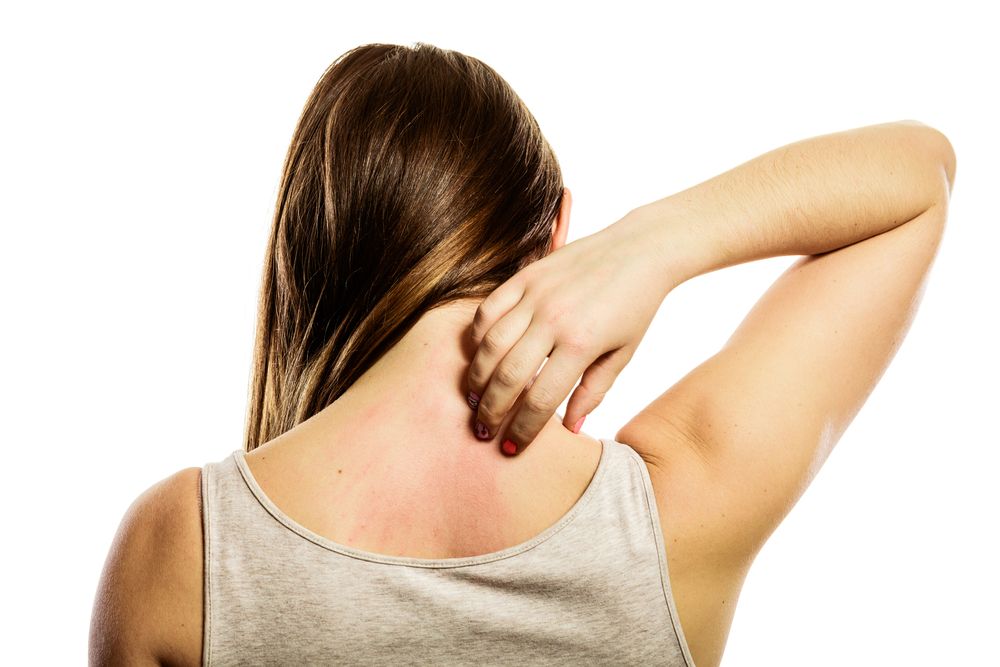
Itchy rash back of neck
Eczema on the neck: Symptoms, treatment, and prevention
A person who notices an itchy rash on their neck may have eczema. Eczema refers to a group of skin conditions that can often appear on the face and neck.
Two examples of eczema that can affect the neck are atopic dermatitis (AD) and contact dermatitis (CD).
This article discusses what eczema is, how it presents on the neck, and the symptoms of eczema on the neck. It also takes a look at how to treat and prevent eczema symptoms.
Eczema refers to a group of conditions that cause itchy and irritated rashes.
Eczema can affect people of all ages, and symptoms can range from very mild to severe. It can affect many areas of the skin, including the skin on the neck.
AD and CD are two common types of eczema.
AD is a skin condition that can develop at any age. It causes itchy rashes and can appear on any area of the skin. However, according to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, it is more likely to appear on the neck in children ages 2 years and older.
CD occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. CD usually develops on the face and neck, as well as the underarms, scalp, and the tops of the feet.
The group of conditions is very common. Over 31 million people in the United States have some type of eczema.
Eczema symptoms may vary from person to person in severity and presentation.
Those who develop CD on the neck may experience:
- itchy skin
- tender skin
- a rash
- a burning or stinging sensation
- fluid-filled blisters that may ooze or leave crusts and scales
- excessively dry skin
If AD appears on the neck, a person may experience an itchy patch of skin. Scratching it can lead to a rash, which will appear red on light skin and dark brown, purple, or gray on dark skin. The skin can become sore and ooze, and weep fluid and blood if a person scratches it.
Over time, scratching can cause the skin to thicken.
Most people find eczema will be mild to moderately itchy. However, some people may find the itching to be intense. They may notice their symptoms vary in intensity, lessening and worsening at different times.
However, some people may find the itching to be intense. They may notice their symptoms vary in intensity, lessening and worsening at different times.
Eczema and psoriasis are both skin conditions that can cause dry, thick, and patchy areas of skin.
Psoriasis has well-defined, thick, scaly patches of skin and tends to occur on areas such as the elbows and knees. It can also occur on the face, buttocks, and scalp.
On white skin, psoriasis appears red or pink. On black skin, it can appear violet, gray, or dark brown. Psoriasis is generally mildly itchy.
Eczema rashes may not be as well defined and often have round blotches. They can range in color from red to brownish-gray.
A dermatologist will be able to properly diagnose eczema or psoriasis.
A person can develop CD due to an irritant or allergen. This can include skin-care products and fragrances.
CD can appear wherever a person has applied the allergen. For example, applying perfume on the neck can lead to a CD rash appearing in the same area.
Examples of irritants that can lead to CD on the neck include:
- detergents
- skin creams and lotions
- soaps
- perfumes
- jewelry containing metals such as nickel
Researchers do not know exactly what causes AD, but studies show that there is a genetic component.
Some people with AD have a mutation of the gene that makes a protein responsible for maintaining a protective outer layer on the skin.
When a person’s body does not produce enough of this protein, the skin’s barrier will allow moisture to escape more easily, making the skin more vulnerable to irritants, viruses, and bacteria.
Additionally, a person may be more likely to develop AD when they have a family history of eczema, other skin conditions, or allergies.
A person with eczema may also have an overactive immune system. When someone with eczema encounters a common trigger inside or outside their body, it can result in inflammation. This inflammation causes itching and rashes.
A doctor can examine a person’s skin during a flare to diagnose eczema on the neck.
During diagnosis, a doctor may ask a person or caregiver about related symptoms and discuss the person’s medical history.
If a doctor suspects allergies may be the cause, they may recommend allergy testing.
If the cause is CD, a person should avoid the irritant. The rash should disappear without treatment over time.
In the meantime, a person can do the following to help relieve any itching:
- Apply a cool compress.
- Apply calamine lotion or take colloidal oatmeal baths.
- Apply and take any medication a dermatologist prescribes.
People should also avoid applying cosmetics, creams, or makeup.
While there is no cure for AD, treatments are available to help manage and reduce the symptoms.
Treatments vary from person to person based on age and the severity of the symptoms. Treatment options include:
- prescription and over-the-counter creams and ointments, such as corticosteroids
- oral medications, including biologics and immunosuppressants
- phototherapy
A person should talk to a doctor to determine the best course of treatment.
Home treatment
To help ease the symptoms of eczema on the neck at home, a person can try the following:
- Moisturize after bathing.
- Choose skin-care products that are fragrance-free.
- Use lukewarm water for bathing.
- Use detergents that are fragrance-free.
- Wash new clothes before wearing them.
Learn more about the top 12 natural remedies for eczema here.
Prevention is a large part of treating eczema flares.
The most important step a person can take to prevent a flare is moisturizing their skin daily.
When eczema appears on the neck, a person should look for substances that come into contact with the skin in that area to identify the triggers.
In addition to avoiding outside triggers, managing stress and working with a doctor to find a gentle, moisturizing skin-care routine can also help prevent flares.
People with eczema are at increased risk for bacterial or viral skin infections.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases notes that 60–90% of people with eczema have a bacteria on their skin called Staphylococcus aureus. Many of them will develop a staph infection.
Many of them will develop a staph infection.
A person can avoid scratching and keep the skin well moisturized to lower their risk of developing a skin infection. These steps can prevent the skin from cracking and bleeding.
Additionally, a person with AD has an increased risk of developing a severe infection as a result of the smallpox vaccine and should not receive it.
A person with eczema should work with a dermatologist to develop a care plan to manage their symptoms. They should contact a doctor if they notice any new or worsening symptoms or changes in their skin.
Anyone with eczema should contact their doctor immediately if they notice any signs of skin infection, including:
- an area of swollen, painful skin
- skin that is warm to the touch
- areas of the skin that have drainage or pus
A fever and general feeling of discomfort may accompany the above symptoms.
Eczema is a common group of skin conditions characterized by areas of dry, itchy skin with a rash-like appearance.
CD and AD are two types of eczema that can affect the neck.
There is no cure for eczema, but medical treatment, a good skin-care routine, and lifestyle changes can help a person avoid flares.
Itchy Neck: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Itchy Neck: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentMedically reviewed by Elaine K. Luo, M.D. — By Scott Frothingham — Updated on March 7, 2019
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Itchy neck causes
An itchy neck rash can result from a number of causes, including:
Hygiene
- improper washing, either not enough or too much
Environment
- overexposure to sun and weather
- heating and cooling systems that reduce humidity
Irritation
- clothing such as wool or polyester
- chemicals
- soaps and detergents
Allergic reactions
- food
- cosmetics
- metals such as nickel
- plants such as to poison ivy
Skin conditions
- eczema
- psoriasis
- scabies
- hives
Nerve disorders
- diabetes
- multiple sclerosis
- shingles
Other conditions
- thyroid problems
- iron deficiency anemia
- liver disease
When your neck itches, additional symptoms — localized to your neck area — could include:
- redness
- warmth
- swelling
- rash, spots, bumps, or blisters
- pain
- dry skin
Some symptoms may mean you should see your doctor. These include if your itch:
These include if your itch:
- doesn’t respond to self-care and lasts for more than 10 days
- interrupts your sleep or your daily routines
- spreads or affects the entire body
It’s also time to call your doctor if your itchy neck is just one of a number of symptoms including:
- fever
- fatigue
- weight loss
- headache
- sore throat
- chills
- sweating
- shortness of breath
- joint stiffness
Often an itchy neck rash can be handled with self-care such as:
- over-the-counter (OTC) anti-itch lotions
- moisturizers such as Cetaphil, Eucerin, or CeraVe
- cooling creams or gels such as calamine lotion
- cool compresses
- avoiding scratching, even if you have to cover your neck
- allergy medications such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
If your itch doesn’t respond to self-care, your doctor might prescribe treatments including:
- corticosteroid creams
- calcineurin inhibitors such as such as tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel)
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft)
- phototherapy using different wavelengths of ultraviolet light
As well as prescribing treatments to relieve the itch, your doctor can perform a full diagnosis to be sure that your neck itch isn’t a symptom of a more serious health concern.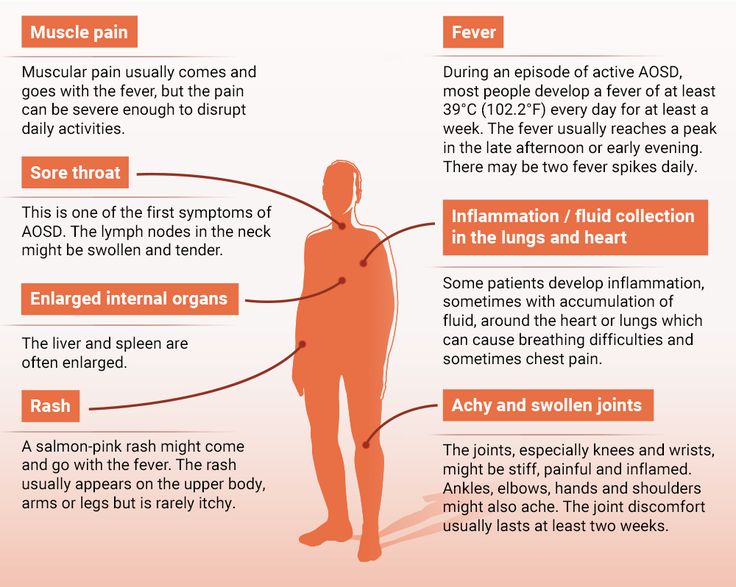
There are a number of simple, self-care steps you can do to treat an itchy neck. If the itchiness persists — or if the itch is one of other concerning symptoms — visit your doctor. They can offer more powerful anti-itch medications and determine whether or not your itchy neck is a symptom of an underlying medical condition that needs to be dealt with.
Last medically reviewed on June 4, 2018
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Itchy skin (pruritus).
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/itchy-skin/symptoms-causes/syc-20355006 - Rashes. (2016).
medlineplus.gov/rashes.html - Red, itchy rash? (2012).
newsinhealth. nih.gov/2012/04/red-itchy-rash
nih.gov/2012/04/red-itchy-rash
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Elaine K. Luo, M.D. — By Scott Frothingham — Updated on March 7, 2019
Read this next
Itchy Skin at Night? Why It Happens and What You Can Do About It
Itchy skin at night, or nocturnal pruritus, can keep you from getting a good night's sleep. Learn about its causes, treatment, and prevention.
READ MORE
Stress Rash: Tips for Identification, Treatment, and More
A stress-induced rash isn’t always a cause for concern, but there are other rashes that may look similar. We’ll tell you how to identify and treat a…
READ MORE
What’s Causing Your Itchy Skin? (with Pictures)
Itchy skin is an irritating and uncontrollable sensation that makes you want to scratch for relief.
 We’ll discuss causes of itching and share home…
We’ll discuss causes of itching and share home…READ MORE
The Best Remedies for Itching
Medically reviewed by Chris Young, DNP, RN, NE-BC, NPD
Itching, also known as "pruritus" can be uncomfortable. Learn when itching is serious and how to treat it.
READ MORE
How to Treat Actinic Cheilitis on Your Lips
Too much sun exposure can lead to swollen, puffy, inflamed lips. This is known as actinic cheilitis, which may turn into skin cancer. But treatment…
READ MORE
Subungual Hematoma: Drainage for Immediate Relief
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.N., CCRN, CPN
For best results, you should see a doctor as soon as possible to have your subungual hematoma drained. Let's look at the timeline for healing:
READ MORE
Rash on the neck - what to do, diagnosis and prevention
A rash on the neck is primarily a signal of a malfunction of internal organs or pathologies, and not just an aesthetic problem.
There is a wide range of reasons and only a doctor can name the exact one after the examination and the tests received.
According to statistics, with the problem of a rash on the neck, people collide no less often than on the back or any other place, but do not pay enough attention to it. Before buying expensive drugs, we strongly recommend visiting a doctor who can establish an accurate diagnosis, otherwise you will rather harm your body. Below, you can find the main causes that cause a rash on the neck in adults:
- Human hormonal problems. For example, in adolescents, red rashes on the face signal the process of restructuring taking place in the body from childhood to adulthood. In this case, such a rash is the norm, but for aesthetic purposes, drugs are still used that eliminate it. It is also considered normal to have red spots on the face during the menstrual period and in pregnant women. As for the rashes in other people associated with changes in hormones, this is a definite failure.
 It must be dealt with, as such problems can negatively affect all human life processes. For diagnosis, tests for hormones are used, which will confirm or refute the problems associated with the hormonal background. It should be noted that the rashes of the first type, associated with the restructuring of the body, and those that occur when the hormonal balance is disturbed, differ from each other. Age-related red rashes resemble blisters or blackheads in another way, they are bright in color, rich, inflamed and watery. As for the spots in pregnant women and with women's problems, they are more like the allergic nature of the rash. In addition, there are many other types of redness due to hormonal changes in the body.
It must be dealt with, as such problems can negatively affect all human life processes. For diagnosis, tests for hormones are used, which will confirm or refute the problems associated with the hormonal background. It should be noted that the rashes of the first type, associated with the restructuring of the body, and those that occur when the hormonal balance is disturbed, differ from each other. Age-related red rashes resemble blisters or blackheads in another way, they are bright in color, rich, inflamed and watery. As for the spots in pregnant women and with women's problems, they are more like the allergic nature of the rash. In addition, there are many other types of redness due to hormonal changes in the body. - Avitaminosis is another reason for the appearance of red spots on the face and body. In this case, the lack of vitamins weakens the immune system, and redness of a different nature acts as a protective reaction. In order to determine which vitamin is lacking in the body, you should undergo a certain examination.
- Allergy. Here we can note the most common irritant in which a rash appears on the neck - this is vitamin D. That is, a reaction to the sun. It is not uncommon for irritants to be food, especially citrus fruits and a variety of fruits. But other factors should not be ruled out: animals, alcohol, clothing materials, and much more.
- Bad habits, in particular smoking. In addition to the fact that they weaken the immune system, a rash on the neck can be a reaction of the body to tobacco, or rather the nicotine contained in it.
- Severe stress. Due to a malfunction of the nervous system, a person has red spots on the body, in particular on the neck. Usually, this happens after a major shock or because of a stable state of stress.
- Side effects of drugs. When taking new medications, redness of the neck is a very common reaction.
- Severe changes in body temperature. Due to hypothermia or vice versa, overheating - red spots form on the skin, after a short time they disappear.
- Substandard cosmetics. Often, hazardous substances can be added to products, especially be careful with fakes of expensive brands.
- Pathologies and diseases of internal organs. The most common case is thyroid problems. But to reveal the exact epicenter of the disease and its nature, it will only be possible to pass an examination and pass tests.
- Problems with the reproductive organs. This problem can occur in both men and women.
- Prickly heat. This disease is associated with non-compliance with hygiene and, as a result, the introduction of infection into the body. In the absence of timely treatment, red spots may not be enough. It is necessary to immediately contact a specialist, in order to avoid complications and the spread of the disease.
- Syphilis. Redness in the neck, usually appear six months after infection. They can have a different size and color intensity. Over time, they will cover the entire neck of the patient. Before obvious redness, areas of the skin begin to darken.
 In the early stages of syphilis, small pimples appear throughout the body. Which at different intervals disappear and appear again. At the stage of reddening of the neck, hair begins to fall out and most of the internal organs fail. This disease can only be treated with the help of an experienced specialist.
In the early stages of syphilis, small pimples appear throughout the body. Which at different intervals disappear and appear again. At the stage of reddening of the neck, hair begins to fall out and most of the internal organs fail. This disease can only be treated with the help of an experienced specialist.
As you could understand, there are a lot of reasons that cause a rash in an adult, and only a specialist can determine the exact cause, who will prescribe the most effective treatment.
Allergic rash - urticaria | Symptoms
Medications, contrast agents (used in imaging studies such as computed tomography)
Signs: Allergic rash that begins within 48 hours after using the drug.
Emotional and physical stimuli (stress and anxiety, cold, exercise, skin pressure, warmth, sunlight, sweating)
Signs: Allergic rash, which usually begins within seconds or minutes after contact with an irritant; an allergic rash that starts within 4 to 6 hours and affects only the area of skin where pressure has been applied, or an allergic rash that only affects the area of skin exposed to sunlight.
Food (food allergens)
Signs: Allergic rash that starts within minutes or hours of consumption.
Infections (bacterial, parasitic, viral)
Signs: Fever, chills, and fatigue. Specific infection symptoms, particularly for parasitic infections, recent travel to a developing country.
Insect bites or burns
Signs: Allergic rash that starts within seconds or minutes of an insect bite or burn.
Serum sickness
Signs: Allergic rash that begins within 7 to 10 days after an injection of a blood product (as in a transfusion), a drug derived from the blood of animals (used to treat venomous snake and spider bites). May be accompanied by fever, joint pain, swollen lymph nodes, and abdominal pain.
Contact allergens (latex, animal saliva or dander, dust, pollen or mold)
Signs: An allergic rash that begins within minutes or hours of contact.
Transfusion reactions
Signs: Allergic rash that usually starts within minutes of a blood product transfusion.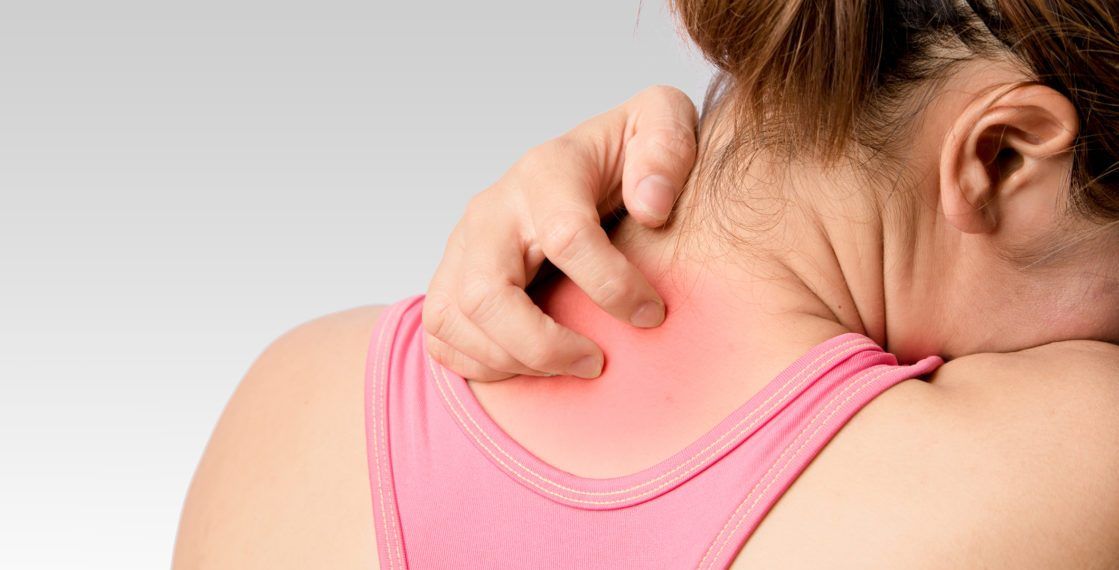
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Signs: Various symptoms depending on the autoimmune disease. With systemic lupus erythematosus, symptoms may include fever, fatigue, headache, joint pain and swelling, pain when breathing, and mouth ulcers.
Sjögren's syndrome
Signs: Dry eyes and dry mouth.
Urticarial vasculitis
Signs: An allergic rash that may be painful but not itchy. Usually lasts more than 24 hours. Does not whiten (brighten) when pressure is applied. May be accompanied by the formation of small blisters and red-violet spots (purpura).
Cancer (digestive or lung or lymphoma)
Signs: Weight loss, night sweats, abdominal pain, cough (sometimes with blood), jaundice, swollen lymph nodes, or a combination of these symptoms.
Chronic idiopathic allergic rash
Signs: Allergic rash that occurs almost daily and itching that lasts for 6 weeks with no apparent cause.