Constipation drops for infants
How Can I Tell If My Baby is Constipated?
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
New parents often worry that their babies are not pooping enough. A baby eating formula usually has a bowel movement at least once most days, but may go 1 to 2 days between bowel movements. For breastfed infants it depends on age. During the first month of life, stooling less than once a day might mean your newborn isn’t eating enough. However, breastfed infants may go several days or even a week between bowel movements, using every drop they eat to make more baby, not poop.
Infants normally work really hard to have a bowel movement, so straining at the stool isn’t necessarily alarming, even when the infant cries or gets red in the face. For an infant to have a bowel movement can be a major effort, and it shows. Just imagine trying to poop lying on your back and you’ll get the picture.
If you're concerned your baby may be constipated, ask yourself the following questions:
Is my baby excessively fussy?
Is my baby spitting up more than usual?
Is my baby having dramatically more or fewer bowel movements than before?
Are my baby's stools unusually hard, or do they contain blood related to hard stools?
Does my baby strain for more than 10 minutes without success?
These signs can all suggest actual constipation.
Is there anything I can give my baby for constipation?
Once your baby is at least a month old, if you think they are constipated, you can try giving them a little apple or pear juice. The sugars in these fruit juices aren’t digested very well, so they draw fluid into the intestines and help loosen stool. Although fruit juice is not recommended for babies under a year of age, as a rule of thumb, you can give 1 ounce a day for every month of life up to about 4 months (a 3-month-old baby would get 3 ounces). Once your infant is taking solid foods you can try vegetables and fruits, especially that old standby, prunes. If these dietary changes don’t help, it’s time to call your child's pediatrician.
Once your infant is taking solid foods you can try vegetables and fruits, especially that old standby, prunes. If these dietary changes don’t help, it’s time to call your child's pediatrician.
More information
Baby's First Days: Bowel Movements & Urination
Common Conditions in Newborns
Choosing a Formula
Constipation in Children
- Last Updated
- 5/12/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Dad to Dad: Parenting Like a Pro (Copyright © American Academy of Pediatrics 2012)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Signs and Ways to Offer Relief
Since baby arrived, you’ve probably talked about poop more than you ever imagined. While it might be frustrating to change all those diapers, it’s even more stressful when baby has trouble going or stops altogether. Baby constipation is rough, but sometimes, it’s hard to tell if baby is actually suffering (how little is too little?). Suffice to say, you’ve got poop questions, and we’ve got answers. So is your wee one plugged up, and what does constipated baby poop look like anyway? Here, we’ll give you the lowdown on baby constipation, symptoms to look for, remedies to try and more. You’ll learn what you need to know to get to the bottom of infant constipation and get baby’s belly back on track.
In this article.
Baby constipation: What’s normal and what’s not?
Signs of constipation in babies
What causes constipation in babies
How to help a constipated baby
Baby constipation: When to worry
How to prevent baby constipation
Baby Constipation: What’s Normal and What’s Not?
To figure out if your child has a bout of baby constipation, it’s helpful to know how often infants tend to go. For the first three months, a breastfed baby might have anywhere from 5 to 40 bowel movements a week. Since breastfed babies absorb so much of the milk they take in, some can go up to three or four days—or maybe even a week—without pooping. But as long as when they finally do go it’s soft, pain-free and blood-free, it’s all good, says Lisa Santo Domingo, a pediatric nurse practitioner and medical director of Johns Hopkins Hospital’s Pediatric Chronic Constipation Clinic. Their formula-fed counterparts can have anywhere from 5 to 28 BMs a week (or about two a day).
For the first three months, a breastfed baby might have anywhere from 5 to 40 bowel movements a week. Since breastfed babies absorb so much of the milk they take in, some can go up to three or four days—or maybe even a week—without pooping. But as long as when they finally do go it’s soft, pain-free and blood-free, it’s all good, says Lisa Santo Domingo, a pediatric nurse practitioner and medical director of Johns Hopkins Hospital’s Pediatric Chronic Constipation Clinic. Their formula-fed counterparts can have anywhere from 5 to 28 BMs a week (or about two a day).
As infants age, breastfed and formula-fed babies start to have about the same number of poops—so from 6 to 12 months, they’ll both experience an average of two poops a day. Keep in mind, these numbers can vary greatly.
There’s a pretty wide range of what’s normal when it comes to how often baby poops. Children up to 4 years of age have to fulfill two or more of the following criteria for at least one month to be diagnosed as constipated, says Santo Domingo:
- Two or less bowel movements per week
- A pattern of painful or hard bowel movements
- History of excessive stool retention
- A large fecal mass felt in the rectum during a physical exam by baby’s doctor
Signs of Constipation in Babies
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, you’ll probably notice a few other signs of baby constipation. Irritability and a decreased appetite, which might disappear shortly after baby passes a large stool, are often telltale clues.
Irritability and a decreased appetite, which might disappear shortly after baby passes a large stool, are often telltale clues.
Worried about all that moaning and groaning? Take a deep breath; it’s perfectly normal and isn’t a sign of constipation in babies. “Grunting and straining to push out a stool is normal in young babies. It’s difficult for them to pass a bowel movement while lying flat on their backs and not getting any benefit from gravity,” says Trina Blythe, MD, a pediatrician at Progress West Hospital in O’Fallon, Missouri.
Babies’ bodies often need time to figure out the whole pooping process, like learning how to relax their pelvic floor to have a bowel movement. “A lot of parents come in and think their child is constipated, when what they’re really dealing with is infant dyschezia—a condition in which an otherwise normal, healthy infant will have at least 10 minutes (though often more) of straining, crying, irritability and maybe turning red or purple in the face while trying to have a bowel movement,” Santo Domingo explains. These symptoms continue until baby finally goes—but the resulting stool is actually soft.
These symptoms continue until baby finally goes—but the resulting stool is actually soft.
Baby constipation can cause a child to be irritable and fussy, refuse food and push away the bottle. Toddlers who can walk may start going to a corner and squatting or hiding. “The most prevalent cue is when a child starts tip-toeing,” Santo Domingo says. It’s like an instinct they have, feeling that the straighter their body, the better they’ll be able to withhold pooping, which may be painful or scary for constipated children. Even babies who are able to pull themselves to stand will try to straighten out as much as possible when they’re dealing with constipation.
What does constipated baby poop look like?
When baby constipation is to blame, baby’s poop comes out in hard balls. “We often use the Bristol Stool Scale, which shows the range of stool textures from one to seven: One is rabbit-like, pellet-shaped poop, and seven is pure liquid,” Santo Domingo says. “We define constipated stool as anything that falls into levels one through three, with three looking like a collection of grapes or corn on the cob. ”
”
Another common sign of constipation in babies is a small amount of blood on the outside of the stool—this can happen when a constipated baby passes stool large enough to create a tiny fissure around the anus. If you’re seeing a significant amount of blood, call your child’s doctor right away.
What Causes Constipation in Babies?
So what causes constipation in babies? Really, it could be due to a number of factors, from foods they’re eating to passing illnesses to family history. Here, we break down the most common reasons behind baby constipation:
-
Change in diet. More often than not, a change in diet is the culprit causing baby constipation—whether it’s because you’re shifting from breast milk to formula, transitioning baby to cow’s milk or introducing solid foods. “The introduction of cow’s milk protein—and an allergy or intolerance to it—is probably the largest contributor to baby constipation,” says Santo Domingo. When baby has a cow’s milk protein intolerance (CMPI), their immune system sees the milk protein as something bad it needs to fight off (like it would with harmful bacteria or viruses).
 This negative reaction to the protein is what leads to a constipated baby with an upset stomach and other intestinal problems. But the good news is that most babies will grow out of it: 50 percent of infants who have CMPI regain tolerance by 12 months, and more than 75 percent will be back on track by age 3.
This negative reaction to the protein is what leads to a constipated baby with an upset stomach and other intestinal problems. But the good news is that most babies will grow out of it: 50 percent of infants who have CMPI regain tolerance by 12 months, and more than 75 percent will be back on track by age 3. -
Solids. When baby is about 4 to 6 months of age, you can start experimenting with different solid foods. This is when many little ones begin to experience baby constipation for the first time. “For infants who have already started baby foods, giving foods that are high in fiber will help treat and prevent baby constipation,” says Blythe. She recommends feeding them at least two servings of fresh fruits and vegetables daily, and making sure they’re well hydrated.
-
Illness. When baby’s not feeling well, they’re probably not eating or drinking as much as usual, which can throw their system out of whack and result in infant constipation.

-
Certain medications. High-dose iron supplements or and certain pain medications can lead to baby constipation. Your doctor can let you know if baby’s medicine could be to blame.
-
Prematurity. Premature babies tend to have more trouble with infant constipation than full-term babies. Since their digestive systems aren’t fully developed yet, food moves more slowly through the GI tract and isn’t always properly processed, which can lead to dry, hard stools.
-
Family history. Certain issues like Hirschsprung’s disease, cystic fibrosis, chronic constipation and celiac disease (which often can’t be diagnosed in children until they’re closer to age 3) can also be a contributing factor.
How to Help a Constipated Baby
No parent likes to see their child in discomfort and distress, so knowing how to help a constipated baby can make a world of difference. First and foremost, though, it’s important to realize that constipation in newborns can be a different issue than constipation in older babies. If your baby is not even a month old yet, talk to your pediatrician right away—at this age, constipation could be a sign of an underlying issue, such as Hirschsprung’s disease, a rare congenital condition that happens in about one out of 5,000 births and typically requires surgery. (FYI: This is among the reasons everyone at the hospital is so obsessed with the timing of your newborn passing their first meconium.)
If your baby is not even a month old yet, talk to your pediatrician right away—at this age, constipation could be a sign of an underlying issue, such as Hirschsprung’s disease, a rare congenital condition that happens in about one out of 5,000 births and typically requires surgery. (FYI: This is among the reasons everyone at the hospital is so obsessed with the timing of your newborn passing their first meconium.)
Additionally, if you’re exclusively breastfeeding, it’s important to count those dirty diapers each day because infrequent stooling might actually be a sign of not enough feeding volume, says Blythe.
But if you’ve spoken to your pediatrician and ruled out other issues, there are some baby constipation home remedies and treatments you can turn to. Here are some things you should—and shouldn’t— try to help a constipated baby:
Baby constipation home remedies
For baby constipation relief, you can try giving infants under 6 months with hard bowel movements some water—about one ounce. Heard of giving apple or prune juice for baby constipation? Babies 6 to 12 months can have two to four ounces of apple, pear or prune juice a day until their stools soften. “The sugars in juice basically bring water into the bowel to help soften the bowel movement,” Santo Domingo says.
Heard of giving apple or prune juice for baby constipation? Babies 6 to 12 months can have two to four ounces of apple, pear or prune juice a day until their stools soften. “The sugars in juice basically bring water into the bowel to help soften the bowel movement,” Santo Domingo says.
You may have been told that using a rectal thermometer can help offer some infant constipation relief, but Santo Domingo doesn’t recommend any kind of rectal stimulation as a remedy. “You always run the risk of perforation, especially given that that area could be irritated,” she says.
She also discourages giving baby mineral oil or Karo syrup for baby constipation. “We’ve found that it doesn’t help. Karo syrup doesn’t soften the stool—it just coats it to make it easier to pass, but you’re still passing a large stool. And with mineral oil, there have been some reports of aspiration.”
Baby constipation medicine
Wondering what to give a constipated baby? The options are limited.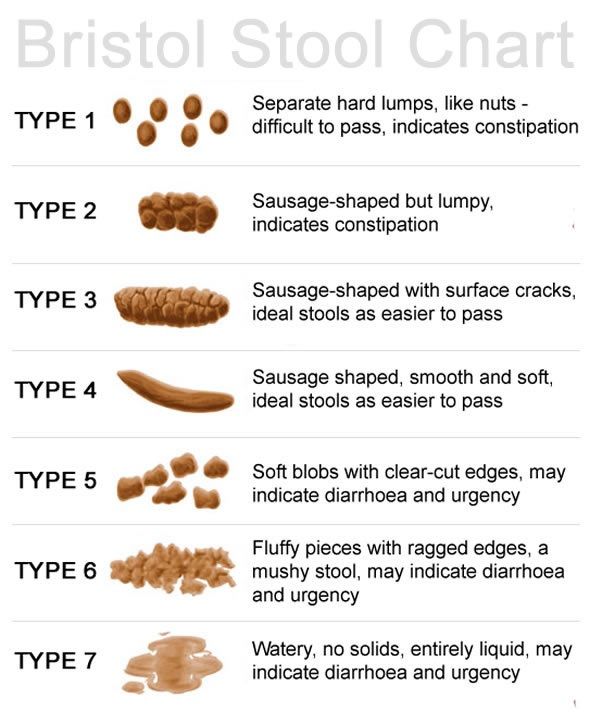 For children who don’t respond to water or juice, you may consider trying a small glycerin suppository to help relieve baby constipation, suggests the Mayo Clinic. It’s important to note, however, that these are meant for occasional use, and shouldn’t be a regular part of baby’s routine.
For children who don’t respond to water or juice, you may consider trying a small glycerin suppository to help relieve baby constipation, suggests the Mayo Clinic. It’s important to note, however, that these are meant for occasional use, and shouldn’t be a regular part of baby’s routine.
Some well-meaning friends may recommend gripe water or gas drops. These remedies are generally considered safe, but there’s little evidence these options work to relieve baby constipation. However, many parents say that the former alleviates colic and other tummy troubles and the latter works miracles breaking up gas bubbles. If your doctor gives you the go ahead, there’s no harm in trying either option.
Similarly, probiotics for baby constipation have been increasing in popularity lately, but Blythe remains skeptical. “Probiotics haven’t yet been proven to relieve constipation in infants, so I generally don’t recommend them.” Still, anecdotally, many parents swear by infant-safe tummy and probiotic drops that can help balance bad and good bacteria in the digestive tract. What’s more, while the evidence isn’t concrete, some research indicates that prophylactic use of probiotics can help alleviate some types of digestive troubles in infants. Suffice to say, it doesn’t hurt to try. Of course, before you give baby constipation medication or remedies at home, check in with your pediatrician.
What’s more, while the evidence isn’t concrete, some research indicates that prophylactic use of probiotics can help alleviate some types of digestive troubles in infants. Suffice to say, it doesn’t hurt to try. Of course, before you give baby constipation medication or remedies at home, check in with your pediatrician.
Baby foods that help with constipation
In some cases, your baby’s doctor may want to consider eliminating cow’s milk for a short period of time to see if that’s causing constipation.
For babies eating solids, you can also offer certain baby foods that help with constipation: Try feeding barley or oatmeal cereals, prunes, peaches, plums, apricots and most vegetables. There’s no need to completely eliminate binding foods like bananas and rice, but it’s a good idea to cut back on them if you’re noticing baby constipation symptoms. “Bananas and rice are common binding agents, because they are soluble fibers that soak up water as they pass through your system, and tend to bulk stools,” Santo Domingo says.
Baby massage for constipation
Want to know how to relieve constipation in babies quickly? One of the easiest things you can try is giving baby a massage. Blythe recommends trying a gentle tummy massage of the left side of the belly to help stimulate the colon. And you can do exercises with baby as well. “Bicycling the hips and holding the knees up in a squat position helps simulate the movements needed to have a bowel movement,” Blythe says. You can also try a warm bath. ‘
Baby Constipation: When to Worry
Baby constipation can be pesky, but it’s typically not cause for concern. Still, if constipation lasts for two or more weeks or if it’s accompanied by other symptoms, including fever and abdominal swelling, reach out to your pediatrician, recommends the Mayo Clinic. If you see blood in your child’s stool, you’ll also want to check in to make sure there are no other issues at play.
How to Prevent Baby Constipation
As for preventing infant constipation, unfortunately there’s a lot you can proactively do. “Prevention really comes down to recognizing the warning signs, and trying to stay on top of them,” Santo Domingo says. Of course, monitoring baby’s diet for foods that cause constipation, giving them a diverse assortment of fibrous fruits and veggies and keeping them hydrated may help.
“Prevention really comes down to recognizing the warning signs, and trying to stay on top of them,” Santo Domingo says. Of course, monitoring baby’s diet for foods that cause constipation, giving them a diverse assortment of fibrous fruits and veggies and keeping them hydrated may help.
About the experts:
Trina Blythe, MD, is a BJC Medical Group pediatrician at Progress West Hospital in O’Fallon, Missouri. She received her medical degree from Albany Medical Center in New York.
Lisa Santo Domingo, DNP, MSN, is a pediatric nurse practitioner and medical director of Johns Hopkins Hospital’s Pediatric Chronic Constipation Clinic. She received her doctor of nursing degree at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
What to Do for a Gassy Baby
Colic 101: How to Help Soothe Your Colicky Baby
Why Babies Get Hiccups (and How to Get Rid of Them)
is it possible for a child to take, the rules of administration, dosage
Features of constipation in children
One can speak of constipation when the time interval between bowel movements increases in comparison with the individual physiological norm or with regular incomplete emptying of the intestine.
For babies of the first months of life on breastfeeding, a stool can normally be from one to 6-7 times during the day. With a gradual transition to the “common table”, the chair becomes thicker and less frequent. Constipation can be considered a decrease in stools - less than 6 times a week for babies up to 3 years 1 .
Constipation can be considered a decrease in stools - less than 6 times a week for babies up to 3 years 1 .
In older children, the frequency of bowel movements can normally range from 3 times a day to 3 times a week. Constipation can be considered less than 3 stools per week for children over
3 years of age 1 .
Non-drug correction
If the baby has constipation, first of all, it is necessary to review and adjust the feeding process: the feeding schedule and the amount of food. It may be necessary to refuse unreasonably early introduction of complementary foods. A nursing mother should drink enough fluids and limit the use of foods that stimulate gas formation and slow down the peristalsis of the large intestine: strong tea and coffee, alcoholic beverages, chocolate, sugar syrups, citrus fruits 2 .
In a bottle-fed baby with constipation, use only adapted milk formulas and avoid frequent changes.

The baby needs to be provided with a sufficient amount of liquid: clean water, you can give herbal tea with fennel or chamomile for babies. Starting from 4-4.5 months, the baby can be given weakly concentrated dried fruit compotes or berry fruit drinks. It is worth introducing complementary foods in the form of vegetable and fruit purees no earlier than the 5th month of a child's life 2 .
Abdominal massage may be helpful for babies with constipation problems before feeding.
Constipation can also be relieved by position therapy (laying the baby on the stomach with legs bent and brought to the body), light massage of the perianal area 2 .
In the diet of a child with constipation older than one year of age, there should be food rich in dietary fiber and vegetable fiber, fermented milk and dairy products containing lacto- and bifidobacteria
2. 3 .
3 . Wheat bran is abundant in dietary fiber, but its use in young children may be limited due to the bran's ability to absorb nutrients in the intestinal lumen. The diet should also include vegetables and fruits 2 . It is also important for the child to observe the drinking regime - drinking enough water 4 .
Physical activity
A necessary condition for preventing constipation is constant regular physical activity (especially morning exercises), sufficient exposure of the child to fresh air (in cold weather - at least 2 hours, in warm - 4 hours or more) 3 .
Formation of toilet habits
To form toilet habits from the age of one and a half years, a child should be put on the pot 2-3 times a day after meals for 5 minutes (toilet training) 1 . At this time, the baby should not play with toys, look at pictures in books, watch TV 3 .
Suppression of the urge to defecate
Suppression of the urge to defecate may be the main causative factor of constipation if the child is constantly busy and his day is scheduled to the minute, as well as in an unusual and uncomfortable environment 1 . Therefore, for normal bowel movements, a comfortable toilet is important, including a footrest, if necessary, to provide support during defecation 4 .
Drug treatment
It is believed that even the initial therapy of constipation in children should not be limited only to the correction of nutrition and regimen. Such changes may increase the frequency of stools in healthy children, but not reduce symptoms in those with constipation 2 .
Some drugs used in adults may be restricted for use in children for various reasons.
Also, some laxatives may have an unpleasant taste or require large amounts of liquid to be taken, which may make children reluctant to take the medicine 2 . It is important to note that many children may have a negative attitude towards rectal manipulation: the use of enemas may cause additional fear and discomfort in children regarding defecation 2.5 . In addition, often the use of rectal laxatives is considered possible only after unsuccessful treatment with oral laxatives 6 .
It is important to note that many children may have a negative attitude towards rectal manipulation: the use of enemas may cause additional fear and discomfort in children regarding defecation 2.5 . In addition, often the use of rectal laxatives is considered possible only after unsuccessful treatment with oral laxatives 6 .
For the treatment of constipation in children, a doctor may prescribe a drug from the group of stimulant laxatives from the age of 0 years - oral drops Guttalax®
2.7 .The active ingredient, sodium picosulfate, is activated directly in the colon by bacterial degradation. Guttalax® promotes the natural process of defecation 7 .
Guttalax® has a dual mechanism of action:
On the one hand, it helps to increase intestinal motility, stimulating the act of defecation, and on the other hand, it helps to soften the stool by attracting water / electrolytes into the lumen of the large intestine 7 .
What else is important to know about Guttalax®
The drug is not addictive when taken in recommended dosages 7
Guttalax® does not affect the digestion and absorption of nutrients in the intestines 7
Guttalax® drops do not have taste and smell, they can be easily added to the child in any food or drink The drug in the form of drops allows you to choose an individual effective dose for the child 7 The use of drugs, including laxatives, such as Guttalax®, in such a special population group as children, is possible only after consultation doctor 7 According to the instructions for medical use, the standard dosage of Guttalax® for children is: 90427 : Instructions for use and dosage*
7 Children from 0 to 4 years old
90®025
Over 10 years old
Dosage: 10-20 drops per day
Children 4 to 10 years old
Dosage: 5-10 drops per day
The laxative effect may take 6-12 hours to develop
To help your child go to the toilet in the morning, you can give him Guttalax® drops at night before bed
* Use Guttalax® in children only after consulting a doctor.
Treatment of constipation involves a holistic approach, including information for parents on toilet training, advice on nutrition, drinking regimen, physical activity and daily routine 2 .
More about the drug
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. IT IS NECESSARY TO CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST.
List of medicines for constipation for newborns (list of laxatives)
Contents
In the baby of the first months of life, the digestive system is not yet fully formed, this is what explains frequent dyspeptic disorders. A newborn baby may have flatulence, loose stools, or constipation (About Constipation: Signs and Causes of Constipation in a Baby). The inability to completely empty the bowels leads to abdominal pain, crying and it is natural that every parent is looking for a cure for constipation for newborns.
First you need to understand exactly what constipation is. Some mothers believe that if their child has not emptied the intestines for three or four days, then this is already a serious problem that needs to be addressed to a doctor. In fact, this is not entirely true, in some babies a rare bowel movement is considered a variant of the norm, and if the general well-being does not suffer, the baby is alert, eats and sleeps well, then your anxiety can be postponed. (How many times should a baby poop)
True constipation is a condition in which the baby, making all his efforts, that is, pushing, straining and groaning, cannot get rid of the accumulated feces. At the same time, he cries, presses his legs to his stomach, worries, refuses to feed.
The impossibility of emptying the intestines can disturb just every few days, and every day, it depends on the physiological characteristics of the body and on what you feed the baby - breast milk or mixtures.
Clickable During constipation, solid stools are excreted, sometimes with an admixture of mucus or blood streaks. During a bowel movement, the baby cries, his face turns red from straining, there is severe anxiety, and this continues until the intestines are completely emptied.
During a bowel movement, the baby cries, his face turns red from straining, there is severe anxiety, and this continues until the intestines are completely emptied.
After the first constipation, you should not immediately run to the pharmacy and look for a laxative for newborns, any medicine is still chemistry and it is unlikely to be useful for the baby's body. First you need to deal with the child's diet and eliminate the identified errors.
Pediatricians often advise young mothers to adhere to the following recommendations:
- If the baby is fed with mother's milk, then you need to be especially careful in compiling your diet. It is not advised to use strengthening foods, nutrition should be diversified with plant components (Nutrition for a nursing mother).
- A child, both bottle-fed and breast-fed, needs additional portions of boiled water. Every day, the baby needs to give several sips of water from a small spoon in between feedings.

- The baby must actively move - daily exercises and a light massage of the tummy have a positive effect on the condition of the intestines. Spreading on the stomach also helps with constipation.
- Babies in the first months of life with problems with stool should be given dill water or a few drops of prunes decoction.
If all the measures taken do not help, then it is necessary to visit a pediatrician - the doctor will assess the general condition of the child and suggest one of the safest laxatives for newborns.
Laxatives recommended and approved for use
Laxatives for babies in their first months of life are available in several dosage forms and most often they are syrups, solutions or suppositories.
Most often, for rare problems with emptying and to provide quick help to the tummy, pediatricians advise resorting to the use of rectal laxative suppositories, you can buy them at any pharmacy.
- Rectal suppositories act at the local level, so they do not have a negative effect on the entire body as a whole. Candles with glycerin are considered the safest, they can be used from the first days of a baby's life, so the expectant mother can stock them up in advance. For newborn babies with constipation, you need to use 1/8 of the candle, for children from a month and older, the dosage is doubled. Laxative suppositories soften feces, make defecation painless and easy. It is only necessary to remember that any medicine is used only in extreme cases, otherwise the intestines will get used to working with the help of its stimulation.
- Syrups and solutions. The pharmaceutical industry produces a wide variety of products to facilitate bowel movements. Moms need to remember that you need to choose only where the age of the child is indicated and the instructions are fully written.
- Prelaks - the main active ingredient of the syrup is lactulose, which improves intestinal motility and positively affects its microflora.
 Prelaks is also used as a prophylactic against constipation, the effect of its first application begins to appear within an hour. More about syrup
Prelaks is also used as a prophylactic against constipation, the effect of its first application begins to appear within an hour. More about syrup - Duphalac is a laxative made from natural whey components. Delicious syrup can be given to a baby from the first days of life, you need to remember that the maximum effect from its use most often develops on the next day. In the first days of taking the baby, flatulence may increase, after a few days it usually disappears. Duphalac has a positive effect on the normalization of the intestinal microflora, which leads to the stabilization of its work. Article about dufalac
- Normolact is another laxative based on lactulose. The drug is started with high doses, then, when the desired effect is achieved, they are gradually reduced. The medicine can be used for a long time.
- Prelaks - the main active ingredient of the syrup is lactulose, which improves intestinal motility and positively affects its microflora.
- Microlax is a new generation drug that acts as a microclyster. The effect of its use comes pretty quickly, the only thing that stops many mothers from buying is a fairly high price.