Milk residue or thrush
Thrush and Other Causes, Plus Treatment
The fragility of a newborn can be one of the most intimidating things in the world. And naturally, you’ll do everything in your power to protect this tiny human from anything that brings worry.
You ever-so-gently lay them down, support their head, dress them lightly, and check every square inch of their body for any unusual signs. And then you notice it: Instead of being perfectly pink, your baby’s tongue looks like it has a white coating on it.
This coating can seem to appear out of nowhere. But here’s the good news — a white tongue in babies isn’t unusual. It’s typically caused by either an overgrowth of yeast — very treatable — or by something as simple as milk residue.
Thrush is a yeast infection caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida — yes, the very same type that causes vaginal yeast infections and diaper rashes.
In the case of oral thrush, though, the infection forms on parts of the mouth involved in sucking. This includes your baby’s lips, tongue, and inner cheeks.
And though we know you put baby first, and you second, you should also know that thrush can spread to the object of your baby’s sucking if you’re breastfeeding: your nipples. Conversely, yeast on your nipples (that you may not even know you have) can contribute to thrush in your baby’s mouth.
The tell-tale signs and symptoms of thrush
Not every white tongue is caused by thrush. So here’s a good rule of thumb: If you’re able to wipe or brush off a white coating, thrush isn’t the culprit. Yeast hangs on for dear life.
Also, if your baby has thrush, it’s unlikely for the white to only appear on their tongue. If you open their mouth, you’ll see a cottage-cheese coating over other areas, too, like inside their cheeks.
If you notice these symptoms, don’t panic. But thrush isn’t something to ignore, even if it’s mild and doesn’t seem to cause any problems. There’s always the chance of the infection getting worse, and if it does, your baby may have pain or discomfort that makes it harder for them to feed or latch onto your breast — and if baby’s not happy, no one’s happy.
Causes of thrush
You might wonder why many babies get oral thrush while it’s rarely a problem for adults. The answer is simple: A baby’s young immune system isn’t always strong enough to fight off germs and infections. And because of their weaker immune system, it’s much easier for yeast to grow on some parts of their little body.
But a weak immune system isn’t the only culprit. If your baby takes an antibiotic to treat another infection — say, one of those pesky ear infections — this drug can kill off good bacteria, also encouraging the growth of yeast.
Treatment for thrush
Hearing that your baby has any type of infection can cause a range of emotions. But there’s no need to worry with this one — thrush is very common and easily treatable.
Your baby’s doctor will likely prescribe a liquid antifungal that you’ll apply directly to white patches. For the medicine to work, you’ll want it to sit on their tongue or inside their mouth for as long as possible. So give your baby treatments at least 30 minutes before feedings.
So give your baby treatments at least 30 minutes before feedings.
Once the medicine is in their system, you can expect the infection to clear in a few days.
Additional considerations if you’re breastfeeding
To be clear, thrush happens in babies who are bottle-fed and breastfed. If you breastfeed, though, know that it’s possible for you and your baby to spread yeast to each other.
This might be a lesser known problem, but it does happen and it’s called nipple thrush. Signs include:
- sore, painful nipples after pain-free breastfeeding
- cracked, itchy, or blistered nipples
- achy breasts after feedings
If you also have thrush, it isn’t enough to treat your baby. Sure, medicine will clear their infection. But if you don’t clear your own infection, you’ll continue to spread thrush back and forth. There are a lot of things you and baby will share over a lifetime — this shouldn’t be one of them.
Applying a topical antifungal cream — available over the- counter in the form of yeast infection creams and others — on and around your nipples after each feeding is usually enough to kill the fungus.
It’s possible that you might need a prescription antifungal for a particularly stubborn infection. Since yeast likes warm, moist areas, let the skin of your breasts air dry as much as possible before putting your bra back on.
Don’t forget to wash off any leftover residue of the cream before nursing. Your symptoms will also clear up in a few days.
It’s completely normal to worry about your baby. And, honestly, you should never let anyone tell you that your worries are foolish. If you see a white coating on your baby’s tongue, you might immediately think it’s thrush and call the pediatrician — and there’s nothing wrong with that.
But there’s also a chance that what you believe to be yeast is only milk residue.
Distinguishing between the two can be tricky, as they have similar appearances. One of the easiest ways to tell the difference is to try and wipe off the residue with a warm, damp cloth.
If the residue comes off or becomes less noticeable, you’re dealing with milk residue and not thrush. Keep in mind that milk residue is more noticeable after feedings and only appears on the tongue.
Keep in mind that milk residue is more noticeable after feedings and only appears on the tongue.
What causes this buildup of milk? Simply put, a lack of saliva.
A newborn’s mouth is different from an adult’s mouth in that babies don’t produce a lot of saliva during the first few months after birth. (That is, until they are about 4 months. Then it’s time for a months-long vacay in droolville.) The less saliva, the harder it is for their mouths to wash away milk.
Milk residue may be more likely to occur if your baby has tongue tie, a condition that restricts movement of their tongue. Your baby’s tongue might be unable to touch the roof of their mouth, in which case the lack of friction causes a buildup of milk residue.
This can also happen if your baby has a high palate, and their tongue can’t reach the roof of their mouth.
Regardless of cause, though, milk residue isn’t permanent, nor a reason for concern. A white tongue goes away once your baby’s mouth produces more saliva, or when they start to eat solid foods.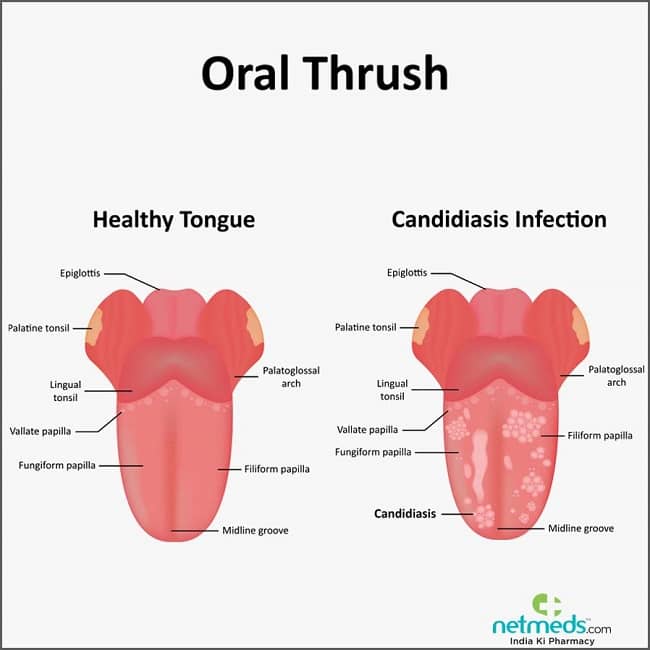
In the meantime, you can consider gently wipe off the residue using a soft, damp cloth after feedings, though this may not be necessary.
Just because thrush is common in babies doesn’t mean you should ignore the problem. Untreated thrush can cause pain and discomfort, and if so, you’ll have a fussy baby on your hands.
See a doctor if your baby develops any creamy, white lesions in their mouth, especially if you can’t remove the whiteness with a damp cloth. It’s likely thrush, but a pediatrician can run tests if they suspect something else.
If your baby has thrush, see your own doctor if your nipples or breasts become sore. It’s important that you’re treated at the same time to stop the spread of the infection.
Gently wiping or brushing your baby’s tongue after each feeding can help prevent a white tongue caused by milk.
As far as thrush goes, your best weapon is to sterilize all equipment used for feedings. This includes bottles, nipples, and your breast pump. You can take it a step further and sterilize pacifiers and any toys your baby puts in their mouth.
You can take it a step further and sterilize pacifiers and any toys your baby puts in their mouth.
If you have thrush on your nipples, prevent recurrent infections by frequently changing your breast pads, and washing your breastfeeding bras in hot water.
Also, if you express or freeze your breast milk with thrush, consider giving this milk to your baby while you’re both being treated. If you give this milk to your baby after the infection clears, there could be a greater chance that the thrush could return.
If you see a white coating on your baby’s tongue, know that it happens and it’s not because you’re doing something wrong. It could be thrush, or it may be something as simple as milk residue.
In the event of thrush, these yeast infections are easily treatable, so see your pediatrician. Your sweet baby will be sticking their perfectly pink tongue out at you before you know it!
Thrush
Is this your child's symptom?
- A yeast infection of the mouth in young babies
- White patches in the front of the mouth
Symptoms of Thrush
- White, odd shaped patches in the mouth
- Coats the inner cheeks or inner lips
- Sometimes also coats the tongue
- Sticks to the mouth.
 It can't be washed away or wiped off easily like milk curds.
It can't be washed away or wiped off easily like milk curds. - Sometimes causes a painful mouth, decreased sucking and reduced milk intake
- Mild discomfort or no symptoms in most newborns
- The infant is bottle-fed or breast-fed
Cause of Thrush
- Caused by a yeast (called Candida)
- Occurs on parts of the mouth involved with sucking
- Made worse by friction from too much time sucking on a pacifier
White Tongue Alone: Not Thrush
- If a white tongue is the only finding, it's not due to thrush.
- A milk diet often causes a white coated tongue.
- This is normal.
- It will go away after your baby starts eating solid foods.
- If white patches occur inside the lips or cheeks, call your child's doctor. It's safe to call during office hours.
When to Call for Thrush
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Dehydration suspected. No urine in more than 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth and no tears.

- Age less than 1 month old and looks or acts abnormal in any way
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Fever occurs
- Bleeding in the mouth
- Drinking less than normal
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Thrush, but none of the symptoms above. Reason: may need a prescription medicine to treat it.
- You have other questions or concerns
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Thrush
- What You Should Know About Thrush:
- Thrush is common during the early months of life.

- It's caused by a yeast infection in the mouth. Most often, it's due to prolonged sucking.
- Thrush causes only mild discomfort. It's easy to treat at home.
- Here is some care advice that should help until you call your doctor.
- Thrush is common during the early months of life.
- Anti-Yeast Medicine (Prescription):
- Your doctor will probably prescribe an anti-yeast liquid medicine. Use it as follows:
- Age Under 1 Month: Use 1 mL.
- Age Over 1 Month: Use 2 mLs.
- Place in the front of the mouth on each side. Also, put it wherever you see the thrush. It doesn't do any good once it's swallowed.
- Do this 4 times per day.
- If the thrush isn't getting better, rub the medicine directly on the thrush. Use a cotton swab to do this.
- Don't feed your baby anything for 30 minutes after the medicine.
- Keep this up for at least 7 days. Also, continue it until all thrush has been gone for 3 days.
- Decrease Sucking Time to 20 Minutes per Feeding:
- Reason: Too much sucking can irritate the lining of the mouth.
 This makes it more prone to a yeast infection. A common example of this is when a baby sleeps with a bottle.
This makes it more prone to a yeast infection. A common example of this is when a baby sleeps with a bottle. - For severe mouth pain with bottle feeding, don't use a bottle. Reason: The nipple can make pain worse.
- Try giving fluids in a cup, spoon or syringe instead.
- Reason: Too much sucking can irritate the lining of the mouth.
- Limit Pacifier Use:
- Too much sucking on a pacifier can irritate the mouth.
- Limit pacifier use to times when nothing else will calm your baby.
- If your infant is using an orthodontic pacifier, switch to a smaller, regular one. Reason: Bigger ones can cause more friction in the mouth.
- Special washing or boiling of pacifiers or bottle nipples is not needed or helpful.
- Special Washing of Pacifiers and Nipples - Not Helpful:
- Pacifiers and bottle nipples can be washed the usual way with soap and water.
- They do not need to be boiled or sterilized.
- They do not need to be thrown out.
- Yeast is a germ that is found in normal mouths.

- It only causes thrush if the lining of the mouth is irritated or damaged.
- Get better results by reducing nipple time and pacifier time.
- Note: Follow your doctor's advice if it is different.
- Breastfeeding and Yeast Symptoms:
- If the mother's nipples are red and sore, it's probably a yeast infection.
- Use an anti-yeast cream (such as Lotrimin) on the nipple area.
- No prescription is needed.
- Put it on 4 times per day after feedings.
- Wash the cream off the nipples before each nursing. Avoid soap which dries out the skin.
- Many mothers will need treatment with an oral anti-yeast medicine (such as Diflucan). Call your PCP or OB within 24 hours for advice.
- Diaper Rash Treatment:
- If there's a bad diaper rash, it can also be due to yeast.
- Use an anti-yeast cream (such as Lotrimin) on the diaper rash.
- No prescription is needed.
- Put it on 4 times per day.

- See Diaper Rash care guide.
- Return to Child Care:
- Thrush cannot be spread to others, since it does not invade normal skin.
- Your child can go to child care with thrush.
- What to Expect:
- With treatment, thrush usually clears up in 4 to 5 days.
- Without treatment, it clears up in 2-8 weeks.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Starts drinking less than normal
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 11/22/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Treatment of thrush in newborns in Kirzhach, make an appointment with a pediatrician
Our license
Our Doctors
Prices
Some parents notice that a whitish coating appears in the mouth of the baby, similar to the remains of milk. This is how thrush usually manifests itself - a disease that is quite common in newborns.
This is how thrush usually manifests itself - a disease that is quite common in newborns.
Thrush (candidiasis) is an inflammatory disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. In infants, the oral mucosa and genital organs are most often affected, less often internal organs. The first sign of the disease, which gave it its name, is the appearance of a white coating in the indicated places, similar to curdled milk. Under this plaque, red foci of inflammation or bleeding erosion may be located.
Causes of thrush
- Candida albicans fungus is found in every person, both in adults and in newborns. In babies, during teething, with a cold, dysbacteriosis, immunity weakens, conditions appear for the active growth of the fungus;
- If the mother does not comply with the hygiene standards (keeping the mammary glands clean, boiling the bottles and nipples, as well as the child's toys), prerequisites for the development of the disease are created;
- Candida likes sweets, so over-sweetened water or a mixture will help them multiply quickly;
- If the child's mother has thrush, the baby is also at risk;
- Taking antibiotics can also cause thrush.

When a disease occurs, find out the cause of the infection so that after treatment the baby does not become re-infected with thrush.
Symptoms of thrush
Candidiasis (thrush) can occur without fever. At first, it doesn't even hurt. But if the white dots in the baby's mouth are not treated, then after a few days the entire mucous membrane will be covered with a dense white coating, which gradually becomes grayish or yellowish.
Thrush in newborns has pronounced symptoms. They include the following.
1. White curdled discharge.
They are usually located on the mucosa. In the mouth, they do not move from the inner surface of the cheeks or lips on their own. Usually, under a curdled rash, if you remove it with a cotton swab or a clean finger, you can observe a small sore. In the vagina, curdled discharge appears more abundantly and is easily removed when washing the child.
2. Itching.
Cheesy white discharge and microcracks that form under it cause itching, which becomes more intense with the progression of the disease. Thrush in the mouth in newborns develops rapidly. A very small child cannot say this, so he often cries and tries to put his fist in his mouth.
Thrush in the mouth in newborns develops rapidly. A very small child cannot say this, so he often cries and tries to put his fist in his mouth.
3. Discoloration of the mucous membranes of the mouth and vagina.
Usually, thrush in girls and boys is equally manifested in swelling and redness of the mouth or vagina. However, this phenomenon in the mouth, which is accompanied by a high temperature and the absence of a curdled discharge, should not be confused with stomatitis, which also occurs in infants.
4. Microcracks in the mucous membrane.
This symptom can be more attributed to girls - microscopic cracks may appear on the mucous membranes of the external genital organs. Some of them are quite capable of bleeding a little. This is due to the fact that the acidity of the flora with thrush rises sharply. As a result, the mucous membrane becomes thin and has gaps in some places.
As a rule, thrush in newborns does not require treatment, that is, oral antifungal drugs are not prescribed. Enzymes in the intestines of infants are not yet fully formed, so the reaction to taking such pills will be negative. Usually, the doctor prescribes local treatment with antifungal solutions, which act quickly enough and relieve itching within 1-1.5 days. However, it should be remembered that the drugs cannot be canceled immediately after the child has calmed down and the curdled discharge has passed. Candida fungi are quite persistent and cannot be destroyed in 2-3 days of using a solution for local exposure. Therefore, it is necessary to continue the course of treatment for exactly as many days as the doctor prescribed. Otherwise, this disease will return in the future anyway.
Enzymes in the intestines of infants are not yet fully formed, so the reaction to taking such pills will be negative. Usually, the doctor prescribes local treatment with antifungal solutions, which act quickly enough and relieve itching within 1-1.5 days. However, it should be remembered that the drugs cannot be canceled immediately after the child has calmed down and the curdled discharge has passed. Candida fungi are quite persistent and cannot be destroyed in 2-3 days of using a solution for local exposure. Therefore, it is necessary to continue the course of treatment for exactly as many days as the doctor prescribed. Otherwise, this disease will return in the future anyway.
Treatment of thrush
If you find curdled plaque in the mouth of a baby, do not panic. Thrush in newborns responds well to treatment. The main thing is to regularly carry out the necessary procedures until complete recovery.
If you find white spots in your baby's mouth, contact your pediatrician. The source of infection in candidiasis is a fungus, and it should be treated only with antifungal drugs.
The source of infection in candidiasis is a fungus, and it should be treated only with antifungal drugs.
Clean your baby's mouth regularly. Treatment of thrush cannot be stopped even with a visible improvement. If thrush is not cured, it will recur over and over again.
Make an appointment with the pediatrician of the Medical Center "Health" by phone 8 (49237) 2-95-56.
Oral candidiasis or thrush, symptoms and underlying causes
Oral candidiasis: what is it?
A fungus of the genus Candida can settle on the lining of the oral cavity, which causes a disease called candidiasis, or oral thrush. With this disease, white plaques appear on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks. During tongue cleaning, they can cause soreness and even slight bleeding. Without treatment, candidiasis can spread to other parts of the mouth, such as the back of the throat, tonsils, gums, and palate.
Although no one is immune from oral candidiasis, it is more common in immunocompromised people, denture wearers, patients taking inhaled corticosteroids, and infants. Oral thrush also occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy, patients with a history of dry mouth syndrome (xerostomia) and smokers.
Oral thrush also occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy, patients with a history of dry mouth syndrome (xerostomia) and smokers.
Causes of oral candidiasis
A number of well-defined factors contribute to the development of oral thrush. The causes of the disease can be both a weakening of the immune system (caused by illness or the use of certain drugs), and the use of antibiotics, which changes the natural microbial balance in the human body.
The result of failures in the work of natural defense mechanisms can be a significant imbalance of "beneficial" and "harmful" microbes. Under normal circumstances, the immune system fights viruses and bacteria that are dangerous to humans, but with a weakened immune system, this fight becomes less effective, which allows the fungus that causes oral candidiasis to multiply.
Vaginal fungal infections, diabetes, most forms of cancer, HIV/AIDS all weaken the body and make it more vulnerable to oral thrush.
Oral candidiasis in immunocompromised adults
Oral candidiasis can spread to other organs such as the lungs, liver, and digestive tract. With the penetration of infection into the intestines, a violation of its work and an even greater weakening of the body are possible.
Depending on the severity of your illness, you may be prescribed antifungal medicines that come in the form of tablets, lozenges, and a mouthwash that you swallow. Amphotericin B, which is often used in the treatment of advanced HIV and other antifungal drug-resistant infections, may also be prescribed.
Because some antifungal drugs can damage the liver, your doctor will likely do regular blood tests and monitor your liver (especially if it has already been infected). This same strategy should be used if you are on long-term treatment or if you have liver disease.
Symptoms of oral thrush in children and adults
In some cases, the symptoms of oral candidiasis may not appear immediately: sometimes they can appear completely unexpectedly. Here are some tell-tale signs that you may have oral thrush:
Here are some tell-tale signs that you may have oral thrush:
- White, cheesy plaques anywhere in the mouth
- Unusual pain with habitual movements of the tongue and jaw
- Bleeding of plaques when rubbed
- Cracks and redness in the corners of the lips (more often when wearing prostheses)
- Dry mouth
- Marked loss of taste in food and drink
Although thrush most often develops in the most visible areas of the mouth, lesions can also occur in the esophagus. This makes swallowing difficult or feels like the food is stuck in the throat. This happens in the most severe cases, and if you have any of these symptoms, you should immediately contact your dentist or GP.
While waiting for treatment, you can relieve pain yourself if you have any. Eat unsweetened yogurt or take probiotics containing lactobacillus acidophilus. Neither is a cure in the truest sense of the word, but it can help restore normal microflora. If the infection persists, your doctor will likely prescribe you an antifungal medication or antibiotics.
If the infection persists, your doctor will likely prescribe you an antifungal medication or antibiotics.
Symptoms of oral candidiasis in infants and nursing mothers
With oral candidiasis, the infant may have difficulty feeding or become more restless and irritable than before. A manifestation of thrush is most likely to be white plaques in the child's mouth. Mothers should keep a close eye on their baby's oral health because candidiasis is transmitted through breastfeeding, and if this happens and the baby then recovers, the mother may inadvertently infect it again.
As a breastfeeding mother, look out for the following signs and symptoms:
- Itching, tenderness or unusual redness of the nipples
- Shiny or flaky skin around alveoli
- Unusual pain during or between feedings
- Severe, piercing pain in the chest
If white plaques appear in your mouth or in your child's mouth, contact your doctor or dentist immediately. Do not postpone a visit to the doctor if symptoms of candidiasis occur in older children or adolescents, since diabetes may be the main disease against which thrush has developed.
Do not postpone a visit to the doctor if symptoms of candidiasis occur in older children or adolescents, since diabetes may be the main disease against which thrush has developed.
Since there are two people to be treated at once, the doctor may use a special strategy, such as starting with two different antifungals: a cream for your breasts and another medicine for your baby.
If you are breastfeeding, use lactation pads to prevent fungus from getting on your clothes. Do not buy liners with plastic membranes, as they only encourage fungus to thrive. Reusable liners (and, of course, the bra itself) should be washed in hot water with bleach to help keep the infection from spreading.
If you are breastfeeding your baby, but also bottle feeding, and give him a pacifier, wash all objects that come into contact with the baby's mouth daily in a solution of equal parts water and vinegar. After washing, let things air dry to prevent the growth of fungus. In the same way, you need to process all parts of the breast pump, especially its removable parts.
Physician or dentist consultation
If you suspect that you have an oral disease that requires medical attention, make a list of all the symptoms you have, including any that you may think are not related to thrush: the doctor will understand whether they are important or not. Also include non-medical events in this list, such as increased stress levels and causes of anxiety. Indicate if you are in the company of people with a weakened immune system.
You will also need to have a list of all the medicines you take. Also, write down the questions you want to ask the doctor. This will help you find out all the details you are interested in and get a comprehensive consultation, regardless of whether you have oral candidiasis or not.
Your doctor may ask you follow-up questions that will allow him to narrow down his search for a diagnosis based on the symptoms he has identified and the symptoms you describe. Try to answer as frankly and honestly as possible so that the doctor can quickly diagnose the disease and begin treatment without waiting for complications.
If the examination of the oral cavity does not allow the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis, he will definitely take a small sample and either examine it himself or give it to the laboratory for analysis.
If the infection has already affected not only the oral cavity, but also the esophagus, a couple of studies may be required. First of all, the doctor will take a swab from the back of the throat to determine which bacteria or fungi have become (and have become) the cause of the symptoms. Then you may need to have an endoscopy, in which your doctor uses an endoscope (flexible tube with light) to look at your esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine. This will determine how far the infection has spread.
Lifestyle and home remedies for oral thrush
At the initial stage of candidiasis, good oral hygiene will help to contain the development of the disease - brushing your teeth twice a day and at least daily flossing will help to timely remove food debris and plaque from the surface of the teeth , from interdental spaces and along the gum line.