How to prevent thrush in newborns
Oral Thrush (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
Reviewed by: Michelle P. Tellado, MD
en español Muguet (candidiasis oral)
What Is Oral Thrush?
Oral thrush is a very common yeast infection in babies. It causes irritation in and around a baby's mouth.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Oral Thrush?
Oral thrush (also called oral candidiasis) can affect anyone, but is most common in babies younger than 6 months old and in older adults.
A baby with oral thrush might have cracked skin in the corners of the mouth or white patches on the lips, tongue, or inside the cheeks that look a little like cottage cheese but can't be wiped away.
Some babies may not feed well or are uncomfortable when sucking because their mouth feels sore, but many babies don't feel any pain or discomfort.
What Causes Oral Thrush?
Oral thrush is caused by the overgrowth of a yeast (a type of fungus) called Candida albicans.
Most people (including infants) naturally have Candida in their mouths and digestive tracts, which is considered normal growth. Usually, a healthy immune system and some "good" bacteria control the amount of this fungus in the body.
But if the immune system is weakened (from an illness or medicines like chemotherapy) or not fully developed (as in babies), Candida in the digestive tract can overgrow and lead to an infection. Candida overgrowth also causes diaper rash and vaginal yeast infections. Babies can have oral thrush and a diaper rash at the same time.
Candida overgrowth also can happen after a baby has been given antibiotics for a bacterial infection because antibiotics can kill off the "good" bacteria that keep the Candida from growing. Oral thrush also can happen after the use of steroid medicines.
How Is Oral Thrush Treated?
See your doctor if you think your baby may have thrush. Some cases go away without medical treatment within a week or two, but the doctor may prescribe an antifungal solution for your baby's mouth. This medicine is usually applied several times a day by "painting" it on the inside of the mouth and tongue with a sponge applicator.
This medicine is usually applied several times a day by "painting" it on the inside of the mouth and tongue with a sponge applicator.
Depending on your baby's age, the doctor also might suggest adding yogurt with lactobacilli to your baby's diet. The lactobacilli are "good" bacteria that can help get rid of the yeast in your child's mouth.
If your baby keeps getting oral thrush, especially if he or she is older than 9 months old, talk with your doctor because this might be a sign of another health issue.
Can Oral Thrush Be Prevented?
Oral thrush is a common infection in babies, but you can help prevent it:
- If you formula-feed your baby or use a pacifier, thoroughly clean the nipples and pacifiers in hot water or a dishwasher after each use. That way, if there's yeast on the bottle nipple or pacifier, your baby won't be reinfected. Store milk and prepared bottles in the refrigerator to prevent yeast from growing.
- If you breastfeed and your nipples are red and sore, you might have a yeast infection on your nipples, which you and your baby can pass back and forth.
 Talk to your doctor, who might recommend using an antifungal ointment on your nipples while your baby is treated with the antifungal solution.
Talk to your doctor, who might recommend using an antifungal ointment on your nipples while your baby is treated with the antifungal solution.
To prevent diaper rash, change diapers often.
Reviewed by: Michelle P. Tellado, MD
Date reviewed: September 2019
What is Oral Thrush in Babies and How to Prevent It?
Is your baby extra fussy these days – especially during feedings? If you’re nursing, have you also noticed your nipples are all of a sudden sore and red? Chances are you both may have a yeast infection known as oral thrush.
Ew, what?! Where? How?
Before you freak out, know that oral thrush is actually a very common and usually harmless breastfeeding problem. Here’s what you need to know to help you and your baby feel better, plus steps to prevent another occurrence.
What is Thrush?
Oral thrush is caused by a yeast-like fungus called Candida albicans. Candida can normally live in our mouth, intestines and genital areas without causing any problems, but sometimes it can grow quickly and become a pain for you and your baby.
“Babies are more at risk of getting and passing thrush to their mothers during breastfeeding,” said Shelbie Radom, RN, at McKee Medical Center in Loveland, CO. “Newborns can get a Candida infection from their mother during birth or may be at higher risk if they have serious health conditions or were born prematurely. It can also occur after mom or baby have taken antibiotics, which can reduce good bacteria in our bodies.”
Signs of Oral Thrush
If you take a peek inside your baby’s mouth and notice white patches on the tongue that don’t rub off or go away, this could be a tell-tale sign they have thrush. Thrush can also be painful, so you may also notice changes in their feeding habits. It’s not unusual for babies to become fussier while nursing, bottle-feeding or sucking on their pacifier or thumb.
“One sign is if your baby has been breastfeeding without difficulty and then suddenly begins to come on and off the breast crying as if in pain,” Radom said. “Another symptom can be an increased or worsening diaper rash that is angry red, painful and hard to treat. ”
”
If you’re nursing, chances are you may also have a yeast infection too! It’s not uncommon for you and your baby to pass it back and forth from their mouth to your breast and back again. Symptoms of nipple thrush include burning or sore nipples. You may also experience shooting pains during or after feedings.
Treating Oral Thrush
Before you Google “home remedies for thrush,” Radom cautions against doing so until after consulting with your baby’s doctor or your lactation consultant.
“Old home remedies may work in mild cases or for very healthy mothers and babies, but thrush is difficult to treat and may require several weeks of treatment, so these remedies may compound the problem,” Radom said.
To prevent ongoing infection or reinfection, the key is for both you and your baby to get treated. If your baby’s doctor determines it is indeed thrush, they may prescribe an antifungal medication, which is applied topically to the insides of their mouth and tongue for 10 days. If you have nipple thrush, your doctor will likely recommend a prescription antifungal cream as well for your nipples.
If you have nipple thrush, your doctor will likely recommend a prescription antifungal cream as well for your nipples.
Important Tip: “Always finish all antibiotics prescribed, even when symptoms are gone,” Radom said.
Preventing Thrush Altogether
Candida is a sneaky, resilient little booger … er, yeast. It thrives in warm, moist environments, so your nipples and baby’s mouth (even baby’s diaper!) are perfect places for yeast and bacteria to hide and spread.
While thrush can be difficult to deal with and sometimes hard to prevent, here are five steps you can do at home that may help:
- Wash your hands. Make sure you wash your hands before and after nursing and after diaper changes. This way you can not only prevent the spread of Candida but also many other common illnesses too.
- Keep anything that comes in contact with your baby’s mouth and your breasts clean. Even if thrush is not a concern, you should always regularly wash items that have been in your baby’s mouth in hot, soapy water.
 This includes bottles, nipples, pacifiers, teethers and even breast pump parts that touch your nipples.
This includes bottles, nipples, pacifiers, teethers and even breast pump parts that touch your nipples. - Change your nursing bra and breast pads regularly. Milk leakage in your nursing bra and nursing pad can be a breeding ground for yeast and bacteria to grow. Change out nursing pads and properly wash your nursing bras when they get wet.
- Add probiotics or yogurt to your daily diet. Taking a probiotic or eating yogurt with active cultures to your diet may help build good bacteria that manages the growth of yeast.
- Let “the girls” hang out to dry after nursing. If you are breastfeeding, allow your nipples to completely dry between feedings before putting your bra back on.
Don’t let a little fungus get you down, mama! Talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns to find the best treatment option for you and your baby. To find a Banner Health specialist near you, visit bannerhealth. com.
com.
For more parent-friendly advice, check out:
- 7 Common Breastfeeding Challenges and How to Solve Them
- 5 Common Teething Questions Answered
- Safe Sleep Practices for Baby
Children's Health Parenting Pregnancy
Join the Conversation
Thrush in the mouth of an infant
0-6 months
Article
0 reviews
Thrush in infants is a common phenomenon caused by microorganisms of the genus Candida. We will look at the causes of candidiasis and ways to prevent the disease.
3 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
80% of people worldwide have Candida in their bodies. They are present on the skin and mucous membranes in small quantities and make themselves felt only under certain circumstances. For a newborn, such a circumstance may be a weak immune system. The microflora of the baby is not yet formed, and pathogenic cells have more freedom to spread and multiply. A baby can get an infection even when passing through the birth canal - fungi are transmitted from mother to child through the mucous membrane. nine0003
They are present on the skin and mucous membranes in small quantities and make themselves felt only under certain circumstances. For a newborn, such a circumstance may be a weak immune system. The microflora of the baby is not yet formed, and pathogenic cells have more freedom to spread and multiply. A baby can get an infection even when passing through the birth canal - fungi are transmitted from mother to child through the mucous membrane. nine0003
Premature and bottle-fed babies are more likely to get candidiasis than full-term breastfed babies
Now you know what thrush is in babies. Now let's look at the causes of candidiasis.
5 causes of thrush in babies
- Weak immunity at birth. All babies have a weak immune system. But at risk are premature babies. Breast milk helps a small body get stronger
- Infectious disease. Allergies, colds - all this increases the risk of developing thrush in infants
- Taking medication.
 It doesn’t matter if the child drinks them himself or if they enter his body through mother’s milk. Antibiotics and other drugs reduce immunity by suppressing both harmful and beneficial bacteria
It doesn’t matter if the child drinks them himself or if they enter his body through mother’s milk. Antibiotics and other drugs reduce immunity by suppressing both harmful and beneficial bacteria - Infection with fungi from the mother's vagina. During childbirth, a mother can infect her baby with Candida fungi from her body
- Cracks in the oral mucosa and frequent regurgitation is another reason for the appearance of thrush on the tongue in a child under the age of
Sometimes a white coating in the mouth of an infant is due to inadequate care in the hospital or at home. For example, due to a poorly sterilized bottle, a dirty nipple or unwashed hands in adults
Symptoms of candidiasis in newborns
Oral thrush manifests itself as follows:
- In the mouth - on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue, gums and palate - white plaque and / or small white pellets. This is the initial and easiest stage of candidiasis
- The second stage is an increase in white plaque and the gradual development of an inflammatory process, which manifests itself in the form of red spots under the milk film
- Third stage - violation of the mucous membrane, the appearance of wounds on the lips and mouth, bleeding
- A neglected case - when a white film tightens not only the mouth, but also the child's throat.
 It is difficult for the baby to swallow, he screams and refuses to suckle, his temperature rises. Then the disease spreads through the intestines, disrupting the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract and further reducing the immunity of the crumbs
It is difficult for the baby to swallow, he screams and refuses to suckle, his temperature rises. Then the disease spreads through the intestines, disrupting the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract and further reducing the immunity of the crumbs
With a long course of the disease without proper treatment, the negative process spreads to the skin, nails, internal and genital organs of the child
How to cure thrush in an infant
Treatment of thrush in newborns involves contacting a pediatrician for examination and consultation. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe taking tests from the affected areas to detect Candida fungi.
Please note that not only the baby, but also the mother must undergo appropriate treatment. This will help to avoid re-infection of the infant while breastfeeding
With proper and timely treatment, the symptoms disappear in a few days or a week. Therefore, the sooner you seek help from a doctor, the sooner you solve the problem.
The best treatment is prevention
You can solve the problem, or you can prevent it. Here are four ways to avoid candidiasis in your newborn:
- Thoroughly clean and sterilize bottles and teats
- Treat all objects that your child touches during the day while playing or feeding. If the item is not sterilizable, use baking soda
- When breastfeeding, the mother should keep her breasts clean and carefully treat all cracks in the nipples
- After feeding, it is important to remove milk residues from the baby's tongue and gums, which can promote the growth of fungi. To do this, give the baby some warm water at the end of feeding and after each spit up
The most difficult are the first 6 months, when the immune system is still very weak and hard to resist infections. After that, the risk of thrush in infants is reduced. Therefore, follow the rules for caring for newborns, and to strengthen a small body, choose breastfeeding. nine0003
nine0003
Latest reviews
Average customer rating
0 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 0
- 4 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- one 0
Candidiasis in the mouth of a child
Contents
What kind of disease is candidiasisSymptomsCausesTreatmentMethods of therapyPreventive measures
Many parents are aware of such a common problem in children as thrush, which is characterized by the appearance of white plaque on the tissues of the oral cavity. In medicine, this pathological condition has the term "candidiasis" and refers to fungal diseases.
Most often, candidiasis develops in the mouth of a child in the first year of life. Symptoms of thrush greatly disturb the baby, but timely treatment allows you to quickly and without consequences get rid of the fungus.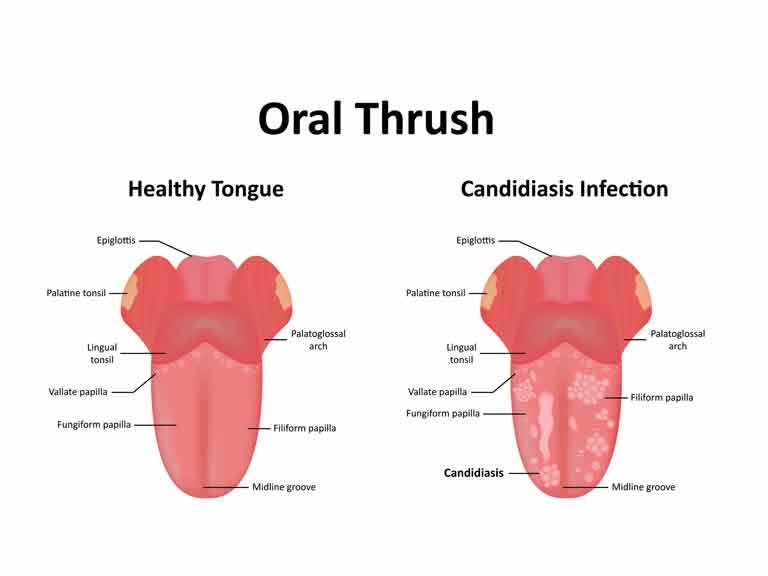 nine0003
nine0003
What kind of disease is candidiasis
According to statistics, about 30% of infants are faced with candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of babies is not yet formed and is not able to withstand pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors. nine0003
With a weakened immune system and the concomitant effect of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. If thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.
Symptoms
Oral candidiasis in children can have a different form of manifestation and severity of symptoms: mild, moderate and severe. As a rule, each form corresponds to the stage of development of the disease. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, then the signs of a fungal infection become more intense and the number of symptoms increases. nine0003
As a rule, each form corresponds to the stage of development of the disease. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, then the signs of a fungal infection become more intense and the number of symptoms increases. nine0003
With a mild form of the disease, a red rash appears on the oral mucosa, which is covered with a white coating on top. At the next stage, the child has swelling of the tissues and the formation of localized white spots with a touch of curd consistency. Gradually, these spots merge into a large affected area. When plaque is removed, bleeding sores open. If the thrush starts, then the fungus already spreads to the entire oral cavity, including the lips, tongue and throat. All fabrics are completely covered with cheesy bloom. nine0003
Common symptoms of candidiasis in children include:
-
burning sensation and itching in the mouth;
-
discomfort and pain when eating;
-
frequent spitting up in babies;
-
the formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
-
temperature rise.
 nine0003
nine0003
Children of the first two years of life report their condition with refusal to eat, constant whims and causeless crying. It is not difficult to see signs of candidiasis, so if a child has a sharp rise in temperature or refuses to eat, pediatricians and dentists recommend checking the oral cavity for white plaque. If you suspect thrush, it is undesirable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses rapidly. nine0003
Causes
The main reason for the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in children is a weakened immune system. If a child is born prematurely, then the likelihood of having thrush is very high. Children who are breastfed or have congenital pathologies are also often exposed to fungal infection.
Provoking factors include:
-
the presence of vaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy - the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal; nine0003
-
insufficient hygiene of the female breast during breastfeeding - the fungus is often localized precisely on the nipples because of the favorable environment for it;
-
poor processing of the child's initial things - bottles, nipples, and so on;
-
the habit of parents to lick the nipples - even if the adult does not have signs of thrush, a fungus may be present in the mouth, which will be transmitted to the child; nine0003
-
long-term use of drugs of the "antibiotics" group - drugs help to reduce one's own immunity;
-
frequent regurgitation in infants - after regurgitation, an increased acidic environment, favorable for the fungus, remains inside the oral cavity;
-
excessive and frequent dry mouth - the absence of saliva, as a protective agent against the activity of pathological microorganisms.
 nine0003
nine0003
Infection with Candida fungus in children older than 2 years can occur as a result of unwashed foods, raw milk or running water. If a child over 3 years of age has suddenly developed signs of thrush, one should be examined not only for a fungal infection, but also for other possible diseases that may be accompanied by a “fading” of the immune system.
Treatment
Children's fungal diseases can be dealt with by a pediatrician, infectious disease specialist or dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of thrush of the oral cavity, then the dentist can also carry out therapy. nine0003
The diagnosis of "candidiasis" is determined in most cases on the basis of a specialist examination of the oral cavity. If there is any doubt, the doctor directs the patient for additional examinations. To confirm the disease, a laboratory method is used to study a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of a fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children involves an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with the adoption of measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe form, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local remedies and compliance with preventive recommendations. nine0003
If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with the adoption of measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe form, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local remedies and compliance with preventive recommendations. nine0003
Methods of therapy
Treatment of candidiasis begins with the treatment of the oral cavity. The first procedure is already performed at the reception. Antiseptic agents are used to remove plaque. The doctor may then apply an antifungal agent.
The parent should carefully monitor the actions of the dentist, as in the future they will have to independently process the oral cavity at home. The necessary drugs will be prescribed by a specialist. Local antifungal agents are dangerous in case of overdose, especially for the child's body, so you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations. nine0003
In advanced cases, medications are prescribed in the form of solutions, drops or tablets.