How to protect my child social security number
How to Protect Your Child From Identity Theft
Through December 31, 2023, Experian, TransUnion and Equifax will offer all U.S. consumers free weekly credit reports through AnnualCreditReport.com to help you protect your financial health during the sudden and unprecedented hardship caused by COVID-19.
In this article:
- What Is Child Identity Theft?
- How to Protect Your Child’s Identity
- Warning Signs of Child Identity Theft
- What to Do if Your Child's Identity Is Stolen
For all their evil ways, identity thieves cannot be accused of age discrimination: They gladly prey on children and adults alike, and the consequences for children can be even more extensive than those for grown-ups. The steps outlined below can help prevent your children from being victimized.
What Is Child Identity Theft?
Child identity theft is a special case of identity theft involving the criminal abuse of personal information belonging to minors, including Social Security numbers (SSNs), dates of birth and home addresses. The nonprofit Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) cites a 2018 study that found that more than 1 million children were targeted for identity theft in 2017, underscoring the significance of the problem.
Crooks can use children's personal data the same ways they do adults', for purposes including:
- Applying for and opening credit card accounts
- Obtaining loans
- Seeking unemployment, Social Security benefits or other government services
- Opening bogus bank accounts for use in fraudulent money transfers
Child identity theft is especially pernicious because children typically don't receive the bank statements, credit card bills and other communications that can alert adults to suspicious financial activity. This means child identity theft can go on for years before it is detected, spawning multiple bogus accounts or loans, all of which can damage the child's credit. While that damage can be undone with time and effort, child identity theft can come to light at a devastating time—when the child's first student loan application is denied, or when the credit check for a first job throws up a red flag, for instance.
Criminals take advantage of the fact that parents—even those who carefully track their own credit and financial histories—may not think to safeguard their children's personal data and credit.
How to Protect Your Child's Identity
Identity thieves constantly devise new schemes for tricking victims into giving up personal information, as well as new means of exploiting personal data. As an example, criminals capitalized on the COVID-19 pandemic with bogus assistance offers aimed at capturing personal information, while also using stolen credentials to falsely claim COVID-relief benefits. Criminal resourcefulness makes it difficult to anticipate every approach fraudsters will use, but a set of basic precautions will go far toward preventing child identity theft.
Consider Security Freezes on Your Child's Credit Reports
There's no reason for most children to have credit reports, since it's illegal for anyone under 16 to apply for a loan or credit card in their own name. Fraudulent loan and credit card applications can generate credit reports, however, and by the time you or the child discovers them, they could be full of unpaid accounts.
Fraudulent loan and credit card applications can generate credit reports, however, and by the time you or the child discovers them, they could be full of unpaid accounts.
You can nip this in the bud by requesting a security freeze for your child at each of the three national credit bureaus (Experian, TransUnion and Equifax). When you request a security freeze, the bureau creates a credit report for your child and then locks it down, so that any lender who attempts to process an application that uses your child's credentials will be denied access to their credit history. This prevents any loans or credit cards from being issued in the child's name. When the child reaches legal age and wants to apply for credit, the freeze can be lifted by contacting each credit bureau individually.
Safeguard Children's Social Security Numbers
You should never share a child's Social Security number with anyone who doesn't have a very good reason for having it—which means it's smart to ask anyone who requests it why they need it.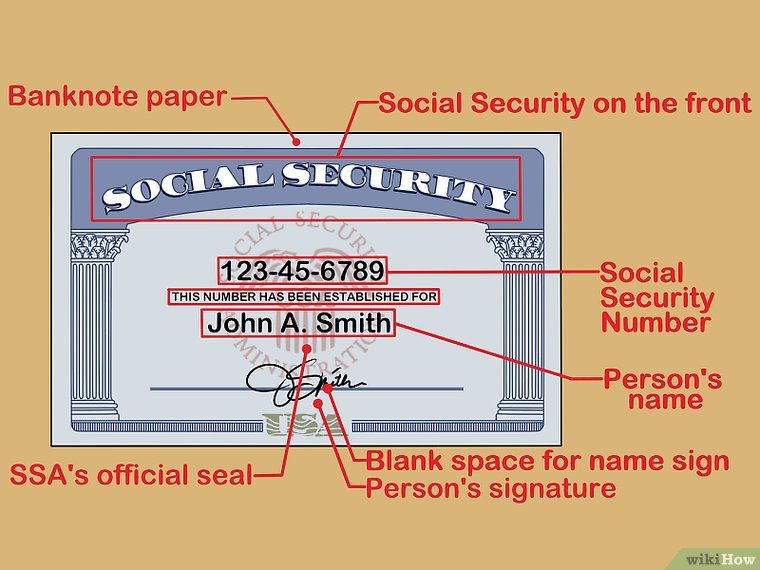 The IRS requires the child's SSN when you're setting up a 529 college savings plan or claiming your child as a dependent, but their day camp and martial arts academy won't really need it. If they insist, you can refuse and seek services elsewhere, or provide the last four digits of the SSN, but beware: Even the "last four" can be useful to identity thieves. Keep your child's Social Security card in a secure place such as a safety deposit box and memorize the number so you don't have to write it down anywhere.
The IRS requires the child's SSN when you're setting up a 529 college savings plan or claiming your child as a dependent, but their day camp and martial arts academy won't really need it. If they insist, you can refuse and seek services elsewhere, or provide the last four digits of the SSN, but beware: Even the "last four" can be useful to identity thieves. Keep your child's Social Security card in a secure place such as a safety deposit box and memorize the number so you don't have to write it down anywhere.
Monitor Your Child's Personal Information
If your child starts receiving credit offers in the mail, or if you see unexpected activity on their email, phone or bank accounts, their personal information may have been compromised. When you first give your children their own phones, advise them that caller ID can't always be trusted, and calls that appear to be from banks or other trusted institutions may be scams.
Although a phone number may seem innocuous, identity thieves can use your child's phone number to get access to accounts. Many companies use a phone number for identity verification, and caller ID spoofing allows identity thieves to make your child's phone number appear when they call one of these companies. They also use automated callers (hoping to get your child to type in or record information), and some may even impersonate institutions and call your child directly.
Many companies use a phone number for identity verification, and caller ID spoofing allows identity thieves to make your child's phone number appear when they call one of these companies. They also use automated callers (hoping to get your child to type in or record information), and some may even impersonate institutions and call your child directly.
Pay Attention to Privacy Policies
Practically all organizations that gather data on kids have privacy policies that detail how the child's private information will be used and protected. Reading these policies can help you identify potential risks to your child's information. If in doubt, never hesitate to ask questions, and don't disclose your child's information if you're not comfortable with what you see in the policy.
Use Your Own Personal Information Instead of Your Child's
It's easy to share kids' personal information without thinking about it—and kids often are eager to do so—enrolling in a restaurant's birthday club to get free dessert, for example. And even if retailers don't abuse your child's information, none are immune to data theft that can expose kids' personal info. To protect your child's personal information, attach their accounts to your email or phone number, rather than the child's, to help you pick up on any suspicious activity.
And even if retailers don't abuse your child's information, none are immune to data theft that can expose kids' personal info. To protect your child's personal information, attach their accounts to your email or phone number, rather than the child's, to help you pick up on any suspicious activity.
Avoid Oversharing on Social Media
Identity thieves comb social media for personal information—from birthdays and addresses to clues about security questions such as "What's your first pet's name?" or "Where did you go to elementary school?" Minimizing the amount of information you share about your kids, limiting your sharing options to "friends" (rather than "public") and confining your circle of "friends" to people you trust and know personally can reduce the risk of exposing children's personal information.
Monitor Your Child's Social Media and Other Online Activity
Think carefully and do research before you allow a minor child to have a social media account attached to their real name. Insist that they make you part of their shared network so you can monitor what they're sharing and with whom. And keep in mind that your child may have access to the internet and smartphones at school or friends' houses, even if you limit or forbid those activities at home. Explain to your children why you're concerned, and advise them on the kinds of information they should never disclose.
Insist that they make you part of their shared network so you can monitor what they're sharing and with whom. And keep in mind that your child may have access to the internet and smartphones at school or friends' houses, even if you limit or forbid those activities at home. Explain to your children why you're concerned, and advise them on the kinds of information they should never disclose.
Keep Your Home Safe
A burglary that results in theft of birth certificates, passports or Social Security cards could enable child identity theft. Always lock doors and windows, set an alarm if you have one, and keep valuable documents offsite, in a safety deposit box or in a safe. (A strongbox could protect your documents in case of fire, but a thief could easily take it away.)
Teach Your Children Well
It's important for kids to understand identity theft risks. Find age-appropriate ways to talk to children about the topic. Make them aware that phone calls, text messages and emails aren't always from who they purport to be, and that they should check with you before responding to any of those that seek personal information. Let them know it's OK to hang up on an adult who asks for sensitive information, no matter who they claim to be.
Let them know it's OK to hang up on an adult who asks for sensitive information, no matter who they claim to be.
Warning Signs of Child Identity Theft
Detecting child identity theft can be difficult, but there are some signs to watch for:
- Offers for credit cards, auto insurance or other age-inappropriate "junk mail" addressed to your child.
- Unexpected bills addressed to your child.
- Collection notices that arrive by mail or phone, targeting your child.
- Denial of government benefits for your child on the basis that they've already been paid to someone using your child's Social Security number.
- A letter from the IRS saying your child owes taxes. (Phone calls purporting to be from the IRS are almost always scams; the IRS communicates with taxpayers only by mail.)
What to Do if Your Child's Identity Is Stolen
If you suspect your child is a victim of identity theft, your first step should be to check his or her credit reports at all three national credit bureaus, which you can do for free at AnnualCreditReport. com.
com.
Unless you've had credit reports created for purposes of security freezes, your child probably won't have a credit report on file at the bureaus. If credit reports already exist when you request a security freeze you should look into the possibility of fraud:
- Notify all three national credit bureaus that fraud may have occurred using your child's credit report and ask them to investigate.
- Notify the business or financial institution that issued the credit or loan, using contact information that appears on the credit report(s). Let the lender know the account was fraudulently opened in the name of your minor child and ask them to investigate.
- File a police report with your local law enforcement agency.
- File a fraud report with the FTC online or by calling 877-438-4338.
Experian has more resources on fraud and identity theft to help you and your family stay informed.
Child identity theft is an ugly side effect of the information age, but attention and caution can help prevent it, or minimize the damage when it occurs. Taking prudent precautions such as applying a security freeze or using a family identity protection program such as Experian IdentityWorksSM can help keep children's personal information secure.
Taking prudent precautions such as applying a security freeze or using a family identity protection program such as Experian IdentityWorksSM can help keep children's personal information secure.
How To Protect Your Child From Identity Theft
Learn what child identity theft is, how to detect it, how to protect your child’s personal information, and what to do if someone steals your child’s identity.
- What Is Child Identity Theft?
- How To Protect Your Child’s Personal Information
- How To Know if Someone Is Using Your Child’s Personal Information
- What To Do if Someone Is Using Your Child’s Personal Information
What Is Child Identity Theft?
Child identity theft happens when someone takes a child’s sensitive personal information and uses it to get services or benefits, or to commit fraud. They might use your child’s Social Security number, name and address, or date of birth. They could use the stolen information to
- apply for government benefits, like health care coverage or nutrition assistance
- open a bank or credit card account
- apply for a loan
- sign up for a utility service, like water or electricity
- rent a place to live
How To Protect Your Child’s Personal Information
Here’s what you can do to protect your child from identity theft.
Ask questions before giving anyone your child’s Social Security number
If your child’s school asks for your child’s Social Security number, ask these questions:
- Why do you need it?
- How will you protect it?
- Can you use a different identifier?
- Can you use just the last four digits of the Social Security number?
Protect documents with personal information
If you have documents with your child’s personal information, like medical bills or their Social Security card, keep them in a safe place, like a locked file cabinet.
When you decide to get rid of those documents, shred them before you throw them away. If you don’t have a shredder, look for a local shred day.
Delete personal information before disposing of a computer or cell phone
Your computer and phone might contain personal information about your child. Find out how to delete that information before you get rid of a computer or a cell phone.
How To Know if Someone Is Using Your Child’s Personal Information
In addition to taking steps to safeguard your child’s personal information, keep an eye out for warning signs that someone is using your child’s personal information. Here are a few:
- You’re denied government benefits (like health care coverage or nutrition assistance) because someone is already using your child’s Social Security number to get those benefits.
- Someone calls you and says your child has an overdue bill, but it’s not an account you opened for the child.
- You get a letter from the IRS that says your child didn’t pay income taxes. This could happen if someone used your child’s Social Security number on tax forms for a new job.
- You’re denied a student loan because your child has bad credit. This could happen if someone used your child’s Social Security number to get a credit card, open a cell phone account, or set up a utility service and has not paid the bills on time or at all.

Signs of Child Identity Theft
- Turned down for government benefits
- Calls about bills in your child’s name
- Letter from the IRS about taxes your child owes
- Child’s student loan application is denied
Check if your child has a credit report
Generally, a child under 18 won’t have a credit report unless someone is using his or her information for fraud. A good way to find out if someone is using your child’s information to commit fraud is to check if your child has a credit report. To do that, contact the three credit bureaus (find their contact information at IdentityTheft.gov) and ask for a manual search for your child's Social Security number. You may have to give the credit bureaus a copy of
- your driver’s license or other government-issued identification card
- proof of your address, like a utility bill, or a credit card or insurance statement
- your child’s birth certificate
- your child’s Social Security card
If you’re not the child’s parent, you may have to give the credit bureaus a copy of documents that prove you are the child’s legal guardian.
When Your Child Turns 16
When your child turns 16, you may want to check if there’s a credit report in his or her name. This could help you spot identity theft, since children under 18 usually don’t have a credit report. If there’s inaccurate information in your child’s credit report, you’ll have time to correct it before he or she applies for a job, a college loan, a car loan, or a credit card, or tries to rent a place to live.
What To Do if Someone Is Using Your Child’s Personal Information
If you discover that someone is using your child’s personal information, here’s what to do right away:
Step 1: Report and close the fraudulent accounts
Contact the companies where fraud happened. Tell each company’s fraud department that someone opened an account using your child’s information, and ask them to close the account. Ask for written confirmation that says that your child isn’t responsible for the account.
Contact the three credit bureaus. Tell each credit bureau that someone opened an account using your child’s information. Ask them to remove any fraudulent accounts from your child’s credit report.
Step 2: Freeze your child’s credit report
If your child is under 16, you can request a free credit freeze, also known as a security freeze, to make it harder for someone to open new accounts in your child's name. The freeze stays in place until you tell the credit bureaus to remove it. (Minors who are 16 or 17 can request and remove a security freeze themselves.)
To activate a credit freeze, contact each of the three credit bureaus. Find their contact information at IdentityTheft.gov.
Step 3: Report child identity theft
Report the child identity theft to the Federal Trade Commission at IdentityTheft.gov. Include as many details as possible.
Child Identity Theft - What to Know, What to Do
This brochure for parents explains what child identity theft is and what to do if it happens to your child.
Order free copies
What to do if a Social Security Number (SSN) is provided
If your Social Security number is in a breach or leak, it's important to act quickly to prevent more damage being done to attackers.
Tip: As you progress through this process, it is a good idea to keep documentation of any steps you take, call, fill out forms, or emails you send. If you need to poke fun at fraudulent payments or activities, having these records can help smooth the job by claiming you're dealing with actual identity theft. nine0003
An ID that has your social security number and other personal information can do a number of things with it, including:
-
Open new credit accounts, such as credit cards or car loans, in your name
-
Request a refund of taxes that are rightfully yours
-
Create a dummy identity to receive a job, department, or other services
-
Request fraudulent benefits in name
-
Receive benefits such as healthcare while pretending to be you
- nine0002 Create a bogus identity to decipher other people or capture other activities in your name
The first step is to post a temporary fraud alert on loan
Also known as an "Initial Security Alert", this alerts major credit providers that you have caused identity theft. If a business attempts to verify your credit, it is notified that a fraud alert has been placed on the account and that it must verify the identity of anyone attempting to open an account or obtain credit with a social security number. nine0003
If a business attempts to verify your credit, it is notified that a fraud alert has been placed on the account and that it must verify the identity of anyone attempting to open an account or obtain credit with a social security number. nine0003
You can place a temporary fraud alert on your account, it does not affect your credit score, and the temporary fraud alert will automatically expire after 1 year, although you can cancel earlier if necessary.
You want to do this right away to reduce the ability to open new accounts in your name.
Posting a Temporary Fraud Alert on Account
Go to the website of any of the three main credit windows and select that you want to add a fraud alert.
Note: This only needs to be done in one credit office. Once you place a fraud alert in any of the three controls, they automatically notify the other two.
-
Experian nine0003
-
TransUnion
-
Equivalence
Temporary fraud alert does not require a reason or any documentation other than proof of identity.
nine0010Removing a fraud alert is a little more difficult than placing one. To display an alert, you need to contact all three of them, and each of them will need to verify your identity. In most cases, it's probably easier to just let the alert expire after one year.
Extended Fraud Alert does the same thing as Temporary Fraud Alert, just for a longer period of time. It usually stays active for 7 years unless you cancel it sooner. nine0003
It usually stays active for 7 years unless you cancel it sooner. nine0003
Also, getting an extended alert is a bit more difficult than a temporary one. It usually requires a policy report showing that you have been the target of identity theft.
This does not prevent the consolidation of the loan, but complicates it. Any business that has been shown how to open an account in your name must take additional steps to verify the identity of the user opening the account. This means that you can still open accounts. You just need to take a few extra steps to confirm that you are the person you claim to be. nine0003
You could also open fraudulent accounts, but impersonation would require more effort.
Second step. Getting a copy of the credit report
Under US federal law, you are entitled to a free copy of your credit report every 12 months from each of the three credit report companies. To request a free copy of your credit report, go to https://annualcreditreport. com. It usually takes only a minute or two to get a report that you can save or print, so you can study it carefully. nine0003
com. It usually takes only a minute or two to get a report that you can save or print, so you can study it carefully. nine0003
Tip: You can request up to 3 copies of your credit report, but we recommend that you request only 1 first. Federal law allows you to receive 3 copies per year, and you will need to review your credit report once or twice in the coming weeks or months to see if new items have appeared.
When you check your credit report, you first look for any unfamiliar accounts or activities. These could be credit cards you didn't recognize, or loans for cars or properties you never applied for. nine0003
If you find unrecognized accounts
Fraud alert escalation before loan freeze
If there is fraudulent activity on your credit report, this means that scammers are trying to use your social security number to come in and secure your credit report. This will make it much harder for them to inflict any additional damage. nine0003
This will make it much harder for them to inflict any additional damage. nine0003
For more information about placing a credit freeze, see "Placing a Credit Freeze".
Report it to Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
If you have fraudulent activity in your name, the FTC wants to know about it. Go to https://IdentityTheft.gov and follow the steps to report fraudulent activity.
nine0096 Contact companies with fraudulent accountsContact companies for accounts you don't recognize. Let them know that you have been the target of identity theft and suspect that the account is fraudulent. Find out when and how an account was opened, what information they can provide, when and how it was used. This information will be useful when creating a policy report. nine0003
Tips:
-
Always remember that the company you contacted does not understand that the account is fraudulent and they are almost as interested in resolving this problem as you are.
 They are unlikely to get paid for a fraudulent account.
They are unlikely to get paid for a fraudulent account. -
If they're having trouble resolving fraudulent accounts, ask if it would make things easier if you have a policy report. If they agree that this is the case, write them down so you can refer back to them after step 3 (create a policy report). nine0003
Third step - generating a policy report
Even if you think a politician is unlikely to reveal his identity, it is still important to file a policy report to establish an official record of identity theft.
Contact your local policy department and let them know that your identity has been stolen and that you want to generate a report. They should give you a copy of the report when it's done, but if it's not offered to you, be sure to ask for it. This is an important tool to fix this problem and protect against any future fraudulent activity. nine0003
nine0003
Fourth step. Submitting a Complaint to the Internet Attack Complaint Center
Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) is a division of the Federal Crisis Division (CEO) that handles reports of online theft such as identity theft. When filing a complaint, they may share this information with other relevant law enforcement agencies.
To file a complaint, go to https://www.ic3.gov. nine0003
Tip: Sometimes it's not very convenient to fill out so many reports, but if attackers open fraudulent accounts or work with your SSN that you need to work with, it can be very useful to show that you have submitted reports to all relevant authorities.
Fifth step. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Notice
It is now common for scammers to file false tax refunds with a Social Security number and claim the tax refund themselves. There are two things you can do to reduce the risk of this. The first is as early as possible in the tax file, and the second is for iRS to know that your social security number has been stolen. nine0003
The first is as early as possible in the tax file, and the second is for iRS to know that your social security number has been stolen. nine0003
You will want to complete and complete Form 14039. This is a short form and will likely take no more than a minute or two to complete. Start here: https://www.irs.gov/individuals/how-irs-id-theft-victim-assistance-works
This alerts the IRS to any suspicious tax claims with a social security number, and if a bogus tax refund is filed in your name, it will be easier for you to protest and clear it.
nine0047 Obtain a PIN from the IRS website. The IRS offers a free six-digit identity protection PIN that can be obtained through the website. When submitting tax returns, you must provide this PIN (which only you and the IRS should know) for identity verification. This makes it much more difficult to send tax refunds in your name, because even if he has your social security number, he does not need to have a pin number.
It is not recommended to do this ahead of time, just to limit the damage that attackers can do later.
Moving on
Unfortunately, once your SSN already exists, attackers can use it at any time, so it pays to take some reasonable steps to protect itself from future problems. nine0003
Filing taxes
Sometimes scams spoof fake tax refunds with the name and social security number of an unintentional person, and then they request a tax refund associated with that person. When a real user later submits their taxes, they will have to go through a complex process to get a refund that would be the right way.
Monitor credit rating
Unexpected changes in credit score may indicate unauthorized activity using a social security number. Most banks and credit card companies these days offer you a credit score as an additional metric for doing business with them. Log in to the website and write down your rating. nine0003
Small changes a few dots up or down are common, but if they suddenly change or suddenly stop working, you should get a new copy of your credit report to find out why it has changed.
View Social Security Application
One of the actions of attackers with a stolen social security number is to set a false name. This often happens if the attacker is not allowed to receive the job using their real identity, or if they are not allowed by US law. nine0003
This often happens if the attacker is not allowed to receive the job using their real identity, or if they are not allowed by US law. nine0003
Advice: It's also possible that someone is working under your social security number as an obvious mistake. They just wrongly influenced their social security number or overwritten several numbers and accidentally assigned their number to your employer.
If they are doing an assignment using your SSN, their employee must report their income to the Social Security Administration (SSA) and that income will appear on your Social Security application. Go to https://www.ssa.gov/myaccount/ and sign in (or create) a free account to check your Social Security claim. Creating an account can be a bit of a process, but after creating an account, it only takes a few seconds to view your social security application online. nine0003
All instructions show that you made total annual profit for a particular year, but if the profit shown is significantly greater than what you know you made for that year, this is probably good enough to contact SSA and investigate further. He takes identity theft seriously and is happy to work with you.
He takes identity theft seriously and is happy to work with you.
Check your Social Security application every year to make sure everything looks right.
nine0002 Tip: If reported income looks too low, that's something else to look into. The income reported by your employees is a factor in the amount of Social Security payments you make on deregistration to make sure you get what you need.Keep checking this credit report
Even if everything looks fine, it's a good idea to go to https://annualcreditreport.com every few months and request another copy of your credit report to make sure everything still looks the way it should. nine0003
Yes, you can, but it's a rather complicated process that requires you to personally apply at the Social Security office and provide a valid reason for changing your Social Security number. Identity theft is considered a valid reason, but only if the theft results in persistent and persistent problems and you need to provide documentation to support your claim. You will also be asked to provide proof of your age and child status (such as a birth certificate). nine0003
Identity theft is considered a valid reason, but only if the theft results in persistent and persistent problems and you need to provide documentation to support your claim. You will also be asked to provide proof of your age and child status (such as a birth certificate). nine0003
If you receive a new number, the old number is not removed. The new number is connected to the old number, which will often result in background checks, which can lead to additional questions.
If you have been issued a new number, you need to make sure that your administrator correctly displays the income information for the new SSN.
Additional information
Online Identity Theft Protection nine0003
The danger of over-disclosure
Microsoft security help and training
Monthly allowance for child care for persons not subject to compulsory social insurance
The applicant has the right to file a complaint against the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services (complaint), including in the pre-trial (out of court) procedure in the following cases: nine0003
- violation of the application registration deadline;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services;
- requirement from the applicant of documents, information or actions not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them; nine0017
- refusal to accept documents, the submission of which is provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- requesting from the applicant, when providing a public service, a fee that is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
- refusal of the authorized body, its officials to correct the misprints and errors made by them in the documents issued as a result of the provision of public services or violation of the deadline for such corrections; nine0017
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services;
- suspension of the provision of public services, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.

nine0234 Subject of complaint
The subject of the complaint is a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, unlawful decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services, violation of the provisions of the administrative regulations and other regulatory legal acts that establish requirements for the provision of public services.
A citizen has the right to file a complaint in writing on paper by mail or in person to any PFR Client Service, as well as in electronic form: nine0003
- on the official website pfr.gov.ru;
- portal vashkontrol.ru;
- portal do.gosuslugi.ru.
The reason for the appeal may be dissatisfaction with the quality of the provision of public services by the PFR, violation of the terms for the provision of services, violation of the terms for registering a request for a service, refusal to correct errors or typos, refusal to provide a public service, refusal to accept documents, demand for an additional fee. nine0003
nine0003
Procedure for filing and handling a complaint
The complaint must contain:
- name of the authorized body, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of its officials providing public services and (or) their leaders, decisions and actions (inaction) of which are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant, information about the place of residence, as well as contact phone number (numbers), e-mail address (s) (if any) and postal address to which the answer should be sent to the applicant; nine0017
- information about the appealed decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head.
The applicant shall submit documents (if any) confirming his arguments or copies thereof.
When filing a complaint in electronic form, the documents specified in paragraph 106 of the administrative regulations may be submitted in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature, the form of which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. In this case, an identity document of the applicant is not required.
In the authorized body, officials authorized to consider complaints are determined, who ensure:
- receiving and handling complaints; nine0017
- sending complaints to the body authorized to consider them.
Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of an official of the authorized body are considered by the head of the authorized body or an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints. Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the head of the authorized body are considered by an official of the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation authorized to consider complaints. nine0003
nine0003
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within 3 working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint.
The authorized body ensures:
- equipment for receiving complaints;
- informing applicants about the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body by posting information on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal; nine0017
- advising applicants on the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body at a personal appointment, by phone, using the website of the authorized body;
- conclusion of agreements on interaction between the multifunctional center and the authorized body in terms of the implementation by the multifunctional center of receiving complaints and issuing the results of consideration of complaints to the applicant;
- formation and quarterly submission to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of reports on received and considered complaints (including the number of satisfied and unsatisfied complaints).
 nine0017
nine0017
Deadlines for considering a complaint
A complaint received by the authorized body shall be subject to registration no later than the working day following the day of its receipt.
The complaint is subject to consideration within 15 working days from the date of its registration, and in the event of an appeal against the refusal of the authorized body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in the event of an appeal against a violation of the established deadline for such corrections - within 5 working days from the date of its registration. nine0003
Result of consideration of the complaint
The result of the consideration of the complaint is the adoption of one of the following decisions:
- satisfy the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision made by the authorized body, correction of typos and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the subjects Russian Federation, municipal legal acts; nine0017
- refuse to satisfy the complaint.

When satisfying the complaint, the authorized body takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant no later than 5 working days from the date of the relevant decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A complaint may be denied in the following cases:
- availability of a court decision that has entered into legal force on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the existence of a decision on a complaint made earlier in accordance with the requirements of the Rules for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations endowed with in accordance with federal laws, the powers to provide public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.
 1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0017
1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0017
A complaint may be left unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive language, threats to life, health and property of an official of the authorized body, as well as members of his family;
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated: nine0003
- name of the public service provider that considered the complaint, position, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official of the authorized body, the decision and (or) action (omission) of which is being appealed;
- surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint; nine0017
- decision made on the complaint;
- if the complaint is found to be justified, the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- information on the procedure for appealing against the decision taken on the complaint.

In the event that, during or as a result of consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints shall send the available materials to the prosecutor's office. nine0003
Procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
A reasoned response based on the results of the consideration of the complaint is signed by the official authorized to consider the complaint and sent to the applicant in writing or, at the request of the applicant, in the form of an electronic document signed by the electronic signature of the official authorized to consider the complaint, the type of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, no later than the day following the day the decision is made on the results of the consideration of the complaint. nine0003
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The applicant has the right to appeal the decision taken on the complaint by sending it to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
If the applicant is not satisfied with the decision made during the consideration of the complaint or the absence of a decision on it, then he has the right to appeal the decision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The applicant's right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint
The applicant has the right to receive comprehensive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Ways to inform complainants about the procedure for filing and handling a complaint
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is posted on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal, and can also be communicated to the applicant orally and (or) in writing. nine0003
List of normative legal acts regulating the procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the authorized body, as well as its officials
The procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeals against decisions and actions (inaction) of the body providing the public service, as well as its officials, is regulated by Federal Law No.