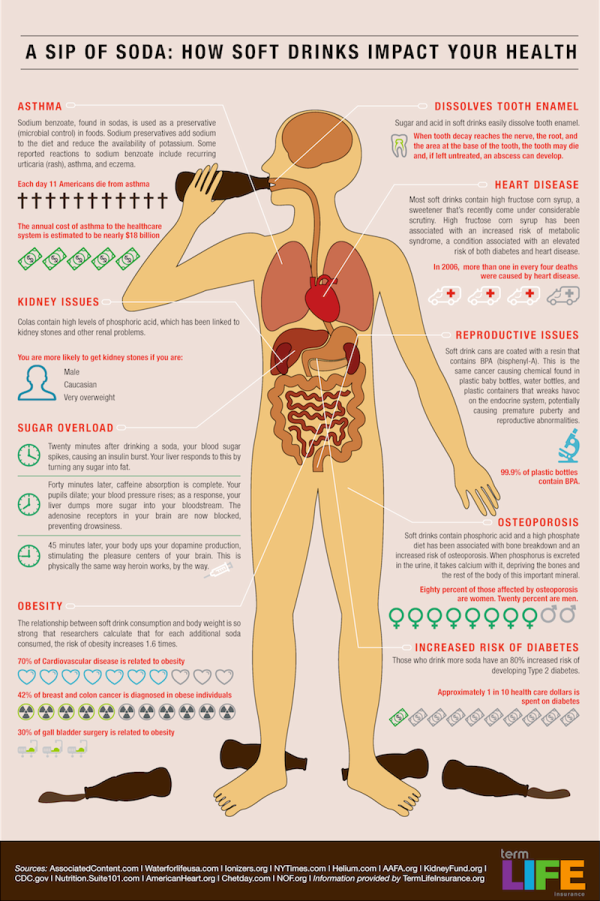
How diabetes develops
Symptoms & Causes of Diabetes
In this section:
- What are the symptoms of diabetes?
- What causes type 1 diabetes?
- What causes type 2 diabetes?
- What causes gestational diabetes?
- What else can cause diabetes?
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes include
- increased thirst and urination
- increased hunger
- fatigue
- blurred vision
- numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- sores that do not heal
- unexplained weight loss
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can start quickly, in a matter of weeks. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly—over the course of several years—and can be so mild that you might not even notice them. Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms. Some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart trouble.
What causes type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system, the body’s system for fighting infection, attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Scientists think type 1 diabetes is caused by genes and environmental factors, such as viruses, that might trigger the disease. Studies such as TrialNet are working to pinpoint causes of type 1 diabetes and possible ways to prevent or slow the disease.
What causes type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes—the most common form of diabetes—is caused by several factors, including lifestyle factors and genes.
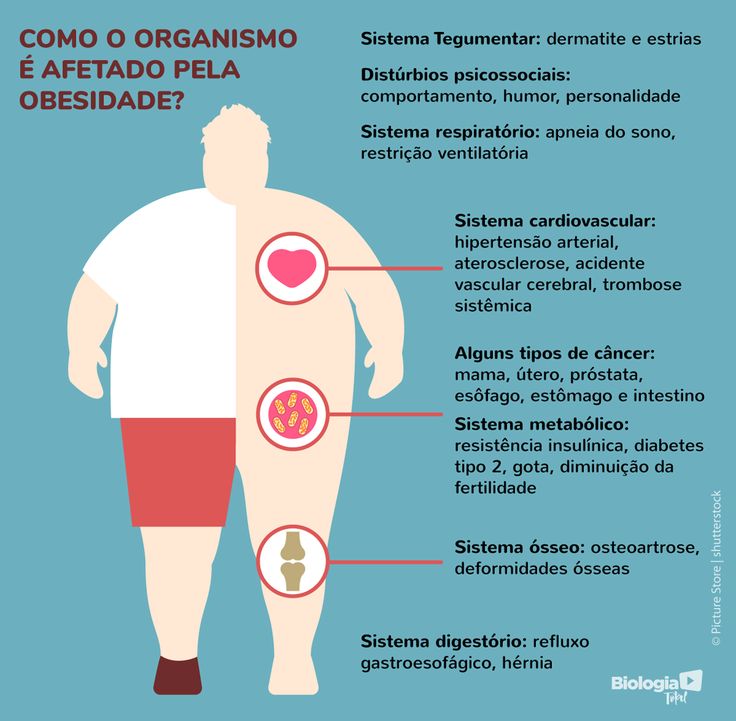
Overweight, obesity, and physical inactivity
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are not physically active and are overweight or have obesity. Extra weight sometimes causes insulin resistance and is common in people with type 2 diabetes. The location of body fat also makes a difference. Extra belly fat is linked to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart and blood vessel disease.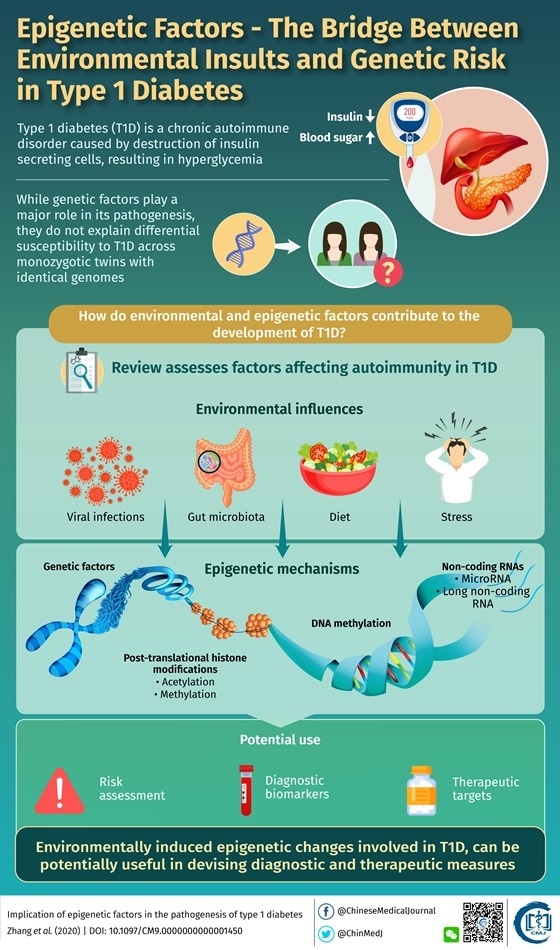 To see if your weight puts you at risk for type 2 diabetes, check out these Body Mass Index (BMI) charts.
To see if your weight puts you at risk for type 2 diabetes, check out these Body Mass Index (BMI) charts.
Insulin resistance
Type 2 diabetes usually begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which muscle, liver, and fat cells do not use insulin well. As a result, your body needs more insulin to help glucose enter cells. At first, the pancreas makes more insulin to keep up with the added demand. Over time, the pancreas can’t make enough insulin, and blood glucose levels rise.
Genes and family history
As in type 1 diabetes, certain genes may make you more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. The disease tends to run in families and occurs more often in these racial/ethnic groups:
- African Americans
- Alaska Natives
- American Indians
- Asian Americans
- Hispanics/Latinos
- Native Hawaiians
- Pacific Islanders
Genes also can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by increasing a person’s tendency to become overweight or have obesity.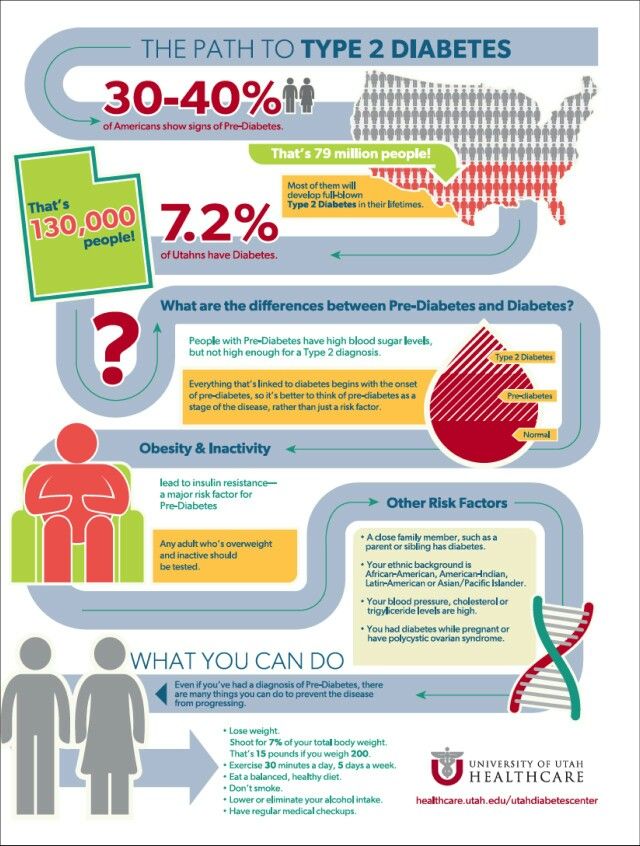
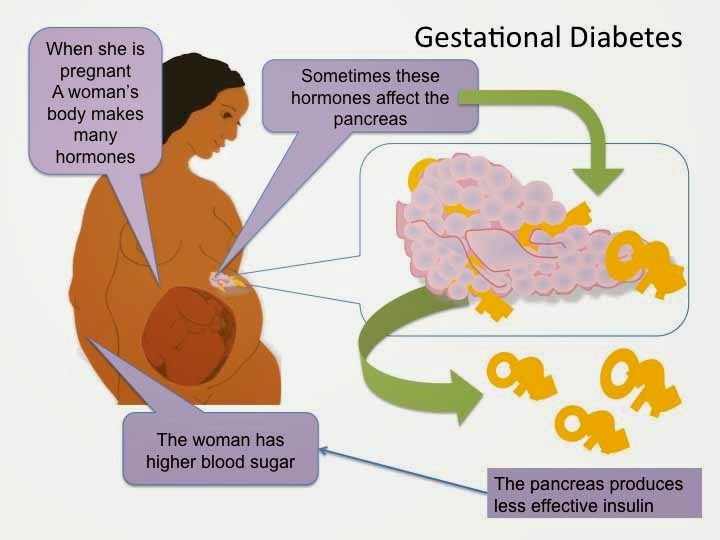
Scientists believe gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, is caused by the hormonal changes of pregnancy along with genetic and lifestyle factors.
Insulin resistance
Hormones produced by the placenta contribute to insulin resistance, which occurs in all women during late pregnancy. Most pregnant women can produce enough insulin to overcome insulin resistance, but some cannot. Gestational diabetes occurs when the pancreas can’t make enough insulin.
As with type 2 diabetes, extra weight is linked to gestational diabetes. Women who are overweight or have obesity may already have insulin resistance when they become pregnant. Gaining too much weight during pregnancy may also be a factor.
Hormonal changes, extra weight, and family history can contribute to gestational diabetes.Genes and family history
Having a family history of diabetes makes it more likely that a woman will develop gestational diabetes, which suggests that genes play a role. Genes may also explain why the disorder occurs more often in African Americans, American Indians, Asians, and Hispanics/Latinas.
Genes may also explain why the disorder occurs more often in African Americans, American Indians, Asians, and Hispanics/Latinas.
What else can cause diabetes?
Genetic mutations, other diseases, damage to the pancreas, and certain medicines may also cause diabetes.
Genetic mutations
- Monogenic diabetes is caused by mutations, or changes, in a single gene. These changes are usually passed through families, but sometimes the gene mutation happens on its own. Most of these gene mutations cause diabetes by making the pancreas less able to make insulin. The most common types of monogenic diabetes are neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). Neonatal diabetes occurs in the first 6 months of life. Doctors usually diagnose MODY during adolescence or early adulthood, but sometimes the disease is not diagnosed until later in life.
- Cystic fibrosis produces thick mucus that causes scarring in the pancreas. This scarring can prevent the pancreas from making enough insulin.
- Hemochromatosis causes the body to store too much iron. If the disease is not treated, iron can build up in and damage the pancreas and other organs.
Hormonal diseases
Some hormonal diseases cause the body to produce too much of certain hormones, which sometimes cause insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Cushing’s syndrome occurs when the body produces too much cortisol—often called the “stress hormone.”
- Acromegaly occurs when the body produces too much growth hormone.
- Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone.
Damage to or removal of the pancreas
Pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, and trauma can all harm the beta cells or make them less able to produce insulin, resulting in diabetes. If the damaged pancreas is removed, diabetes will occur due to the loss of the beta cells.
Medicines
Sometimes certain medicines can harm beta cells or disrupt the way insulin works. These include
These include
- niacin, a type of vitamin B3
- certain types of diuretics, also called water pills
- anti-seizure drugs
- psychiatric drugs
- drugs to treat human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- pentamidine, a drug used to treat a type of pneumonia
- glucocorticoids—medicines used to treat inflammatory illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, lupus, and ulcerative colitis
- anti-rejection medicines, used to help stop the body from rejecting a transplanted organ
Statins, which are medicines to reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, can slightly increase the chance that you’ll develop diabetes. However, statins help protect you from heart disease and stroke. For this reason, the strong benefits of taking statins outweigh the small chance that you could develop diabetes.
If you take any of these medicines and are concerned about their side effects, talk with your doctor.
How do people develop diabetes?
Diabetes develops when the body cannot make enough insulin or use it properly.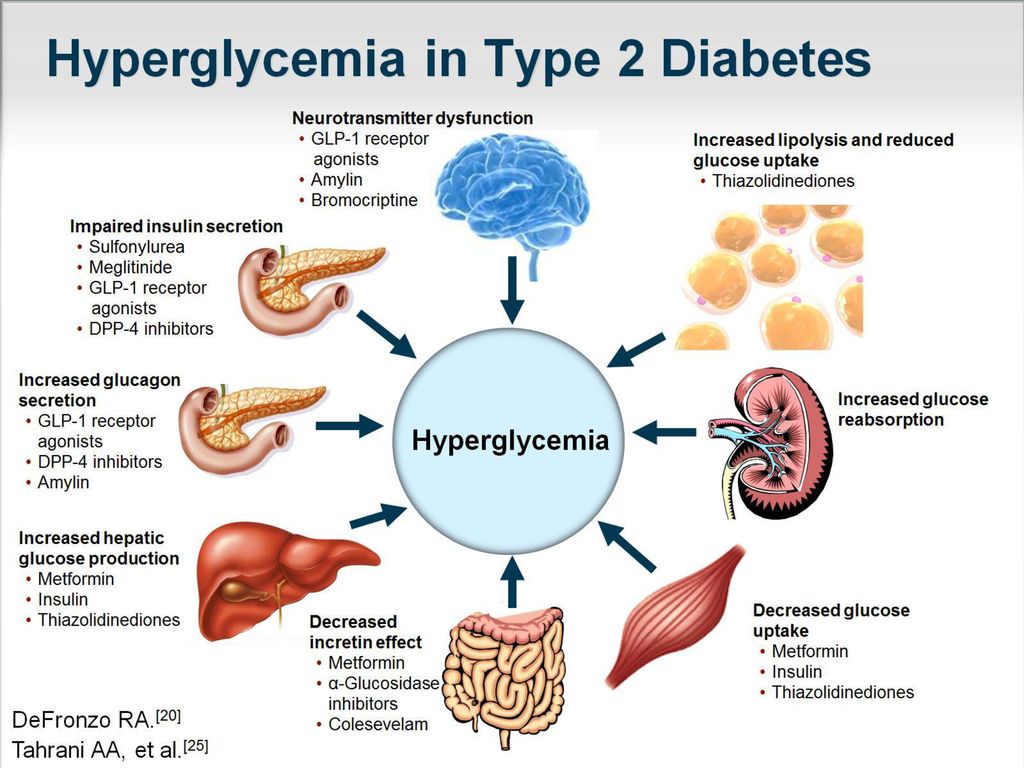 Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood glucose levels, and without a sufficient amount working correctly, health complications can occur. There are many types of diabetes that can result from different factors, such as genetics or lifestyle choices.
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood glucose levels, and without a sufficient amount working correctly, health complications can occur. There are many types of diabetes that can result from different factors, such as genetics or lifestyle choices.
Diabetes is a condition that occurs when a person is unable to regulate their blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels. Typically, the pancreas produces a hormone called insulin that allows cells to absorb glucose from the blood. This allows the body to use the glucose for energy and keep the blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
However, many factors can result in either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or cells being unable to use insulin effectively. This can cause too much glucose to accumulate in the blood and lead to the development of diabetes.
This article discusses some ways that different types of diabetes can develop.
Diabetes is a condition where insulin is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels.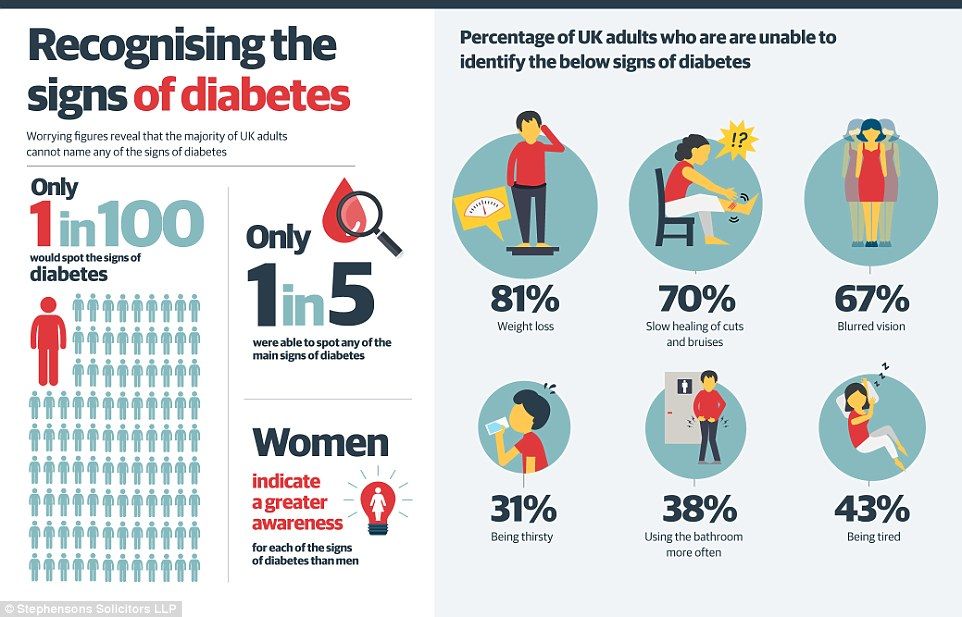 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) estimates that more than 34 million Americans had diabetes in 2018, and around 7 million of those cases were undiagnosed.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) estimates that more than 34 million Americans had diabetes in 2018, and around 7 million of those cases were undiagnosed.
Evidence suggests that diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. However, the true number of deaths is likely higher as death certificates do not consistently report diabetes as a cause. In addition to various symptoms, such as tiredness, vision problems, and increased thirst and urination, diabetes also increases the risk of many serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
Diabetes causes problems with how the body uses or produces insulin. The body breaks food down into glucose, which it releases into the bloodstream. Glucose is a source of energy that the body either takes into cells or stores for later use. Insulin is a hormone that guides glucose for use in cells or storage in the muscle or liver tissues.
The pancreas normally releases enough insulin depending on how much glucose is in the bloodstream. However, insulin is unable to properly regulate glucose in people with diabetes. This causes glucose to stay in the bloodstream so long that it becomes harmful to the body.
However, insulin is unable to properly regulate glucose in people with diabetes. This causes glucose to stay in the bloodstream so long that it becomes harmful to the body.
The reason insulin is unable to regulate glucose properly depends on the type of diabetes. The most common types are:
- Prediabetes: Prediabetes, or borderline diabetes, occurs before type 2 diabetes develops. By this stage, blood sugar, blood pressure, and insulin resistance may start reaching harmful levels.
- Type 1 diabetes: The body cannot produce enough insulin because the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It is unclear what causes type 1 diabetes to develop, and it may be due to genetic and environmental factors.
- Type 2 diabetes: The body fails to use insulin effectively enough to regulate blood sugar levels. For example, some tissues become insulin resistant and require more insulin. Type 2 diabetes can occur due to several factors, including genetics, unhealthy weight, and physical inactivity.

- Gestational diabetes: Pregnancy can cause hormonal changes that lead to insulin resistance. Genetics and lifestyle factors may also contribute to gestational diabetes.
There are also several less common types of diabetes with different causes, such as:
- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): A collection of conditions where inherited genetic mutations limit a person’s ability to produce insulin. They typically develop in adolescence and young adulthood.
- Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA): A form of diabetes where the immune system interferes with how insulin regulates blood sugar levels. The disease progresses more slowly than type 1 diabetes, but most people will move from oral medication to insulin treatment 6 months after diagnosis.
- Neonatal diabetes: A rare form of diabetes that occurs in babies under 6 months old and prevents the pancreas from producing enough insulin.

- Wolfram syndrome: A genetic disease that can cause diabetes with vision and hearing problems.
- Alström syndrome: Another rare genetic disorder that can lead to type 2 diabetes with several other problems, including obesity, vision or hearing loss, and kidney failure.
- Steroid-induced diabetes: Steroids are artificial versions of hormones that can increase blood sugar levels by causing the liver to release more glucose. This can result in insulin resistance.
- Cystic fibrosis diabetes: A genetic condition that causes mucus to build up and damage the pancreas, leading to high blood sugar.
- Type 3c diabetes: Also known as pancreatogenic diabetes, it occurs when illness, injury, or surgery of the pancreas causes it to stop producing insulin.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), risk factors for diabetes can include:
- genetics and family history
- age, which includes younger ages for type 1 diabetes or older ages for type 2
- overweight and obesity
- physical inactivity
- an unhealthy diet
- hormone disorders, such as polycystic ovary syndrome
- certain ethnic backgrounds, such as African American or Hispanic American
- having certain diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- previously having gestational diabetes
- giving birth to a baby over 9 pounds
Diabetes symptoms will vary depending on the type and cause but may include:
- fatigue
- blurred vision
- increased thirst and urination
- hunger
- numbness in the hands and feet
- persistent sores
- unexpected weight loss
Diabetes can also lead to serious health complications without treatment, such as heart disease or stroke.
There are currently no cures for diabetes. But there are many forms of treatment available, depending on its type. The goal of treatment is to keep blood glucose levels within a healthy range to manage symptoms and the risk of complications.
Treatment for common types of diabetes can include:
- Prediabetes: Losing weight by eating a healthy diet and increasing physical activity can prevent prediabetes from developing into type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: Daily insulin doses are necessary to regulate blood sugar. These could be through a syringe, insulin pen, or pump.
- Type 2 diabetes: Lifestyle changes may be necessary, such as a healthier diet or increased physical activity. Many people will also require oral medications and later may need insulin. In some cases, weight loss surgery may be an option.
- Gestational diabetes: Lifestyle changes can help to lower blood sugar, such as dietary changes.
 Doctors may also suggest diabetes medicines where lifestyle changes are not working.
Doctors may also suggest diabetes medicines where lifestyle changes are not working.
Some forms of diabetes could be reversible. For example, people with prediabetes can prevent type 2 diabetes and reduce their blood sugar levels by losing weight and regularly exercising.
People with type 2 diabetes can enter remission. This is where blood sugar levels stay within the normal range for at least 6 months without medications. It is achievable through healthy lifestyle changes.
However, other forms of diabetes are not reversible. For example, type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that requires daily insulin doses for life.
Diabetes is a serious condition that requires medical attention. Anyone experiencing signs or symptoms of diabetes should visit a doctor for advice and treatment. The CDC recommends seeing a doctor for a blood test for the following symptoms:
- urinating regularly, including at night
- frequent thirst and hunger
- unexpected weight loss
- blurry vision
- numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- regular tiredness
- very dry skin
- frequent infections
Diabetes causes high blood sugar levels due to problems with insulin. The body either makes too little insulin or uses it poorly. There are many possible causes of insulin problems, which range from genetic to lifestyle factors.
The body either makes too little insulin or uses it poorly. There are many possible causes of insulin problems, which range from genetic to lifestyle factors.
Some forms of diabetes are reversible through lifestyle changes and treatments, such as prediabetes. Other types of diabetes, such as type 1 diabetes, are currently without a cure. However, regular insulin medication can help to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
how it starts and can it be prevented
10 November 2020 09:31
The most common features that indicate that something is wrong with the body and that more attention needs to be paid to health can be: in food)
- dry mouth
- thirst
- increased fatigue
These signs are especially pronounced in children. Attentive parents should notice if the child suddenly woke up with a "brutal" appetite and inexplicable thirst for no reason - this is a reason not to hesitate to visit the pediatrician! In order to try to prevent the disease, you need to know and remember the causes that cause it:
1. Heredity. If the next of kin suffer from diabetes, the risk of getting sick is high, but you can take timely measures: adjust your diet, lifestyle, reconsider your attitude to bad habits (for example, alcohol abuse), uncontrolled medication.
Heredity. If the next of kin suffer from diabetes, the risk of getting sick is high, but you can take timely measures: adjust your diet, lifestyle, reconsider your attitude to bad habits (for example, alcohol abuse), uncontrolled medication.
2. Some viral diseases have a particularly negative effect on the pancreas, which is responsible for the production of insulin. These are viral hepatitis, rubella, chicken pox. If a child has had the disease, the risk of getting sick in childhood increases. nine0007 3. Bad habits: excessive alcohol consumption, regular overeating, especially in terms of sweet and fatty foods, fast food, flour products, lack of diet.
4. Frequent stress. “All diseases are from nerves” - this folk wisdom has a completely scientific justification.
A combination of any of these factors, if left unchecked and predisposed to diabetes, will almost certainly trigger the disease.
The main insidiousness of diabetes is that this disease develops imperceptibly, and can disguise itself as various diseases, a common symptom of which is fatigue, weakness, even with enough time for sleep and rest.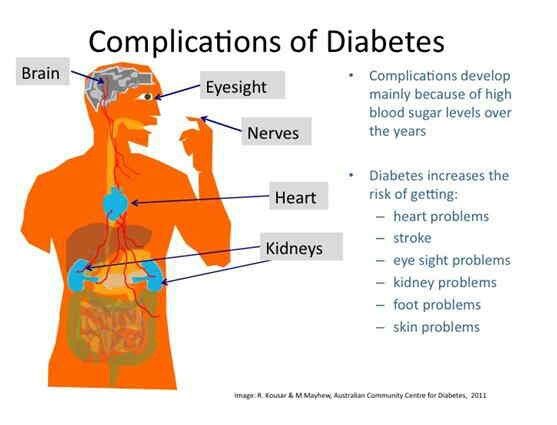 In diabetes, all types of metabolism are disrupted, which means that all organs suffer, losing the ability to function normally. Believe me, the body will definitely tell you that it needs help: don’t be patient and don’t hope that “it will pass by itself”. Metabolic disorders do not go away on their own. nine0003
In diabetes, all types of metabolism are disrupted, which means that all organs suffer, losing the ability to function normally. Believe me, the body will definitely tell you that it needs help: don’t be patient and don’t hope that “it will pass by itself”. Metabolic disorders do not go away on their own. nine0003
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent diabetes) and type 2 diabetes (non-insulin-dependent diabetes). In type 1 diabetes, more than 90% of the pancreatic islet beta cells that produce insulin are destroyed. Therefore, diabetics need insulin injections every day. It is possible for type 2 diabetes to develop into type 1 diabetes. In the second type, the pancreas sometimes produces even more insulin than it needs, but it is not absorbed by the body, and a person may also need insulin injections. nine0003
Symptoms of diabetes mellitus:
polyuria - frequent urination
thirst (when, regardless of the amount of liquid, a person cannot quench it)
increased appetite
increased fatigue and severe weakness both in the morning and in the evening;
frequent SARS;
itching, dry skin and mucous membranes, itching and irritation in the genital area;
purulent skin diseases;
irritability.
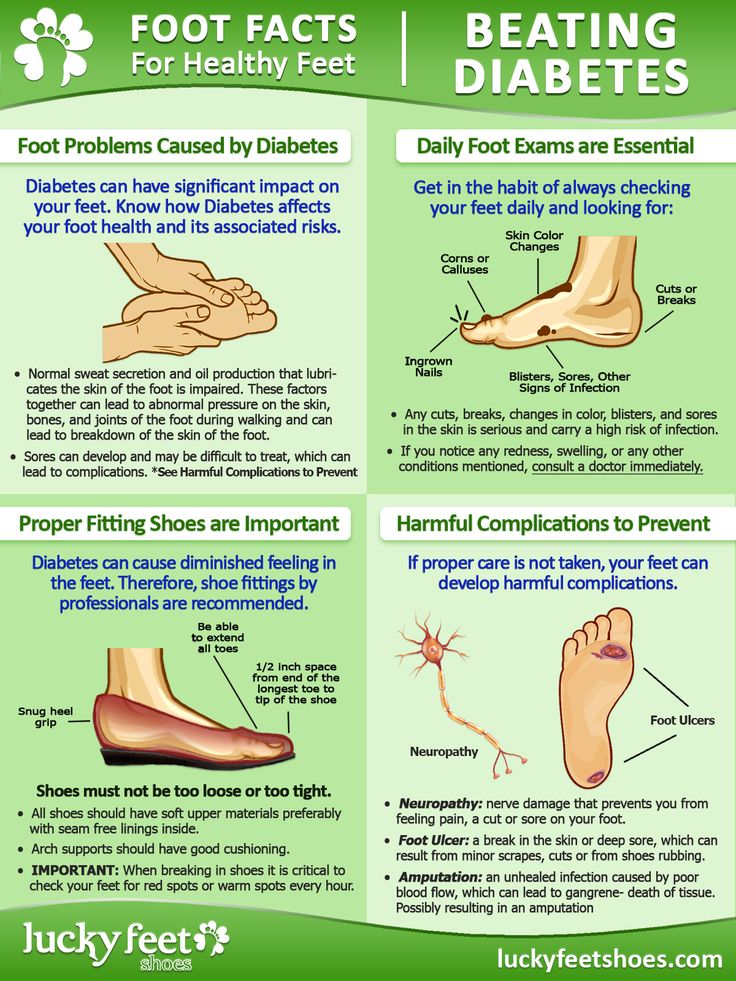
The danger of diabetes in its complications. The most severe are trophic ulcers that do not heal and are practically not treated, the so-called "diabetic foot", when, due to a deterioration in the blood supply to the tissues of the limb, tissue necrosis develops, damage to the vessels of the retina of the eyes, which can lead to a serious deterioration in vision, and in some cases - and to blindness. Since diabetes damages the walls of blood vessels, the blood supply to tissues and organs worsens. Patients with diabetes should strictly monitor their diet all their lives, avoid eating prohibited foods, since a violation of the diet inevitably leads to a worsening of the course of the disease, and ignoring the prohibitions leads to serious complications, which are often impossible to cure. nine0003
What can you do if you are at high risk of getting sick?
The first is to pay attention to what you eat. The second is to analyze how often you are nervous, and for what reasons, you may be able to reduce the amount of stress in your life.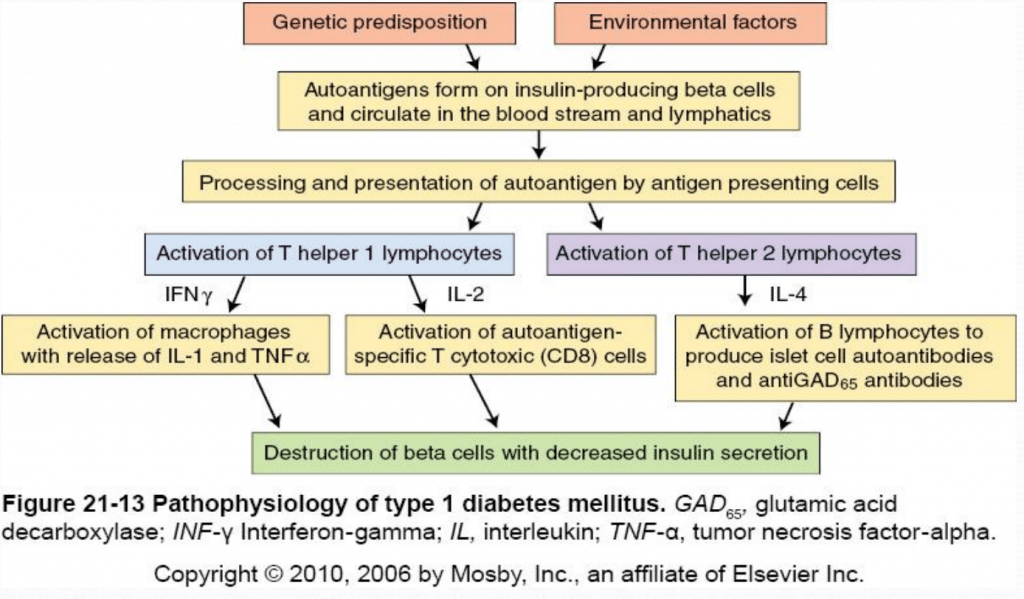 And the third thing is to remember that you yourself should take care of your health first of all. Observe your body, do not ignore the emerging "strangeness", set out to find out the cause of frequent SARS. If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor. You can sign up for a consultation with an endocrinologist on your own, or first contact a therapist to pass the most common test - blood sugar. Based on the results, the doctor will determine a further follow-up strategy. You don’t need to self-diagnose yourself, and even more so, prescribe treatment. The use of drugs without a doctor's prescription to lower blood sugar levels is unacceptable. Those who trust exclusively folk methods of treatment should remember that no methods of diabetes will cure, since there are no natural analogues of insulin. Plant-based preparations can be used, but only after prior consultation with a doctor. nine0003
And the third thing is to remember that you yourself should take care of your health first of all. Observe your body, do not ignore the emerging "strangeness", set out to find out the cause of frequent SARS. If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor. You can sign up for a consultation with an endocrinologist on your own, or first contact a therapist to pass the most common test - blood sugar. Based on the results, the doctor will determine a further follow-up strategy. You don’t need to self-diagnose yourself, and even more so, prescribe treatment. The use of drugs without a doctor's prescription to lower blood sugar levels is unacceptable. Those who trust exclusively folk methods of treatment should remember that no methods of diabetes will cure, since there are no natural analogues of insulin. Plant-based preparations can be used, but only after prior consultation with a doctor. nine0003
Change in diet will help reduce blood sugar levels: reducing or completely eliminating the use of flour, starchy foods, processed meat (sausages and others), white sugar, sweet carbonated drinks, alcohol in any form. At the same time, it must be remembered that honey is not a safe substitute for sugar, as it contains fructose, and you need to use it carefully. Just like sweet fruits and berries. Of the fruits, apples are most preferable, since many others contain a large amount of natural sugar - fructose, and this should also be avoided. nine0003
At the same time, it must be remembered that honey is not a safe substitute for sugar, as it contains fructose, and you need to use it carefully. Just like sweet fruits and berries. Of the fruits, apples are most preferable, since many others contain a large amount of natural sugar - fructose, and this should also be avoided. nine0003
If abnormalities are found after the examination, the doctor will definitely give you nutritional recommendations, and the more carefully you follow them, the better you will feel.
This equally applies to both adults and children, because, unfortunately, cases of diabetes among them are not decreasing, and it is much more difficult for a child to comply with forced restrictions due to illness than for an adult.
When symptoms of diabetes appear, it is imperative to consult a doctor, as the development of the disease without appropriate treatment threatens life-threatening conditions. nine0003
How not to get diabetes? And what do we know about this disease?
Sign up for our ”Context” newsletter: it will help you understand the events.
Image copyright, Getty Images
Photo caption,Type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence. Sometimes it has a genetic cause, but it can also be caused by a viral infection
Diabetes is a serious disease that kills more than a million people every year and can affect anyone. nine0064
Diabetes occurs when our body cannot cope with the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The blood becomes thick, and over time, this can lead to heart attack, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, and gangrene of the lower extremities.
Diabetes is on the rise: there are 422 million diabetics in the world today, almost four times as many as just 40 years ago, according to WHO.
However, despite the huge threat that diabetes poses to health, half of diabetics are not even aware of their disease. nine0003
- Scientists: serious illnesses can be cured by "deceiving" the patient's nervous system
- We reduce our sleep ourselves, and the consequences are very disturbing
- Experiment: why we get fat from stress It is enough to simply change your habits and adjust your lifestyle.
 Here's how it's done.
Here's how it's done. What causes diabetes?
When we eat food, our body converts the carbohydrates it contains into sugar (glucose). Insulin, a pancreatic hormone, is responsible for its absorption, which gives the cells a signal to absorb glucose dissolved in the blood and use it as an energy source. nine0003
Diabetes occurs when the production of insulin stops or the hormone stops working properly, causing sugar to build up in the blood.
Image copyright Getty Images
What are the types of diabetes?
There are several types of diabetes.
In type 1 diabetes the pancreas stops producing insulin and sugar begins to accumulate in the blood. Most often this happens quite early - in childhood or adolescence. nine0003
Scientists still do not know exactly why this happens, but they believe that a genetic predisposition or a viral infection that damages the cells of the pancreas responsible for the production of insulin may play a role.
 Approximately 10% of diabetics suffer from type 1 diabetes.
Approximately 10% of diabetics suffer from type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetics insulin production does not stop completely, but either not enough is produced, or something prevents it from working effectively. nine0003
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image captionInsulin, which helps our bodies process sugar, is produced by the pancreas
This usually occurs in middle age or later in life, but type 2 diabetes can also occur in younger people if they are obese or lead a sedentary lifestyle. Representatives of certain peoples are also more inclined to it - especially people from South Asia.
Pregnant women are sometimes diagnosed with gestational diabetes - this means that their body does not produce enough insulin to provide enough for themselves and the unborn child. nine0003
Depending on the assessment criteria, between 6 and 16% of all pregnant women can be diagnosed with this diagnosis - they need to carefully monitor their blood sugar levels, keeping them normal through diet, exercise and / or insulin injections so that they do not developed type 2 diabetes.
There is also the so-called pre-diabetes - an increased level of glucose in the blood, which can also lead to the development of a full-fledged disease.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image caption,Fatigue, persistent thirst, and frequent urination can be signs of developing diabetes
Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Constant thirst
- unusually frequent urination, especially at night
- increased fatigue
- weight loss for no reason
- decreased visual acuity
- cuts and scrapes that take a long time to heal
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes most often develop during childhood or adolescence and are much more pronounced.
The risk group for type 2 diabetes usually includes people over 40 years of age (South Asians - over 25), as well as relatives of diabetics (siblings, children) and people who are overweight.

Can I prevent the disease?
The risk of developing diabetes depends on genetic and environmental factors, but you can keep your blood sugar at normal levels through a healthy diet and an active lifestyle. nine0003
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image caption,One way to reduce your risk of diabetes is to replace refined sugars and white flour products with fruits and whole grain products
Skip the Podcast and continue reading.
Podcast
What was that?
We quickly, simply and clearly explain what happened, why it's important and what's next.
episodes
The End of the Story Podcast
You can start by cutting back on confectionery and sugary drinks, and replacing white bread and pasta with wholemeal products.
 nine0003
nine0003 Foods made from refined sugar and refined grains contain fewer nutrients because vitamins and fibers are found predominantly in the hulls of grains. Examples of such foods are white flour, white bread, white rice, white pasta, baked goods, sodas, sweets, and sugar-added breakfast cereals.
A healthy diet includes vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains, as well as healthy vegetable oils, nuts, and fish varieties rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as sardine, salmon, or mackerel. nine0003
It is important to eat at regular intervals to avoid overeating.
Exercise can also help lower blood sugar levels. Doctors recommend spending at least two and a half hours a week doing aerobic activities like walking or climbing stairs.
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image caption,Avoiding a sedentary lifestyle and exercising at least two and a half hours a week is important
It will be easier for the body to maintain normal blood sugar levels if you are not overweight.
 But if you need to lose weight, it is better to do it slowly, losing no more than 0.5-1 kg per week.
But if you need to lose weight, it is better to do it slowly, losing no more than 0.5-1 kg per week. The best way to reduce your risk of heart disease is to not smoke and keep your cholesterol levels under control.
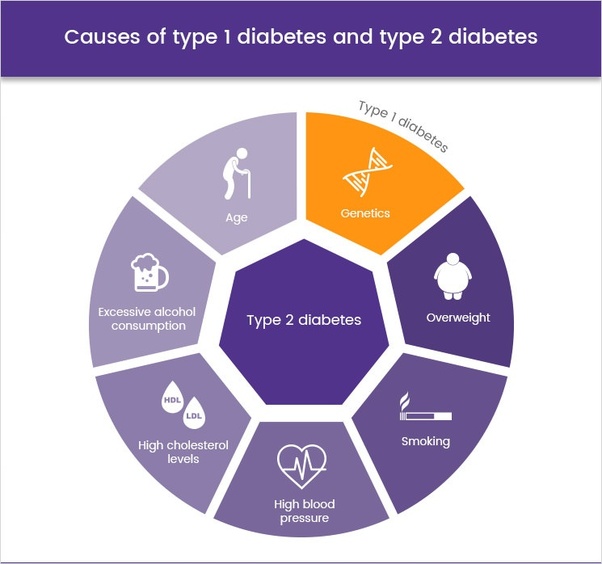
What are the complications of diabetes?
High blood sugar levels can severely damage blood vessels.
When the blood thickens, it becomes more difficult for it to move around the body - it may not reach some cells at all, which increases the risk of nerve damage (loss of sensation and pain), loss of vision and infectious diseases of the feet. nine0003
According to WHO, diabetes is one of the main causes of blindness, kidney failure, heart attack, stroke and gangrene of the lower extremities leading to leg amputation.
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image caption,A heart attack is one of the possible complications of diabetes
In 2016 alone, about 1.