat you with an antiviral medicine to help prevent you from getting the flu and having serious complications.
Three medicines are approved in the United States to prevent or treat the flu in pregnant women and women who recently had a baby. Talk to your provider about which one is right for you:
- Oseltamivir (brand name Tamiflu®).This medicine comes as a capsule or liquid.
- Zanamivir (brand name Relenza®). This medicine is a powder that you breathe in by mouth. It isn’t recommended for people with breathing problems, like asthma.
- Peramivir (Rapivab®). This medicine is given through a needle into a vein (also called IV) by a health care provider.
If you have a fever, call your provider as soon as possible. Before taking any over-the-counter medication, be sure to check with your provider first. Not all medication is safe to take during pregnancy. If you have the flu, get lots of rest and drink plenty of fluids. You may not want to eat much. Try eating small meals to help your body get better.
You may not want to eat much. Try eating small meals to help your body get better.
How can you stop the flu from spreading?
When you have the flu, you can spread it to others. Here’s what you can do to help prevent it from spreading:
- Stay home when you’re sick and limit contact with others.
- Cough or sneeze into a tissue or into your arm. Throw used tissues in the trash.
- Try not to touch your eyes, nose or mouth.
- Wash your hands with soap and water before touching anyone. You also can use alcohol-based hand sanitizers. Use enough hand sanitizer so that it takes at least 15 seconds for your hands to dry.
- Wash your dishes and utensils well with hot soapy water, or in a dishwasher if you have one.
- Don’t share your dishes, glasses, utensils or toothbrush.
Why is the flu so harmful during pregnancy?
The flu can be dangerous during pregnancy because pregnancy affects your immune system, heart and lungs.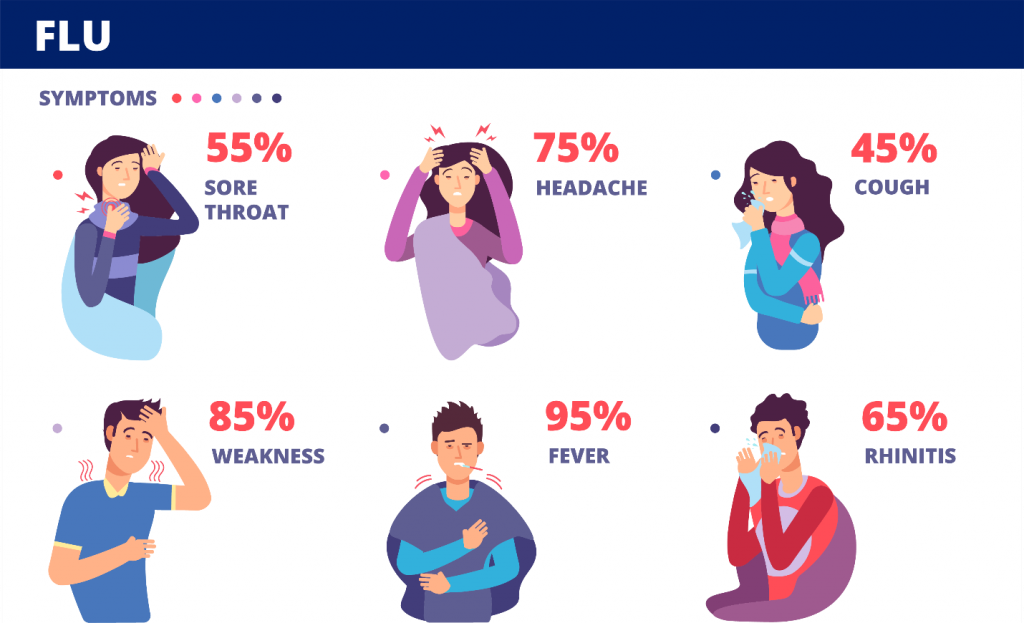 Your immune system is your body’s way of protecting itself from illnesses and diseases. When your body senses something like a virus that can harm your health, your immune system works hard to fight the virus.
Your immune system is your body’s way of protecting itself from illnesses and diseases. When your body senses something like a virus that can harm your health, your immune system works hard to fight the virus.
When you’re pregnant, your immune system isn’t as quick to respond to illnesses as it was before pregnancy. A lowered immune system means you’re more likely get sick with viruses like the flu.
During pregnancy, your lungs need more oxygen, especially in the second and third trimesters. Your growing belly puts pressure on your lungs, making them work harder in a smaller space. You may even find yourself feeling shortness of breath at times. Your heart is working hard, too. It’s busy supplying blood to you and your baby. All of this means your body is stressed during pregnancy. This stress on your body can make you more likely to get the flu. If you’re pregnant or had a baby within the last 2 weeks, you’re more likely than other women to have serious health problems from the flu.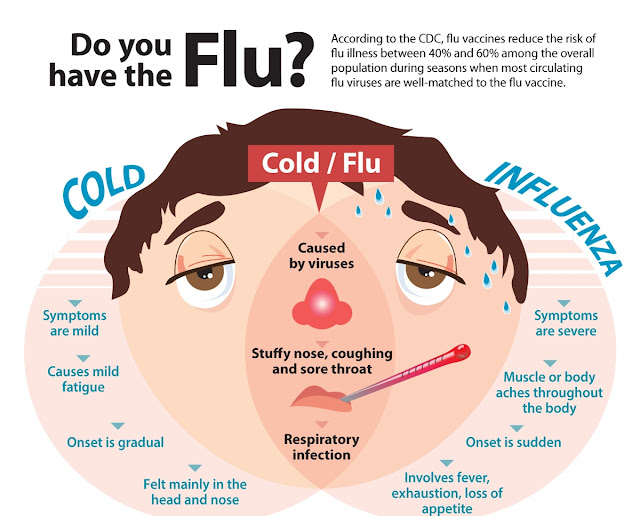
More information
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Flu & Pregnancy
Flu.gov
What is the Flu? Common Influenza Questions (familiesfightingflu.org)
Last reviewed: November, 2022
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms: 10 Unexpected Ones
Everyone knows the classic signs of pregnancy. You’ve missed your period. Your breasts are tender. And you’re tired all the time.
But pregnant women also experience a whole host of symptoms beyond these first signs. From mucus discharge to tasting metal to headaches, expect the unexpected.
Here’s a list of 10 weird early pregnancy symptoms no one tells you about.
While many women experience vaginal discharge, it’s not often associated with pregnancy. But most pregnant women will secrete sticky, white, or pale-yellow mucus early on in the first trimester and throughout their pregnancy.
Increased hormones and vaginal blood flow cause the discharge. It increases during pregnancy to prevent infections as your cervix and vaginal walls soften.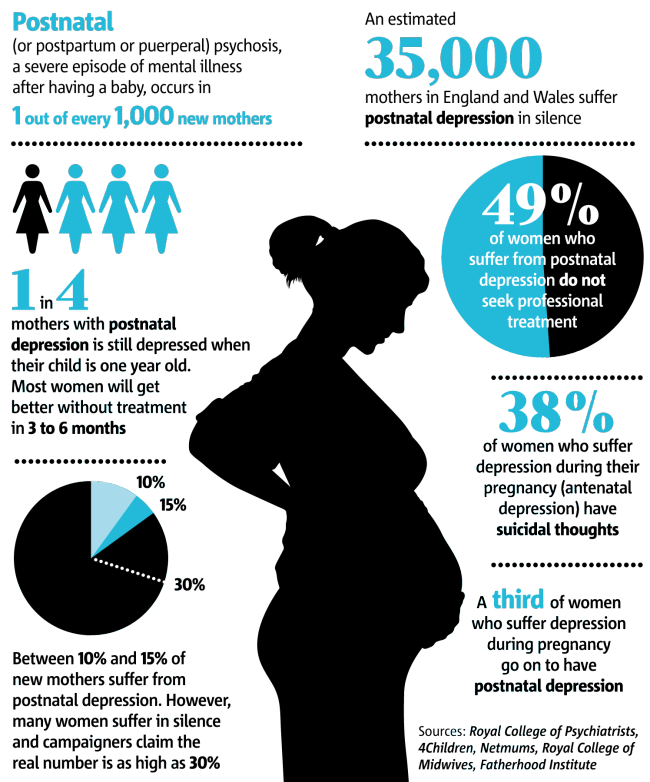 Visit your doctor if the discharge starts to:
Visit your doctor if the discharge starts to:
- smell
- burn
- itch
- turn greenish-yellow
- becomes very thick or watery
These may be signs of an infection.
Share on Pinterest
When you first wake up in the morning after ovulation, your body temperature is slightly elevated. It stays that way until you get your next period.
But if this temperature, known as basal body temperature, stays elevated for more than two weeks, you may be pregnant.
Share on Pinterest
It’s not uncommon for pregnant women to feel lightheaded or dizzy in the first trimester. Pregnancy causes blood pressure to drop and blood vessels to dilate.
But pay close attention to your symptoms. Severe dizziness coupled with vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Make sure to see a doctor right away to avoid life-threatening complications.
Share on Pinterest
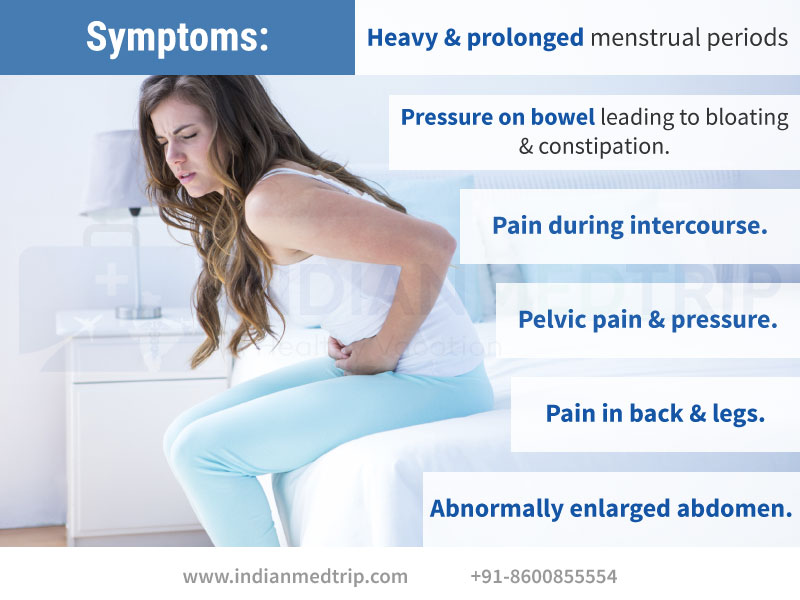
You may feel bloated, like you want to pass gas or go number two. But it’s just not happening. That’s because pregnancy’s hormonal changes can lead to constipation, as can prenatal vitamins.
Your digestive system slows down during pregnancy. This gives nutrients just enough extra time to absorb into your bloodstream and reach your little one.
If you can’t go, add more fiber into your diet, drink plenty of fluids, and exercise regularly. If needed, you can also check with your doctor about adding a pregnancy-safe stool softener.
Share on Pinterest
About 25 to 40 percent of pregnant women will lightly bleed or notice spotting early on in their pregnancy. The slight bleeding can happen when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. This is known as implantation bleeding. It’s common about two weeks after conception.
Bleeding can also be caused by cervical irritation, an ectopic pregnancy, or a threatened miscarriage. Make sure to get medical help right away if your light bleeding gets heavier or is accompanied by severe cramps, back pain, or stabbing pains.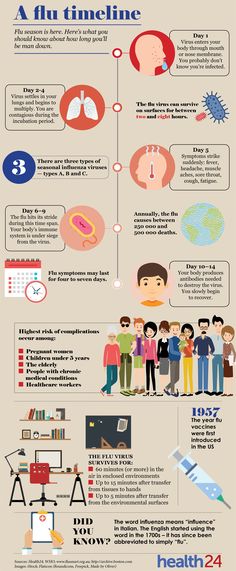
Share on Pinterest
Pregnancy lowers your immunity. This means you’re more prone to a cough, colds, and the flu. It’s not uncommon for pregnant women to experience cold- or flu-like symptoms early in pregnancy.
Talk to your doctor about pregnancy-safe treatment options. Pregnant women are more vulnerable to severe illnesses from the flu. This can lead to serious health problems for your baby.
Share on Pinterest
Hormones change everything during pregnancy. This includes the valve between your stomach and esophagus. This area becomes relaxed during pregnancy, which can cause stomach acid to leak into your esophagus, causing heartburn.
Fight back by eating smaller, more frequent meals. Also cut out fried grub. Try to avoid fizzy drinks, citrus fruits, juices, and spicy foods.
Share on Pinterest
Your hormones suddenly change when you become pregnant. This can throw your emotions out of whack. You’ll feel unusually weepy and emotional. Your libido goes from hot to cold then back to hot again.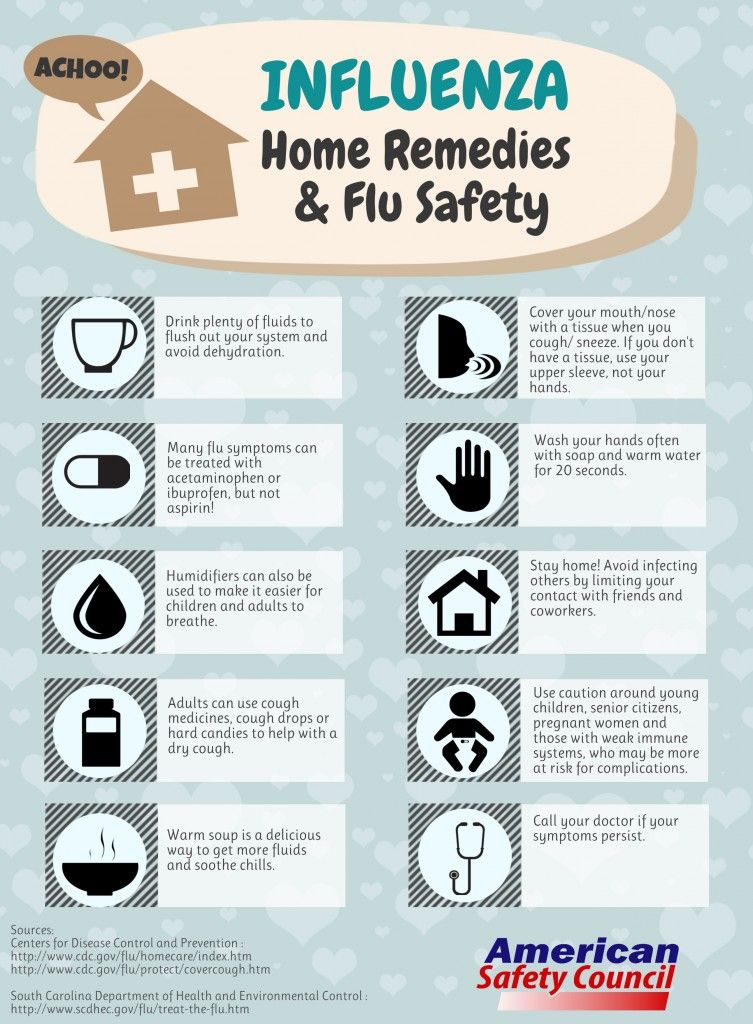 You might also experience mood swings. This is very common during early pregnancy.
You might also experience mood swings. This is very common during early pregnancy.
Share on Pinterest
Increases in estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy can lead to changes in taste for many pregnant women.
A condition called dysegusia has some pregnant women tasting metal. You’ll feel like you were chomping on some old pennies with your lunch. Get rid of the metallic flavor by munching on saltines and chewing sugarless gum. Also try drinking colder liquids or eating spicier foods.
Some of the symptoms listed above may make you think you’re just stressed and run down. But experienced together, they can point to pregnancy.
Pay attention to what your body is telling you. It might be time to see your doctor for a pregnancy test.
Influenza during pregnancy: symptoms
Pregnancy is a special condition for a woman, which is particularly vulnerable. Pregnancy lasts 9 months and during this time the expectant mother will have to deal with various viruses that can cause both a mild cold and severe illness. In the process of bearing a child, a woman's body works in an enhanced mode, so the immune system does not always manage to easily defeat a cold.
In the process of bearing a child, a woman's body works in an enhanced mode, so the immune system does not always manage to easily defeat a cold.
One of the most dangerous viral infections for a woman who is expecting a baby is the flu. It can have a negative effect on the placenta, amniotic fluid and the fetus itself. Influenza in the early stages of pregnancy can cause miscarriage, in the later stages - premature birth and malformations in the baby. Therefore, with severe cold symptoms, the expectant mother needs to be under the supervision of doctors. Medical monitoring of the health of a pregnant woman will reduce the risk of complications and termination of pregnancy. If the disease is severe, the woman is hospitalized in a hospital. nine0003
How can you tell influenza from other viral infections?
Influenza, like other SARS, is spread by airborne droplets. Once in the body, the virus begins to multiply very quickly. The main sign of this infection is a rapidly growing powerful intoxication of the body, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- severe weakness;
- pressing headache;
- redness and pain in the eyes;
- photophobia; nine0013 muscle aches;
- lacrimation;
- chills;
- sweating.

The onset of the disease is always acute, with a sharp rise in temperature, which can reach 40 degrees. The virus infects the respiratory tract, which is manifested by a runny nose, cough, difficulty breathing, dry mucous membranes, pain and sore throat.
The disease is more severe than ordinary ARVI and carries a greater risk of complications. The patient may develop pneumonia, otitis, sinusitis, myocarditis. In addition to the threat of miscarriage and premature birth, the expectant mother may develop chronic diseases or develop a bacterial infection. nine0003
Consequences of influenza during pregnancy
The consequences of influenza in pregnant women are dangerous and unpredictable. Most often, complications occur in the second and third trimester. No less dangerous is the flu in the first weeks of pregnancy. Up to 12 weeks, all organs and tissues of the child are laid. Therefore, it is important that the body of the future mother is not exposed to viral loads during this period.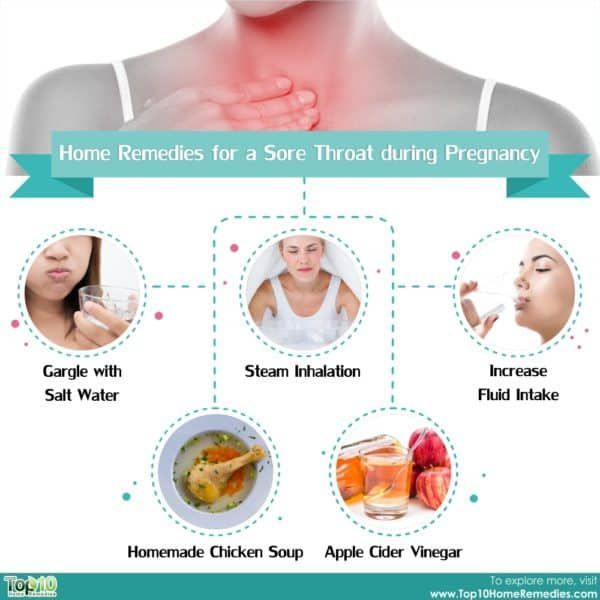
Illness in the last months can cause premature birth. The virus easily crosses the placenta and affects the auditory, visual, nervous system of the baby. Intrauterine infection sometimes causes deviations in mental and physical development, as well as the death of the child. nine0003
Influenza virus during pregnancy in the third trimester depresses the immunity of not only the mother, but also the baby. There is also a risk that the newborn will be susceptible to pathogens of various infections. But in fact, no doctor can say with accuracy how a viral infection affects a child, since each pregnancy proceeds individually. The consequences of the disease are influenced by many factors - the age of the expectant mother, the state of immunity, concomitant and past diseases.
A woman who gets the flu during pregnancy needs to carefully monitor her condition to prevent the development of complications. If you feel unwell, call an ambulance. "Red flags" that indicate that the patient needs hospitalization:
- prolonged body temperature above 38 degrees, which does not go astray;
- palpitations;
- severe dyspnea;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- suspected development of pneumonia.
 nine0014
nine0014
The risk of complications from influenza is increased by smoking and the presence of chronic diseases.
How to treat influenza during pregnancy?
Unfortunately, childbearing limits the choice of drugs for the treatment of colds. Pregnant women are contraindicated in vasoconstrictor drops, antipyretics based on acetylsalicylic acid, and some antitussives. Before taking the medicine, you need to make sure that it will not have a toxic effect on the fetus. Therefore, what to drink with the flu during pregnancy should be decided by the attending physician. nine0003
What to do if the mother-to-be has flu-like symptoms:
- Stay at home and call the doctor if you have the first symptoms of a cold. He will examine the patient, listen to the lungs for wheezing, prescribe drugs that are allowed for pregnant women. Women carrying a child with colds are prescribed:
- antipyretics;
- antivirals - the doctor may recommend Flustop.
 The appointment of etiotropic therapy for influenza as early as possible from the onset of the disease is shown, taking into account the available data on the safety, pathogenicity of the circulating strain of the influenza virus and the condition of the pregnant woman in any trimester of pregnancy (instruction for the medical use of the drug Flustop). nine0014
The appointment of etiotropic therapy for influenza as early as possible from the onset of the disease is shown, taking into account the available data on the safety, pathogenicity of the circulating strain of the influenza virus and the condition of the pregnant woman in any trimester of pregnancy (instruction for the medical use of the drug Flustop). nine0014 - antitussives;
- nasal saline solutions;
- solutions for gargling.
- Plentiful warm drink is a prerequisite for the treatment of viral diseases. A large amount of liquid helps to cope with intoxication. It is allowed to drink tea, fruit drinks, cocoa, juices, fruit and berry compotes.
- It is advisable to take antipyretic drugs for influenza during pregnancy at a body temperature of at least 38 degrees. It is necessary to limit the number of tablets to four per day. To reduce the temperature, you can use rubbing with water at room temperature. nine0014
- Ask loved ones to ventilate and carry out daily wet cleaning in your room.
 This will help to avoid dry mucous membranes, as well as reduce the amount of viral particles in the room.
This will help to avoid dry mucous membranes, as well as reduce the amount of viral particles in the room. - Don't skip meals. Eat foods that are easy to digest. Give preference to liquid foods - broths, milk, yogurt, soups, fruit purees.
- Stay in bed to reduce stress on the immune, cardiovascular, and other systems of the body. Do not rush to do household and work chores until you feel that you have finally recovered. nine0014
If you get sick with a cold and flu during pregnancy, do not use folk remedies for treatment. It is strictly forbidden to soar the legs of pregnant women, inhalations with essential oils can provoke an allergic reaction, and some herbal preparations have a toxic effect on the fetus. Do not take antibiotics - they do not help with viral infections. A doctor may prescribe antibiotics only if a bacterial infection has joined the flu.
How can I avoid getting colds and flu during pregnancy?
To avoid contracting viral infections, follow these guidelines:
- Avoid crowded places.

- Wash your hands frequently with soap and use hand sanitizer when visiting crowded places.
- Restrict travel on public transport.
- Spend more time outdoors.
- If there are no contraindications, regularly engage in exercise, yoga or other form of physical activity. nine0014
- Try to touch your face less with your hands so as not to infect the mucous membranes.
- Ventilate the room before going to bed and the room in which you work.
- To avoid the negative impact of influenza on pregnancy, wear a protective mask in clinics, pharmacies, shops, shopping centers. Remember to change it every two to three hours.
- If someone in the household is sick, isolate yourself from him and do not forget about the mask mode.
- Eat a varied diet - the diet should be balanced. nine0014
- Avoid stress, sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Flush your nose with saline before and after going to crowded places.
- Take vitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor.
Vaccination is an effective way to protect against influenza. Modern vaccines can be vaccinated while pregnant. Immunity from vaccination is transmitted to the baby and lasts up to six months. The expectant mother can discuss vaccination issues with her doctor. nine0003
If you do feel sick and get the flu during pregnancy, stay in bed and drink plenty of warm fluids. Do not be nervous and do not panic, so as not to harm the baby. For prescription of medications, contact your doctor. With a competent approach to treatment, the dangerous consequences of the disease for the child will be minimized.
Everything you need to know about the flu during pregnancy
Latest news
During pregnancy, a woman's immune system may undergo some changes that make it difficult to fight infections. Thus, pregnant women are more susceptible to contracting certain diseases, such as the flu.
Influenza is a contagious disease caused by a virus that is easily transmitted from person to person. Influenza virus appears annually in winter, during the cold months. Symptoms of flu during pregnancy are the same as in the rest of the population and include:
Influenza virus appears annually in winter, during the cold months. Symptoms of flu during pregnancy are the same as in the rest of the population and include:
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Temperature 37.5°C to 40°C.
Other symptoms may include body aches, headache, fatigue, vomiting, and diarrhea. Influenza during pregnancy and in the puerperium may be more serious and complications ( pneumonia, need for hospitalization, premature birth , etc.) may occur, requiring special treatment.
Prevention of influenza in pregnant women
Vaccination against influenza is the main preventive measure to avoid influenza virus and its complications. Pregnant women are considered a risk group for severe influenza , so all pregnant women are recommended to be vaccinated against influenza at the start of the influenza vaccination campaign (in Spain this is usually in October-November). Also pregnant women are advised to follow these general tips to prevent infections :
Also pregnant women are advised to follow these general tips to prevent infections :
- Avoid close contact with people with influenza and do not share food or utensils (glasses, cutlery, napkins) or other items without proper cleaning.
- Avoid touching eyes, nose and throat.
- Use disposable wipes.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water or alcohol-based hand sanitizer (especially after touching shared surfaces such as railings, doorknobs, public transport handrails, keyboards, etc.). nine0014
- Ventilate enclosed spaces frequently
Flu shot during pregnancy
If you are pregnant , you may be concerned about whether the flu shot is safe for pregnant women . However, you should remember that you are advised to get vaccinated because while mild influenza does not harm your pregnancy or your baby, if the condition worsens, you could put yourself and your unborn baby at risk. nine0003
nine0003
Symptoms such as high fever can lead, for example, to premature birth or low birth weight.
Numerous studies have shown that the influenza vaccine is safe for pregnant women and fetuses and can be given at any stage of pregnancy and lactation. It can also be given with pertussis vaccine which is also recommended for all pregnant women . After a flu shot is given to a pregnant woman, may experience mild side effects such as headache, nausea, redness in the area where the vaccine was given, muscle pain, or fever.
If these symptoms do occur, they usually last a day or two. If they persist for a longer time, consult your doctor. You can get flu shot at any stage of pregnancy and even if you are just planning a pregnancy, vaccination is important. In addition to protection, the protective antibodies you acquire with flu shots are passed on to your baby through the placenta and breast milk and will protect him during the first months of life.