Meningitis rash glass test baby
Meningitis Glass Test - Meningitis Rash Test
A rash that does not fade under pressure can be a sign of meningococcal septicaemia (meningococcal bacteria can cause meningitis and septicaemia). Using the glass test on a rash that appears on someone's skin will help you to determine whether the rash is a medical emergency or not
People with septicaemia may develop a red rash of tiny ‘pin pricks’, which can develop into purple bruising.
This rash does not fade under pressure.
The meningitis glass test
Performing the meningitis glass test is very straight forward, follow the instructions below:
- Press the side of a clear glass firmly against the skin
- Spots/rash may fade at first
- Keep checking
- Fever with spots/rash that do not fade under pressure is a medical emergency
- Do not wait for a rash. If someone is ill and getting worse, get medical help immediately
On dark skin, the spots/rash can be more difficult to see, check lighter areas such as the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, inside the eyelids and the roof of the mouth. Be aware of all meningitis signs and symptoms.
What is the rash?
The rash associated with meningitis is actually caused by septicaemia, more information below:
- Meningococcal bacteria can cause meningitis and septicaemia
- People will often have both together
- When the bacteria are in the bloodstream, they multiply rapidly and begin to release endotoxins (poisons) from their outer coating
- The body’s natural defences have little effect on these poisons and eventually blood vessels become damaged. As septicaemia advances, it affects the whole body and can cause organ damage or failure
- The rash associated with septicaemia is caused by blood leaking into the tissues under the skin
It’s important to know that septicaemia can also cause other more specific symptoms to look out for (as well as the red rash):
- Fever with cold hands and feet
- Joint or muscle pain
- Rapid breathing
- Stomach cramps and diarrhoea
If you are worried about spotting the symptoms in time, let us help you. Download our phone optimised videos and images on your phone, or request one of our free credit-card sized signs and symptoms cards by calling our Meningitis Helpline on 0808 80 10 388.
Download our phone optimised videos and images on your phone, or request one of our free credit-card sized signs and symptoms cards by calling our Meningitis Helpline on 0808 80 10 388.
Concerned about meningitis?
- If you live on your own, always make sure you tell someone if you are not feeling well. They can check up on you and take action if needed
- Trust your instincts. You know your loved ones, and your own body, best
- Describe the symptoms and say you think it could be meningitis or septicaemia
- Early diagnosis can be difficult. If you have had medical advice and are still worried, get medical help again
Do not wait for a rash. If someone is ill and getting worse, get medical help immediately.
Septicaemia and sepsis
Many medical experts now use the term sepsis instead of septicaemia. Sepsis describes the life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to an infection injures its own tissues and organs.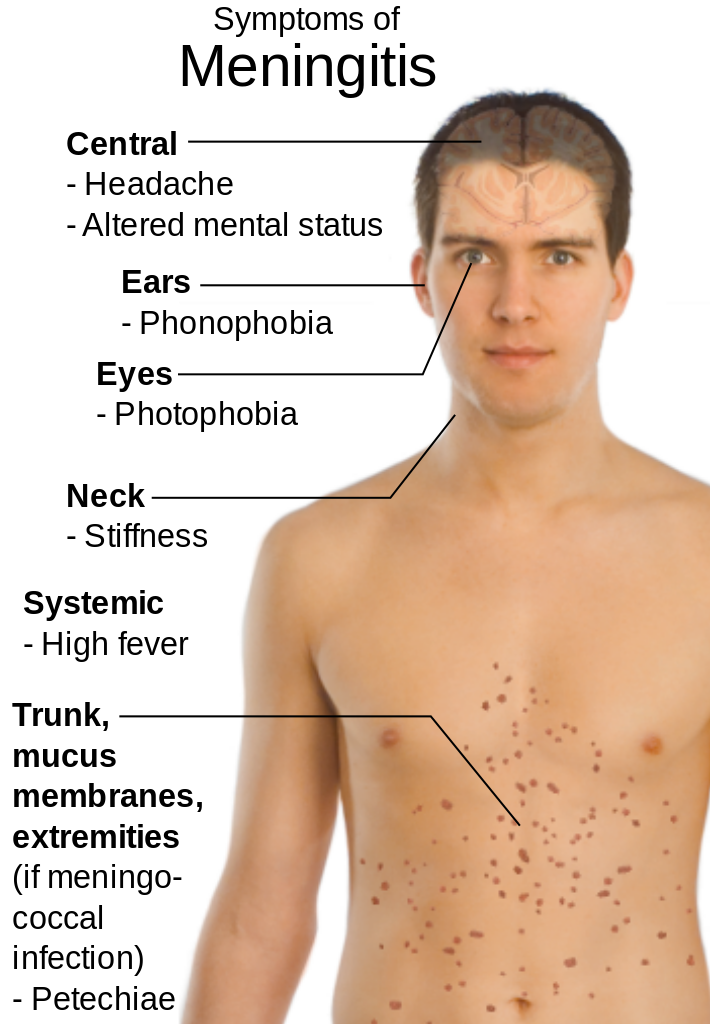
Did you find this information useful?
Meningitis - Symptoms - NHS
Symptoms of meningitis can appear in any order. Some may not appear at all. In the early stages, there may not be a rash, or the rash may fade when pressure is applied.
You should get medical help immediately if you're concerned about yourself or your child.
Trust your instincts and do not wait for all the symptoms to appear or until a rash develops.
Symptoms of meningitis and sepsis include:
- a high temperature
- cold hands and feet
- vomiting
- confusion
- breathing quickly
- muscle and joint pain
- pale, mottled or blotchy skin (this may be harder to see on brown or black skin)
- spots or a rash (this may be harder to see on brown or black skin)
- headache
- a stiff neck
- a dislike of bright lights
- being very sleepy or difficult to wake
- fits (seizures)
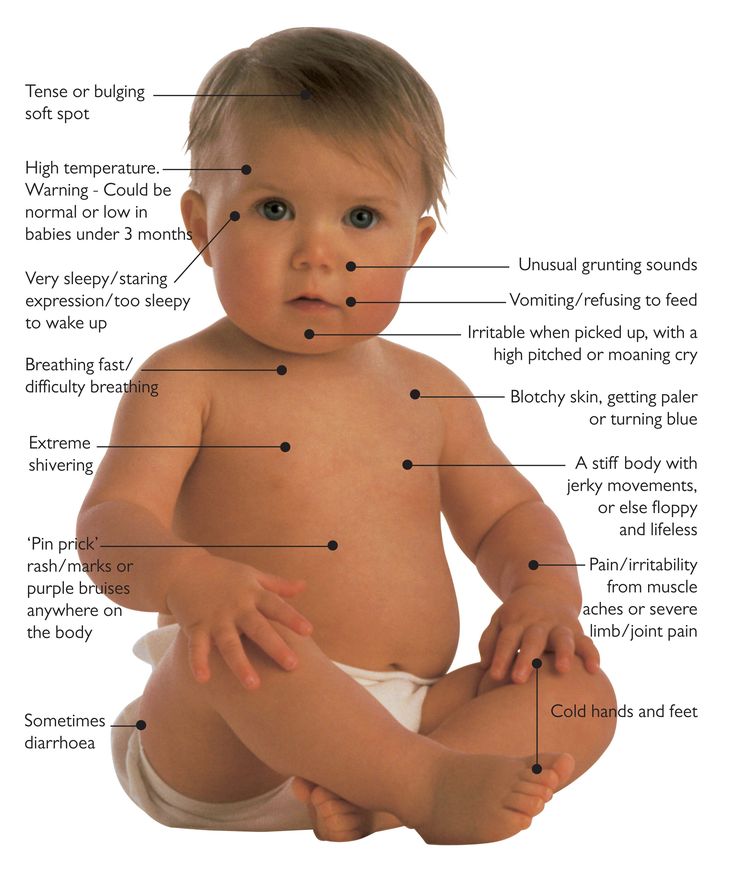
Babies may also:
- refuse feeds
- be irritable
- have a high-pitched cry
- have a stiff body or be floppy or unresponsive
- have a bulging soft spot on the top of their head
Someone with meningitis or sepsis can get a lot worse very quickly.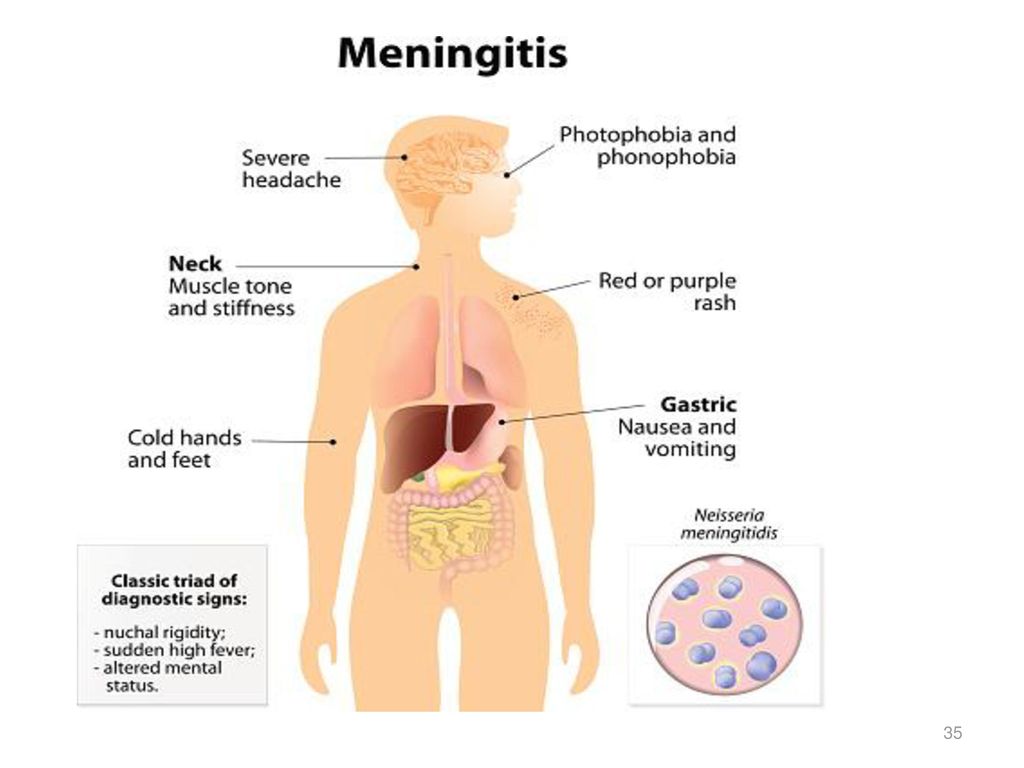
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A&E immediately if you think you or someone you look after could have meningitis or sepsis.
Call NHS 111 for advice if you're not sure if it's anything serious.
If you’ve had medical advice and are still worried or any symptoms get worse, get medical help again.
The rash usually starts as small, red pinpricks before spreading quickly and turning into red or purple blotches.Credit:
Mediscan / Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/meningococcal-rash-image1683649.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=83D4AFC7-AC4B-4271-B09C-727E90532943&p=17774&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dATB0C2%26qt_raw%3dATB0C2%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d788068%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
It does not fade if you press the side of a clear glass firmly against the skin.
Credit:
Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/testing-of-meningococcal-rash-image589611.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=6C8D2A33-C874-43AF-A58B-398C0D9552AF&p=17774&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dA8FF2B%26qt_raw%3dA8FF2B%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d195878%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
The rash can be harder to see on brown or black skin. Check paler areas, such as the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, roof of the mouth, tummy, whites of the eyes or the inside of the eyelids.
Check paler areas, such as the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, roof of the mouth, tummy, whites of the eyes or the inside of the eyelids. Credit:
Meningitis Research UK https://hscic365.sharepoint.com/sites/Pilot/NHSUK/Health%20AZ/Forms/AllItems.aspx?id=%2Fsites%2FPilot%2FNHSUK%2FHealth%20AZ%2FHealth%20A%2DZ%2FA%2DZ%20content%20audit%2FM%2FMeningitis%2FImage%20and%20section%20review%2007%202019%2FRe%5FPhotography%20of%20the%20meningitis%20rash%2Eeml&parent=%2Fsites%2FPilot%2FNHSUK%2FHealth%20AZ%2FHealth%20A%2DZ%2FA%2DZ%20content%20audit%2FM%2FMeningitis%2FImage%20and%20section%20review%2007%202019
If a rash does not fade under a glass, it can be a sign of sepsis (sometimes called septicaemia or blood poisoning) caused by meningitis and you should call 999 straight away.
Page last reviewed: 25 October 2022
Next review due: 25 October 2025
Meningitis, meningococcal infection.
 Description of the elements of the rash.
Description of the elements of the rash. Contents: rash in children.
Meningitis - inflammation of the pia mater of the brain or spinal cord, usually manifested by a triad of symptoms: fever, severe headache and / or change in mental status, stiff neck, but in some cases meningitis manifests itself with a rash .
Rash in children.
Rash in children on the face, on the trunk, on the extremities. Rash...
Rash in the form of small bruises, begins with small blue star-shaped spots and rapidly increases in number and diameter. One of the most dangerous rashes in children is a hemorrhagic rash with meningococcal infection (meningitis) .
This is an extremely dangerous disease, threatening the life of a child . If all of a sudden, against the background of a child’s high temperature, you find such a rash in him, especially if new elements of the rash appear one by one in a matter of minutes - URGENTLY call an ambulance .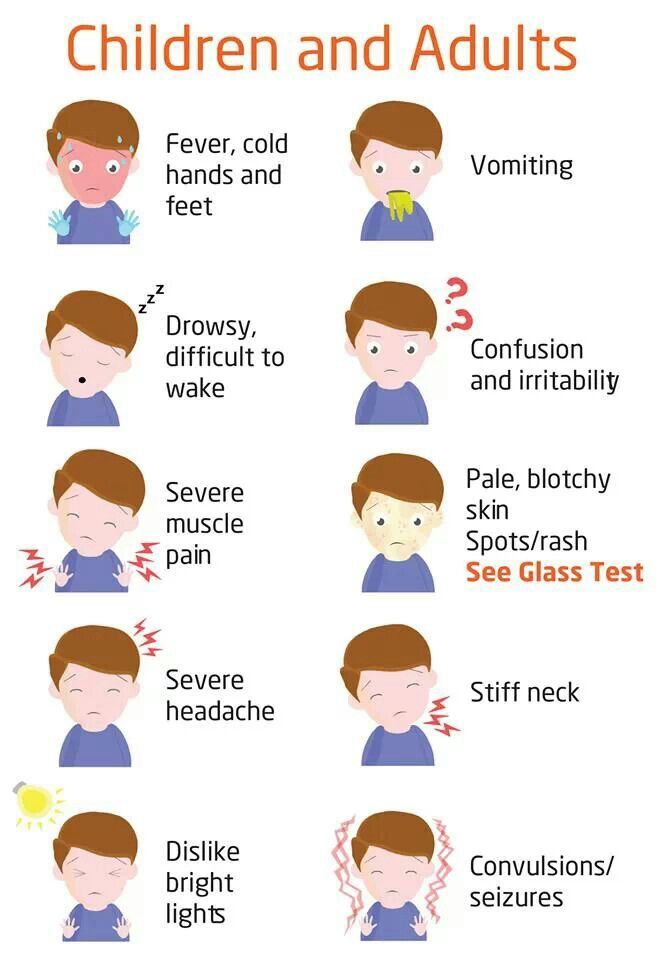
Despite the fact that meningitis usually manifests itself as a fairly bright clinical picture, there are no pathognomonic symptoms indicating specifically meningitis , and therefore any manifestation of the disease - especially such a bright one as a rash - can help in the early diagnosis of such a formidable disease Read more: MENINGITIS. SYMPTOMS, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION
With meningitis there is a so-called. petechial rash caused by multiple small hemorrhages into the skin. Most often, such a rash occurs with bacterial meningitis or with the most formidable course of meningitis - meningococcemia (meningococcal sepsis). The spots do not protrude from the surface of the skin, the color of the spots is pink to purple. nine0003
The rash is a small bruising that begins as small, often star-shaped spots and rapidly increases in number and diameter. New spots form right before your eyes. The spots that appear often merge, increasing in size, this can happen very quickly - this course of the disease is called lightning purpura .
New spots form right before your eyes. The spots that appear often merge, increasing in size, this can happen very quickly - this course of the disease is called lightning purpura .
Petechia (petechia; Italian petecchie spots, rash; synonym: petechial hemorrhage, pinpoint hemorrhage) - a spot on the skin or mucous membrane with a diameter of 1-2 mm, caused by capillary hemorrhage. nine0028In order to distinguish a meningeal rash from any other, a simple glass beaker test is usually suggested:
Take a thin glass beaker and press it against the rash. If the rash has not disappeared or has not faded to almost complete disappearance, then this is a petechial rash that requires immediate examination by a doctor.
The glass beaker test is not a reliable test, and if the patient has the triad of symptoms characteristic of meningitis, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.
nine0003
Bacterial meningitis - the second most common, but most formidable form of inflammation of the meninges . With bacterial meningitis, a fulminant course of the disease is possible, when only a few hours pass from the moment of the first symptoms to death . Read more: MENINGOCOCCAL MENINGITIS
Fever or fever
Any increase in body temperature is called a fever. What...
A meningitis rash can be difficult to see in dark areas of the skin. Light areas such as the palms and soles of the feet should be examined.IMPORTANT: The appearance of a rash with symptoms of meningitis may indicate a deadly form of this disease meningococcemia or sepsis . If you find such a rash, contact your doctor immediately.
Contents: rash in children.
Author: Sergey Butriy
How to do the glass test (with pictures)
').
insertAfter("#intro"),$('
').insertBefore( ".youmightalsolike"),$('
').insertBefore("#quiz_container"),$('
').insertBefore("#newsletter_block_main"),ja(!0),c=document.getElementsByClassName( "scrolltomarker"),a=0;a
In this article:
glass test
Other signs and symptoms
Health care
Additional articles nine0003
Sources
Meningitis causes inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord. The organisms that cause meningitis can also lead to septicemia (blood poisoning), although it can develop in the absence of meningitis. [1] X Sourse of information Both conditions are life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Although treatment should not be delayed until a skin rash appears, the presence of such a rash is often indicative of meningitis and/or septicemia, and a test with a clear glass or strong plastic cup can be done to check for this.
nine0106 [2] X Reliable source National Health Service (UK) Go to source Knowing how to do this test and knowing other symptoms of meningitis and septicemia can save the life of yourself or a loved one.
Steps
1
Find out what a meningitis rash looks like. The rash caused by meningococcal septicemia appears as a scattering of small pink dots, similar to a pin prick. These points gradually merge into purple-red spots and / or hematomas. nine0118 [3] X Sourse of information
- Unlike most rashes, the meningococcal septicemia rash does not go away or fade when pressed. In the test with a glass, this feature is used to identify such a rash. [4] X Reliable source National Health Service (UK) Go to source
2
Select a clear glass. An ordinary transparent glass or plastic beaker with sufficiently thick walls can be used for this test.
The plastic cup must be strong enough to withstand the pressure without flattening or cracking. nine0134 [5] X Sourse of information
- The sides of the glass must be transparent. Through too dense or translucent glass (plastic), it will be more difficult to see the rash.
- It is best to use a glass or cup. However, if necessary, you can also take a transparent glass or plastic plate.
3
Select a suitable area of skin. Before doing the test, a rather pale area of skin covered with rash spots should be selected. nine0150 [6] X Sourse of information
- Meningitis rash is more difficult to see on dark skin. Look for patches of rash on lighter areas of the skin, such as the palms of your hands or the soles of your feet. [7] X Sourse of information
4
Press the glass on the rash.
Gently press the side of the glass against the rash. In this case, it is necessary that you see the rash through the walls of the glass. Experiment by holding the glass in place or rolling it over your skin so that you can see the rash patches as best as possible. nine0003
- Apply enough pressure to cause the skin around the rash to turn pale. When pressure is applied, the blood leaves the tiny blood vessels near the surface of the skin. If the skin around the rash hasn't turned white, then you haven't been able to apply enough pressure to properly evaluate the test results.
- At first, the rash may also appear pale and discolored. However, this impression can be misleading, as the skin around the rash turns pale with pressure. You should not end the test on these results. nine0125
- If the rash appears to be blanching, continue to apply pressure on the glass and try moving it to another rashed area to see if the rash is actually blanching under pressure. [8] X Sourse of information
5
Watch for spots to fade.
As you roll the glass over the rash, see if not only the skin, but the rash itself is discolored. Pay close attention to see if the rash really disappears and check the result several times. nine0003
- If the rash disappears, it is most likely not caused by meningitis or septicemia.
- If the rash does not fade, this is a dangerous sign of meningococcal septicemia.
6
Seek immediate medical attention if the test is positive. A rash that does not go away on pressure may be caused by meningococcal septicemia, which is very dangerous. You will need immediate medical attention as this disease can be fatal. Call a doctor or go to an emergency room immediately. nine0003
- If the rash clears up but there are other signs of meningitis or other serious health problems, you should still seek immediate medical attention. By itself, the rash does not serve as a clear and unambiguous sign of meningitis; with this disease, it may turn pale or be absent altogether.
- If meningitis is suspected, you should not wait for a rash to appear before seeking medical attention. If you suspect you have meningitis, then immediately call an ambulance to get to the nearest hospital as soon as possible. nine0125
Advertising
1
Be aware of the symptoms of meningitis in adults and children. These are often similar to flu symptoms, but meningitis is much more dangerous. Symptoms can appear very quickly, within a few hours, or after one to two days. [9] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source The most common symptoms in both children and adults include:
- Sudden increase in body temperature [10] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Acute headache other than common migraine [11] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Neck stiffness and difficulty turning head [12] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Nausea and/or vomiting [13] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Confusion of thoughts, difficulty concentrating and concentrating [14] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Increased fatigue, drowsiness [15] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Hypersensitivity to light [16] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Decreased appetite and persistent thirst [17] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- In some cases (not all), skin rash [18] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Seizures and loss of consciousness [19] X Sourse of information
2
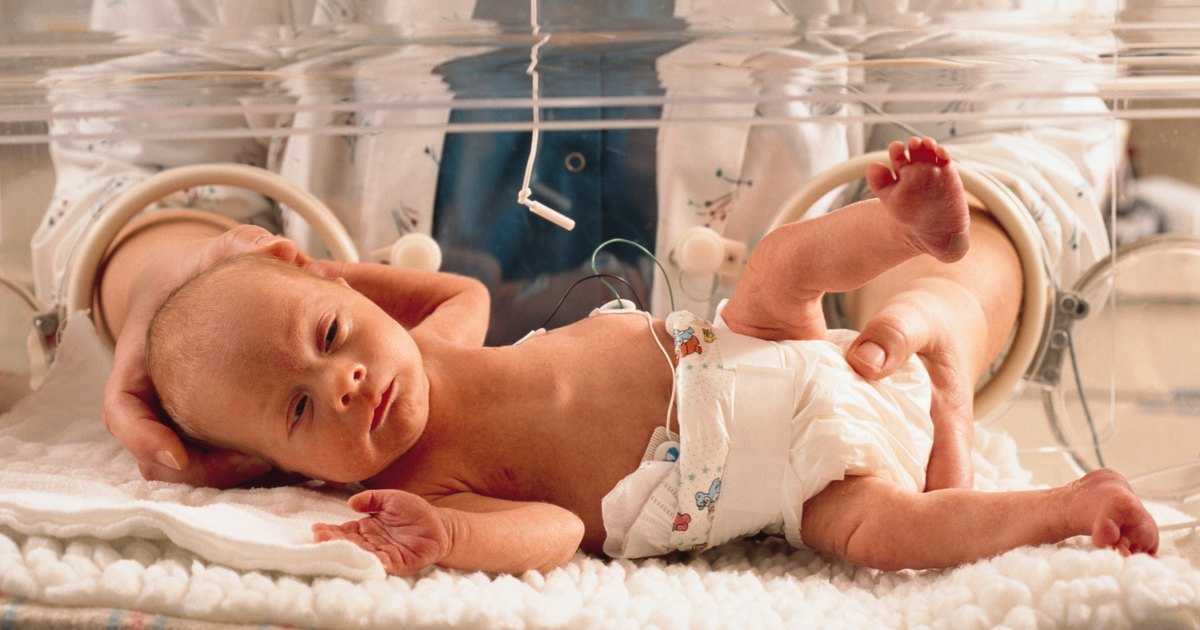
Be aware of symptoms in newborns.
Newborns and infants are unable to tell others where they feel pain or numbness and may not have some other signs such as nausea or confusion. When diagnosing meningitis in newborns and infants, look for the following symptoms: nine0003
- High body temperature [20] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Incessant crying, inability to calm the child [21] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Excessive fatigue, lethargy, irritability [22] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Malnutrition and lack of appetite [23] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source nine0105
- Rigidity of the body accompanied by convulsions, or flaccid flexibility and “lifelessness” [24] X Sourse of information
- Lump and/or mild swelling on the crown [25] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
3
Check for cold hands and feet.
An abnormally low temperature of the extremities is one of the signs of meningitis, especially if it is observed against the background of a high temperature of the rest of the body. nine0302 [26] X Sourse of information
- Another symptom is trembling. If the patient experiences uncontrollable shivering while warm, this may indicate the development of septicemia. [27] X Sourse of information
4
Note unusual pain and stiffness (numbness). Typically, stiffness in meningitis occurs mainly in the neck, but the patient may experience unusual pain and stiffness in other areas of the body as well, which is another sign of this disease. nine0318 [28] X Sourse of information
- Pain often occurs in the joints and/or muscles. [29] X Sourse of information
5
Look for possible digestive disorders.
Meningitis is often accompanied by stomach cramps and diarrhoea. [30] X Sourse of information If these symptoms are present along with others, they may indicate meningitis.
- Many people with meningitis also experience loss of appetite, nausea, and recurrent vomiting. nine0339 [31] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
6
Be aware of meningitis rash. Rash is one of the late symptoms of the disease, and it may not occur at all. [32] X Reliable source National Health Service (UK) Go to source Therefore, be aware of other signs and symptoms of meningitis.
- Be aware that there is no rash in viral meningitis. If a rash appears, it indicates bacterial meningitis. nine0355 [33] X Reliable source National Health Service (UK) Go to source
- As the meningitis-causing bacteria multiply in the bloodstream, the endotoxins they release are released into the bloodstream.
The human body is usually unable to resist these toxins, and poisoning with them leads to damage to the blood vessels. This process is called septicemia. [34] X Sourse of information
- As septicemia progresses, it can lead to damage to various organs. A characteristic rash occurs when poisoned blood penetrates the subcutaneous tissues. nine0363 [35] X Sourse of information
Advertising
1
Seek immediate medical attention. Meningitis is a very serious disease. Symptoms may appear within a couple of hours or a few days, but if you suspect that the symptoms you are experiencing are indicative of meningitis, immediately contact the nearest clinic or hospital. [36] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source nine0105
- The success of treatment often depends on how early it is started, so if you suspect meningitis, do not hesitate and seek medical help immediately.
- Because many of the symptoms of meningitis can be associated with common but less serious conditions, you may not recognize the disease in its early stages. However, when these symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear that are specific to meningitis (neck stiffness, rash that does not fade when pressed), medical attention should be sought as soon as possible. nine0125
2
Check for meningitis. Only a doctor can tell if you have meningitis. Your doctor or emergency room staff will likely take a sample of your blood or cerebrospinal fluid to test for meningitis. [37] X Reliable source Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Go to source
- To take a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, your doctor will use a syringe with a special spinal tap needle. With its help, he or she will extract some fluid from the spinal canal, which will then be tested for the presence of meningitis pathogens.
nine0399 [38] X Reliable source Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Go to source
- CBC and blood cultures, urinalysis, and chest x-rays can also help detect signs of infection.
- If a diagnosis of bacterial meningitis is confirmed, your blood or cerebrospinal fluid may be used to culture the bacteria in a laboratory to compare it to existing strains. Your treatment and the type of antibiotics you use will depend on the specific strain. nine0405 [39] X Reliable source Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Go to source
- Depending on the circumstances, your doctor may also send you for a CT scan or an MRI to check how much brain tissue is swollen and look for other damage. [40] X Sourse of information
3
Prepare for hospitalization. When diagnosed with bacterial or acute viral meningitis, patients are almost always hospitalized.
However, the need for hospitalization and its duration are determined mainly by the type of meningitis and the severity of the symptoms. nine0420 [41] X Sourse of information
- In the hospital, patients are given antibiotics, antivirals, corticosteroids, and antipyretics. Patients with breathing difficulties may also receive oxygen therapy. Supportive care, such as intravenous injections, is given as needed. [42] X Sourse of information
4
Protect yourself from contracting meningitis. In most cases, meningitis is contracted through contact with its carriers. The disease can be transmitted by airborne droplets (for example, when coughing or sneezing) or by contact (with kisses, shared utensils, and so on). nine0436 [43] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source The spread and transmission of meningitis can be prevented by following standard precautions:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and frequently [44] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
- Do not eat from shared utensils or share eating utensils, drinking straws, or sharing food, drinks, lip ointment, cigarettes, or toothbrushes [45] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source nine0105
- When coughing or sneezing, cover your nose and mouth [46] X Reliable source Mayo Clinic Go to source
Advertising
What will you need
- Clear glass or durable plastic cup
Sources
About this article
Other languages
How to do the cup test - Wiki How English
Meningitis causes inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord.