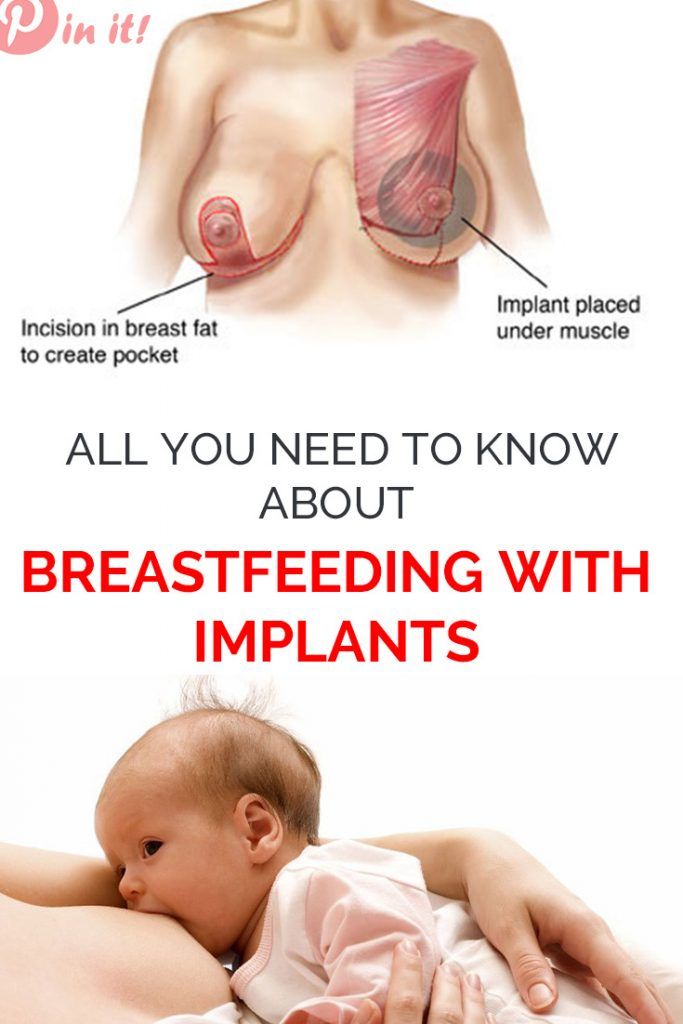
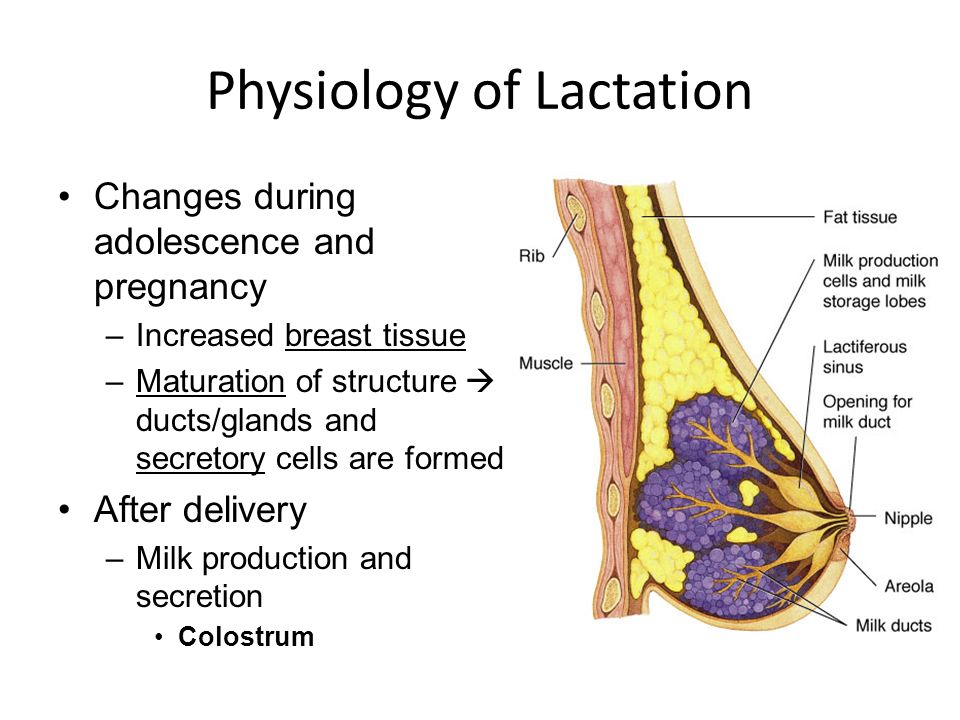
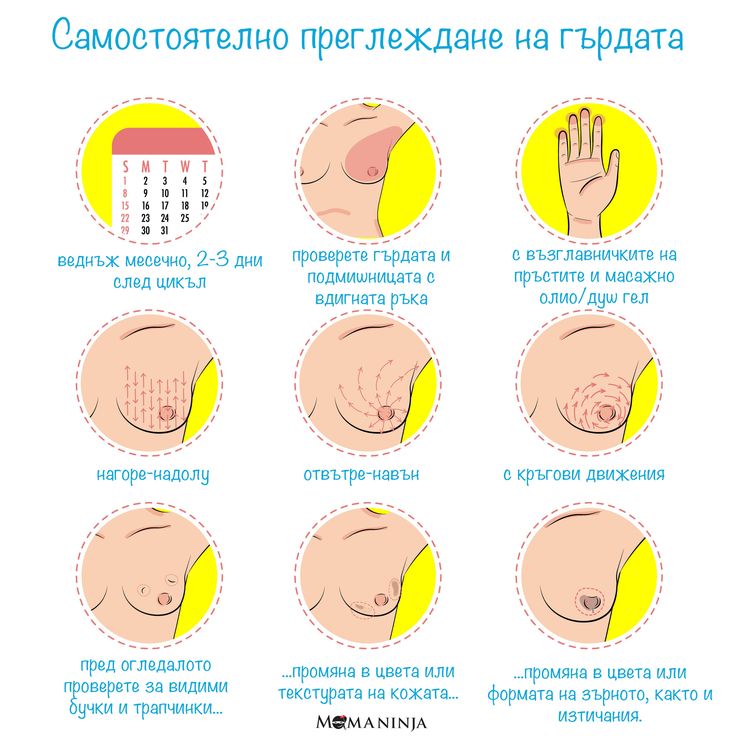
How to stimulate breast for lactation
Breastfeeding: Tips to Increase Your Milk Supply l University Hospitals l Northeast Ohio
Signs That a Breastfed Baby Is Being Well Nourished
- Your baby nurses at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours, or every 2 to 3 hours. Your baby may be fussy once or twice a day. At these times, he or she wants to nurse often for several hours before seeming full. This is called cluster feeding.
- Your baby wets at least 6 cloth or 5 disposable diapers and has at least 1 bowel movement in 24 hours. This occurs by 1 week of age.
- You can hear your baby swallow milk while nursing or you can feel your baby swallow when lightly touching his or her throat.
- Your breasts seem softer after nursing.
- Your baby gains 4 to 8 ounces a week after the first week. There is no need to weigh your baby at home. Your baby’s doctor will do this for you. You may notice that your baby has outgrown his or her clothing.
- Your baby has regained his/her birthweight by 10 to 14 days after birth.
Factors Which Can Cause Your Milk Supply to Decrease
- Your baby feeds fewer than 8 to 16 times in 24 hours. Milk production is affected by how well the breast is drained.
- Your baby has a very weak suck, or has an improper latch.
- Giving bottles of formula or water after nursing. Most babies will suck on a bottle after nursing. This just means they need to suck. It does not mean they are still hungry. Babies cry or fuss for many reasons, such as being tired, bored, wet, hot or cold.
- Giving solid foods too early and/or before you breastfeed. Most babies do not need solid foods for the first 6 months if they are breastfeeding 8 to 16 times a day.
- Smoking can cause a decreased milk supply and interfere with the letdown reflex. Here are some things you should do:
- Try to quit or cut down.
- Smoke after nursing, not before.
- Don’t smoke in the same room with your baby.
- Beginning birth control pills too soon can decrease your milk supply.
 Wait at least 6 weeks before taking birth control pills and then use only the mini-pill (Progestin). If you still notice a decrease in your milk supply, talk to your doctor about other birth control options. Other medications may also affect milk supply. Check with your doctor. (Refer to PI-682, Breastfeeding and Birth Control: You Have Options.)
Wait at least 6 weeks before taking birth control pills and then use only the mini-pill (Progestin). If you still notice a decrease in your milk supply, talk to your doctor about other birth control options. Other medications may also affect milk supply. Check with your doctor. (Refer to PI-682, Breastfeeding and Birth Control: You Have Options.) - Mothers who are exhausted may notice a decrease in milk supply. To keep yourself from getting too tired:
- Sleep or relax when your baby sleeps.
- Eat balanced diet that includes high-protein food.
- Drink when you are thirsty so that your urine is pale yellow in color. Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply.
- Take an iron supplement if your healthcare provider says you are anemic.
- Talk with your doctor or nurse midwife about the need for vitamin supplement.
- Accept help when it is offered.
- Use nipple shields and pacifiers with caution.
- A breast flange that is too small or too large in size can hurt your milk supply.
- Pregnancy
- Breast reduction surgery may reduce milk supply.
If You Notice Your Milk Supply Is Low
You can increase your milk supply by:
- Nursing your baby often. Nurse every 2 hours during the day and every 3 to 4 hours at night (at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours). If your baby will not nurse, use a good quality double electric breast pump to increase milk production. Pumping after breastfeeding signals your body to produce more milk.
- Nurse your baby at least 15 minutes at each breast. Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply.
- Gently massage breast before and during feedings.

- Use relaxation techniques to reduce stress and promote the flow of breast milk.
- Provide skin to skin time with your baby for about 20 minutes after feeds. This “kangaroo care” has been shown to increase milk supply.
- Be sure baby is positioned and latched correctly.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding.
- Try breast compression during the feeding to help drain the breast.
- Pump immediately after breastfeeding during the day. Rest at night. Some mothers find that they get more milk if they pump for 5 minutes, rest for 5 minutes, and pump for another 10 minutes.
Talk to your doctor about using medication or the herb fenugreek.
Works Cited
Wambach, Karen and Riordan, Jan “Breastfeeding and Human Lactation”, Fifth edition, Jones & Bartlett, 2016.
Breastfeeding Without Giving Birth - La Leche League International
Alyssa Schnell, St. Louis, Missouri, USA
Alyssa Schnell is an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) based in the United States.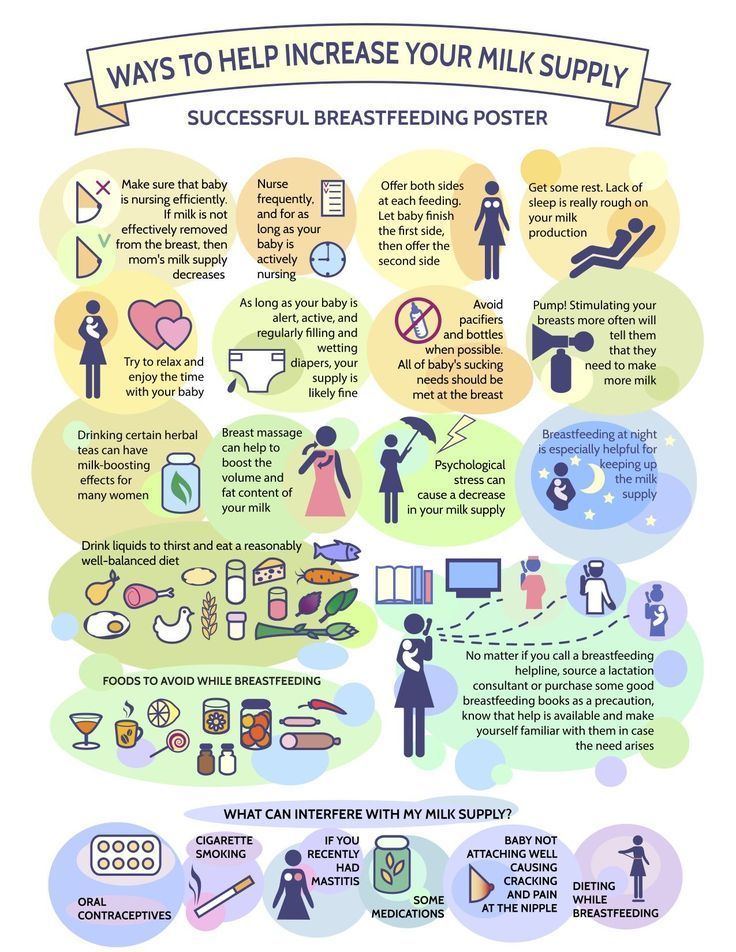 She speaks internationally about inducing lactation and relactation and specializes in helping parents who have not given birth (non-gestational parents) to breastfeed their babies. In this article Alyssa discusses how parents who have not given birth can breastfeed by inducing lactation and how La Leche League Leaders can support them.
She speaks internationally about inducing lactation and relactation and specializes in helping parents who have not given birth (non-gestational parents) to breastfeed their babies. In this article Alyssa discusses how parents who have not given birth can breastfeed by inducing lactation and how La Leche League Leaders can support them.
Breastfeeding is a special gift a baby receives from their gestational parent[1]. However, many non-gestational parents—adoptive parents, intended parents (through surrogacy), parents whose partner is birthing, and transwomen—are finding out that this wonderful experience is also available to them. Because parents who haven’t given birth do not have the hormones of pregnancy to get their bodies started with making milk, they need more information and support to make breastfeeding a reality.
Why Would a Non-Gestational Parent Choose to Breastfeed or Chestfeed?- Attachment.
 Breastfeeding helps the parent and baby form a secure attachment, a particular concern when babies are separated from their gestational parent or gestational carrier (in surrogacy).
Breastfeeding helps the parent and baby form a secure attachment, a particular concern when babies are separated from their gestational parent or gestational carrier (in surrogacy). - Nutrition. Human milk provides the optimal nutrition and necessary immunities for human babies.
Healing. Breastfeeding can help heal the heartache of infertility, and provides a biological connection between mother/parent and baby. Breastfeeding is much more than breast milk. Breastfeeding is a close, intimate, physical and emotional relationship between two or more people who love each other. - Sharing. When both parents are breastfeeding, they share the caregiving role.
Facts about breastfeeding without birthing
- Women have breastfed babies they did not birth throughout history. With the easy availability and common use of bottles and infant formula in modern developed countries, culture has largely lost track of how breastfeeding can also be an option for non-gestational parents.
- Non-gestational parents can start preparing for breastfeeding as soon as they decide to grow their family[2], after an adoption match has occurred or once their partner or gestational carrier is pregnant. They can even wait until the baby is in their arms.
- The amount of milk produced when inducing lactation can vary widely. While some parents make no milk and others make all the milk their babies need, most will make a partial milk supply. Fortunately, breastfeeding is possible no matter how much or little milk is produced—even if it is none at all! Human milk feeding can be simulated with a nursing supplementer: a bag or bottle that holds human milk or formula carried to the nipple via a tiny feeding tube. Parents who are not making any milk may also choose to feed with a bottle while their baby comforts and connects with them by suckling at the (dry) breast.
- Newborn babies are wired to initiate breastfeeding, but with gentle and patient encouragement, along with a few handy tools and techniques, even older babies can learn to breastfeed.
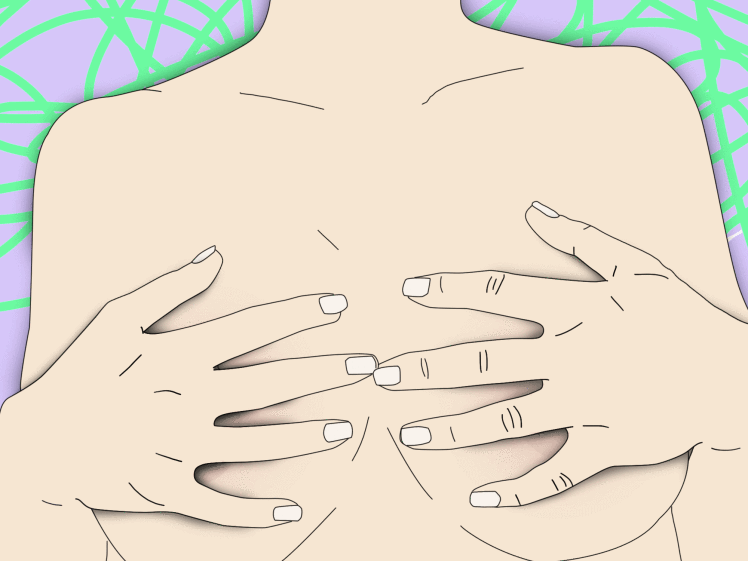
- Some mothers will take medications or herbs to help them make more milk, but this is not essential. The only necessary component to induce lactation—the official term for making milk without pregnancy and birth—is to stimulate and drain the breasts. That stimulation or emptying can happen with baby breastfeeding, with an electric breast pump, or using a variety of manual techniques.[3]
- The composition of milk produced by inducing lactation is comparable to that produced following birth.[4],[5] The milk does not contain dangerous levels of artificial hormones—in fact, it very rarely contains any artificial hormones at all. In most cases, the only artificial hormones that are taken are estrogen and/or progesterone before there is milk production (Step 1 below.) Progesterone and estrogen levels are high during pregnancy and taking these hormones artificially may help to make the body think it is pregnant. Estrogen and progesterone play a role in breast development in pregnancy.
- It is not necessary to be fertile—or even to have ovaries or a uterus—to breastfeed. The hormones responsible for milk production (prolactin) and milk ejection (oxytocin) are released from the pituitary gland located at the base of the brain.
- Both parents, whether or not one has given birth, can share the breastfeeding role. This is called co-nursing.
As stated above, the primary way to induce lactation is through breast emptying: breastfeeding, pumping, or hand expression. The effectiveness of these physical techniques can be enhanced with the use of galactogogues: medications, herbs and homeopathic remedies that support the production of milk. These tools can be put together in a variety of ways to be effective and applicable to each individual parent. While the use of medications, herbs or homeopathic preparations is an individual choice, parents should always discuss their individual situation with their health care providers.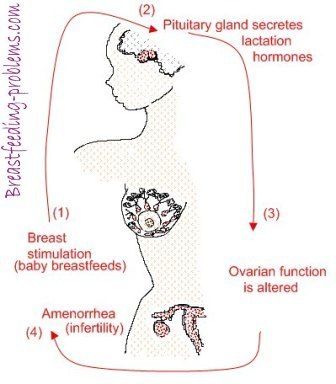
Generic protocols are available (such as Dr Jack Newman’s protocol) or an experienced International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) can work with parents to develop a personalized protocol customized to meet their specific health history, circumstances, and values. The process can be broken down into three steps:
Step 1: Preparing the Breasts for Lactation
This step mimics the hormonal and breast changes that occur during pregnancy. This step is not about making milk; it is about growing and developing the glandular breast tissue in preparation for making milk. Many parents will take hormone therapy for a period of time to achieve this. However, this step is optional.
Step 2: Starting to Make Milk Before Baby Arrives
Milk is often produced very, very slowly when lactation is induced compared with the sudden increase in milk supply between days 3-5 following birth. In order to have a milk supply by the time baby arrives, parents will often start the process of growing their milk production several weeks or months before. The main component of Step 2 for many parents is frequent pumping. Ideally, parents will express their milk as frequently as a baby nurses—just like for birthing parents, frequent breast drainage “places the order” for healthy milk production. Parents can store any milk they produce for use when baby arrives.
The main component of Step 2 for many parents is frequent pumping. Ideally, parents will express their milk as frequently as a baby nurses—just like for birthing parents, frequent breast drainage “places the order” for healthy milk production. Parents can store any milk they produce for use when baby arrives.
Step 3: Feeding Baby and Continuing to Grow Milk Production
This is the big payoff! Baby is here and the parent can begin feeding baby their milk. This step generally involves putting baby to breast.
Not every parent’s protocol will use all three steps. Each parent’s needs and circumstances determine which steps will be appropriate for them. For most parents with adequate information and support, milk production begins within 6-8 weeks of beginning the process of inducing lactation.
What is the role of a La Leche League Leader?Although extremely rewarding, inducing lactation can be a challenging breastfeeding situation.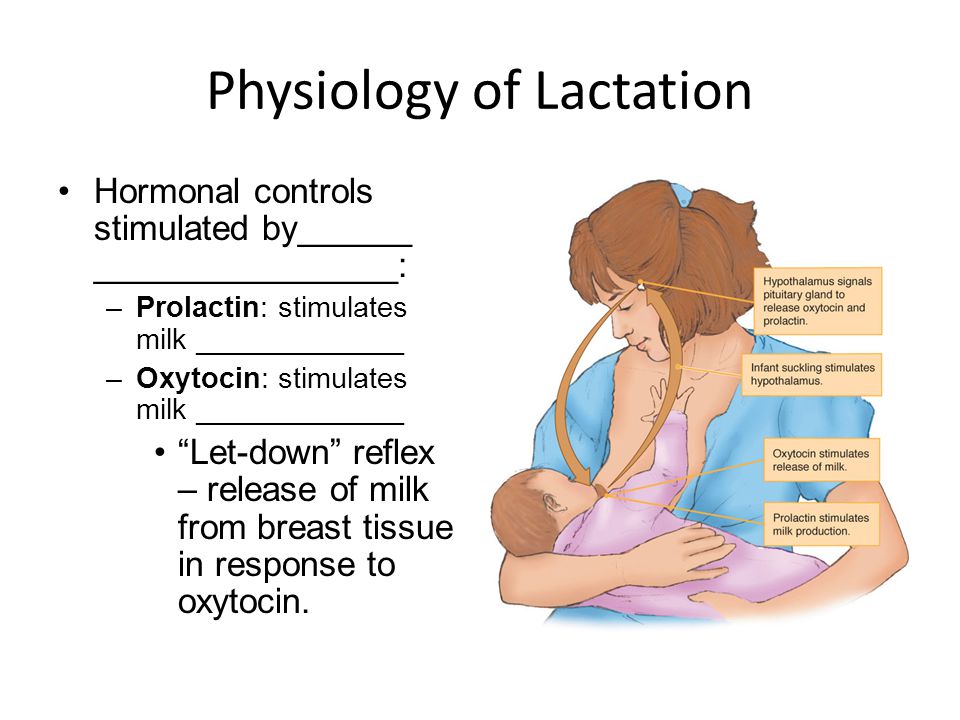 Mothers/parents need and deserve all of the support they can get. While working with an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) is highly recommended, La Leche League Leaders can also play a very valuable role. As always, Leaders provide essential information and encouragement. More specifically, La Leche League Leaders may:
Mothers/parents need and deserve all of the support they can get. While working with an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) is highly recommended, La Leche League Leaders can also play a very valuable role. As always, Leaders provide essential information and encouragement. More specifically, La Leche League Leaders may:
- Refer parents to resources on inducing lactation (see below).
- Provide support for inducing lactation.
- Facilitate La Leche League Group meetings where older babies who are bottle-feeding can observe breastfeeding babies, and parents can participate in a breastfeeding culture. Group meetings are also opportunities for parents to connect with other mothers who are nursing in a variety of situations.
- Facilitate healthy social media information and interaction.
- Share information about donor milk.
Breastfeeding without birthing may not be easy, but it is possible and it is powerful. La Leche League Leaders can be part of the team supporting these parents and their babies.
- La Leche League Inducing Lactation and Relactation Facebook Group
- “Breastfeeding an Adopted Baby”, LLLI website
- Breastfeeding Without Birthing by Alyssa Schnell
- Breastfeeding Outside the Box podcast or other podcast app
Alyssa Schnell has been helping parents and babies with breastfeeding for the past 17 years, first as a La Leche League Leader and now as an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC). Her private practice, Sweet Pea Breastfeeding Support, provides individual lactation consultations either in person or by phone or video-conference for parents throughout the United States and beyond. Alyssa is also the co-host of the Breastfeeding Outside the Box podcast, which is devoted to families breastfeeding or chestfeeding in extraordinary situations. Alyssa enjoys working with all parents and babies, but she has a special place in her heart for helping non-gestational parents to breastfeed/chestfeed their babies.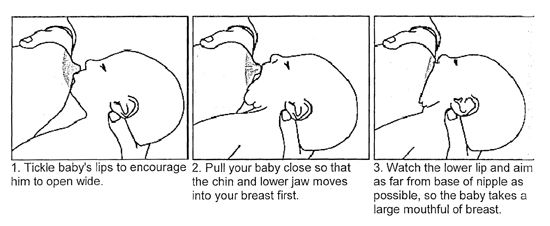 She is the author of Breastfeeding Without Birthing: A Breastfeeding Guide for Mothers Through Adoption, Surrogacy, and Other Special Circumstances and is an international speaker on the topics of inducing lactation, relactation, and other related topics. Alyssa lives in St. Louis, Missouri, USA and is the proud mother of three breastfed children—two by birth and one by adoption.
She is the author of Breastfeeding Without Birthing: A Breastfeeding Guide for Mothers Through Adoption, Surrogacy, and Other Special Circumstances and is an international speaker on the topics of inducing lactation, relactation, and other related topics. Alyssa lives in St. Louis, Missouri, USA and is the proud mother of three breastfed children—two by birth and one by adoption.
[1] Some notes about language: The term “gestational” is used throughout this article instead of “biological.” In surrogacy, the intended mother is often the biological mother (baby is often conceived with her egg) even though she is not gestating (pregnant with) the baby. And oftentimes same-sex female couples will conceive baby via in vitro fertilization (IVF) using the egg of one parent (biological parent) implanted in the uterus of the other parent (gestational parent). This article also attempts to use gender-inclusive language such as parent versus mother and breastfeeding/chestfeeding versus breastfeeding.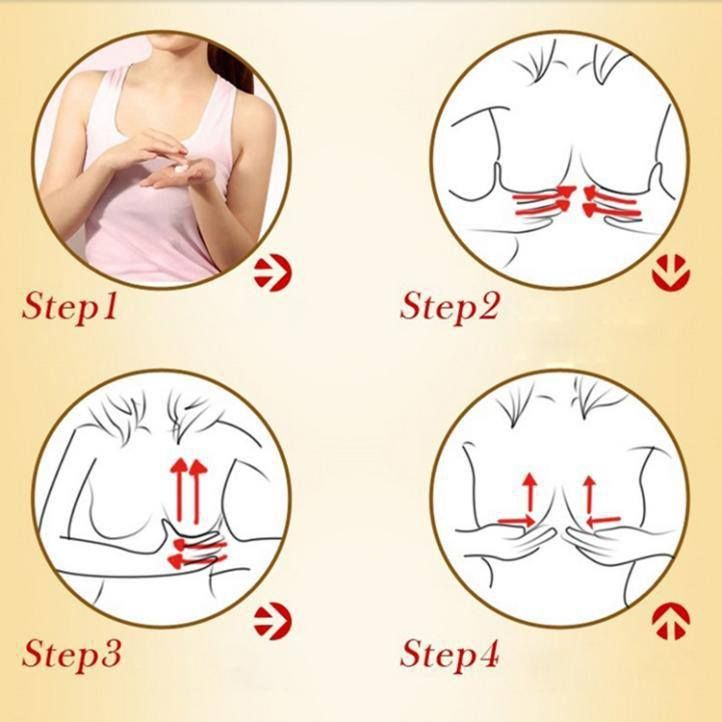 Some of the parents referred to in this article may be cis male, trans male, or non-binary.
Some of the parents referred to in this article may be cis male, trans male, or non-binary.
[2] Note: inducing lactation with medication should not be started unless the parent has an approximate timeline for their baby’s arrival. Taking medication without a definite end could be hazardous.
[3] Other manual approaches might include breast massage, nipple manipulation (gently pulling out and twisting of the nipple), and a partner suckling.
[4] Kulski, J. K., Hartmann, P. E., Saint, W. J., Giles, P. F., & Gutteridge, D. H. (1981). Changes in the milk composition of nonpuerperal women. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 139(5), 597-604.
[5] Perrin, M. T., Wilson, E., Chetwynd, E., & Fogleman, A. (2015). A pilot study on the protein composition of induced nonpuerperal human milk. Journal of Human Lactation, 31(1), 166-171.
obstetrician-gynecologist Starostina Antonina Viktorovna.
For the normal development of lactation, first of all, it is necessary to organize the feeding of the child (feeding on demand, without a night break, the absence of nipples and pacifiers that suppress the suckling reflex of the baby), properly care for the breast, use a breast pump to stimulate and increase lactation, use according to indications other accessories for breastfeeding.
Sleep should be at least 10 hours a day - night and day. Outdoor walks for at least 2 hours. Frequent breastfeeding from birth (at least 10 times a day) with obligatory night feedings. Good nutrition and an increase in the amount of fluid consumed up to 1.5 - 2 liters per day (this is tea, soups, decoctions, milk, dairy products). Shower-massage: after feeding the baby and expressing milk, pour hot water (45 degrees) from the shower over the mammary gland that was fed, while massaging in circular motions from the nipple to the periphery and from top to bottom, while expressing milk. Duration 5-10 minutes. nine0003
Perform the procedure 2 times for the left and 2 times for the right breast during the day. Drink hot tea with milk 30 minutes before feeding.
Drink in small sips throughout the day.
- Steep 3 teaspoons of dry nettle with 2 cups of boiling water and infuse for 10-15 minutes (we only infuse fresh herb for 2 minutes). The resulting drink should be used during the day.

- A very effective remedy that stimulates the flow of milk and helps increase lactation is an infusion of walnuts, which is prepared as follows: brew 0.5 cups of peeled walnuts with 0.5 liters of boiling milk in a thermos and infuse for 3-4 hours. Infusion take 1/3 cup 20 minutes before each feeding, but not daily, but every other day. nine0012
- A mixture that promotes lactation is very good: 100 g dried apricots, 100 g raisins, 100 g figs, 1 glass of walnuts. Grind everything and mix with 100 g of honey and 100 g of butter. Use 1 tbsp. spoon 15-20 minutes before feeding. Watch your child's reaction! Allergy is possible.
- Useful green tea with dill seeds, raspberry leaves, linden, oregano, lemon balm.
Be sure to use special multivitamin complexes for pregnant and lactating women, which also help improve lactation. They will improve the quality of milk and increase its quantity:
- Hipp tea for nursing mothers.
- Apilac 0.01 under the tongue and dissolve.
 Take 2-3 times a day. Pay attention to the child's reaction! Allergy is possible.
Take 2-3 times a day. Pay attention to the child's reaction! Allergy is possible. - Vitamin E capsules 0.1-0.2 - 2 times a day.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) up to 1 g per day.
- Brewer's yeast - liquid 60 g 3 times a day, dry 1 tsp. 4 times a day.
- Calcium pantothenate 1 tab. 3 times a day.
- Asparkam 1 tab. 3 times a day
In European countries, homeopathic remedies are widely used to stimulate lactation. Of the many homeopathic remedies to enhance lactation, the following remedies can be recommended: before each feeding of the child (20 minutes) \ Urtika urens 3 and Agnus castus 3 alternately and at night - Pulsatilla 6. Take 5 grains until the effect is obtained (from 3 days to 3 weeks). But in any case, you need to consult a doctor.
How to increase the amount of milk for a nursing mother? – an article in the blog of the Health Center for Children in Moscow
Breastfeeding is a guarantee of good health and mental peace of the child for years to come. But besides this, breastfeeding solves most of the mother's issues: from financial issues to the convenience of building your day and bonding with your child. Galina Vladimirovna Loseva, our most sought-after pediatrician with more than 20 years of experience, tells how to increase the amount of milk for good nutrition of a child
But besides this, breastfeeding solves most of the mother's issues: from financial issues to the convenience of building your day and bonding with your child. Galina Vladimirovna Loseva, our most sought-after pediatrician with more than 20 years of experience, tells how to increase the amount of milk for good nutrition of a child
The problem of lack of milk can occur both in the early neonatal period, when lactation is becoming established, and later, for example, during lactation crises, which can occur at certain periods of time (3-6 weeks, 3-4 months, 6 months), as well as after temporary weaning during the mother’s illness or the need to take certain medications that are incompatible with breastfeeding. nine0003
Ways to increase lactation:
- Feeding on demand , especially during lactation. Frequent feedings in the first weeks of life are essential for maximizing the number of prolactin receptors to ensure sufficient milk production in the long term.
 Without these receptors, lactation will be at risk by 2-3 months of age. It is advisable to attach the baby to the breast as soon as possible after childbirth. If possible, do not use bottle supplements without a good reason. Night feedings are obligatory, the need for them usually lasts up to about 6 months. nine0012
Without these receptors, lactation will be at risk by 2-3 months of age. It is advisable to attach the baby to the breast as soon as possible after childbirth. If possible, do not use bottle supplements without a good reason. Night feedings are obligatory, the need for them usually lasts up to about 6 months. nine0012 - Proper breastfeeding. The baby must have both the nipple and the areola. His mouth should be wide open with his lower lip turned outward
- You can use post-feeding which will increase milk production. And at the same time, freeze milk to create a reserve in case the mother leaves or a case of illness in which it is necessary to interrupt breastfeeding.
- Rational nutrition for breastfeeding women. The menu should contain cereals, vegetables, fish, meat, eggs, fruits, dairy products are better than sour-milk, a small amount of nuts is acceptable. The use of strict hypoallergenic diets in a woman without an allergic history is unacceptable.
 Spicy dishes, spices, fried foods are excluded, this can affect the taste and smell of milk. nine0012
Spicy dishes, spices, fried foods are excluded, this can affect the taste and smell of milk. nine0012 - Drinking enough liquid - water, green tea, compotes, fruit drinks. Drinks should preferably be warm or hot. It is recommended to take liquid 20-40 minutes before feeding.
- Avoid alcohol, nicotine, including passive smoking.
- Compliance with the rest regimen , psycho-emotional peace, positive attitude. This is largely determined by the attitude of close people who can help a nursing mother in household chores, caring for other children, etc. nine0012
- Warm shower, light breast massage just before feeding.
- If you still need supplementary feeding, then it is better to give it with a pipette, spoon, syringe without a needle.
- Pharmaceutical products: Laktogon, Femilak. From herbs, galega, cumin, anise are considered safe. However, relying only on these funds is not worth it if the above points are not observed.