How to get legal guardianship of a child in georgia
How to Become a Legal Guardian in Georgia (What to Know)
Selecting a guardian or conservator can be a complicated process, where emotions often run high. At Turner Law, we work diligently to dispel the anxiety by offering sound counsel and advocacy in elder law throughout each stage of the process.
We also help families avoid the need for guardianship when there are alternatives, such as powers of attorney and advance health care directives. We represent adult children, parents, concerned family members and even proposed wards in Decatur, Atlanta and the surrounding areas of Georgia.
Becoming A Guardian Or Conservator
To become a guardian or conservator, you must file a petition with the local probate court where your loved one currently resides. The proposed ward (the person for whom guardianship is sought) will be informed of the petition and given the opportunity to hire his or her own lawyer. He or she will also undergo a mental evaluation by a doctor, psychologist or licensed clinical social worker.
Then, a hearing will be scheduled to review and finalize the petition. The court must approve someone who will best serve the interests of the proposed ward. In general, it follows this order of preference when choosing a guardian:
- The person chosen by the ward, in writing, when he or she was of sound mind
- The spouse of the proposed wardAn adult child or parent (in the case of minor guardianship) of the proposed ward
- A previously appointed guardian in Georgia or another state
- A capable volunteer the court finds suitable to the task
- A county guardian, who is a public official appointed by the county to stand in as guardian if no other suitable candidate is found
This process usually takes about a month, though it may be sped up if you have reason to believe your loved one is in real danger by filing an emergency guardianship. A temporary guardian can possibly be appointed within a week if necessary to protect your loved one. Whatever side of this issue you fall on, you can rely on our firm’s ability to find a resolution that fits your family’s unique situation.
Whatever side of this issue you fall on, you can rely on our firm’s ability to find a resolution that fits your family’s unique situation.
An Often Overlooked Issue In Guardianship Petitions
Many people do not realize that as a conservator in Georgia, you must have a bond of insurance in addition to a willing heart. The bond serves to protect the financial interests of the proposed ward in case the conservator breaches his or her fiduciary duty with respect to the ward’s assets.
Robert Turner can help you meet this often overlooked requirement, either by locating a suitable bond company or by advising you on alternative options to protect your loved one’s estate.
What If We Don’t Agree On Guardianship?
Petitioning for guardianship of another person can be difficult for the entire family, especially if relatives do not agree on who should be appointed guardian or conservator. What starts out as a wish to protect mom from financial predators can become a fight over control of mom’s money.
Attorney Robert Turner is skilled at handling guardianship petitions, working to minimize the negative impact on the lives of the involved parties. We notify all relatives of pending guardianships or conservatorships to identify any ongoing disputes within the family. In all communications with loved ones, we address objections quickly and skillfully resolve them.
Helping Protect The Ones You Love
As a guardian or conservator, you want to take care of your family member, manage their resources properly and ensure no one takes advantage of them. We can help you do this. Contact Turner Law, LLC online or call phone number(866) 768-5365 toll free to discuss your needs today.
Chatham County, GA - Court System
Due to Supreme Court Emergency Orders, the Probate Court has been accepting guardianship petitions by mail and drop box only. Probate Court will begin accepting pleadings by appointment on August 3, 2021. To make an appointment to file a Guardianship or Conservatorship pleading or to get information, please go to the following:
To make an appointment to file a Guardianship or Conservatorship pleading or to get information, please go to the following:
Minor Guardianship Appointments for Filing or Information
Video Guardians and Conservators - English
Video Guardians and Conservators - Spanish
Handbook for Guardians and Conservator of Adults in Georgia
Handbook for Conservators of Minors in Georgia
The clerk and deputy clerks desire to help all parties that ask for assistance and will attempt to do so. The clerk and deputy clerks are strictly forbidden to practice law by statute and are restricted in what they can give advice about or assistance in preparing. Sound legal advice must only come from a licensed practicing attorney and the clerk's office encourages all parties to seek competent legal advice. We ask that you be understanding with our staff as we attempt to assist you, knowing the limitations we face in assisting each individual party to a case.
We ask that you be understanding with our staff as we attempt to assist you, knowing the limitations we face in assisting each individual party to a case.
The Probate Court is located at 133 Montgomery Street, Room 509, Savannah, Georgia 31401 (Map and Directions). The office accepts filings Monday through Friday, excluding holidays, from 8:00 a.m. to 4:30 p.m.
All pleadings filed with the Chatham County Probate Court by mail must be signed, verified, and have the appropriate filing fees. Pleadings without fees will be returned without filing.
Temporary Guardianship of a Minor
In which county do I file my Petition for Temporary Guardianship of a Minor?
- If you are a Georgia resident you must file the petition for temporary guardianship in the county of your domicile.

- If you are a non-resident of this state you must file the petition in the county where the minor is found and you must have physical control of the minor at the time of filing the petition.
What is required at the time of filing?
The following documents must be presented or filed with the petition:
- A completed petition along with all applicable fees
- Petition for Temporary Letters of Guardianship of a Minor
- A copy of the minor’s birth certificate
- A valid state issued Driver’s License or identification card. If you are a Chatham County resident and your Driver’s license has an address other than your present Chatham County address, additional proof of residence is required in the form of a utility bill, rental lease agreement, etc.

The petition will require:
- the name, address, and county of domicile of any living parent of the minor; and
- the consent of one or both of the parents in a notarized writing consenting to the appointment of the petitioner as temporary guardian and, if so, that the consents are attached to the petition. If the sole parent or both parents have not consented to the appointment of the temporary guardian, a statement of the circumstances that give rise to the need for the appointment of a temporary guardian. O.C.G.A. § 29-2-5
Criminal Background Search:
At the time of filing, the proposed guardian will be required to complete a consent for a criminal background search and a guardian information form. The Probate Court staff will complete a background search for the proposed guardian and, if a criminal history is revealed, the Judge will determine whether the guardianship will be granted or the petition will be referred to Juvenile Court where attorneys and guardian ad litem can determine what is in the best interests of the child(ren).
The Probate Court staff will complete a background search for the proposed guardian and, if a criminal history is revealed, the Judge will determine whether the guardianship will be granted or the petition will be referred to Juvenile Court where attorneys and guardian ad litem can determine what is in the best interests of the child(ren).
The Petitioner(s) must appear in person and take an oath before Letters of Temporary Guardianship will be issued.
If you are filing to become a temporary guardian for more than one child, you must file a separate petition and pay a separate filing fee for each child.
What if the minor is already subject to a custody or temporary guardianship order entered by another court?
This Court will not grant temporary guardianship to a non-custodial parent when a custody order is in place. Also, this Court will not create a new temporary guardianship if a minor is already subject to a temporary guardianship created in another state or by another Georgia court. In both cases, you must return to the original court and request modification, transfer or termination of the custody or guardianship order that is in place over the child.
Also, this Court will not create a new temporary guardianship if a minor is already subject to a temporary guardianship created in another state or by another Georgia court. In both cases, you must return to the original court and request modification, transfer or termination of the custody or guardianship order that is in place over the child.
Filing Fees
A petition for temporary guardianship of a minor costs $105 plus $2.00/ page (Probate Fees). Fee waivers are available based upon the Federal Poverty Guidelines. You will be required to provide proof of your current income in the form of pay stubs, W2 forms, tax returns, etc.
- Fee Waiver Application
The Probate Court is not currently accepting cash or personal checks. Mailed in pleadings and requests must be paid by money order or cashier’s checks. Credit and Debit cards will be accepted if services are rendered on premises.
Credit and Debit cards will be accepted if services are rendered on premises.
What are my responsibilities as Guardian and/or Conservator?
When you are appointed temporary guardian of a minor, you are entitled to “exercise any of the powers of a natural guardian.” You will assume the “obligation to support the minor while the temporary guardianship is in effect.” You do not have the authority to delegate your responsibility or your possession of the minor child to another person or back to the parent without petitioning this Court to either terminate the guardianship or transfer the guardianship to another temporary guardian.
This Court will require annual reports from temporary guardians to maintain current information on address, education, health and condition of the minor child. The Court reviews the reports to ensure that the temporary guardian is being responsible and that the minor is safe and secure.
The Court reviews the reports to ensure that the temporary guardian is being responsible and that the minor is safe and secure.
- Personal Status Report (Guardian)
Conservator Class – Probate Court Standing Order
Entered September 14, 2022, pursuant to Uniform Probate Court Rule 1.3
Effective October 1, 2022, a petitioner asking to be appointed conservator for a minor or incapacitated adult will be required to attend the Conservator Class offered by the Probate Court of Chatham County twice each month. Please read the Standing Order and print out the Conservator Class Flyer for more information. Conservators are required to manage and safeguard the property and funds of the ward and the Probate Court is required by law to oversee the conservators. Conservators are required to file two (2) financial reports annually which are reviewed by the Probate Court with the assistance of a local CPA firm. Beginning October 1, 2022, the Conservator Class can be taken before filing a petition but must be completed no later than two months after appointment. Understanding the responsibilities and the required forms will help conservators be efficient, effective and prepared. Please sign up for the Conservator Class through the following link.
Conservators are required to file two (2) financial reports annually which are reviewed by the Probate Court with the assistance of a local CPA firm. Beginning October 1, 2022, the Conservator Class can be taken before filing a petition but must be completed no later than two months after appointment. Understanding the responsibilities and the required forms will help conservators be efficient, effective and prepared. Please sign up for the Conservator Class through the following link.
Conservator Class Sign Up
Please read the Standing Order and print out the Conservator Class Flyer for more information.
- Standing Order Requiring Training in Conservatorship Matters (September 14, 2022)
- Conservator Class Flyer (September 2022)
How do I end the Temporary Guardianship?
If you are the natural guardian of the minor and you would like to end the temporary guardianship, you must file a Petition to Terminate Temporary Guardianship. The temporary guardian may consent to the Petition, but if he or she does not, the Court must have the temporary guardian personally served with a copy of your Petition. If the temporary guardian objects to the termination of the temporary guardianship, the parent(s) and guardian will be ordered to mediation. If no agreement is reached, the case will be transferred to the Chatham County Juvenile Court for a final decision.
The temporary guardian may consent to the Petition, but if he or she does not, the Court must have the temporary guardian personally served with a copy of your Petition. If the temporary guardian objects to the termination of the temporary guardianship, the parent(s) and guardian will be ordered to mediation. If no agreement is reached, the case will be transferred to the Chatham County Juvenile Court for a final decision.
- Petition to Terminate Guardianship of a Minor
If you are the temporary guardian and you would like to resign as temporary guardian, you must sign consent for resignation and the successor temporary guardian(s) would need to file a Petition for Letters of Temporary Guardianship of a Minor. Your temporary guardianship automatically terminates on the day the minor turns 18, is adopted, becomes emancipated, or dies. A court order may also terminate a guardianship.
Your temporary guardianship automatically terminates on the day the minor turns 18, is adopted, becomes emancipated, or dies. A court order may also terminate a guardianship.
- Petition for Temporary Letters of Guardianship of a Minor
For additional information:
Appointment of Guardians for Children under Georgia Law
Authored By: Atlanta Legal Aid society Inc.
Website
If you have any further questions specific to a temporary guardianships of a minor, please call (912) 652-7264 (Option 6).
90,000 Treaty between the Russian Federation and the Republic of Georgia Treaty
between the Russian Federation and the Republic of Georgia
On legal assistance and legal relations for civilian,
Family and Criminal Cases
(Tbilisi, September 15, 1995 years)
The Russian Federation and the Republic of Georgia,
Attaching great importance to the development of cooperation in the field of legal assistance in civil, family and criminal cases,
have agreed as follows:
PART ONE. GENERAL PROVISIONS
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1
Legal protection
1. Citizens of one Contracting Party shall enjoy in the territory of the other Contracting Party, in respect of their personal and property rights, the same legal protection as citizens of that Contracting Party.
This also applies to legal entities established under the laws of one of the Contracting Parties.
2. Citizens of one Contracting Party shall have the right to apply freely and without hindrance to the courts, prosecutor's office, notaries' offices (hereinafter referred to as "institutions of justice") and other institutions of the other Contracting Party whose competence includes civil, family and criminal matters, may act in them, file petitions, file suits and carry out other procedural actions on the same conditions as their own citizens.
Guardianship and guardianship
Article 35
. In this case, the legislation of that Contracting Party shall apply.
2. Legal relations between a guardian or custodian and a person under guardianship or guardianship shall be determined by the legislation of the Contracting Party whose body of guardianship has appointed the guardian or custodian.
Article 36
1. If measures of guardianship or guardianship are necessary in the interests of a person under guardianship or a person under guardianship whose place of residence or residence or property is located in the territory of another Contracting Party, then the guardianship and guardianship authority of that Contracting Party shall immediately notify the guardianship and guardianship authority of the Contracting Party competent in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 35 of this Treaty.
2. In urgent cases, the guardianship and guardianship authority of the other Contracting Party may itself take the necessary measures, but it must immediately notify the guardianship and guardianship authority competent in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 35 of this Treaty of the preliminary measures taken. The measures taken shall remain in effect until the authority decides otherwise.
The measures taken shall remain in effect until the authority decides otherwise.
Article 37
1. The guardianship or guardianship authority competent in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 35 may transfer guardianship or trusteeship to the appropriate authorities of the other Contracting Party if the place of residence or residence or property of the person under guardianship or under guardianship is located in that State. The transfer is valid only if the requested authority agrees to accept guardianship or guardianship and notifies the requesting authority.
2. An authority that, in accordance with paragraph 1 of this article, has accepted guardianship or trusteeship shall exercise it in accordance with the laws of its state. He is not entitled, however, to decide on matters relating to the personal status of a person under guardianship or guardianship, but may give permission for marriage, as required by the law of the Contracting Party of which the person is a national.
Property legal relations
Article 38
Right of ownership
1. The right of ownership of immovable property is determined by the legislation of the Contracting Party in whose territory the immovable property is located.
2. The right of ownership of vehicles subject to entry into state registers is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Contracting Party in whose territory the body that registered the vehicle is located.
3. The emergence and termination of the right of ownership or other real right to property shall be determined in accordance with the legislation of the Contracting Party in whose territory the property was located at the time when an action or other circumstance took place that served as the basis for the emergence or termination of such a right. The emergence and termination of the right of ownership or other real right to the property that is the subject of the transaction are determined by the legislation of the place of the transaction, unless otherwise provided by agreement of the parties.
Are citizens of the CIS countries considered foreigners for the purpose of adopting or taking custody of Russian orphans?. International adoption
Attention:
the last update of the site materials - 01/01/2017.
Dear adoptive parents!
This section contains all information about international adoptions that I have.
For any non-standard situations and questions, please contact lawyers specializing in international adoption. For example, lawyer Alexander Golovanov (I did not personally work with him, but I know about successful cases with his participation) or others.
Home — Intercountry adoption
Are citizens of the CIS countries considered foreigners for the purposes of adoption or foster care of Russian orphans?
« Back to the list of questions
The Convention "On Legal Assistance and Legal Relations in Civil, Family and Criminal Matters" was signed in Minsk on January 22, 1993.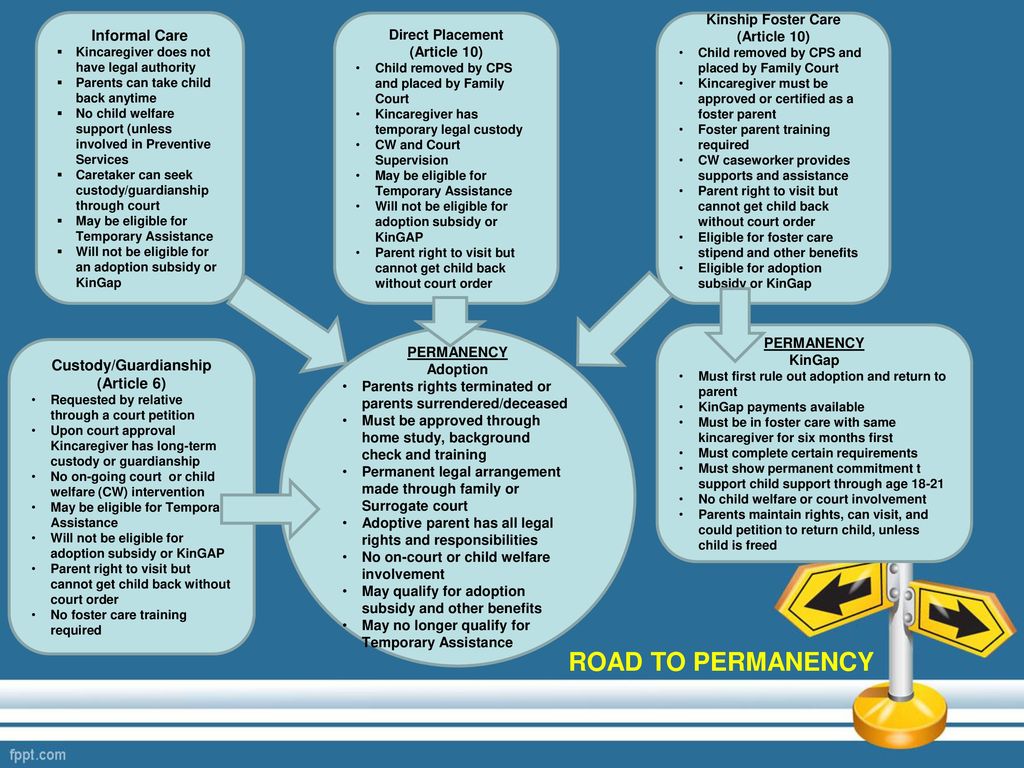 This document contains conflict of law rules, i.e. norms that determine the law applicable to the settlement of certain relations between citizens of the states parties to the Convention. As of March 6, 2015, the Convention entered into force for: Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine.
This document contains conflict of law rules, i.e. norms that determine the law applicable to the settlement of certain relations between citizens of the states parties to the Convention. As of March 6, 2015, the Convention entered into force for: Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine.
Based on the content of art. 33-36 of the Convention, the author of the site draws the following conclusions:
Guardianship (guardianship)
- Establishment or cancellation of guardianship is carried out according to the legislation of the state whose citizen is the person in respect of which guardianship is established or canceled. Those. if guardianship is established in respect of a child who is a citizen of the Russian Federation, then the same requirements apply to a candidate for guardianship from a country party to the Convention as to Russian candidates.
- The legal relationship between a guardian and a ward shall be governed by the law of the state whose institution appointed the guardian.
 Thus (and taking into account paragraph 1 above), when establishing guardianship in respect of a child who is a citizen of the Russian Federation, the legal relationship between the guardian who is a citizen of a country party to the Convention and the ward is regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Thus (and taking into account paragraph 1 above), when establishing guardianship in respect of a child who is a citizen of the Russian Federation, the legal relationship between the guardian who is a citizen of a country party to the Convention and the ward is regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation. - A citizen of a state party to the Convention may be appointed guardian of a child who is a citizen of the Russian Federation only subject to that the guardian lives on the territory of the Russian Federation (it is understood - legally).
Adoption
- Adoption or its revocation is determined by the law of the state of which the adopter is a citizen at the time of application for adoption or its revocation. In fact, this means that citizens of the countries participating in the Convention adopt children who are citizens of the Russian Federation according to the rules of international adoption: they receive a conclusion on the possibility of being an adoptive parent according to the rules of the country of origin, when communicating with the operator of the data bank and when submitting an application to the Russian court, the rules of family law will be applied Russian Federation in relation to adoptive parents-foreigners.