Labia swelling in pregnancy
Swollen labia: Why it happens during pregnancy and postpartum
Many women experience swollen labia during pregnancy because of the increased blood flow to the area; some women even develop blue or purple veins on their labia, also known as vulvar varicosities, due to the growing uterus compressing the veins in the pelvis. There’s not much you can do to prevent swollen labia, but you can find relief by avoiding sitting or standing for long periods of time.
Labia swelling: What does it mean?
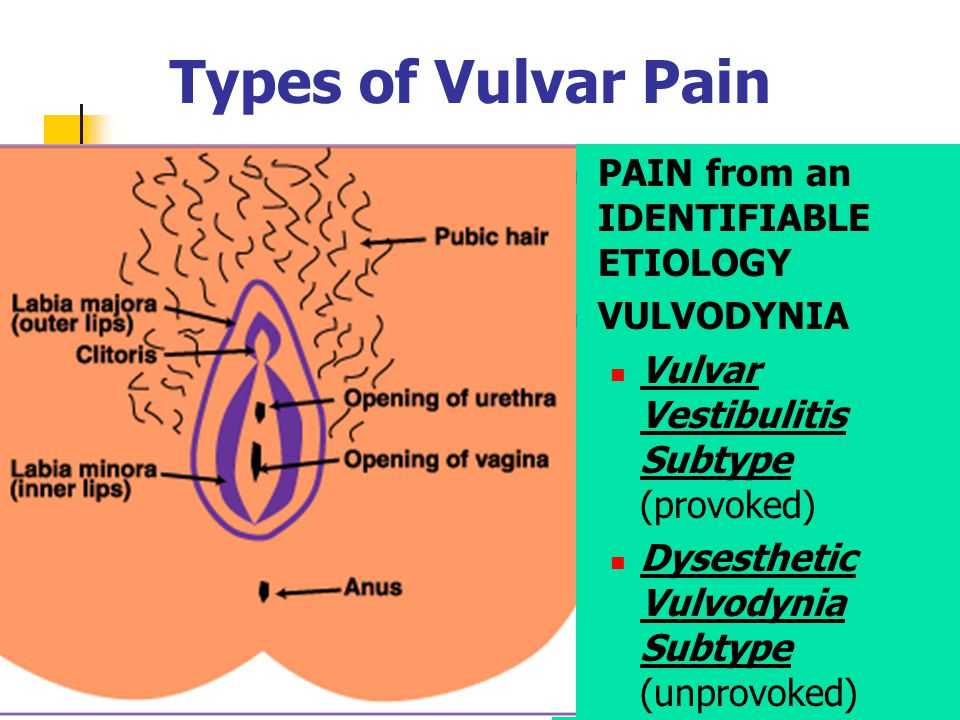
Some women find that their labia – the lips that surround the opening of the vagina – feel swollen during pregnancy. FYI, the labia has two folds of skin: The outer folds are called the labia majora and the inner folds are the labia minora. The area may not look very swollen, but it may feel full, irritated, or even itchy. The skin of your labia may also appear darker.
All of your external genitalia – including labia, vaginal opening, urethral opening, and clitoris – are known as the vulva. The changes to your vulva during pregnancy are due to increased blood flow to the area from the demands of your growing uterus and baby.
Is it normal to have swollen labia during pregnancy?
Having swollen labia during pregnancy may start as early as your first trimester and may grow more intense as your pregnancy progresses. This could be because your uterus and baby are getting larger and applying more pressure to the area. And you may feel more pressure late in pregnancy when your baby "drops." This happens when the baby's head moves lower into the pelvis in preparation for labor.
You may also notice blue or purple veins on your swollen labia minora or majora. These varicose veins (known as vulvar varicosities) are caused by your growing uterus compressing the veins in your pelvis and increasing the pressure inside them. Changes in pregnancy hormones also cause your veins to widen and relax, allowing them to swell.
What's more, the increase in your blood volume during pregnancy limits how quickly your blood returns from your lower body to your heart. The result is that blood accumulates in the veins of your legs and vulva, causing them to bulge.
The result is that blood accumulates in the veins of your legs and vulva, causing them to bulge.
You may notice that your symptoms are worse after standing, exercise, or sex. If you develop varicose veins in your labia during pregnancy, they tend to go away within six weeks after delivery.
However, if you have swollen labia minora with a lump, it could be a sign of a vaginal boil or Bartholin's cyst. This might also be an explanation for why there is swelling on one side of your labia. A Bartholin cyst forms when fluid gets stuck in your Bartholin's glands, which are on either side of your vulva. If the fluid in the Bartholin's cyst gets infected, you may develop pus around the area.
Pus around a small bump on your vulva can also be a vaginal boil, which you can develop from an infected hair follicle or an injury, like a cut from shaving. Vaginal boils look like small, red bumps that are swollen and painful. while a Bartholin cyst is painless, if the cyst gets infected, it will become very painful. Bartholin cysts usually go away on their own, but you can talk to your doctor about trying some at-home remedies, like a sitz bath. If you have a Bartholin cyst that becomes infected or a vaginal boil, you'll likely need antibiotics that your doctor can prescribe.
Bartholin cysts usually go away on their own, but you can talk to your doctor about trying some at-home remedies, like a sitz bath. If you have a Bartholin cyst that becomes infected or a vaginal boil, you'll likely need antibiotics that your doctor can prescribe.
Either way, if you develop swollen labia during pregnancy, you should bring it up to your doctor to make sure it isn't a more serious issue; it will also put your mind at ease about any other changes to your vagina.
Advertisement | page continues below
How can I get relief from swollen labia during pregnancy and beyond?
While there's not much you can do to prevent swollen labia during pregnancy, you can find some relief from the discomfort by trying the following tips:
- Change position frequently. Avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Put your feet up. Elevate your legs above your heart (prop them on pillows) while lying down to help promote circulation.

- Use cold compresses. Apply a cold pack covered in a cloth to your vulva to ease your discomfort.
- Use a support garment. Look for a compression band, support strap, or underwear designed for vulvar varicosities. Some also provide support for the lower abdomen and lower back.
Will I continue to experience swollen labia postpartum?
It's common for your labia to be swollen and sore after a vaginal birth. The miraculous process of giving birth does tend to traumatize the tissues in the vaginal area. Fortunately, your body's ability to heal is equally miraculous.
The tender treatment you're probably already giving your perineum – ice packs for the first 12 to 24 hours and warm, soothing sitz baths after that – will do wonders for your labia, too.
The amount of time it takes the swelling to go down depends on the cause of the swelling. Bartholin cysts rarely go away, while swelling due to fluid retention or varicose veins usually gest better within days or weeks of giving birth. And two weeks postpartum, you should definitely be on the mend. If you haven't noticed significant improvement by then, ask your health provider about it. (For more details on postpartum care for the vaginal area, see our article on caring for a sore perineum.)
And two weeks postpartum, you should definitely be on the mend. If you haven't noticed significant improvement by then, ask your health provider about it. (For more details on postpartum care for the vaginal area, see our article on caring for a sore perineum.)
Should I ever be concerned about swollen labia?
If you develop swollen labia postpartum, it's usually nothing to worry about and will heal on its own. However, you should still bring it up with your provider so they can keep a close eye on the area.
If you aren't pregnant and develop swollen labia, it could be a symptom of vulvitis, or inflammation of the vulva. Pinpointing what causes vulvitis can be difficult, but using vaginal sprays and deodorants and douching are common triggers. In addition to swelling, you may experience extreme itchiness, redness, clear, fluid-filled blisters, and scaly patches of skin. Because these symptoms are commonly shared with other vaginal issues, like bacterial vaginosis and a yeast infection, see your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Learn more:
- 12 icky pregnancy side effects
- Pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
How to Ease Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
Swelling is a common side effect of pregnancy, especially when it comes to your feet and hands. But there’s one area that can also swell during pregnancy that doesn’t get a lot of attention: Your vagina. If you notice you have a swollen vagina during pregnancy, know you’re not the only woman going through this! Still, we’re guessing you might have questions about why this is happening. Here’s what you need to know, plus how to minimize the swelling and ease any discomfort.
In this article:
Symptoms of vaginal swelling during pregnancy
What causes vaginal swelling during pregnancy?
How to reduce vaginal swelling during pregnancy
How to prevent vaginal swelling during pregnancy
Symptoms of Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
Every woman and every pregnancy is different—which means the symptoms of vaginal swelling during pregnancy can differ from person to person. In general, though, you might experience the following:
In general, though, you might experience the following:
• Noticeable swelling. You’re probably familiar on at least some level with what your vulva and vaginal area usually feels like. If it’s swollen, it can feel noticeably bigger or puffier, says Frederick Friedman, Jr., MD, associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. “There may just be a general feeling of swelling or fullness in the vaginal area,” adds Julie Lamppa, APRN, CNM, a certified nurse midwife at Mayo Clinic, which can lead to overall discomfort.
• Bumps. Some women who experience vaginal swelling during pregnancy can have varicose veins surface in their vulvar area, which can cause swelling and a bumpy feel down there, Lamppa says.
• Itchiness. This isn’t the case for every woman, but itchiness can sometimes accompany vaginal swelling, Lamppa says.
What Causes Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy?
There are several reasons why you might develop vaginal swelling in pregnancy. Here are some of the most common ones:
Here are some of the most common ones:
• An increase in blood volume. Your blood volume increases during pregnancy to help support the growing baby. As your uterus grows, there’s also an increase in pressure of the blood vessels in your pelvis, Lamppa explains. The combination of these two things can lead to swelling.
• Varicose veins in your vulva. Varicose veins are swollen, bumpy veins that develop when valves let blood pool in one spot or flow backward. Just like you can develop varicose veins in your legs, you can also develop these in your vulva during pregnancy, Lamppa says. “These aren’t dangerous, but they can be alarming to women when they suddenly show up.”
• A yeast infection. Yeast infections are common among moms-to-be, and they can also lead to a swollen vagina during pregnancy, Friedman says. “The inflammation that results from the infection can cause more swelling,” he explains.
• Excess fluid. Excess fluid can get trapped in your body’s tissues during pregnancy, and that can cause swelling down there, Friedman says.
Excess fluid can get trapped in your body’s tissues during pregnancy, and that can cause swelling down there, Friedman says.
How to Reduce Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
If you suspect that your vaginal swelling is due to excess fluid, compression or support stockings might help. “There are products on the market that you can buy that give vulvar support,” Lamppa says. (Just check in with your doctor first to make sure it’s okay for you to use.)
For direct relief, Lamppa recommends applying a cool pack directly to your vulva. That should help with discomfort as well as cut down on some of the swelling.
If you’re experiencing vaginal swelling along with symptoms of a yeast infection—such as an itchy vaginal area during pregnancy, accompanied by white vaginal discharge—Lamppa recommends seeing your doctor for an evaluation. If they determine that you do, in fact, have a yeast infection, your care provider will likely recommend that you use an over-the-counter cream.
How to Prevent Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
Sorry, but there isn’t a ton you can do to lower the odds you’ll experience vaginal swelling during pregnancy, given that it’s a normal side effect of being pregnant, Lamppa says. However, doing your best to avoid sitting or standing for long periods of time may be helpful, Friedman suggests.
While it’s pretty common, it’s a good idea to flag any vaginal swelling during pregnancy for your care provider so they can help pinpoint the cause and get you sweet relief ASAP.
Updated January 2020
Expert bios:
Frederick Friedman, Jr., MD, is an associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. He also serves as director for both the division of obstetrics and the division of generalists in the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science at the Mount Sinai Health System, and maintains a clinical practice in general obstetrics and gynecology.
Julie Lamppa, APRN, CNM, is a certified nurse midwife and medical editor at Mayo Clinic, and maintains a midwifery practice in Rochester, New York.
*Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances. *
Plus, more from The Bump:
Swelling in Pregnancy: Why It Happens and How to Deal
How Your Vaginal Discharge Can Change During Pregnancy
10 Surprising Pregnancy Symptoms No One Warned You About
possible causes, therapy and prevention
The female body changes during pregnancy, often all hidden diseases make themselves felt, manifesting themselves immediately or over time.
The genitals change during pregnancy due to the enlargement of the uterus, very often there is discomfort, pain in the genitals. During this period, immunity decreases, and therefore swelling of the labia may be due to genital infections, such as bartholinitis or vulvovaginitis.
During this period, immunity decreases, and therefore swelling of the labia may be due to genital infections, such as bartholinitis or vulvovaginitis.
Pregnancy edema
During the first weeks of pregnancy, physical changes to the outer genitalia are considered normal, including discoloration and slight swelling. Changing the color of the labia and a little itching is a natural process that occurs in all women. In the case when the lips bleed, discharge and severe swelling appear, this will serve as a reason to consult a specialist, because this is not normal.
How does the vagina change during pregnancy?
Today we will talk about how the vagina changes during pregnancy and after childbirth. Except...
Candidiasis
Itching along with swelling may be due to infection. Almost all pregnant women have one disease - candidiasis (thrush). Symptoms of illness:
- white discharge, similar to milk;
- vaginal mucosa swells;
- there is itching in the perineum and pain.

Gardnerellosis
Another reason for swelling of the labia is the defeat of Gardnerella bacteria. Infection occurs through sexual contact with a carrier of the pathogen. As a result, the disease gardnerellosis is formed. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:0003
- very severe itching of the labia;
- dry mucous;
- swelling of the outer part of the vulva;
- pain in the perineum that is aggravated by walking, intercourse, exercise;
- The discharge becomes larger and greenish or gray in color.
Genital herpes
Swelling of the labia, on which bubbles with liquid appear, which do not disappear up to 7 days, we can talk about genital herpes. A woman may feel weakness, itching on the genitals, an increase in body temperature. nine0003
Vaginal redness: possible causes and treatment
An alarming sign in women is redness of the external genitalia. Such a state in...
Sometimes, when a disease appears, a person does not even suspect about it. The main symptom by which the disease is determined is rash. They can be found on the walls of the vagina, labia and cervix. This ailment is especially dangerous for the unborn child, often, if herpes appeared for the first time, doctors insist on an abortion. Another reason for the development of the disease is a decrease in immunity, at which point herpes worsens. With a neglected degree, the development of the child is disturbed, deviations in physical development occur, defects in the central nervous system and brain, often this causes fetal loss. Rashes and symptoms go away on their own after a couple of weeks, but you can’t do nothing, you need to urgently contact a gynecologist at the first sign of herpes. nine0003
The main symptom by which the disease is determined is rash. They can be found on the walls of the vagina, labia and cervix. This ailment is especially dangerous for the unborn child, often, if herpes appeared for the first time, doctors insist on an abortion. Another reason for the development of the disease is a decrease in immunity, at which point herpes worsens. With a neglected degree, the development of the child is disturbed, deviations in physical development occur, defects in the central nervous system and brain, often this causes fetal loss. Rashes and symptoms go away on their own after a couple of weeks, but you can’t do nothing, you need to urgently contact a gynecologist at the first sign of herpes. nine0003
Bartholinitis
There are cases when edema appears only on one side and is accompanied by acute painful manifestations in the perineum. Such symptoms appear when infected with bartholinitis. In the presence of this disease, the glands that are responsible for the production of vaginal lubrication become clogged. Bartholin's glands are a paired organ located in the thickness of the labia majora. Symptoms of the disease:
Bartholin's glands are a paired organ located in the thickness of the labia majora. Symptoms of the disease:
Enlargement of the labia: features, causes and possible...
Main causes of labia enlargement: pregnancy, sexual intercourse, candidiasis, inflammatory...
- pain in surrounding tissues;
- swelling of the labia;
- mucosal redness;
- constant pain.
During pregnancy, swelling of the labia appears due to a decrease in immunity. It can be provoked by:
- E. coli;
- staphylococci and streptococci;
- specific microorganisms;
- pathogenic bacteria.
In the later weeks of pregnancy, swelling occurs due to varicose veins of the labia. This happens because the veins in the labia expand.
Diagnosis
Due to the fact that the causes of the appearance of the main symptom are quite diverse, it is not possible to establish a correct diagnosis based on symptoms alone. Patients are shown laboratory and instrumental examinations, before prescribing which the clinician should:
Patients are shown laboratory and instrumental examinations, before prescribing which the clinician should:
- Interrogate the patient in detail about the first time of the appearance of labia edema during pregnancy and the nature of the expression, both the main symptom and additional ones;
- study the patient's medical history and life history;
- perform a gynecological examination and assess the condition of the skin of the labia to reveal what symptoms are accompanied by swelling.
How to treat the labia?
Immediately before treatment, the cause of the disease is established, after which they proceed to the therapy procedure. It happens according to the following criteria:0003
- Infections appear due to a violation of personal hygiene, first you need to determine the cause of the pathogen, and only then proceed to the antibiotic treatment itself. Candidiasis is often treated with Fluconazole and Clotrimazole at the same time (ointments, suppositories and orally).
 The genital herpes virus is treated with drugs based on acyclovir. But it is contraindicated a month before childbirth and in the first 3-4 months after conception.
The genital herpes virus is treated with drugs based on acyclovir. But it is contraindicated a month before childbirth and in the first 3-4 months after conception. - Very often swollen labia during pregnancy appear after intercourse, in which case it will go away on its own. nine0021
- There are cases when edema occurs before critical days and PMS, in this case, treatment is not required, since everything will go away by itself.
- Maternity underwear is recommended. What is its beauty? Since the cause may be the impact on the female organs of poor quality material, such underwear for pregnant women is made from natural fabrics, it will not irritate delicate areas.
- In case of diabetes, treatment is prohibited, except perhaps with insulin. The most effective solution is to carry out the washing procedure with warm and cool water alternately on an ongoing basis. It is very useful to wipe the intimate parts of the body with a weak solution of citric acid or vinegar: half a teaspoon in a glass of water.
 You need to wash it several times a day. This procedure will help restore the acid balance. nine0021
You need to wash it several times a day. This procedure will help restore the acid balance. nine0021 - Very often, swelling of the labia during pregnancy disappears on its own after childbirth. It is believed that edema cannot be treated during pregnancy, because most types of therapy to remove fluid from the body harm the baby much more than the edema itself. Many experts recommend switching to melted, soft, structured water like "Longavity".
- Vulvovaginitis is treated by a doctor. It consists in taking antifungal drugs, hormone replacements, antibiotics. It is also necessary to carry out douching with acceptable, prescribed drugs. During the treatment of labia edema during pregnancy, the vaginal microflora is restored by applying probiotics, eliminating allergens and other factors that act as irritants. nine0021
- Bed rest and abstinence from sexual activity are recommended for bartholinitis. If the labia is swollen, only a doctor prescribes treatment. With severe pain, it is allowed to apply ice to the inflamed area.
 The following drugs are also allowed: imidazoles, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, penicillins. It is necessary to treat swollen places with a special ointment and apply small compresses with Levomikol or ichthyol ointment. It is allowed to use a solution with chlorhexidine or miramistin for swelling of the labia during pregnancy. nine0021
The following drugs are also allowed: imidazoles, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, penicillins. It is necessary to treat swollen places with a special ointment and apply small compresses with Levomikol or ichthyol ointment. It is allowed to use a solution with chlorhexidine or miramistin for swelling of the labia during pregnancy. nine0021
Prevention
Preventive measures are as follows:
- If the labia is swollen, promiscuity and unfinished sex should be avoided.
- Wear only good quality underwear made from natural material so that it is of a normal size.
- Daily personal hygiene with special products, do not use bath foam and shower gel.
- Use panty liners for genital swelling. nine0021
- Do not wear thermal underwear.
- Maintain good hygiene. After using the toilet, wipe from front to back to keep the genital area clean and dry.
- The vaginal area should be moistened with a cream containing glycerin and non-allergic lubricants.

Changes in a woman's body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. nine0003
During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity. nine0003
nine0003
Cardio The mother's vascular system has to pump more blood during pregnancy to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of the blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for enhanced
to supply tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), craving for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur. nine0003
In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur. nine0003
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. nine0003
nine0003
The walls of the vagina loosen and become more elastic.
External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth. nine0003
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released. Changes of the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This accomplishes two goals. On the one hand, this helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the pelvic bones (especially the pubic joint) and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Secondly, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
Changes of the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This accomplishes two goals. On the one hand, this helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the pelvic bones (especially the pubic joint) and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Secondly, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Conclusion. nine0149 Summarizing the facts concerning changes in a woman's body during pregnancy, it is worth emphasizing that these changes reflect the processes of physiological adaptation of the mother's body to the process of intrauterine development of the fetus.