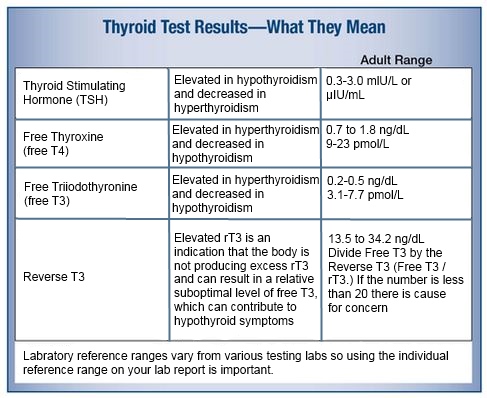
Blood test to check hormone levels for pregnancy
HCG blood test - quantitative
Medical Tests
Definition
A quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. HCG is a hormone produced in the body during pregnancy.
Other HCG tests include:
- HCG urine test
- HCG blood test -- qualitative
Alternative Names
Serial beta HCG; Repeat quantitative beta HCG; Human chorionic gonadotropin blood test - quantitative; Beta-HCG blood test - quantitative; Pregnancy test - blood - quantitative
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This is most often taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
HCG appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception. Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
This test is also done to diagnose abnormal conditions not related to pregnancy that can raise HCG level.
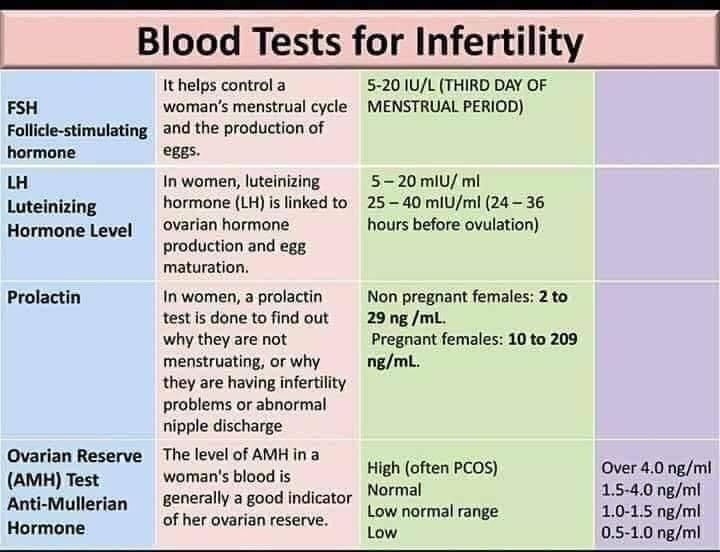
Normal Results
Results are given in milli-international units per milliliter (mUI/mL).
Normal levels are found in:
- Non-pregnant women: less than 5 mIU/mL
- Healthy men: less than 2 mIU/mL
In pregnancy, HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester and then declines slightly. The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
- 3 weeks: 5 - 72 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 10 -708 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 217 - 8,245 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 152 - 32,177 mIU/mL
- 7 weeks: 4,059 - 153,767 mIU/mL
- 8 weeks: 31,366 - 149,094 mIU/mL
- 9 weeks: 59,109 - 135,901 mIU/mL
- 10 weeks: 44,186 - 170,409 mIU/mL
- 12 weeks: 27,107 - 201,165 mIU/mL
- 14 weeks: 24,302 - 93,646 mIU/mL
- 15 weeks: 12,540 - 69,747 mIU/mL
- 16 weeks: 8,904 - 55,332 mIU/mL
- 17 weeks: 8,240 - 51,793 mIU/mL
- 18 weeks: 9,649 - 55,271 mIU/mL
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal level may indicate:
- More than one fetus, for example, twins or triplets
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus
- Hydatidiform mole of the uterus
- Ovarian cancer
- Testicular cancer (in men)
During pregnancy, lower than normal levels based on the gestational age may indicate:
- Fetal death
- Incomplete miscarriage
- Threatened spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Risks
Risks of having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Blood accumulating under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Jain S, Pincus MR, Bluth MH, McPherson RA, Bowne WB, Lee P. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers.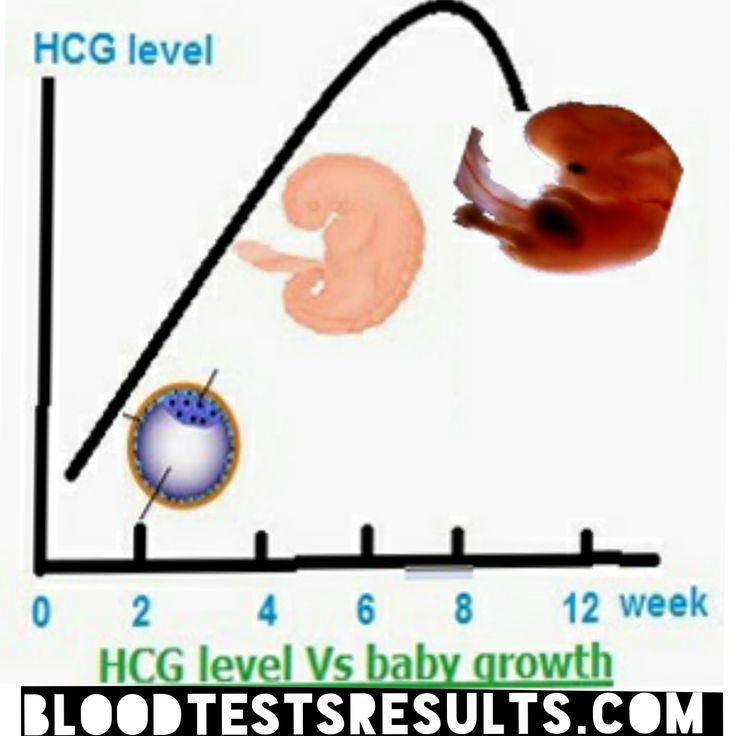 In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 25.
University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories. Test directory: HCG - pregnancy, serum, quantitative. www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/path_handbook/rhandbook/test1549.html. Updated December 14, 2017. Accessed February 18, 2019.
Yarbrough ML, Stout M, Gronowski AM. Pregnancy and its disorders. In: Rifai N, ed. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
Review Date: 09/25/2018
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition.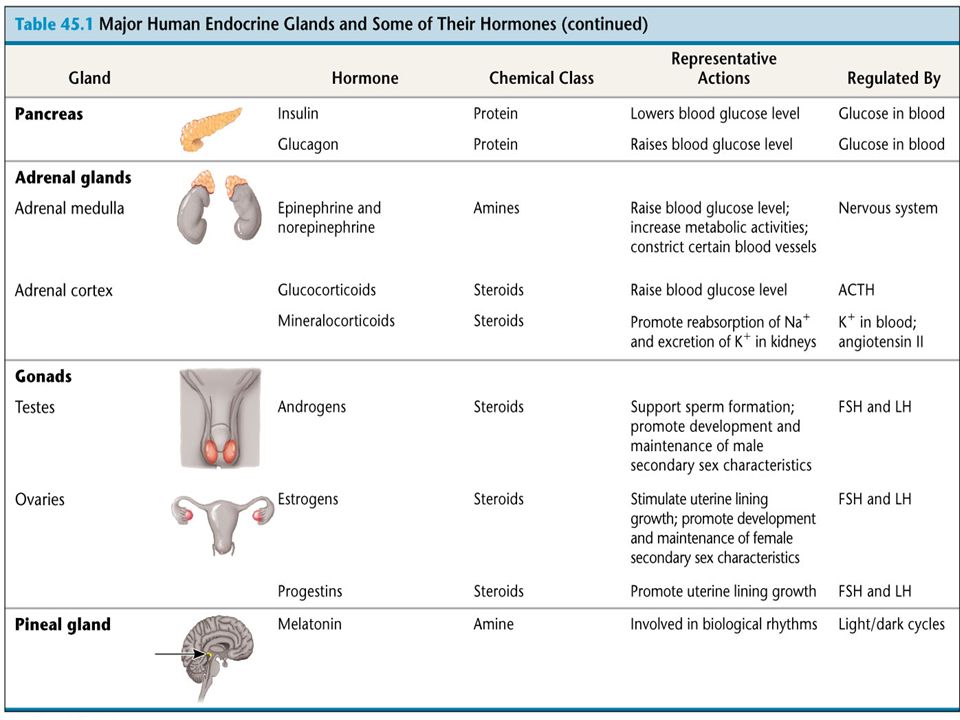 A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Information developed by A.D.A.M., Inc. regarding tests and test results may not directly correspond with information provided by UCSF Health. Please discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you may have.
Progesterone Test: MedlinePlus Medical Test
What is a progesterone test?
A progesterone test measures the level of progesterone in a sample of your blood. Progesterone is a hormone that's made mainly by the ovaries, which are two glands in the female reproductive system that contain eggs.
Each month, progesterone prepares your uterus for pregnancy.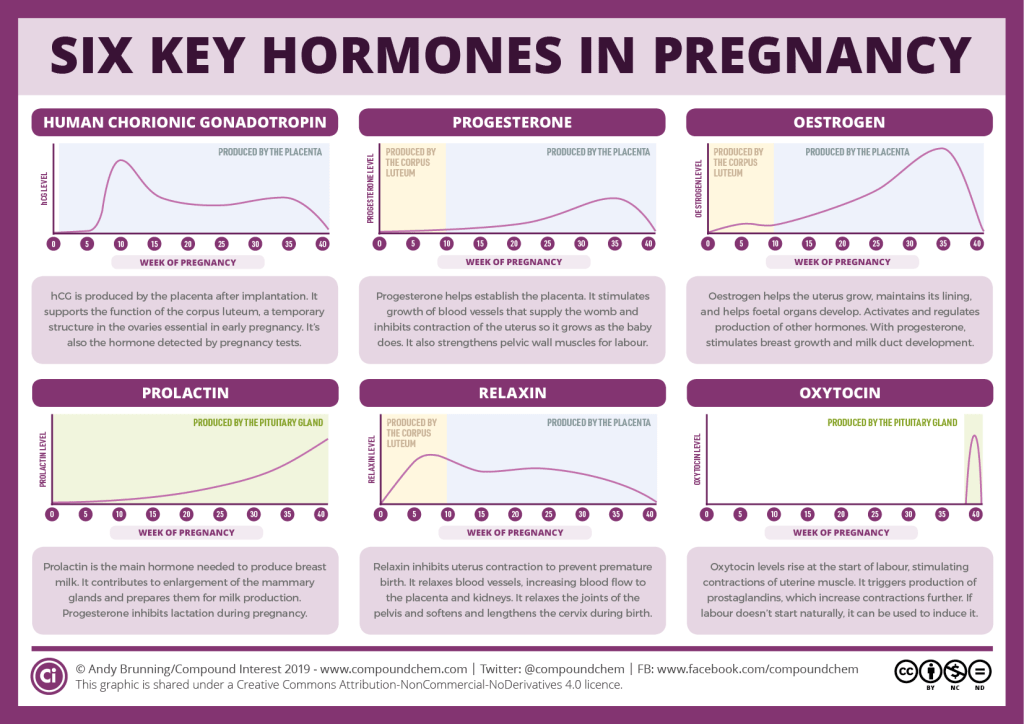 During a normal menstrual cycle, an ovary releases an egg and your progesterone levels begin to rise. Progesterone makes the lining of your uterus grow thicker so that a fertilized egg can attach (implant) inside of the uterus and grow into a baby.
During a normal menstrual cycle, an ovary releases an egg and your progesterone levels begin to rise. Progesterone makes the lining of your uterus grow thicker so that a fertilized egg can attach (implant) inside of the uterus and grow into a baby.
If you don't become pregnant, your progesterone levels will fall. The lining of your uterus will become thinner again. When your uterus starts to get rid of the extra blood and tissue, your menstrual period will begin.
If you become pregnant, progesterone levels will continue to rise to about 10 times higher than usual to support the pregnancy. High levels of progesterone prevent the uterus from contracting (squeezing) and causing pre-term labor. Much of the progesterone you need for a healthy pregnancy is made by the placenta. The placenta is the organ that grows in the uterus to provide nutrients and oxygen to the unborn baby.
A progesterone test can help show whether low progesterone levels are causing female infertility (problems getting pregnant after a year of trying) or problems during pregnancy. The test may also help diagnose certain problems with the adrenal glands that may cause high levels of progesterone in both females and males.
The test may also help diagnose certain problems with the adrenal glands that may cause high levels of progesterone in both females and males.
Other names: serum progesterone, progesterone blood test, PGSN
What is it used for?
A progesterone test may be used to help:
- Find the cause of female infertility.
- Check to see if fertility treatments are working.
- Find out your risk of a miscarriage (loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks).
- Diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, which is a fertilized egg that tries to grow outside of the uterus. The egg cannot grow into a baby when it's in the wrong place. It must be removed to avoid damage to your organs. This can be a medical emergency.
- Check the health of a high-risk pregnancy.
- Diagnose ovarian cancer or problems with your adrenal glands. Normally, your adrenal glands make small amounts of progesterone. High levels of progesterone may be a sign of an adrenal gland disorder in both females and males.
Why do I need a progesterone test?
You may need a progesterone test if:
- You are having trouble getting pregnant. A progesterone test can help your health care provider see if your ovaries are releasing eggs (ovulating) normally.
- You are having fertility treatments.
- You are having abnormal bleeding when you're not pregnant.
- You are pregnant and:
- You're having progesterone therapy to prevent a miscarriage.
- Your provider wants to check the health of your pregnancy because you have a higher risk for miscarriage or other pregnancy complications.
- You have signs of a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy, such as cramps or bleeding
What happens during a progesterone test?
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out.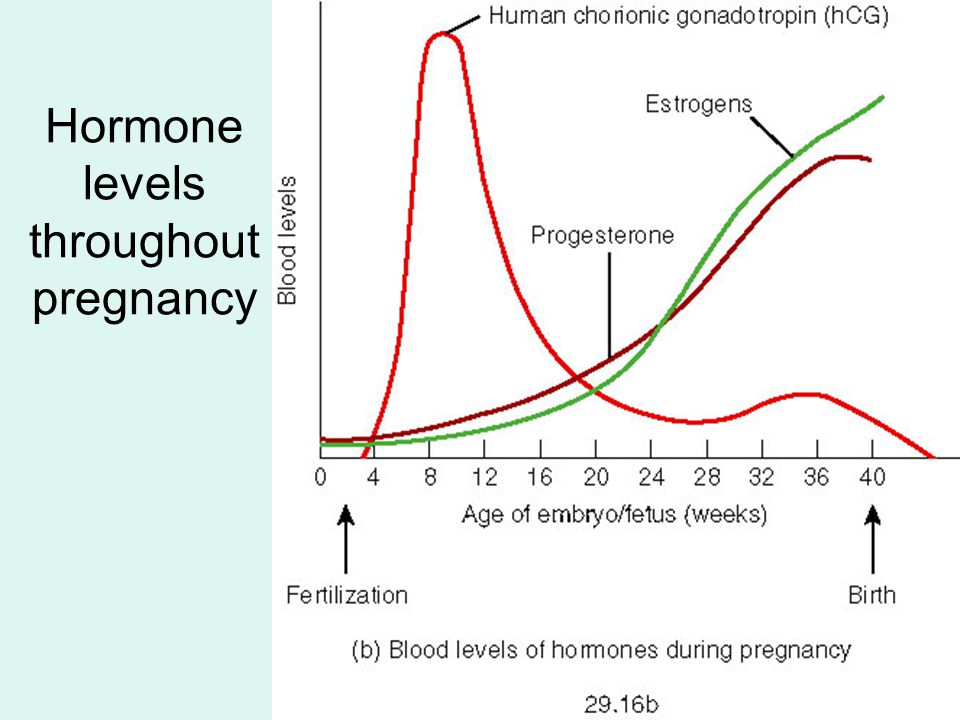 This usually takes less than five minutes.
This usually takes less than five minutes.
Will I need to do anything to prepare for the test?
You usually don't need any other preparations for a progesterone test. In certain cases, you may need to know the first day of your last menstrual period. Your provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before the test. But never stop taking medicine unless your provider tells you.
Are there any risks to the test?
There is very little risk to having a blood test. You may have slight pain or bruising at the spot where the needle was put in, but most symptoms go away quickly.
What do the results mean?
The meaning of your test results depends on:
- Why you had the test
- Where you were in your menstrual cycle when your blood sample was taken
High progesterone levels:
- When you're not pregnant may be linked to:
- A cyst on your ovaries
- Ovarian cancer
- Adrenal gland problems, including adrenal gland cancer, or an inherited disorder called congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
- Higher than expected progesterone levels when you are pregnant, may mean you're having two or more babies.

High progesterone levels may also be a sign of a molar pregnancy, which is an abnormal growth of tissue in the uterus. It's caused by a fertilized egg with such severe genetic problems that it cannot become a baby. The growth can turn into cancer and must be removed.
Low progesterone levels:
- When you're not pregnant, may be linked to:
- Not ovulating normally
- Not having a menstrual period (amenorrhea)
- When you're pregnant, may be linked to:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Miscarriage or a high risk of miscarriage
- Pre-eclampsia
Your provider can explain what your test results say about your health.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Is there anything else I need to know about a progesterone test?
Because progesterone levels change throughout your pregnancy and menstrual cycle, you may need to be tested several times.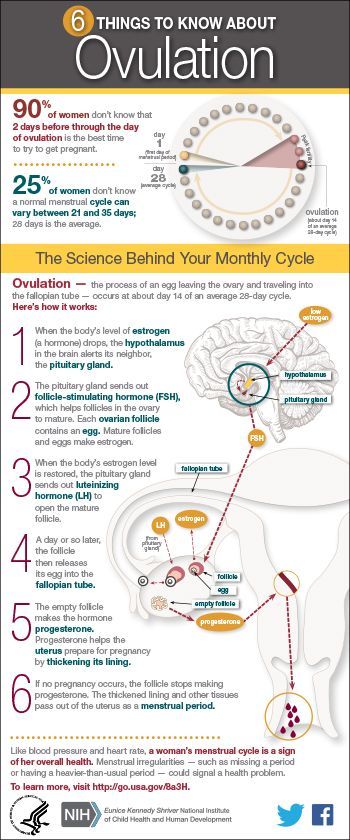
References
- Cable JK, Grider MH. Physiology, Progesterone. [Updated 2022 May 8; cited 2022 Jun 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558960/
- Mayo Clinic: Mayo Medical Laboratories [Internet]. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research; c1995–2012. Test ID: PGSN: Progesterone Serum: Overview; [cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://www.mayomedicallaboratories.com/test-catalog/Overview/8141
- Merck Manual Consumer Version [Internet]. Kenilworth (NJ): Merck & Co. Inc.; c2022. Overview of the Female Reproductive System; [reviewed 2022 Apr; cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/biology-of-the-female-reproductive-system/overview-of-the-female-reproductive-system
- Merck Manual Consumer Version [Internet]. Kenilworth (NJ): Merck & Co. Inc.
 ; c2022. Quick Facts: Ectopic Pregnancy; [reviewed 2021 Jun; cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-women-s-health-issues/complications-of-pregnancy/ectopic-pregnancy
; c2022. Quick Facts: Ectopic Pregnancy; [reviewed 2021 Jun; cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-women-s-health-issues/complications-of-pregnancy/ectopic-pregnancy - Testing.com [Internet]. Seattle (WA).: OneCare Media; c2022. Progesterone; [modified 2021 Nov 9; cited 2022 June 21]; [about 12 screens]. Available from: https://www.testing.com/tests/progesterone/
- UF Health: University of Florida Health [Internet]. University of Florida; c2022. Serum Progesterone: Overview; [updated 2019 Mar 28; cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://ufhealth.org/serum-progesterone
- University of Rochester Medical Center [Internet]. Rochester (NY): University of Rochester Medical Center; c2022. Health Encyclopedia: Progesterone; [cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 4 screens]. Available from: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167& ontented=progesterone
- UW Health [Internet].
 Madison (WI): University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics Authority; c2022. Health Information: Progesterone: Results; [current 2022 Feb 23; cited 2022 Jun 213]; [about 6 screens]. Available from: https://patient.uwhealth.org/healthwise/article/en-us/hw42146
Madison (WI): University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics Authority; c2022. Health Information: Progesterone: Results; [current 2022 Feb 23; cited 2022 Jun 213]; [about 6 screens]. Available from: https://patient.uwhealth.org/healthwise/article/en-us/hw42146 - WomensHealth.gov [Internet]. Washington DC: Office on Women's Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Menstrual Cycle: Your Menstrual Cycle; [updated 2021 Feb 22; cited 2022 Jun 21]; [about 4 screens]. Available from: https://www.womenshealth.gov/menstrual-cycle/your-menstrual-cycle
Blood test for pregnancy in the early stages - why you need and how to donate blood
Blood test for pregnancy is a procedure that is necessary to identify existing pathologies. It also allows you to determine the very presence of pregnancy, since it detects the presence in the blood of a woman of a hormone called "chorionic gonadotropin" (hCG).
In a situation where conception has not occurred, this substance is not produced in the patient's body, since its appearance is associated with the formation of the chorion. This is the tissue that occurs between the endometrium and the zygote after the attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. nine0003
This is the tissue that occurs between the endometrium and the zygote after the attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. nine0003
Reasons for testing
A blood test can show pregnancy as early as six days after a successful conception. Whereas a standard pregnancy test in some cases can give incorrect results. Therefore, tests during pregnancy are prescribed to determine such conditions as:
- Establishment of the actual fact of conception
- Assessment of hormonal background for failures
- Tracking abnormal pregnancy types:
- Frozen - in this case, at a certain stage, the embryo stops its development
- Ectopic - in this situation, the zygote is not attached to the wall of the uterus, but in the fallopian tube
Also, a blood test shows the presence of infections, other types of body dysfunctions and diseases such as:
- Cytomegalovirus
- Diphtheria
- Tetanus
- Herpes
- Chlamydia
- Hepatitis
- Ureaplasmosis
- HIV
- Mycoplasmosis
- Syphilis
- Leptospirosis
- Chlamydia
Any of these diseases is a danger not only to the body of the woman herself, but also to her unborn child. Therefore, if there are deviations in the results of the blood test, the doctor sends the patient for an additional examination. nine0003
Therefore, if there are deviations in the results of the blood test, the doctor sends the patient for an additional examination. nine0003
Changes in hCG during pregnancy
After the physical onset of conception, the level of hCG in the female body begins to rise, and every two to three days its concentration almost doubles. It reaches its highest level at 8-11 weeks, and then it begins to gradually decrease.
The first analysis can be taken on the 6th day of the expected delay, but the result will be more accurate on the 11-12th day. Therefore, doctors recommend undergoing a blood test two to three times (every two days later). nine0003
Monitoring the level of hCG allows you to monitor the dynamics of pregnancy, the appearance of pathologies, etc.:
- In ectopic pregnancy, the level of the hormone practically does not increase
- If the development of the embryo has stopped, then the level of hCG drops from the moment of its death
Usually the result of the analysis is compared with a special table. In the first or second weeks, the concentration of hCG can range from 25 to 700 units, at the peak of the value it can reach 18,000–240,000 units, and at the end of the gestational age - 2,179-60,000 units.
In the first or second weeks, the concentration of hCG can range from 25 to 700 units, at the peak of the value it can reach 18,000–240,000 units, and at the end of the gestational age - 2,179-60,000 units.
After establishing the fact of conception, the doctor refers the patient to other blood tests:
- General
- Biochemical
- For clotting
- For hepatitis and HIV
- For TORCH infections
- For genetic pathologies
- For Rh factor and blood group (if not previously determined) nine0011 For the content of hormones produced by the thyroid gland
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- For STDs
Causes of deviation from the norm of the hormone hCG
Normally, after the onset of pregnancy, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin should gradually increase. If it decreases, then the doctor may assume the presence of such problems as:
- In the early stages:
- Fetal death
- Probability of spontaneous termination of pregnancy
- Missing embryo in ovum
- Late term:
- Placental abruption
In some cases, a low level of hCG may be associated with an incorrectly calculated gestational age.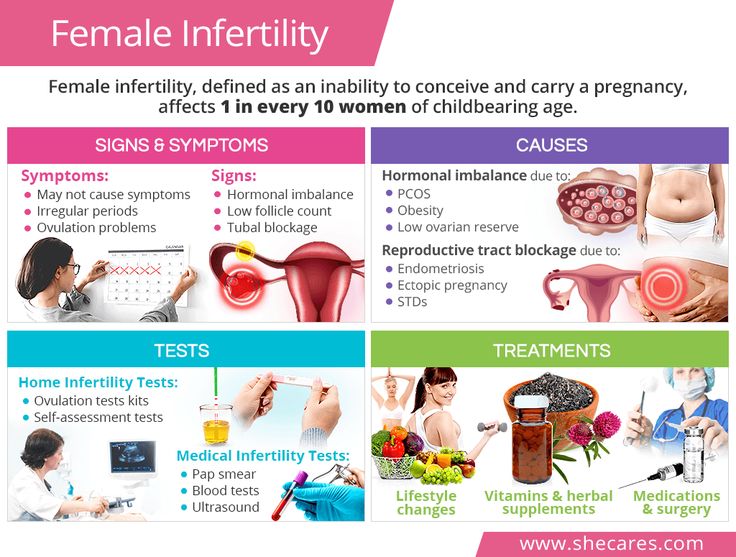 Therefore, in order to determine the exact cause of low hormone levels, early pregnancy tests are usually performed, as well as several types of other examinations. nine0003
Therefore, in order to determine the exact cause of low hormone levels, early pregnancy tests are usually performed, as well as several types of other examinations. nine0003
Causes of an increase in hCG levels
In the results of blood tests, the level of hCG can be seriously higher than normal for the following reasons:
- Presence of toxicosis
- More than one fetus
- Occurrence of hydatidiform mole
- Presence of genetic problems
- Complication due to diabetes mellitus
The level of human chorionic gonadotropin can be increased not only due to pregnancy, but also due to some abnormalities:
- Extremely high hCG levels due to hormonal drugs
- The presence of a malignant neoplasm in various organs (kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, uterus, lungs, etc.)
- Preservation of an unstable hormonal background as a result of an abortion
In rare cases, in the presence of serious hormonal disorders, men can also be found to have elevated levels of hCG.
Preparation for procedure
The following preparations are required before taking hCG tests for pregnant women:
- Fasting for 7-8 hours before the procedure
- Limiting the intake of any liquid a few hours before the examination
Also tell your doctor if you are taking any medications.
Statistics show that the highest concentration of hCG in the blood is observed in the first half of the day, so the doctor usually prescribes such an analysis in the morning. nine0003
If the recommendations are not followed, the study may show an unreliable result, so additional procedures will have to be carried out.
How blood sampling is performed
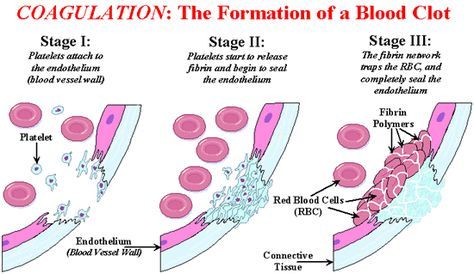
Blood tests for pregnant women are taken from a vein in the area located on the inside of the arm at the elbow. The procedure is as follows:
- The patient sits on a couch or chair and exposes her left or right arm
- Medic applying a tourniquet above the elbow
- After that, the woman performs several clenching of the palm into a fist
- The doctor lubricates the area of the future puncture with a disinfectant
- He then inserts the needle into the vein and fills the syringe (about 10 ml of blood is needed for the test)
- After that, the tourniquet is removed, and a cotton swab is applied to the puncture area, which the patient must hold with her arm bent at the elbow (this helps to stop the release of fluid from the wound)
After these manipulations, the blood in the test tube is sent to the laboratory for analysis. The results of the analysis can be transferred directly to the attending physician, or issued to the patient. A woman can independently compare these indicators with the values in the tables, but it is recommended to entrust this process to professionals.
The results of the analysis can be transferred directly to the attending physician, or issued to the patient. A woman can independently compare these indicators with the values in the tables, but it is recommended to entrust this process to professionals.
Advantages of the procedure at MEDSI
- Highly qualified doctors work in the clinics, who not only develop comprehensive examination and treatment programs, but also help to properly prepare for childbirth in case of pregnancy
- Special consultation mechanisms have been established for prospective parents
- Clinics have their own laboratory for receiving and checking tests, which allows you to get an accurate result in the shortest possible time
- For examinations and therapy, modern devices from leading manufacturers from countries such as Japan, USA, Germany, etc. are used.
- Originator drugs (not generics) are used
To make an appointment, call 8 (495) 7-800-500 or contact one of the many registries located in Moscow, the region and regions of the Russian Federation..jpg)
Do not delay treatment, see a doctor now:
- Pregnancy test
- Gynecological appointment
- Planning and management of pregnancy
- Reproductive health
what shows the norm during pregnancy, how and when to take, transcript
June 2, 2020
608232
0
share
Contents
What is HCG?
The role of the hormone in the diagnosis of pregnancy
When should I donate blood for hCG?
How to prepare for the analysis?
HCG test interpretation
How accurate is the hCG test? nine0003
An hCG blood test is one of the most important tools for monitoring a developing pregnancy.
What is HCG?
An hCG blood test is a reliable way to determine pregnancy in the early stages. HCG is a protein consisting of two units. Alpha particles of the hormone are similar to biologically active substances secreted by the pituitary gland. Beta particles are unique. The mass of the CG molecule is approximately 46 kDa. During pregnancy, glycoprotein is synthesized in the placenta. The biological properties of CG are in many ways similar to the properties of other hormones: luteinizing and follicle-stimulating. In some malignant diseases, hCG begins to produce tumor cells. In a non-pregnant woman and a healthy man, the hormone is practically absent in blood tests. nine0003
In obstetrics and gynecology, the test for b hCG, along with ultrasound, is used to monitor pregnancy throughout the entire period. Deviations in the readings of the analysis are the basis for further examination and require the consultation of a geneticist. An artificial increase in the level of hCG is used in the IVF process.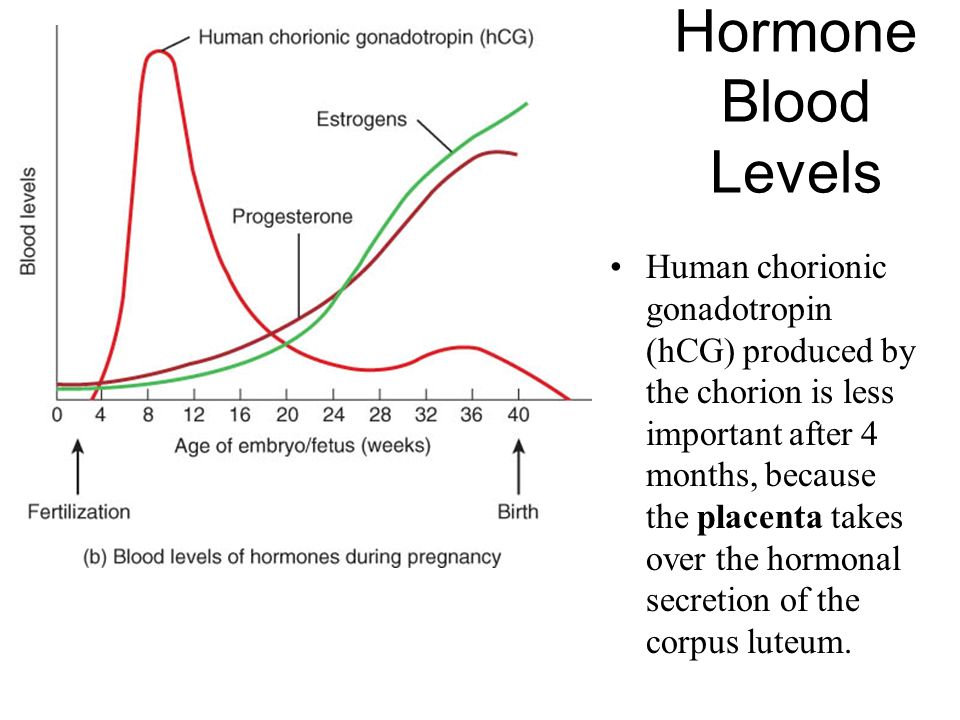 As a result of injections of hCG in women, the maturation and release of the egg is stimulated, the production of estrogen and progesterone increases. In men, the introduction of exogenous hCG activates the growth of the number of spermatozoa. nine0003
As a result of injections of hCG in women, the maturation and release of the egg is stimulated, the production of estrogen and progesterone increases. In men, the introduction of exogenous hCG activates the growth of the number of spermatozoa. nine0003
It is proved that the substance also has the properties of corticotropic hormone. HCG has an effect on the adrenal glands, stimulating the synthesis of steroids in their cortex. Thus, he is involved in preparing the body of a pregnant woman for the upcoming physiological stress. Since the fetus is perceived as foreign by the mother's body, some immunosuppressive influence of hormones, including hCG, is required for its normal development.
HCG promotes the maturation of placental tissues. Thanks to him and other hormones, its functional activity increases and the number of chorionic villi increases. nine0003
Without the hormone, the normal development of the embryo is not possible. HCG ensures the production of estrogens and progesterone, and also maintains their balance in the body of the expectant mother. Therefore, any pregnancy support program always contains regular tests for hCG levels.
Therefore, any pregnancy support program always contains regular tests for hCG levels.
Urinalysis for hCG (beta particles)
Compared to blood, expectant mother's urine contains less of the hormone. Therefore, determining the concentration of a substance in the urine can diagnose pregnancy only from a period of 8-10 days. Like a laboratory study, pharmacy tests are also based on the determination of hCG in the urine. Home tests have a lower threshold of sensitivity than laboratory tests, and, accordingly, a lower degree of reliability. Their positive result requires a visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist to confirm a normal pregnancy. nine0003
Free hCG assay (beta-hCG subunit)
The range of application of this test is quite wide. In oncology, it is in demand as a marker of malignant tumors. Measurement of the number of independent particles of hCG in the blood is informative in relation to testicular cancer in men. In addition, this indicator is important in the diagnosis of trophoblastic tumors in women. It is included in 1 and 2 pregnancy screenings. The study helps to assess the risk of such congenital fetal pathologies as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. nine0003
It is included in 1 and 2 pregnancy screenings. The study helps to assess the risk of such congenital fetal pathologies as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. nine0003
The role of the hormone in the diagnosis of pregnancy
An analysis of the amount of total hCG occupies a special place in confirming pregnancy in the early stages. This is due to the fact that the hormone begins to be actively released already a few days after the attachment of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. With the normal development of the embryo, the level of the substance doubles every 1.5-2 days. By the tenth week, the amount of hCG in a woman's tests can reach maximum values - up to 225,000 mU / ml. nine0003
Simultaneously with the blood for total hCG, other examinations are prescribed for the pregnant woman. So the patient should visit the ultrasound scanning room at least three times. Within nine months, several studies may be required. Comprehensive screenings of the 1st and 2nd trimesters also include an hCG test.
When to donate blood for hCG
A blood test for the hormone is given as needed. The hCG test is prescribed for the first time directly during the diagnosis of pregnancy itself. The second is as part of screening with ultrasound and other tests. Screening is designed to identify a risk group for congenital fetal pathologies among pregnant women. nine0003
Approximate dates of studies on hCG:
- confirmation of pregnancy - from the 6th day after conception;
- first - from 11 to 13 weeks;
- second from 19 to 23 weeks;
- 3rd trimester screening is done after 28 weeks of gestation.
How to prepare for a blood test
Preparing for an hCG test involves a number of standard requirements for hormone testing. The analysis is given on an empty stomach, after an overnight fast in the morning or afternoon. You should come to the treatment room in good health. In order for the results of the hCG test to be as reliable as possible, it is recommended in 2-3 days: nine0003
- stop drinking alcohol;
- exclude spicy and fatty foods from the diet;
- cancel strength training;
- Avoid smoking a couple of hours before donating blood.