Baby grows in tube
Ectopic Pregnancy (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
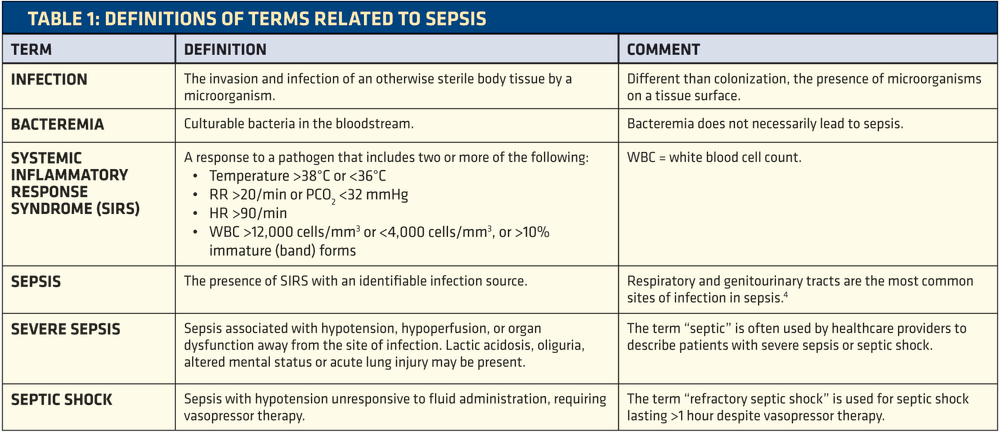
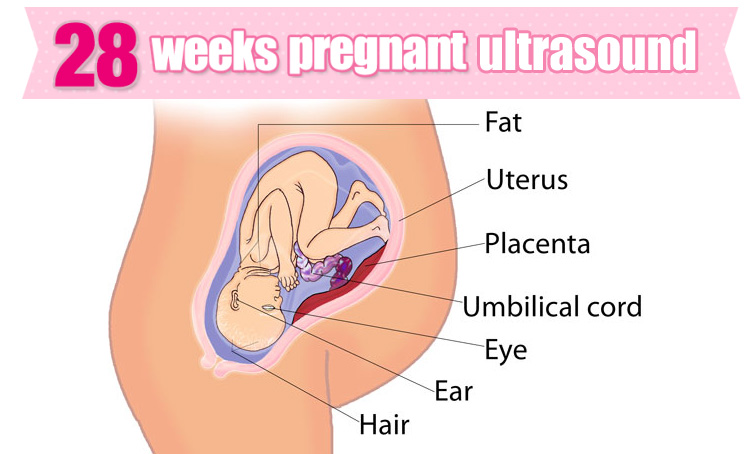
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and develops in the uterus. In an ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants somewhere other than the uterus — often, in the fallopian tubes. This is why ectopic pregnancies are commonly called "tubal pregnancies." The egg also can implant in the ovary, abdomen, or the cervix.
None of these areas has the right space or nurturing tissue for a pregnancy to develop. As the fetus grows, it will eventually burst the organ that contains it. This can cause severe bleeding and endanger the mother's life. A classical ectopic pregnancy does not develop into a live birth.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy can be hard to diagnose because symptoms often are like those of a normal early pregnancy. These can include missed periods, breast tenderness, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, or frequent urination (peeing).
Often, the first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy are pain or vaginal bleeding. There might be pain in the pelvis, abdomen, or even the shoulder or neck (if blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy builds up and irritates certain nerves). The pain can range from mild and dull to severe and sharp. It might be felt on just one side of the pelvis or all over.
These symptoms also might happen with an ectopic pregnancy:
- vaginal spotting
- dizziness or fainting (caused by blood loss)
- low blood pressure (also caused by blood loss)
- lower back pain
What Causes an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy usually happens because a fertilized egg couldn’t quickly move down the fallopian tube into the uterus. The tube can get blocked from an infection or inflammation. The tube can get blocked from:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- endometriosis, when cells from the lining of the uterus implant and grow elsewhere in the body
- scar tissue from previous abdominal or fallopian surgeries
- rarely, birth defects that changed the shape of the tube
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
If a woman might have an ectopic pregnancy, her doctor may do an ultrasound to see where the developing fetus is. Often, pregnancies are too small to see on ultrasound until more than 5 or 6 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. If an external ultrasound can’t show the pregnancy, the doctor might do the test with a wand-like device in the vagina.
Often, pregnancies are too small to see on ultrasound until more than 5 or 6 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. If an external ultrasound can’t show the pregnancy, the doctor might do the test with a wand-like device in the vagina.
A woman might need testing every few days if the first tests can’t confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy.
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Treated?
How doctors treat an ectopic pregnancy depends on things like the size and location of the pregnancy.
Sometimes they can treat an early ectopic pregnancy with an injection of methotrexate, which stops the growth of the embryo. The tissue usually is then absorbed by the woman’s body.
If the pregnancy is farther along, doctors usually need to do surgery to remove the abnormal pregnancy.
Whatever treatment she gets, a woman will see her doctor regularly afterward to make sure her pregnancy hormone levels return to zero. This may take several weeks. An elevated level could mean that some ectopic tissue was missed. If so, she might need more methotrexate or surgery.
If so, she might need more methotrexate or surgery.
What About Future Pregnancies?
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can have normal pregnancies in the future. Having had one ectopic pregnancy does increase a woman’s risk of having another one.
What Else Should I Know?
Any woman can have an ectopic pregnancy. But the risk is higher for women who are older than 35 and those who have had:
- PID
- a previous ectopic pregnancy
- surgery on a fallopian tube
- infertility problems or medicine to stimulate ovulation
Some birth control methods also can affect a woman's risk of ectopic pregnancy. Those who become pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) might be more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy. Smoking and having multiple sexual partners also increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
If you believe you're at risk for an ectopic pregnancy, meet with your doctor to talk about your options before you become pregnant. If you are pregnant and have any concerns about the pregnancy being ectopic, talk to your doctor — it's important to find it early. Your doctor might want to check your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound to ensure that your pregnancy is developing normally.
If you are pregnant and have any concerns about the pregnancy being ectopic, talk to your doctor — it's important to find it early. Your doctor might want to check your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound to ensure that your pregnancy is developing normally.
Call your doctor right away if you're pregnant and having any pain, bleeding, or other symptoms of ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic (Extrauterine) Pregnancy
Series Ectopic Pregnancy
Written by Shishira Sreenivas
What Is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Usually, a fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining in your uterus. But with an ectopic pregnancy (also called extrauterine pregnancy), the fertilized egg grows outside your uterus. This can include other areas like a fallopian tube, the ovaries, in your belly, or the lower part of your cervix, which is above the vagina. In more than 90% of cases, the egg attaches itself in a fallopian tube. This is called a tubal pregnancy.
Rates are hard to determine, but one study suggests that about 1 in 50 pregnancies in the U. S. are ectopic. As the fertilized egg grows, it can burst (rupture) and can cause life-threatening bleeding. If this happens, you will need medical care right away. If you don’t treat it, it can be deadly. In fact, ectopic pregnancies are the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the first trimester.
S. are ectopic. As the fertilized egg grows, it can burst (rupture) and can cause life-threatening bleeding. If this happens, you will need medical care right away. If you don’t treat it, it can be deadly. In fact, ectopic pregnancies are the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the first trimester.
It’s important to note that the fertilized egg in an ectopic pregnancy is not “viable.” That means it’s impossible for the egg to survive and grow into a baby that can survive in or outside your body. It will always result in a pregnancy loss. That’s because the egg can’t get the blood supply and support it needs to grow outside of the uterus.
Ectopic Pregnancy Signs and Symptoms
Most of the time, an ectopic pregnancy happens within the first few weeks of pregnancy. You might not even know that you're pregnant and may not notice any problems.
Early signs of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- Light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain
- Upset stomach and vomiting
- Sharp abdominal cramps
- Pain on one side of your body
- Dizziness or weakness
- Pain in your shoulder, neck, or rectum
An ectopic pregnancy can cause your fallopian tube to burst or rupture. Emergency symptoms include major pain, with or without severe bleeding. Call your doctor right away if you have heavy vaginal bleeding with lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain, or if you have severe belly pain, especially on one side.
Emergency symptoms include major pain, with or without severe bleeding. Call your doctor right away if you have heavy vaginal bleeding with lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain, or if you have severe belly pain, especially on one side.
You might need to call 911 or head to the nearest hospital to have it treated right away.
Ectopic Pregnancy Causes and Risk Factors
You may never know why you have an ectopic pregnancy. One cause could be a damaged fallopian tube. It could keep the fertilized egg from getting into your uterus.
You’re more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy if you:
- Have pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Smoke cigarettes
- Are older than 35
- Have a sexually transmitted infection
- Have scarring from pelvic surgery
- Had a previous ectopic pregnancy
- Tried to have tubal ligation (tubes tied) or tubal ligation reversal
- Use fertility drugs
- Had fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF)
It could also happen if you become pregnant while you have an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control.
Ectopic Pregnancy Complications
During an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg is wrapped in a structure that can grow for several weeks outside your uterus. But the structure usually bursts between 6 and 16 weeks. This can cause severe bleeding. If the bleeding isn’t stopped, your body might start to shut down due to the blood loss (hemorrhagic shock), and the odds of dying from it increases. If it’s treated before it bursts, it rarely results in death.
If the structure does burst, it may damage the fallopian tube it was attached to. Your doctor might remove the fallopian tube during the surgery. But you have two fallopian tubes. If your other fallopian tube is healthy, you should still be able to get pregnant. But if your other fallopian tube is damaged or not there, you may have fertility issues. In this case, talk to your doctor about other ways to get pregnant, like IVF (in vitro fertilization).
Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
Your doctor will probably do tests that include a pregnancy test and a pelvic exam. They might give you an ultrasound to look at your uterus and fallopian tubes.
They might give you an ultrasound to look at your uterus and fallopian tubes.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Because a fertilized egg can’t survive outside a uterus, your doctor will need to take it out, so you don’t have serious health problems. They’ll use one of two methods: medication or surgery.
Medication. If your fallopian tube hasn’t ruptured and your pregnancy isn’t far along, your doctor can give you a shot of methotrexate (Trexall). You only need one dose of the injection. It stops the fertilized egg from growing. Your body will absorb the egg in about 4-6 weeks. With this treatment, there’s no need to remove the fallopian tube.
Before you can take methotrexate, your doctor will need to run a few blood tests to measure your hCG levels (human chorionic gonadotropin). It’s the hormone your body produces when it detects a pregnancy. You won’t be able to take methotrexate if you’re breastfeeding or have certain health problems.
Once you get the shot, the doctor will check your hCG levels during follow-up appointments. If your levels don’t drop after the first dose, you might need a second dose of the same medication. You’ll need to follow up until your blood no longer has hCG.
If your levels don’t drop after the first dose, you might need a second dose of the same medication. You’ll need to follow up until your blood no longer has hCG.
It’s important to note that taking methotrexate is not the same as having a medical abortion, as you could get if you had a “viable” pregnancy in which the fertilized egg attaches inside the uterus. For a medical abortion, you need a combination of two prescription drugs: mifepristone and misoprostol.
The methotrexate that you take during an ectopic pregnancy before the egg bursts is medically necessary. It can lower your risk of dying or other serious complications.
Surgery. In other cases, you’ll need surgery. The most common is laparoscopy. Your doctor will make very small cuts in your lower belly and insert a thin, flexible tube called a laparoscope to remove the ectopic pregnancy. If your fallopian tube is damaged, they may have to remove it as well. If you’re bleeding a lot or your doctor suspects that your fallopian tube is ruptured, you might need emergency surgery with a larger cut. This is called a laparotomy.
This is called a laparotomy.
Surgery side effects can include:
- Pain
- Fatigue
- Bleeding
- Infection
Whether you take methotrexate or have surgery, you may feel tired for a few weeks and have some discomfort in your belly. You may continue to have pregnancy-like symptoms for a bit. It might take a few period cycles before you feel back to normal.
After an Ectopic Pregnancy
It might be hard for you to have a typical pregnancy afterward. Consider talking to a fertility specialist, especially if you had a fallopian tube removed.
And talk to your doctor about how long to wait before trying again. Some experts suggest giving yourself at least 3 months so your body has time to heal.
An ectopic pregnancy raises your risk of having another one. If you think you’re having another pregnancy, be mindful of the changes in your body. Check with your doctor, and they can confirm it and take the necessary steps.
An ectopic pregnancy can take a toll on your mental health, too. Don’t hesitate to reach out to mental health experts like a licensed counselor or therapist.
There’s no way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. But you can lower your odds with certain lifestyle choices.
You can:
- Use a condom when you have sex. This can lower your risk for PID and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid using a vaginal douche. Studies show that using a douche can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Next In Ectopic Pregnancy Series:
SymptomsWhat does a child do while it is in the mother’s stomach
August 17, 2018
In 9 months, a child goes a long way from a tiny embryo to a chubby baby and already in the womb acquires some features that will remain with him for life: for example, you can understand whether he will become right-handed or left-handed and what kind of food he will prefer. In a fairly short period of time, a lot of interesting things happen to a child, and today we invite you to go through the path from birth to birth with your baby.
1st trimester of pregnancy
1st–2nd week
So the long journey began. For the first 4 days, the future person is smaller than a grain of salt - its size is only 0.14 mm. However, starting from the 5th day, it begins to grow and by the 6th it almost doubles - up to as much as 0.2 mm. On the 4th day, the embryo "comes" to where it will spend the next 9 months - into the uterus, and on the 8th day it is implanted in its wall.
3rd–4th week
© EDITORIAL USE ONLY/East News
Embryo at the 4th week of pregnancy.
Around the 20th day of pregnancy, a very important event occurs: the neural tube appears, which will then turn into the spinal cord and brain of the child. Already on the 21st day, his heart begins to beat and all important organs, such as the kidneys and liver, begin to form. The eyes have not yet taken their usual position - the bubbles from which they will then take shape are located on the sides of the head. By the end of the 1st month, the embryo has a circulatory system, and the spine and muscles begin to develop.
5th–6th week
© EDITORIAL USE ONLY/East News © lunar caustic/wikimedia
At the 5th week, the hands appear in the embryo, however, the fingers are still very difficult to distinguish, but in the joints the arms and legs are already bent. It was at this time that the external genitalia begin to form, but it is not yet possible to see on an ultrasound whether it is a boy or a girl. By the way, since its appearance, the embryo has grown a lot - it has increased by as much as 10 thousand times. Already now, the baby's face is beginning to form, and the eyes, which will be closed for a very long time, darken, becoming more human-like.
7th–8th week
The 7th week of pregnancy is the time when the baby begins to move, however, so far completely unnoticed by the mother, and the fingers and toes become almost the same as in adults. At this stage, the rudiments of milk teeth appear in the embryo and the reproductive system develops, and the kidneys begin to produce urine. Despite the fact that the growth of the fetus is only 2.5 cm, it acquires its own facial expressions, it has eyelids, and the tip of the nose becomes more defined.
At this stage, the rudiments of milk teeth appear in the embryo and the reproductive system develops, and the kidneys begin to produce urine. Despite the fact that the growth of the fetus is only 2.5 cm, it acquires its own facial expressions, it has eyelids, and the tip of the nose becomes more defined.
9th–10th week
© lunarcaustic/wikimedia
Baby at 9-10 weeks of gestation.
By this time, the baby has already grown well - its weight is 4 grams, and its height is 2-3 cm. Despite its tiny size, the brain is already divided into two hemispheres, and milk teeth and taste buds are beginning to form. The baby's tail and membranes between the fingers on the hands disappear, he begins to swim in the amniotic fluid and move even more actively, although still unnoticed by the mother. It was at this time that the child's individual facial features appear, and hair begins to grow on the head.
11–12 weeks
At this time, the genital organs are formed in the child, so it is already possible to find out his sex on an ultrasound scan, although the probability of an error is still high. The child still looks a little alien: he has a big head and a small body, but his face is more and more like an adult. The ears are almost in the right position, eyebrows and eyelashes appear. The cartilage that makes up the skeleton gradually ossifies, new blood vessels appear, and hormone production begins. By the way, the baby has already grown up to 6 cm and weighs about 20 grams.
The child still looks a little alien: he has a big head and a small body, but his face is more and more like an adult. The ears are almost in the right position, eyebrows and eyelashes appear. The cartilage that makes up the skeleton gradually ossifies, new blood vessels appear, and hormone production begins. By the way, the baby has already grown up to 6 cm and weighs about 20 grams.
13th-14th week
Baby at 14 weeks pregnant.
Despite the fact that the child's head is half the length of the entire body, the face is more and more reminiscent of an adult, and the rudiments of all 20 milk teeth have already been formed in the oral cavity. The child is already able to put his finger in his mouth, but he will learn to suck a little later. Due to the active formation of blood vessels, the baby's skin is red and very thin, so vellus hair appears on the body - lanugo, which is necessary to maintain a special lubricant that protects against hypothermia.
2nd trimester of pregnancy
15th–16th week
By the 15th week, the baby has grown to 10 cm and is gaining weight - now he weighs about 70 grams. Despite the fact that the eyes are still quite low, the face is already quite recognizable, moreover, the child begins to “make faces”, since the facial muscles are well developed. By this time, he already knows how to suck his thumb, and the sebaceous and sweat glands begin their work.
17th–18th week
And finally, the child's auditory canals are formed, so he begins to distinguish sounds well and hears the mother's voice, moreover, he is able to recognize it. In addition to the milk teeth, the embryos of the molars also appear, the bones are finally formed and begin to harden. By the way, the bones of the skull will remain mobile until birth - when passing through the birth canal, they will overlap each other to make it easier for the baby to be born. But the mother is finally beginning to feel the movements of the child, who has grown to 14 cm and 190 grams.
But the mother is finally beginning to feel the movements of the child, who has grown to 14 cm and 190 grams.
19th-20th week
Baby at 20 weeks pregnant.
Despite the fact that the child's eyes are still closed, he is already well oriented in the surrounding space. Moreover, now you can understand whether the child will be right-handed or left-handed, because right now he begins to use his dominant hand more actively. Fingerprints appear on the baby's fingers - another unique sign of each of us. By the way, the child is already beginning to gradually distinguish day from night and is active at a certain time.
21–22 weeks
The 21st week is the time when the baby begins to gain weight due to the formation of subcutaneous fat. Soon, the folds that newborns have will appear on his arms and legs. On the 22nd week, those neurons are formed in the brain that will be with a person all his life. Very soon the child will open his eyes, he is already trying to do this, and the eyeballs move almost like an adult.
23–24 weeks
At 23 weeks, the baby may begin to dream, and his face is so formed that an ultrasound can determine whose facial features he has inherited. His skin becomes opaque, his eyes open, and the child can already react to light, moreover, bright flashes can scare him. By the 24th week, the baby grows to almost 30 cm, and its weight reaches 0.5 kg.
25th–26th week
At this time, the taste buds of the child are finally formed and, tasting the amniotic fluid, he can frown if he does not like it. By the way, this is how eating habits are formed - already in the womb we have our favorite and unloved foods. Very soon the child will learn to blink and can already see a little, however, so far it is very, very vague.
3rd trimester of pregnancy
27th–28th week
Baby at 27–28 weeks of gestation.
If you do an ultrasound at this time, you can see how the baby smiles and intensively sucks his thumb. At this time, the baby has the first "toy" - his own umbilical cord, and he actively studies his body. At the end of the 7th month of pregnancy, the child develops an individual metabolism, which he will have all his life. The baby is already quite large - his weight reaches 1.2 kg, and his height is 35 cm.
At this time, the baby has the first "toy" - his own umbilical cord, and he actively studies his body. At the end of the 7th month of pregnancy, the child develops an individual metabolism, which he will have all his life. The baby is already quite large - his weight reaches 1.2 kg, and his height is 35 cm.
29th-30th week
© East News
Baby at 30 weeks pregnant.
The layer of subcutaneous fat is increasing, and the baby is becoming more and more plump and well-fed. In addition, he already knows how to cry, cough, and even sometimes hiccups - this happens, most likely, when he swallows too much amniotic fluid. By the 30th week, the baby's brain is already so developed that it is quite capable of remembering and even analyzing information.
31–32 weeks
At this time, a person has all 5 senses, and his daily routine is more and more reminiscent of the one he will follow after birth. The child hears the work of all the organs of the mother, knows her voice perfectly, thanks to which, immediately after birth, he is able to distinguish her from all other people. The baby's immune system begins to produce antibodies that will protect him from all kinds of infections that may lie in wait in the first days and months after birth.
The child hears the work of all the organs of the mother, knows her voice perfectly, thanks to which, immediately after birth, he is able to distinguish her from all other people. The baby's immune system begins to produce antibodies that will protect him from all kinds of infections that may lie in wait in the first days and months after birth.
33–34th week
And finally, subcutaneous fat is already formed, and lanugo disappears from the body of the fetus. By this time, the baby has grown a lot - the length of his body reaches 40 cm, and the weight is very close to or even exceeds 2 kg. The baby's nervous system is already fully formed, but the lungs are still developing.
35th–36th week
© East News
The child yawns. 3D ultrasound at 36 weeks pregnant.
At this time, the child looks almost exactly the same as when he was born. He is still quite thin, but the layer of subcutaneous fat is increasing more and more intensively. However, his hair and nails are already fully developed, and he himself becomes so big that he has almost no room to maneuver, so he can move less than in earlier stages.
However, his hair and nails are already fully developed, and he himself becomes so big that he has almost no room to maneuver, so he can move less than in earlier stages.
37–38th week
And finally, the process of forming a person has finally ended - now he is completely ready for birth, and obstetricians consider the pregnancy to be full-term. Lanugo completely disappears from his body and can only sometimes remain on his arms and legs. Since there is almost no space left in the uterus, it may seem to the mother that the child has begun to move more intensively, but in fact the force of the blows has increased, because the child's muscles have already completely formed and strengthened.
39th–40th week
© depositphotos.com
The first minutes after birth.
The lungs of a child continue to form until the very birth, and only at the time of birth they release the right amount of surfactant - a substance that prevents the alveoli from sticking together after the first independent breath. Very soon, the baby will announce its birth with the first cry and begin its long journey through a large and interesting world.
Very soon, the baby will announce its birth with the first cry and begin its long journey through a large and interesting world.
show all
hCG in ectopic pregnancy - Juno
hCG in ectopic pregnancy: article content
hCG in ectopic pregnancy: features
Fertilization should take place in the fallopian tube, but after that the embryo normally moves into the uterine cavity and is fixed there. For various reasons, for example, due to health problems, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the embryo remains in the tube and is fixed in it. In 2-3% of cases, the pathological process does not occur in the tube, but in the abdominal cavity or on the cervix.
The embryo secretes hCG (chorionic gonadotropin) in any case - during normal and ectopic pregnancy. However, in the second case, the level of the hormone is lower. There is no chance of saving a child with ectopic implantation, since the fallopian tube will burst when the embryo grows. In the early stages, a woman may feel normal or feel symptoms characteristic of the first trimester - nausea, drowsiness, frequent urination. It is the low concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood that makes it possible to suspect something is wrong and terminate a threatening pregnancy in time.
In the early stages, a woman may feel normal or feel symptoms characteristic of the first trimester - nausea, drowsiness, frequent urination. It is the low concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood that makes it possible to suspect something is wrong and terminate a threatening pregnancy in time.
How does hCG increase during ectopic pregnancy
HCG is produced approximately 4-8 days after conception. The hormone provides optimal conditions for the development of the fetus, maintains the required level of other hormones.
The concentration depends on the timing, as well as the size of the fetus. The level of hCG in an ectopic pregnancy from the very beginning is less than in a normal one. From an early date, deviations can be suspected if, for example, even with a long delay on a home test, the second strip is too dull.
Does hCG indicate an ectopic pregnancy
The slow growth of the hormone may indicate not only that the fetus develops outside the uterus, but also the following pathologies:
- miscarriage;
- threatened miscarriage;
- retardation in fetal development.

If the level rises, this may be a sign of diabetes mellitus, multiple pregnancy, tumors, sometimes the phenomenon occurs when taking hormonal drugs or when there is an error in determining the term. If the doctor suspects that the embryo has not attached to the uterus, then he prescribes repeated tests, and assesses the situation based on the results.
Dynamics: how it should be
During normal pregnancy, hCG rises every 2 days by an average of 60-70%. The hormone level reaches its maximum figures by the end of the first trimester - by the 12th week. After that, the numbers go down. The increase in hCG during an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages is insignificant, although there are exceptions. For example, there are cases when an ectopic pregnancy was detected at high hCG, and vice versa, at low values, the fetus developed normally in the uterus.
It is reasonable to conduct additional diagnostics if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected. For example, at values below 1000-1500 mU/ml by the end of the first month of pregnancy, the risk of pathology is 40-50%. If hCG grows slowly - by 50-60% per week or less, it is necessary to exclude not only ectopic pregnancy, but also other pathologies.
For example, at values below 1000-1500 mU/ml by the end of the first month of pregnancy, the risk of pathology is 40-50%. If hCG grows slowly - by 50-60% per week or less, it is necessary to exclude not only ectopic pregnancy, but also other pathologies.
HCG level table: weekly norms
Indicators of normal values at different weeks of pregnancy:
| weeks of pregnancy | HCG, honey / ml |
| 1 to 2 | 21–160 |
| From 2 to 3 | 103–4800 |
| 3 to 4 | 1100–31000 |
| 4 to 5 | 2530–82300 |
| From 5 to 6 | 23080–150900 |
| 6 to 7 | 27080–232000 |
| 7 to 10 | 21000–2 |
| 11 to 15 | 6190–102995 |
| From 16 to 20 | 4790–80094 |
| 21 to 39 | 2698–78098 |
If we count the period from menstruation, then at 1-2 weeks it is too early to do a test or analysis - it will not show hCG during an ectopic pregnancy.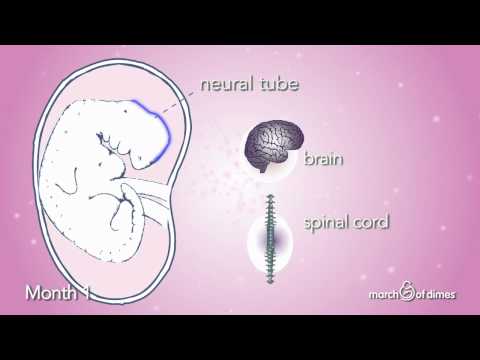 To correctly determine compliance with the standards in the table, you need to remember that the period is calculated from the moment of conception, and not menstruation.
To correctly determine compliance with the standards in the table, you need to remember that the period is calculated from the moment of conception, and not menstruation.
Methods for determining hCG in ectopic pregnancy and timing
Available diagnostic options:
- Test. It makes sense to do not earlier than 1 day of delay. It is advisable to choose highly sensitive ones and use the morning portion of urine. The second strip may be less bright and with a normal pregnancy;
- Urinalysis. It does not always reliably show hCG numbers, especially if you drink a lot of liquid before analysis;
- Blood test. It will show hCG already 4-5 days after the attachment of the embryo.
For reliable results, it is better to use all methods in combination and repeat the diagnosis at least twice.
HCG test for ectopic pregnancy
The most reliable way to determine the level of the hormone is to donate venous blood. How long should it take from the delay and should I wait for it? Take the test no earlier than 7-10 days after the intended conception, and preferably with a 2-5 day delay in menstruation.
How long should it take from the delay and should I wait for it? Take the test no earlier than 7-10 days after the intended conception, and preferably with a 2-5 day delay in menstruation.
With normal indicators, a reanalysis is taken at the end of the 1st trimester. If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected in the early stages, a blood test is prescribed with an interval of 2-3 days.
Often, in addition to blood tests, especially if the results are questionable, ultrasound may be prescribed. In the early stages, the fetus may be poorly visible, and a woman has to wait 1-2 weeks for the embryo to begin to be visualized during ultrasound diagnostics. If a pathology is suspected, a pregnant woman can be admitted to a hospital for observation and the opportunity to take emergency measures.
Low hCG in ectopic pregnancy and other signs of pathology
At the very beginning of pregnancy, a woman may feel well. The following symptoms may indicate the ectopic attachment of the embryo, in addition to low hCG values:
- Drawing pains in the lower abdomen.
 They can be of varying intensity from small to very disturbing, more often on the one hand, if the embryo is in the tube cavity or in the abdominal cavity. When it is attached in the cervical canal, pain is given to the perineum;
They can be of varying intensity from small to very disturbing, more often on the one hand, if the embryo is in the tube cavity or in the abdominal cavity. When it is attached in the cervical canal, pain is given to the perineum; - Bloody discharge. They can be smearing or pronounced. You need to contact a doctor right away. Over time, the intensity of the discharge increases;
- Sleep disorders and problems with appetite. This may be a sign of toxicosis, but sometimes symbolizes an ectopic pregnancy;
- Dizziness, weakness, loss of working capacity. The body thus shows that something is going wrong;
- Fever, loss of consciousness. Signs of severe intoxication, acute inflammation, sometimes rupture of the fallopian tube.
Unfortunately, no woman is immune from ectopic pregnancy. It is impossible to unequivocally point to the reasons that lead to this pathology. The risk increases in the presence of inflammatory processes in the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, hormonal disorders.