How to increase platelets count in child
How to and what to know
Platelets are blood cells that promote blood clotting to help prevent bleeding. A person may be able to increase their platelet count naturally by consuming foods that are high in certain vitamins.
It is essential to maintain adequate platelet levels to ensure that the blood clots correctly. Doctors diagnose people with thrombocytopenia if they have a low platelet count. They can offer advice on ways to increase platelet levels through nutrition, including both the diet itself and supplements.
This article describes what thrombocytopenia is, including its symptoms. It also lists foods and supplements that may help increase platelet counts and those that may decrease them. Finally, it provides tips that could help a person determine whether their platelet count is low.
Thrombocytopenia is the medical term for a low blood platelet count. Platelets are colorless blood cells that play a vital role in blood clotting. If a person sustains an injury, these cells will clump together to form a seal over the injured blood vessel, thereby helping prevent bleeding.
According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), the platelet count in adults is somewhere in the range of 150,000—450,000 platelets per microliter (μl) of blood. Thrombocytopenia is when a person’s platelet count falls below 150,000 platelets per μl of blood.
Platelets are essential to blood clotting, so a person with thrombocytopenia will be more prone to bleeding. According to the NHLBI, most symptoms of thrombocytopenia related to bleeding.
Mild thrombocytopenia often does not cause any symptoms. In these cases, a person may only learn that they have the condition following a routine blood test.
The symptoms of thrombocytopenia usually only occur when a person’s platelet levels are particularly low. They may include:
- persistent bleeding following even a small injury
- nosebleeds
- bleeding gums
- blood in the urine
- blood in the stool, which may appear bright red, dark, or tarry
- heavy menstrual bleeding
- bruising easily
- petechiae, which are small, flat, red or brown spots beneath the skin due to leaking blood vessels
- purpura, which is a red, purple, or brownish-yellow skin patch due to bleeding beneath the skin
People who experience symptoms should contact a doctor immediately. Without treatment, thrombocytopenia can cause severe complications.
Without treatment, thrombocytopenia can cause severe complications.
Several vitamins and minerals can promote a higher platelet count.
Folate-rich foods
Folate, or vitamin B9, is an essential B vitamin for healthy blood cells. Folic acid is the synthetic form of folate.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), adults require at least 400 micrograms (mcg) of folate daily, with pregnant people needing 600 mcg.
Foods containing folate or folic acid include:
- beef liver
- dark, leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and Brussels sprouts
- black-eyed peas
- fortified breakfast cereals and dairy alternatives
- rice
- yeast
People should be careful not to consume excessive amounts of folic acid from supplements or fortified foods because high levels can interfere with vitamin B12 function.
Vitamin B12-rich foods
Vitamin B12 is necessary for the formation of red blood cells. Low levels of vitamin B12 in the body may also contribute to low platelet counts.
According to the NIH, people aged 14 years and over require 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 daily. People who are pregnant or nursing require up to 2.8 mcg.
Vitamin B12 is primarily present in animal-based products, including:
- beef and beef liver
- eggs
- fish, such as:
- clams
- trout
- salmon
- tuna
People who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet can get vitamin B12 from the following:
- fortified cereals
- fortified dairy alternatives, such as almond milk or soy milk
- supplements
Vitamin C-rich foods
Vitamin C plays a vital role in immune function. It also helps the platelets function correctly and enhances the body’s ability to absorb iron, which is another nutrient that is essential for a healthy platelet count.
Many fruits and vegetables contain vitamin C, including:
- broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- red and green bell peppers
- citrus fruits, such as oranges and grapefruit
- kiwifruit
- strawberries
Vitamin D-rich foods
Vitamin D contributes to the proper functioning of the bones, muscles, nerves, and immune system.
According to the Platelet Disorder Support Association (PDSA), vitamin D also plays an essential role in the function of the bone marrow cells that produce platelets and other blood cells.
The body can produce vitamin D from sun exposure. However, not everybody receives enough sunlight each day, especially if they live in colder climates or regions that are farther away from the equator.
Adults aged 19–70 years require 15 mcg of vitamin D daily, while those over 70 years of age require 20 mcg per day.
Food sources of vitamin D include:
- egg yolk
- oily fish, such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel
- fish liver oil
- fortified milk and yogurt
People who follow a vegan diet can get vitamin D from the following:
- fortified breakfast cereals
- fortified dairy alternatives, such as soy milk and soy yogurt
- fortified orange juice
- UV-exposed mushrooms
- supplements
Vitamin K-rich foods
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health.
In an informal PDSA survey, almost 27% and 32% of people who took vitamin K reported an improvement in their platelet counts and bleeding symptoms, respectively.
An adequate intake of vitamin K for adults aged 19 years and over is 120 mcg for males and 90 mcg for females.
Foods rich in vitamin K include:
- leafy greens, such as collards, turnip greens, spinach, and kale
- broccoli
- pumpkin
- soybeans and soybean oil
- natto, which is a fermented soybean dish
Certain foods and drinks can decrease platelet counts. Examples include:
- the artificial sweetener aspartame
- cranberry juice
- quinine, a substance in tonic water and bitter lemon
According to a 2020 review, regular excessive alcohol consumption may also reduce platelet counts.
Some supplements can also increase platelet counts.
However, it is important to check with a doctor before taking a new supplement, as some can worsen certain conditions or interact negatively with other medications or supplements.
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment in plants. Algae-based supplements, such as chlorella, are rich in chlorophyll.
Taking chlorophyll may alleviate some of the symptoms of a low platelet count, although research on its effectiveness is limited. The PDSA mentions chlorella as a potential supplement for those with a low platelet count.
In the PDSA survey, of the participants who took chlorella, 19% reported increased platelet counts, and 33% reported improvements in their bleeding symptoms.
Papaya leaf extract
A 2017 study investigated the effect of papaya leaf extract (PLE) on platelet count among people with chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia.
The researchers divided the 40 participants into two groups of 20. All participants had completed a round of chemotherapy 7 days before the start of the study. One group received 7 days of treatment with PLE, and the other did not receive any treatment.
The study found that by day 13 post-chemotherapy, platelet counts significantly increased for the group who had taken the PLE. There was no significant increase in platelet counts for the group that did not receive any treatment. These findings suggest that PLE may help boost platelet counts, though controlled clinical trials are necessary to support this claim.
There was no significant increase in platelet counts for the group that did not receive any treatment. These findings suggest that PLE may help boost platelet counts, though controlled clinical trials are necessary to support this claim.
Papaya leaf extract is available in health stores in pill form.
According to the PDSA, certain supplements can reduce platelet levels. Supplements to avoid include L-tryptophan and vitamin B3, or niacin.
It is not yet clear whether other supplements may also reduce a person’s platelet counts. As a result, the PDSA warns that a person who receives a diagnosis of thrombocytopenia should notify the doctor of any new supplements they have been taking.
People with a low platelet count may be able to improve their condition by eating specific foods and taking certain supplements. Foods that may be of benefit include those containing folate and those rich in vitamins B12, C, D, or K.
Supplements that may help include chlorophyll and papaya leaf extract. However, a person should always ask for a doctor’s advice before starting a new supplement, as some can interact negatively with other medications or supplements.
However, a person should always ask for a doctor’s advice before starting a new supplement, as some can interact negatively with other medications or supplements.
People with thrombocytopenia should also avoid substances that could decrease their platelet count, such as cranberry juice, aspartame, and quinine. They should also avoid the supplements L-tryptophan and niacin.
It is advisable to seek medical advice before adjusting the diet, as dietary adjustments alone may not be sufficient to restore platelet levels.
How to Improve Platelet Count in Child? Foods to Increase Platelets
Children suffering from low platelet count are at a risk of bleeding more when compared to others. Here is a list of foods that can help increase the blood platelet count naturally
After last week's visit to the family doctor, Rati Agnihotri, mother to six-year-old Drupad, is worried for her son. For the past few months, Rati has been noticing that whenever Drupad sustained an injury or a cut during play, the bleeding would continue for a long time. Initially, Rati thought it wasn't anything serious. However, when it persisted, she sought a medical opinion and discovered her son was suffering from thrombocytopenia a condition caused by a low platelet count in the blood. This caused her son to bleed excessively when compared to other children.
Initially, Rati thought it wasn't anything serious. However, when it persisted, she sought a medical opinion and discovered her son was suffering from thrombocytopenia a condition caused by a low platelet count in the blood. This caused her son to bleed excessively when compared to other children.
Often, children with a low platelet count are prone to bleeding and bruising easily. Even a minor injury like a cut after a fall may lead to excess bleeding.
What is a platelet count?
Platelets are a component of blood that helps in blood clotting by clumping together and forming plugs. A platelet count represents the number of platelets present in 1 microlitre of blood.
Typically, the normal range for platelet count is 1,50,000 to 3,00,000 per microlitre of blood. In the case of thrombocytopenia, the patient's platelet count would be well below the normal count of 1,50,000. When there is a significant drop in the platelet count, say below 20,000, additional platelets need to be given through transfusion* to support the child as there is a serious risk of excessive blood loss during injury, says Dr Santanu Sen, Consultant in Paediatrics, Paediatric Oncology & Stem Cell Transplantation.
*Transfused platelets only last for three days; so some children may require more than one transfusion.
What causes low platelet count in children?
The reason for low platelet count or thrombocytopenia in children is often due to a condition known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). The immune system of the body mistakenly starts attacking and destroying the platelets due to unknown causes. Low platelet count can also be due to disorders such as bacterial or viral infections, blood cancer, bone marrow failure, a side effect of medications and exposure to toxic chemicals.
When there is a significant drop in the platelet count, say below 20,000, additional platelets need to be given through transfusion to support the child as there is a serious risk of excessive blood loss during injury Does blood transfusion help increase platelet count?
Blood transfusion plays no role in increasing the platelet count, says Dr Sen. At the most, transfusion will only improve haemoglobin levels for an anemic child. For the platelet count to move up, the child who has a low platelet count will need a platelet transfusion. Treatment and medication can also help ease the condition, he adds.
At the most, transfusion will only improve haemoglobin levels for an anemic child. For the platelet count to move up, the child who has a low platelet count will need a platelet transfusion. Treatment and medication can also help ease the condition, he adds.
How to increase low platelet count in children?
Often, the medication to boost platelet count in children is expensive and treatment options involve hospitalization. While many cases may require the child to undergo medical treatment, the best way to increase platelet count in children is through the consumption of certain foods such as:
- Folate-rich food
- Food loaded with vitamins B-12, C, D and K
- Iron-rich food
Foods that increase blood platelets count naturally in kids
1. Pomegranate
This fruit contains minerals that help fight low platelet count in children. It is rich in antioxidants, which help in boosting the immune system. You can either give your child pomegranate juice or add the fruit to different types of salad.
You can either give your child pomegranate juice or add the fruit to different types of salad.
2. Papaya
This fruit is known for its medicinal properties that include maintaining a good platelet count. Children who are suffering from dengue should have papaya to revive their blood platelet count. Fresh papaya helps the body produce healthy blood cells.
3. Pumpkin
Along with its seeds, pumpkin helps in the production of new red blood cells and reviving the platelet count. Pumpkin contains high levels of iron, which spikes the production of platelets in the bloodstream.
4. Eggs
Eggs contain significant amounts of vitamin B12, which play an important role in the formation of red blood cells. Low levels of this vitamin may contribute to low platelet count in children.
Consuming eggs regularly can help children get the required amount of vitamin B12 in the body. This, in turn, prevents the platelet count from falling below normal.
This, in turn, prevents the platelet count from falling below normal.
5. Broccoli
This green vegetable is loaded with vitamin C, which enhances the ability of the body to absorb iron, which in turn helps increase platelets.
6. Milk and yogurt
These are both rich in vitamin D, which plays a vital role in the normal functioning of the bone marrow that produces platelets and other blood cells.
Tips for children with low platelet count
Although it is difficult to prevent the occurrence of excessive bleeding completely in children suffering from low platelet count or thrombocytopenia, certain tips may help as mentioned below:
- Let them avoid or limit sports activities that involve rough play like football or contact sports.
- Pad their bed as this could help protect them from unforeseeable cuts or bruises at night.
- Make them exercise with great care when they are around sharp and pointed objects (in fact, this will apply to children in general; always ensure they are supervised).
- During hospital visits, let the doctor know of your childs condition before any injection or vaccination is administered.
The vital role of platelets
The University of Rochester Medical Centers Health Encyclopedia describes platelets thus: Platelets are tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding. If one of your blood vessels gets damaged, it sends out signals that are picked up by platelets. The platelets then rush to the site of damage and form a plug or clot to repair the damage. So, if your child gets a cut anywhere on his body during play or an accident, the platelets will be responsible for stopping the bleeding. But, in the case of low platelet count, excess blood loss can occur resulting in health conditions like anemia.
Thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytosis
If your child has over 4,50,000 platelets, it is not a healthy count. In fact, it can be a sign of thrombocytosis. The excess number of platelets in the blood may indicate a blood and bone marrow disease.
There are two types of thrombocytosis:
- Primary thrombocytosis: This is caused by the presence of abnormal cells in the bone marrow.
- Secondary thrombocytosis: This is caused by anemia or cancer.
Thrombocytopenia
If your child has less than 1,50,000 platelets, it is a sign of thrombocytopenia. Symptoms of such a low platelet count include easy bruising, frequent bleeding from the gums and nose, and abnormal bleeding from cuts.
If you suspect your child may have a low platelet count, a simple blood test will confirm or rule it out. Also, having a low platelet count does not mean your child should stop playing games or going out completely, for fear of an injury or a cut. If proper preventive measures are followed, including ways to control the bleeding, as advised by your doctor, then it will go a long way in helping your child.
Platelets in children: nutrition to increase platelets
Tips for mothers
How to increase platelets in children?
- Photo
- Getty
Low platelets in children: causes
Platelet count is one of the most important indicators of health status.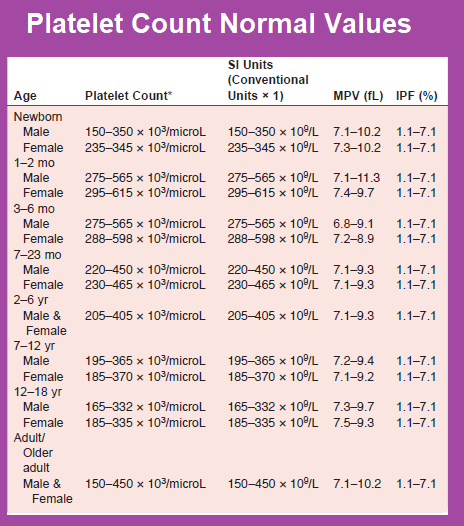 After all, these cells are involved in the processes of blood clotting and healing of damaged areas of blood vessels. A decrease or increase in the number of platelets in a child may indicate the presence of serious diseases.
After all, these cells are involved in the processes of blood clotting and healing of damaged areas of blood vessels. A decrease or increase in the number of platelets in a child may indicate the presence of serious diseases.
The most common condition is when the level of these blood cells in a child is low. It's called thrombocytopenia. This condition is dangerous in that the blood does not coagulate well and with the slightest injury there can be severe bleeding. A decrease in platelet levels can be caused by various factors:
- taking certain medications: antibiotics, painkillers, diuretics or corticosteroids;
- anemia;
- parasitic infestation;
- malnutrition;
- lack of certain vitamins;
- chemical poisoning;
- infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, measles or rubella.
Thrombocytopenia is very dangerous because the walls of blood vessels become thin. The most common complication of this condition is internal bleeding and large blood loss.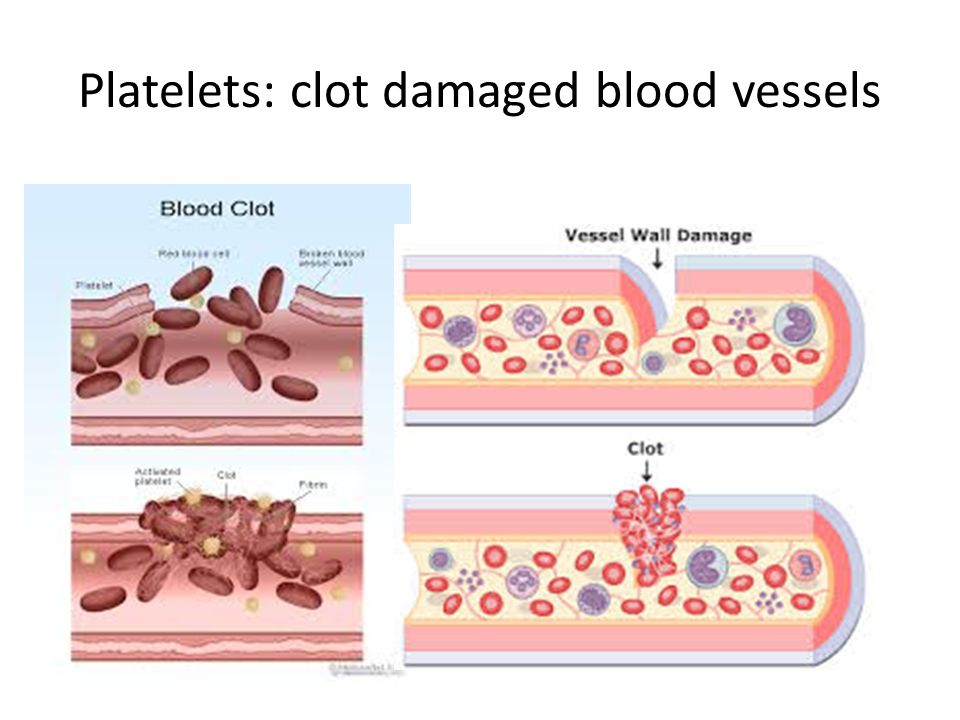
How to understand that platelets are low in a child
The level of blood cells is determined by analysis. But even without him, parents can understand that the child's platelets are low. This is indicated by the following symptoms:0003
- bruises and hematomas often appear on the body;
- epistaxis or intestinal bleeding;
- after the slightest damage to the skin it is very difficult to stop the bleeding;
- skin may have red dots, asterisks;
- gums bleed after brushing teeth.
If you notice these symptoms, it's time to take a blood test and see a doctor to decipher it.
Nutrition to increase platelets in children
Treatment of thrombocytopenia is prescribed taking into account the underlying disease that caused it. But it is very important for parents to know how to behave with such a child. For a sick baby, adult care is needed, compliance with measures to prevent bleeding. You need to protect him from injury. The child should move less, sleep well, spend a lot of time outdoors and eat right. It is nutrition that is effective in increasing platelets in children.
The child should move less, sleep well, spend a lot of time outdoors and eat right. It is nutrition that is effective in increasing platelets in children.
There are foods that thin the blood. They should be excluded from the diet of a child with thrombocytopenia. These are ginger, tomato juice, citrus fruits, raspberries, cucumbers, cranberries and some other products.
A child with thrombocytopenia needs a change in diet. It needs to be enriched with foods rich in vitamins C, A and B. Parents should try to ensure that the child adheres to the following rules:
- consume as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible;
- refused canned food and products with artificial flavors and colors;
- excluded from food spicy dishes, too hot and cold, and coarse food that can damage the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- did not eat high-calorie meals.
Foods that increase platelets in children should include the following foods: nuts, parsley, eggs, buckwheat and rice, liver, sea fish, legumes, pomegranates, melons, linseed oil, and beets. It is useful to add sesame oil to food.
It is useful to add sesame oil to food.
If there is a risk of internal bleeding, the food should be sparing: not hot, not spicy and puree. It is advisable to additionally take vitamin preparations recommended by the doctor.
Parents need to be very attentive to the health of the child. At the slightest suspicion of a change in the composition of the blood, it is necessary to consult a doctor for an examination.
Read also: the skin on the hands will peel off
Wday.ru editors
Read today and other flashes of stars: 55 embarrassing photos
Six fingers, three nipples: 18 stars with congenital flaws, which they are not at all embarrassed about
Voting for the most beautiful office employee starts 2022
7 signs that say that there were serfs in your family - and you did not know
Thrombocytopenia in children and adults: causes, treatment, symptoms
General practitioner
Ablyazov
Irshat Ravilevich
Experience 22 years
District therapist of the highest category. Member of the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists.
Member of the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists.
Make an appointment
Thrombocytopenia is a single disease or a symptom of another disease, which is characterized by low platelets (less than 150,000 units per microliter). The condition is accompanied by high bleeding, as well as a slow stop of bleeding from small vessels.
Risk groups
Most often, the disease manifests itself either in preschool age, or after forty years. In children, thrombocytopenia is much less common - about 50 cases per million. Women suffer from this condition more often - three times more than men.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia include:
- Purple. So called hemorrhages in mucous tissues or skin. In fact, it looks like red spots - most often they can be seen in places of strong contact with clothing. The spots do not hurt, they can be pinpoint or quite extensive - including bruising, bruising of different colors (depending on the time of formation).

- Regular nosebleeds. Since the small vessels are weakened, bleeding can begin due to a cold, sneezing, or a minor injury. Bright red blood can flow for ten minutes or more, so the patient is at risk of losing a lot of blood.
- Bleeding gums, prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction. The mechanism is the same: due to weak blood vessels, the blood cannot quickly stop with small and large injuries.
- Bleeding of internal organs. For example, there is blood in the gastrointestinal tract when the feces become colored, or in the genitourinary system - then the urine is already stained. Both symptoms are very disturbing and require immediate medical attention.
- Menses too profuse and long. Moreover, bleeding can be observed on other days of the cycle.
All of these symptoms may indicate other diseases - both concomitant thrombocytopenia, and independent. The situation is also complicated by the fact that there are a lot of reasons and mechanisms for the development of this condition. In medicine, there are several types of such a disease.
In medicine, there are several types of such a disease.
Classification of thrombocytopenia
Let's talk about what causes thrombocytopenia underlie different types of this disease.
Hereditary thrombocytopenia
These conditions are based on diseases of genetic origin. These can be May-Hegglin anomaly, Bernard-Soulier syndrome, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, TAR syndrome, as well as congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia.
Each of these diseases has many characteristics. For example, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome occurs exclusively in boys and occurs in four to ten cases per million. Bernard-Soulier syndrome can only develop in a baby who received an altered gene from both parents, and May-Hegglin anomaly can develop in 50% of cases, provided that only one parent has the prerequisites for this.
As a rule, all of these diseases have among the symptoms not only a low level of platelets, but also a number of other pathological conditions, and therefore require special treatment.
Productive thrombocytopenia
They are also caused by a huge list of causes and factors of very different origins. All of them are connected with the fact that in the red bone marrow the processes of formation of platelets are disturbed.
For example, this includes some types of anemia, cancer metastases, acute leukemia, and the use of cytotoxic drugs. There are even factors such as radiation or alcohol abuse.
For example, in acute leukemia, a disease of the circulatory system provides a mutation of the bone marrow stem cell. Because of this, it divides and begins to displace hematopoietic cells. As a result, the number of not only platelets decreases, but also leukocytes, erythrocytes, and lymphocytes. This condition is called pancytopenia. That is, immune thrombocytopenia in this case is part of it.
If we are talking about the effect of medications, then most often a decrease in the level of platelets is caused by drugs from the following groups:
- antidiabetic,
- anti-inflammatory,
- antipsychotics,
- antithyroid,
- antibiotics,
- diuretics,
- anticonvulsants.
Of course, not all medicines and not in all cases are capable of causing such a reaction, but this is another reason to think that you should not prescribe any medicines on your own and drink without the supervision of your doctor.
Moreover, there is also such a factor as hypersensitivity to certain medications. Usually it is initially determined by a kind of genetic predisposition, but this is quite rare.
When we talk about radiation, we are talking not only about a person's stay in dangerous areas, but also about treatment with radiation therapy. When the tumors are destroyed, the hematopoietic cells of the red brain can be affected, so the condition when the level of platelets drops can become a side effect of cancer treatment.
The development of symptoms of thrombocytopenia with alcohol abuse most often occurs against the background of binges and is associated with a high level of ethyl alcohol in the blood. It has a negative and long-term effect on the bone marrow and usually causes a temporary decrease in platelets. If binges become frequent and too long, there is a risk that the changes will be irreversible.
If binges become frequent and too long, there is a risk that the changes will be irreversible.
Thrombocytopenia destruction
Here we are talking about the active destruction of platelets, which is usually observed in the spleen. Such processes are also caused by a large number of factors. Among them are the use of certain drugs, certain viruses, Fisher-Evans syndrome, etc.
A separate consideration is idiopathic thrombocytopenia. This is the case when it is not possible to establish the cause even with a huge number of possible options. At the same time, doctors note that even in such a situation, the action of provoking factors is observed. For example, the problem manifests itself after bacterial and viral infections, preventive vaccinations, the use of a number of medications, hypothermia or prolonged exposure to the sun.
This condition also occurs in newborns. It begins to form in the womb, when antibodies in her body cause the destruction of the baby's platelets.
Fisher-Evans syndrome is also not an independent cause, since he himself is a consequence of various systemic diseases. Such a syndrome occurs in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, but in some cases it can be an independent deviation.
As for viruses, rubella, chicken pox, measles, influenza can lead to a decrease in platelet levels. Sometimes this is a reaction to vaccination, although such a mechanism is described quite rarely and almost never occurs.
Thrombocytopenia of consumption
Here the mechanism is as follows: for some reason, platelets begin to be activated in the vascular bed. In response to this, the red bone marrow begins to actively produce them - and as a result, its capabilities are slowly depleted. After that, the level of red cells begins to fall.
One of the causes of consumption thrombocytopenia is DIC. It stands for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Syndrome. And it can develop against the background of severe tissue destruction during operations, burns, injuries, due to severe infections, chemotherapy, organ transplants, etc.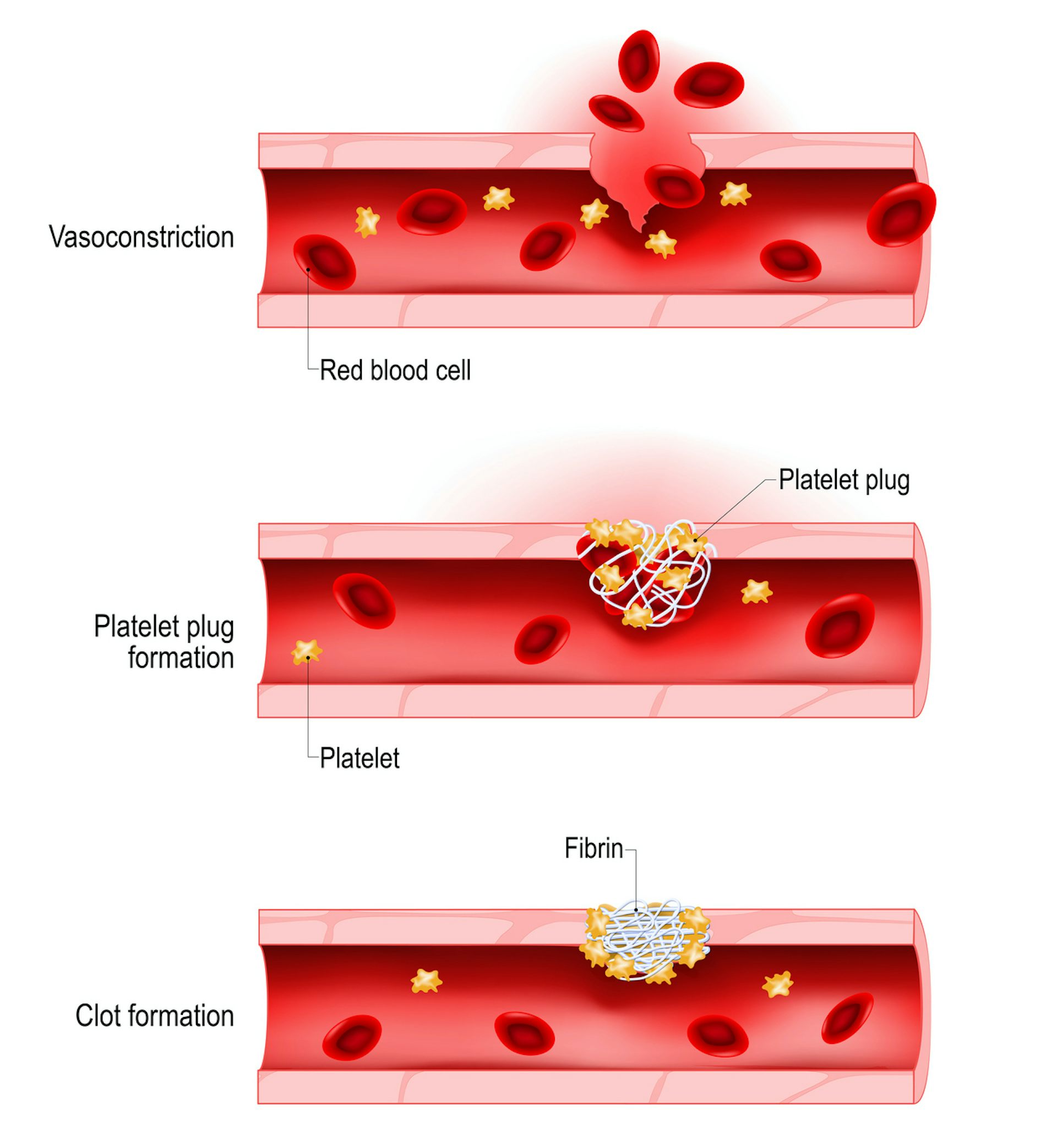 That is, there are many reasons that can cause a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood.
That is, there are many reasons that can cause a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood.
Thrombocytopenia redistribution
If it is very simple to explain this mechanism, then it looks like this: against the background of some reasons, the patient has an enlarged spleen. And if under normal conditions it stores up to 30% of platelets, then in an enlarged state it retains up to 90% of these cells. At the same time, the system does not see that there are not enough platelets, and does not trigger a compensatory mechanism.
The mechanism is also based on various reasons: cirrhosis of the liver, some infections like tuberculosis, autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus), tumors of the circulatory system, alcoholism.
Thrombocytopenia dilution
This condition is usually observed in people who receive a large number of transfusions of various liquids: for example, plasma, plasma substitutes, etc. As a result, the level of platelets decreases due to the banal dilution of blood.
Given the huge number of reasons that can cause immune thrombocytopenia (and we have named far from all the options), a patient with its symptoms should immediately consult a doctor who will find the essence of the problem and prescribe an effective treatment.
Diagnostics
Since there are a lot of reasons, it is not possible to name diagnostic measures in detail - everything will depend on the specific situation. But we can distinguish the main components of the diagnosis:
- Complete blood count.
- Bleeding time test (Duke analysis).
- Determining the time it takes for blood to clot.
- Red bone marrow puncture. The method allows to reveal quantitative and qualitative changes in cells.
- Determination of antibodies in the blood.
- Examination for genetic diseases.
- Ultrasound of internal organs. Most often, the liver and spleen are immediately studied, but this list can be very large.

- MRI. Used to study internal organs and blood vessels.
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a visit to a general practitioner, who, based on a survey, initial examinations and analyzes, already appoints a visit to other specialists.
Treatment and severity
Treatment of thrombocytopenia most often comes down to identifying the primary disease and treating it, as well as eliminating various unpleasant symptoms.
In the process, it is also important to consider that the severity of thrombocytopenia varies:
Easy degree. Assumes that the concentration of platelets is from 50 to 150 thousand units per microliter. The condition of the capillaries is usually normal, bleeding does not develop. Usually at this stage, treatment is not needed - doctors recommend waiting and monitoring the development of the patient's condition.
Average degree. In this case, the concentration is 20-50 thousand units of platelets per microliter.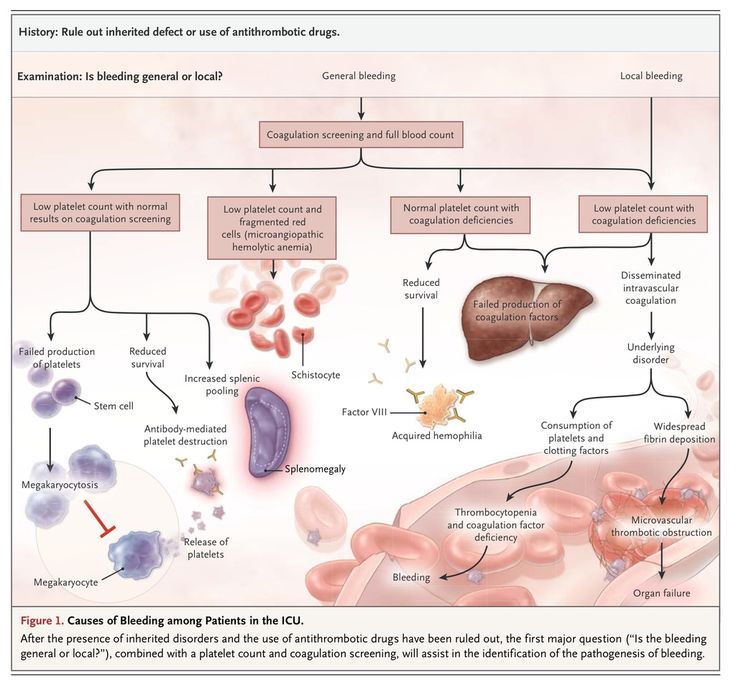 Under this condition, bleeding gums, nosebleeds are observed. If injuries and bruises occur, serious hemorrhages form in the skin. At this stage, drug therapy may be prescribed.
Under this condition, bleeding gums, nosebleeds are observed. If injuries and bruises occur, serious hemorrhages form in the skin. At this stage, drug therapy may be prescribed.
Severe degree. The platelet concentration is below 20 thousand, hemorrhages are spontaneous and strong. At the same time, the patient himself can feel quite comfortable, does not complain about feeling unwell, but the tests show that he needs help.
Since the treatment of thrombocytopenia requires the most thorough and detailed diagnosis, it is important to choose a modern clinic that will help you. JSC "Medicina" in Moscow is just the place where you can get qualified help from the best specialists. The clinic has everything necessary for the examination and treatment of each patient.
Questions and answers
What are the prognosis for thrombocytopenia?
It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously. Predictions can be calculated solely on the basis of the disease or factor that underlies the symptom.












