How to cut umbilical cord at home
Umbilical cord care | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
In the womb, the umbilical cord delivers the oxygen and nutrients needed to allow your baby to grow. After birth, the cord is clamped and cut, leaving a stump. This eventually falls off, healing to form the umbilicus (belly button). There are ways for you to prevent problems during healing.
What happens immediately after the birth?
After birth, the doctor or midwife cuts your baby’s cord from the placenta and puts a clamp on the remaining stump to pinch it off. After a couple of days, once the cord has dried, you can take the clamp off.
How long does the cord stay attached for?
The cord stump usually stays attached for 5 to 15 days. Over this time, the cord dries, shrinks and turns black. Sometimes, especially in the day or so before it falls off, the stump can ooze a little and may leave marks on your baby’s clothes.
Do not pull the cord stump off, even if it looks like it will come off easily, as this can prolong healing time and cause scarring. Let the cord stump fall off by itself in its own time.
When the stump falls off, there is sometimes a little bleeding at the stump site. This is normal and it should stop quickly.
Please see your doctor or maternal and child health nurse if you have any concerns, or speak to Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436.
Caring for the umbilical cord
Wash the cord stump as part of your baby’s usual bathing routine.
Make sure you wash your hands first. Use only water and cotton pads, and dry it carefully. If wee or poo gets on the stump, you can use a mild soap to help clean it off. You don’t need to use antiseptics and alcohol.
Let the cord sit out of the nappy so it dries out in the air; this can be done by folding the nappy under the cord stump.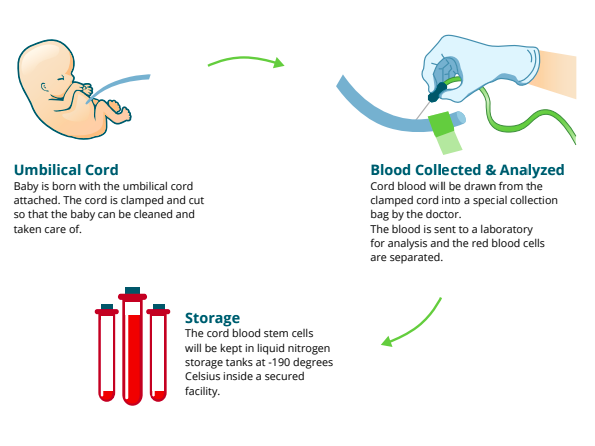 There is no need to cover the cord stump with Band-Aids or bandages, as this stops airflow around the stump.
There is no need to cover the cord stump with Band-Aids or bandages, as this stops airflow around the stump.
If you’re not washing the cord stump, try not to handle it.
How long does the belly button take to heal?
The belly button should heal completely in days. It may bleed or ooze a little after the cord falls off, but if there is continuous stickiness or discharge, it may be infected and you should show your doctor or maternal and child health nurse.
Sometimes the belly button does not heal completely and moist red tissue forms over the stump site, often with a lump present. This is called a ‘granuloma’. It is usually harmless, but you should ask your doctor or child and family nurse to have a look at it.
How to tell if the cord is infected
Signs of an infection of the belly button may include:
- redness, swelling, stickiness or a bad smell on or around the belly button
- fevers, poor feeding and tiredness in your baby
If you think your baby’s cord stump or belly button is infected, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Sources:
Victorian Agency for Health Information (Umbilical cord care for neonates), Raising Children Network (Umbilical care), Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne (Umbilical granuloma – pre-referral), Cochrane (Topical umbilical cord care at birth)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- What is the placenta?
- Mum's first 24 hours after birth
- Baby's first 24 hours
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Umbilical cord cutting: everything you need to know | Pregnancy
The umbilical cord cutting is a special moment — after all, it’s what’s kept you and your baby connected for the past 40 weeks of pregnancy. You may choose to cut the umbilical cord yourself, have your partner do it; a loved one, or just get your doctor or midwife to do it.
Delayed cord clamping (also known as ‘optimal cord clamping’) is when you wait at least one minute before cutting the umbilical cord after your baby is born. The method is recommended safe and effective by the World Health Organisation and is believed to be better for your baby, rather than cutting the cord immediately after birth.
We explain everything you need to know about umbilical cord cutting, including how it's done and the benefits of delayed cord clamping.
What is the umbilical cord?
The umbilical cord is a tube made up of two arteries and one vein, which is covered in a thick substance known as ‘wharton’s jelly’. It forms when you’re around five weeks pregnant and it serves as a lifeline to your baby. It transports nutrients and oxygen from you to your baby and passes back waste from the baby via the placenta.
It forms when you’re around five weeks pregnant and it serves as a lifeline to your baby. It transports nutrients and oxygen from you to your baby and passes back waste from the baby via the placenta.
It grows up to two feet long and runs from your baby’s belly button to the placenta. There may be some facts that you may not know about the umbilical cord too, for example some women donate it after giving birth as its blood is rich in stem cells which can help cure diseases.
How the umbilical cord is cut
You and your baby won’t feel the umbilical cord being cut. Whoever cuts it the process will be the same:
• Your doctor or midwife will make sure the umbilical cord has stopped pulsating
• Two clamps will be placed on the cord
• Whoever is cutting the cord will hold a section of it with a piece of gauze underneath it
• They’ll then be given a pair of sterile scissors and cut between the two clamps
When should the umbilical cord be cut?
Traditionally the umbilical cord would be cut immediately after you had given birth to your baby — whether that be a vaginal birth or C-section. However, new guidelines recommend a delayed umbilical cord cutting, where you wait a minimum of a minute before cutting the cord.
However, new guidelines recommend a delayed umbilical cord cutting, where you wait a minimum of a minute before cutting the cord.
The NHS says that by doing this the amount of iron in your baby’s blood will increase, which is essential for your baby’s brain development and neurodevelopment in later childhood. It also allows more blood to flow from the placenta, which keeps your baby’s blood pressure more stable once the cord is cut (which creates a sudden drop).
Your doctor or midwife may recommend you don’t have a delayed cord clamping if there’s concerns about your baby’s heartbeat or if they have breathing problems.
If your baby is premature then delayed cord clamping is even more beneficial as your baby's organs are fragile. By delaying cutting the umbilical cord it can improve your baby's blood pressure and protect their delicate organs. The same applies if your baby is sick.
When is delayed cord clamping not recommended?
Although delayed cord clamping is beneficial in most situations, there are certain circumstances where it may not be recommended, including:
• If you’re bleeding heavily and are in need of immediate medical treatment
• If there’s a problem with the placenta
• If the umbilical cord is bleeding so the blood isn’t able to reach your baby
• If your baby is struggling to breathe and needs resuscitation
• If you’re having monochorionic twins then delayed cord clamping is not recommended. This is because the twins will share the same placenta and there is a risk that blood could move from one twin to another. If one twin has more blood than the other, delayed cord clamping could make the situation worse.
This is because the twins will share the same placenta and there is a risk that blood could move from one twin to another. If one twin has more blood than the other, delayed cord clamping could make the situation worse.
Anymore questions on the umbilical cord? Give the below video a watch by Lamaze Certified Childbirth Educator Alice Turner.
Just so you know, whilst we may receive a commission or other compensation from the links on this website, we never allow this to influence product selections - read why you should trust us
Childbirth at home: pros and cons, danger and harm | NGS24
Most often, doctors oppose giving birth at home under the supervision of a doula
Photo: Artyom Lents
hugging her perfectly round pregnant belly.
For sure, in the caption to the photo, this diva denies the whole world of evidence-based medicine, telling how she decided to give birth at home under the supervision of a doula, because our ancestors did it, no matter how she never regretted it. And that after giving birth, her baby lay next to her for several hours with an uncut umbilical cord, because it is very useful - and she also read about this on Instagram, only from another, even more popular insta-diva. And that then from this umbilical cord and placenta she will definitely make herself a smoothie, because everyone does it.
And that after giving birth, her baby lay next to her for several hours with an uncut umbilical cord, because it is very useful - and she also read about this on Instagram, only from another, even more popular insta-diva. And that then from this umbilical cord and placenta she will definitely make herself a smoothie, because everyone does it.
Before scolding both the insta-diva and world medicine, let's see if there is any sense in all this, and most importantly, is it dangerous? We compiled a complete educational program on fashionable childbirth together with the candidate of medical sciences, deputy chief physician for the medical department of the Krasnoyarsk Interdistrict Clinical Hospital No. 4, obstetrician-gynecologist Evgenia Sivova.
obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences Evgenia Sivova
Photo: courtesy of Evgenia Sivova
Share
- From a medical point of view, home births may or may not be planned. Speaking of fashion, we probably first of all have in mind a planned home birth, when a woman deliberately decides that she will give birth at home. In some foreign countries, this format of childbirth is regulated by law; there is also a midwife or even a family doctor present along with the woman in labor. In Russia, this is not regulated by law in any way, it is not written anywhere how such childbirth should actually take place.
Speaking of fashion, we probably first of all have in mind a planned home birth, when a woman deliberately decides that she will give birth at home. In some foreign countries, this format of childbirth is regulated by law; there is also a midwife or even a family doctor present along with the woman in labor. In Russia, this is not regulated by law in any way, it is not written anywhere how such childbirth should actually take place.
Home births increase the risk of maternal and infant mortality. During childbirth, unforeseen situations may arise that can be controlled and resolved in a medical organization. If a woman gives birth at home, she is not controlled by anyone, which means that the consequences can be very different.
What is the danger of such childbirth?
Autohemotransfusion (transfusion of one's own blood) is possible in a medical facility, but at home the situation can be fatal.
Another danger is acute fetal hypoxia, for example in case of cord entanglement.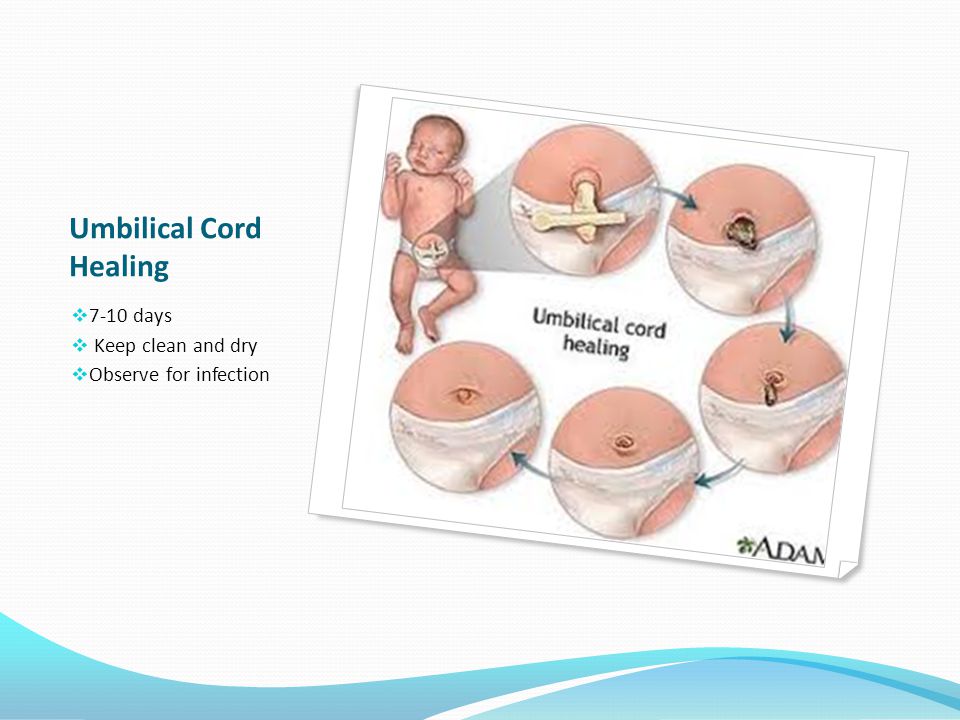 This situation cannot be foreseen in advance, therefore it is important that a qualified specialist is nearby. Plus, during childbirth, the doctor monitors the fetal heartbeat and, if something goes wrong, will be able to quickly respond. In addition, any childbirth, if there are difficulties, can end with a caesarean section, which is impossible to perform at home.
This situation cannot be foreseen in advance, therefore it is important that a qualified specialist is nearby. Plus, during childbirth, the doctor monitors the fetal heartbeat and, if something goes wrong, will be able to quickly respond. In addition, any childbirth, if there are difficulties, can end with a caesarean section, which is impossible to perform at home.
— Proponents of home births often make an argument: they used to give birth in an open field, and nothing. What can you say about this?
- In this case, let's take into account that our population is not getting healthier, there is a tendency for the general state of people's health to worsen. It is also worthwhile to understand that earlier, after a cesarean section, a woman in labor died, because they only knew how to perform a cerebrosection, the operation technique was unknown. Now, after a caesarean section, women live and enjoy the joy of motherhood.
In the end, girls used to give birth at the age of 16–19, but now many women in labor over 35 years old come to us, with increasing age, diseases and the possibility of complications are acquired, so it’s better to give birth under the supervision of doctors, and not on your own .
— What about doulas, the so-called birth assistants? Women sometimes trust them more than doctors.
- Doulas are usually people without medical education, so they cannot prescribe drugs, use medical methods, conduct examinations, that is, the doula does not control anything, does not analyze and does not provide obstetric care. In fact, this is a mother who supports her daughter during pregnancy, or a partner who is nearby during partner childbirth.
There is an understanding that the concept of "dola" in our reality has been changed, tied to home births and endowed with the functions of medical support. But within the framework of skilled medical care in the 21st century, what kind of doulas can we talk about? This person will not replace a medical team - a midwife, an obstetrician-gynecologist, a neonatologist. This must be understood.
Lotus childbirth is one of the latest fashion trends in childbirth, when after the birth of a child, the umbilical cord is not cut for several hours. Often it is not touched in any way until it falls off on its own. According to supporters of this method, the child's body is better saturated with oxygen and blood.
Often it is not touched in any way until it falls off on its own. According to supporters of this method, the child's body is better saturated with oxygen and blood.
— In the umbilical cord, which connects the mother and fetus, there are vessels and arteries, thanks to which blood is exchanged between them. Physiologically, this blood flow ceases after birth, but can persist for a maximum of 20 minutes. Therefore, there is absolutely no point in lying in this position for several hours. It doesn't carry any value.
Perhaps the idea that this is necessary came from somewhat distorted information about a study by American scientists, according to which it makes sense to somewhat delay cutting the umbilical cord - but not for several hours, but for a maximum of 1-3 minutes. It is believed that this time is enough for part of the blood to finish its current and thus saturate the child's blood so that the child's hemoglobin increases. The study also says that within 3-6 months, this helps the child gain weight better.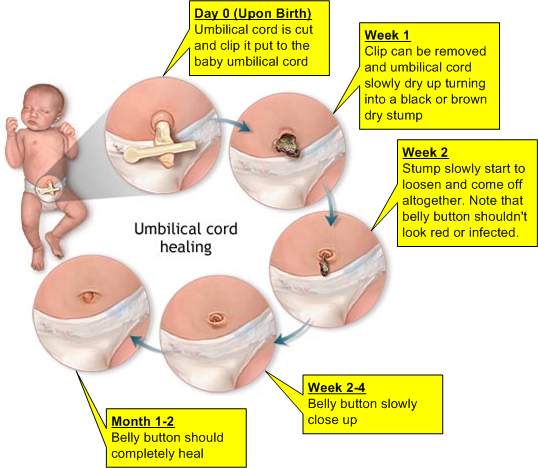
- There is an opinion that it is precisely because the child's umbilical cord is immediately cut that it turns blue. Therefore, the umbilical cord must be left intact.
- As soon as a child is born, he takes his first breath and his lungs open. He starts to breathe on his own, and that's the whole point. The fact that they can have a bluish color indicates that during childbirth the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, which is completely normal, because during contractions the vessels are pinched, but this is all a physiological process.
- Women eat placenta because they believe it helps them recover faster after childbirth, increase energy levels, stimulate milk production, and improve hormone levels. Many also refer to the fact that all animals eat the placenta after childbirth, which means that it is useful.
- The benefits of eating the placenta have not been proven. Now all over the world, studies are being conducted on this subject, but so far they have not given positive results, and there is no point in taking it by itself or drugs made from it.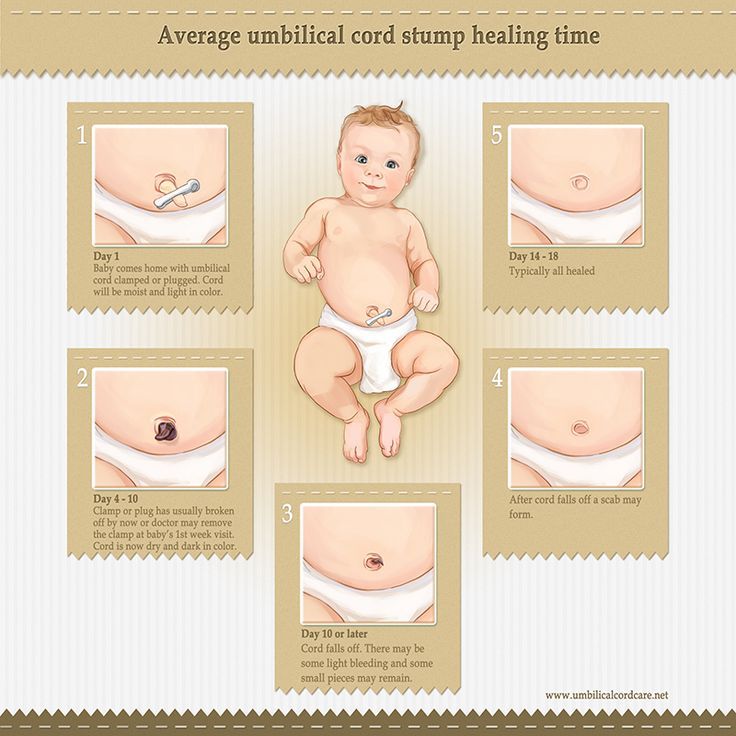 As a rule, studies are conducted as follows: among a very large number of subjects, it is compared whether there was a positive effect from taking placental drugs or not. And if not, then why is all this necessary? But in order to conduct these studies, a lot of time and resources are needed, so this work is still in progress.
As a rule, studies are conducted as follows: among a very large number of subjects, it is compared whether there was a positive effect from taking placental drugs or not. And if not, then why is all this necessary? But in order to conduct these studies, a lot of time and resources are needed, so this work is still in progress.
The placenta performs several functions - gas exchange, hormonal and excretory, it is a barrier between the mother and the fetus, helps the fetus grow and protects it from various external influences, while not protecting it from drugs, alcohol, drugs, nicotine. That is, it, as a temporary organ, works until the moment of childbirth, and after that it no longer exists.
The argument that animals eat the placenta cannot be considered justified either, since animals do this not for reasons of benefit, but because the placenta attracts the attention of predators. By eating it, animals protect themselves and their offspring from danger.
More vitamins: how much dietary supplements do pregnant women need?
— In Instagram, the blogs of the so-called healers, who advise taking a huge amount of dietary supplements, are very common. At the beginning of summer, there was a big scandal with this: the famous Instagram blogger Elena Kornilova prescribed through her blog to women, including pregnant women, a large amount of vitamins from the well-known American site Iherb, some of which contained dangerous elements. Nevertheless, there is an opinion that pregnant women need a lot of vitamins to maintain the health of the body. Is it so?
At the beginning of summer, there was a big scandal with this: the famous Instagram blogger Elena Kornilova prescribed through her blog to women, including pregnant women, a large amount of vitamins from the well-known American site Iherb, some of which contained dangerous elements. Nevertheless, there is an opinion that pregnant women need a lot of vitamins to maintain the health of the body. Is it so?
- Any medical advice on Instagram needs to be said categorically "no". The person behind the blog can present themselves as they please, and there is no way you can verify this data. There is also a fashion consultation based on the results of analyzes, but this does not work that way. A doctor does not treat tests, he treats a person, it is necessary to communicate with the patient, to see him.
All over the world, medical research on pregnant women is prohibited, so even on specialized vitamins and medicines it is written that they should be taken with caution by pregnant women. There is the concept of drug safety.
There is the concept of drug safety.
Almost all pregnant women take folic acid, some drugs are selected individually according to indications, someone takes medicines necessary for the treatment of chronic diseases. Take what has been proven to be beneficial, but as prescribed by doctors. Picking something for yourself is dangerous.
We give birth like at home - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Zimina Natalya Nikolaevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
MD GROUP Clinical Hospital
How home birth is represented
The most typical arguments of supporters of home births:
- A woman's body is designed specifically to give birth to children. By nature, it has all the necessary strengths and capabilities to give birth to a healthy child on its own, which means that the help of a doctor in this process is completely unnecessary.
- The maternity hospital is not needed, because the atmosphere in it is official, hospital, and this does not contribute to relaxation in contractions and the opening of the cervix.

- When giving birth at home, you can take any position that is comfortable for the woman.
- And at home, you can give birth in the water (in the bath), or at least just relieve contractions by immersion in water.
- During home birth, not strangers (doctors, midwives) will be nearby, but the husband, relatives or friends.
- From the first minutes of birth, the child will be constantly next to his mother, he will not be supplemented, he will not be subjected to unnecessary manipulations and examinations.
Well, ideally, supporters of home births present them like this: effective contractions begin at 40 weeks, the first stage of labor lasts no longer than 10-12 hours. At this time, the woman in labor behaves in a way that is convenient for her, takes comfortable postures, uses techniques to anesthetize contractions (massage, breathing, water). Then comes the complete opening of the cervix, water spontaneously pours out, there are attempts, during which a healthy baby is born without much effort. The child is immediately applied to the mother's breast - he sucks it as much as he wants, the umbilical cord is cut only after the end of the pulsation. Mom has no breaks, the child is absolutely healthy. In general, everyone is satisfied and happy.
The child is immediately applied to the mother's breast - he sucks it as much as he wants, the umbilical cord is cut only after the end of the pulsation. Mom has no breaks, the child is absolutely healthy. In general, everyone is satisfied and happy.
Actually
The picture of home birth is presented, of course, idyllically. And how happy ordinary women would be, and doctors too, if every birth went that way. But it’s not always possible to give birth the way you breathe. In childbirth or immediately after them, various unpleasant situations can arise with a woman or a child. We will not list them so as not to upset anyone. Let's just say that often the life and health of mother and baby depend on how quickly they received medical assistance . But what can be done at home in such a situation? The only thing is to call an ambulance, because it is impossible to help a child with asphyxia or a woman with bleeding or high blood pressure without certain drugs, equipment, and simply medical skills.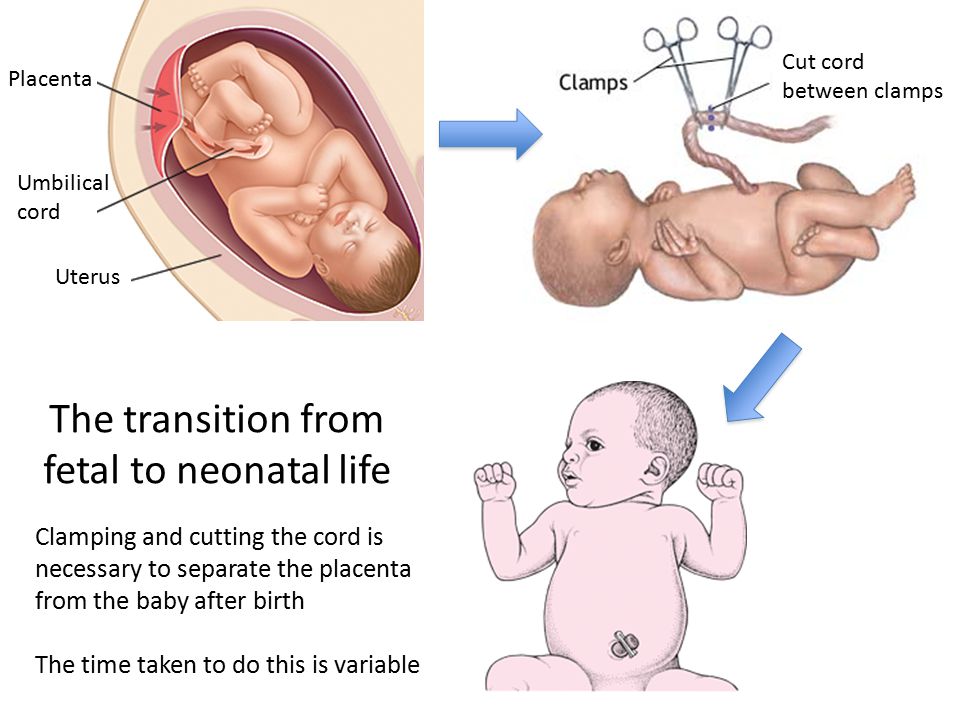 But after all, one of the specialists will be present at the birth with the expectant mother? Good obstetricians and gynecologists are well aware of the high risk of home births, so they do not accept births at home, and a midwife, even with experience, will only cope with the simplest situation. In addition, many so-called spiritual obstetricians, as a rule, do not even have a higher, often secondary medical education, and, of course, they do not bear any legal responsibility for the outcome of childbirth. And it happens that sometimes in home births there is no midwife at all (did not come or the woman was convinced that she was not needed). Therefore, of course, we can agree that the home environment helps a lot, but will it be possible to give birth in it in the event of some non-standard or difficult situation?
But after all, one of the specialists will be present at the birth with the expectant mother? Good obstetricians and gynecologists are well aware of the high risk of home births, so they do not accept births at home, and a midwife, even with experience, will only cope with the simplest situation. In addition, many so-called spiritual obstetricians, as a rule, do not even have a higher, often secondary medical education, and, of course, they do not bear any legal responsibility for the outcome of childbirth. And it happens that sometimes in home births there is no midwife at all (did not come or the woman was convinced that she was not needed). Therefore, of course, we can agree that the home environment helps a lot, but will it be possible to give birth in it in the event of some non-standard or difficult situation?
Natural childbirth is possible
But how then to ensure naturalness in childbirth and are there such childbirth at all? In fact, today, natural childbirth is widely carried out in most maternity hospitals, and is not only carried out, but also actively promoted . If everything goes well, if the birth proceeds correctly, if the baby’s heart beats evenly, and the mother feels good, the doctors of the maternity hospital do not interfere with the birth, but simply observe their course. A woman gives birth on her own, as nature dictates. But what about the notorious home comfort in childbirth? Turns out today many maternity hospitals provide natural childbirth "at home" :
If everything goes well, if the birth proceeds correctly, if the baby’s heart beats evenly, and the mother feels good, the doctors of the maternity hospital do not interfere with the birth, but simply observe their course. A woman gives birth on her own, as nature dictates. But what about the notorious home comfort in childbirth? Turns out today many maternity hospitals provide natural childbirth "at home" :
- Almost everywhere is now actively practiced free behavior during childbirth : a woman in labor does not have to lie on the bed all the contractions, but can choose any position.
- In many maternity hospitals there are various devices to facilitate contractions : transforming beds, balls, ropes (with their help you can take different positions in contractions), and in some, in addition to the shower, there is even a jacuzzi in which you can spend the first stage of childbirth.
- Of course, not all, but already many Russian maternity hospitals have either been renovated or built in accordance with modern ideas about beauty and comfort .
 Even in free maternity hospitals there are cozy double rooms with a private bathroom, fresh renovation and beautiful linens. What can we say about childbirth under a contract or in a commercial clinic - the conditions there are more than excellent.
Even in free maternity hospitals there are cozy double rooms with a private bathroom, fresh renovation and beautiful linens. What can we say about childbirth under a contract or in a commercial clinic - the conditions there are more than excellent. - According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, in any maternity hospital where there are separate maternity boxes, a husband, girlfriend, personal midwife or even a psychologist can be present at the birth, and absolutely free of charge . So, the expectant mother will not be left without support.
- Today, in all maternity hospitals, babies are immediately applied to the mother's breast; it is also possible for mother and baby to stay together in the postpartum department.
- Now you can easily find a maternity hospital where you can live together with your husband after childbirth in a comfortable family room . All this, of course, is not free - but if you really want it, then it is quite feasible.
So do not be afraid of the maternity hospital: it has all the conditions for natural and safe childbirth. And home birth is an unjustified risk and an unknown result.
Have you read at least one story about childbirth at home that ended unsuccessfully? Hardly. And if they read it, it is not enough. And the reason for this, as a rule, is the same: with an unfavorable development of childbirth and problems with the child, a woman is aware of her carelessness and simply keeps silent about it.
“They used to give birth in the field” is one of the popular arguments of supporters of home births. They gave birth, but only the mortality rate in childbirth (both children and mothers) was extremely high.
An individual approach to a future mother and her baby, living together, free behavior during childbirth, the opportunity to choose a doctor and midwife, take a husband to give birth - all this is now available in many Russian maternity hospitals
5 signs that you are having a natural birth in the hospital
- Freedom of movement: in the maternity box there is a multifunctional bed-transformer, balls, ropes.