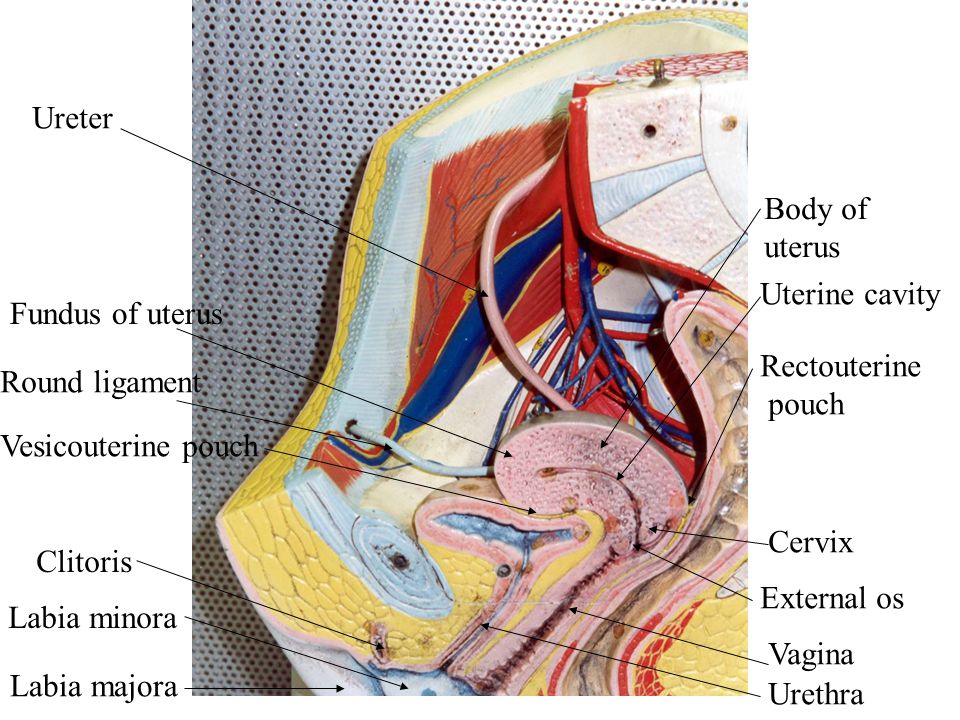
Pregnancy levels at 6 weeks
Low hCG Levels: Causes, Treatments, and Symptoms
Low hCG Levels: Causes, Treatments, and SymptomsMedically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Becky Young on November 3, 2017
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
What is an hCG test?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced by your placenta once an embryo implants in the uterus.
The purpose of the hormone is to tell your body to continue to produce progesterone, which prevents menstruation from occurring. This protects the endometrial uterine lining and your pregnancy.
A pregnancy test can detect hCG in your urine if your levels are high enough. This is how the test identifies that you are pregnant. But only a blood test can give you a precise numerical hCG reading.
Purchase pregnancy tests here.
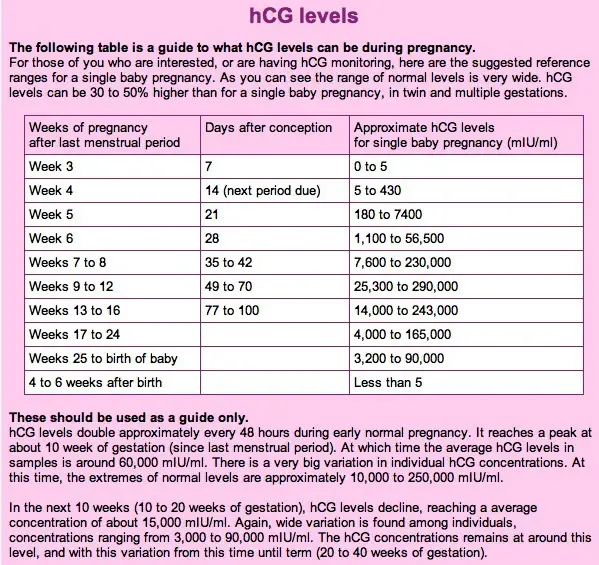
Standard hCG levels
Standard hCG levels vary quite massively from woman to woman. This is because hCG levels really depend on what is normal for you, how your body responds to pregnancy, as well as how many embryos you are carrying. The way a woman’s body reacts to pregnancy is entirely unique.
The table below gives you a guideline as to the normal wide range of hCG levels in each week of pregnancy. hCG levels are measured in milli-international units of hCG hormone per milliliter of blood (mIU/mL).
hCG levels usually consistently rise until around week 10–12 of your pregnancy, when the levels plateau or even decrease. This is the reason why pregnancy symptoms can be greater in the first trimester and ease off after this time for many women.
In early pregnancy, hCG levels usually double every two to three days. Interestingly, when the measurements start off high they don’t expand at the same rate. If they start off more slowly, the increase ends up happening much quicker.
If your hCG levels fall below the normal range, your doctor may want you to have a blood test every two to three days to ensure the levels are increasing. A single measurement of your hCG level is not useful. To give an accurate indication, a series of hCG blood tests needs to be taken a couple of days apart and the readings compared. There is often variation with a rapid increase in numbers, especially in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
A single measurement of your hCG level is not useful. To give an accurate indication, a series of hCG blood tests needs to be taken a couple of days apart and the readings compared. There is often variation with a rapid increase in numbers, especially in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Causes of low hCG levels
If your hCG levels fall below the normal range, it’s not necessarily a cause for concern. Many women have gone on to have healthy pregnancies and babies with low hCG levels. Most women don’t ever have cause to find out what their hCG levels are specifically.
However, sometimes low hCG levels can be caused by an underlying problem.
Gestational age miscalculated
Typically, the gestational age of your baby is calculated by the date of your last menstruation. This can be easily miscalculated, particularly if you have a history of irregular periods or are unsure of your dates.
When low hCG levels are detected, it’s often because a pregnancy that was thought to be between 6 and 12 weeks is actually not that far along. An ultrasound and further hCG tests can be used to calculate the gestational age correctly. This is usually the first step when low hCG levels are detected.
An ultrasound and further hCG tests can be used to calculate the gestational age correctly. This is usually the first step when low hCG levels are detected.
Miscarriage
A miscarriage is a pregnancy loss that occurs before 20 weeks of gestation. Sometimes low hCG levels can indicate that you have had or will have a miscarriage. If the pregnancy fails to develop a placenta, then the levels may be normal initially but fail to rise. Common signs that you are experiencing a miscarriage are:
- vaginal bleeding
- abdominal cramps
- passing tissue or clots
- cessation of pregnancy symptoms
- discharge of white/pink mucus
Blighted ovum
This is when an egg is fertilized and attaches to the wall of your womb, but does not continue to develop. When the gestational sac develops, hCG hormone can be released, but the level does not rise since the egg doesn’t develop.
This occurs very early in pregnancy. Most women won’t even know that it’s taken place. Usually you’ll experience your normal menstruation symptoms and assume it’s your usual period. However, if you’re trying to conceive, you may do an early pregnancy test that could pick up the presence of hCG.
Usually you’ll experience your normal menstruation symptoms and assume it’s your usual period. However, if you’re trying to conceive, you may do an early pregnancy test that could pick up the presence of hCG.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tube and continues to develop. It’s a dangerous and life-threatening condition, as it may cause the fallopian tube to rupture and bleed excessively. Low hCG levels can help to indicate an ectopic pregnancy. At first the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can be similar to those of a normal pregnancy, but as it progresses you can experience the following:
- abdominal or pelvic pain that worsens with straining or movement (this can happen strongly on one side initially and then spread)
- heavy vaginal bleeding
- shoulder pain caused by internal bleeding (the bleeding aggravates the diaphragm and presents as pain at the tip of the shoulder)
- pain during intercourse
- pain during a pelvic examination
- dizziness or fainting due to internal bleeding
- symptoms of shock
How is it treated?
Unfortunately, there is nothing that can be done to treat low hCG levels, though low levels alone are not always a cause for concern.
If your low hCG levels have been caused by a miscarriage, it’s possible that you may need treatment if any pregnancy tissue is left inside your womb. If there’s no tissue retained, then you won’t require any treatment at all. If there is, then there are three treatment options available:
- You can wait for the tissue to pass naturally.
- You can take medication to help you to pass the tissue.
- You can have it surgically removed.
Your doctor will discuss with you what the best course of action is.
The treatments for an ectopic pregnancy are similar. Medications are given to prevent the pregnancy from continuing to grow. If surgery is required, it’s standard for the doctors to remove the affected fallopian tube as well as the pregnancy.
What’s the outlook?
Low hCG levels alone are not necessarily a reason to be worried. There are many factors that affect the levels, and the normal range varies hugely between individual women. Your doctor will be able to monitor your hCG levels for you if you have concerns. Even if they remain low, there is nothing that you can do. It’s also important to remember that low hCG isn’t caused by anything you’ve done.
Your doctor will be able to monitor your hCG levels for you if you have concerns. Even if they remain low, there is nothing that you can do. It’s also important to remember that low hCG isn’t caused by anything you’ve done.
If your low hCG levels are due to a pregnancy loss, this doesn’t necessarily mean that you won’t be able to get pregnant and carry to term in the future. If you lose a fallopian tube due to an ectopic pregnancy, your fertility shouldn’t change significantly as long as your other tube is functioning. Even if it isn’t, reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization can help lead to successful pregnancy.
Last medically reviewed on November 3, 2017
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Fan J, et al. (2017). Advances in human chorionic gonadotropin detection technologies: A review.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29056064 - Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG): The pregnancy hormone. (2017).
americanpregnancy.org/while-pregnant/hcg-levels/ - Lawrenz B, et al. (2017). Luteal phase serum progesterone levels after GnRH-agonist trigger – how low is still high enough for an ongoing pregnancy?
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29037085 - Matson PL, et al. (1990). Measurement of human chorionic gonadotropin during early pregnancy: A comparison of two immunoradiometric assays.
link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF01135683 - Schumacher A. (2017). Human chorionic gonadotropin as a pivotal endocrine immune regulator initiating and preserving fetal tolerance.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29039764
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Nov 3, 2017
By
Becky Young
Edited By
Phil Riches
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Becky Young on November 3, 2017
Read this next
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) Blood Test
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Get the facts on the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) blood test. Although it's often used to detect pregnancy, it has other uses such as detecting…
READ MORE
Can Taking Prometrium Vaginally Prevent Miscarriage?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
Progesterone is known as the “pregnancy hormone.” Without enough progesterone, a woman’s body can’t continue to grow a fertilized egg. If you’ve…
READ MORE
How Does Clomid Work for Fertility?
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Clomid is also known as clomiphene citrate.
 It’s an oral medication that is often used to treat certain types of female infertility.
It’s an oral medication that is often used to treat certain types of female infertility. READ MORE
How Many Eggs Are Women Born With? And Other Questions About Egg Supply
If you're looking to get pregnant, you may wonder how many eggs you have at various points in life. The short answer: It goes from millions to none.
READ MORE
Your Guide to the Egg Donation Process
Medically reviewed by Fernando Mariz, MD
There are many reasons you might consider donating your eggs. Learn more about the egg donation process, including possible risks, legal…
READ MORE
What’s the Connection Between Your Biological Clock and Fertility?
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
The biological clock describes the pressure people may feel to get pregnant while at the peak of their reproductive years, before fertility declines.

READ MORE
How Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Affects Fertility and What to Do
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common cause of infertility. We'll discuss why and what you can do.
READ MORE
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
- 3 weeks: 6 – 70 IU/L
- 4 weeks: 10 - 750 IU/L
- 5 weeks: 200 - 7,100 IU/L
- 6 weeks: 160 - 32,000 IU/L
- 7 weeks: 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L
- 8 weeks: 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L
- 9 weeks: 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L
- 10 weeks: 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L
- 12 weeks: 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L
- 14 weeks: 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L
- 15 weeks: 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L
- 16 weeks: 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L
- 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester): 1,400 - 53,000 IUL
- 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester): 940 - 60,000 IU/L
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.
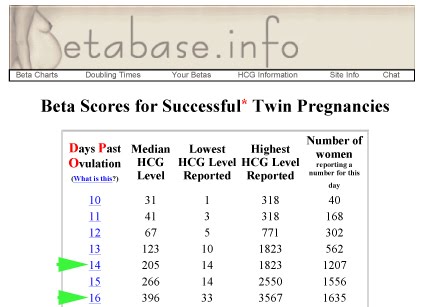
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet), Lab Tests Online (Human chorionic gonadotropin), UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
Sometimes, a home pregnancy test may be positive when a woman isn’t pregnant.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness. Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
Read more on Parenthub website
Support for Girls - Brave Foundation
Yes, it sounds like in the movies, but food cravings sometimes can be a sign of pregnancy
Read more on Brave Foundation website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
signs, sensations, size and development of the fetus
PreviousNext
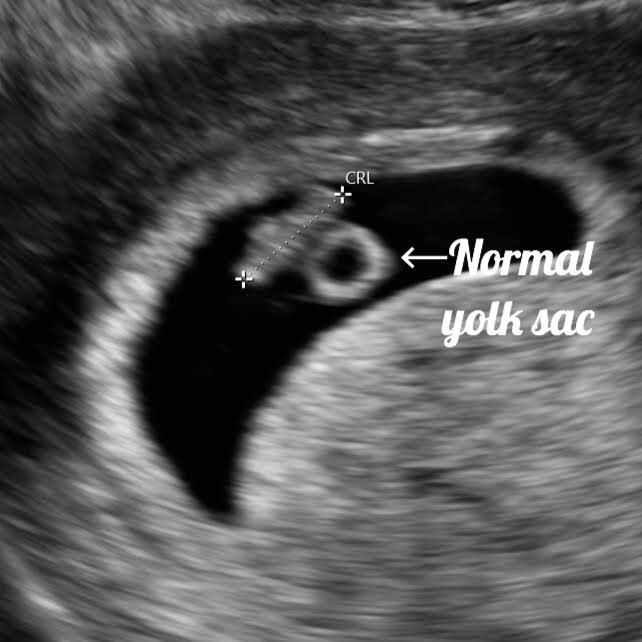
If you suspect you are pregnant but have not yet taken a test, do so now. At the 6th week, the baby can already be measured. The standard practice for ultrasound is to measure from crown to coccyx, and it is now approximately 5-6 mm.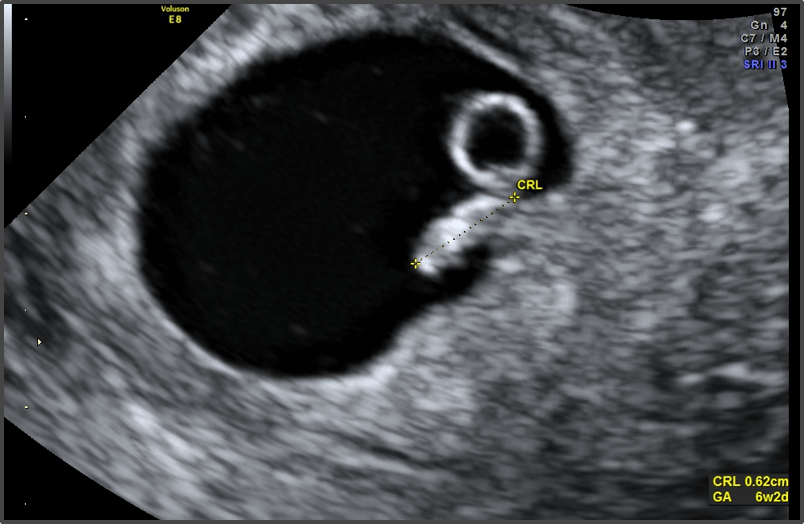
The child's head is still very large in relation to the body, but small wrinkles are already visible where the face and jaw will later appear. There are small outgrowths on both sides of the body, which will eventually become the arms and legs of the baby, and cavities appear on the sides of the head, from which the auditory canals are formed. The child's eyes and nose begin to develop, therefore, facial features are already being formed. Everything happens very quickly, but so far your pregnancy is not obvious to anyone but you.
Physical changes this week
-
Most likely, you feel the same symptoms as last week, only they have become stronger. More nausea, more sensitivity to smells, more fatigue and less energy. Be patient and don't try to fight nature. Ironically, there are good reasons why you feel the way you do, and they're not all that bad.
-
You may feel sick or hungry most of the time.
 Some women have a sharp increase in appetite, and they want products that they usually did not even think about. Meat, fish and seafood, fruits and even ice are some of the most common taste preferences.
Some women have a sharp increase in appetite, and they want products that they usually did not even think about. Meat, fish and seafood, fruits and even ice are some of the most common taste preferences. -
Your breasts and nipples may become even more sensitive. The breasts may take on a bluish tint due to the fullness of the veins with blood, their size may increase, and the nipples may darken.
-
You may experience vaginal discharge. If they are too heavy, itchy, or have a strange smell, check with your doctor. The increased activity of hormones during pregnancy leads to changes in the vaginal flora and normal acid-base balance. This can lead to fungal infections.
-
You may find yourself swallowing more often. Some pregnant women have increased saliva production and have to constantly swallow to cope. This is normal and will pass with time.
-
Some women complain of headaches during this period.
 Try not to take medication and choose natural ways to deal with this problem, such as going to bed, eating something healthy, drinking water, or taking a warm shower. Head massage can also help.
Try not to take medication and choose natural ways to deal with this problem, such as going to bed, eating something healthy, drinking water, or taking a warm shower. Head massage can also help. -
If you are pregnant for the second time (or more), you may notice that your clothes are a little tighter around the waist and bust. But this is not due to the fact that the baby has grown a lot - he is still in your pelvic area.
Emotional changes this week
-
This period can be interesting emotionally. Your pregnancy is becoming more than real, which means that the time has come to give up the usual pleasures. Smoking, drinking alcohol or drugs are all risky things, especially now. It's time to stop, because your child is at a crucial stage in his development.
-
You may still be worried every time you go to the toilet. Even though your period hasn't come for a couple of weeks and your pregnancy is confirmed, you may be afraid of a miscarriage.
 This is a common fear, especially in the first trimester.
This is a common fear, especially in the first trimester. -
You may be itching to share the news, but due to the possibility of a miscarriage, you haven't told anyone yet. Discuss with the future dad when you tell the world about your joy.
What's happening to the baby this week
-
Your baby looks like a tadpole with a huge head, a small body, and small outgrowths where legs and arms will later appear. However, his appearance at the 6th week changes rapidly. Even when you are sleeping.
-
A transvaginal ultrasound can see the baby's tiny heart beating. If you count, it turns out that it gives out about 80 beats per minute.
-
Important internal organs such as the liver, kidneys and lungs are laid. It is no wonder that you are so tired: your energy is spent on the development of the child.
-
Your baby's jaw, chin and cheeks begin to form this week.
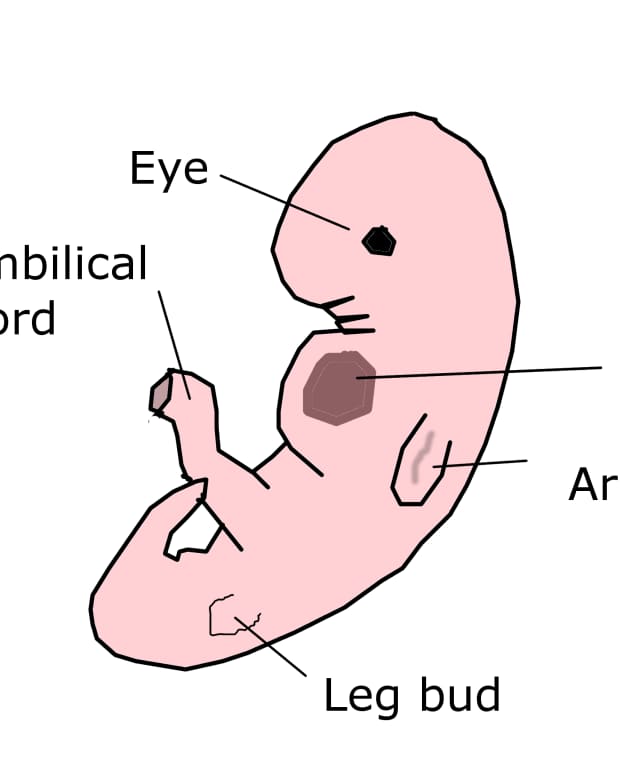 So far they are tiny, but they will grow every day.
So far they are tiny, but they will grow every day.
Tips of the week
-
Keep some small snacks in your bag at all times. Salty crackers, sweet biscuits and water can be indispensable in the fight against nausea during pregnancy.
-
Put a container with a lid in the car in case of nausea. Make sure the cover can be quickly removed. There is no need to be ashamed if an attack of nausea catches you in front of other people. This has happened to many women.
-
Avoid all toxins, chemicals, drugs, alcohol, x-rays, and risky behavior in general. The sixth week is an important time for embryo development.
-
Don't worry if you lost a little weight in week 6. Nausea and vomiting can lead to weight loss, but you will have plenty of time to recover and surpass your pre-pregnancy weight.
Let's see what's there in the 7th week.
PreviousNext
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics
Content
- Table of average hCG norms
- Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins
- Table of average hCG values after IVF with engrafted twins
- Guidelines for free β-hCG subunit
- Norm РАРР-А
- What if I am at high risk?
- How to confirm or deny the results of screening?
- The doctor says I need an abortion. What to do?
One of the main tests during pregnancy is the study of the level of the pregnancy hormone - hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin. If expectant mothers want to know if the hormone level is normal, we made a summary table of values
Table of average hCG norms:
| Gestation period | HCG in mU/ml | HCG in mIU/ml | HCG in ng/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 25-156 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 2-3 weeks | 101-4870 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 3-4 weeks | 1100 – 31500 | 25-156 | - |
| 4-5 weeks | 2560 – 82300 | 101-4870 | - |
| 5-6 weeks | 23100 – 151000 | 1110 -31500 | - |
| 6-7 weeks | 27300 – 233000 | 2560 -82300 | - |
| 7-11 weeks | 20900 – 291000 | 23100 -233000 | 23. 7 - 130.4 7 - 130.4 |
| 11-16 weeks | 6140 – 103000 | 20900 -103000 | 17.4 - 50.0 |
| 16-21 weeks | 4720 – 80100 | 6140 – 80100 | 4.67 - 33.3 |
| 21-39 weeks | 2700 – 78100 | 2700 -78100 | - |
Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins:
| Gestation period, weeks | Mean hCG concentration range (mU/ml) |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 112 |
| 2-3 weeks | 209 – 9740 |
| 3-4 weeks | 2220 – 63000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 5122 – 164600 |
| 5-6 weeks | 46200 – 302000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 54610 – 466000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 41810 – 582000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 12280 – 206000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 9440 – 160210 |
| 21-39 weeks | 5400 – 156200 |
Table of average hCG values after IVF with engrafted twins:
| Gestational age, weeks | HCG range, mU/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 600 |
| 2-3 weeks | 3000 - 10000 |
| 3-4 weeks | 20000 – 60000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 5-6 weeks | 100000 – 400000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 100000 – 400000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 40000 – 120000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 20000 – 70000 |
| 21-39 weeks | 20000 – 120000 |
Free hCG β-subunit limits
Measuring free hCG β-subunit levels can more accurately determine the risk of Down syndrome in an unborn child than measuring total hCG.
Norms for free β-hCG subunit in the first trimester:
| Gestational age, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 9 weeks | 23.6 - 193.1 ng/ml, or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 10 weeks | 25.8 - 181.6 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 11 weeks | 17.4 - 130.4 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 12 weeks | 13.4 - 128.5 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 13 weeks | 14.2 - 114.7 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM.
If hCG is abnormal, then:
- If the free β-subunit of hCG is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, then the child has an increased risk of Down syndrome.
- If the free hCG β-subunit is below normal for your gestational age, or is less than 0.5 MoM, then the baby is at increased risk of Edwards syndrome.
PAPP-A norm
PAPP-A, or "pregnancy-associated plasma protein A" as it is called, is the second indicator used in first trimester biochemical screening. The level of this protein constantly increases during pregnancy, and deviations in the indicator may indicate various diseases in the unborn child.
Norm for PAPP-A depending on the duration of pregnancy:
| Gestational period, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 8-9 weeks | 0.17 - 1.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 9-10 weeks | 0.32 - 2.42 mU/mL or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 10-11 weeks | 0.46 - 3.73 mIU/mL, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 11-12 weeks | 0.79- 4.76 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 12-13 weeks | 1. 03 - 6.01 mIU/mL, or 0.5 to 2 MoM 03 - 6.01 mIU/mL, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 13-14 weeks | 1.47 - 8.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM.
If PAPP-A is abnormal:
- If PAPP-A is lower for your gestational age, or less than 0.5 MoM, your baby is at increased risk of Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome.
- If PAPP-A is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, but other screening values are normal, then there is no cause for concern.
Studies have shown that women with elevated PAPP-A levels during pregnancy are not at greater risk of fetal disease or pregnancy complications than other women with normal PAPP-A.
What if I am at high risk?
If your screening reveals an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, then this is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy.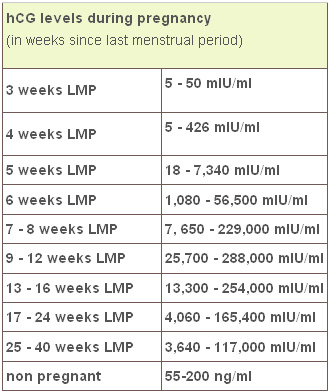 You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
How to confirm or refute the screening results?
If you think the screening was not done correctly, then you should be re-examined at another clinic, but for this you need to retake all the tests and get an ultrasound. This method is possible only if the gestational age at the time of the examination does not exceed 13 weeks and 6 days.
The doctor says I need an abortion. What to do?
Unfortunately, there are times when a doctor strongly recommends or even forces an abortion based on screening results. Remember: no doctor has the right to such actions. Screening is not a definitive method for diagnosing Down syndrome and, based on poor results alone, a pregnancy should not be terminated.
Say that you want to consult a geneticist and undergo diagnostic procedures for Down syndrome (or other disease): chorionic villus biopsy (if you are 10-13 weeks pregnant) or amniocentesis (if you are 16-17 weeks pregnant).
The author of the article:
Ananyina Anna Alexandrovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Work experience since 2010
Sign up
Eat more foods rich in iron: beef tongue, liver, buckwheat and oatmeal, prunes, dried apricots, green apples, etc. But diet alone will not work to raise hemoglobin.
Medical therapy with iron supplements is required. If the problem is associated with insufficient intake of iron into the body, one set of drugs is needed, if with absorption, another. The doctor must select drugs.
Injection therapy may be required for more severe anemia.
If there are no contraindications, natural childbirth is possible. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist should decide on the possibility of EP.
Get tested
- Chest X-ray
- KSR
- Hepatitis B HBsAg
- Hepatitis C Anti-HCV
- Rubella IgM
- Rubella IgG
- HIV
- B/P for flora and senses.
 - from throat
- from throat
Specialist consultation:
- General practitioner consultation
With an increase in the duration of pregnancy and the growth of the baby, the uterus increases - this can lead to increased tone. Sometimes tension arises in response to the movements of the child. Strong physical exertion, stress, overwork of a pregnant woman can also lead to increased tone.
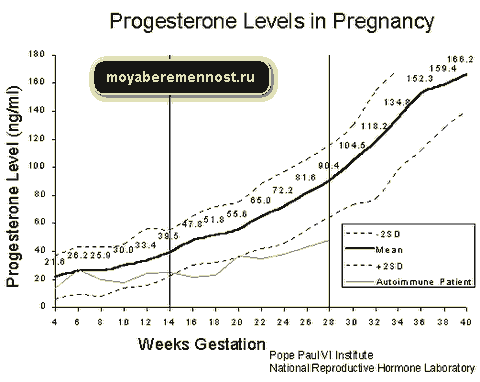
In early pregnancy, uterine tone may be associated primarily with reduced progesterone production. In this case, the doctor prescribes the patient treatment with progesterone preparations.
Symptoms of increased tone
All pregnant women experience tone differently. Someone - like heaviness and tension in the lower abdomen. Others - as a pulling pain in the lumbar region. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, a woman can feel the tone by putting her hand on her stomach: the uterus becomes "stone", then relaxes.
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Ph.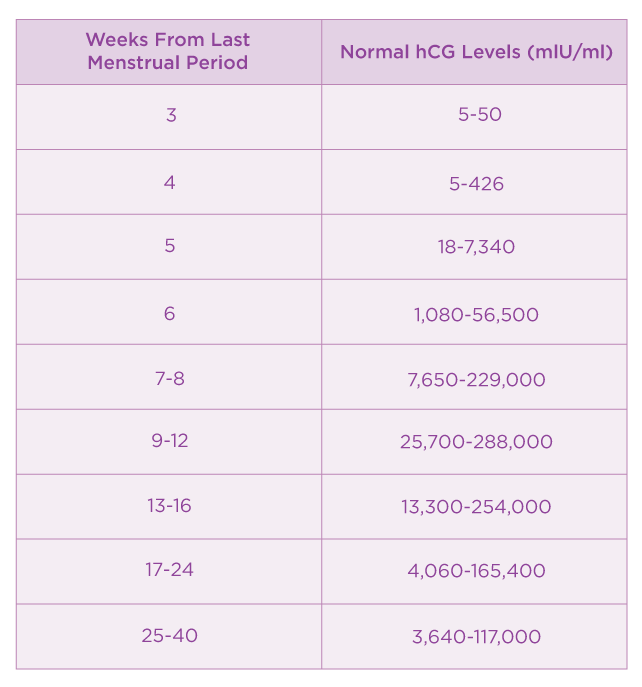 D.
D.
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Check the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist / Gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the second category
Check the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Mobile application of the clinic
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more.