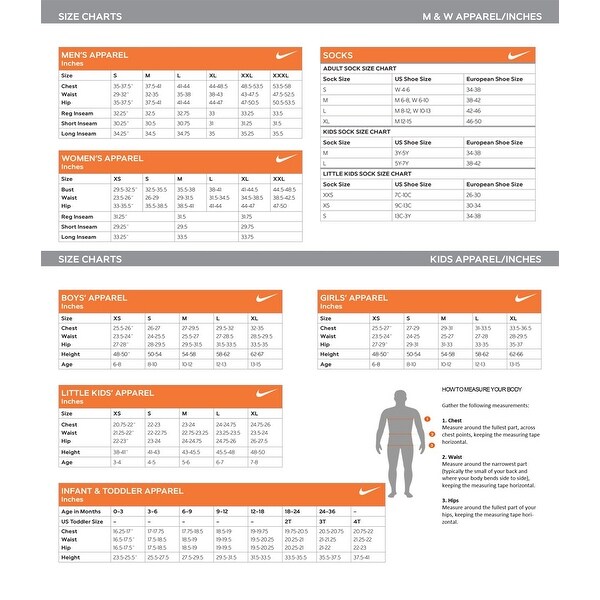
Mucus in newborn eye
Is it normal and how to treat it?
Eye discharge is common in newborns and typically occurs due to a blocked tear duct. This is often treatable at home, but additional symptoms such as a yellow eye discharge require medical attention.
Eye discharge is typically harmless and self-resolving. However, discharge that occurs alongside other symptoms in the eye area, such as swelling or tenderness, could indicate an infection or another eye problem. A parent or caregiver of a newborn with these symptoms will need to consult a doctor.
This article discusses how common eye discharge is and explains how to treat it at home. We also cover medical treatment, other causes, complications, and when to contact a doctor.
Eye discharge in newborns is common and rarely a cause for concern. A common cause of eye discharge is a blocked tear duct.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, almost 20% of newborns have a blocked tear duct. This condition can occur because the end of the tear duct does not open properly when the baby is born.
Tears form in the lacrimal gland, which sits just above the eye. Tear fluid helps clean and lubricate the surface of the eye. When a person blinks, the eyelids sweep the tear fluid into these ducts, which drain it into the nose.
If something blocks a tear duct, fluid may no longer be able to drain away from the eye’s surface. Blockages can cause very watery eyes, and sticky discharge may form in the corners.
Learn more about blocked tear ducts.
Blocked tear ducts are a common cause of eye discharge in infants. However, other conditions and factors can also cause discharge.
Conjunctivitis
Eye discharge in newborns can also be a sign of conjunctivitis or pinkeye. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, a thin membrane that protects the front of the eye. Unlike a blocked tear duct, conjunctivitis often causes the white part of the eye to appear red.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in newborns can include:
- drainage or discharge that develops between 5 and 12 days after birth
- puffy or tender eyelids, often with skin discoloration
- red, irritated eyes
Conjunctivitis in newborns can sometimes occur alongside a blocked tear duct.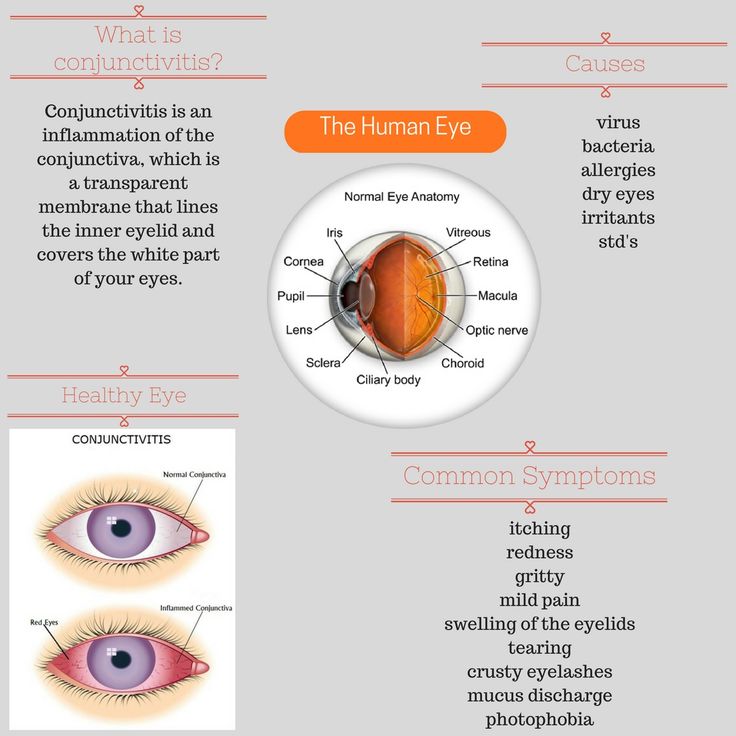 However, a pregnant person can also pass on a bacterial or viral infection to their baby when giving birth, leading to conjunctivitis.
However, a pregnant person can also pass on a bacterial or viral infection to their baby when giving birth, leading to conjunctivitis.
Learn more about the symptoms of eye infections.
Chemical irritation
Chemical irritation can also cause conjunctivitis in newborns. Healthcare professionals often give antibacterial eye drops to newborns to prevent infections. These eye drops can sometimes cause irritation that can result in conjunctivitis symptoms.
Learn more about eye irritation.
If the eye discharge is due to a blocked tear duct, it will usually resolve without treatment within 4–6 months.
However, wind, cold weather, and strong sunlight can also worsen symptoms, so a parent or caregiver should aim to protect a newborn’s eyes from these elements.
Clearing discharge
A parent or caregiver can often treat a newborn with a blocked tear duct at home. Before touching the area close to the child’s eyes, it is essential to wash the hands with soap and warm water to prevent infections. A person should also take care to rinse the hands thoroughly after cleaning them to avoid getting soap in the baby’s eye.
A person should also take care to rinse the hands thoroughly after cleaning them to avoid getting soap in the baby’s eye.
To clear away discharge, dip a clean piece of gauze or soft cloth in some lukewarm water, then gently wipe the corner of the eye. If a blocked tear duct affects both eyes, always use a new area of the cloth or gauze to clean the other eye.
Tearduct massage
A doctor may also recommend gently massaging the blocked tear duct to help it open, and they will demonstrate how to do this safely.
To massage the tear duct:
- Lightly press the tip of the index finger against the inside bridge of the newborn’s nose, on the side of the blocked tear duct.
- Make 2 or 3 short downward strokes with the finger along the side of the nose. These should be gentle but firm.
- Perform the massage twice a day — once in the morning and once in the evening.
If the side of the newborn’s nose becomes red or swollen, stop the massage immediately and contact a doctor.
In newborns, blocked tear ducts tend to open up within several months of birth. However, medical intervention may be necessary in some cases.
Surgery
If the blockage has not gone away by the baby is 1 year of age, a doctor may recommend a medical treatment called a nasolacrimal duct probing.
This procedure involves inserting a small probe into the infant’s tear duct. By using probes that gradually increase in size, a doctor will be able to open up the tear duct. They will then use a saline solution to flush out any remaining debris.
Sometimes, the doctor may also insert a small tube, or stent, into the duct to keep it open.
Probing is usually successful in opening the tear duct. For children with a severe blockage, a doctor may recommend a more complicated surgical procedure called a dacryocystorhinostomy to clear out and open the tear duct.
Antibiotics
If an infection is causing eye discharge, the newborn will need prompt medical attention. To treat cases of infectious discharge, a doctor may prescribe topical, oral, or intravenous antibiotics.
To treat cases of infectious discharge, a doctor may prescribe topical, oral, or intravenous antibiotics.
Blocked tear ducts can sometimes lead to an infection called dacryocystitis. Symptoms of this condition may include:
- excessive thick discharge from the eye
- redness in the corner of the eye
- a tender bump or swelling at the side of the nose
- fever
If a newborn has any of these symptoms, a parent or caregiver should consult a doctor.
Newborns with eye discharge or very watery eyes should speak with a pediatrician or an eye doctor specializing in children, called a pediatric ophthalmologist. These healthcare professionals can diagnose the cause of the discharge and check for signs of infection.
Parents or caregivers should seek medical attention if an infant’s eye discharge persists for more than 6 months.
Newborns with signs of an eye infection require immediate medical attention. Signs of an eye infection can include:
- sore or puffy eyes
- swollen eyelids
- yellow or green pus or discharge
- a bump or swelling on the inside corner of the eye
If a parent or caregiver notices any of these symptoms, they should contact a doctor immediately.
Eye discharge in newborns is common and often results from a blocked tear duct. The blockage will usually clear up by itself within 4 to 6 months.
However, newborns with eye redness, eye discharge, or excessive watering of the eyes should speak with a doctor to diagnose the cause and rule out an eye infection.
Parents and caregivers can treat a baby with a blocked tear duct at home by wiping away any discharge and gently massaging the area twice a day. A doctor can demonstrate how to do this.
Discoloration, swelling, or soreness in the eye can indicate an eye infection. Speak with a doctor immediately if an infant has these signs.
Is My Baby’s Eye Discharge Normal?
Written by Nicole Blades
In this Article
- What’s Normal?
- When It’s Conjunctivitis
- When Treatment Is Needed
As the parent of a newborn, nothing beats staring lovingly into your sweet little bundle’s eyes. (Well, watching your baby sleeping soundly comes pretty close!) But what if when you look into your child’s eyes, you see that they have goopy, sticky discharge? Is it something to be concerned about?
What’s Normal?
First of all, take a breath, because sticky eye discharge in newborns is very common. If the white part of your baby’s eye -- the sclera -- is clear and there is no redness, but there is discharge, it’s most likely a blocked tear duct.
If the white part of your baby’s eye -- the sclera -- is clear and there is no redness, but there is discharge, it’s most likely a blocked tear duct.
About 1 in 5 babies are born with tear ducts that haven’t fully developed. The blockage is usually in one eye but can be in both. It often clears up on its own. A warm compress can help, but if it lasts a long time, it might need surgery.
When It’s Conjunctivitis
Since a newborn hasn’t been around that long -- under 2 months -- it’s not common for them to get a lot of viral infections. But sometimes their clogged tear duct can lead to an infection such as conjunctivitis.
This happens when there is inflammation of the thin layer of tissue (conjunctiva) that covers the sclera. Symptoms are similar to the sticky, watery eyes that come with a blocked tear duct. But with conjunctivitis, there is more swelling, tenderness, and redness of the eye area, and the whites of the eye will be pink or red. Your baby’s eyelid might be red, sticky, and itchy, and the discharge takes on a yellowish color. Also, their eyes might be more watery than usual. The infection often starts in one eye and spreads to the other.
Also, their eyes might be more watery than usual. The infection often starts in one eye and spreads to the other.
Chemical conjunctivitis can happen when eye drops and ointments, typically used on newborns at birth to help prevent infection, actually cause the irritation. It can show up as mildly red eyes and some puffiness in the eyelids.
It’s rare, but red, angry, itchy eyes with swollen eyelids and discharging pus could mean ophthalmia neonatorum (ON).This is a bacterial infection that can happen during childbirth if the baby passes through a birth canal infected with chlamydia. The symptoms usually show up 5-12 days after birth. Among newborns with ON, half also have the infection other areas of their bodies.
Call the doctor if the baby has a fever and:
- Your baby cannot open their eyes or you cannot see the eye
- The area is tender to touch and the skin around the eye is red
- There is a lot of eye discharge
These may be signs of a bacterial infection of the sclera.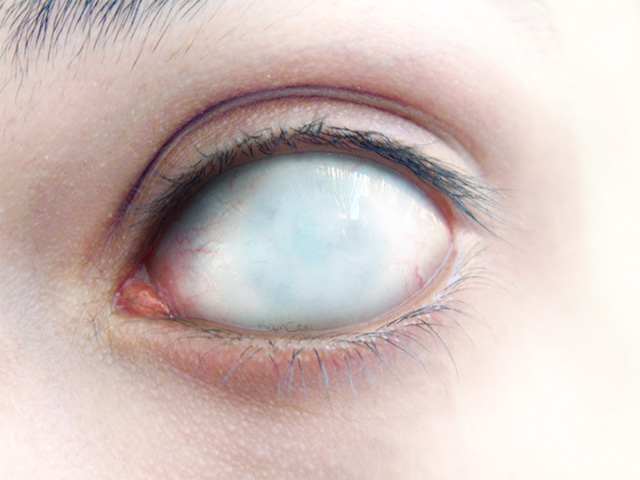
When Treatment Is Needed
Doctors usually recommend a wait-and-see approach, as this issue often clears up on its own. You can also apply a warm compress to the bothered eye.
If the tear duct is still blocked and the eye discharge continues up to the baby’s first birthday, you should see your child’s doctor. They may refer you to a pediatric eye specialist, as it may need surgery.
To treat conjunctivitis caused by the blocked tear duct, try a gentle warm massage with your clean hand between your baby’s eye and nasal area. For chemical conjunctivitis, the symptoms usually only last for 1-3 days after birth, so no treatment is needed. And if it’s ON, doctors usually treat that with oral antibiotics.
The eyes of a child fester - causes, treatment and prevention of diseases
Contents
- Causes of festering eyes in children
- Causes of suppuration of the eyes in children over one year old
- Treatment of eye suppuration in children
- Prevention of eye suppuration in infants and children over one year of age
- What can be dangerous if a child has festering eyes
Suppuration of the eyes is a common problem in newborns. The fact is that during the period of attempts, infection of the fetus can occur, infection occurs. To prevent this from happening, doctors can disinfect the eyes with special solutions in children in the first hours of life. In some cases, decontamination may not help, and the infection will still spread. nine0003
The fact is that during the period of attempts, infection of the fetus can occur, infection occurs. To prevent this from happening, doctors can disinfect the eyes with special solutions in children in the first hours of life. In some cases, decontamination may not help, and the infection will still spread. nine0003
Causes of suppuration of the eyes in children
- Infectious eye diseases - conjunctivitis, in most cases bacterial, keratitis.
- Inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Foreign object in the eye.
- Inflammation of the skin layers around the eyes, which is medically called "orbital cellulitis".
- Styes can also cause pus in the eye of a child.
- Blockage of tear ducts. nine0006
- Allergic reactions.
Let's analyze each reason in more detail. Ophthalmologists say that in the vast majority of cases in infants, infection occurs against the background of dacryocystitis , a condition in which swelling occurs in the area of the lacrimal sac. Experts say that suppuration of the eyes in newborns can also occur due to inflammatory processes in the mother's reproductive system.
Experts say that suppuration of the eyes in newborns can also occur due to inflammatory processes in the mother's reproductive system.
Conjunctivitis is characterized by inflammation of the tissues around the eyes. They look red and swollen. Bacterial conjunctivitis must be treated according to a plan drawn up by an ophthalmologist. nine0003
Sometimes mote, speck of dust, cat hair can get into the eye . As a response, lacrimation, irritation of the mucous membrane of the eye may occur. In this case, you should contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Orbital cellulitis occurs due to infection of the deeper layers of the skin around the eyes. This is a dangerous disease that is fraught with further spread of infection to other areas. The progression of pathology is dangerous for children's vision. nine0003
Stye is a small firm swelling in the area of the eyelid. Barley is able to further develop into a chalazion, a more dangerous condition.
Allergic reactions resulting in suppuration usually occur in children older than one year. Purulent discharge from the eyes is one of the symptoms of allergies. This condition often occurs during periods of seasonal allergies, during periods of flowering plants that are considered allergens. nine0003
Causes of suppuration of the eyes in children older than one year
A common cause of suppuration of the eyes in older children can be a cold, flu due to the spread of a viral infection. In this case, it is necessary to take measures to treat the infection.
Colds can provoke an inflammatory process in the sinuses. This is called sinusitis. This condition is accompanied by symptoms such as an increase in body temperature to a high level, a runny nose, and suppuration of the eyes. nine0003
Conjunctivitis, keratitis can also be factors that provoked suppuration of the eyes in a child. Conjunctivitis can occur against the background of the spread of viruses and bacteria.
Treatment of eye suppuration in children
Before talking about treatment, it is important to understand the symptoms that need attention. These include swelling of the eyelids, profuse purulent discharge from the eyes, decreased visual acuity, pain in the eye area, profuse lacrimation, redness of the eyes. nine0003
If these symptoms occur, see an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. Infectious diseases in children progress very quickly and treatment should be started as soon as possible. In some cases, antibiotic treatment may even be needed if staphylococcus aureus caused the suppuration of the eyes.
The method of treatment depends on the cause that caused suppuration of the eyes in the child. As a rule, treatment is therapeutic in nature. The ophthalmologist may prescribe special antibacterial drops or ointments, eyewashes. nine0003
In the case of dacryocystitis, the outcome of the appointment of surgical intervention is likely. The operation can be performed if the patency in the tear ducts is impaired.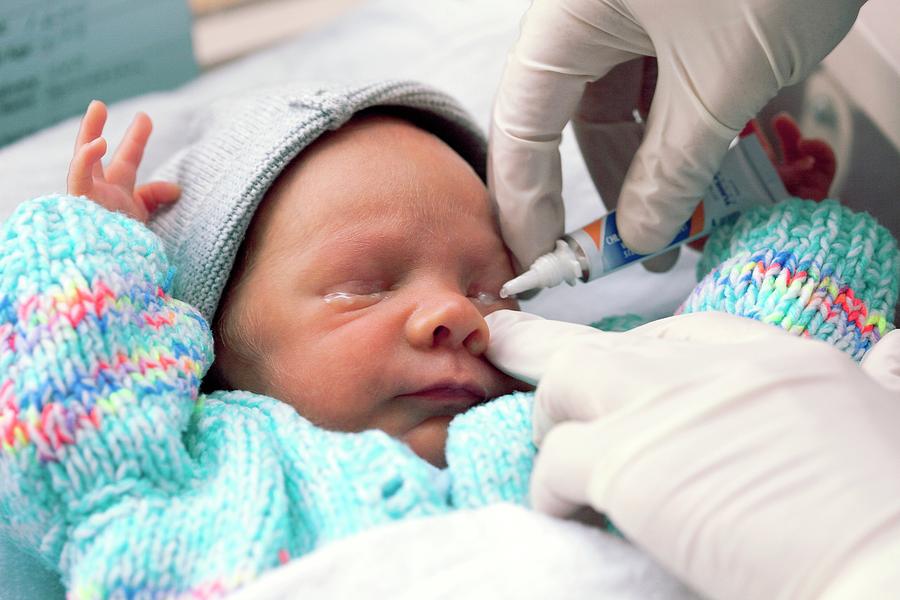
Suppuration caused by allergic reactions can be cured if the cause of the allergy is removed. To suppress symptomatic manifestations, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines in combination with other drugs.
Do not self-medicate. The only correct approach to treatment is to immediately show the child to an ophthalmologist and begin treatment. nine0003
Prevention of eye suppuration in infants and children older than one year
Regularly observe the child with a pediatric ophthalmologist in order to diagnose possible deviations from the visual norm in time.
Teach your child about hygiene. Inspire the child that you can not touch the eyes with dirty hands, touch the eyelids.
Make sure your child's diet is varied and contains all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Good nutrition will have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system. A normal level of immune response is very important for fighting viruses and bacteria that enter the child's body. nine0003
nine0003
Be careful with small objects to avoid getting foreign objects in the eye.
If the eyes are festering in newborns, preventive measures cannot prevent the pathological process. To prevent festering in older children, it is important to adhere to the following preventive recommendations to reduce the risk of festering:
What can be dangerous if a child has festering eyes
If festering eyes in children are not treated, the symptom may return in an even more severe condition. Infectious diseases - conjunctivitis, keratitis - can progress and can lead to complications in the child's vision. nine0003
Suppuration of the eyes can lead to the appearance of other unpleasant symptoms for the child - itching, burning in the eyes, watery eyes. Discomfort will cause the child to have a decrease in mood, complexes, difficulties in doing homework.
Be attentive to the health of your children. It is very important to ensure the normal development of the child's visual system in order to maintain a high quality of vision in the future.
Article score: 4.6/5 (37 ratings)
Rate the article nine0003
Recording evaluation...
Thank you for your evaluation.
The eye of a newborn is festering. What to do?
11/12/2021 126957
Content of article
- Why does a newborn's eye fester?
- How to treat before going to the doctor
- How to wash the eye of a newborn?
- What treatments are used if conservative treatment fails
It happens that even in the maternity hospital or in the first weeks after discharge, the mother notices purulent discharge from one or both eyes in the newborn: they accumulate in the corner of the eye and dry out in crusts, they can even glue the eyelids and cilia. Despite the frightening appearance of young parents, this condition is usually not dangerous for the health of the child. However, it is impossible to leave it without treatment so that severe complications do not develop. nine0003
Despite the frightening appearance of young parents, this condition is usually not dangerous for the health of the child. However, it is impossible to leave it without treatment so that severe complications do not develop. nine0003
Why does the eye of a newborn fester?
There are two main reasons why a newborn may start to fester in the eye: conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by viruses, bacteria or allergies. Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac, it can be congenital. While the baby is in the mother's abdomen, its tear ducts are covered with thin films and filled with a gelatinous mass (mucus) so that amniotic fluid does not get inside. By the time of birth, the film usually resolves, and during the first cry, the mucus comes out, freeing the tear ducts. If for some reason this does not happen, the path to tears remains blocked. The fluid stagnates in the lacrimal sac, inflammation may begin. nine0003
nine0003
Dacryocystitis in newborns is more common than conjunctivitis. It usually affects one eye, while conjunctivitis affects both. Also, dacryocystitis can be suspected if, when pressed, mucus or pus is released from the lacrimal canal. But since the appearance of the diseases is similar, and the treatment will be different, the final diagnosis should be made by the doctor during the examination.
How to treat before going to the doctor
Before going to the doctor, a newborn should not categorically instill drops or ointment in the eye. Only a doctor can prescribe medication. Also, do not start to massage the lacrimal canal, guided by videos or articles from the Internet. If the diagnosis of dacryocystitis is confirmed, the doctor will show how and in what direction to massage. Wrong actions can only aggravate the disease. nine0003
This is important!
Before the appointment of treatment, you can only carry out the toilet of the eye, that is, remove the purulent plaque in a timely manner and rinse the eyes.
How to wash the eye of a newborn?
You can wash the festering eyes of a baby with a solution of furacilin: it is sold ready-made or in tablets. In the latter case, the tablet must be diluted in a glass of warm boiled water. If furatsilina is not at hand, you can use saline, infusion of pharmacy chamomile or just boiled water. nine0003
You can’t wash your child’s eyes with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate - the proportions of the solution of these drugs can be easily broken, and then you can seriously damage the baby’s eye. If the doctor considers that furatsilin is too weak or ineffective in your case, he, when prescribing treatment, will describe in detail how and with what to wash the eyes of a newborn.
Be sure to wash your hands with soap and water before you start rinsing. To wash each eye, use only a clean cotton pad or a piece of bandage, otherwise you can bring an infection from a diseased eye into a healthy one. nine0003
nine0003
This is important!
It is necessary to wash the eyes in the direction from the temple to the nose and in no case vice versa, so that the collected pus is definitely brought out of the eye, and not left behind the eyelid.
What treatments are used if conservative treatment fails
The sooner you start treating a festering eye, the higher the chances of getting by with only conservative treatment, that is, washing, massage and antibacterial drops. nine0003
So, massage helps to cure dacryocystitis in a third of babies under the age of two months and in a fifth - up to four months. If there is no improvement or the condition of the eye has worsened, you need to contact an ophthalmologist to adjust the treatment. The next step in the treatment of dacryocystitis is probing the lacrimal canal. Usually it is carried out for babies older than a month, in a hospital. The effect of this manipulation is very high: more than 99% of babies under the age of three months are completely cured after a single procedure.