Infant urinary tract infections
Urinary Tract Infections In Babies
AddictionAllergies & AsthmaAmbulatoryAudiologyAutismAwardsBC4TeensBehavioral HealthBehind the ScenesBurn CenterCancerCardiologyCenter for Healthy Weight and NutritionCenter for Injury Research and PolicyChild BehaviorChild DevelopmentColorectal and Pelvic ReconstructionCommunity EducationCommunity ResourcesCoronavirusDentistryDermatologyDiseases & ConditionsDiversity and InclusionEndocrinologyENTEpilepsyEverything MattersFertility and Reproductive Health ProgramFundraising EventsGastroenterologyGeneticsGynecologyHematologyHomecareHospiceHospital NewsInfants & NewbornsInfectious DiseaseKids & TeensLaboratory ServicesMake Safe HappenMarathonNeonatologyNephrologyNeurologyNeurosurgeryNew HospitalNICUNutrition & FitnessOccupational TherapyOphthalmologyOrthopedicsOur PatientsOur staffPalliative CareParentingPediatric NewsPharmacyPhysical Therapy - Sports and OrthopedicPlastic SurgeryPopulation HealthPregnancyPrimary CarePsychologyPulmonaryRadiologyReach Out and ReadRehabilitationResearchRheumatologySafety & PreventionSports MedicineSurgical ServicesThe Center for Family Safety and HealingTherapeutic RecreationTherapyTHRIVE ProgramToddlers & PreschoolersUrgent CareUrology
Aaron Barber, AT, ATC, PESAbbie Roth, MWCAbby Orkis, MSW, LSWAdam Ostendorf, MDAdriane Baylis, PhD, CCC-SLPAdrienne M. Flood, CPNP-ACAdvanced Healthcare Provider CouncilAila Co, MDAlaina White, AT, ATCAlana Milton, MDAlana Milton, MDAlecia Jayne, AuDAlena SchuckmannAlessandra Gasior, DOAlex Kemper, MDAlexandra Funk, PharmD, DABATAlexandra Sankovic, MDAlexis Klenke, RD, LDAlice Bass, CPNP-PCAlison PeggAllie DePoyAllison Rowland, AT, ATCAllison Strouse, MS, AT, ATCAmanda E. Graf, MDAmanda GoetzAmanda Smith, RN, BSN, CPNAmanda Sonk, LMTAmanda Whitaker, MDAmber Patterson, MDAmberle Prater, PhD, LPCCAmy Brown Schlegel, MDAmy Coleman, LISWAmy Dunn, MDAmy E. Valasek, MD, MScAmy Fanning, PT, DPTAmy Garee, CPNP-PCAmy Hahn, PhDAmy HessAmy Leber, PhDAmy LeRoy, CCLSAmy Moffett, CPNP-PCAmy Randall-McSorley, MMC, EdD CandidateAmy Thomas, BSN, RN, IBCLCAmy Wahl, APNAnastasia Fischer, MD, FACSMAndala HardyAndrea Brun, CPNP-PCAndrea M. Boerger, MEd, CCC-SLPAndrea Sattler, MDAndrea ShellowAndrew AxelsonAndrew Kroger, MD, MPHAndrew SchwadererAndria Haynes, RNAngela AbenaimAngela Billingslea, LISW-SAnn Pakalnis, MDAnna Lillis, MD, PhDAnnette Haban-BartzAnnie Drapeau, MDAnnie Temple, MS, CCC-SLP, CLCAnnie Truelove, MPHAnthony Audino, MDAnup D.
 Patel, MDAri Rabkin, PhDAriana Hoet, PhDArielle Sheftall, PhDArleen KarczewskiAshlee HallAshleigh Kussman, MDAshley Debeljack, PsyDAshley Ebersole, MDAshley EcksteinAshley Kroon Van DiestAshley M. Davidson, AT, ATC, MSAshley Minnick, MSAH, AT, ATCAshley Overall, FNPAshley Parikh, CPNP-PCAshley Parker MSW, LISW-SAshley Parker, LISW-SAshley Tuisku, CTRSAsuncion Mejias, MD, PhDAurelia Wood, MDBailey Young, DOBecky Corbitt, RNBelinda Mills, MDBenjamin Fields, PhD, MEdBenjamin Kopp, MDBernadette Burke, AT, ATC, MSBeth Martin, RNBeth Villanueva, OTD, OTR/LBethany Uhl, MDBethany Walker, PhDBhuvana Setty, MDBill Kulju, MS, ATBlake SkinnerBonnie Gourley, MSW, LSWBrad Childers, RRT, BSBrandi Cogdill, RN, BSN, CFRN, EMT-PBrandon MorganBreanne L. Bowers, PT, DPT, CHT, CFSTBrendan Boyle, MD, MPHBrian Boe, MDBrian K. Kaspar, PhDBrian Kellogg, MDBriana Crowe, PT, DPT, OCSBrigid Pargeon, MS, MT-BCBrittney Hardin, MOT, OTR/LBrooke Sims, LPCC, ATRCagri Toruner, MDCaitlin Bauer, RD, LDCaitlin TullyCaleb MosleyCallista DammannCallista PoppCami Winkelspecht, PhDCamille Wilson, PhDCanice Crerand, PhDCara Inglis, PsyDCarl H.
Patel, MDAri Rabkin, PhDAriana Hoet, PhDArielle Sheftall, PhDArleen KarczewskiAshlee HallAshleigh Kussman, MDAshley Debeljack, PsyDAshley Ebersole, MDAshley EcksteinAshley Kroon Van DiestAshley M. Davidson, AT, ATC, MSAshley Minnick, MSAH, AT, ATCAshley Overall, FNPAshley Parikh, CPNP-PCAshley Parker MSW, LISW-SAshley Parker, LISW-SAshley Tuisku, CTRSAsuncion Mejias, MD, PhDAurelia Wood, MDBailey Young, DOBecky Corbitt, RNBelinda Mills, MDBenjamin Fields, PhD, MEdBenjamin Kopp, MDBernadette Burke, AT, ATC, MSBeth Martin, RNBeth Villanueva, OTD, OTR/LBethany Uhl, MDBethany Walker, PhDBhuvana Setty, MDBill Kulju, MS, ATBlake SkinnerBonnie Gourley, MSW, LSWBrad Childers, RRT, BSBrandi Cogdill, RN, BSN, CFRN, EMT-PBrandon MorganBreanne L. Bowers, PT, DPT, CHT, CFSTBrendan Boyle, MD, MPHBrian Boe, MDBrian K. Kaspar, PhDBrian Kellogg, MDBriana Crowe, PT, DPT, OCSBrigid Pargeon, MS, MT-BCBrittney Hardin, MOT, OTR/LBrooke Sims, LPCC, ATRCagri Toruner, MDCaitlin Bauer, RD, LDCaitlin TullyCaleb MosleyCallista DammannCallista PoppCami Winkelspecht, PhDCamille Wilson, PhDCanice Crerand, PhDCara Inglis, PsyDCarl H.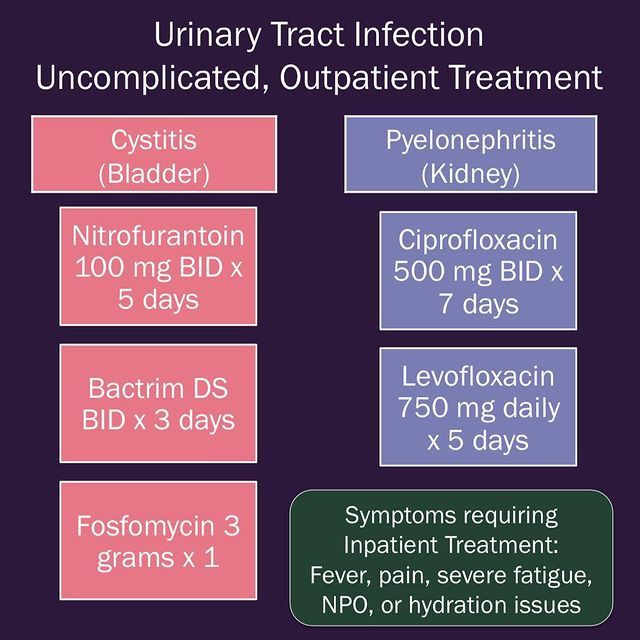 Backes, MDCarlo Di Lorenzo, MDCarly FawcettCarol Baumhardt, LMTCarolyn FigiCarrie Rhodes, CPST-I, MTSA, CHESCasey Cottrill, MD, MPHCasey TrimbleCassandra McNabb, RN-BSNCatherine Earlenbaugh, RNCatherine Sinclair, MDCatherine Trimble, FNPCatrina Litzenburg, PhDCharae Keys, MSW, LISW-SCharles Elmaraghy, MDChelsea Britton, MS, RD, LD, CLC Chelsea Kebodeaux, MDChelsie Doster, BSCheryl Boop, MS, OTR/LCheryl G. Baxter, CPNPCheryl Gariepy, MDChet Kaczor, PharmD, MBAChris MarreroChris Smith, RNChristina Ching, MDChristina DayChristine Johnson, MA, CCC-SLPChristine Koterba, PhDChristine Mansfield, PT, DPT, OCS, ATCChristine PrusaChristopher Goettee, PT, DPT, OCSChristopher Iobst, MDChristopher Ouellette, MDChristy Lumpkins, LISW-SCindy IskeClaire Kopko PT, DPT, OCS, NASM-PESCody Hostutler, PhDConnor McDanel, MSW, LSWCorey Rood, MDCorinne Syfers, CCLSCourtney Bishop. PA-CCourtney Brown, MDCourtney Hall, CPNP-PCCourtney Porter, RN, MSCristina Tomatis Souverbielle, MDCrystal MilnerCurt Daniels, MDCynthia Holland-Hall, MD, MPHDana Lenobel, FNPDana Noffsinger, CPNP-ACDane Snyder, MDDaniel Coury, MDDaniel DaJusta, MDDanielle Peifer, PT, DPTDavid A Wessells, PT, MHADavid Axelson, MDDavid Stukus, MDDean Lee, MD, PhDDebbie Terry, NPDeborah Hill, LSWDeborah Zerkle, LMTDeena Chisolm, PhDDeipanjan Nandi, MD MScDenis King, MDDenise EllDennis Cunningham, MDDennis McTigue, DDSDiane LangDominique R.
Backes, MDCarlo Di Lorenzo, MDCarly FawcettCarol Baumhardt, LMTCarolyn FigiCarrie Rhodes, CPST-I, MTSA, CHESCasey Cottrill, MD, MPHCasey TrimbleCassandra McNabb, RN-BSNCatherine Earlenbaugh, RNCatherine Sinclair, MDCatherine Trimble, FNPCatrina Litzenburg, PhDCharae Keys, MSW, LISW-SCharles Elmaraghy, MDChelsea Britton, MS, RD, LD, CLC Chelsea Kebodeaux, MDChelsie Doster, BSCheryl Boop, MS, OTR/LCheryl G. Baxter, CPNPCheryl Gariepy, MDChet Kaczor, PharmD, MBAChris MarreroChris Smith, RNChristina Ching, MDChristina DayChristine Johnson, MA, CCC-SLPChristine Koterba, PhDChristine Mansfield, PT, DPT, OCS, ATCChristine PrusaChristopher Goettee, PT, DPT, OCSChristopher Iobst, MDChristopher Ouellette, MDChristy Lumpkins, LISW-SCindy IskeClaire Kopko PT, DPT, OCS, NASM-PESCody Hostutler, PhDConnor McDanel, MSW, LSWCorey Rood, MDCorinne Syfers, CCLSCourtney Bishop. PA-CCourtney Brown, MDCourtney Hall, CPNP-PCCourtney Porter, RN, MSCristina Tomatis Souverbielle, MDCrystal MilnerCurt Daniels, MDCynthia Holland-Hall, MD, MPHDana Lenobel, FNPDana Noffsinger, CPNP-ACDane Snyder, MDDaniel Coury, MDDaniel DaJusta, MDDanielle Peifer, PT, DPTDavid A Wessells, PT, MHADavid Axelson, MDDavid Stukus, MDDean Lee, MD, PhDDebbie Terry, NPDeborah Hill, LSWDeborah Zerkle, LMTDeena Chisolm, PhDDeipanjan Nandi, MD MScDenis King, MDDenise EllDennis Cunningham, MDDennis McTigue, DDSDiane LangDominique R. Williams, MD, MPH, FAAP, Dipl ABOMDonna M. Trentel, MSA, CCLSDonna Ruch, PhDDonna TeachDoug WolfDouglas McLaughlin, MDDrew Duerson, MDEd MinerEdward Oberle, MD, RhMSUSEdward Shepherd, MDEileen Chaves, PhDElena CamachoElise Berlan, MDElise DawkinsElizabeth A. Cannon, LPCCElizabeth Cipollone, LPCC-SElizabeth Zmuda, DOEllyn Hamm, MM, MT-BCEmily A. Stuart, MDEmily Decker, MDEmily GetschmanEmma Wysocki, PharmD, RDNEric Butter, PhDEric Leighton, AT, ATCEric Sribnick, MD, PhDErica Domrose, RD, LDEricca L Lovegrove, RD, LDErika RobertsErin Gates, PT, DPTErin Johnson, M.Ed., C.S.C.S.Erin McKnight, MD, MPHErin Shann, BSN, RNErin TebbenFarah W. Brink, MDFatimah MasoodFrances Fei, MDGail Bagwell, DNP, APRN, CNSGail Besner, MDGail Swisher, ATGarey Noritz, MDGary A. Smith, MD, DrPHGeri Hewitt, MDGina Hounam, PhDGina McDowellGina MinotGrace Paul, MDGregory D. Pearson, MDGriffin Stout, MDGuliz Erdem, MDHailey Blosser, MA, CCC-SLPHanna MathessHeather Battles, MDHeather ClarkHeather L. Terry, MSN, RN, FNP-C, CUNPHeather Yardley, PhDHenry SpillerHenry Xiang, MD, MPH, PhDHerman Hundley, MS, AT, ATC, CSCSHilary Michel, MDHiren Patel, MDHolly Deckling, MSSW, LISWHoma Amini, DDS, MPH, MSHoward Jacobs, MDHunter Wernick, DOIbrahim Khansa, MDIhuoma Eneli, MDIlana Moss, PhDIlene Crabtree, PTIrene Mikhail, MDIrina Buhimschi, MDIvor Hill, MDJackie Cronau, RN, CWOCNJacqueline Wynn, PhD, BCBA-DJacquelyn Doxie King, PhDJaime-Dawn Twanow, MDJaimie D.
Williams, MD, MPH, FAAP, Dipl ABOMDonna M. Trentel, MSA, CCLSDonna Ruch, PhDDonna TeachDoug WolfDouglas McLaughlin, MDDrew Duerson, MDEd MinerEdward Oberle, MD, RhMSUSEdward Shepherd, MDEileen Chaves, PhDElena CamachoElise Berlan, MDElise DawkinsElizabeth A. Cannon, LPCCElizabeth Cipollone, LPCC-SElizabeth Zmuda, DOEllyn Hamm, MM, MT-BCEmily A. Stuart, MDEmily Decker, MDEmily GetschmanEmma Wysocki, PharmD, RDNEric Butter, PhDEric Leighton, AT, ATCEric Sribnick, MD, PhDErica Domrose, RD, LDEricca L Lovegrove, RD, LDErika RobertsErin Gates, PT, DPTErin Johnson, M.Ed., C.S.C.S.Erin McKnight, MD, MPHErin Shann, BSN, RNErin TebbenFarah W. Brink, MDFatimah MasoodFrances Fei, MDGail Bagwell, DNP, APRN, CNSGail Besner, MDGail Swisher, ATGarey Noritz, MDGary A. Smith, MD, DrPHGeri Hewitt, MDGina Hounam, PhDGina McDowellGina MinotGrace Paul, MDGregory D. Pearson, MDGriffin Stout, MDGuliz Erdem, MDHailey Blosser, MA, CCC-SLPHanna MathessHeather Battles, MDHeather ClarkHeather L. Terry, MSN, RN, FNP-C, CUNPHeather Yardley, PhDHenry SpillerHenry Xiang, MD, MPH, PhDHerman Hundley, MS, AT, ATC, CSCSHilary Michel, MDHiren Patel, MDHolly Deckling, MSSW, LISWHoma Amini, DDS, MPH, MSHoward Jacobs, MDHunter Wernick, DOIbrahim Khansa, MDIhuoma Eneli, MDIlana Moss, PhDIlene Crabtree, PTIrene Mikhail, MDIrina Buhimschi, MDIvor Hill, MDJackie Cronau, RN, CWOCNJacqueline Wynn, PhD, BCBA-DJacquelyn Doxie King, PhDJaime-Dawn Twanow, MDJaimie D.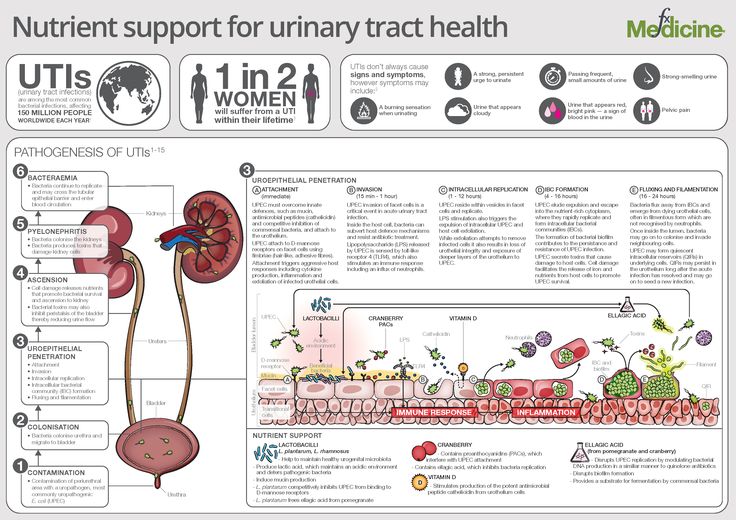 Nathan, MD, FACSJames Murakami, MDJames Popp, MDJames Ruda, MDJameson Mattingly, MDJamie Macklin, MDJamie ReedyJane AbelJanelle Huefner, MA, CCC-SLPJanice M. Moreland, CPNP-PC, DNPJanice Townsend, DDS, MSJared SylvesterJason JacksonJason P. Garee, PhDJaysson EicholtzJean Hruschak, MA, CCC/SLPJeff Sydes, CSCSJeffery Auletta, MDJeffrey Bennett, MD, PhDJeffrey Hoffman, MDJeffrey Leonard, MDJen Campbell, PT, MSPTJena HeckJenn Gonya, PhDJennie Aldrink, MDJennifer Borda, PT, DPTJennifer HofherrJennifer LockerJennifer PrinzJennifer Reese, PsyDJennifer Smith, MS, RD, CSP, LD, LMTJennifer Walton, MD, MPH, FAAPJenny Worthington, PT, DPTJerry R. Mendell, MDJessalyn Mayer, MSOT, OTR/LJessica Bailey, PsyDJessica Bogacik, MS, MT-BCJessica Bowman, MDJessica BrockJessica Bullock, MA/CCC-SLPJessica Buschmann, RDJessica Scherr, PhDJim O’Shea OT, MOT, CHTJoan Fraser, MSW, LISW-SJohn Ackerman, PhDJohn Caballero, PT, DPT, CSCSJohn Kovalchin, MDJonathan D. Thackeray, MDJonathan Finlay, MB, ChB, FRCPJonathan M.
Nathan, MD, FACSJames Murakami, MDJames Popp, MDJames Ruda, MDJameson Mattingly, MDJamie Macklin, MDJamie ReedyJane AbelJanelle Huefner, MA, CCC-SLPJanice M. Moreland, CPNP-PC, DNPJanice Townsend, DDS, MSJared SylvesterJason JacksonJason P. Garee, PhDJaysson EicholtzJean Hruschak, MA, CCC/SLPJeff Sydes, CSCSJeffery Auletta, MDJeffrey Bennett, MD, PhDJeffrey Hoffman, MDJeffrey Leonard, MDJen Campbell, PT, MSPTJena HeckJenn Gonya, PhDJennie Aldrink, MDJennifer Borda, PT, DPTJennifer HofherrJennifer LockerJennifer PrinzJennifer Reese, PsyDJennifer Smith, MS, RD, CSP, LD, LMTJennifer Walton, MD, MPH, FAAPJenny Worthington, PT, DPTJerry R. Mendell, MDJessalyn Mayer, MSOT, OTR/LJessica Bailey, PsyDJessica Bogacik, MS, MT-BCJessica Bowman, MDJessica BrockJessica Bullock, MA/CCC-SLPJessica Buschmann, RDJessica Scherr, PhDJim O’Shea OT, MOT, CHTJoan Fraser, MSW, LISW-SJohn Ackerman, PhDJohn Caballero, PT, DPT, CSCSJohn Kovalchin, MDJonathan D. Thackeray, MDJonathan Finlay, MB, ChB, FRCPJonathan M.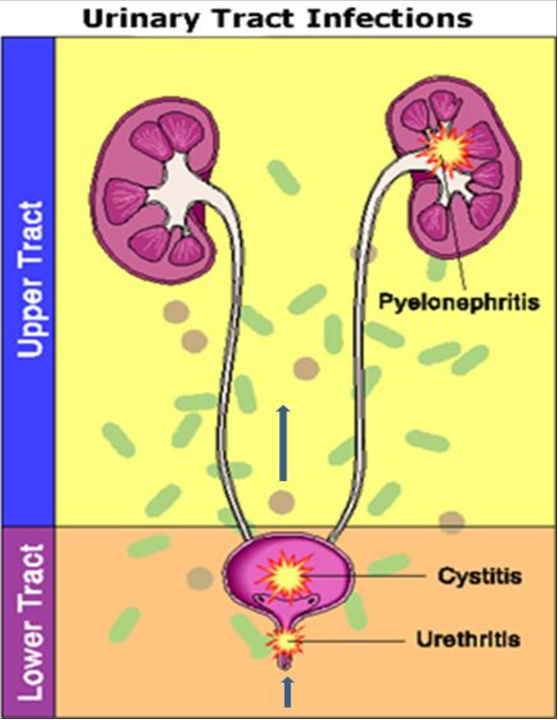 Grischkan, MDJonathan Napolitano, MDJoshua Prudent, MDJoshua Watson, MDJulee Eing, CRA, RT(R)Julia Colman, MOT, OTR/LJulie ApthorpeJulie Lange, MDJulie Leonard, MD, MPHJulie Racine, PhDJulie Samora, MDJustin Indyk, MD, PhDKady LacyKaitrin Kramer, DDS, MS, PhDKaleigh Hague, MA, MT-BCKaleigh MatesickKamilah Twymon, LPCC-SKara Malone, MDKara Miller, OTR/LKaren A. Diefenbach, MDKaren Allen, MDKaren Days, MBAKaren Rachuba, RD, LD, CLCKari A. Meeks, OTKari Cardiff, ODKari Dubro, MS, RD, LD, CWWSKari Phang, MDKarla Vaz, MDKaryn L. Kassis, MD, MPHKasey Strothman, MDKatherine Deans, MDKatherine McCracken, MD FACOGKathleen (Katie) RoushKathryn Blocher, CPNP-PCKathryn J. Junge, RN, BSNKathryn Obrynba, MDKatia Camille Halabi, MDKatie Brind'Amour, MSKatie DonovanKatie Thomas, APRKatrina Hall, MA, CCLSKatrina Ruege, LPCC-SKatya Harfmann, MDKayla Zimpfer, PCCKaylan Guzman Schauer, LPCC-SKeli YoungKelley SwopeKelli Dilver, PT, DPTKelly AbramsKelly BooneKelly HustonKelly J. Kelleher, MDKelly McNally, PhDKelly N.
Grischkan, MDJonathan Napolitano, MDJoshua Prudent, MDJoshua Watson, MDJulee Eing, CRA, RT(R)Julia Colman, MOT, OTR/LJulie ApthorpeJulie Lange, MDJulie Leonard, MD, MPHJulie Racine, PhDJulie Samora, MDJustin Indyk, MD, PhDKady LacyKaitrin Kramer, DDS, MS, PhDKaleigh Hague, MA, MT-BCKaleigh MatesickKamilah Twymon, LPCC-SKara Malone, MDKara Miller, OTR/LKaren A. Diefenbach, MDKaren Allen, MDKaren Days, MBAKaren Rachuba, RD, LD, CLCKari A. Meeks, OTKari Cardiff, ODKari Dubro, MS, RD, LD, CWWSKari Phang, MDKarla Vaz, MDKaryn L. Kassis, MD, MPHKasey Strothman, MDKatherine Deans, MDKatherine McCracken, MD FACOGKathleen (Katie) RoushKathryn Blocher, CPNP-PCKathryn J. Junge, RN, BSNKathryn Obrynba, MDKatia Camille Halabi, MDKatie Brind'Amour, MSKatie DonovanKatie Thomas, APRKatrina Hall, MA, CCLSKatrina Ruege, LPCC-SKatya Harfmann, MDKayla Zimpfer, PCCKaylan Guzman Schauer, LPCC-SKeli YoungKelley SwopeKelli Dilver, PT, DPTKelly AbramsKelly BooneKelly HustonKelly J. Kelleher, MDKelly McNally, PhDKelly N. Day, CPNP-PCKelly Pack, LISW-SKelly Tanner,PhD, OTR/L, BCPKelly Wesolowski, PsyDKelly Wise, PharmDKent Williams, MDKevin Bosse, PhDKevin Klingele, MDKim Bjorklund, MDKim Hammersmith, DDS, MPH, MSKimberly Bates, MDKimberly Sisto, PT, DPT, SCSKimberly Van Camp, PT, DPT, SCSKirk SabalkaKris Jatana, MD, FAAPKrista Winner, AuD, CCC-AKristen Armbrust, LISW-SKristen Cannon, MDKristen E. Beck, MDKristen Martin, OTR/LKristi Roberts, MS MPHKristina Booth, MSN, CFNPKristina Reber, MDKristol Das, MDKyle DavisLance Governale, MDLara McKenzie, PhD, MALaura Brubaker, BSN, RNLaura Dattner, MALaura Martin, MDLaurel Biever, LPCLauren Durinka, AuDLauren Garbacz, PhDLauren Justice, OTR/L, MOTLauren Madhoun, MS, CCC-SLPLauryn Rozum, MS, CCLSLeah Middelberg, MDLee Hlad, DPMLeena Nahata, MDLelia Emery, MT-BCLeslie Appiah, MDLinda Stoverock, DNP, RN NEA-BCLindsay Kneen, MDLindsay Pietruszewski, PT, DPTLindsay SchwartzLindsey Vater, PsyDLisa GoldenLisa Halloran, CNPLisa M. Humphrey, MDLogan Blankemeyer, MA, CCC-SLPLori Grisez PT, DPTLorraine Kelley-QuonLouis Bezold, MDLourdes Hill, LPCC-S Lubna Mazin, PharmDLuke Tipple, MS, CSCSLynda Wolfe, PhDLyndsey MillerLynn RosenthalLynne Ruess, MDMaggy Rule, MS, AT, ATCMahmoud Kallash, MDManmohan K Kamboj, MDMarc P.
Day, CPNP-PCKelly Pack, LISW-SKelly Tanner,PhD, OTR/L, BCPKelly Wesolowski, PsyDKelly Wise, PharmDKent Williams, MDKevin Bosse, PhDKevin Klingele, MDKim Bjorklund, MDKim Hammersmith, DDS, MPH, MSKimberly Bates, MDKimberly Sisto, PT, DPT, SCSKimberly Van Camp, PT, DPT, SCSKirk SabalkaKris Jatana, MD, FAAPKrista Winner, AuD, CCC-AKristen Armbrust, LISW-SKristen Cannon, MDKristen E. Beck, MDKristen Martin, OTR/LKristi Roberts, MS MPHKristina Booth, MSN, CFNPKristina Reber, MDKristol Das, MDKyle DavisLance Governale, MDLara McKenzie, PhD, MALaura Brubaker, BSN, RNLaura Dattner, MALaura Martin, MDLaurel Biever, LPCLauren Durinka, AuDLauren Garbacz, PhDLauren Justice, OTR/L, MOTLauren Madhoun, MS, CCC-SLPLauryn Rozum, MS, CCLSLeah Middelberg, MDLee Hlad, DPMLeena Nahata, MDLelia Emery, MT-BCLeslie Appiah, MDLinda Stoverock, DNP, RN NEA-BCLindsay Kneen, MDLindsay Pietruszewski, PT, DPTLindsay SchwartzLindsey Vater, PsyDLisa GoldenLisa Halloran, CNPLisa M. Humphrey, MDLogan Blankemeyer, MA, CCC-SLPLori Grisez PT, DPTLorraine Kelley-QuonLouis Bezold, MDLourdes Hill, LPCC-S Lubna Mazin, PharmDLuke Tipple, MS, CSCSLynda Wolfe, PhDLyndsey MillerLynn RosenthalLynne Ruess, MDMaggy Rule, MS, AT, ATCMahmoud Kallash, MDManmohan K Kamboj, MDMarc P. Michalsky, MDMarcel J. Casavant, MDMarci Johnson, LISW-SMarcie RehmarMarco Corridore, MDMargaret Bassi, OTR/LMaria HaghnazariMaria Vegh, MSN, RN, CPNMarissa Condon, BSN, RNMarissa E. Larouere, MBA, BSN, RNMark E. Galantowicz, MDMark Smith, MS RT R (MR), ABMP PhysicistMarnie Wagner, MDMary Ann Abrams, MD, MPHMary Fristad, PhD, ABPPMary Kay SharrettMary Shull, MDMatthew Washam, MD, MPHMeagan Horn, MAMegan Brundrett, MDMegan Dominik, OTR/LMegan FrancisMegan Letson, MD, M.EdMeghan Cass, PT, DPTMeghan Fisher, BSN, RNMeika Eby, MDMelanie Fluellen, LPCCMelanie Luken, LISW-SMelissa and Mikael McLarenMelissa McMillen, CTRSMelissa Winterhalter, MDMeredith Merz Lind, MDMichael Flores, PhDMichael T. Brady, MDMichelle Ross, MHA, RD, LD, ALCMike Patrick, MDMindy Deno, PT, DPTMitch Ellinger, CPNP-PCMolly Dienhart, MDMolly Gardner, PhDMonica Ardura, DOMonica EllisMonique Goldschmidt, MDMotao Zhu, MD, MS, PhDMurugu Manickam, MDNancy AuerNancy Cunningham, PsyDNancy Wright, BS, RRT, RCP, AE-C Naomi Kertesz, MDNatalie DeBaccoNatalie I.
Michalsky, MDMarcel J. Casavant, MDMarci Johnson, LISW-SMarcie RehmarMarco Corridore, MDMargaret Bassi, OTR/LMaria HaghnazariMaria Vegh, MSN, RN, CPNMarissa Condon, BSN, RNMarissa E. Larouere, MBA, BSN, RNMark E. Galantowicz, MDMark Smith, MS RT R (MR), ABMP PhysicistMarnie Wagner, MDMary Ann Abrams, MD, MPHMary Fristad, PhD, ABPPMary Kay SharrettMary Shull, MDMatthew Washam, MD, MPHMeagan Horn, MAMegan Brundrett, MDMegan Dominik, OTR/LMegan FrancisMegan Letson, MD, M.EdMeghan Cass, PT, DPTMeghan Fisher, BSN, RNMeika Eby, MDMelanie Fluellen, LPCCMelanie Luken, LISW-SMelissa and Mikael McLarenMelissa McMillen, CTRSMelissa Winterhalter, MDMeredith Merz Lind, MDMichael Flores, PhDMichael T. Brady, MDMichelle Ross, MHA, RD, LD, ALCMike Patrick, MDMindy Deno, PT, DPTMitch Ellinger, CPNP-PCMolly Dienhart, MDMolly Gardner, PhDMonica Ardura, DOMonica EllisMonique Goldschmidt, MDMotao Zhu, MD, MS, PhDMurugu Manickam, MDNancy AuerNancy Cunningham, PsyDNancy Wright, BS, RRT, RCP, AE-C Naomi Kertesz, MDNatalie DeBaccoNatalie I. Rine, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCPNatalie Powell, LPCC-S, LICDC-CSNatalie Rose, BSN, RNNathalie Maitre, MD, PhDNationwide Children's HospitalNationwide Children's Hospital Behavioral Health ExpertsNeetu Bali, MD, MPHNehal Parikh, DO, MSNichole Mayer, OTR/L, MOTNicole Caldwell, MDNicole Dempster, PhDNicole Greenwood, MDNicole Parente, LSWNicole Powell, PsyD, BCBA-DNina WestNkeiruka Orajiaka, MBBSOctavio Ramilo, MDOliver Adunka, MD, FACSOlivia Stranges, CPNP-PCOlivia Thomas, MDOmar Khalid, MD, FAAP, FACCOnnalisa Nash, CPNP-PCOula KhouryPaige Duly, CTRSParker Huston, PhDPatrick C. Walz, MDPatrick Queen, BSN, RNPedro Weisleder, MDPeter Minneci, MDPeter White, PhDPitty JenningsPreeti Jaggi, MDPriyal Patel, DORachael Morocco-Zanotti, DORachel D’Amico, MDRachel Schrader, CPNP-PCRachel Tyson, LSWRajan Thakkar, MDRaymond Troy, MDRebecca Fisher, PTRebecca Hicks, CCLSRebecca Lewis, AuD, CCC-ARebecca M. Romero, RD, LD, CLC Reggie Ash Jr.Reno Ravindran, MDRichard Kirschner, MDRichard Wood, MDRobert A. Kowatch, MD, Ph.
Rine, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCPNatalie Powell, LPCC-S, LICDC-CSNatalie Rose, BSN, RNNathalie Maitre, MD, PhDNationwide Children's HospitalNationwide Children's Hospital Behavioral Health ExpertsNeetu Bali, MD, MPHNehal Parikh, DO, MSNichole Mayer, OTR/L, MOTNicole Caldwell, MDNicole Dempster, PhDNicole Greenwood, MDNicole Parente, LSWNicole Powell, PsyD, BCBA-DNina WestNkeiruka Orajiaka, MBBSOctavio Ramilo, MDOliver Adunka, MD, FACSOlivia Stranges, CPNP-PCOlivia Thomas, MDOmar Khalid, MD, FAAP, FACCOnnalisa Nash, CPNP-PCOula KhouryPaige Duly, CTRSParker Huston, PhDPatrick C. Walz, MDPatrick Queen, BSN, RNPedro Weisleder, MDPeter Minneci, MDPeter White, PhDPitty JenningsPreeti Jaggi, MDPriyal Patel, DORachael Morocco-Zanotti, DORachel D’Amico, MDRachel Schrader, CPNP-PCRachel Tyson, LSWRajan Thakkar, MDRaymond Troy, MDRebecca Fisher, PTRebecca Hicks, CCLSRebecca Lewis, AuD, CCC-ARebecca M. Romero, RD, LD, CLC Reggie Ash Jr.Reno Ravindran, MDRichard Kirschner, MDRichard Wood, MDRobert A. Kowatch, MD, Ph. D.Robert Hoffman, MDRochelle Krouse, CTRSRohan Henry, MD, MSRose Ayoob, MDRose Schroedl, PhDRosemary Martoma, MDRoss Maltz, MDRyan Ingley AT, ATCSamanta Boddapati, PhDSamantha MaloneSammy CygnorSandra C. Kim, MDSara Bentley, MT-BCSara Bode, MDSara Breidigan, MS, AT, ATCSara N. Smith, MSN, APRNSara O'Rourke, MOT, OTR/L, Clinical LeadSara Schroder, MDSarah A. Denny, MDSarah Cline, CRA, RT(R)Sarah Driesbach, CPN, APNSarah GreenbergSarah Hastie, BSN, RNC-NIC Sarah Keim, PhDSarah MyersSarah O'Brien, MDSarah SaxbeSarah Schmidt, LISW-SSarah ScottSarah TraceySarah VerLee, PhDSasigarn Bowden, MDSatya Gedela, MD, MRCP(UK)Scott Coven, DO, MPHScott Hickey, MDSean EingSean Rose, MDSeth Alpert, MDShalini C. Reshmi, PhD, FACMGShana Moore, MA, CCC-AShannon Reinhart, LISW-SShari UncapherSharon Wrona, DNP, PNP, PMHSShaun Coffman PT, DPT, OCSShawn Pitcher, BS, RD, USAWShawNaye Scott-MillerShea SmoskeSheena PaceSheila GilesShelly BrackmanSimon Lee, MDSini James, MDStacy Ardoin, MDStacy Whiteside APRN, MS, CPNP-AC/PC, CPONStefanie Bester, MDStefanie Hirota, OTR/LStephanie Burkhardt, MPH, CCRCStephanie CannonStephanie Santoro, MDStephanie Vyrostek BSN, RNStephen Hersey, MDSteve Allen, MDSteven C.
D.Robert Hoffman, MDRochelle Krouse, CTRSRohan Henry, MD, MSRose Ayoob, MDRose Schroedl, PhDRosemary Martoma, MDRoss Maltz, MDRyan Ingley AT, ATCSamanta Boddapati, PhDSamantha MaloneSammy CygnorSandra C. Kim, MDSara Bentley, MT-BCSara Bode, MDSara Breidigan, MS, AT, ATCSara N. Smith, MSN, APRNSara O'Rourke, MOT, OTR/L, Clinical LeadSara Schroder, MDSarah A. Denny, MDSarah Cline, CRA, RT(R)Sarah Driesbach, CPN, APNSarah GreenbergSarah Hastie, BSN, RNC-NIC Sarah Keim, PhDSarah MyersSarah O'Brien, MDSarah SaxbeSarah Schmidt, LISW-SSarah ScottSarah TraceySarah VerLee, PhDSasigarn Bowden, MDSatya Gedela, MD, MRCP(UK)Scott Coven, DO, MPHScott Hickey, MDSean EingSean Rose, MDSeth Alpert, MDShalini C. Reshmi, PhD, FACMGShana Moore, MA, CCC-AShannon Reinhart, LISW-SShari UncapherSharon Wrona, DNP, PNP, PMHSShaun Coffman PT, DPT, OCSShawn Pitcher, BS, RD, USAWShawNaye Scott-MillerShea SmoskeSheena PaceSheila GilesShelly BrackmanSimon Lee, MDSini James, MDStacy Ardoin, MDStacy Whiteside APRN, MS, CPNP-AC/PC, CPONStefanie Bester, MDStefanie Hirota, OTR/LStephanie Burkhardt, MPH, CCRCStephanie CannonStephanie Santoro, MDStephanie Vyrostek BSN, RNStephen Hersey, MDSteve Allen, MDSteven C.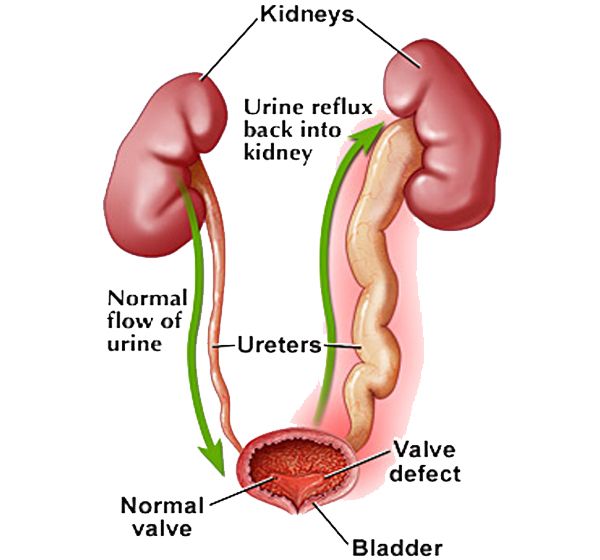 Matson, MDSteven Ciciora, MDSteven CuffSuellen Sharp, OTR/L, MOTSurlina AsamoaSusan Colace, MDSusan Creary, MDSwaroop Pinto, MDTabatha BallardTabbetha GrecoTabi Evans, PsyDTabitha Jones-McKnight, DOTahagod Mohamed, MDTamara MappTammi Young-Saleme, PhDTaylor Hartlaub, MD, MPHTerry Barber, MDTerry Bravender, MD, MPHTerry Laurila, MS, RPhTheresa Miller, BA, RRT, RCP, AE-C, CPFTThomas Pommering, DOTiasha Letostak, PhDTiffanie Ryan, BCBA Tim RobinsonTim Smith, MDTimothy Cripe, MD, PhDTimothy Landers PhD RN APRN-CNP CIC FAANTracey L. Sisk, RN, BSN, MHATracie Steinke RD, LD, CDETracy Mehan, MATravis Gallagher, ATTrevor MillerTria Shadeed, NNPTyanna Snider, PsyDTyler Congrove, ATValencia Walker, MD, MPH, FAAPVanessa Shanks, MD, FAAPVenkata Rama Jayanthi, MDVidu Garg, MDVidya Raman, MDW. Garrett Hunt, MDWalter Samora, MDWarren D. Lo, MDWendy Anderson, MDWendy Cleveland, MA, LPCC-SWhitney McCormick, CTRSWhitney Raglin Bignall, PhDWilliam Cotton, MDWilliam J. Barson, MDWilliam Ray, PhDWilliam W. Long, MD
Matson, MDSteven Ciciora, MDSteven CuffSuellen Sharp, OTR/L, MOTSurlina AsamoaSusan Colace, MDSusan Creary, MDSwaroop Pinto, MDTabatha BallardTabbetha GrecoTabi Evans, PsyDTabitha Jones-McKnight, DOTahagod Mohamed, MDTamara MappTammi Young-Saleme, PhDTaylor Hartlaub, MD, MPHTerry Barber, MDTerry Bravender, MD, MPHTerry Laurila, MS, RPhTheresa Miller, BA, RRT, RCP, AE-C, CPFTThomas Pommering, DOTiasha Letostak, PhDTiffanie Ryan, BCBA Tim RobinsonTim Smith, MDTimothy Cripe, MD, PhDTimothy Landers PhD RN APRN-CNP CIC FAANTracey L. Sisk, RN, BSN, MHATracie Steinke RD, LD, CDETracy Mehan, MATravis Gallagher, ATTrevor MillerTria Shadeed, NNPTyanna Snider, PsyDTyler Congrove, ATValencia Walker, MD, MPH, FAAPVanessa Shanks, MD, FAAPVenkata Rama Jayanthi, MDVidu Garg, MDVidya Raman, MDW. Garrett Hunt, MDWalter Samora, MDWarren D. Lo, MDWendy Anderson, MDWendy Cleveland, MA, LPCC-SWhitney McCormick, CTRSWhitney Raglin Bignall, PhDWilliam Cotton, MDWilliam J. Barson, MDWilliam Ray, PhDWilliam W. Long, MD
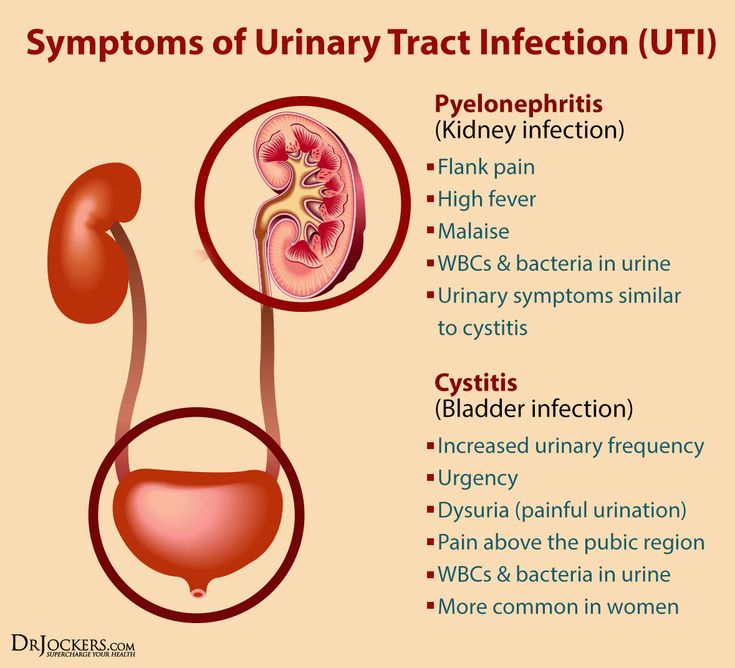
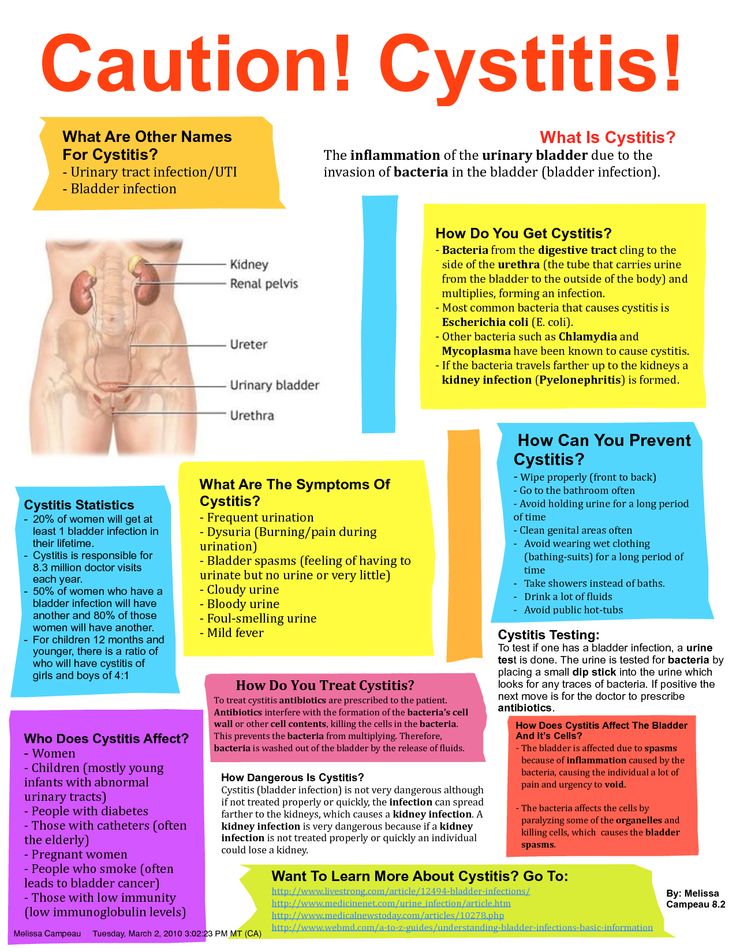
Urinary Tract Infections in the Infant
1. Shaikh N, Morone NE, Bost JE, et al. Prevalence of urinary tract infection in childhood: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008;27:302–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shaikh N, Morone NE, Bost JE, et al. Prevalence of urinary tract infection in childhood: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008;27:302–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2. Ismaili K, Lolin K, Damry N, et al. Febrile urinary tract infections in 0- to 3-month-old infants: a prospective follow-up study. J Pediatr. 2011;158:91–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
3. Zorc JJ, Levine DA, Platt SL, et al. Clinical and demographic factors associated with urinary tract infection in young febrile infants. Pediatrics. 2005;116:644–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
4. Lin DS, Huang SH, Lin CC, et al. Urinary tract infection in febrile infants younger than eight weeks of Age. Pediatrics. 2000;105:E20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
5. Bonadio W, Maida G. Urinary tract infection in outpatient febrile infants younger than 30 days of age: a 10-year evaluation. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:342–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
6. Morley EJ, Lapoint JM, Roy LW, et al. Rates of positive blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid cultures in children younger than 60 days during the vaccination era. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28:125–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28:125–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
7. Visser VE, Hall RT. Urine culture in the evaluation of suspected neonatal sepsis. J Pediatr. 1979;94:635–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
8. Tamim MM, Alesseh H, Aziz H. Analysis of the efficacy of urine culture as part of sepsis evaluation in the premature infant. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:805–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
9. Riskin A, Toropine A, Bader D, et al. Is it justified to include urine cultures in early (<72 hours) neonatal sepsis evaluations of term and late preterm infants? Am J Perinatol. 2013;30:499–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
10. Samayam P, Ravi Chander B. Study of urinary tract infection and bacteriuria in neonatal sepsis. Indian J Pediatr. 2012;79:1033–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
11. Wang SF, Huang FY, Chiu NC, et al. Urinary tract infection in infants less than 2 months of age. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1994;35:294–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
12. Kanellopoulos TA, Salakos C, Spiliopoulou I, et al. First urinary tract infection in neonates, infants and young children: a comparative study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:1131–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kanellopoulos TA, Salakos C, Spiliopoulou I, et al. First urinary tract infection in neonates, infants and young children: a comparative study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:1131–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
13. Didier C, Streicher MP, Chognot D, et al. Late-onset neonatal infections: incidences and pathogens in the era of antenatal antibiotics. Eur J Pediatr. 2012;171:681–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
14. Watt K, Waddle E, Jhaveri R. Changing epidemiology of serious bacterial infections in febrile infants without localizing signs. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
15. Lo DS, Shieh HH, Ragazzi SL, et al. Community-acquired urinary tract infection: age and gender-dependent etiology. J Bras Nefrol. 2013;35:93–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
16. Bitsori M, Maraki S, Raissaki M, et al. Community-acquired enterococcal urinary tract infections. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005;20:1583–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
17. Zurina Z, Rohani A, Neela V, et al. Late onset group b beta-hemolytic streptococcus infection in a neonate manifesting as a urinary tract infection: a rare clinical presentation. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2012;43:1470–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Late onset group b beta-hemolytic streptococcus infection in a neonate manifesting as a urinary tract infection: a rare clinical presentation. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2012;43:1470–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
18. Hassoun A, Stankovic C, Rogers A, et al. Listeria and enterococcal infections in neonates 28 days of age and younger: is empiric parenteral ampicillin still indicated? Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30:240–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
19. Downey LC, Benjamin DK, Jr, Clark RH, et al. Urinary tract infection concordance with positive blood and cerebrospinal fluid cultures in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Perinatol. 2013;33:302–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
20. Jean-Baptiste N, Benjamin DK, Jr, Cohen-Wolkowiez M, et al. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal infections in the neonatal intensive care unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011;32:679–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
21. Phillips JR, Karlowicz MG.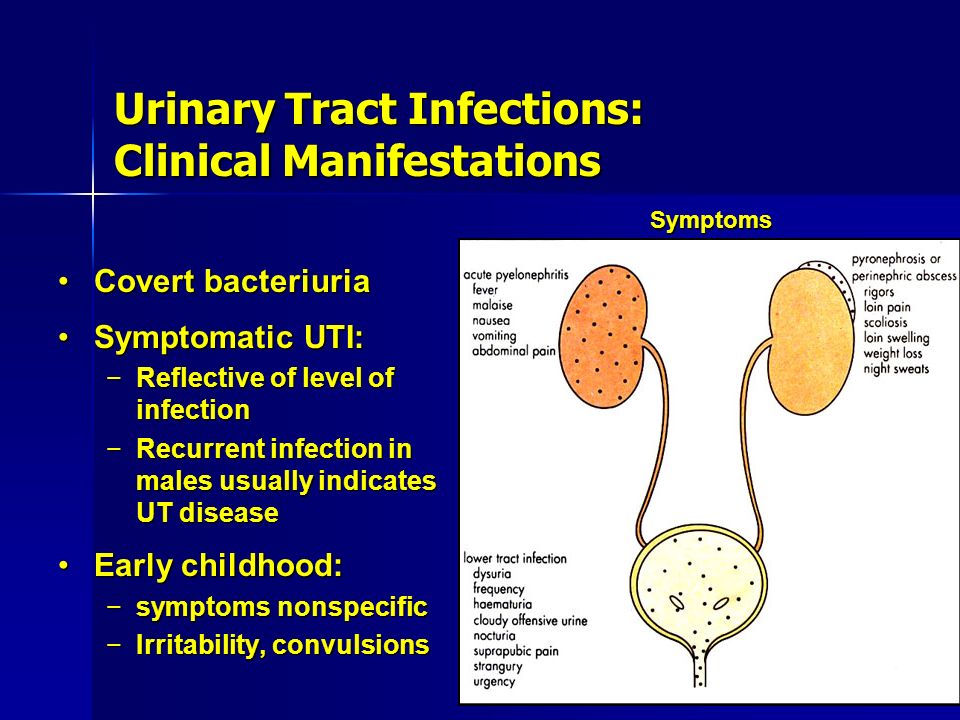 Prevalence of Candida species in hospital-acquired urinary tract infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997;16:190–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prevalence of Candida species in hospital-acquired urinary tract infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997;16:190–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
22. Airede AI. Urinary-tract infections in African neonates. J Infect. 1992;25:55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
23. Eliakim A, Dolfin T, Korzets Z, et al. Urinary tract infection in premature infants: the role of imaging studies and prophylactic therapy. J Perinatol. 1997;17:304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
24. Shim YH, Lee JW, Lee SJ. The risk factors of recurrent urinary tract infection in infants with normal urinary systems. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:309–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
25. Laway MA, Wani ML, Patnaik R, et al. Does circumcision alter the periurethral uropathogenic bacterial flora. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2012;9:109–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
26. Cleper R, Krause I, Eisenstein B, et al. Prevalence of vesicoureteral reflux in neonatal urinary tract infection. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2004;43:619–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[PubMed] [Google Scholar]
27. Jantunen ME, Siitonen A, Ala-Houhala M, et al. Predictive factors associated with significant urinary tract abnormalities in infants with pyelonephritis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
28. Goldman M, Lahat E, Strauss S, et al. Imaging after urinary tract infection in male neonates. Pediatrics. 2000;105:1232–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
29. Sastre JB, Aparicio AR, Cotallo GD, et al. Urinary tract infection in the newborn: clinical and radio imaging studies. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:1735–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
30. Khalesi N, Khosravi N, Jalali A, et al. Evaluation of maternal urinary tract infection as a potential risk factor for neonatal urinary tract infection. J Family Reprod Health. 2014;8:59–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
31. Milas V, Puseljić S, Stimac M, et al. Urinary tract infection (UTI) in newborns: risk factors, identification and prevention of consequences. Coll Antropol. 2013;37:871–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2013;37:871–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
32. Littlewood JM. 66 infants with urinary tract infection in first month of life. Arch Dis Child. 1972;47:218–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
33. Levy I, Comarsca J, Davidovits M, et al. Urinary tract infection in preterm infants: the protective role of breastfeeding. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:527–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
34. Levine DA, Platt SL, Dayan PS, et al. Risk of serious bacterial infection in young febrile infants with respiratory syncytial virus infections. Pediatrics. 2004;113:1728–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
35. Shahian M, Rashtian P, Kalani M. Unexplained neonatal jaundice as an early diagnostic sign of urinary tract infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2012;16:e487–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
36. Pashapour N, Nikibahksh AA, Golmohammadlou S. Urinary tract infection in term neonates with prolonged jaundice. Urol J. 2007;4:91–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
37. Garcia FJ, Nager AL. Jaundice as an early diagnostic sign of urinary tract infection in infancy. Pediatrics. 2002;109:846–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pediatrics. 2002;109:846–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
38. Mutlu M, Cayir Y, Asian Y. Urinary tract infections in neonates with jaundice in their first two weeks of life. World J Pediatr. 2014;10:164–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
39. Xinias I, Demertzidou V, Mavroudi A, et al. Bilirubin levels predict renal cortical changes in jaundiced neonates with urinary tract infection. World J Pediatr. 2009;5:42–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
40. American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia. Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics. 2004;114:297–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
41. Fang SB, Lee HC, Yeung CY, et al. Urinary tract infections in young infants with prolonged jaundice. Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 2005;46:356–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
42. Chen HT, Jeng MJ, Soong WJ, et al. Hyperbilirubinemia with urinary tract infection in infants younger than eight weeks old. J Chin Med Assoc. 2011;74:159–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[PubMed] [Google Scholar]
43. Tebruegge M, Pantazidou A, Clifford V, et al. The age-related risk of co-existing meningitis in children with urinary tract infection. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
44. Foglia EE, Lorch SA. Clinical predictors of urinary tract infection in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2012;5:327–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
45. Karacan C, Erkek N, Senel S, et al. Evaluation of urine collection methods for the diagnosis of urinary tract infection in children. Med Princ Pract. 2010;19:188–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
46. Tosif S, Baker A, Oakley E, et al. Contamination rates of different urine collection methods for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections in young children: an observational cohort study. J Paediatr Child Health. 2012;48:659–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
47. Hoberman A, Wald ER. Urinary tract infections in young febrile children. Pediatr Infect Dis J.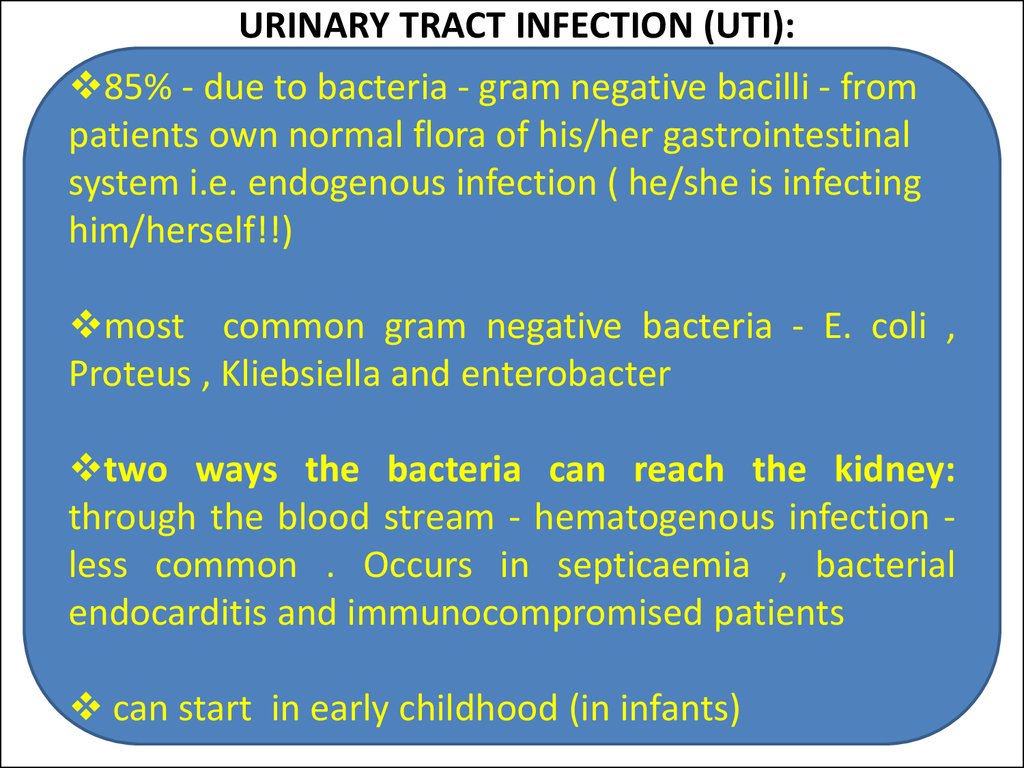 1997;16:11–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
1997;16:11–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
48. Crain EF, Gershel JC. Urinary tract infections in febrile infants younger than 8 weeks of age. Pediatrics. 1990;86:363–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
49. Dukes C. The examination of urine for pus. Br Med J. 1928;1:391–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
50. Hoberman A, Wald ER, Reynolds EA, et al. Pyuria and bacteriuria in urine specimens obtained by catheter from young children with fever. J Pediatr. 1994;124:513–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
51. Shah AP, Cobb BT, Lower DR, et al. Enhanced versus automated urinalysis for screening of urinary tract infections in children in the emergency department. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:272–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
52. Mori R, Yonemoto N, Fitzgerald A, et al. Diagnostic performance of urine dipstick testing in children with suspected UTI: a systematic review of relationship with age and comparison with microscopy. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:581–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
53. Glissmeyer EW, Korgenski EK, Wilkes J, et al. Dipstick screening for urinary tract infection in febrile infants. Pediatrics. 2014;133(5):e1121–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Glissmeyer EW, Korgenski EK, Wilkes J, et al. Dipstick screening for urinary tract infection in febrile infants. Pediatrics. 2014;133(5):e1121–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
54. Hasvold J, Bradford L, Nelson C, et al. Gentamicin resistance among Escherichia coli strains isolated in neonatal sepsis. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2013;6:173–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
55. Shakir SM, Goldbeck JM, Robison D, et al. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Invasive Neonatal Escherichia coli Clinical Isolates. Am J Perinatol. 2014;31:975–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
56. Taheri PA, Navabi B, Shariat M. Neonatal urinary tract infection: clinical response to empirical therapy versus in vitro susceptibility at Bahrami Children's Hospital-Neonatal Ward: 2001–2010. Acta Med Iran. 2012;50:348–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
57. Williamson JC, Craft DW, Butts JD, et al. In vitro assessment of urinary isolates of ampicillin-resistant enterococci. Ann Pharmacother. 2002;36:246–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2002;36:246–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
58. Laugel V, Kuhn R, Beladdale J, et al. Effects of antenatal antibiotics on the incidence and bacteriological profile of early-onset neonatal sepsis. A retrospective study over five years Biol Neonate. 2003;84:24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
59. Kuhn P, Dheu C, Bolender C, et al. Incidence and distribution of pathogens in early-onset neonatal sepsis in the era of antenatal antibiotics. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2010;24:479–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
60. Glasgow TS, Young PC, Wallin J, et al. Association of intrapartum antibiotic exposure and late-onset serious bacterial infections in infants. Pediatrics. 2005;116:696–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
61. Benador D, Neuhaus TJ, Papazyan JP, et al. Randomised controlled trial of three day versus 10 day intravenous antibiotics in acute pyelonephritis: effect on renal scarring. Arch Dis Child. 2001;84:241–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
62. Cherry J, Demmler-Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, et al. Feigin and Cherry's textbook of pediatric infectious diseases. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2013. [Google Scholar]
Feigin and Cherry's textbook of pediatric infectious diseases. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2013. [Google Scholar]
63. Nowell L, Moran C, Smith PB, et al. Prevalence of renal anomalies after urinary tract infections in hospitalized infants less than 2 months of age. J Perinatol. 2010;30:281–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
64. Siomou E, Giapros V, Fotopoulos A, et al. Implications of 99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy performed during urinary tract infection in neonates. Pediatrics. 2009;124:881–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
65. Biyikli NK, Alpay H, Ozek E, et al. Neonatal urinary tract infections: analysis of the patients and recurrences. Pediatr Int. 2004;46:21–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
66. Garin EH, Olavarria F, Garcia Nieto V, et al. Clinical significance of primary vesicoureteral reflux and urinary antibiotic prophylaxis after acute pyelonephritis: a multicenter, randomized, controlled study. Pediatrics. 2006;117:626–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
67. Hayashi Y, Kojima Y, Kamisawa H, et al. Is antibiotic prophylaxis effective in preventing urinary tract infections in patients with vesicoureteral reflux? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010;8:51–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hayashi Y, Kojima Y, Kamisawa H, et al. Is antibiotic prophylaxis effective in preventing urinary tract infections in patients with vesicoureteral reflux? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010;8:51–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
68. Williams GJ, Wei L, Lee A, et al. Long-term antibiotics for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(19) CD001534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
69. RIVUR Trial Investigators. Hoberman A, Greenfield SP, et al. Antimicrobial prophylaxis for children with vesicoureteral reflux. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2367–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
70. Harris MC, Deuber C, Polin RA, et al. Investigation of apparent false-positive urine latex particle agglutination tests for the detection of group B streptococcus antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1989;27:2214–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
71. Benjamin DK, Jr, Stoll BJ, Gantz MG, et al. Neonatal candidiasis: epidemiology, risk factors, and clinical judgment. Pediatrics. 2010;26:e865–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pediatrics. 2010;26:e865–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
72. Cantey JB, Wozniak PS, Sánchez PJ. Prospective surveillance of antibiotic use in the neonatal intensive care unit: results from the SCOUT study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 [Epub ahead of print] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Urinary tract infection in newborns.
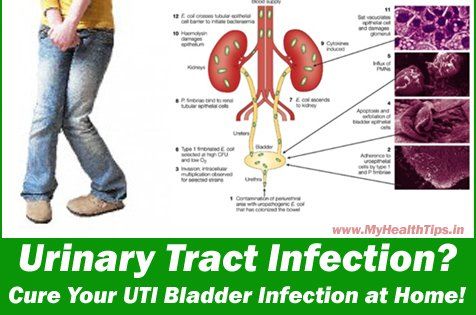
Urinary tract infection in young children is no less common than viral respiratory infections. Vomiting and nausea, cramps in the abdomen are often attributed by parents to colic, malnutrition, or intestinal infections. However, with such symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor. If this is a urinary tract infection, then its untimely diagnosis and treatment will lead to unpleasant consequences for the baby.
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria in the child's body begin to multiply rapidly in the urinary tract.
Most often this pathology is caused by microbes such as:
- Escherichia coli,
- Staphylococcus aureus,
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
- Klebsiella
These include:
- vesicoureteral reflux;
- narrowing of the ureters;
- malposition of the organs of the urinary system;
- horseshoe kidney and others
Another cause of infection is the presence of a microbial focus in the body. With an infectious-inflammatory pathology of other organs, the bacterial flora can enter the kidneys and urinary tract, causing inflammation there. Also, the bacterium can enter the baby's body from the mother during breastfeeding.
With an infectious-inflammatory pathology of other organs, the bacterial flora can enter the kidneys and urinary tract, causing inflammation there. Also, the bacterium can enter the baby's body from the mother during breastfeeding.
Genitourinary infection in infants presents with the same symptoms as in adults. The problem is that a newborn baby cannot complain.
Parents should keep a close eye on their child to detect symptoms of illness.
Initial symptoms include tearfulness, restlessness, poor sleep and loss of appetite.
In children under one year old, a urinary tract infection may be manifested by a decrease or increase from the age norm of urine excreted, a change in the color and saturation of urine (the child's urine may become bright yellow (with an increase in the concentration of urine, which is usually accompanied by a decrease in its quantity), red or brown (admixture of blood.) When bacteria appear, the urine does not change its color, but becomes cloudy and loses its transparency.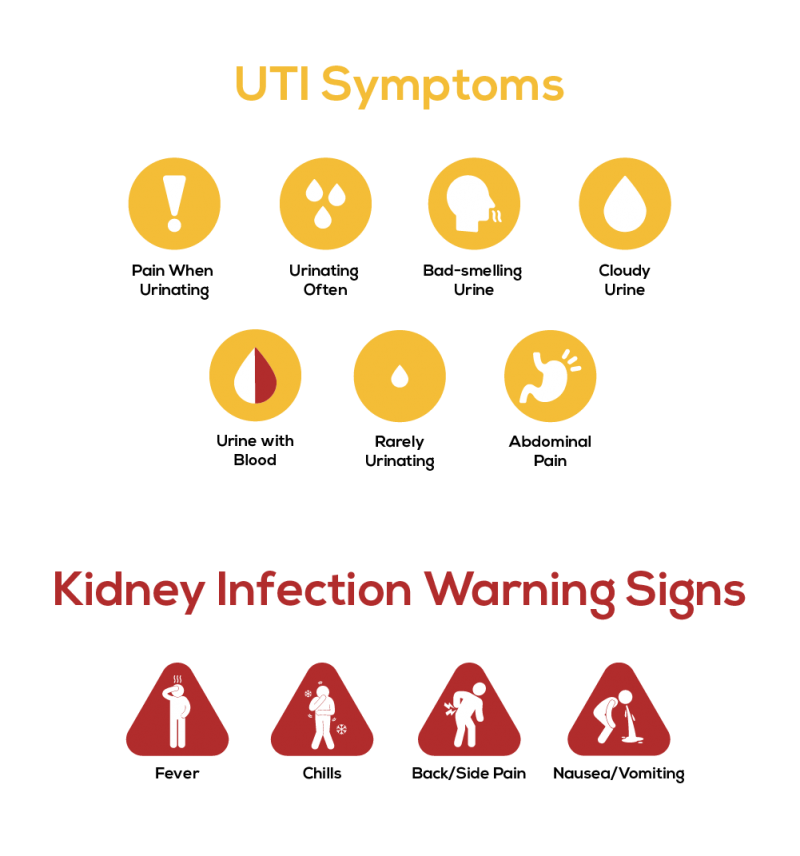 0003
0003
Edema may appear due to the characteristics of the baby's body, the appearance of an unpleasant smell from the diaper.
The appearance of restlessness and crying when urinating, which indicates the presence of pain and cramps in the baby. Often, mothers note that the child strains when urinating. In this case, an intermittent stream of urine is recorded.
The rise in temperature to high numbers, if it does not go away after taking antipyretics and persists for several days, this is a reason to suspect an infection.
Infection of the genitourinary system in infants is detected by laboratory analysis of urine, urine culture, blood test, b / x blood test.
In case of inflammation, blood and urine tests show an increase in the number of leukocytes. With bakposev, it is possible to identify which bacterium caused the infection, and determine the individual sensitivity of the microbe to the antibiotic.
As noted above, the cause of infection in infants may be a congenital malformation of the genitourinary organs.
If this pathology is suspected, the following examinations should be performed:
- ultrasound examination of the urinary system organs;
- voiding cystography;
- retrograde radiography of the kidneys;
- CT or MRI of the kidneys.
The basis for the treatment of urinary tract infection is antibiotic therapy. A broad-spectrum antibiotic or a drug based on sensitivity is prescribed. The antibiotic is taken orally or injected intravenously.
It is important that if an infection is detected, the infant must be hospitalized for the duration of treatment.
In addition to antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and antipyretics are used. Moreover, many medicines are produced in a convenient form of application, for example, in candles.
Herbal uroseptics are often prescribed, which do not have a toxic effect and contribute to the recovery of the child. In no case should you start treatment on your own or cancel medications without a doctor's prescription.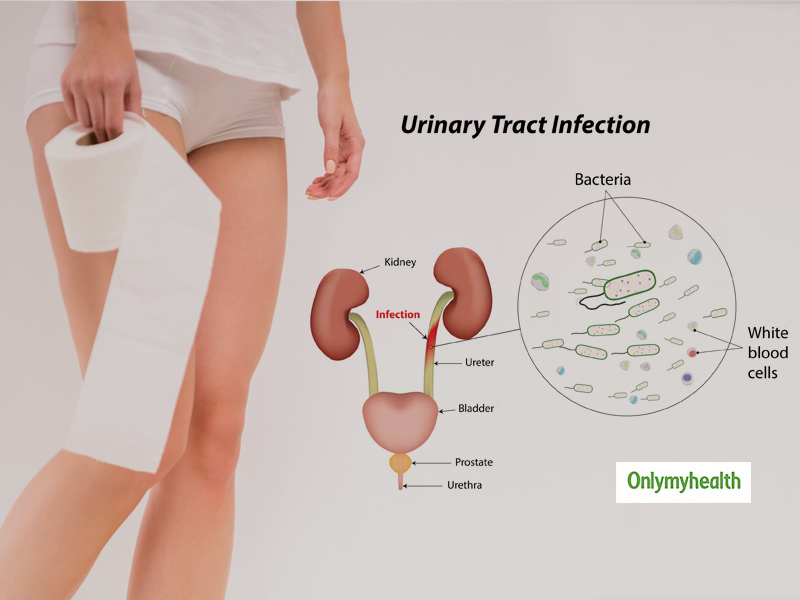 This will lead to the fact that the disease will go into a latent stage and will periodically worsen, again and again causing unpleasant symptoms. In addition, many drugs are contraindicated for children and their uncontrolled use will bring irreparable harm to the child.
This will lead to the fact that the disease will go into a latent stage and will periodically worsen, again and again causing unpleasant symptoms. In addition, many drugs are contraindicated for children and their uncontrolled use will bring irreparable harm to the child.
Infection in infants with malformations will constantly recur despite good treatment. Therefore, the only way out is to carry out an operational correction of the defect. It should be noted that the operation is possible only after the acute inflammatory process is eliminated.
Prevention of urinary tract infections in infants.
In order to rule out an illness in a child, the following points should be followed:
- Carefully monitor the hygiene of the child's urinary organs.
- avoid hypothermia of the baby;
- monitor the rationality of nutrition.
Every year about 1400 children are treated in the Department of Prematurity and Pathology of Newborns. Of these, with urinary tract infection 65-70, with various congenital malformations of the kidneys and urinary system 28-30 children. All children undergo a complex of examinations and treatment according to the developed standards. All children are discharged with improvement and recovery and are subsequently observed by nephrologists and urologists in the regional children's clinic.
All children undergo a complex of examinations and treatment according to the developed standards. All children are discharged with improvement and recovery and are subsequently observed by nephrologists and urologists in the regional children's clinic.
Infection of the genitourinary system is not such a terrible diagnosis. With a complete examination and high-quality, adequately selected therapy, the child will recover without any residual effects.
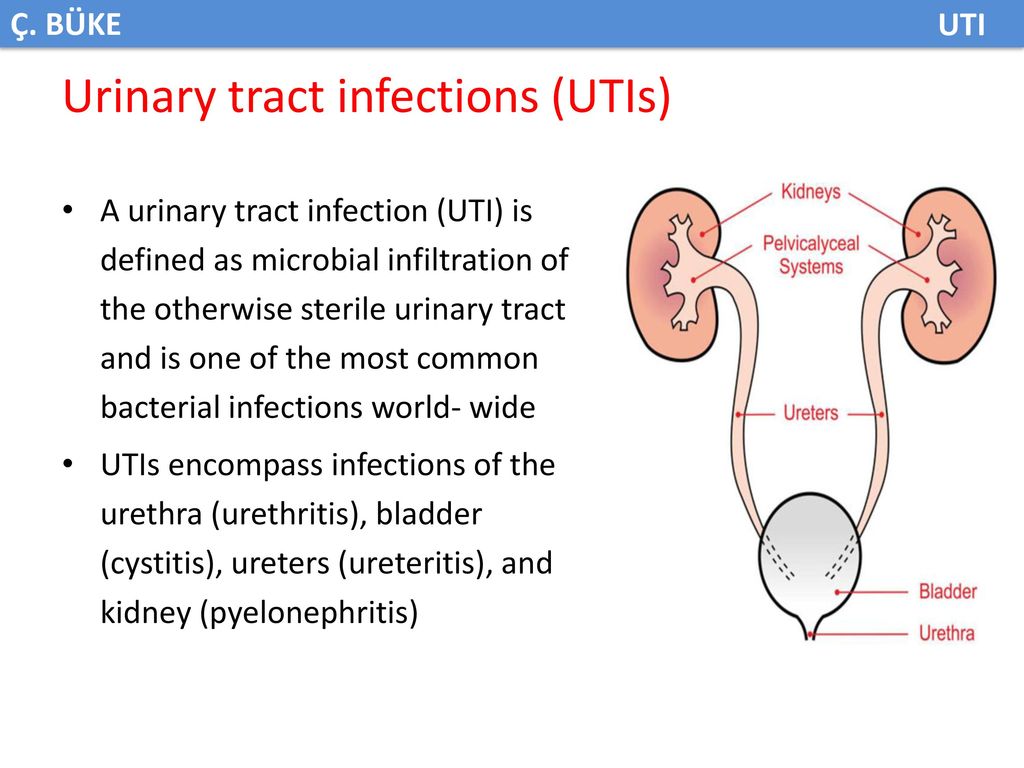
Urinary tract infection in children
Urinary tract infection is the presence of a clinically significant number of bacteria in the urinary tract in a patient with clinical manifestations of infection [2]. This definition is given to us by foreign colleagues. In domestic recommendations, the definition is somewhat simpler, and this, in our opinion, creates some confusion in the heads of doctors, and, as a result, parents.
A urinary tract infection is a growth of bacteria in the urinary tract.
A little later I will explain why the difference in definitions is so important.
Urinary tract infection occurs at different ages with different frequency. It is customary to say that in children under 3 months the average frequency is about 7.2%, while in girls it is about 7.5%, and in boys it is 2.3% with circumcised foreskin and 20.1% without circumcision. At the age of over 3 months, such striking differences are no longer found, and the frequency of occurrence is 4.5–6.5%. And it remains approximately the same throughout the entire period of childhood, while in girls the frequency of occurrence is approximately 4 times higher than in boys [1].
Why is a urinary tract infection dangerous?
First of all, the fact that as a result of the course of the infectious process, the death of some parts of the renal tissue may occur, as a result of which scars will form. This is called nephrosclerosis. It is bad because the scar, unlike the renal tissue, which is called the parenchyma, does not perform the functions of the kidney, that is, the renal function decreases.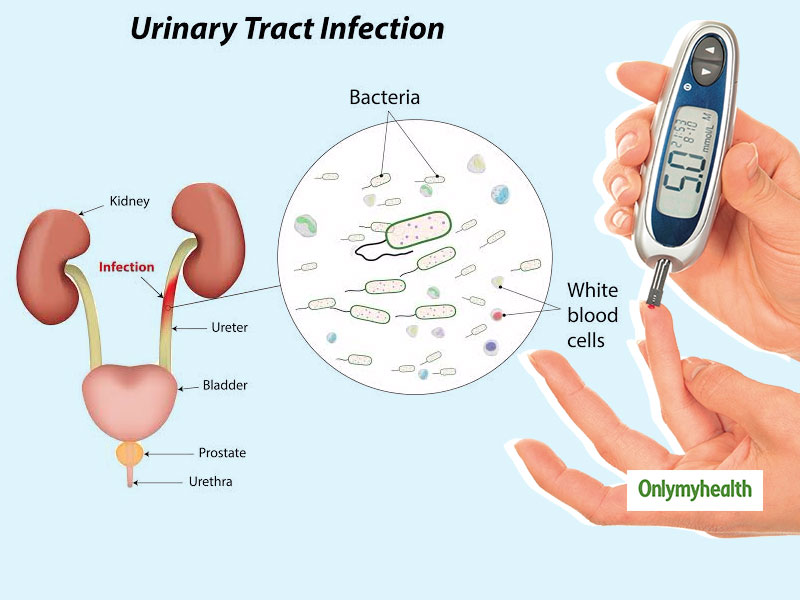 As a result, chronic kidney disease develops, or, as it was previously called, chronic renal failure.
As a result, chronic kidney disease develops, or, as it was previously called, chronic renal failure.
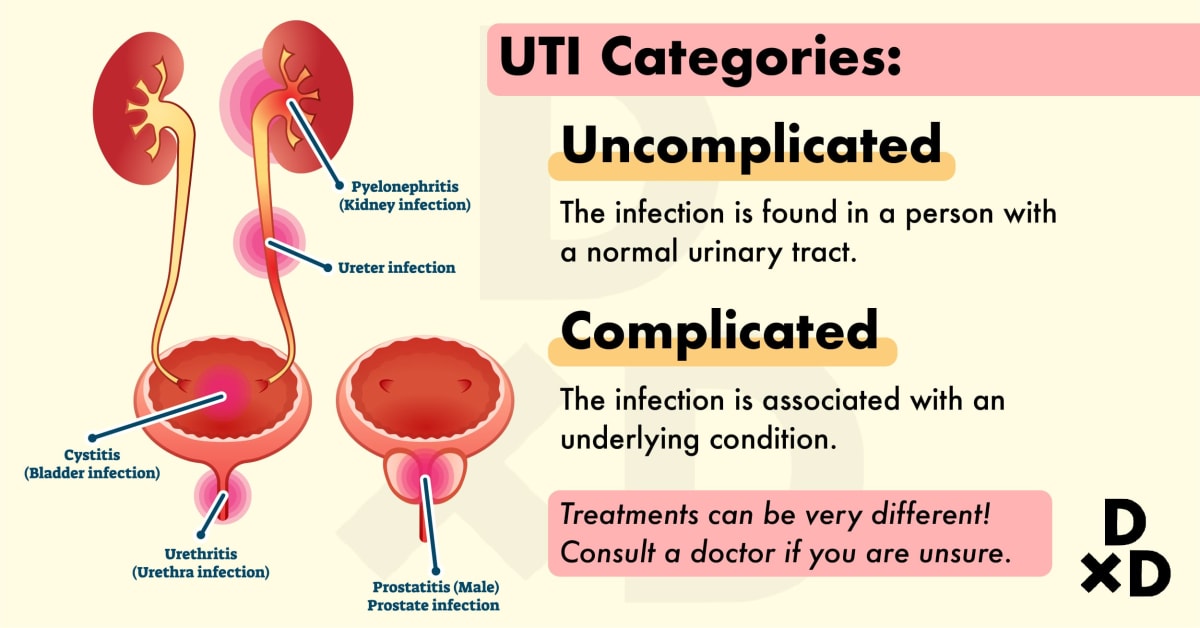
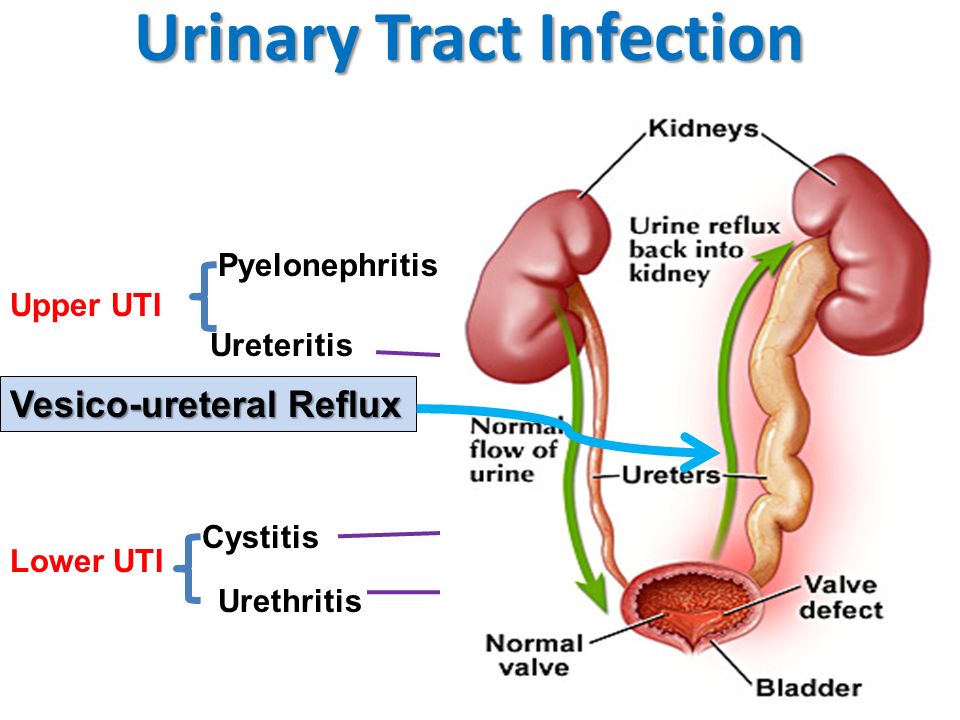
Also, until we started discussing the causes and other things associated with UTIs in children, I want to note that the division of urinary tract infections in children into the usual cystitis, pyelonephritis at an early age is extremely difficult, in this regard, it is customary to use a broad term UTI for children under two years of age.
Causes
The causes of any infection are infectious agents. There are several of them: bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa . In the case of urinary tract infections in children, the most common cause is bacteria . Urinary tract infections of viral etiology are extremely rare in children, usually they are children older than two years and it manifests itself most often as cystitis, fungal infections are always associated with immunodeficiencies, and therefore are also quite rare [3,2].
About bacteria: the leader in this matter is E. coli. Its share in the structure of the incidence of urinary infections accounts for about 80%. Of course, both Klebsiela and Proteus and various types of Staphylococci are capable of causing UTI and even cause it, but their proportion is not very large. Moreover, if we focus on the global evidence base, it is urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli that most often lead to the formation of nephrosclerosis [1,3,4].
coli. Its share in the structure of the incidence of urinary infections accounts for about 80%. Of course, both Klebsiela and Proteus and various types of Staphylococci are capable of causing UTI and even cause it, but their proportion is not very large. Moreover, if we focus on the global evidence base, it is urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli that most often lead to the formation of nephrosclerosis [1,3,4].
Pathogenesis
A terrible word, this will probably be the most difficult to read section of this article, but without understanding it, it will be quite difficult to understand the logic of diagnosis and treatment. We will try to make it as accessible as possible.
A huge amount of research tells us that bacteria enter the urinary tract from below. In medicine, this is called the ascending pathway of penetration, but this is not particularly important. From below, this is not from the floor, as one might think, but from the skin of the perineum and the mucous membrane of the genital organs.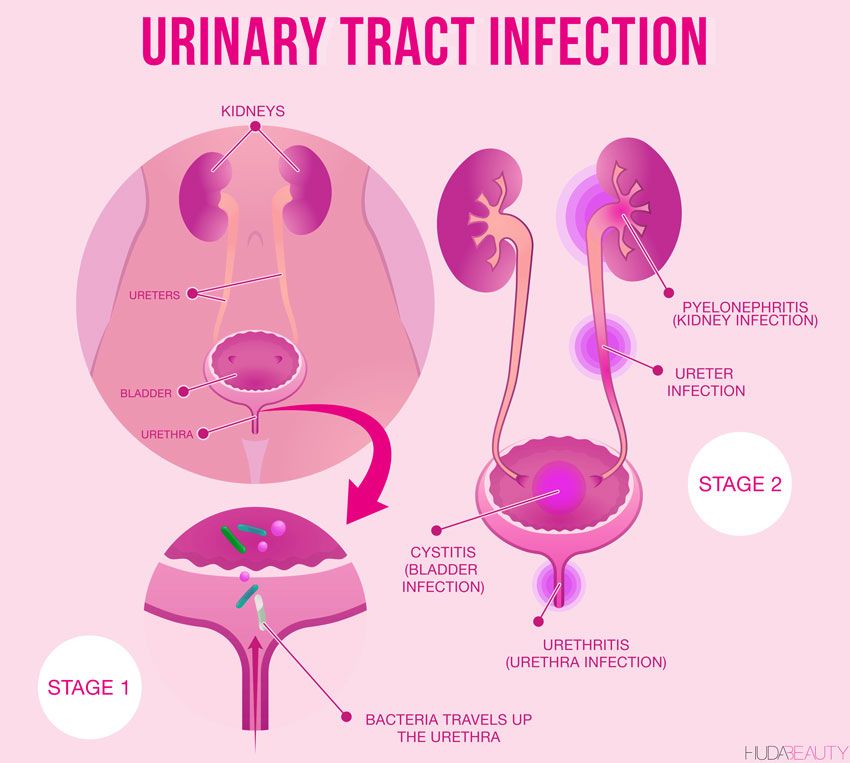 However, this does not mean at all that it is urgent to wash the child with antibacterial soap.
However, this does not mean at all that it is urgent to wash the child with antibacterial soap.
- First, antibacterial soap was invented to wash the surgeon's hands before surgery.
- Secondly, in principle, washing the perineum with soap is not very good, bacteria will be there anyway, because their home is there.
Bacteria adapt - this is important.
In order for bacteria, like any organism, to survive, they have all sorts of useful devices. For example, small legs (drank), with which they can attach to the mucous membrane, or a capsule that protects the cell wall from an aggressive environment. All these things, bacteria acquire in the process of evolution and interaction with various environments. In addition, we ourselves actively help them in this matter, for example, when they use antibacterial drugs uncontrollably and incorrectly. [6, 7, 8]
After the bacteria have entered the urethra, they diligently begin to climb higher, and here our body has something to oppose to them.
-
The mucous membrane begins to actively produce mucus . The more bacteria, the more active. Mucus - firstly, it makes the attachment of bacteria not so strong. Try to hang on a dry horizontal bar yourself and hang on a horizontal bar that has been lathered with soap. The difference will be very obvious. In addition, when mucus is produced, the blood flow increases, and with the blood flow, a huge amount of very useful for protection comes to this place, including leukocytes and other substances that are so “favorite” by mothers, which, after getting into place, come to grips with the intruder. [1,6].
-
The next defense mechanism is urine itself (just try to take it out of context and start using it, I will come in terrible dreams for the rest of my life).
-
The third protective factor that helps the body fight infection is urinary tract epithelium . It updates very quickly. And if the inflammatory process flows
The main protective properties of urine should be attributed to the fact that it flows and this current washes away bacteria that do not cling very tightly to the wall due to mucus.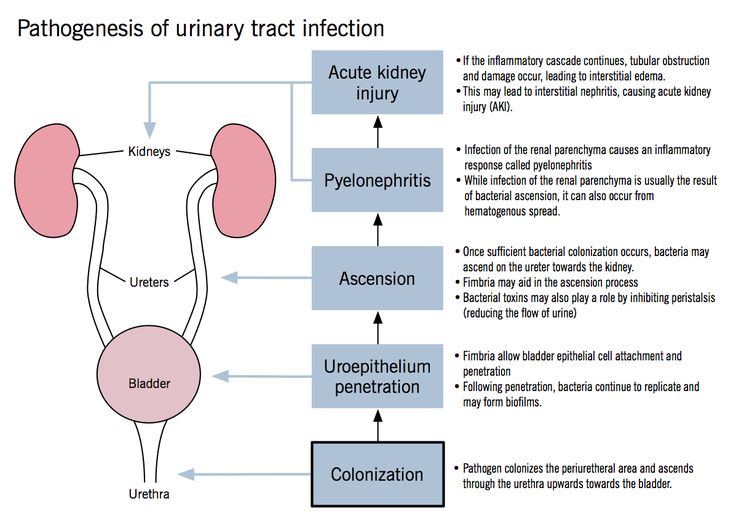
The second no less important property of urine is that it is acidic, and most bacteria do not really like an acidic environment and, if they do not die immediately in it, then at least stop multiplying.
It is on this fact that the idea of taking cranberry-based drugs or products for prevention is based. The only problem is that the body is a little more complicated than a pot of soup, but more on that later.
So why does infection still occur?
Mucus is released, urination has become more frequent, urine is acidic in itself, but this does not save if there are too many bacteria.
No matter how cool the 3 musketeers are, but there are only three of them, if the guardsmen have a numerical advantage, the musketeers cannot cope.
When is there a lot of bacteria?
-
When the path to be taken by bacteria is short (the female urethra is only 8–9cm, and men's - 20-25)
-
When a child cannot control a bowel movement (for example, in a diaper)
-
When there is an obstruction to the outflow of urine (hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, posterior urethral valve, bladder dysfunction, chronic constipation)
Usually these are the most common reasons that bacteria still break into the urinary tract. After they have broken through, they begin to actively share, and here the help of doctors is needed.
It seems that we figured out the pathogenesis, drove on. I hope those who read carefully will be a little less afraid of a urine test with 3 leukocytes.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of UTIs in children differ depending on the age of the child [1].
It is customary to talk about signs of infection in a child younger than two years old.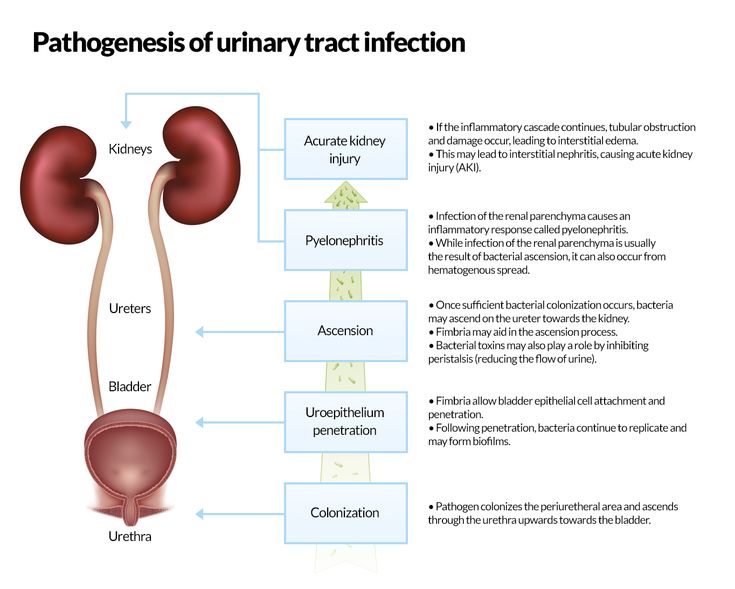
Why are the manifestations different?
Most likely this is due to the fact that it is extremely difficult for a child under 2 years old to complain, and we are forced to focus on objective indicators of the disease.
Objective symptoms of UTI in a child under 2 years of age, most often only one - an increase in body temperature above 38.5 degrees Celsius, without other signs of infection. Namely, the pediatrician examines and ascertains the absence of cough, redness of the throat, runny nose and other signs of respiratory infections.
There are no other manifestations of urinary tract infection at this age!
What about our favorite urine test. Urine analysis is of clinical importance only if there is a guarantee of a sterile set of this very urine. Recommendations say that the guarantee of a clean collection is collection with a sterile urinary catheter or suprapubic puncture of the bladder. And one and the other way is only suitable for a doctor. That is, the urine collected by the mother in a jar to assess the presence of a urinary tract infection is not suitable. [1,2,4,5].
That is, the urine collected by the mother in a jar to assess the presence of a urinary tract infection is not suitable. [1,2,4,5].
In children older than two years, additional symptoms of a urinary tract infection may appear, such as: frequent urination, pain when urinating, pain in the lumbar region or above the pubis.
But, here it is also very important that all this should be the same against the background of an increase in temperature above 38.5 degrees. Urinary tract infection in healthy children always occurs with fever. No other is given. [9, 5] All parents whose children were diagnosed with chronic pyelonephritis by urinalysis, in the absence of clinical symptoms - congratulations. You most likely do not have any chronic pyelonephritis.
Separately, I would like to note such a moment as the smell of urine. There is a discrepancy between our recommendations and foreign ones. Foreigners say that the smell of urine is not a diagnostic symptom of urinary tract infection in children and at the same time refer to a number of clinical studies in which parents, using a questionnaire, noted that the smell was different from the usual one, and doctors, not knowing about the questionnaire, diagnosed UTIs.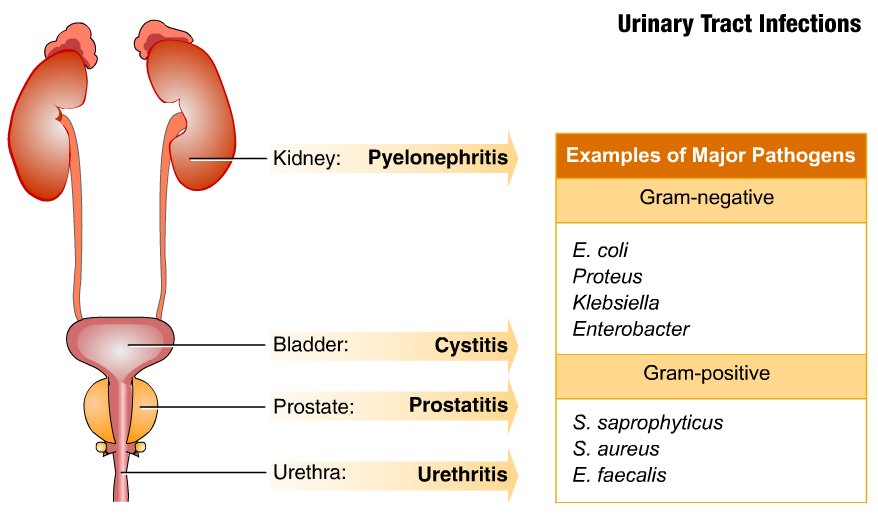 As a result, most studies have not found a clear statistically significant relationship between urine odor and UTI in children [1].
As a result, most studies have not found a clear statistically significant relationship between urine odor and UTI in children [1].
Our guidelines state that foul-smelling urine is a clinical criterion for urinary tract infection, without reference to anything [4]. This is how we write recommendations, nothing can be done about it. Although, it should be noted that this is also not the main feature, so let's forgive our creators this discrepancy.
Why, in my opinion, the smell of urine has no clinical significance? Because the smell changes depending on a bunch of different factors that cannot be objectively taken into account.
Given the very minor manifestations of urinary tract infections in children, there are very few diagnostic methods, not because there are few methods, but because more is simply not needed. To diagnose a urinary tract infection in children, an examination by a pediatrician is sufficient. If the child can collect an average portion of urine, then a urine test will also help.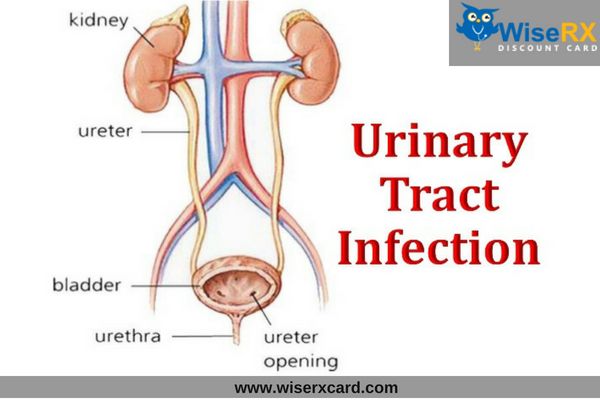
Also, if a urinary tract infection is suspected, ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is performed in order to assess the state of these same organs [2].
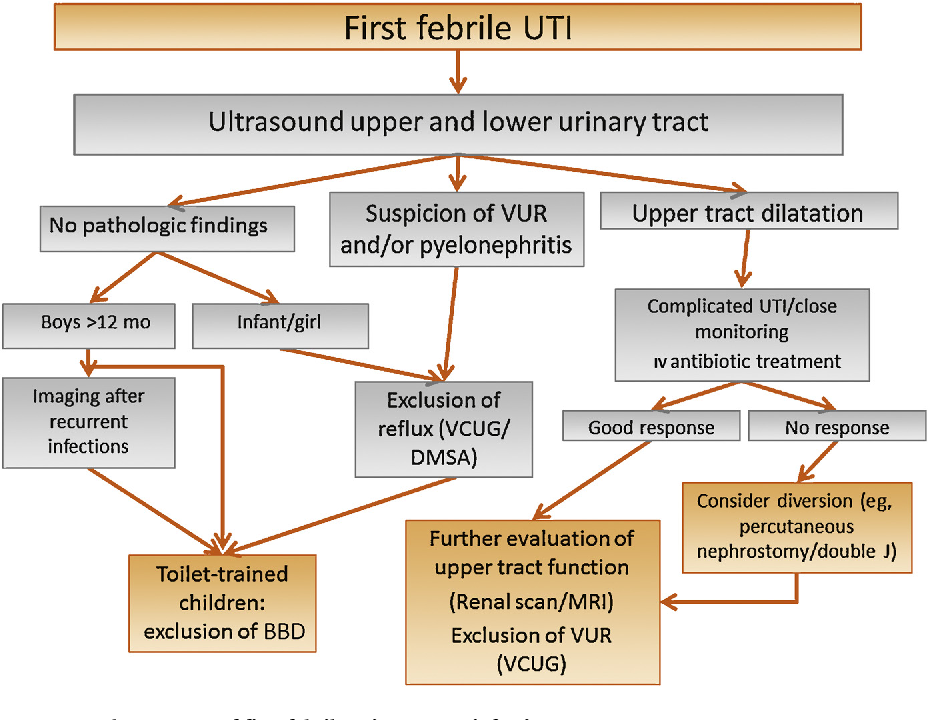
The main examinations begin after a urinary tract infection, as we need to exclude what is called in medical language - a complicated urinary tract infection. Namely, anomalies in the development of the urinary tract.
Here again we run into differences, this time between the recommendations of pediatricians and the recommendations of urologists. The American Academy of Pediatrics considers that a single episode of urinary tract infection is not a reason to conduct an examination [1]. The American Association of Urology (there are no separate pediatric urologists and this is reasonable) does not agree with this idea, because there is about a 40% chance of missing vesicoureteral reflux and other pathologies that do not manifest themselves.
The European Association of Pediatric Urology also disagrees with the idea of no examination for a single urinary tract infection.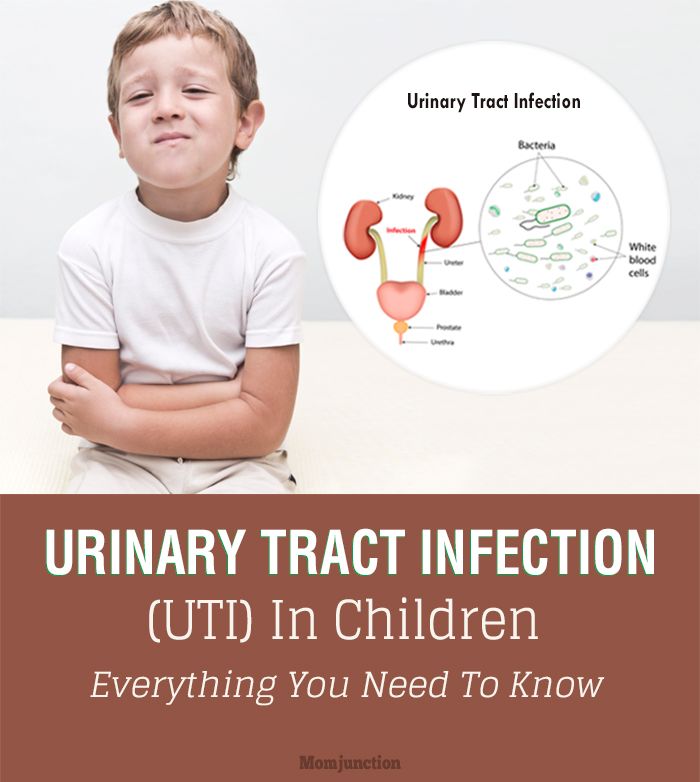 As a result, until a consensus was reached in the following way: if the child had a urinary tract infection and, according to ultrasound, he does not have signs of expansion of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys, then you can not examine, but control the ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. If the child had a urinary tract infection more than 1 time, even without changes according to ultrasound, a complete urological examination is indicated [10].
As a result, until a consensus was reached in the following way: if the child had a urinary tract infection and, according to ultrasound, he does not have signs of expansion of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys, then you can not examine, but control the ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. If the child had a urinary tract infection more than 1 time, even without changes according to ultrasound, a complete urological examination is indicated [10].
Here, it is important to remember that the infection must be confirmed clinically. That is, there should be a clinical picture if we are talking about children under 2 years old. If the child is older than two years, then there should be a clinical picture, analysis and urine culture.
And the second point, which is no less important for children older than two years. If they have a urinary tract infection, it is imperative to indicate the location of the infection. This is where the well-known come on stage: cystitis and pyelonephritis.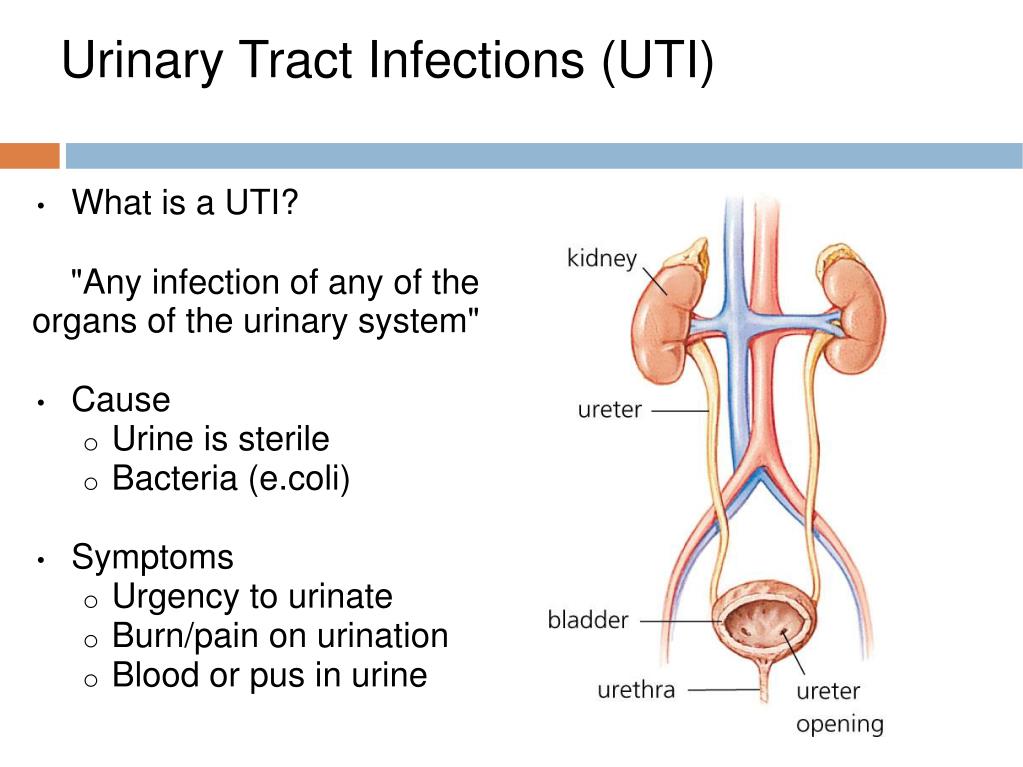
How to treat?
Given the fact that we are talking about an infection, that is, about the presence of bacteria, we treat it with antibacterial drugs. The doctor at the appointment will tell you about the dosage, duration, etc., but there is no other method of treating the infection. If someone says: you have a urinary tract infection - drink vitamins, dietary supplements, herbal remedies - this has nothing to do with treatment. In order to cure the infection, you need to kill the bacteria in the urinary tract.
Where, then, are all the different preparations for prophylaxis?
They are for prevention. But prevention is the measures we take to prevent re-infection. It is usually done after treatment, when we have proven clear test results and understand that there are no bacteria in the urinary tract.
What methods are available to prevent UTIs in children?
Given the fact that there are natural functions of the body that protect us from the penetration of bacteria into the urinary tract, prevention should begin influencing these same functions:
-
Drinking regimen - there is no norm for fluid intake.
 Here it is important to dance from the characteristics of the body, someone needs a little more, someone a little less, however, when a girl of 7-8 years old comes to the reception, fills out a urination diary and we understand that she drinks 400-500 milliliters of fluid per day - it is still very small.
Here it is important to dance from the characteristics of the body, someone needs a little more, someone a little less, however, when a girl of 7-8 years old comes to the reception, fills out a urination diary and we understand that she drinks 400-500 milliliters of fluid per day - it is still very small.
A child under 3 years old usually drinks 200-900 ml. liquids. A child over 3 years of age usually drinks more than 1 liter. It is important to take into account all the liquid, and water and juice and tea and compote. That is, if a child drinks a cup of tea and 1 glass of water 4 times a day, most likely he does not have a deficit in fluid intake. Here our task is rather to offer a drink, as children tend to forget about it when they are busy with something interesting. -
An integral part of the drinking regime - urination . Just as a child can forget to drink, go to the toilet, he too can forget or delay. It is important to remind the child of this.
 On average, this must be done 1 time in 2-2.5 hours.
On average, this must be done 1 time in 2-2.5 hours.
-
Control of vaginal microflora in girls . Yes, unfortunately, even in little girls, often recurrent urinary tract infections occur due to problems in the vagina or problems associated with the vulva. Examination by a gynecologist is very important, as often the symptoms attributed to cystitis are not related to it.
-
Control of stool regularity . A constipated child is the number 1 candidate for a urinary tract infection. It is important to consume a sufficient amount of fiber, to monitor the regularity of the stool. If you can’t solve problems with the stool on your own, you need to contact a pediatrician or gastroenterologist.
-
Antibiotic prophylaxis - a situation where a child is prescribed to take uroseptic drugs for a long time. Yes, there is such a method. Yes, it's in the instructions. But antibiotics do not cure the cause.
 If the infection recurs, there is a reason. The antibiotic treats the infection. The cause remains, which means that after the antibiotic is discontinued, it is likely to reappear.
If the infection recurs, there is a reason. The antibiotic treats the infection. The cause remains, which means that after the antibiotic is discontinued, it is likely to reappear.
Bladder infusions and instillations, physiotherapy do not appear in recommendations and decent studies, since there is no data on their effectiveness.
Currently, bacteriophage preparations are being actively studied and used for the prevention of urinary tract infections, including in children. According to currently available data, these methods show good efficiency, but research is ongoing.
Terminals
As a conclusion, I would like to say that urinary tract infection is a rather wide problem for a number of reasons:
- Firstly, outpatient doctors have obvious difficulties in understanding the criteria for making this diagnosis and the tactics of examination and treatment of such children.
- Secondly, the cheapness and availability of basic urinalysis results in a huge stream of children with "bad" urinalysis who are prescribed therapy for the sole purpose of curing the analysis.
- Thirdly, at the same time, there is a fairly large number of children with recurrent cystitis, the diagnosis and treatment of which is carried out without taking into account any recommendations, using "author's" treatment regimens, which is unacceptable in medicine in general, and especially in pediatric practice. The inefficiency of such methods significantly increases the duration of the disease, reduces the quality of life of children and parents, in addition, economically, these methods can be very costly for the family budget.
The problem of urinary tract infections in children is multidisciplinary in nature and requires the collaboration of several specialists to achieve a good result in the treatment of small patients.
Sources :
Nader Shaikh, MDAlejandro Hoberman, MD Urinary tract infections in children: Epidemiology and risk factors, https://www.uptodate.com/contents/urinary-tract-infections-in-children-epidemiology-and-risk-factors
Nader Shaikh, MDAlejandro Hoberman, MD, Urinary tract infections in infants and children older than one month: Clinical features and diagnosis, https://www.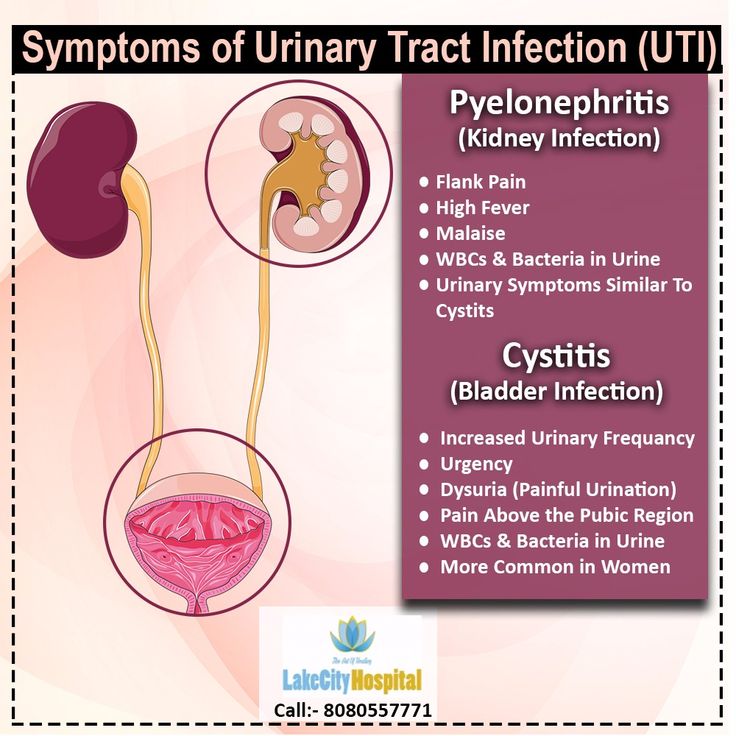 uptodate.com/contents/urinary-tract-infections-in-infants-and-children -older-than-one-mo...
uptodate.com/contents/urinary-tract-infections-in-infants-and-children -older-than-one-mo...
Wald ER. Cystitis and pyelonephritis. In: Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 8th ed, Cherry JD, Harrison G, Kaplan SL, et al (Eds), Elsevier, Philadelphia 2019. p.395.
Urinary tract infection, clinical guidelines of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 2021, 33 p.
L.B. Menovshchikova, Yu.E. Rudin, T.N. Garmanova, V.A. Shaderkina Clinical guidelines for pediatric urology-andrology. M.: Pero Publishing House, 2015.
Oelschlaeger TA, Dobrindt U, Hacker J Virulence factors of uropathogens. Curr Opin Urol. 2002;12(1):33.
Mulvey MA Adhesion and entry of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell Microbiol. 2002;4(5):257.
Nielubowicz GR, Mobley HL, Host-pathogen interactions in urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol. 2010 Aug;7(8):430-41.
Shaikh N, Craig JC, Rovers MM, Da Dalt L, Gardikis S, Hoberman A, Montini G, Rodrigo C, Taskinen S, Tuerlinckx D, Shope T, Identification of children and adolescents at risk for renal scarring after a first urinary tract infection : a meta-analysis with individual patient data.