Best time for nt scan
First Trimester Ultrasound and Nuchal Translucency – San Diego Perinatal Center
First trimester ultrasound performed between 11 and 14 weeks is an important early assessment of your pregnancy. This scan can be used to accurately date your pregnancy, to evaluate abnormalities in your ovaries and cervix, to accurately determine chorionicity in twins, to assess for placental abnormalities and to perform a nuchal translucency screen. In addition, at San Diego Perinatal Center, with our high resolution equipment, we are able to detect 40% of major fetal anomalies such as neural tube defects, abdominal wall defects, renal, limb and cardiac abnormalities on this early scan.
Nuchal translucency/First trimester screening – this blood test screens for Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) and Trisomy 18. It is part of the California Prenatal Screening Program and is a free service to all pregnant women. Additional testing and counseling would be recommended if the test is positive. This test has about an 85 % detection rate for Down Syndrome.
Nuchal Translucency Screening for Detecting Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) and Trisomy 18.
During development of the embryo, there is a clear space beneath the skin at the back of the neck which we call the nuchal translucency. Between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy, this space can be measured by ultrasound and the size of this space is associated with the risk for fetal chromosome abnormalities and the risk for fetal heart defects. We use this measurement as an early screening tool to identify pregnancies at higher risk for these conditions.
If we can accurately measure the nuchal translucency, then a computer program can be used to calculate the risk for Down Syndrome and Trisomy 18 using the mother’s age and blood hormone markers. Women who screen positive at increased risk would then be offered further testing. The nuchal translucency screen will identify 85-90 percent of Down syndrome cases and 80-85 percent of Trisomy 18 cases. Approximately 5-10% of the time, we are unable to obtain this measurement either because the baby does not cooperate or there are other technical factors like abdominal wall scarring, fibroids or maternal obesity.
Approximately 5-10% of the time, we are unable to obtain this measurement either because the baby does not cooperate or there are other technical factors like abdominal wall scarring, fibroids or maternal obesity.
In the State of California, there is a prenatal screening program which is used for risk calculations. The state requires that all first and second trimester blood specimens are performed in the state laboratory system. https://www.cdph.ca.gov/Programs/CFH/DGDS/Pages/pns/
It is important to realize that the only way to be certain that a baby does not have a numeric chromosome abnormality like Down syndrome is by means of Amniocentesis or Chorionic Villous sampling.
Risk for Other Birth Defects
The nuchal translucency measurement is more than just a screening for Down syndrome. A very small nuchal translucency measurement – less than 2.5 mm – places the pregnancy in a low-risk group for problems, such as fetal heart abnormalities. Pregnancies where the nuchal translucency measurement is between about 2.5 and 3.5 mm are in an intermediate-risk group, and for these women, a genetic sonogram at about 18 weeks into the pregnancy plus a detailed sonogram of the heart (called a fetal echocardiogram) at about 22 weeks are recommended. Women with a nuchal translucency measurement of 3.5 mm or more have pregnancies at increased risk for chromosome problems, for abnormalities of the fetal heart, and for other birth defects, ranging from abnormalities of the skeletal system to the baby’s diaphragm. For these pregnancies, genetic counseling and a genetic sonogram at 18 weeks, and a fetal echocardiogram and a detailed scan at about 22 weeks, are recommended.
Pregnancies where the nuchal translucency measurement is between about 2.5 and 3.5 mm are in an intermediate-risk group, and for these women, a genetic sonogram at about 18 weeks into the pregnancy plus a detailed sonogram of the heart (called a fetal echocardiogram) at about 22 weeks are recommended. Women with a nuchal translucency measurement of 3.5 mm or more have pregnancies at increased risk for chromosome problems, for abnormalities of the fetal heart, and for other birth defects, ranging from abnormalities of the skeletal system to the baby’s diaphragm. For these pregnancies, genetic counseling and a genetic sonogram at 18 weeks, and a fetal echocardiogram and a detailed scan at about 22 weeks, are recommended.
In the past, sonography at 11 to 14 weeks was not an effective way to screen for birth defects of the baby. The embryo at that stage was just too small to evaluate well. As time has gone on, the ultrasound equipment and our ability to interpret the images have both improved. Now, at the 11 to 14-week scan, we are able to identify many major central nervous system, cardiac, abdominal, and limb abnormalities. Our center’s goal is to identify 40 percent of major structural malformations at the time of the nuchal translucency scan.
Now, at the 11 to 14-week scan, we are able to identify many major central nervous system, cardiac, abdominal, and limb abnormalities. Our center’s goal is to identify 40 percent of major structural malformations at the time of the nuchal translucency scan.
When is the best time to schedule a nuchal translucency scan?
The accuracy is highest when the lab work is done between 10 and 11 weeks into the pregnancy, and we recommend scheduling the nuchal scan between 12 and 13 weeks. As long as the lab test has been done more than a week before, we should be able to provide you with the Down syndrome and trisomy 18 risk calculations at the time of your ultrasound scan.
Nuchal translucency scan - 12 week scan, down's syndrome screening.
This is often parents’ favourite scan – you will be amazed at just how much detail you can see and if everything looks normal, the risk of miscarriage and major abnormality becomes very small. If you haven’t had a scan yet, this scan will:
- Make sure that the pregnancy is in the right place
- Count how many babies there are!
- Accurately date your pregnancy and decide on a definite due date for you
- Look at the basic structure of the baby
But the main purpose of this particular scan is to screen for chromosomal abnormalities such as Down’s syndrome. Down’s syndrome is something that affects about 1 in 700 pregnancies overall, but it becomes more common as a mother gets older. It happens because the egg that is released at conception has an extra copy of chromosome 21 and this in turn leads to every cell in the baby having an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Down’s syndrome is something that affects about 1 in 700 pregnancies overall, but it becomes more common as a mother gets older. It happens because the egg that is released at conception has an extra copy of chromosome 21 and this in turn leads to every cell in the baby having an extra copy of chromosome 21.
This causes a wide range of both physical disability and learning difficulties. At the moment there still isn’t a completely safe test that will tell you that your baby definitely does or doesn’t have Down’s syndrome, but the NHS offers everyone combined first trimester screening, which is a test performed at around 12 weeks using a combination of ultrasound scan findings and a basic blood test to assess the likelihood of whether your baby is or isn’t affected. The key ultrasound marker at this stage is the nuchal translucency measurement, or the space at the back of the baby’s neck. At this stage in the baby’s development it is normal for some fluid to build up in this space at the back of the baby’s neck – it happens to every baby so a little bit of fluid is entirely normal, but a baby with problems will often retain more fluid and the nuchal translucency measurement is increased.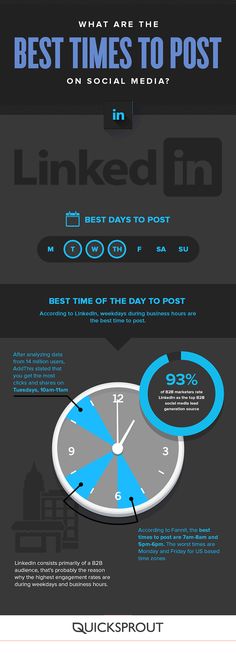 As well as being a good marker for babies with Down’s syndrome, an increased nuchal translucency measurement can also pick up other genetic conditions, such as Edwards’ syndrome (where the baby has an extra copy of chromosome 18) and Patau’s syndrome (an extra copy of chromosome 13), and some other structural problems, including heart abnormalities.
As well as being a good marker for babies with Down’s syndrome, an increased nuchal translucency measurement can also pick up other genetic conditions, such as Edwards’ syndrome (where the baby has an extra copy of chromosome 18) and Patau’s syndrome (an extra copy of chromosome 13), and some other structural problems, including heart abnormalities.
The nuchal translucency scan is best done during the 12th week, but it can be done from 11 weeks and 3 days up until 14 weeks and your local NHS hospital will offer you an appointment to have this done at around this time. Nevertheless, some parents may opt to have this done privately instead.
Reasons why patients choose to have it done at Beard Mill Clinic include:
Plenty Of Time
Each appointment at Beard Mill Clinic is allocated one hour to make sure that there is plenty of time to do the scan and discuss the results with you.
Wealth Of Experience
Victoria has spent over 20 years working with Professor Kypros Nicolaides who has been the leading pioneer in developing the nuchal translucency scan and screening for abnormalities at this stage of pregnancy. During this time, she has been directly involved in developing the risk calculation software and in teaching other people how to perform the nuchal scan. In doing this, she has come to understand the screening process inside out and can use her expertise to give you the best possible advice.
During this time, she has been directly involved in developing the risk calculation software and in teaching other people how to perform the nuchal scan. In doing this, she has come to understand the screening process inside out and can use her expertise to give you the best possible advice.
Extra Markers
Victoria is trained and certified to look at the additional markers for Down’s syndrome that are not routinely offered at most other scanning clinics. These additional markers include:
- Looking at the baby’s nose bone and its profile
- Listening to the flow of blood across a valve in the baby’s heart (the tricuspid valve)
- Measuring the resistance in the vessel that takes blood into the baby’s heart (the ductus venosus)
Babies with Down’s syndrome are more likely to have a small or absent nose bone, with a flat profile. They often have leakage across the tricuspid valve and reverse flow in the ductus venosus. So adding in these additional markers will take the average detection rate of the standard technique of 80% up to 95%.
Same Day Results
When the blood has been taken in advance of the scan, Victoria is able to process all the results straight away and explain both the scan findings and blood results to you, showing you how your measurements fall within the context of the “normal” range and how this then affects your own specific risk for Down’s syndrome.
The risk calculation software used at Beard Mill Clinic displays simple graphs which really help you understand what the risk means and Victoria gives you plenty of time to ask questions and clarify anything you are not sure about. You then take away a comprehensive report with all the results clearly documented.
Even if the blood results are not available, Victoria will give you as much explanation as she can based on the scan findings and help you to understand how the blood results fit into the risk assessment. She is able to process blood samples within 24 hours, so will ring you the following day with the final result and then e-mail you your report.
Early Blood Tests
The blood test that is used to screen for Down’s syndrome is usually taken at the time of the nuchal translucency scan, but the research data suggests that the results are actually more accurate if the blood is taken at 9 weeks, rather than 12 weeks. So wherever possible, Victoria will try to arrange for you to have your blood test before your scan. This has the double advantage of giving you the best possible result and ensuring that the blood results are ready when you come for your scan, so that your risk can be discussed with you face-to-face, rather than given to you by letter a week or two later, or over the phone.
Of course this isn’t always possible to arrange, in which case, it can be done at the same time as the scan. But as an added incentive, Victoria will offer to do a quick scan if you come to Beard Mill Clinic early to have the bloods taken, allowing you to hear the heart beat and to check your dates. There is no additional charge for this.
Awkward Babies
Some of the patients who contact Beard Mill Clinic about the nuchal translucency scan do so because it hasn’t been possible to measure the nuchal when they went for their routine NHS appointment. This is often because the baby wasn’t in the right position, but Victoria has the luxury of much more time and has not yet failed to get a nuchal measurement. So if you find yourself in this position, do ring to make an appointment.
Referral For Further Tests
In most cases, patients will be reassured by their result, but if your risk of Down’s syndrome is high, or a problem is suspected, Victoria will arrange a direct referral to your own NHS consultant and ensure you receive the right follow-up.
Full Explanation
Taking the measurements is the easy bit, interpreting the results and communicating these to the parents can sometimes be the more challenging part of screening. And this is where Victoria’s expertise comes into its own.
Through her training, she has acquired a deep understanding of how the individual components of the screening tests work and endeavours to explain this as fully as she can.
She is passionate about providing each and every patient with the best possible standard of screening and then equipping them with the knowledge and understanding to use this information appropriately.
Using the OpenVAS Vulnerability Scanner / Habr
Vulnerability scanners are software or hardware tools used to diagnose and monitor network computers, allowing you to scan networks, computers and applications for possible security problems, assess and fix vulnerabilities. (Wikipedia).
Well-known commercial scanners are Nessus, GFI LANguard, XSpider.
Unlike others, OpenVAS is free, works without any restrictions and can be useful for both network administrators and information security specialists to identify current problems in their infrastructure. nine0003
OpenVAS is based on a constantly updated collection of NVT security tests (of which there are already more than 30,000), as well as connection to the CVE database describing known vulnerabilities. The execution of NVT tests allows you to identify a vulnerability, and CVE provides a description of the problem and how to solve it.
The execution of NVT tests allows you to identify a vulnerability, and CVE provides a description of the problem and how to solve it.
Let's get started.
1. Iron selection.
Everything is simple here, if you have to scan often and large ranges of addresses, then the more powerful the hardware, the better. You can increase the number of parallel threads processing network addresses, and the scanning itself for each host will be faster. nine0004
2. Installation.
Here I choose the least problematic way for me to install from packages.
Let's go to the address.
www.openvas.org/install-packages.html
Select the desired distribution and install.
In my case, this is CentOS and the atomicorp repository. The script itself will download all the dependencies, carry out an initial update of the vulnerability database and prescribe the necessary settings. In the process, you will be asked to come up with a username and password to access Openvas. nine0004
nine0004
3. Usage.
We go to the address localhost:9392, enter the login and password and we are in the Greenbone Security Assistant management console.
The following is an example of using Openvas to scan a range of the internal network. The main settings are tailored to the optimal speed of checking each host.
3.1 Select the scanning configuration.
We go to the section Configuration - Scan Configs.
We see 4 standard policies and 1 empty one. nine0004
Policies are divided into 2 groups - fast and deep.
The fundamental difference is that deep does not take into account the work of each previous verification script and the collection of information starts anew.
In my tests, this significantly increased the time it took to scan each host, with no significant result. Therefore, for greater speed, we select the Full and fast ultimate policy and clone it by clicking on the sheep icon.
Now, for the clone, we have the editing options available and by clicking on the wrench icon , let's look inside. nine0004
nine0004
There are a lot of options, several hundred, on the screen, just the very beginning. All options are grouped into subsections of NVT tests by different types of operating systems and network equipment, by settings of various plug-in utilities such as nmap, nikto, etc.
Let's call our new policy Office_scan_config.
Let's go down.
I draw your attention to the following points.
safe_check - disabling will allow potentially dangerous NVT tests to run, the execution of which can cause the host under test to crash. Use carefully. nine0004
optimize_test - a switch that specifies whether to use fast or deep scanning.
Next, we go down to the PingHost items and set the switches, as in the screenshot.
This will immediately exclude empty addresses and not waste the scanner time on them. We do not touch the rest of the items.
Don't forget to save your changes.
3.2 Register an account for local checks.
If this item is configured, then Openvas will go to each machine, scan installed software, local security settings and throw out alerts if problems are found. nine0003 Naturally, this will increase the scanning time.
If not configured, Openvas will limit itself to remote checks.
Go to the Configuration –Credentials section.
Create a new entry by clicking on the star icon .
Let's say we have a windows network in the domain, there is a sec_check user with local administrator rights on the necessary machines, then it will look like this.
Save and move on.
3.3 Set scanning targets. nine0015
Next, we need to fill in the range of addresses for scanning and determine the set of ports that Openvas will check.
Go to the Configuration –Target section. Create a new goal by clicking on the star icon. We give it the name office.
In principle, everything is clear here, in the SMB section, we connected the previously created user to conduct local checks.
In the PortList section, the required range of ports is connected, in this case the set of popular ports offered by Nmap. The choice in favor of such a range was again made in favor of optimization, so as not to shovel all 65 thousand. nine0003 In the Hosts section, specify the ip range.
3.4 Launch!
We go to the ScanManagement - Task section. Create a new task by clicking on the star icon.
Select the previously created configurations one by one and click the CreateTask button.
Let's start.
Let's go drink some tea. Depending on the saturation of the network and the capacity of the server, the process can take up to several hours.
At the end of the process, we can click on the magnifying glass icon and view all the problems found. nine0004
Typical alert.
4. Updates.
Periodically, it is necessary to download up-to-date information about vulnerabilities and tests that detect them.
This is done either from the browser in the Administration section. (alternately in all 3 sections: nvt, scap, cert)
Either from the command line, by sequential commands.
openvas-nvt-sync
openvassd
openvasmd --rebuild
openvas-scapdata-sync
openvas-certdata-sync
killall openvassd
/etc/init.d/openvas-scanner restart
/etc/init.d/openvas-manager restart
/etc/init.d/openvas-administrator restart
/etc/init.d/greenbone-security-assistant restart
Owners of powerful hardware can look into the Settings section and set a larger number of parallel threads.
Greenbone Security Assistant useful tricks. can be found here
www.greenbone.net/learningcenter/index.html
Good luck with your use.
review of products that are on the market / Sudo Null IT News
Aloha to all Habravchans! I'm Vlad, Cloud4Y system administrator. In this article, I will tell you how we chose a vulnerability scanning product, why it is important to control which services are available from the outside, and why it is necessary to constantly audit the state of the network. Tea, coffee, pa-a-a-let's go!
Tea, coffee, pa-a-a-let's go!
Vulnerability Scanner
Let's understand the concept of a vulnerability scanner. Vulnerability scanner allows you to scan various systems, applications and networks for possible vulnerabilities that an attacker can use to compromise your data and systems, check open ports, evaluate and suggest a way to eliminate vulnerabilities. nine0004
I divided the scanner operation into the following stages:
-
Checking open ports, detecting running services and OS.
-
Vulnerability detection.
-
Safety assessment.
-
Reporting.
-
Vulnerability exploitation (performed only with the permission of the administrator of the system being checked, as it may lead to a malfunction).
Scan types
Vulnerability scanning is one of the initial stages of a penetration testing (pentest) task. Scanning for vulnerabilities, like penetration testing or any testing, is divided into several types. Let's consider each through the prism of a vulnerability scanner:
Let's consider each through the prism of a vulnerability scanner:
WhiteBox . The scanner is launched inside the network under investigation, which allows a more complete and comprehensive study of vulnerabilities, there is no need to "guess" the type of service or OS. The advantage of the method is in a complete and comprehensive approach to research, and the disadvantage is that it is less close to the situation of a real attack by an attacker. nine0004
BlackBox . "Black box". The scanner is launched from outside the studied network, which leads to the need to work through public interfaces. The application needs to analyze open ports, "guess" services and services, and identify vulnerabilities based on the information received. This option is as close as possible to the real situation: as initial data, the scanner has only an IP or a domain name for verification. Of the minuses, it can be mentioned that the vulnerabilities of applications used in the DMZ will remain undetected.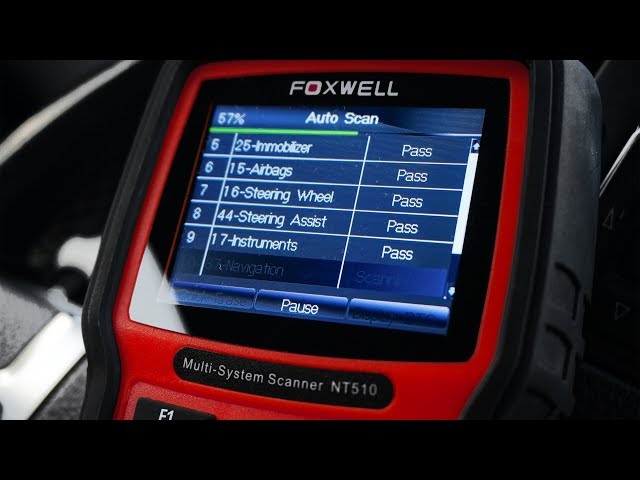 nine0004
nine0004
Of course, one can argue for a long time about the pros and cons of different types of scanning, but hardly anyone will dispute the need for testing. And practice shows that the combination of both methods allows you to get the best results. I think it makes more sense to scan BlackBox first and then WhiteBox. By the way, now we are working on creating a service for customers that will allow using BlackBox scanning to check the infrastructure located in the Cloud4Y data center. The service will save you from unpleasant accidents when ports were not closed or other potentially dangerous “holes” were left due to the human factor. nine0004
Product selection is the basis of service
For a competent product selection, you must specify the criteria that it must meet:
Required :
-
Free or paid version restrictions that match the parameters.
-
Qualitative search for open ports.
-
Works with IP addresses.

-
Looks for vulnerabilities - links to CVE databases, threat level by CVSS metric or similar. nine0004
-
Flexible settings.
-
Report output.
Optional :
-
Availability of technical documentation, technical forums.
-
GUI.
-
Report output in a convenient format.
-
Sending results by mail.
-
API.
Not every product on the market meets this set of criteria, especially in the free software segment, but there is a problem, but we will find a solution. Let's analyze what is now fashionable in cybersecurity circles as free solutions. After searching and analyzing solutions, several products were selected for study:
-
OpenVas.
-
Tenable Nessus.
-
Gobysec / Goby.
-
Tsunami-security-scanner.
-
Flan Scan.
-
D9scan.

-
Rustscan.
-
Owasp ZAP.
-
W9Scan.
-
Nmap.
Let's go in order and take a closer look at each of them
1. Greenbone Vulnerability Management (https://www.greenbone.net/) - the former OpenVas - reorganized, changed the name and distribution model of its software. Only the Greenbone Security Manager TRIAL product is distributed free of charge, which contains support for the Greenbone Community Feed. After installing and configuring the product, I started scanning the IP address behind which was OpenSSH server vers 7.2p2. The operating time of the software for scanning 1 IP address is 28 minutes. 28, Carl…
Product found CVE vulnerabilities. Only here for OpenSSH server vers 7.2p2 there is at least CVE-2016-8858 with a CVSS rating of 7.8. nine0004
Open ports: there are really 8 of them open, but, apparently, due to the limitations of the trial version, I saw only 2 out of 8. Eh, let's move on.
2. Tenable Nessus (https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus) is a well-known tool. There is a free version of the product, ahem, with a limit on scanning 16 IP addresses, that's not enough for us, let's move on.
3. Gobysec/Goby is a very promising free product. Lives here: https://gobies.org/. At the time of writing, beta version 1.9 is available.320. Very friendly interface, intuitive menu, there are extensions, API, upload reports and everything works out of the box (Windows 10). It is a pleasure to work with such a product. There are flaws, but this is beta. After the launch, the scanner worked for 15 minutes (why soooo long! &), found all 8 open ports (hooray!), correctly identified product versions, but, unfortunately, I did not see any vulnerabilities.
It all started so well, didn't it? However, I will follow the development of the product. next candidate. nine0004
4. Tsunami-security-scanner is an unofficial product from Google. Repository: https://github.com/google/tsunami-security-scanner. The solution is based on a bunch of nmap + vulners plugin + ncrack and everything is wrapped in docker. What prevents us from using the same nmap in conjunction with the plugin? So I also decided that nothing. Let's explore the next candidate.
Repository: https://github.com/google/tsunami-security-scanner. The solution is based on a bunch of nmap + vulners plugin + ncrack and everything is wrapped in docker. What prevents us from using the same nmap in conjunction with the plugin? So I also decided that nothing. Let's explore the next candidate.
5. Flan Scan is a solution from CloudFlare, repository at: https://github.com/cloudflare/flan. The product also uses a bunch of nmap + vulners (which is increasingly convincing of the need to use nmap to solve the problem), but there are a couple of features:
Definitely, such a product meets all the mandatory criteria and passes to the next stage of selection. But you also see that this is nmap plus a few non-trivial chips? Next!
6. D9Scan - "Python Network Scanner with Backdoor Detection on Network" was found on github.com. Under the hood of the script is a python and what would you think ... nmap again! Download, run, test, repeat. The results are similar to the tsunami and flan tested earlier, only without CVE reports, but my console turned a nice green color. nine0004 Next one
The results are similar to the tsunami and flan tested earlier, only without CVE reports, but my console turned a nice green color. nine0004 Next one
7. Couldn't get past solution Rustscan (https://github.com/RustScan/RustScan). Yes, here again nmap is used as a scanner, but interest in the product is spurred on by the statement “Scans all 65k ports in 3 seconds.” Impressive? Me too. The scanning speed is insane. Check and see for yourself:
docker run -it --rm --name rustscan rustscan/rustscan:1.10.0
For our purposes, the product is not very suitable, since open ports Edge can be built using the vCloud Director's API. You can learn how to use the vCloud Director API here. nine0004
8. Owasp Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) is "the world's most popular web application scanner, free and open source," listed on the product home page. Without a doubt, an excellent product from the OWASP team (if you are not familiar, be sure to read about them), cool site, training videos, lots of documentation, great community. Download => install JRE => Install ZAP => Test. Unfortunately, the product refused to scan only IP addresses and asked for a valid URL. nine0004
Download => install JRE => Install ZAP => Test. Unfortunately, the product refused to scan only IP addresses and asked for a valid URL. nine0004
It should be noted that as soon as the "valid url" appeared in the URL field: http://scanme.nmap.org/ the scanner immediately started scanning and quickly found problems:
Bottom line: the software is simple, cool, but does not check by IP -addresses, which is a mandatory criterion.
9. The same situation happened with W9Scan (https://github.com/w-digital-scanner/w9scan). When you try to enter an IP address for scanning, the software converts it to http:// 10. So, the last item on the list is nmap (https://nmap.org/). Nmap ("Network Mapper") is an open source tool for network exploration, security auditing, OS versioning, various services, and more. Do not forget about the NSE scripting engine. NSE (Nmap Scripting Engine) is a component of Nmap that allows you to write scripts and automate some tasks, such as detecting and / or exploiting vulnerabilities. Let's check whether it matches the mandatory list of criteria: Free? Completely free. Qualitative search for open ports? There is. Works with IP addresses? No problem! Looking for vulnerabilities (links to CVE databases, threat level by CVSS metric or similar)? Include plugins like vulners or vulscan. nine0004 Customization flexibility? A huge number of settings that allow you to adjust the type of scan. Report output? Supported: txt, grep, xml. Convenient report output? I found https://github.com/honze-net/nmap-bootstrap-xsl which is amazing in terms of usability and beauty. GUI? Zenmap (https://nmap. Community? Huge! Oh, sorry, reports are not sent to the post office ... I summarized the results in a table: 3 products made it to the final selection: FlanScan, Rustscan, nmap. Rustscan is not bad, but the speed of finding open ports is leveled by the list collected via the API. In other words, the API allows you to pull open ports, and I don't just need a quick port scan, I need a high-quality one. FlanScan = nmap + beautiful reports and uploading to the cloud. I can make beautiful reports myself. And there is nothing to say about the cloud. Nmap is the product on which all the services that made it to the final are based, and customization will help us solve the problem of implementing a vulnerability scanner. nine0004 It's all subjective, obviously, but from what I've seen, nmap is the go-to tool for doing reconnaissance (of any kind) before pentesting. See above how many well-known brand products are based on nmap - flan (cloudflare), tsunami (google), rustscan and that, not to mention 1. Of course, the choice of the “best” tool is always up to you, but if you are already thinking about conducting a security audit of your network, then you are already on the right track. Be aware that any scan of your infrastructure will allow you to be sure that you do not have "holes" - forgotten open ports, not updated software, or misconfigured services - that script kiddies can use to exploit a vulnerability. Forewarned is forearmed! nine0004 P. S. While searching, I came across https://github.com/infobyte/faraday. Infobyte's authors claim to have created an IDE to work with data obtained from security audits. Faraday's product has not only console execution, but also a nice GUI. This product relates only partially to the problem of choosing a scanner for vulnerabilities, but the information security department in your company may be of interest. The basis is the Lua scripting language interpreter. Let's check nmap in action. I ran a scan on the subject's IP address with options
The basis is the Lua scripting language interpreter. Let's check nmap in action. I ran a scan on the subject's IP address with options –p- -sV --script=vulners , and when I saw the console output, I immediately understood what product we needed.
 org/zenmap/)
org/zenmap/)  8k forks on github and almost 6k stars. Based on the above, we have come to the conclusion that nmap will be an excellent basis for our vulnerability scanning service.
8k forks on github and almost 6k stars. Based on the above, we have come to the conclusion that nmap will be an excellent basis for our vulnerability scanning service.