How to tell if my child has pinworms
Pinworms
Is this your child's symptom?
- Tiny, harmless worms that can cause anal itching
- The pinworms live in the colon (large bowel)
Symptoms of Pinworms
- Itching and irritation of the anus and buttocks is the main symptom
- Sometimes, moves to the vagina and causes vaginal itching or discharge
Cause
- A white, very thin, threadlike worm, about ¼ inch (6 mm) long.
- It moves. If it doesn't wiggle, it's probably lint or a thread.
- The worm may be seen around the anus or on the child's bottom. It is especially active at night or early morning.
- Rarely, the pinworm is seen on the surface of a stool.
- The pinworm's secretions are a strong skin irritant and cause the itching.
When to Call for Pinworms
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Pinworm is seen. Reason: needs a pinworm medicine.
- Red and tender skin around the anus. Reason: could be Strep infection.
- Anal itching lasts more than 1 week
- You think your child needs to be seen
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Anal itching without a pinworm being seen
- Questions about pinworm exposure or contact
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
- Virtual Urgent Care
Care Advice
Treatment for Pinworms
- What You Should Know About Pinworm Treatment:
- Pinworms are the most common worm infection in the US.

- Pinworms can cause anal itching.
- Pinworms do not carry any diseases.
- Treatment is very helpful.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Pinworms are the most common worm infection in the US.
- Pinworm Medicine:
- If a pinworm was seen, your child's doctor will suggest a special pinworm medicine. Pinworm medicines are available without a prescription (such as Reese's Pinworm Medicine). There are also prescription medicines that treat pinworms. Your doctor will decide which one is best for your child. Take as directed.
- Give a repeat dose of the pinworm medicine in 2 weeks. Reason: To prevent the pinworms from coming back.
- The repeat dose is needed because eggs can live for 1 to 2 weeks. Temperature and humidity levels also affect how long the eggs can stay alive.
- Treating Family Members and Close Contacts:
- Pinworms can spread to others within the same home. How often others get pinworms varies.
- Treat any child who sleeps with the infected child.

- Treat family members only if they have symptoms.
- Treat all family members if other family members develop symptoms.
- If any of your child's friends have symptoms, be sure to tell their parents. These children should get tested or checked for pinworms.
- Return to School:
- Children with pinworms do not need to miss any child care or school.
- What to Expect:
- After taking the pinworm medicine, itching should stop in 5 to 7 days.
- Prevention of Pinworms:
- Wash hands and fingernails well before meals and after using the toilet.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Anal symptoms last over 1 week after treatment
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
Treatment for Anal Itching Without Pinworm Being Seen
- What You Should Know About Anal Itching:
- There are many causes of itching around the anus.
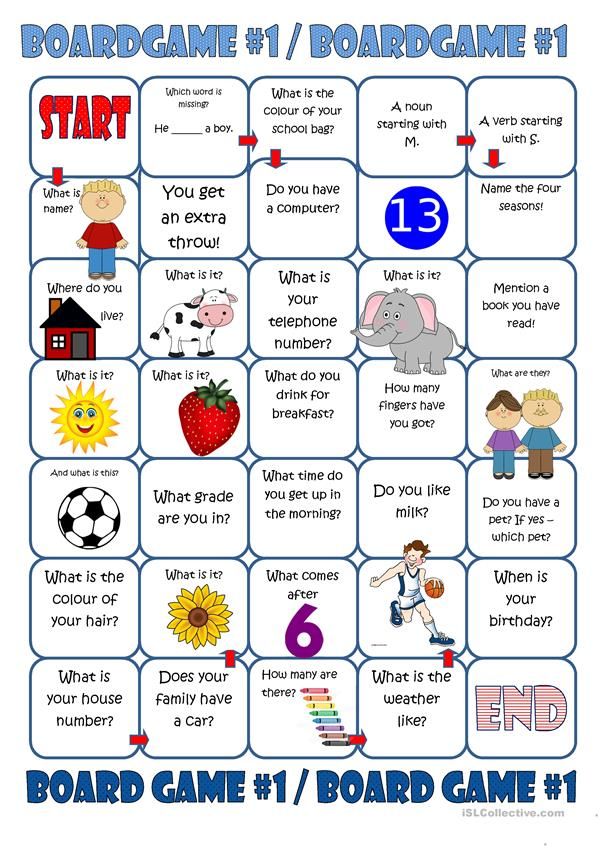 Some are more common than pinworms.
Some are more common than pinworms. - The most common cause is stool that has been left on the skin. Stool contains chemicals and germs that can cause itchy skin rashes. Try to prevent this by washing the skin off. After wiping off stool with toilet tissue, cleanse the skin with warm water.
- Bubble bath can also cause an itchy bottom. Children with dry skin are at increased risk. Avoid bubble bath or any soapy bath water.
- If these changes don't get rid of the anal itching, get a pinworm test.
- There are many causes of itching around the anus.
- Pinworm Checks: Check your child for pinworms.
- Examine the area around the anus, using a flashlight.
- Look for a ¼-inch (6 mm), white, threadlike worm that moves.
- Do this a few hours after your child goes to bed. Check him 2 nights in a row. Also, check him first thing in the morning for 2 days.
- Scotch Tape Test:
- If no adult pinworm is seen, call your doctor's office. Ask for instructions on doing a Scotch-tape test for pinworm eggs.
 You can also use the technique below:
You can also use the technique below: - Take a piece of clear Scotch tape with the sticky side down. Touch it to the skin on both sides of the anus. Do this in the morning soon after your child has awakened. Also, do this before any bath or shower.
- Put the sticky tape side that touched the skin on a slide. If you don't have a slide, put it on a second piece of tape.
- Do it 2 mornings in a row.
- Bring the 2 samples in to be looked at under a microscope.
- If no adult pinworm is seen, call your doctor's office. Ask for instructions on doing a Scotch-tape test for pinworm eggs.
- Steroid Cream for Itching:
- For the itching, wash the skin around the anus with warm water.
- For severe itch, use 1% hydrocortisone cream (such as Cortaid) 2 times per day. Use for 1 or 2 days. No prescription is needed.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Pinworm is seen
- Skin around the anus gets red or tender
- Anal itching lasts more than 1 week
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
Treatment for Pinworm Exposure
- Low Risk for Getting Pinworms:
- Your child has had contact with a child with pinworms, but no symptoms now.
 Your child probably won't get them. This is especially likely if over a month has passed.
Your child probably won't get them. This is especially likely if over a month has passed. - If contact is within the last month, your child may get pinworms. This risk is small.
- Pinworms are harmless. They are never present very long without being seen or causing anal itching.
- Your child has had contact with a child with pinworms, but no symptoms now.
- Scotch Tape Test:
- If you're still worried, call your doctor's office. Ask for instructions on doing a Scotch tape test. This can be done to look for pinworm eggs.
- Do this about 1 month after contact.
- Reason: The swallowed egg will not become an adult pinworm for 3 or 4 weeks.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Pinworm is seen (white, ¼ inch or 6 mm, and moves)
- Anal itching lasts more than 1 week
- You think your child needs to be seen
Treatment for Reducing Reinfection or Spread to Others
- Preventing Pinworm Infections:
- Infection is caused by swallowing pinworm eggs.

- A child can get pinworms no matter how carefully you clean.
- The following hygiene measures, however, can help to reduce the chances of reinfection. It also can reduce the chance of new infections in other people.
- Pets don't carry pinworms.
- Infection is caused by swallowing pinworm eggs.
- Wash Hands:
- Have your child scrub the hands and fingernails well before each meal. Also, wash the hands well after each use of the toilet.
- Keep the fingernails cut short, because eggs can collect here.
- Help your child give up thumb sucking and nail biting.
- Shower:
- Each morning, give your child a shower during the 2 weeks of treatment.
- Always rinse the anal area.
- Continue for 3 days after taking the second dose of pinworm medicine.
- Vacuum:
- Vacuum or wet-mop your child's bedroom once a week.
- Any eggs left on the floor can still infect others for 1 or 2 weeks.
- Wash Clothes:
- Have the infected child wear underwear at night during the 2 weeks of treatment.
 Caution: it may contain pinworm eggs. Remove it carefully just before showering. Wash the underwear each morning.
Caution: it may contain pinworm eggs. Remove it carefully just before showering. Wash the underwear each morning. - Bed sheets can also be washed on a more frequent basis.
- Wash clothes and bedding at a hot temperature. This will kill any eggs left in them.
- Have the infected child wear underwear at night during the 2 weeks of treatment.
- Return to School:
- Children with pinworms do not need to miss any child care or school.
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 02/26/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Pinworm Infections (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Are Pinworms?
Pinworms are tiny worms that can cause an infection in the intestines. Pinworm infections affects millions of people each year, especially school-age kids
If your child develops a pinworm infection, try not to worry. Pinworms don't cause any harm (just itching and restless sleep), and it won't take long to get rid of them.
Pinworms don't cause any harm (just itching and restless sleep), and it won't take long to get rid of them.
How Do Pinworm Infections Spread?
Pinworm infections are contagious. The worms get into the body when people swallow the tiny pinworm eggs. The eggs can be on contaminated hands, under fingernails, and on things people touch a lot, such as:
- clothing, bed linens, and towels
- bathroom surfaces
- drinking glasses and eating utensils
- toys
- kitchen surfaces
- desks or lunch tables at school
Less often, eggs can spread when someone shakes out contaminated clothing or sheets, sending the eggs into the air, where they can get inhaled.
The eggs pass into the digestive system, where they hatch. About 1 to 2 months later, adult female pinworms lay eggs on the skin right around the anus, which makes the area itchy. Often, this happens at night.
When someone scratches the itchy area, tiny pinworm eggs get on their fingers. Contaminated fingers can then carry pinworm eggs to the mouth, where they go back into the body, or onto touched surfaces, where they can live for 2 to 3 weeks.
Contaminated fingers can then carry pinworm eggs to the mouth, where they go back into the body, or onto touched surfaces, where they can live for 2 to 3 weeks.
Family pets can't give your child an infection, as pinworms don't come from animals.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Pinworm Infection?
Common signs of a pinworm infection are:
- itching around the anus (especially at night)
- trouble sleeping
- vaginal discharge in girls, if pinworms spread to the vagina
- sore, red infected anal skin (which can happen from scratching)
- tiny white worms (like a piece of thread, as big as a staple):
- around the anus (check after your child has been asleep for 2–3 hours)
- in the toilet or on the toilet paper after your child goes to the bathroom
- in the underwear in the morning
Belly pain and nausea are less common symptoms but can happen if there are many pinworms in the intestines.
How Are Pinworm Infections Diagnosed?
The doctor will ask questions about your child’s symptoms and check your child’s bottom. The doctor may ask you to help make the diagnosis of pinworms by doing a tape test:
- Press the sticky side of a piece of clear tape against the skin around your child's anus at night or when they first wake up (pinworm eggs will stick to the tape).
- Wash your hands.
- Take the tape to the doctor to check for eggs with a microscope.
The doctor also might take some samples from under a child's fingernails to look for eggs.
How Are Pinworm Infections Treated?
If your child has a pinworm infection, the doctor will recommend an over-the-counter or prescription antiworm medicine. This is given in one dose, then repeated in 2 weeks. The doctor may decide to treat the entire family, especially if your child has had a pinworm infection before.
Although medicine takes care of the worm infection, the itching may continue for about a week. So the doctor also might give your child a cream or other medicine to help stop the itching.
So the doctor also might give your child a cream or other medicine to help stop the itching.
Can Pinworm Infections Be Prevented?
When someone in the house has a pinworm infection, it often spreads to others.
To help prevent a pinworm infection from spreading in your family:
- Remind kids to wash their hands well and often, especially after using the toilet, after playing outside, and before eating.
- Keep kids' fingernails short and clean.
- Make sure your kids shower or bathe every day. Doing so in the morning can help wash away any eggs.
- Change and wash underwear and pajamas daily.
- Wash towels, clothes, and sheets in hot water often (daily, if you can).
- Tell kids not to scratch around their bottom or bite their nails.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call the doctor if your child complains of itchy skin or always seems to be scratching the anal or vaginal area.
Also ask if pinworms could be why your child has trouble sleeping or has begun to wet the bed. (Pinworms can irritate the urethra — the tube through which pee leaves the body — and lead to bedwetting.)
(Pinworms can irritate the urethra — the tube through which pee leaves the body — and lead to bedwetting.)
Remember that pinworms are quite common among kids and aren't harmful. By taking medicine and following some prevention tips, you'll be rid of the worms in no time.
Reviewed by: Melanie L. Pitone, MD
Date reviewed: November 2022
Enterobiasis (pinworms) in children - symptoms and treatment, clinical guidelines
Enterobiasis is a helminthiasis that develops when the colon and rectum of a person are infected with pinworms. It is diagnosed most often in children, although adults can also be infected. Diagnosis is carried out by microscopic detection of eggs. Pinworms in children cause characteristic symptoms. Treatment includes hygiene and deworming. The clinic "RebenOK" carries out diagnostics taking into account the symptoms and treatment of enterobiasis at the best prices in Moscow.
After ascariasis, enterobiasis is in 2nd place. Approximately 400 million people suffer from this disease. Most often, children become infected due to insufficient personal hygiene, as well as people working in children's groups (boarding schools, schools, preschool institutions).
Approximately 400 million people suffer from this disease. Most often, children become infected due to insufficient personal hygiene, as well as people working in children's groups (boarding schools, schools, preschool institutions).
The pinworm is highly contagious. The eggs of the parasite Enterobius vermicularis are transmitted from person to person. They survive outside the host organism up to 2-3 weeks. There are two mechanisms of infection with enterobiasis - fecal-oral and aerosol (by air). In the first case, we are talking about the contact-household, water and alimentary (food) form of infection. The transmission factor is dirty hands, which contain pinworm eggs. Infection through the water of pools, rivers and lakes is unlikely.
The development of pinworms in the human body is a cycle:
- As soon as the eggs penetrate, they reach the small intestine where the larvae form.
- They pass into the large intestine, where they parasitize at the stage of maturation.
- After 1-2 months, adult females lay eggs in the rectal area.
Because of the unbearable itching, children comb the anal area. In this case, the eggs of the parasite fall under the overgrown edge of the nail plate. In the absence of proper hygiene, they penetrate the oral cavity and the life cycle of the nematode resumes.
Worms of the nematode class have a rounded pointed body. The length of the female reaches 1.3 cm, the male - 0.5 cm. Males die after fertilization. The life expectancy of a female is 1 month, during which they produce offspring (lay eggs). After fertilization, the size of the body increases, the possibility of fixation is lost. Reaching the rectum, they crawl out, laying eggs in the perinatal folds.
The uterus of a female can contain up to 17,000 eggs. The larvae develop under certain conditions: at a temperature of 22-39degrees and exposure to oxygen. It takes 5 hours for the larva to reach the invasive stage. Pinworm eggs have high levels of protection - they survive and remain invasive for up to 1 month, and sometimes longer.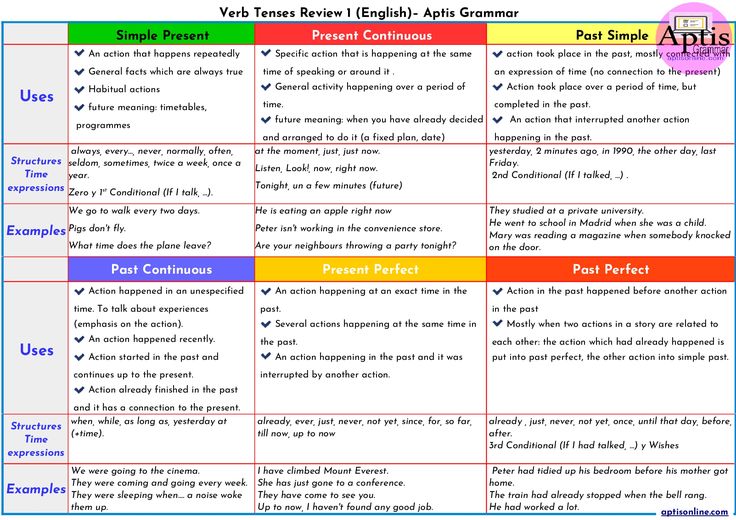 They are not sensitive to many disinfectants, but quickly die under the influence of a soapy solution, when boiled and ironed.
They are not sensitive to many disinfectants, but quickly die under the influence of a soapy solution, when boiled and ironed.
Nematode eggs can survive on food and drinks, dishes, countertops, doorknobs, bedding, clothes, etc. It is impossible to get pinworms from pets, because they do not participate in the life cycle of the parasite. Enterobius vermicularis parasites are tiny but can be seen with the naked eye.
Pinworms cause severe itching in the perinatal folds around the anus. In women and girls, hookworms can also cause vaginal itching and a characteristic discharge.
The condition worsens at night, which is associated with the activity of the parasite at night. This leads to insomnia, irritability and nervousness. Adults and children with enterobiasis can spend a lot of time in the shower, as water helps to cope with the symptoms of the disease, improving the condition.
The most common symptoms of pinworms in children are:
- rash and itching around the anus;
- irritable bowel and increased gas;
- accelerated (3-4 times a day) decorated chair;
- excessive irritability, moodiness, tearfulness;
- headaches, memory impairment.

Nighttime urinary incontinence is another possible symptom of enterobiasis in children, which is prevalent predominantly in preschoolers. This is because pinworms irritate the urethra, the thin tube through which urine leaves the bladder and exits the body.
Children and adults who develop enterobiasis scratch the itchy area. This leads to swelling, redness and bleeding. Bacteria can enter the wound, leading to a rectal abscess.
By exerting a mechanical effect on the walls of the intestinal mucosa, nematodes provoke dysmotility and secretion, causing inflammation of the digestive organs. Against this background, enteritis may develop.
Pinworms sometimes cause digestive symptoms
- abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite.
This condition is accompanied by weight loss and characteristic weakness. As parasites, pinworms suck out essential nutrients from the body, leading to the development of deficient conditions. Sometimes pinworms spread to the female reproductive tract, leading to complications (urinary tract infections, vaginitis).
Sometimes pinworms spread to the female reproductive tract, leading to complications (urinary tract infections, vaginitis).
Against the background of enterobiasis, a decrease in the protective functions of the body is observed. For this reason, the child is more likely to suffer from acute respiratory diseases. Exacerbation of chronic diseases is observed. A slight increase in body temperature is not excluded.
Enterobiasis is usually diagnosed based on symptoms. However, there are other causes of pruritus ani, including skin irritation, diarrhea, and infections other than parasitic infestation. The diagnosis can be confirmed by identifying eggs or worms in specimens examined under a microscope. Sometimes parents themselves manage to detect pinworms on the folds of the skin near the anus or in the feces.
To confirm the diagnosis, clinical symptoms and the general condition of the patient are taken into account.
Screening is carried out in two ways: from the perianal folds (imprint with adhesive tape), scraping for enterobiasis in children (using a cotton swab).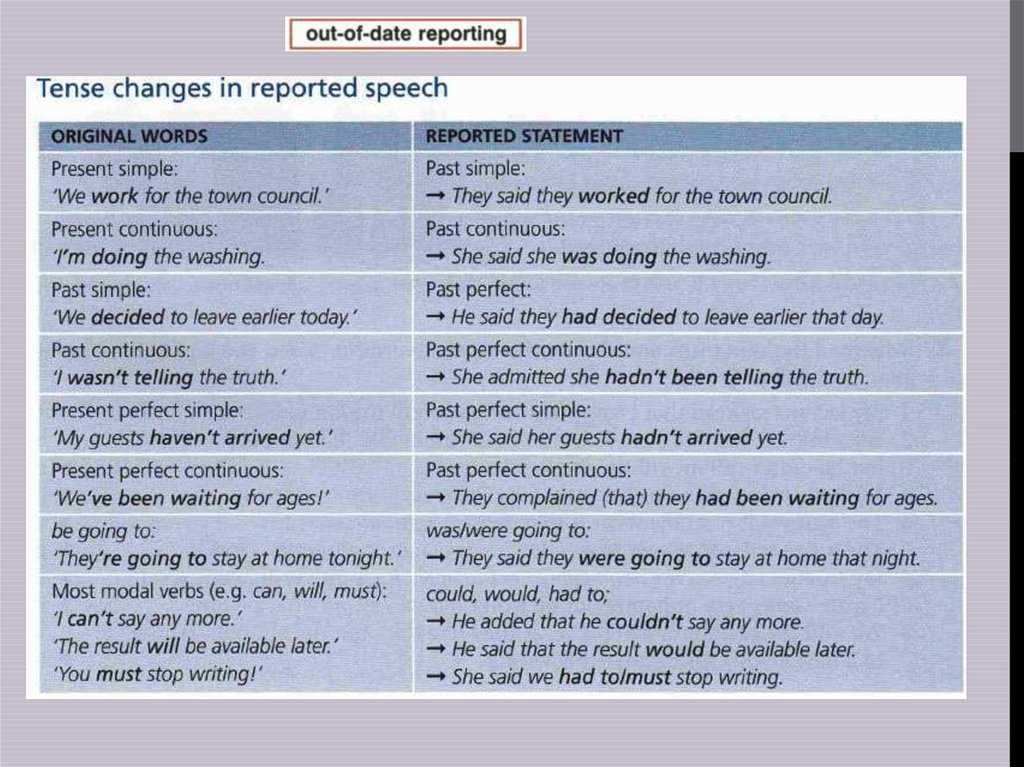 To obtain reliable information, the study is repeated 2-3 times at a certain interval. When conducting a coprogram, nematode eggs can be detected in rare cases.
To obtain reliable information, the study is repeated 2-3 times at a certain interval. When conducting a coprogram, nematode eggs can be detected in rare cases.
Before treating pinworms in children, the diagnosis should be confirmed. Enterobiasis can be cured without medication, by carefully carrying out hygiene procedures to prevent re-infection. This method is applicable to children who have contraindications to anthelmintics. Recovery occurs over a longer period than with drug treatment.
Key recommendations for non-pharmacological treatment:
- The child should wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water after going to the toilet and walking.
- Care must be taken to ensure that the child does not lick his hands.
- Nails must be cut short.
- Bed linen should be changed daily, boiled and ironed.
- Wash your child with soap in the morning and evening.
The use of tablets for the treatment of enterobiasis in children is a more reliable way that ensures a quick recovery. Anthelmintic drugs cause the death of the parasite.
Anthelmintic drugs cause the death of the parasite.
14 days after deworming, you need to re-diagnose. If the test result for enterobiasis in children is negative, then the child is considered recovered. If the clinical picture of helminthic invasion persists, then the drugs are repeated in the same dosage.
Treatment of pinworms in children is carried out under the supervision of a pediatrician. An incorrectly selected drug can lead to the introduction of pinworms into the mucous and submucosal layers of the intestine. Pinworms can cause the development of a purulent inflammatory process. This leads to indigestion, impaired motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
Preventive measures are aimed at instilling standard hygiene habits in children.
Clinical recommendations for enterobiasis in children:
- be sure to cut your nails as they grow back;
- wash hands before sitting down to eat, after going to the toilet and after returning home from the street.

Children who attend educational institutions are examined for enterobiasis for prevention purposes. This approach allows to exclude mass infection.
Enterobiosis is a common helminthiasis that contributes to the development of a number of somatic diseases. Pinworms lead to an exacerbation of chronic diseases, and this fact has been scientifically proven.
Medicines and personal hygiene are the main therapeutic measures for enterobiasis. If contact with the source of infection is maintained, re-infection is not ruled out.
If you have symptoms of helminthic invasion, contact the RebenOK clinic. An experienced pediatrician will diagnose and tell you how to treat enterobiasis in children by prescribing effective drugs for pinworms.
Sources:
- Arakelyan R.S., Sergeeva N.A., Konnova O.V. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of enterobiasis in schoolchildren // Children's infections. 2018. URL: https://cyberleninka.
 ru/article/n/kliniko-epidemiologicheskie-aspekty-techeniya-enterobioza-u-detey-shkolnogo-vozrasta (Accessed: 06/10/2022).
ru/article/n/kliniko-epidemiologicheskie-aspekty-techeniya-enterobioza-u-detey-shkolnogo-vozrasta (Accessed: 06/10/2022). - Rustamova G., Mukhammadieva L. Enterobiosis in children: modern diagnostic problems // International scientific review. 2020. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/enterobioz-u-detey-sovremennye-problemy-diagnostiki (date of access: 06/10/2022)
- Letyushev A.N., Stepanova T.F. The activity of the epidemiological process of enterobiasis in the Russian Federation // Population health and habitat. 2020. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/aktivnost-epidemicheskogo-protsessa-enterobioza-v-rossiyskoy-federatsii (Date of access: 06/10/2022).
- Dusmagambetov M.U., Dusmagambetova A.M. Detectability of helminthic invasions at the outpatient level // Eurasian Union of Scientists. 2019. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vyyavlyaemost-glistnyh-invaziy-na-ambulatornom-urovne (Date of access: 06/10/2022).
- Yasyrova D.S., Vozgorkova E.