How to get your child back after losing custody
Lost Sole Custody of Your Children? 10 Ways to Regain Your Child Custody Rights
When going through a divorce or legal separation, a California family court of law may grant you sole or joint physical custody of your children. These arrangements will be detailed in the custody order, which outlines each parent’s child custody and visitation rights.
Family courts don’t prefer one ruling over the other. Instead, sole or joint custody is awarded based on the children’s best interests.
If you were awarded sole custody of your children, then you may have been granted sole physical custody or sole legal custody, or both.
Speak with a custody attorney near you. Call (858) 371-5569 or contact us online today to set up a consultation at Griffith, Young & Lass.
Sole Physical Custody in CA
Sole physical custody is referred to in family law as primary physical custody. This is where you have total rights to control the children’s whereabouts, school enrollment, after-school care, housing arrangements, medical and dental appointments, as well as the planning of any holidays or vacations.
Sole physical custody also means that the child would live solely with you at all times. You can usually travel in and out of state without restrictions unless those details are listed in the court order.
The non-custodial parent can still see the children, only that individual’s rights are limited to approved court visitation. Under family law, the noncustodial parent has the right to frequent contact and visitations with the children. The court may order supervised visitation or no visitation for extreme cases, such as in those cases where the noncustodial parent is known to abuse drugs, alcohol, or commit violent acts, for instance.
If you were awarded sole physical custody over the children, and you recently lost that right, it could have been for a number of reasons.
Reasons for Losing Sole Custody
In most cases, the process of stripping you of sole physical custody begins with the other parent notifying the courts of some type of issue concerning your parentage over the children. The other parent may cite abuse, neglect, or some other serious issue that they deem is a danger to the children’s well-being.
The other parent may cite abuse, neglect, or some other serious issue that they deem is a danger to the children’s well-being.
The act of notifying the courts of any sole custody issues is known as a request for order. During this process, the alleging parent will provide a declaration to the court in addition to any evidence of wrongdoing. Evidence could consist of video evidence of any abuse or neglect, social media posts, text messages, or any other mediums to support their case.
If the family court judge believes that there is an immediate threat to the children’s safety, you might be stripped of sole physical custody right there and then.
If the judge believes that there is no imminent threat to the children, a child custody investigation will begin before a final ruling is issued.
The investigation will be conducted by a court-appointed special investigator who will begin looking into the allegations presented by the noncustodial parent.
If the investigation shows that your parentage is questionable after all, you could lose sole physical custody of the children.
Here are some of the common reasons you may lose sole custody of your children.
- A History of Drug and/or Alcohol Use – Under Family Code 3011(d), when making a child custody determination, the family law courts will consider any habitual or continued illegal use of controlled substances, alcohol, or even the habitual or continual abuse of prescribed controlled substances. Read more about how drug and alcohol abuse can impact child custody visitation rights here.
- Child Abuse – California Family Code 3011 states that when making a child custody determination, the court must consider any history of abuse by the parent against any children to whom the parent is related. Child abuse is often evident through indicators like bruises, cuts, scars, and other visible marks. Child abuse can be caused by the parent’s anger issues or it can be the result of inappropriate sexual contact initiated by the parent.
- Domestic Violence or Spousal Abuse – Family Code 3044(a) states that child custody orders must take into account any history of abuse against the other parent.
 If you have ever committed domestic violence against the parent within the previous five years, a “rebuttable presumption” will take effect that indicates that joint or sole custody of the children will be detrimental to the children’s best interests.
If you have ever committed domestic violence against the parent within the previous five years, a “rebuttable presumption” will take effect that indicates that joint or sole custody of the children will be detrimental to the children’s best interests.
These represent only a few reasons why sole custody may be lost. If you weren’t in the children’s lives prior to the divorce or child custody hearing, as in you lack intimate knowledge of the kids’ schooling, doctor visits, health, hobbies, and others, you could also lose sole physical custody of the children.
How to Get Your Child Back After Losing Sole Custody
Losing sole physical and legal custody of the children can be an emotionally-draining affair. You want to do everything possible to regain custody in order to get back to how life was before the courts deemed you an unfit parent, or whatever other reason was given for stripping you of your sole custody rights.
How to Regain Sole Physical Custody of Your Child
If you've lost sole custody of your child, then here are some steps to take to possibly get them reinstated by a California family court judge:
- Look into the details of where it all went wrong
- Contact a qualified family attorney
- Take any contingency actions
- request a child custody re-evaluation
- Heed the court's requests
- Be patient
- Consider alternatives to sole custody
- Maintain a clean and safe environment for your children
- Drive safely
- Vet your contact list
Keep reading for a deeper dive into each of these!
Look into the Details of Where it All Went Wrong
This is a time to be extremely honest with yourself. If the judge in your case made a decision to award custody to the other parent or some other family member or guardian, you must examine your life and figure out why.
If the judge in your case made a decision to award custody to the other parent or some other family member or guardian, you must examine your life and figure out why.
Whether the reason was substance abuse, one or more violent acts, sexual abuse, or neglect, you should make a plan to rectify the situation immediately.
If you have been wrongly accused of any of the above or other reasons, it is still important to cooperate with any court-ordered investigations, despite how frustrating or infuriating this process may be for you.
You are encouraged to gather friends, co-workers, neighbors, and any family members to give positive statements to the investigator on your behalf. With those closest to you speaking frankly and honestly about your parenting abilities, and if no abuse or other negative factors are discovered, the court may grant you sole custody once more.
Contact a Qualified Custody Attorney
It is not wise to go through this process all on your own. Instead, call on the help of a skilled and qualified family law attorney. To win back sole custody of your children, an attorney will help you file all the necessary documents, discuss your child custody options, and keep you informed of the process as you work to regain the sole custody you have lost.
Instead, call on the help of a skilled and qualified family law attorney. To win back sole custody of your children, an attorney will help you file all the necessary documents, discuss your child custody options, and keep you informed of the process as you work to regain the sole custody you have lost.
Take Any Contingency Actions
In your case, reinstatement of sole custody may be based on your ability to follow through on one or more special actions. These actions may include drug or alcohol treatment, counseling, or parenting classes.
Your family attorney can help you determine if the court has placed any stipulations on your ability to regain sole custody of your children. If the court has placed these stipulations on your case, follow through and complete all of the Judge’s demands.
The wrong path to take is to argue over the validity of these actions. Complying with the court will reflect favorably on you during the child custody re-evaluation process.
Request a Child Custody Re-Evaluation
When you’ve begun working with a lawyer and you’ve started to undergo any actions requested by the court, you’ll want to request an in-home child custody evaluation.
This process will give the courts an updated assessment of your home environment, which could help you regain sole custody.
Heed the Court’s Requests
If, during the evaluation process, the court requests anything of you, don’t delay. Just do it. This means that you should show up for every court hearing fully-prepared.
For best results, try not to reschedule appointments with the children’s guardian ad litem, which is the nomenclature for a court-ordered mediator.
Be Patient
The re-evaluation of your sole custody rights may not happen overnight. The best thing for you to do is remain patient during this process. In the meantime, make sure you exercise your rights to visitation and parenting time to show the courts that the re-granting of custody to you is in the children’s best interests.
Whatever you do, try not to aggravate the situation in any way. This means being polite to all court-ordered personnel like mediators and investigators. Most importantly, ensure you are as friendly as possible when picking up your kids for any visits.
Most importantly, ensure you are as friendly as possible when picking up your kids for any visits.
Consider Alternatives to Sole Child Custody
Losing sole custody usually means that you want those rights reinstated so badly that they’re all you think about. This can cause you to fail to consider any other custody arrangements.
However, even shared custody will allow you equal time with the children, and that may be in their best interests.
For that reason, speak with your lawyer, work with your ex, and re-evaluate your own desires. If you’ve lost complete custody, joint custody is better than no time with the children at all.
Maintain a Clean and Safe Environment
Try to avoid doing anything that might showcase a questionable character. That means keeping your home as clean as possible. Of course, a little clutter is expected, especially when there are little ones around, but your home should be kept sanitary and comfortable to live in.
You will also want to ensure that your home is childproof. This means locking-up any firearms, putting laundry detergent pods (which can look like candy to kids) on a high shelf where children cannot reach, and keeping prescription drugs and alcohol out of sight.
This means locking-up any firearms, putting laundry detergent pods (which can look like candy to kids) on a high shelf where children cannot reach, and keeping prescription drugs and alcohol out of sight.
Whatever you do, never keep illegal drugs in your home, particularly when the children are present.
Additional tips include avoiding anything that might be seen as sexual behavior. Even if your intentions are entirely innocent, you’ll want to avoid bathing with the children, walking around them naked, and even letting them sleep in your bed.
Drive Safely
During this process, do your best to maintain a clean driving record. You should maintain speed limits at all times and avoid road rage or other driving-related incidents, especially when the kids are present.
When the children are in the car with you, make sure they wear their safety belts and use car seats when necessary.
Vet Your Contact List
Don’t let anyone around your kids who may be seen as dangerous by the courts. This may include those with felony or sex offenses, those who use drugs, and drug dealers.
This may include those with felony or sex offenses, those who use drugs, and drug dealers.
Even close family members who may have done time for drugs, violence or sexual-related offenses in the past should be avoided while your sole-custody re-evaluation is ongoing. This is the case even if their crimes occurred decades ago.
If you have a new partner, it’s best to avoid allowing that person to stay in your home right after you’ve separated from your spouse, as doing so could upset your kids.
On the other hand, if you’ve been separated for some time, such as six months or more, it’s far more reasonable to introduce your kids to your new long-term partner.
You will also want to avoid inappropriate gatherings and vet all babysitters extremely carefully. Even if a friend from college wants to sleep on your couch for a night, you’ll want to seriously consider the ramifications if that person is found to have a criminal past or uses drugs and/or alcohol frequently.
At the same time, avoid going to bars, rock concerts, and R-rated movies while you have your children. Instead, be sure to explore any adult interests when the children aren’t around.
Instead, be sure to explore any adult interests when the children aren’t around.
Keep in mind that your children are always absorbing the things going on around them and those that are said. If they repeat any questionable conversions or report on behavior or guests that fill them with unease, this could reflect negatively on you during your evaluation.
Lost Sole Custody of Your Children? We Can Help!
When you find yourself being stripped of your sole custody rights, don’t hesitate. Call a qualified family lawyer at Griffith, Young, and Lass in Carlsbad, California. Our attorneys have experience with all aspects of child custody and other family law matters.
We can help you fight for your rights to have sole custody reinstated or pursue another arrangement, like joint custody, or whatever is in the best interests of the children.
Schedule a legal consultation online or call us at (858) 371-5569 today! We can discuss your case with you and help you pursue your options as you seek to get sole custody reinstated.
After Losing Custody, Can I Get It Back?
Losing the right to live with and make decisions about your child can be devastating. But losing custody isn’t necessarily permanent. Family law courts use the best interests of the child as a guiding principle when deciding custody. And as children grow, those interests may change. Thus, New Jersey custody orders are rarely set in stone. If you lose custody, you might be able to regain your custodial rights. Winning back custody, however, can be a fight.
Hold on to Hope
If you’ve lost custody, don’t give up hope. Instead, consult with a child custody attorney, if you haven’t already. Discuss your case and your goals to regain custody. A knowledgeable New Jersey custody attorney can explain the possible reasoning behind the judge’s custody decision and the process for getting custody back. Before you have that conversation, here are a few pieces of information that might help you.
Losing Custody Isn’t Forever
The judge probably won’t consider modifying custody right away.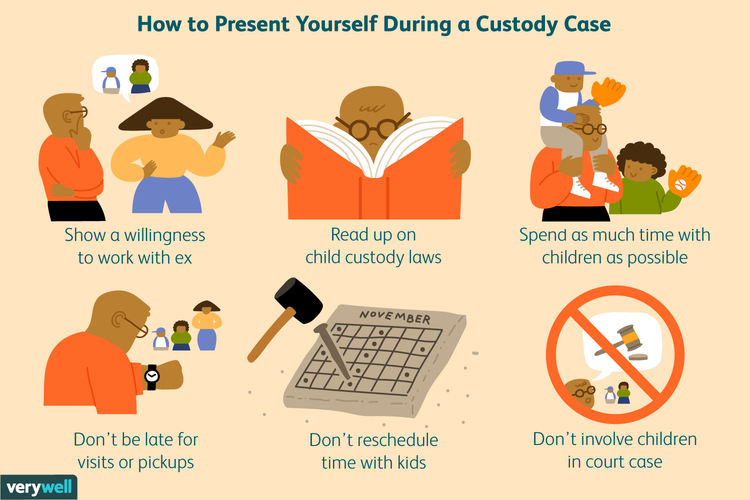 A judge will only modify a custody order if there has been a significant change in circumstances. A change in custody can affect a child. Children need constancy in their caregiving while growing up. Frequently shifting hands and living situations can do more harm than good. Thus, it’s important for you to think about why you lost custody and the reasons why you think you deserve to get it back.
A judge will only modify a custody order if there has been a significant change in circumstances. A change in custody can affect a child. Children need constancy in their caregiving while growing up. Frequently shifting hands and living situations can do more harm than good. Thus, it’s important for you to think about why you lost custody and the reasons why you think you deserve to get it back.
You might be able to appeal the judge’s decision. But bear in mind, appeals cases can be even tougher, and you bear the burden of proving why the judge’s decision was wrong. Again, you would need to speak with an attorney about whether an appeal is right for you.
Also, go over the reasons why you lost custody. You will have to address and resolve those issues before the court would consider reinstating your custodial rights. For example, if you lost custody because you struggle with substance abuse or were unable to meet your child’s needs, you need to take steps to correct these problems or learn the skills you need to be a custodial parent. You might not have a good chance of getting custody if you do not make any changes.
You might not have a good chance of getting custody if you do not make any changes.
Don’t Plan Your Strategy Alone
Challenging a custody decision can take a lot of resources, both regarding your time, energy, and money. Therefore, you shouldn’t try to win back custody on your own. You will need an advocate who can provide legal guidance. A seasoned New Jersey child custody attorney can help you figure out exactly what you need to do to regain your custodial rights. You might not have an easy road in front of you, but a competent attorney can give you the best possible chance of winning back custody.
Are you seeking custody? If so, Williams Law Group, LLC can help. Our skilled attorneys can advise you of your rights and help you protect them, your child’s best interests, and your family. Located in Short Hills, New Jersey, Williams Law Group, LLC provides compassionate and dedicated legal services to Union, Bergen, Essex, Hudson, Morris, Monmouth, and Middlesex counties, and the surrounding areas. Our knowledgeable attorneys handle divorce and family law, child custody, and child abuse/neglect cases. Call our office at (908) 810-1083, email us at [email protected], or contact us through our confidential online form to schedule a consultation and ultimately get you connected with an experienced New Jersey divorce and child custody attorney.
Our knowledgeable attorneys handle divorce and family law, child custody, and child abuse/neglect cases. Call our office at (908) 810-1083, email us at [email protected], or contact us through our confidential online form to schedule a consultation and ultimately get you connected with an experienced New Jersey divorce and child custody attorney.
How to return a child from custody?
Good afternoon!
Unfortunately, it is not possible to deduce from your question what circumstances preceded this situation.
If you were absent for a long time, leaving the child to the grandmother, then the grandmother could apply to the guardianship authority with an application for the establishment of guardianship, just at least to receive child support and legally take care of the child, for example, as a legal representative to take the child kindergarten and hospital. Otherwise, you had to leave a notarized power of attorney for her to represent the interests of the child. Moreover, you write that de jure she is not a grandmother, but only de facto. nine0003
Moreover, you write that de jure she is not a grandmother, but only de facto. nine0003
P. 3. Art. 148 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation establishes the right of children under guardianship or guardianship to maintenance, the funds for which are paid monthly in the manner and in the amount established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, except in cases where guardians or trustees are appointed at the request of parents in the manner , defined by Part 1., Article 13 of the Federal Law “On guardianship and guardianship”. These funds are spent by guardians or trustees in the manner prescribed by Art. 37 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. nine0003
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 145 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, guardianship or guardianship is established over children left without parental care for the purpose of their maintenance, upbringing and education, as well as for the protection of their rights and interests. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 121 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation protection of the rights and interests of children in cases of death of parents, deprivation of their parental rights, restriction of their parental rights, recognition of parents as incapacitated, illness of parents, prolonged absence of parents , evasion of parents from raising children or from protecting their rights and interests , posing a threat to the life or health of children or hindering their normal upbringing and development, as well as in other cases of lack of parental care, is assigned to the guardianship and guardianship authorities. nine0003
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 121 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation protection of the rights and interests of children in cases of death of parents, deprivation of their parental rights, restriction of their parental rights, recognition of parents as incapacitated, illness of parents, prolonged absence of parents , evasion of parents from raising children or from protecting their rights and interests , posing a threat to the life or health of children or hindering their normal upbringing and development, as well as in other cases of lack of parental care, is assigned to the guardianship and guardianship authorities. nine0003
In accordance with 5. Art. 10 of the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship" grandparents, parents, spouses, adult children, adult grandchildren, brothers and sisters of an adult ward, as well as grandparents, adult brothers and sisters of a minor ward have the priority right to be his guardians or trustees over all by other persons.
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 11 of the above law, the guardian or trustee is appointed with their consent or at their request in writing by the guardianship and guardianship body at the place of residence of the person in need of establishing guardianship or guardianship over him, within a month from the moment when the specified body became aware of the need establishment of guardianship or guardianship over such a person. In the presence of noteworthy circumstances, the guardian or custodian may be appointed by the body of guardianship and guardianship at the place of residence of the guardian or custodian. nine0003
It must be understood whether the grandmother's guardianship is still provisional or already permanent at the moment.
Preliminary guardianship or guardianship shall be terminated if, before the expiration of six months from the date of adoption of the act on the temporary appointment of a guardian or custodian, the temporarily appointed guardian or custodian is not appointed by the general procedure as a guardian or custodian. In exceptional circumstances, this period may be extended up to eight months. If the body of guardianship and trusteeship has appointed a person who performed duties by virtue of preliminary guardianship or guardianship within the established period in accordance with the general procedure, the rights and obligations of the guardian or trustee shall be deemed to have arisen from the moment the act on the temporary appointment of the guardian or trustee is adopted. nine0003
In exceptional circumstances, this period may be extended up to eight months. If the body of guardianship and trusteeship has appointed a person who performed duties by virtue of preliminary guardianship or guardianship within the established period in accordance with the general procedure, the rights and obligations of the guardian or trustee shall be deemed to have arisen from the moment the act on the temporary appointment of the guardian or trustee is adopted. nine0003
You need to contact the guardianship authority that appointed the grandmother as a temporary guardian and inform that you are the mother of the child and are ready to continue your parental duties.
According to Art. 148.1 of the RF IC, any actions (inaction) on the implementation of guardianship or guardianship by the guardian or guardian of the child may be appealed by the parents or other relatives or adoptive parents of the child to the guardianship and guardianship authority.
The body of guardianship and guardianship has the right to oblige the guardian or custodian to eliminate violations of the rights and legitimate interests of the child or his parents or other relatives or adoptive parents. nine0003
nine0003
If the guardian or trustee does not comply with the decision of the guardianship and guardianship authority, parents or other relatives or adoptive parents of the child have the right to apply to the court with a request to protect the rights and legitimate interests of the child and (or) their rights and legitimate interests . The court resolves the dispute based on the interests of the child and taking into account his opinion. Failure to comply with the court decision is the basis for the removal of the guardian or trustee from the performance of their duties. nine0003
A guardian or custodian may not prevent a child from communicating with his or her parents and other relatives, unless such communication is not in the interests of the child.
Good day.
Maria Paulus, lawyer
Release of a guardian or custodian from their duties
Applicants have the right to a pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) taken (carried out) by local governments, officials, municipal employees of local governments in the course of providing public services. The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure does not exclude the possibility of appealing against decisions and actions (inaction) taken (carried out) in the course of providing public services in court. The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure is not mandatory for the applicant. nine0003
The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure does not exclude the possibility of appealing against decisions and actions (inaction) taken (carried out) in the course of providing public services in court. The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure is not mandatory for the applicant. nine0003
The subject of pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal are:
- violation of the deadline for registration of the applicant's request for the provision of public services;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services;
- requiring the applicant to provide documents that are not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, the regulatory legal acts of St. Petersburg, for the provision of a public service;
- refusal to accept documents from the applicant, the provision of which is provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, the regulatory legal acts of St. Petersburg, for the provision of public services; nine0062
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, regulatory legal acts of St.
 Petersburg;
Petersburg; - requirement from the applicant when providing a public service for a fee not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, the regulatory legal acts of St. Petersburg;
- refusal of a local self-government body, a municipal employee of a local self-government body providing a public service, to correct misprints and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of a public service, or violation of the deadline for such corrections. nine0062
The complaint is submitted in writing on paper, in electronic form to the local government. Complaints against decisions made by an official of a local self-government body are submitted to the Government of St. Petersburg.
A complaint can be sent by mail, through the MFC, using the Internet information and telecommunications network, the official website of the local government, a single portal of state and municipal services or a regional portal of state and municipal services, and can also be accepted at the personal reception of the applicant. nine0003
nine0003
The complaint must contain:
- name of the local self-government body, official of the local self-government body or municipal employee of the local self-government body whose decisions and actions (inaction) are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (the last one, if any), information about the place of residence of the applicant - an individual or name, information about the location of the applicant - a legal entity, as well as the contact phone number (numbers), email address (s) (if available) and the postal address to which the response should be sent to the applicant; nine0062
- information about appealed decisions and actions (inaction) of a local government body, an official of a local government body or a municipal employee of a local government body;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decision and action (inaction) of the local government, an official of the local government, or a municipal employee of the local government.
 The applicant may submit documents (if any) or their copies confirming the applicant's arguments. nine0062
The applicant may submit documents (if any) or their copies confirming the applicant's arguments. nine0062
The complaint received by the local authorities is subject to consideration within the following terms:
- within fifteen working days from the date of registration of the complaint;
- within five working days from the date of registration of the complaint in the event of an appeal against the refusal of a local government body, an official of a local government body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in case of appealing against a violation of the deadline for such corrections; nine0062
- at other times in cases established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Based on the results of consideration of the complaint, the local government takes one of the following decisions:
- satisfies the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision, correction of misprints and errors made by the local government in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services;
- refuses to satisfy the complaint.
 nine0062
nine0062
Not later than the day following the day of the decision, the applicant in writing and at the request of the applicant in electronic form shall be sent a reasoned response on the results of the consideration of the complaint.
When considering a complaint by a local self-government body, a citizen has the right to:
- get acquainted with the documents and materials related to the consideration of the complaint, if this does not affect the rights, freedoms and legitimate interests of other persons and if these documents and materials do not contain information constituting a state or other secret protected by federal law; nine0062
- receive a written response on the merits of the issues raised in the complaint, notification of forwarding the written appeal to the state body, local government or official whose competence includes resolving the issues raised in the appeal;
- appeal against the decision or action (inaction) in connection with the consideration of the appeal in an administrative and (or) judicial manner in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation; nine0061 submit additional documents and materials or apply for their reclamation, including in electronic form;
- apply for termination of consideration of the complaint.

In the event that, during or as a result of the consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, the official empowered to consider complaints immediately forwards the available materials to the prosecutor's office. nine0003
The applicant has the right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the appeal (complaint). Local self-government bodies, its officials, municipal employees of the local self-government body are obliged to provide the applicant with the opportunity to familiarize themselves with the documents and materials related to the consideration of the appeal (complaint), if this does not affect the rights, freedoms and legitimate interests of other persons and if these documents and materials do not contains information constituting a state or other secret protected by federal law. nine0003
Executive bodies of state power of St. Petersburg and officials to whom the complaint (claim) of the applicant may be addressed in the pre-trial (out-of-court) procedure
If the subject of the complaint (claim) of the applicant is the actions of the local government providing public services, the complaint (claim) may be sent to the Committee for Social Policy of St.