How to cure dry cough in child
Causes, Treatments & When To See A Doctor
Coughing is your body’s way of getting rid of an irritant. Many things can cause a dry cough in kids, from a simple cold to an inhaled object.
Coughing is an important part of your body’s defense system, helping rid your body of potentially harmful microbes and irritants.
Coughs come in many types, including wet and dry. Wet coughs produce, or sound like they are producing, phlegm, or mucus. Dry coughs, on the other hand, don’t.
These are some common causes of cough in children:
Infections
Various viral or bacterial respiratory infections can lead to coughing due to irritation and inflammation in the airways.
The most familiar cause is the common cold, an infection in your upper respiratory tract with symptoms including sneezing, runny nose, and coughing. Rhinovirus is the most common cause of the common cold.
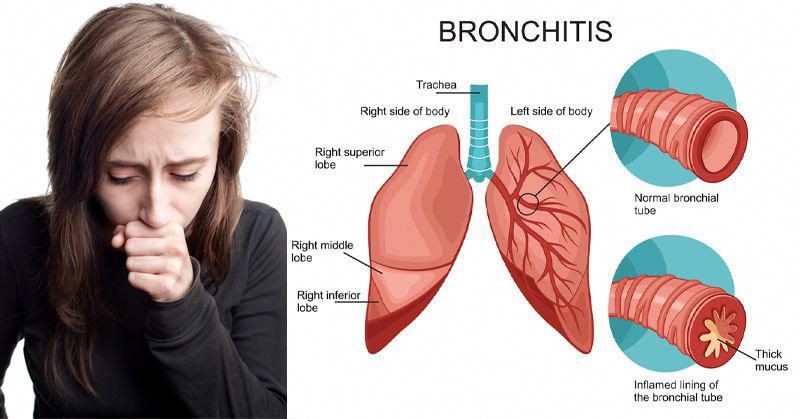
Another common cause is bronchitis, which can occur as a result of either the common cold or the flu. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis is usually a result of an infection. Chronic bronchitis can happen due to smoking or being exposed to air pollution.
Other infections that can lead to dry cough in kids include:
- croup: a viral condition that causes swelling around the vocal cords. It is usually viral but may be bacterial less commonly.
- pneumonia: an infection that causes inflammation in the lungs. It can be viral or bacterial.
- bronchiolitis: a viral infection that causes inflammation in the bronchioles or smallest passages in your lungs.
- pertussis: known as whooping cough, it’s a bacterial respiratory infection that causes violent, uncontrollable coughing that can make it hard to breathe. Whooping cough can be prevented through vaccination.
- COVID-19: The coronavirus can present with dry cough in children.
Depending on the infection, the cough may sound hoarse or have more of a wheezing sound. It may also worsen at night due to mucus from the nose trickling down the throat, irritating.
It may also worsen at night due to mucus from the nose trickling down the throat, irritating.
Other signs that your child may have a viral infection include:
- fever
- runny or stuffy nose
- sneezing
- headache
- body aches and pains
Unlike bacterial infections, viral infections don’t respond to antibiotic treatment. Instead, treatment relies on getting plenty of rest and fluids.
If your child is over 6 months old, they can be given ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) to help relieve fevers and body aches. Babies younger than 6 months can get acetaminophen (Tylenol). Avoid giving them aspirin, which can cause Reye’s syndrome in children.
Sometimes a cough can linger for several weeks after a viral respiratory infection. This is called post-viral cough. It likely occurs due to lingering inflammation or sensitivity in the airways following infection.
There’s no specific treatment for post-viral cough, but symptoms typically go away on their own after a few weeks.
Allergies
Allergies happen when the immune system mistakes something harmless for a foreign invader and overreacts.
The thing that causes an allergic reaction is called an allergen. There are many allergens, including pollen, animal dander, and specific foods or medications.
A substance called histamine is released during an allergic reaction and can cause respiratory symptoms.
Hoarse, dry coughing can be a symptom of allergies, particularly if it begins at a certain time of year or occurs after exposure to something specific like dust. For example, seasonal allergy or allergic rhinitis may develop in the spring when pollen is in the air.
Other allergy symptoms include:
- sneezing
- itchy, watery eyes
- runny nose
- rash
The best way to manage allergies is to avoid things that trigger your child’s symptoms. You can also try over-the-counter (OTC) allergy remedies, but follow the product instructions and ensure it’s appropriate for your child’s age and size.
If your child seems to experience allergies often, you may want to visit an allergy specialist. They can help you narrow potential allergens and recommend a long-term management plan.
Asthma
Allergies can also make asthma worse. This chronic disease causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it hard to breathe. Symptoms of asthma can also be triggered by respiratory illness or exercise.
Frequent spells of coughing, which can be dry or productive, are one of the signs of asthma in kids. Coughing may be more frequent at night or while playing. You may also hear a whistling noise when your child breathes in or out.
In some cases, chronic coughing may be the only symptom of asthma. This is called cough-variant asthma.
Other symptoms of asthma that you may see can include:
- difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- rapid breathing
- low energy levels
- chest tightness or pain
If your child is diagnosed with asthma, their healthcare professional will work with you to develop an asthma action plan. The plan will include your child’s asthma triggers and how and when they should take their medication.
The plan will include your child’s asthma triggers and how and when they should take their medication.
Asthma medication helps lower the inflammation in your child’s airways. Your child will likely have two types of medication — one for long-term asthma control and one for quick relief of asthma symptoms.
Environmental irritants
Exposure to various environmental irritants can cause throat inflammation, leading to a dry cough.
Common irritants that can cause a cough include:
- cigarette smoke
- car exhaust
- air pollution
- air that’s too cold or dry
The dry cough may become chronic if your child is frequently exposed to an irritant. Your child may be more susceptible to irritation if they also have allergies or asthma.
Coughs caused by exposure to irritants usually resolve once the irritant is removed.
Inhaled or swallowed foreign object
It’s not unusual for young children to put things in their mouths or noses, including buttons, beads, and other small objects. If they inhale too deeply, the object may get lodged in their airway. Or they might swallow the object, causing it to get stuck in their esophagus.
If they inhale too deeply, the object may get lodged in their airway. Or they might swallow the object, causing it to get stuck in their esophagus.
If your child has swallowed or inhaled something, their cough could be a sign that their body is trying to dislodge the object. You may also hear wheezing or choking noises.
If you believe your child has inhaled or swallowed a foreign object, seek immediate treatment.
A bronchoscopy may be needed to find and remove the object.
After removing the object, you’ll want to monitor them for signs of infection or further irritation.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is chronic acid reflux that can cause regurgitation, which is when the stomach’s content rises back up into the esophagus.
The burning sensation your child may feel is what we call heartburn. In some cases, however, some children with GERD can also experience persistent cough, hoarseness, or wheezing.
Different triggers for GERD in children may include exposure to secondhand smoking, obesity, and coexisting conditions that affect the lungs or the nervous system.
Somatic cough
A psychosomatic or somatic cough is a term that doctors use to refer to a cough that doesn’t have a clear cause and doesn’t respond to treatment. An underlying psychological issue or distress usually causes these coughs.
But these coughs are rarely diagnosed as there is more often a physical cause for the cough. If they occur, these coughs often last for more than 6 months and get in the way of day-to-day activities.
If your child’s healthcare professional has ruled out all the potential causes of their dry cough, they may diagnose it as a somatic cough. You’ll likely be referred to a child psychologist or psychiatrist.
It can take some time to figure out the cause of a dry cough in children. The main treatment will depend on the underlying cause.
These tips can help to provide some relief in the meantime:
- Inhale warm, moist air. Turn on the shower in your bathroom and close the door, allowing the room to steam up.
 Sit with your child for about 20 minutes as they inhale the warm mist.
Sit with your child for about 20 minutes as they inhale the warm mist. - Use a cool mist humidifier. If the air in your house is dry, it can also dry out your child’s airways. Try using a cool mist humidifier to add moisture to the air. Avoid heated humidifiers as these can cause burns.
- Drink warm fluids. Warm fluids can feel soothing if your child’s throat is sore from coughing. If your child is at least a year old, you can add some honey for added relief.
Coughing helps your body get rid of potentially harmful microbes and irritants. In children, dry coughs can be caused by many things, including viral or bacterial infections, asthma, allergies, and irritants.
OTC cough medications, inhaling steam from warm fluid, and using a cool-mist humidifier may help relieve cough symptoms. But you should discuss with your pediatrician which medication is appropriate for your child based on age and the right dosage.
Most coughs will resolve in 1 to 2 weeks, but contact a doctor if your child’s cough lasts longer than 2 to 3 weeks.
Here you will find answers to some common questions about dry cough in children:
What can I give my child for a dry cough?
In some cases, giving your child OTC cough medicines may be appropriate. But only give it to a child older than 6, and ensure to carefully follow the dosing directions on the packaging.
Children under age 6 shouldn’t take OTC cough medication unless it is recommended by their healthcare professional, especially decongestants, which can be associated with dangerous side effects.
If an OTC cough medication does not seem to help, there is no benefit to continuing to use it. These medicines do not cure a cough or help it go away faster.
Should I take my child to the doctor for a dry cough?
Most coughs will resolve in 1 to 2 weeks. If your child’s cough lasts longer than 2 to 3 weeks, contact a doctor.
When should I be concerned about my child’s cough?
Reasons for concern and seeking medical attention include:
- if you observed your child choking or think they may have swallowed an object
- if your child’s cough is increasingly frustrating
- if it persists longer than you think is reasonable
- if your child coughs up blood
- if the cough is affecting your child’s ability to participate in daily activities
- If your child is struggling to breathe or breathing fast
Treatment and when to see a doctor
Share on PinterestThe common cold, pertussis, and asthma can cause a dry cough in children.
Coughing is a natural defense mechanism the body uses to clear the airway and remove microbes and foreign objects.
People often produce dry coughs, also called nonproductive coughs, to clear an itch or irritation in the throat. These coughs are usually symptoms of an underlying condition in the upper respiratory tract.
Many things can cause dry cough in children, and its treatment depends on the cause. Taking note of other symptoms accompanying the cough can help identify its cause.
If a child feels like they are struggling to breathe, their caregiver should contact emergency services immediately.
In some cases, a caregiver can help prevent a dry cough by taking preventative measures. These may include getting the child appropriate vaccinations or avoiding exposure to allergens or irritants.
If a caregiver is not sure what is causing the cough, they may want to talk with the child’s doctor to get a diagnosis.
Types of infections
Viral infections invade the cells in the airway. This causes irritation and inflammation that may lead to coughing. A child may catch a virus from inhaling particles in the air or through close contact.
This causes irritation and inflammation that may lead to coughing. A child may catch a virus from inhaling particles in the air or through close contact.
Common cold
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), common colds are the main reason children miss school. While many viruses can cause colds, rhinoviruses are the most common.
Influenza (
flu)Flu is an infectious respiratory disease that is more dangerous than the common cold for children, especially those younger than 5 years old. The influenza virus causes it.
The flu can cause complications like pneumonia, dehydration, brain dysfunction, and, rarely, death.
Symptoms include fever, chills, body aches, runny or stuffy nose, and tiredness.
Pneumonia
A child may develop pneumonia from a virus, bacteria, or fungi. Globally, pneumonia is the leading cause of death among children who are past the newborn phase but under 5 years old.
While death from pneumonia is less common in the United States, pneumonia is still one of the most common reasons children get hospitalized.
Symptoms include:
- rapid breathing
- grunting or wheezing
- cough
- fever
- chest pain, or pain while coughing
Note: While the cough that occurs with pneumonia may be dry, in some cases it may sound wet or appear as a productive cough.
COVID-19
COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, a type of coronavirus. Symptomatic COVID-19 appears to be less common and less severe in children.
A child may or may not show symptoms similar to those of the common cold and flu. They may have pneumonia, with or without showing any symptoms.
The cough that comes with COVID-19 is often continuous. A child may cough frequently for more than an hour or have three or more coughing episodes within 24 hours.
Bronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis is a common viral infection in infants and children younger than 2 years old. Swollen small airways (bronchioles) make breathing difficult, causing wheezing and coughing.
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, preschool children who go to daycare can develop roughly eight viral respiratory infections in a year. Typically, each infection will last for 10 days.
Typically, each infection will last for 10 days.
If the child’s cough occurs toward the end of an upper respiratory infection, such as a cold, and clears within 1–2 weeks, a parent or caregiver typically does not need to do anything specific to treat the cough.
According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), coughing during a cold can help the body clear out mucus from the airways. It can also protect the lungs.
However, if the cough is dry or nonproductive, a caregiver should ensure that the child drinks plenty of fluids and warm drinks to help soothe their throat.
Other methods a caregiver can try include:
- using a humidifier in the child’s room
- running a hot shower with the door and windows or vents closed and having the child sit in the room
- opening a window or freezer to provide cold air for the child to breathe in if croup is causing the cough
A caregiver can also try giving the child honey, but only if the child is 12 months or older. Infants below this age do not have immunity to certain bacteria that may be present in honey.
Infants below this age do not have immunity to certain bacteria that may be present in honey.
A 2021 review found that honey was better than standard treatments for cough in reducing symptoms, severity, and frequency of upper respiratory tract infections.
Vaccines are the best way to prevent influenza and COVID-19 infections. Vaccines protect a child against illnesses, improve their immune response, and protect them against complications.
Pertussis
Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a bacterial infection that can be deadly in unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated children under 12 months old.
According to the CDC, a doctor can treat pertussis with antibiotics and supportive therapies in infants. However, the risk of serious illness and potentially death is higher in infants under 12 months.
Asthma is a chronic disease that occurs when the lung’s airways become inflamed. Asthma can be life threatening. A parent or caregiver should seek immediate medical attention if the child’s symptoms appear to be worsening.
They should also seek emergency medical help if the following occurs:
- retractions, or fast breathing where the skin sucks in around the chest plate or rib bones when the child inhales
- blue coloring in the face, fingernails, or lips
- flaring, which is when the nostrils move rapidly
- an expanded chest does not deflate when the child exhales
- an infant does not recognize or respond to a caregiver
- the ribs or stomach move in and out quickly
Children over the age of 6 months, including those with asthma, should get a yearly flu shot in the fall.
To treat asthma in children, a doctor or allergist may prescribe medication for quick symptom relief and long-term control.
The medication usually comes in the form of an inhaler. A person may also use a nebulizer. A healthcare professional can teach the caregiver and child how to use this device.
Irritants
Children may inhale irritants in the environment that irritate the airway and cause inflammation, leading to dry cough. These include:
These include:
- air pollution
- cigarette smoke
- fumes and vapors
- dust
- molds
- dry air
Removal of the irritant usually resolves the cough. However, a child repeatedly exposed to irritants may develop a chronic cough.
Allergies
Allergies can cause a dry cough in children. A caregiver can help a child use:
- over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines
- nasal sprays
- decongestants
If the allergies are severe, a child may need allergy shots.
A caregiver should seek emergency medical help if a child experiences:
- severe hives
- nausea
- vomiting
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- difficulty breathing
- tightness in the throat
- fainting
- rapid heartbeat
Acid reflux and GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when the stomach contents return to the esophagus. Infants and children can have reflux occasionally, but only 1 in 4 children has symptoms of GERD.
GERD in children may cause dry cough, problems in swallowing, and asthma symptoms. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition.
Doctors may advise parents to try lifestyle changes like avoiding certain foods, eating smaller meals, and changing sleep position.
They may also prescribe medications like h3 blockers and proton pump inhibitors or surgery in severe cases.
Somatic cough
Some children present with a cough with no medical diagnosis and do not respond to treatment. Doctors previously labeled it psychogenic, habit, or tic cough.
This rare condition is often diagnosed late, after prolonged attempts to diagnose and treat a child’s chronic cough. Most happen in children from 8–14 years old.
Habit coughs may be related to anxiety and stress. Parents can help identify triggers to diminish the coughing.
A 2020 study found that behavioral therapy is a successful treatment for the condition.
Foreign objects
It is typical for infants and young children to place things in their mouths. However, small objects may lodge in a child’s airway, and coughing may be their body’s attempt to remove the object.
However, small objects may lodge in a child’s airway, and coughing may be their body’s attempt to remove the object.
If a child shows signs of choking, caregivers should immediately perform the Heimlich maneuver or seek immediate help.
Signs of choking include:
- inability to cry or make sounds
- struggling to breathe
- chest and ribs pulling inward
- becoming reddish to bluish in the face
- fainting
A doctor will examine the child and ask questions about other symptoms and how long they have had the cough. During the exam, the doctor or other healthcare professional will evaluate the child’s breathing, vital signs, lungs, and other areas of the body.
Often the sound of the child’s cough, physical exam, and additional symptoms will be enough to determine the cause of the cough.
In some cases, such as allergic reactions, allergy tests may be required to determine the cause. A child may need to see an allergist for treatment in these cases.
A caregiver should take their child in for a medical evaluation if they have a cough that lasts longer than 2–3 weeks. Other reasons to seek medical care include the following signs and symptoms:
- a high fever or any fever in an infant
- rapid breathing
- trouble breathing or catching breath
- coughing up blood
- signs of dehydration
- a whooping sound when the child coughs
- a wheezing sound when the child breathes
A caregiver should also seek emergency care for a child if they show signs of a severe asthma attack or severe allergic reaction.
If a caregiver is ever unsure about what is causing the cough or is concerned, they should take the child to see a doctor or other healthcare professional, such as a physician assistant (PA) or nurse practitioner (NP).
There are several potential causes of a dry cough, including infections, allergens, pollutants, and asthma.
If a child has a dry cough, a caregiver may be able to monitor and treat the cough at home.
If a child has a known underlying condition, treating that condition should help the cough clear. However, if a caregiver does not know what is causing the cough, or a child has a high fever or other symptoms, they should take the child to see their doctor.
Treat dry cough in a child
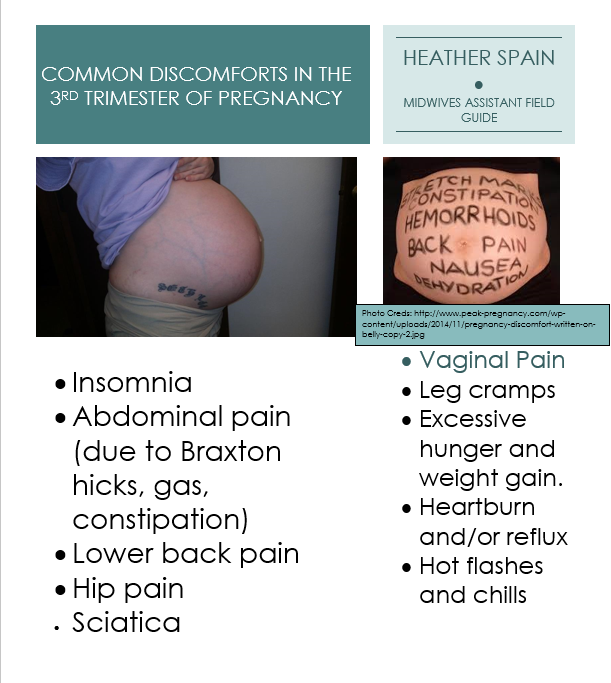
Parents are very sensitive to the health of their children and go to the doctor for any, even the slightest, reason. And rightly so, since in childhood even minor ailments can soon develop into a dangerous disease. An example of such a symptom in a child is a dry cough. It occurs quite often, so it is useful for parents to know what causes a cough and how to treat it properly. A dry cough is characterized by the fact that a secret ceases to be secreted in the airways (a substance that “lubricates” the throat), or the cough has a high viscosity, as in pneumonia. In addition, dry cough is caused by dirt or a foreign body entering the respiratory tract, swelling of the vocal cords, or narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi during their spasm.
Causes of dry cough
Doctors identify several causes of dry cough in children.
- Cough with inflammation of the vocal cords. With this pathology, the lumen of the glottis decreases in a person. As a result, a dry cough can be either loud and harsh (a "barking" cough) or, conversely, very quiet. Inflammation of the vocal cords in medicine is called laryngitis and usually appears due to damage to the vocal cords by a viral or other infection. Laryngitis can also appear without the influence of microbes - for example, the ligaments become inflamed when inhaled vapors of harmful substances, with allergies, or even with a loud cry.
- Bacterial infection. They are dangerous because dry cough is just one of the many signs of exposure to the body. Diseases such as tuberculosis, diphtheria, whooping cough and some others infect the entire body with toxins, causing a lot of trouble for a person, and in especially severe cases, leading to the death of the patient.
 These diseases lead to swelling of the tissues of the child's respiratory tract, accumulation of sputum in the bronchi, inflammation of the lymph nodes and other pathologies. From this, the patient begins to cough reflexively, and his cough can be both dry and with a large amount of sputum, which is difficult to excrete from the body.
These diseases lead to swelling of the tissues of the child's respiratory tract, accumulation of sputum in the bronchi, inflammation of the lymph nodes and other pathologies. From this, the patient begins to cough reflexively, and his cough can be both dry and with a large amount of sputum, which is difficult to excrete from the body. - SARS. One of the most common causes of dry cough in a child. Viruses enter the respiratory tract by airborne droplets, where they infect cells that soon die. This leads to irritation of the receptors in the throat, and a strong dry cough begins in a person. There are several varieties of respiratory tract infections, each with its own type of cough. For example, the most "upper" cough is observed with pharyngitis, when the pharynx is affected. Tracheitis is accompanied by irritation of receptors in the trachea, bronchitis - in the bronchi, and pneumonia, which is otherwise called pneumonia, is most difficult to tolerate.
- Pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura).
 Inflammation of the lining of the lungs can also be the cause of reflex dry cough in children and adults.
Inflammation of the lining of the lungs can also be the cause of reflex dry cough in children and adults.
- Allergic reactions. Another well-known cause of developing dry cough. An allergy can be recognized by its seasonal nature, as well as by the absence of other severe symptoms, such as fever. But if, simultaneously with a cough, a child has a severe runny nose and tearing, then it is possible to speak with a high degree of certainty about allergies. As a rule, it worsens in spring or autumn. Most often, children are allergic to pollen and pet dander.
- Gastroesophageal reflux. This term hides such an unusual pathology as the reverse flow of the contents of internal organs. In this case, we are talking about cases where gastric juice "rises" through the esophagus and enters the mouth or windpipe, causing coughing. As a rule, reflux appears after eating and in a supine position.
- Rare causes. They are not so common, but, nevertheless, they can be the cause of the development of dry cough.
 These include inflammation of the bronchial lymph nodes, lung tumors, inflammation of the respiratory tract, aortic aneurysm, and some types of heart defects.
These include inflammation of the bronchial lymph nodes, lung tumors, inflammation of the respiratory tract, aortic aneurysm, and some types of heart defects.
Treatment of dry cough in a child
Treatment of children is always more difficult than treatment of adults, and the situation with dry cough is no exception. Moreover, children under two years of age should not be given medication at all due to the high likelihood of overdose. Older children can be given drugs that fight the cough reflex, but for very young patients, other methods should be used to reduce irritation of receptors in the airways.
In any case, when choosing a drug, you need to carefully study the instructions for possible side effects. Usually, dry cough remedies are characterized by weakness, dizziness, and drowsiness that may occur after taking them. Therefore, doctors prescribe taking such drugs before bedtime.
It is important to know that, in addition to the indicated side effects, drugs must be compatible with other drugs and must not have contraindications for each patient. You can not treat a dry cough in a child on your own, because in this case there is a high risk of harming him.
You can not treat a dry cough in a child on your own, because in this case there is a high risk of harming him.
Parents should take their child to the doctor at the first sign of a dry cough to be examined and treated. The drugs that are used for this effectively relieve the child of irritation of the respiratory tract for up to 12 hours.
For home treatment, your doctor may recommend steam inhalation. In this case, you should always use additional air humidification to make the steam cooler. In this case, the swelling of the airways subsides, they “open” and eliminate irritation in the throat.
A good remedy is made from a mixture of a spoonful of honey and a spoonful of lemon juice, which should be used when a dry cough worsens. And if the disease is infectious, then to speed up the metabolism and remove toxins from the body, the child should be given plenty of fluids, hot tea and chicken broth. Cough drops can be given from the age of four; from about the same time, you can teach a child to rinse the rod with warm salted water.
Folk recipes for cough control
Folk medicines can also be useful in the treatment of dry cough in a child. In addition, many of them are also delicious, which children cannot but like. Here are just a few of them:
- Add black radish juice to honey and take one tablespoon. However, parents need to be careful, as children often have allergies to these products.
- Boil the syrup in a spoon with sugar until it turns dark yellow (the color of burnt sugar). Then it must be diluted in water to make caramel candy. This is not only a useful remedy for dry cough, but also very tasty.
- And this cough remedy is not so tasty anymore, but it is very effective. A glass of milk should be poured into a small saucepan and put a small onion there. When the onion is cooked, the milk should be filtered and slightly cooled, but it should be drunk warm.
- A good remedy for dry cough is medicinal tea, or rather, a decoction of herbs.
 They include peppermint, thyme, licorice root, coltsfoot, wild rosemary and marshmallow. You can either brew all the herbs together at once, or make various combinations of them.
They include peppermint, thyme, licorice root, coltsfoot, wild rosemary and marshmallow. You can either brew all the herbs together at once, or make various combinations of them.
As for the daily routine, a small body needs to be provided with complete rest in the form of bed rest. From the diet you need to exclude spicy dishes and in general any seasonings. And once again we repeat that at the first signs of malaise and dry cough, you need to seek help from a pediatrician.
Child care
The child's room must be at a comfortable room temperature. Humidity should be slightly above average, as dry air provokes coughing fits. For this purpose, it is necessary to wipe the floor more often with a wet cloth and wipe the dust. You can put a bucket or pots of water in the room. You should also protect the child from the smell of smoke (especially dangerous tobacco smoke) and in general any smell.
Diet for children should be sparing. Dishes should be light and not burdensome for the gastrointestinal tract. Ideal for the treatment of dry cough jelly, jelly, fruit puree or potatoes with ghee. All meals should be low-calorie, and drinks - with a slightly elevated pH (that is, slightly alkaline). These include still mineral water, warm tea and milk.
Ideal for the treatment of dry cough jelly, jelly, fruit puree or potatoes with ghee. All meals should be low-calorie, and drinks - with a slightly elevated pH (that is, slightly alkaline). These include still mineral water, warm tea and milk.
You can also give your child steam inhalations. They can be either prescribed by a doctor (inhaling a decoction of herbs), or simply performed by inhaling hot, moist air in a closed bathroom. It will also be useful to apply warm compresses in order to relieve swelling from the respiratory tract. To do this, you need to put the compress on the chest, and after removing it, immediately dress the child warmly and hide him under the covers.
Dry cough without fever
In some cases, dry cough occurs without fever or other signs that may indicate an allergy or infection. The reason may be simple: the usual ingestion of a foreign object in the throat causes a strong dry cough. Moreover, irritants are different - from ordinary fine dust to toys. Such a dry cough develops rapidly and is often accompanied by suffocation. To get rid of this problem, you need to act quickly, but carefully so as not to frighten the child.
Such a dry cough develops rapidly and is often accompanied by suffocation. To get rid of this problem, you need to act quickly, but carefully so as not to frighten the child.
Parents should place their child face down on their lap. Then, with gentle blows between the shoulder blades, a foreign object should be “knocked out” from the windpipe. When the object falls out, the child still needs to be shown to the doctor to determine possible damage to the respiratory tract. It happens that infants cough heavily after sleep. There is nothing wrong with such a dry cough, since in this way the child gets rid of sputum that has accumulated in the airways during the night.
If a child's dry cough does not go away after home methods, it should be shown to a specialist doctor - an otolaryngologist. Most likely, this doctor will appoint consultations with other specialists - a pulmonologist and a phthisiatrician. In addition, a set of studies and analyzes will be required to identify the causes of dry cough, since it can be caused by dangerous pathogens that require immediate treatment. In the spring and autumn periods, a prolonged dry cough may be the result of worms or an allergic reaction of the body.
In the spring and autumn periods, a prolonged dry cough may be the result of worms or an allergic reaction of the body.
Dry cough in a child: how to understand the causes and prescribe treatment
What is a cough and how it occurs
The appearance of a dry cough in a child is a frequent cause for concern for parents. Many of them immediately start looking for suitable medicines.
But, according to Ryneyskaya, first you need to understand what a cough is and what its causes are, because it is far from always an acute respiratory viral infection.
“Cough is a complex mechanism for self-purification of the respiratory tract both from foreign bodies that have entered from the outside, and from products that have formed inside - mucus, pus, blood, etc. This mechanism is reflex in nature and its main task is to restore the so-called transport of bronchial secretions and airway patency,” explained Ryneyskaya.
The expert added that often cough is one of the leading, and sometimes the only symptom of acute respiratory diseases localized in the upper (nose, nasopharynx, oropharynx) and lower (larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs) respiratory tract.
“Many parents talk about the appearance of a dry cough with an acute respiratory viral infection if the child does not have sputum. But in some situations, even if there is sputum in the bronchi, the cough can be dry, unproductive, i.e. do not lead to sputum separation, ”said the specialist.
She added that the appearance of a dry cough without sputum may also be related to the child's age, since in younger children the sputum is more viscous and the chest muscles are underdeveloped.
Difficulties with sputum production can also be associated with the cause that caused the cough, for example, bronchospasm, narrowing of the lumen of the bronchus, making it difficult to expectorate.
close
100%
“Without examining the child, assessing his condition, identifying the possible cause of the dry cough, sometimes even prescribing additional examinations (clinical blood test, nasopharynx or chest X-ray, examination by an ENT doctor), it is unacceptable to prescribe any medicines for the treatment of dry cough in children," the specialist said.
How to get rid of a dry cough in a child at home
How to get rid of a dry cough in a child depends on the cause of this cough. In case of an acute respiratory viral infection of the upper and lower respiratory tract, the treatment will not be the same as when foreign bodies enter the respiratory tract, the doctor explained. She named and analyzed the most common causes of dry cough.
Physiological cause of cough in a child
Why does a child cry in a dream: a pediatrician, a neurologist and a psychologist answer
Sometimes children cry at night without waking up, and this fact causes great concern among adults about...
31 August 14:08
Dry cough for this reason may occur in children as young as four months of age.
“Such a dry cough is associated with the beginning of the active functioning of the salivary glands, the child seems to be choking, coughing. Also, many physiologists claim that a healthy child can cough up to 10-15 times a day, mostly in the morning. This is due to the accumulation of mucus in the larynx, which is produced when polluted air enters the respiratory tract. A small child, due to his height, inhales the most polluted air, and dry cough in children in the first months of life is a normal reaction to the airways being cleared,” the doctor explained.
This is due to the accumulation of mucus in the larynx, which is produced when polluted air enters the respiratory tract. A small child, due to his height, inhales the most polluted air, and dry cough in children in the first months of life is a normal reaction to the airways being cleared,” the doctor explained.
Infectious cause of cough in a child
Such a dry cough in a child can be caused by viruses and bacteria, fungi and parasites.
“It all depends on the infectious agent itself and on the localization of the inflammatory process. Even with acute rhinitis, in other words, an elementary runny nose in a child, or adenoiditis, a dry cough may occur. In young children, due to the structure of the nasopharynx, retronasal edema occurs, that is, sputum along the back wall of the pharynx.
And if there is little discharge, a reflex dry cough occurs due to irritation of the back wall of the pharynx.
And in diseases such as whooping cough or parapertussis, the main cause of cough is the formation of a focus of excitation in the cough center of the brain,” the doctor said.
Allergic cause of cough in a child
The doctor clarified that an allergic agent can cause both a short dry cough in a child, which disappears after the allergen stops entering the body and the mucosa is cleared of it, and lead to the development of a serious disease - allergic tracheobronchitis or even bronchial asthma, which requires long and complex treatment.
Foreign objects in the airways as a cause of dry cough in a child
“Understand that the presence of a foreign object has become the cause of a dry cough in a child, the following symptoms help: abrupt onset, paroxysmal character, suffocation. Young children are very fond of trying the world “by mouth”, which can lead to swallowing or getting small objects into the airways,” the doctor explained.
Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract as a cause of dry cough in a child
“In particular, we are talking about gastroesophageal reflux, when the contents of the stomach with gastric juice are thrown into the esophagus, sometimes into the trachea. As a result - irritation of the mucous membrane, burning sensation, sore throat, dry cough in a child. Most often, such a dry cough manifests itself some time after eating, in a horizontal position, ”said Ryneyskaya.
As a result - irritation of the mucous membrane, burning sensation, sore throat, dry cough in a child. Most often, such a dry cough manifests itself some time after eating, in a horizontal position, ”said Ryneyskaya.
Psychogenic cause of cough in a child
“Such a dry cough in a child occurs against the background of stress, neurological disorders, in the form of neurotic reactions, it is more cough than cough. Most often it takes place in a dream or when the child is passionate about something, ”the specialist said.
close
100%
How to alleviate a dry cough in a child
The doctor reminded that the treatment of dry cough and prescribing medicines should take place with an understanding of the underlying cause that caused it. She added that a combination of several causes of coughing cannot be ruled out. For example, an infectious-allergic cause of the disease.
The specialist gave recommendations on the treatment and relief of attacks of dry cough in children:
1. Organization of the correct daily routine and nutrition of the child with dry cough.
Organization of the correct daily routine and nutrition of the child with dry cough.
2. Ensuring the humidity and temperature conditions of the room in which the child is located, ventilation, dosed walks in the fresh air.
How to correctly wash the nose of a child and choose a solution
Washing the nose of a child will help clear the nasal passages from mucus, it is useful for treating and ...
24 August 08:25
3. Water and drinking regimen (warm water, warm milk, herbal decoctions, in the absence of allergic reactions to them).
4. Inhalation through a nebulizer - it is possible to use physiological salt solution (aka saline). During inhalation, the drug is deposited on the mucous membrane, moisturizing it, clearing it of irritants: viruses, bacteria, allergens.
5. Physiotherapy - prescribed during the recovery period.
6. Drug therapy - medicines for dry cough caused by acute respiratory viral infection, inflammatory process or any other reasons can be prescribed only by a specialist, based on the cause of the cough.