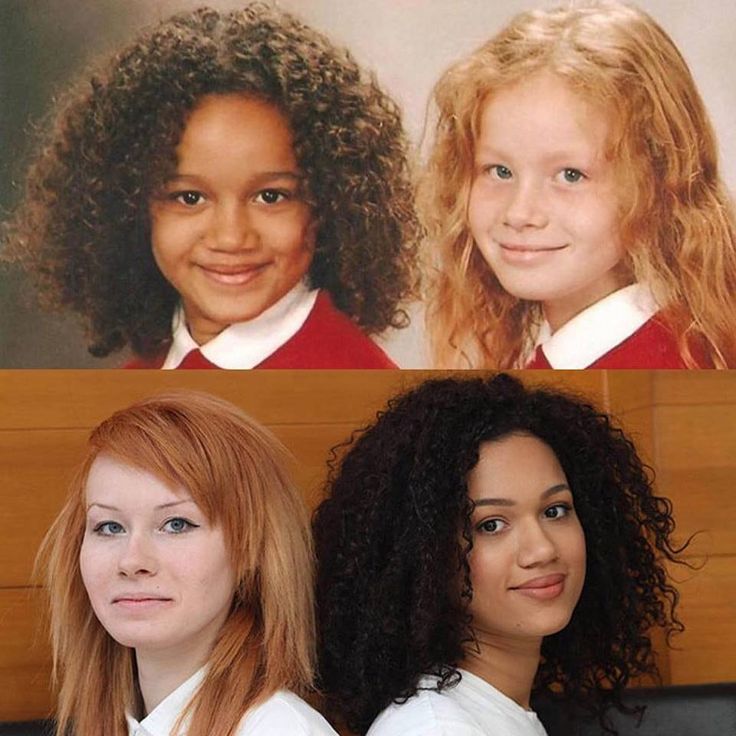
When you have twins are there two placentas
The Difference Between Identical and Fraternal Twins
Log in | Register
Family Life
Family Life
Listen
Español
Text Size
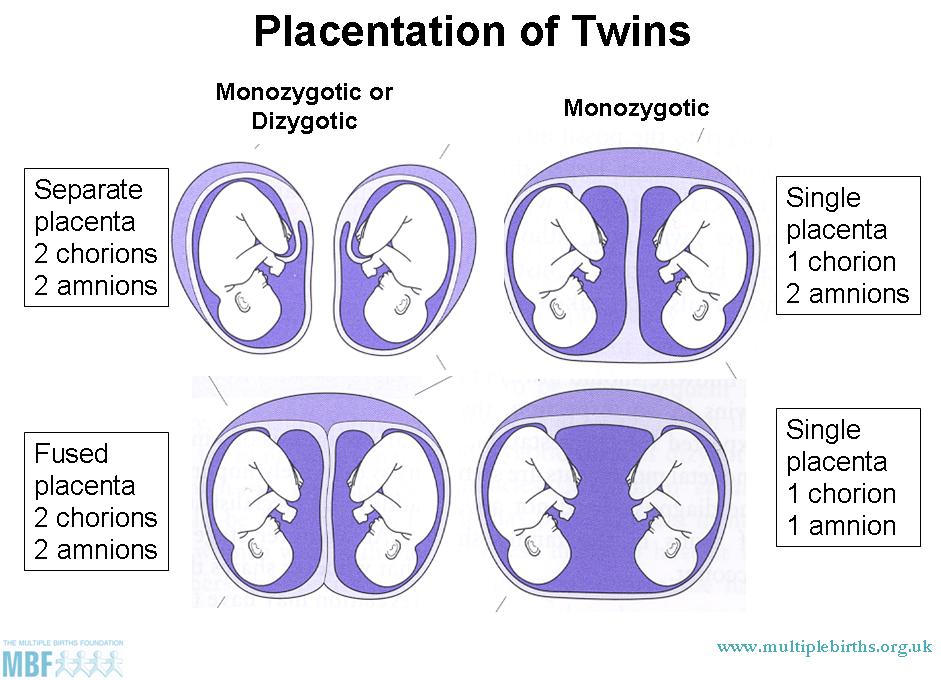
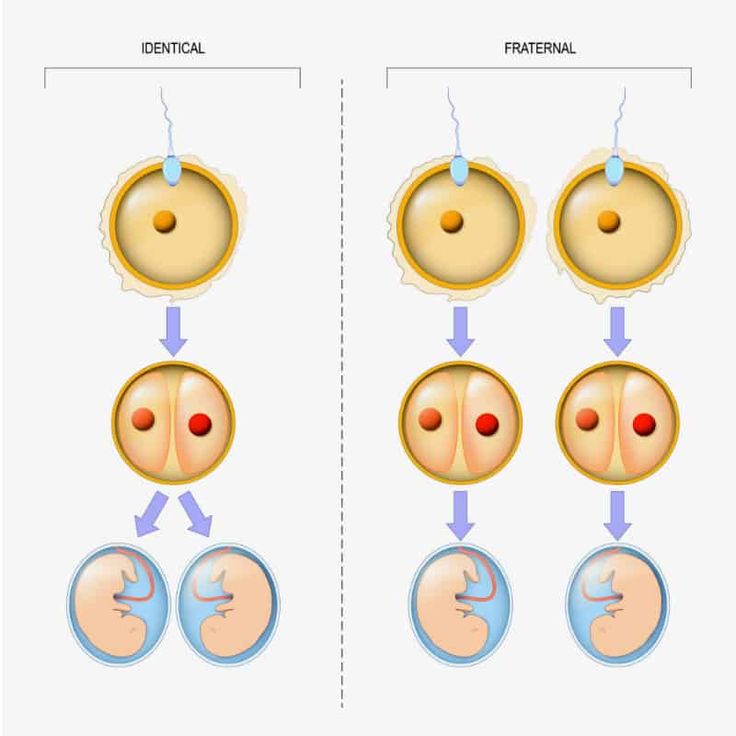
Because fraternal, or dizygotic, twins are 2 separate fertilized eggs, they usually develop 2 separate amniotic sacs, placentas, and supporting structures. Identical, or monozygotic, twins may or may not share the same amniotic sac, depending on how early the single fertilized egg divides into 2.
If twins are a boy and a girl, clearly they are fraternal twins, as they do not have the same DNA. A boy has XY chromosomes and a girl has XX chromosomes. Girl-boy twins occur when one X egg is fertilized with an X sperm, and a Y sperm fertilizes the other X egg.
Sometimes health care professionals identify same-sex twins as fraternal or identical based on ultrasound findings or by examining the membranes at the time of delivery. The best way to determine if twins are identical or fraternal is by examining each child’s DNA. Occasionally a family is told that their twins are fraternal based on placenta findings, when they are in fact identical. Other times, a family may see the minor differences in identical twins and declare the twins fraternal based on these differences in appearance. There are a few commercial laboratories that, for a fee, will send families DNA collection kits to determine if the twins are identical or fraternal. The families swab the insides of each child’s cheek for a DNA sample and send the kit back to the laboratory to await results.
Identical twins have the same DNA; however, they may not look exactly identical to one another because of environmental factors such as womb position and life experiences after being born. Our family joke about one of our twin’s stitches for a lacerated upper lip was that he wanted to distinguish himself from his identical twin brother! In addition to life’s bumps, bruises, and differing hairstyles, a child’s DNA is constantly adapting to that child’s experiences.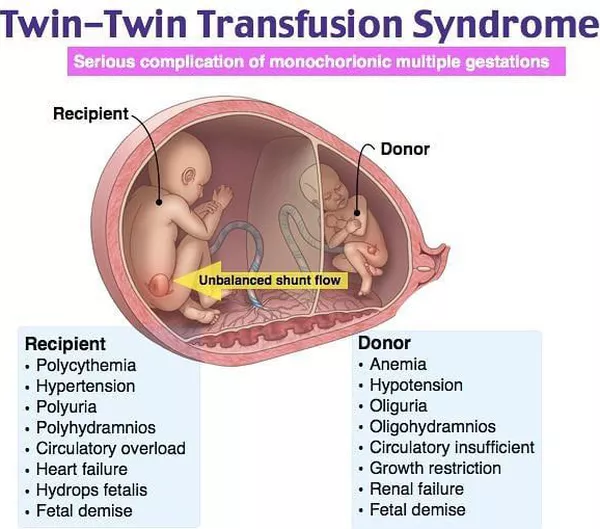 Different stretches of one’s DNA can turn on or off in response to environmental surroundings—therefore, over time, a pair of identical twins’ DNA becomes more and more distinctive. All twins, whether fraternal or identical, are truly 2 separate, unique individuals.
Different stretches of one’s DNA can turn on or off in response to environmental surroundings—therefore, over time, a pair of identical twins’ DNA becomes more and more distinctive. All twins, whether fraternal or identical, are truly 2 separate, unique individuals.
- Author
- Shelly Vaziri Flais, MD, FAAP
- Last Updated
- 11/7/2019
- Source
- Raising Twins: From Pregnancy to Preschool (Copyright © 2010 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
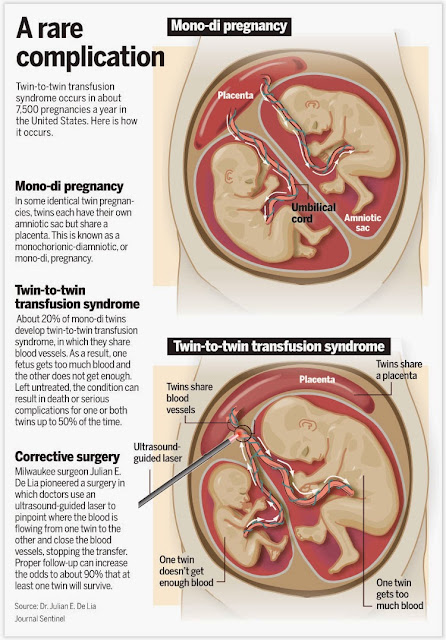
Twin Pregnancy: Answers from an Expert
Twin Pregnancy: Answers from an Expert | Johns Hopkins MedicineReviewed By:
When you’re expecting twins, you know you’ll need two of everything for your registry. But what about staying healthy during your pregnancy? Do you need to double your food intake, weight gain and visits to the doctor? With regard to the babies, are there two placentas and two amniotic sacs, or can they share these?
Johns Hopkins maternal-fetal medicine specialist Jeanne Sheffield answers eight commonly asked questions.
Do twins share a placenta and an amniotic sac?
While some twins may share a placenta and an amniotic sac, that is not the case for the vast majority of pregnancies. Here are three major possibilities that exist:
- Two placentas and two amniotic sacs.
 A twin pregnancy with two placentas and two amniotic sacs is the optimal twin pregnancy, as each baby has its own nutritional source and protective membrane.
A twin pregnancy with two placentas and two amniotic sacs is the optimal twin pregnancy, as each baby has its own nutritional source and protective membrane. - One placenta and two amniotic sacs. In pregnancies with one placenta and two amniotic sacs, you will definitely have identical twins. Additionally, when your babies share a placenta, there is a greater risk for complications, such as twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. Your physician will closely monitor your pregnancy to check for potential problems.
- One placenta and one amniotic sac. This is the riskiest and rarest type of twin pregnancy. Fetal complications can arise due to tangling of the umbilical cords or an imbalance in nutrients, blood or other vital life supporting systems.
- Two placentas and two amniotic sacs.
Do I need to double my caloric intake during a twin pregnancy?
A common misconception surrounding twin pregnancy is that you need to double your caloric intake to provide your babies with enough nutrients.
 However, pregnancy nutrition guidelines aren’t simply based on the number of babies you’re carrying. Instead, they’re based on your body mass index at the time you became pregnant.
However, pregnancy nutrition guidelines aren’t simply based on the number of babies you’re carrying. Instead, they’re based on your body mass index at the time you became pregnant. Your doctor will make individualized recommendations based on your starting weight. On average, it’s estimated that a woman’s caloric requirements will increase about 40 percent for a twin pregnancy. What’s most important, though, is that a woman eats as healthy as possible.
Do I need to take different prenatal vitamins for twins?
If you’re pregnant with twins, you should take the same prenatal vitamins you would take for any pregnancy, but your physician will recommend extra folic acid and iron. The additional folic acid and extra iron will help ward off iron-deficiency anemia, which is more common when you’re pregnant with multiples.
Will I need to visit my doctor more frequently?
While every pregnancy is different, most women carrying twins will have more frequent prenatal visits than women carrying only one baby.
 If your twins are sharing one placenta, you will automatically have a more frequent monitoring schedule.
If your twins are sharing one placenta, you will automatically have a more frequent monitoring schedule. If your pregnancy doesn’t have complications, your prenatal visits may not differ much from a singleton pregnancy until you get to the end of your second trimester. At that point, you’ll be seen more frequently because there is a higher risk of pre-eclampsia and preterm labor.
Do I have to see a maternal-fetal medicine specialist for a twin pregnancy?
Maternal-fetal medicine specialists see high-risk pregnancies, but not every twin pregnancy will fall into this category.
To find the best care provider for your twins, make sure that the physician is comfortable managing twins, including vaginal delivery of twins rather than only offering a cesarean section (C-section) for delivery.
Are all twin pregnancies delivered preterm?
A little more than half of twin pregnancies end in preterm delivery (before 37 weeks).
 While 40 weeks is the full gestation period of the average pregnancy, most twin pregnancies are delivered at approximately 36 weeks (range 32-38 weeks depending on the type of twin pregnancy).
While 40 weeks is the full gestation period of the average pregnancy, most twin pregnancies are delivered at approximately 36 weeks (range 32-38 weeks depending on the type of twin pregnancy). Unfortunately, preventing preterm labor with multiples is more challenging than with a singleton pregnancy because the interventions used with singleton pregnancies are not as effective with multiples.
Can bed rest reduce the risk of preterm delivery?
Scientific data show that bed rest does not prevent preterm delivery. In fact, bed rest can increase your risk of developing blood clots and have negative financial and social consequences.
Although bed rest is not prescribed as frequently as it once was, your doctor may suggest reducing your activity level if you’re showing signs of early labor at the end of your second trimester or early in your third trimester.
Is labor and delivery significantly different with twins?
Labor is generally the same whether you’re having one baby or two.
 During delivery is when things differ significantly.
During delivery is when things differ significantly. When it’s time to deliver your twins, you will go to an operating room even if you are delivering vaginally. This is a safety precaution known as a double setup. Following the vaginal delivery of the first baby, there is a small risk of an emergency cesarean section for the second baby. There is also the possibility of the second twin being delivered breech, which is a safe form of vaginal delivery if the obstetrician is experienced in this type of delivery.
Of women giving birth to twins over 32 weeks, only about 4 percent who try for a vaginal delivery will have a combined vaginal and cesarean section delivery. While it doesn’t happen very often, by delivering both babies in the operating room, physicians are better prepared to protect the health of the mother and the babies.
Although being pregnant with twins can seem very different, your doctor will treat your pregnancy like any other unless a complication occurs.

Sign Up for Our Free Newsletter
One of the best things you can do to protect and improve your health is to stay informed. Your Health is a FREE e-newsletter that serves as your smart, simple connection to the world-class expertise of Johns Hopkins.
Sign Up
Related
-
Planning a Pregnancy
How to Prepare for Pregnancy
-
Fertility, Pregnancy and Childbirth
Complications of Pregnancy
-
The Second Trimester
The Second Trimester
Related Topics
Multiple pregnancy
Author: Mikheeva Natalia Grigoryevna, Malyshok magazine
A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy in which two or more fetuses develop simultaneously in the uterus. Multiple pregnancy occurs in 0.4 - 1.6% of all pregnancies. Recently, there has been an obvious trend towards an increase in the incidence of such pregnancies due to the active use of assisted reproduction technologies, including in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Multiple pregnancy occurs in 0.4 - 1.6% of all pregnancies. Recently, there has been an obvious trend towards an increase in the incidence of such pregnancies due to the active use of assisted reproduction technologies, including in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Types of multiple pregnancies
Children born in multiple pregnancies are called TWINS. There are two main types of twins: monozygotic (identical, homologous, identical, similar) and dizygotic (fraternal, heterologous, different). African countries have the highest twin birth rate, Europe and the USA have an average rate, and Asian countries have a low rate.
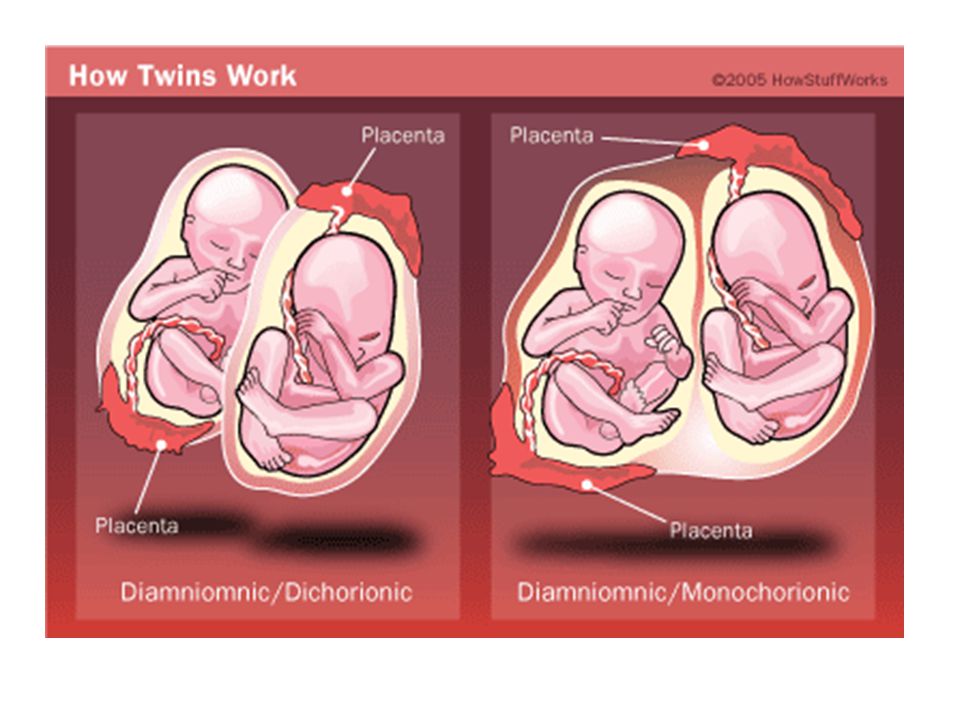
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins are more common (in 66-75% of all twins). The birth rate of dizygotic twins varies from 4 to 50 per 1000 births. Dizygotic twins occur when two separate eggs are fertilized. The maturation of two or more eggs can occur both in one ovary and in two. The predisposition to develop dizygotic twins may be maternally inherited. Dizygotic twins can be either same-sex or opposite-sex, they look like each other like ordinary brothers and sisters. With fraternal twins, two placentas are always formed, which can be very close, even touching, but they can always be separated. Two fruit spaces (i.e., fetal bladders or two “houses”) are separated from each other by a septum consisting of two chorionic and two amniotic membranes. Such twins are called dizygotic dichorionic diamniotic twins.
Dizygotic twins can be either same-sex or opposite-sex, they look like each other like ordinary brothers and sisters. With fraternal twins, two placentas are always formed, which can be very close, even touching, but they can always be separated. Two fruit spaces (i.e., fetal bladders or two “houses”) are separated from each other by a septum consisting of two chorionic and two amniotic membranes. Such twins are called dizygotic dichorionic diamniotic twins.
Monozygotic (identical) twins are formed as a result of the separation of one fetal egg at various stages of its development. The frequency of birth of monozygotic twins is 3-5 per 1000 births. The division of a fertilized egg into two equal parts can occur as a result of a delay in implantation (immersion of the embryo in the uterine mucosa) and oxygen deficiency, as well as due to a violation of the acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. The emergence of monozygotic twins is also associated with the fertilization of an egg that had two or more nuclei. If the separation of the fetal egg occurs in the first 3 days after fertilization, then monozygotic twins have two placentas and two amniotic cavities, and are called monozygotic diamniotic dichoriones (Fig. A). If the division of the ovum occurs between 4 - 8 days after fertilization, then two embryos will form, each in a separate amniotic sac. Two amniotic sacs will be surrounded by a common chorionic membrane with one placenta for two. Such twins are called monozygotic diamniotic monochorionic twins (Fig. B). If division occurs by 9- 10th day after fertilization, then two embryos are formed with a common amniotic sac and placenta. Such twins are called monozygotic monoamniotic monochorionic (Fig. B) If the egg is separated at a later date on the 13th - 15th day after conception, the separation will be incomplete, which will lead to the appearance of conjoined (undivided, Siamese) twins. This type is quite rare, approximately 1 observation in 1500 multiple pregnancies or 1: 50,000 - 100,000 newborns.
If the separation of the fetal egg occurs in the first 3 days after fertilization, then monozygotic twins have two placentas and two amniotic cavities, and are called monozygotic diamniotic dichoriones (Fig. A). If the division of the ovum occurs between 4 - 8 days after fertilization, then two embryos will form, each in a separate amniotic sac. Two amniotic sacs will be surrounded by a common chorionic membrane with one placenta for two. Such twins are called monozygotic diamniotic monochorionic twins (Fig. B). If division occurs by 9- 10th day after fertilization, then two embryos are formed with a common amniotic sac and placenta. Such twins are called monozygotic monoamniotic monochorionic (Fig. B) If the egg is separated at a later date on the 13th - 15th day after conception, the separation will be incomplete, which will lead to the appearance of conjoined (undivided, Siamese) twins. This type is quite rare, approximately 1 observation in 1500 multiple pregnancies or 1: 50,000 - 100,000 newborns. Monozygotic twins are always the same sex, have the same blood type, have the same eye color, hair, skin texture of the fingers, and are very similar to each other.
Monozygotic twins are always the same sex, have the same blood type, have the same eye color, hair, skin texture of the fingers, and are very similar to each other.
Twin births occur once in 87 births, triplets - once in 87 2 (6400) twins, quadruples - once in 87 3 (51200) triplets, etc. (according to the Gallin formula). The origin of triplets, quadruplets, and more twins varies. So, triplets can be formed from three separate eggs, from two or one egg. They can be monozygotic and heterozygous. Quadruples can also be identical and fraternal.
Features of the course of multiple pregnancy
In case of multiple pregnancies, the woman's body is subject to increased requirements. All organs and systems function with great tension. In connection with the displacement of the diaphragm by the enlarged uterus, the activity of the heart becomes difficult, shortness of breath, fatigue occur. Enlargement of the uterus, especially towards the end of pregnancy, leads to compression of the internal organs, which is manifested by impaired bowel function, frequent urination, and heartburn.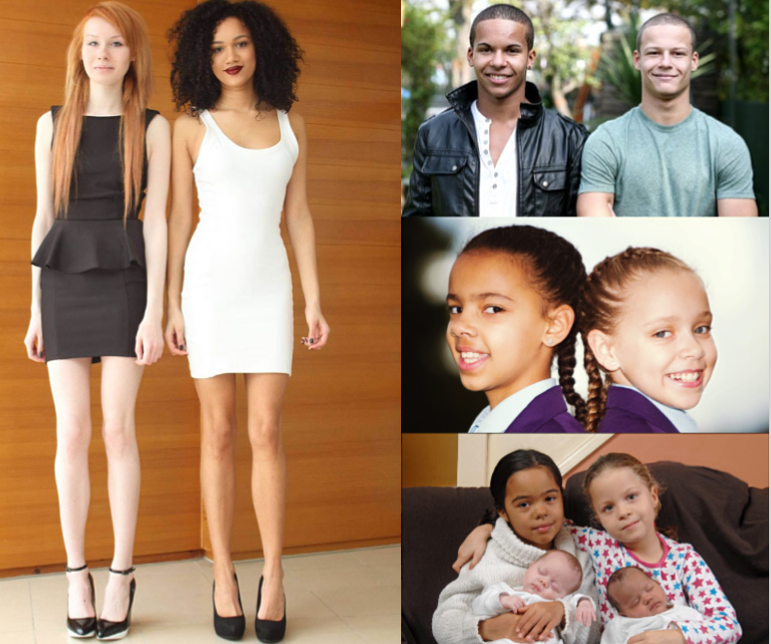 Almost 4-5 times more often there is the development of preeclampsia, which is characterized by an earlier onset, a protracted and more severe clinical course, often combined with acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women. Due to the increased need and consumption of iron, iron deficiency anemia often develops in pregnant women. Significantly more often than with a singleton pregnancy, complications such as bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, anomalies in labor, and a low location of the placenta are observed. Often, with multiple pregnancies, abnormal positions of the fetus occur. One of the most common complications in multiple pregnancy is its premature termination. Preterm birth is observed in 25-50% of cases of such pregnancies.
Almost 4-5 times more often there is the development of preeclampsia, which is characterized by an earlier onset, a protracted and more severe clinical course, often combined with acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women. Due to the increased need and consumption of iron, iron deficiency anemia often develops in pregnant women. Significantly more often than with a singleton pregnancy, complications such as bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, anomalies in labor, and a low location of the placenta are observed. Often, with multiple pregnancies, abnormal positions of the fetus occur. One of the most common complications in multiple pregnancy is its premature termination. Preterm birth is observed in 25-50% of cases of such pregnancies.
The development of term twins is normal in most cases. However, their body weight is usually less (by 10% or more) than in singleton pregnancies. With twins, the weight of children at birth less than 2500 g is observed in 40-60%. The low weight of twins is most often due to insufficiency of the uteroplacental system, which is not able to adequately provide several fetuses with nutrients, trace elements and oxygen. The consequence of this is a delay in the development of the fetus, which is a common occurrence in multiple pregnancies. The mass of twins, respectively, decreases in proportion to their number (triplets, quadruplets, etc.).
The consequence of this is a delay in the development of the fetus, which is a common occurrence in multiple pregnancies. The mass of twins, respectively, decreases in proportion to their number (triplets, quadruplets, etc.).
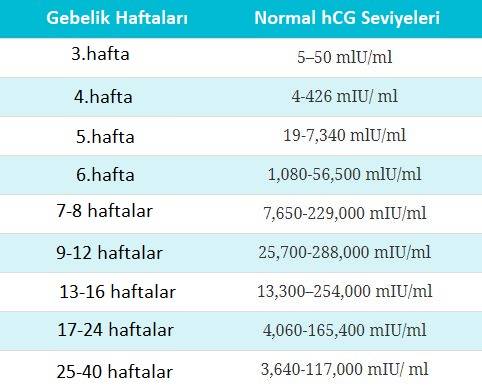
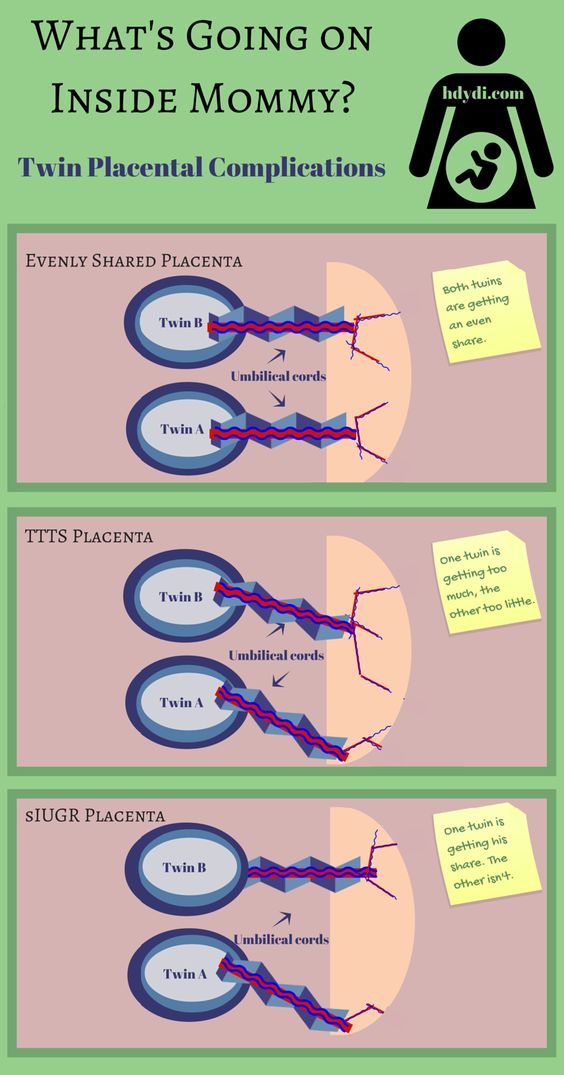
With monochorionic twins in the placenta, anastomoses are often formed between the vascular systems of the fetus, which can lead to a serious complication - the syndrome of feto-fetal transfusion. In this case, there is a redistribution of blood from one fetus to another, the so-called "stealing". The severity of feto-fetal transfusion (mild, moderate, severe) depends on the degree of redistribution of blood through the anastomoses, which vary in size, number and direction.
Diagnosis in multiple pregnancy
The most reliable method for diagnosing multiple pregnancies is ultrasound, which allows not only early diagnosis of multiple pregnancies, but also to determine the position and presentation of fetuses, localization, structure and number of placentas, the number of amniotic cavities, the volume of amniotic fluid, congenital malformations and antenatal fetal death, the state of the fetus from a functional point of view, the nature of the uteroplacental and fetal-placental blood flow.
In multiple pregnancies, due to the higher risk of complications, ultrasound monitoring is performed more frequently than in singleton pregnancies. With dizygotic twins, about once every 3-4 weeks, with monozygotic twins - once every 2 weeks.
In addition, examinations and control of clinical tests are carried out with great care, and CTG is regularly recorded from 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Birth management
Indications for caesarean section associated with multiple pregnancies are triplets (quadruple), the transverse position of both or one of the fetuses, breech presentation of both fetuses or the first of them, and not associated with multiple pregnancy - fetal hypoxia, anomalies labor activity, prolapse of the umbilical cord, extragenital pathology of the mother, severe gestosis, placenta previa and abruption, etc.
-
ECO
In the department of assisted reproductive technologies of the Maternity Hospital No. 2
2
, IVF is performed at the expense of the Republican budget for couples
who have received a positive decision from the Minsk city or regional commissions to provide one free IVF attempt.
No drug supply problem. There is no waiting list. -
Farewoman
-
Individual care for patients
-
Ultrasound diagnostics
- Pregnant women often complain of fatigue and shortness of breath, which increases towards the end of pregnancy.
 The cause of shortness of breath is a difficulty in the activity of the heart due to a significant displacement of the diaphragm by the bottom of the uterus, the size of which is larger in multiple pregnancy than in singleton.
The cause of shortness of breath is a difficulty in the activity of the heart due to a significant displacement of the diaphragm by the bottom of the uterus, the size of which is larger in multiple pregnancy than in singleton. - Often there is a dilation of the veins of the lower extremities. By the end of pregnancy, there is often an increase in the urge to urinate due to the pressure of a large fetus on the bladder.
- Pregnant women often complain of heartburn and constipation.
- In multiple pregnancies, toxicosis occurs more often than in singleton pregnancies: vomiting, salivation, edema, nephropathy, eclampsia.
- With twins, polyhydramnios of one of the fetuses is often found, which leads to a sharp increase and overstretching of the uterus, shortness of breath, tachycardia and other disorders. Polyhydramnios is more common in one of the identical twins. In some cases, the polyhydramnios of one twin is accompanied by an oligohydramnios of the other fetus.
- Premature termination of multiple pregnancies often occurs.
- With twins, preterm birth is observed in at least 25% of women.
- Triplets are more likely to miscarry than twins. The greater the number of gestated fetuses, the more often preterm births are observed.
- Development of term twins is normal in most cases. However, their body weight is usually less than that of single fetuses. Often there is a difference in body weight of twins by 200-300 g, and sometimes more.
- Uneven development of twins is associated with unequal intake of nutrients from a single placental circulation.
- Often there is a difference not only in weight, but also in the length of the body of the twins. In connection with this, the theory of supergenesis (superfoetatio) was put forward. Proponents of this hypothesis believe that fertilization of eggs of different ovulation periods is possible, i.e., the onset of a new pregnancy in the presence of an already existing, previously occurring, pregnancy.
- Due to the uneven delivery of nutrients and oxygen, a significant developmental disorder and even death of one of the twins can occur. This is more commonly seen in identical twins. The dead fetus is squeezed by the second, well-growing fetus, the amniotic fluid is absorbed, the placenta undergoes regression. The compressed mummified fetus ("paper fetus") is released from the uterus along with the placenta after the birth of a live twin. Polyhydramnios of one fetus, which occurs during multiple pregnancies, often also prevents the other twin from developing correctly. With pronounced polyhydramnios, certain anomalies in the development of the fetus, which grows with an excess of amniotic fluid, are often observed. Rarely, fused twins are born (fusion can be in the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis) and twins with other malformations.
- The position of the fetuses in the uterine cavity in most cases (about 90%) is normal. In the longitudinal position, different presentation options are observed: both fetuses are presented with the head, both with the pelvic end, one with the head, and the other with the pelvic end.
 With longitudinal presentation, one fetus may be behind the other, which makes diagnosis difficult. Less commonly observed is the longitudinal position of one fetus and the transverse position of the other. The most rare is the transverse position of both twins.
With longitudinal presentation, one fetus may be behind the other, which makes diagnosis difficult. Less commonly observed is the longitudinal position of one fetus and the transverse position of the other. The most rare is the transverse position of both twins. - The position of the twins in the uterus, both fetuses are presented with the head, one fetus is presented with the head, the second - with the pelvic end, both fetuses are in the transverse position
- In case of multiple pregnancies, women are taken into special account and carefully monitored. When the earliest signs of complications appear, the pregnant woman is sent to the pregnancy pathology department of the maternity hospital. Given the frequent occurrence of preterm birth, it is recommended that a pregnant woman with twins be sent to the maternity hospital 2 to 3 weeks before delivery, even in the absence of complications.
- The enlargement of the uterus in multiple pregnancies occurs faster than in pregnancy with one fetus, so the size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age. The bottom of the uterus is usually high, especially at the end of pregnancy, the circumference of the abdomen during this period reaches 100-110 cm or more.
- The following signs are unstable and not sufficiently reliable: a) deepening of the uterine fundus (saddle uterus), the formation of which is associated with protrusion of the corners of the uterus with large parts of the fetus; b) the presence of a longitudinal depression on the anterior wall of the uterus, which is formed as a result of the fruits that are in a longitudinal position adjacent to each other; c) the presence of a horizontal groove on the anterior wall of the uterus with the transverse position of the fetus.

- The small size of the presenting head with a significant volume of the pregnant uterus and the high standing of its bottom also make it possible to suspect a multiple pregnancy. The presence of this sign is explained by the fact that the study determines the head of one and the pelvic end (in the bottom of the uterus) of another fetus, which lies slightly higher.
- Feeling the movement of the fetus in different places and probing parts of the fetus in different parts of the abdomen (both on the right and on the left) also indicate multiple pregnancies.
Curious facts are
0
, how many are the Geminis? up to 80 million pairs of twins.
The number of twins born in relation to the total number of newborns in different countries and on different continents is different, but in general the trend is such that it continues to grow. Compared with the 60s, the percentage of twins has increased from 1.18 to 2.78, that is, almost 2.5 times.
The largest number of children
The largest number of children born to one mother, according to official data, is 69. According to reports made in 1782, between 1725 and 1765.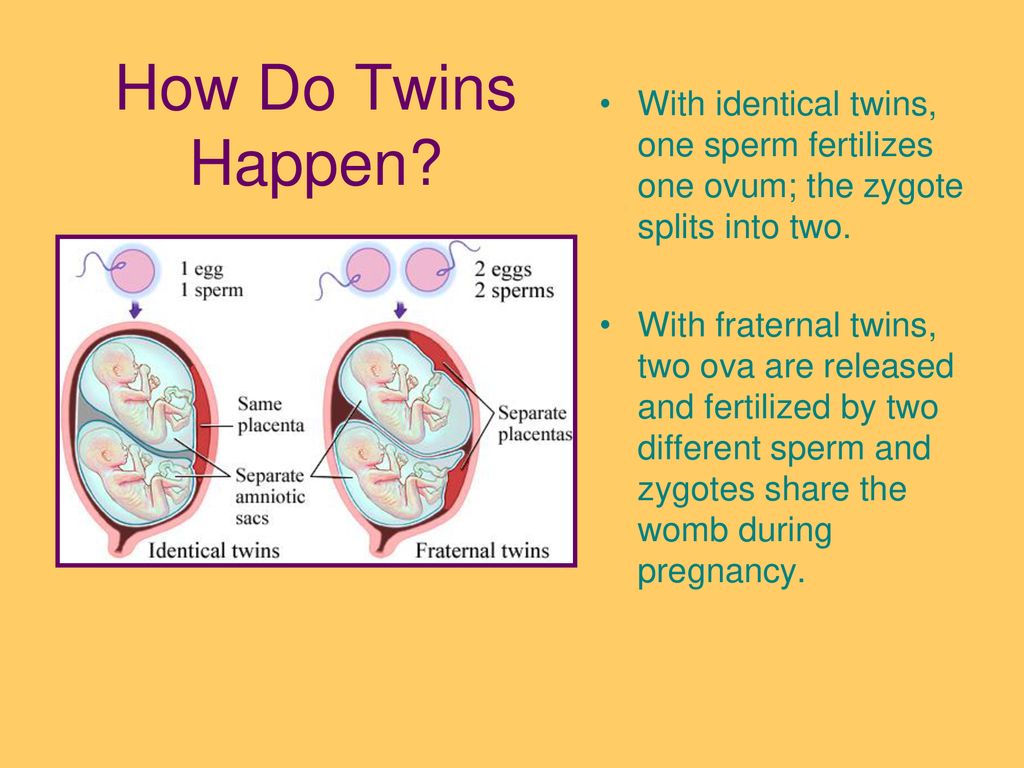 The wife of a Russian peasant Fyodor Vasiliev gave birth 27 times, giving birth to twins 16 times, triplets 7 times and 4 twins 4 times. Of these, only 2 children died in infancy.
The wife of a Russian peasant Fyodor Vasiliev gave birth 27 times, giving birth to twins 16 times, triplets 7 times and 4 twins 4 times. Of these, only 2 children died in infancy.
The most prolific mother of our contemporaries is considered to be Leontina Albina (or Alvina) of San Antonio, Chile, who at 1943-81 years gave birth to 55 children. As a result of the first 5 pregnancies, she gave birth to triplets, and exclusively male.
Most birthed
The record 38 births are said to be Elizabeth Greenhillies Abbots-Langley, c. Hertfordshire, UK. She had 39 children - 32 daughters and 7 sons.
The largest number of multiple births in one family
Maddalena Pomegranate from Italy (b. 1839) had triplets born 15 times.
There is also information about the birth on May 29, 1971 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, and in May 1977 in Bagarhat, Bangladesh, 11 twins. In both cases, no child survived.
Most fertile pregnancies
Dr. Gennaro Montanino, Rome, Italy, claimed to have removed, in July 1971, the embryos of 10 girls and 5 boys from the uterus of a 35-year-old woman who was 4 months pregnant. This unique case of 15-fertility was the result of infertility pills.
Gennaro Montanino, Rome, Italy, claimed to have removed, in July 1971, the embryos of 10 girls and 5 boys from the uterus of a 35-year-old woman who was 4 months pregnant. This unique case of 15-fertility was the result of infertility pills.
9 children - the largest number in one pregnancy - were born on June 13, 1971 by Geraldine Broadrick in Sydney, Australia. 5 boys and 4 girls were born: 2 boys were stillborn, and none of the rest survived more than 6 days.
The birth of 10 twins (2 boys and 8 girls) is known from reports from Spain (1924), China (1936) and Brazil (April 1946).
The father with many children
The largest father in the history of Russia is Yakov Kirillov, a peasant from the village of Vvedensky, who in 1755 was presented to the court in connection with this (he was then 60 years old). The first wife of a peasant gave birth to 57 children: 4 times four, 7 times three, 9once twice and 2 times once. The second wife gave birth to 15 children.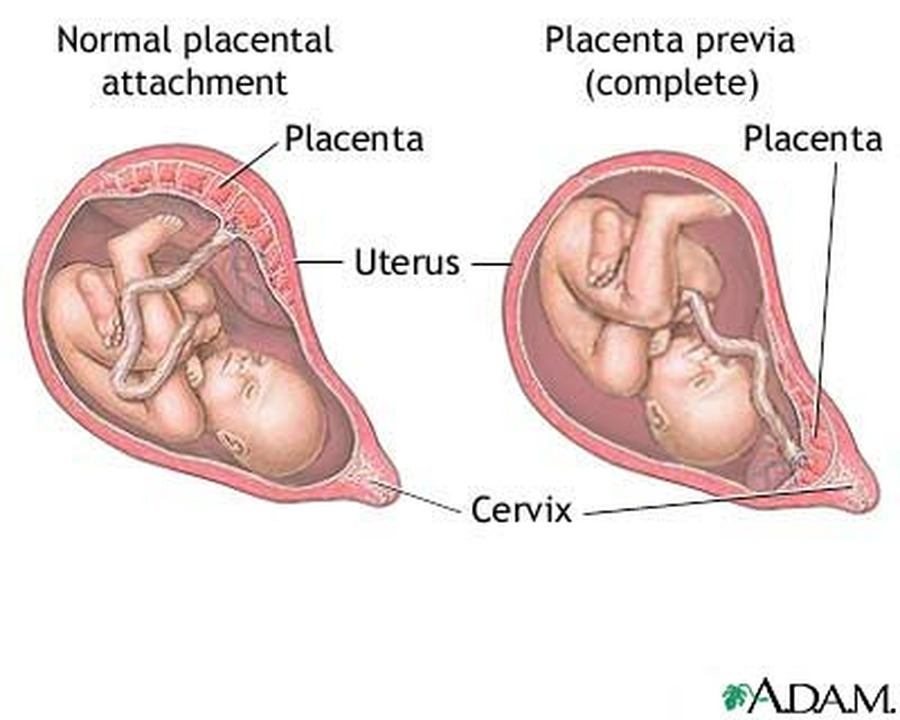 Thus, Yakov Kirillov had 72 children from two wives.
Thus, Yakov Kirillov had 72 children from two wives.
Longest Birth Intervals for Multiple Pregnancies
Peggy Lynn of Huntington Pennsylvania, USA, gave birth to a girl, Hanna, on November 11, 1995, and the second of the twins, Erika, only 84 days later (February 2, 1996).
Siamese twins
United twins became known as "Siamese" after Chang and Eng Bunkers were born fused in the area of the sternum on May 11, 1811 in the Maeklong region of Siam (Thailand). They married Sarah and Adelaide Yates of pc. North Carolina, USA, and had 10 and 12 children, respectively. They died in 1874, and with a difference of 3 hours.
The science of twins - gemellology.
"Secret language"
Twins often talk to each other in a language that others do not understand. This phenomenon is called cryptophasia.
Left-handed twins
18-22% of left-handed twins (for non-twins this percentage is 10).
articles from specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Arifullina Claudia Viktorovna
Gastroenterologist
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
There is data on the frequency of twins in case of anomalies in the development of the uterus, characterized by its bifurcation (bicornuate uterus, having a septum in the cavity, etc. ). The cause of polyembryony may be the separation of blastomeres (in the early stages of crushing), resulting from hypoxia, cooling, acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of the fertilization of two or more simultaneously mature eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg.
). The cause of polyembryony may be the separation of blastomeres (in the early stages of crushing), resulting from hypoxia, cooling, acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of the fertilization of two or more simultaneously mature eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg.
Twins formed from two (three, etc.) eggs are called dizygotic (polyzygotic), those arising from one are called identical. The origin of fraternal twins (polyzygotic twins): the simultaneous maturation (and ovulation) of two or more follicles in one ovary is possible. There may be maturation of two or more follicles and ovulation in both ovaries.
A third way of the origin of fraternal (multi-ovular) twins is possible - the fertilization of two or more eggs that have matured in one follicle. The origin of identical twins: most often, the occurrence of identical twins is associated with the fertilization of an egg that has two or more nuclei.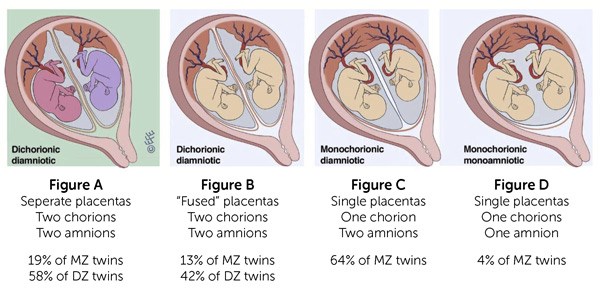 a single embryonic germ in the stage of crushing is divided into two parts; from each part an embryo (fruit) is formed. Twin twin. Fertilized eggs develop on their own. After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and fleecy membranes; in the future, each twin forms its own placenta with an independent network of vessels, each fetal egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or different-sex (boy and girl). Their blood type can be the same or different. Identical twin. Identical twins have a common capsular and fleecy membrane and a common placenta; the vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate with the help of numerous anastomoses. The water membrane of each twin is separate, the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two water membranes (biamniotic twins).
a single embryonic germ in the stage of crushing is divided into two parts; from each part an embryo (fruit) is formed. Twin twin. Fertilized eggs develop on their own. After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and fleecy membranes; in the future, each twin forms its own placenta with an independent network of vessels, each fetal egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or different-sex (boy and girl). Their blood type can be the same or different. Identical twin. Identical twins have a common capsular and fleecy membrane and a common placenta; the vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate with the help of numerous anastomoses. The water membrane of each twin is separate, the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two water membranes (biamniotic twins).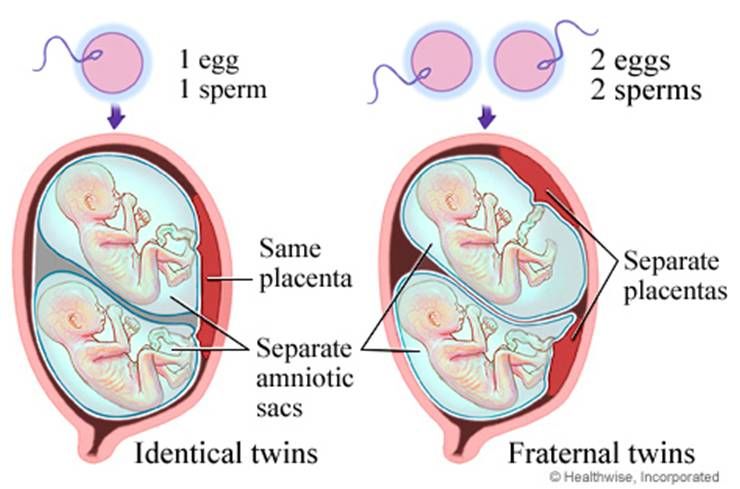
Identical twins always belong to the same sex (both boys or both girls), look alike, have the same blood group.
In fraternal twins, the membranes in the septum are arranged as follows: amnion - chorion, chorion - amnion; with monozygotic amnion-amnion.
Important signs for the diagnosis are: blood type (and other blood factors), eye color, hair color, skin texture of the fingertips, shape and location of teeth. In identical twins, these signs are completely the same. Fraternal twins share the same similarities as normal siblings.
MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
With multiple pregnancy, increased demands are made on the woman's body: the cardiovascular system, lungs, liver, nights and other organs function with great stress. In this regard, multiple pregnancies are more difficult than single pregnancies.
RECOGNITION OF MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
Diagnosis of multiple pregnancy often presents significant difficulties, especially in its first half.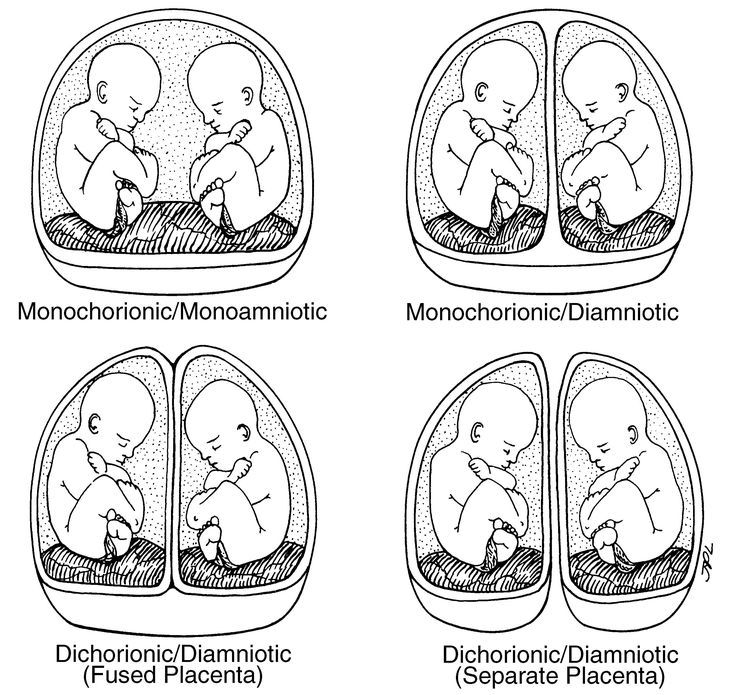 In the second half, towards the end of pregnancy, the recognition of twins (triplets) is facilitated. However, diagnostic errors occur during the study at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
In the second half, towards the end of pregnancy, the recognition of twins (triplets) is facilitated. However, diagnostic errors occur during the study at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
When recognizing a multiple pregnancy, the following signs are taken into account:
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Arifullina Claudia Viktorovna
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
GastroenterologyPediatric Gastroenterology
By clicking on the submit button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" Group of Companies "Mother and Child"Novosibirsk Center for Reproductive Medicine
All directionsGynecological proceduresSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical studiesProcedure roomTherapeutic studiesUltrasound examinations for adults
.