Leg cramps during pregnancy second trimester
Leg cramps during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Leg cramps during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Leg pain can sometimes be a sign of a blood clot. If pain in your leg doesn’t go away, or if your leg is red, warm or swollen, see your doctor immediately.
Key facts
- Up to 3 in 10 people who are pregnant get leg cramps.
- Cramps are most common in your calf muscles.
- Cramps commonly happen at night in late pregnancy.
- To prevent leg cramps, try stretching your leg muscles before you go to bed and drink plenty of water.
- To ease a cramp, pull your toes up towards your ankle, rub the muscle, walk around or apply a heat pack.
What are leg cramps?
Leg cramps (pains) affect up to 3 in 10 people who are pregnant. They usually occur in your calf muscles, but can also occur in your thighs or feet. A cramp is a sign that your muscles are contracting very tightly when they shouldn’t be. This happens when acid builds up in your muscles.
Cramps usually happen at night. They are more common in your second and third trimesters.
Leg cramps are not the same as pelvic cramps.
What causes leg cramps during pregnancy?
There are many reasons suggested for cramps while you’re pregnant, such as changes to your metabolism, having a vitamin deficiency, being too active or not being active enough. However, nobody really knows why they occur in pregnancy.
How can I get rid of cramps?
To ease a leg cramp, you can try:
- stretching the muscle by pulling your toes hard up towards the front of your ankle
- rubbing the muscle firmly
- walking around
- a heat pack
If you have a partner, you could ask them to help.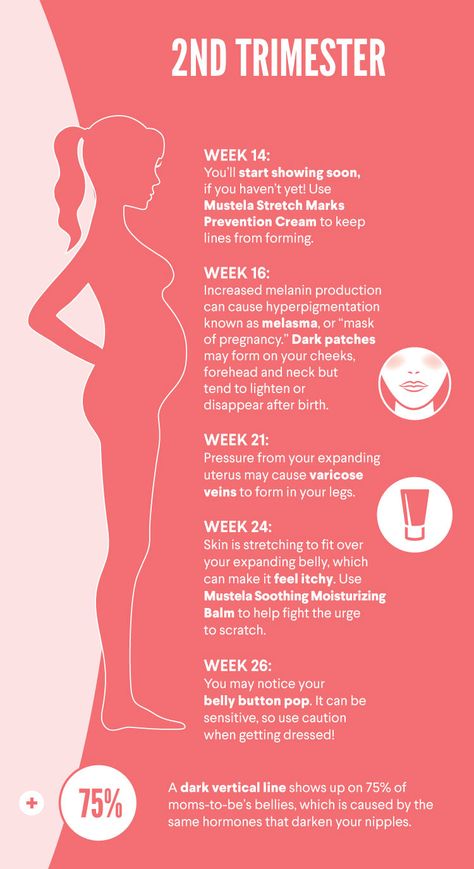
If your muscles are still sore after the cramp has gone, you can take paracetamol for pain relief.
How can I prevent leg cramps?
Things you can try that might help prevent cramps include:
- stretching your calf muscles before you go to bed
- drinking plenty of water
- having a warm bath before you go to bed
- eating a balanced diet
- avoiding stretching your leg while pointing your toes
Magnesium, calcium, vitamin B and vitamin C have been suggested as a treatment for cramps. It’s not clear whether any of these supplements work, but people often try magnesium and calcium. If you’re interested in trying supplements, talk to your doctor or midwife about whether they might be suitable for you.
When should I talk to my doctor or midwife about cramps?
If leg cramps are bothering you, talk to your doctor or midwife.
Leg pain can sometimes be a sign of a blood clot. If pain in your leg doesn’t go away, or if your leg is red, warm or swollen, see your doctor immediately.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Therapeutic Guidelines (Muscle cramps, including leg cramps in pregnant women), NSW Government (Having a baby), Queensland Health (6 weird things that may happen to your body during pregnancy), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Minor Symptoms or Disorders in Pregnancy King Edward Memorial Hospital Clinical Guidelines: Obstetrics & Midwifery), Queensland Health (VTE in pregnancy (a blood clot in the vein)), NPS (Magnesium, a treatment for leg cramps?), Royal Women’s Hospital (Common concerns in early pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
- Swelling during pregnancy
- Varicose veins
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 28
You are now in the third trimester and you'll probably be feeling many of the common discomforts of pregnancy, like a sore back, swelling, heartburn or cramps.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Common discomforts during pregnancy
Your body has a great deal to do during pregnancy. Sometimes the changes taking place will cause irritation or discomfort, and on occasions they may seem quite alarming.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health problems & complications | Raising Children Network
Many pregnancy health problems are mild, but always call your doctor if you’re worried about symptoms. A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms - Better Health Channel
All women experience pregnancy differently, and you will experience different symptoms at different stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Sleep during pregnancy
Sleep can become a problem when you're pregnant. Here are some tips to help you get as much sleep as possible so you’re ready for your baby's arrival.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 33
Your baby's brain and nervous system are now fully developed, and the baby is continuing to gain weight.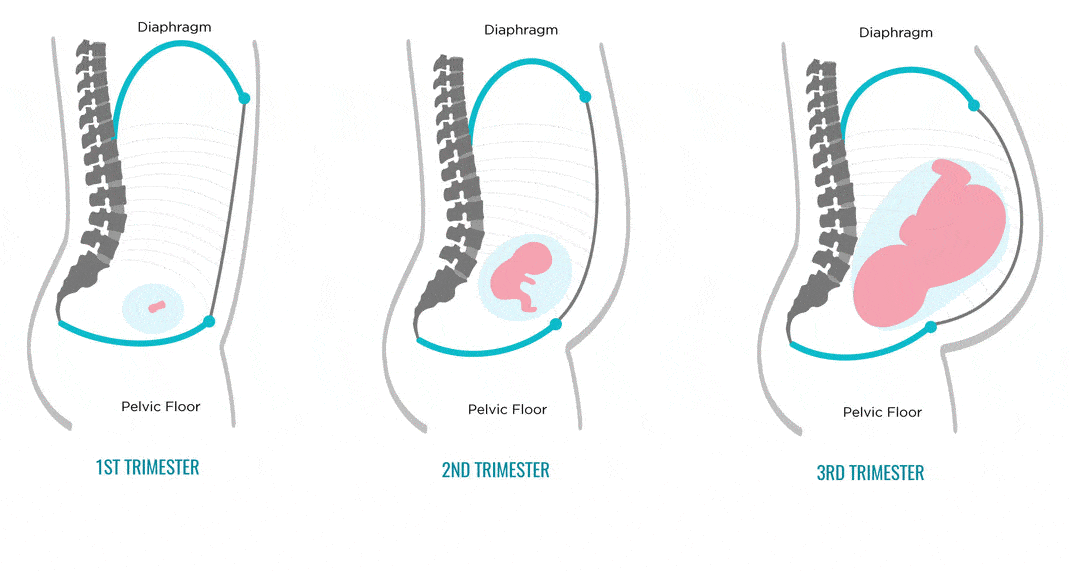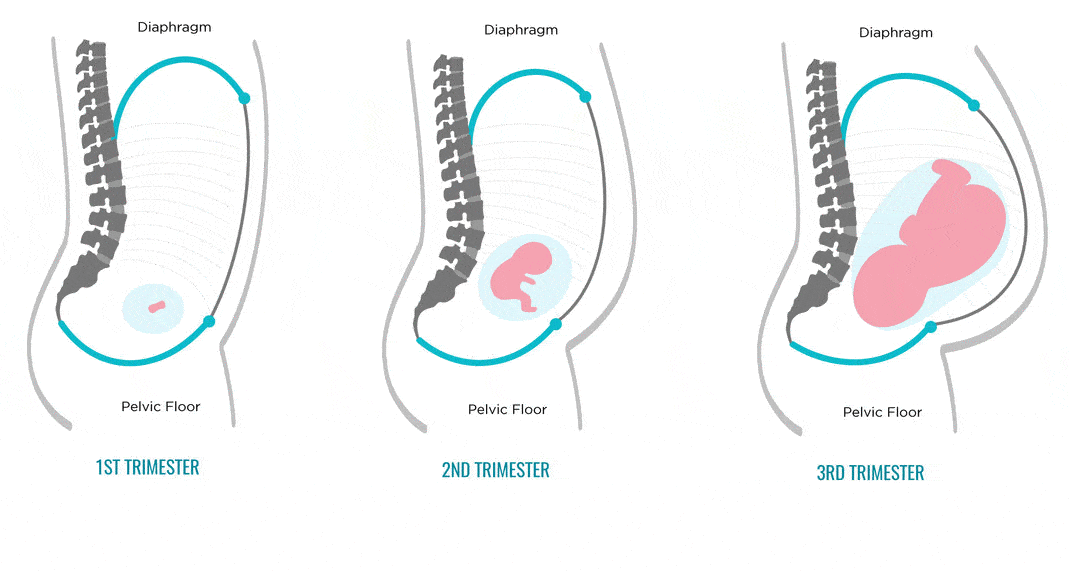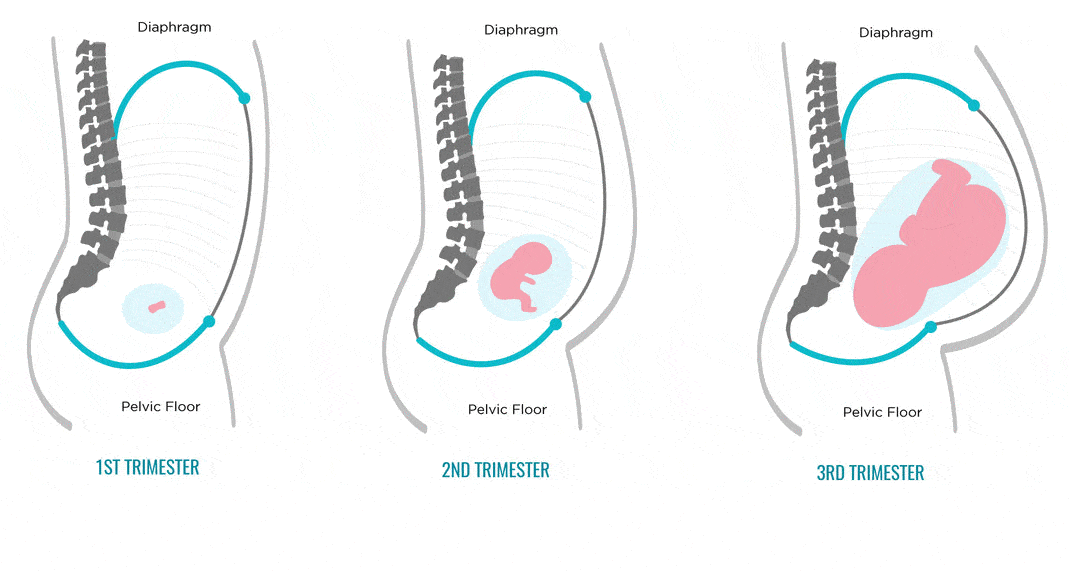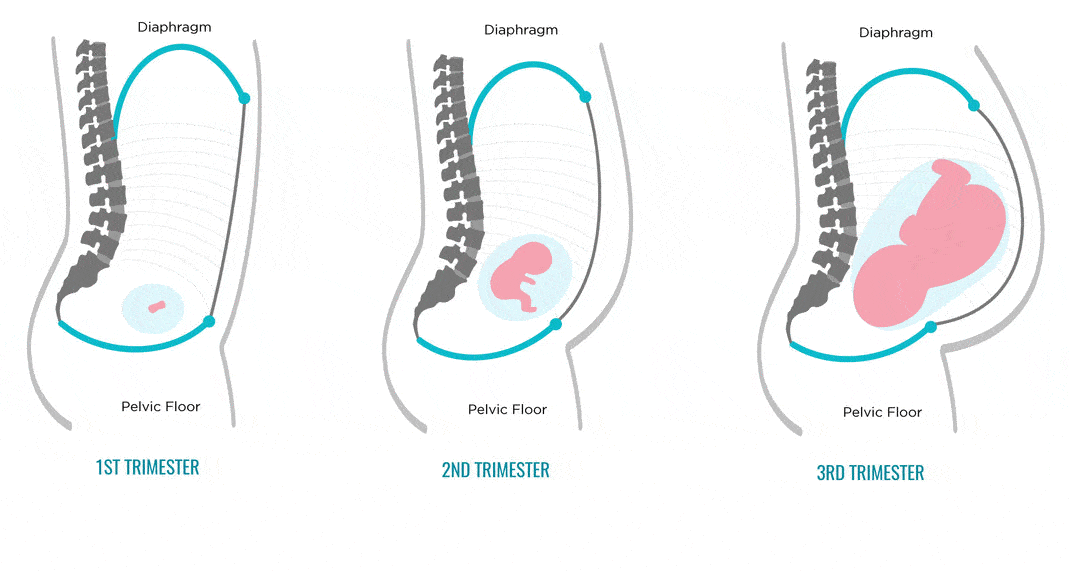 You'll probably also be feeling sore and tired.
You'll probably also be feeling sore and tired.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 25
As you are approaching the end of the second trimester, you might be starting to feel a bit uncomfortable as your baby continues to grow.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 26
Your baby is starting to put on fat and muscle and as your baby grows, your centre of gravity will shift, so you might find that you are starting to walk differently and maybe even a little clumsy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and your mental health - Better Health Channel
Finding out you are pregnant can be a very exciting time.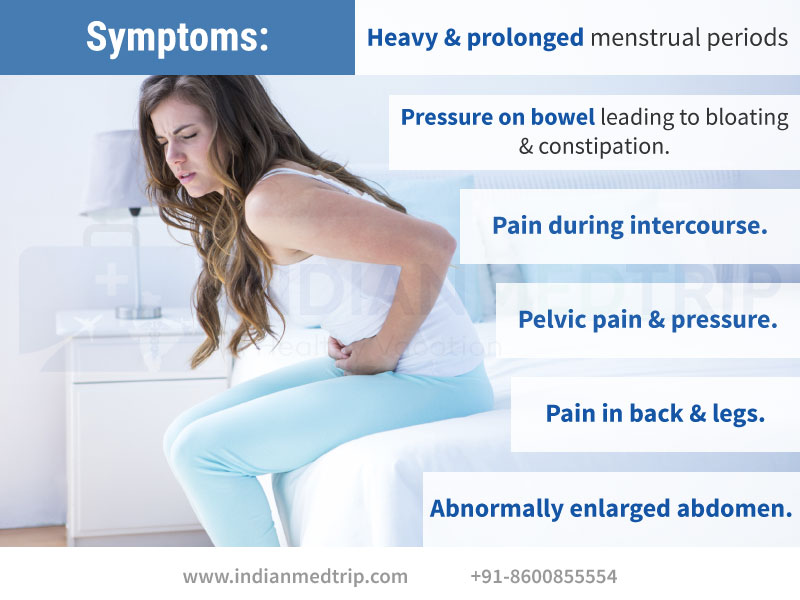 But it can also make you feel uncomfortable, unwell, worried and make you wonder how you are going to cope. And it doesn’t stop when the baby arrives. Some mums find it easy to adjust to life with a new baby. But others don’t!
But it can also make you feel uncomfortable, unwell, worried and make you wonder how you are going to cope. And it doesn’t stop when the baby arrives. Some mums find it easy to adjust to life with a new baby. But others don’t!
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Sclerotherapy - MyDr.com.au
Sclerotherapy is a treatment that involves the injection of a chemical solution into blood vessels, usually spider veins or superficial (surface) varicose veins on the legs.
Read more on myDr website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.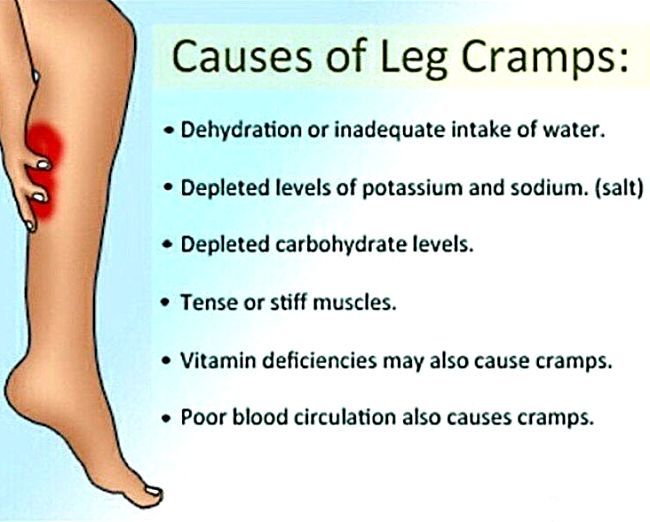
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Second trimester pains: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Although all pregnancies are different, certain symptoms tend to occur in each trimester. For some women, the second trimester means the end of morning sickness and fatigue, but it also means the onset of specific types of pain.
Pregnancy consists of three trimesters. The second trimester lasts from weeks 13 to 28.
The second trimester lasts from weeks 13 to 28.
In this article, learn what causes pain in the second trimester and how to find relief.
Second trimester pains are not uncommon, as the uterus and abdomen are expanding.
Increased pressure from a growing uterus, along with hormonal changes, can lead to various types of pain.
Some common causes of second trimester pains include:
Round ligament pain
Share on PinterestCommon causes of second trimester pains include round ligament pain and back pain.The round ligaments support the uterus and hold it in place. During pregnancy, the expanding uterus causes these ligaments to stretch.
Round ligament pain often starts as the belly grows in the second trimester.
Symptoms of round ligament pain include:
- a sharp or aching sensation, usually on one side of the belly
- pain that is more noticeable after exercise or when changing positions
- pain that may radiate to the groin or hip
Round ligament pain may last from a few seconds to several minutes.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
Braxton-Hicks contractions may start anytime in the second trimester of pregnancy. They involve the tightening of the uterus’ muscles.
These contractions differ from true labor in a few critical ways — they are brief and do not come at regular intervals.
Symptoms of Braxton-Hicks contractions include:
- squeezing or tightening of the uterus
- pain that occurs more frequently at night
- pain lasting anywhere from 30 seconds to 2 minutes
Braxton-Hicks contractions may be mild at first, but they can become more painful as pregnancy progresses.
Leg cramps
Leg cramps are a common cause of pain during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
They can develop when blood vessels or nerves in the legs are compressed. A lack of magnesium in the diet can also cause leg cramps.
Restless legs syndrome, which causes discomfort in the legs, can also occur during pregnancy.
Some research indicates that restless legs syndrome develops 2 to 3 times more often in pregnant women than the rest of the population.
Symptoms of leg cramps include:
- sudden pain in the calf or foot
- involuntary contractions of the muscles in the calf
- pain that may be worse at night
Symphysis pubis dysfunction
Symphysis pubis dysfunction, or pelvic girdle pain, may occur in about 31 percent of pregnant women.
The weight of the uterus can place extra stress on the pelvic joints, causing them to move unevenly.
Symphysis pubis dysfunction can also result from hormonal changes. During pregnancy, the body releases hormones that loosen and stretch certain ligaments in preparation for childbirth. These changes can contribute to pelvic pain.
Symptoms of symphysis pubis dysfunction include:
- pain in the center of the pubic bone
- pain radiating to the thighs or perineum (the area between the vagina and anus)
- difficulty walking
Back pain
Low back pain is one of the most common types to arise during pregnancy, and it often starts during the second trimester.
According to some research, about two-thirds of pregnant women develop low back pain.
Usually, it occurs because the growing abdomen is placing strain on the back muscles and causing changes in posture.
Symptoms of low back pain include:
- achy or dull pain in the lower back
- pain that worsens when bending forward
- stiffness in the back
Share on PinterestWomen who experience vaginal bleeding, vomiting, or fever during the second trimester should see a doctor.
Most common causes of second trimester pain do not require medical attention. However, pain at this stage of pregnancy can signify a problem, such as preterm labor, an infection, or another complication.
See a doctor if any of the following symptoms develop:
- contractions that occur at regular intervals
- vaginal pressure
- vaginal bleeding
- a severe headache
- sharp pain in the belly that persists, even after resting or changing positions
- vomiting, chills, or fever
- menstrual-like cramps that grow more severe over time
- fluid leaking from the vagina
Before using pain relievers during the second trimester, it is vital to speak to a doctor. Some pain medications are not safe to take during pregnancy.
Some pain medications are not safe to take during pregnancy.
Certain complementary therapies may help reduce low back or pelvic pain.
A study involving 191 pregnant women found that complementary therapies, including acupuncture, aromatherapy, and reflexology, reduced symptoms in 85 percent of the participants.
Before trying any of these approaches during pregnancy, it is essential to talk with a doctor.
Home remedies can usually relieve second trimester pain, and the best approach will depend on the type of pain.
The following strategies may help:
- taking a warm (not hot) bath
- doing some light stretching to ease stiffness
- using a heating pad on the lower back
- wearing a maternity support belt
- using chairs with good back support
- avoiding standing in one spot for too long
- sleeping on the right or left side with a pillow between the legs
- avoiding changing positions too fast
- resting
Many types of pain can arise in the second trimester, including round ligament pain, back pain, and pain that results from symphysis pubis dysfunction.
In most cases, the underlying cause is a common issue, and a person can treat it at home.
In some instances, pain during the second trimester is a sign of something more serious. It is always best to see a doctor if the pain does not improve or otherwise causes concern.
Interventions for leg cramps during pregnancy
What is the problem?
Leg cramps manifest themselves as sudden, intense involuntary contractions of the leg muscles. This is a common problem during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester. They are painful and can interfere with daily activities, disrupt sleep, and reduce quality of life. Various types of interventions are used to treat leg cramps during pregnancy, including medications, electrolytes (magnesium, calcium, sodium) and vitamins, as well as non-drug therapies such as muscle stretching.
Why is this important?
The aim of this review was to find out which treatment for leg cramps during pregnancy is effective and safe.
What evidence did we find?
In September 2019, we searched for evidence and identified eight randomized controlled trials in 576 women 14 to 36 weeks pregnant comparing magnesium, calcium, calcium with vitamin D or B vitamins versus placebo or no treatment, and compared vitamin C with calcium. All drugs were given as tablets to chew or swallow.
Magnesium supplements may reduce the incidence of leg cramps in women compared with placebo or no treatment, although studies have not been consistent. Different studies have assessed the effect of magnesium supplementation differently. Some studies have shown magnesium to help reduce the incidence of leg cramps, while others have shown little or no effect. Data on the effect of magnesium on pain reduction was also inconclusive, with only one study showing a reduction in pain intensity, while others showed no difference. Differences in the occurrence of side effects such as nausea and diarrhea were negligible or non-existent.
Differences in the occurrence of side effects such as nausea and diarrhea were negligible or non-existent.
Calcium did not always reduce the incidence of leg cramps in women after treatment compared to those who did not receive any treatment. It also found that the evidence was of very low quality, so we cannot be sure of the results.
More women who received B-vitamin supplements made a full recovery compared to those who received no treatment; however, these results were based on a small sample size and the study had design limitations.
Frequency of leg cramps did not differ between women receiving calcium and women receiving vitamin C. with placebo.
What does this mean?
The quality of the evidence was low to very low. This was mainly due to small study sample sizes and study design weaknesses. Four studies were well-conducted and presented their reports. The remaining four had flaws in their design: in several studies, women were not best assigned to different treatment groups, and in two studies, women knew whether they were receiving treatment or not.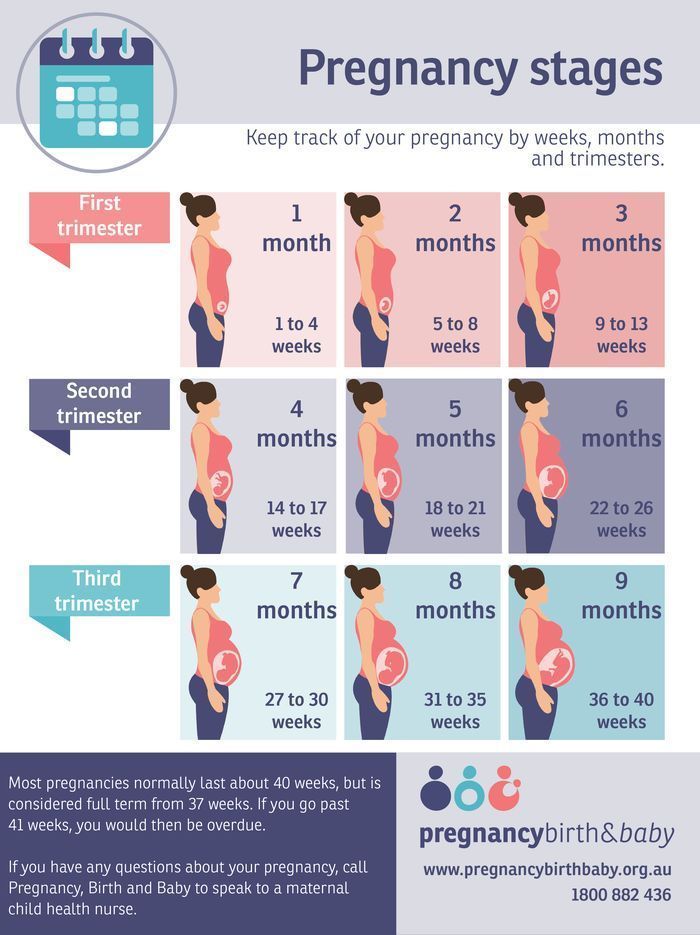 Adverse effects, such as the effect of treatment on complications of pregnancy, childbirth and child, were not reported. Several studies have focused primarily on serum calcium and magnesium levels. The frequency and intensity of seizures and duration of pain were not uniformly reported, and there was often no information on whether they were assessed during treatment, at the end of treatment, or after treatment was discontinued.
Adverse effects, such as the effect of treatment on complications of pregnancy, childbirth and child, were not reported. Several studies have focused primarily on serum calcium and magnesium levels. The frequency and intensity of seizures and duration of pain were not uniformly reported, and there was often no information on whether they were assessed during treatment, at the end of treatment, or after treatment was discontinued.
It is not clear from the evidence reviewed whether any oral interventions (magnesium, calcium, calcium with vitamin D, B vitamins, vitamin D, or vitamin C) are an effective and safe treatment for leg cramps during pregnancy. Supplements can have different effects depending on how women usually take them. None of the trials looked at forms of treatment such as muscle stretching, massage, relaxation, or heat therapy.
Translation notes:
Translation: Luzan Maria Alexandrovna. Editing: Yudina Ekaterina Viktorovna. Russian translation project coordination: Cochrane Russia - Cochrane Russia, Cochrane Geographic Group Associated to Cochrane Nordic. For questions related to this transfer, please contact us at: [email protected]
For questions related to this transfer, please contact us at: [email protected]
Reduces legs during pregnancy: what to do?
Pregnancy is a time of waiting and doubts. Probably, women never have so many questions. Why does it bring her legs together so often? What to do if you wake up with cramps at night? How to deal with this scourge and avoid bouts of pain in the legs? We are looking for answers to these and other questions.
What are seizures?
Legs cramps not only during pregnancy, from time to time every person faces unpleasant painful cramps. A cramp is a sudden, uncontrollable muscle contraction that a person cannot relax. This condition can be caused by neurological disorders (for example, seizures are characteristic of epilepsy), a number of diseases (such as diabetes mellitus, osteochondrosis, and others), and can also be associated with physiological conditions. After all, convulsions occur, for example, after a strong overload, dehydration, hypothermia, etc.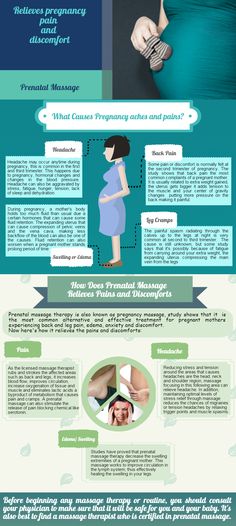 Sometimes cramps cause severe sharp pain. Sometimes it seems that the legs are pulling. During pregnancy, this condition, unfortunately, is noted quite regularly.
Sometimes cramps cause severe sharp pain. Sometimes it seems that the legs are pulling. During pregnancy, this condition, unfortunately, is noted quite regularly.
Why do pregnant women cramp their legs?
The mechanism of muscle contraction is quite complex, it involves different ions (charged particles): potassium, calcium, sodium and magnesium. If we are talking about a cramp, that is, a condition when we cannot relax a muscle, then magnesium ions play a leading role here. It is their lack that leads to the fact that women cramp their calves during pregnancy at night.
The lack of minerals in the body of the expectant mother is simply explained: such consequences are the restructuring of metabolism and functioning in the "double load" mode. In particular, the expectant mother needs one and a half times more magnesium than usual.
In addition to helping muscles relax, magnesium is also involved in a number of important physiological processes.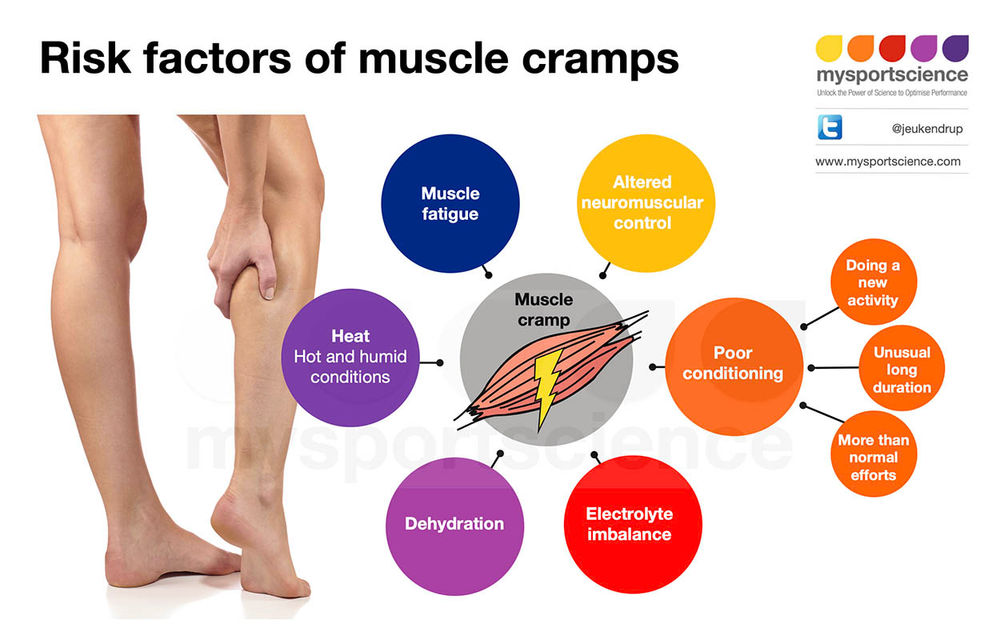 In particular, magnesium is needed to regulate the processes of formation and expenditure of energy, it is involved in several hundred enzymatic reactions, and if there is little magnesium, then disturbances can occur in the work of almost any body system. Therefore, if magnesium preparations are prescribed during pregnancy, this recommendation should not be ignored.
In particular, magnesium is needed to regulate the processes of formation and expenditure of energy, it is involved in several hundred enzymatic reactions, and if there is little magnesium, then disturbances can occur in the work of almost any body system. Therefore, if magnesium preparations are prescribed during pregnancy, this recommendation should not be ignored.
Why do pregnant women cramp their legs at night?
The answer to this question is very simple. The fact is that during the day the body of the expectant mother bears an increased load. And the longer the gestation period, the greater this load. Violation of blood circulation, increased stress on the muscles - all this can cause night cramps.
What should I do if my legs cramp during pregnancy?
To begin with, tell the doctor you are seeing about this. The magnesium preparations already mentioned, which he most likely recommends to you, can help solve the problem.
However, the reason that the expectant mother cramps her legs during pregnancy may be not only a metabolic disorder. Often muscle spasms begin as a result of varicose veins - the "faithful" companion of pregnancy. The veins of a woman carrying a baby are subject to increased stress. In addition, hormonal changes in the body seriously affect the state of blood vessels. All this contributes to the development of varicose veins. And a violation of the blood supply to the muscles of the legs, in turn, leads to convulsions.
Often muscle spasms begin as a result of varicose veins - the "faithful" companion of pregnancy. The veins of a woman carrying a baby are subject to increased stress. In addition, hormonal changes in the body seriously affect the state of blood vessels. All this contributes to the development of varicose veins. And a violation of the blood supply to the muscles of the legs, in turn, leads to convulsions.
If the expectant mother is faced with varicose veins, then the best prevention of its progression is to wear compression stockings selected by the doctor in accordance with the gestational age. You also need to give birth in stockings, so that during a particularly intense load on the veins to avoid worsening their condition.
It is important to remember that any discomfort in the well-being of a pregnant woman must be discussed with the doctor who is seeing the expectant mother. Even if the legs cramp infrequently, what to do during pregnancy should be determined by a specialist.