Hand swelling after walking
Exercise, Other Causes, and Treatment
Overview
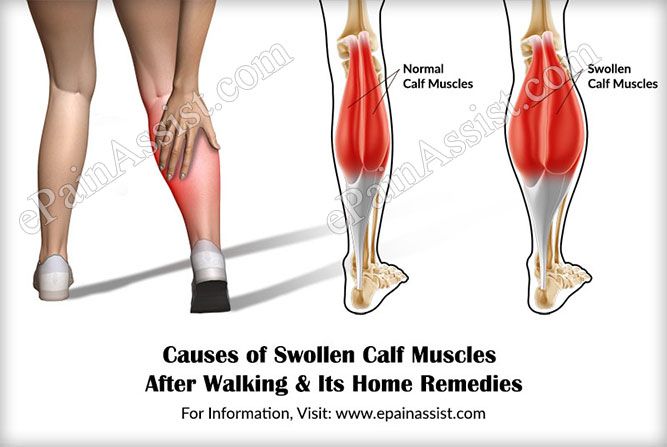
Having swollen hands is often both annoying and uncomfortable. No one wants to feel like their rings are cutting off their circulation. Swelling, also known as edema, can happen anywhere in the body. It’s commonly seen in the hands, arms, feet, ankles, and legs.
Swelling occurs when extra fluid gets trapped in your body’s tissues. Several things can cause this, including heat, exercise, or medical conditions. While swollen hands usually aren’t anything to worry about, they can sometimes be a sign of an underlying illness that needs treatment.
Exercising increases blood flow to your heart, lungs, and muscles. It can also reduce blood flow to your hands, making them cooler. Sometimes the blood vessels in your hands will counteract this by opening up, which can make your hands swell.
In addition, exercising makes your muscles produce heat. In response, your body pushes blood toward the vessels closest to your body’s surface to get rid of some of the heat. This process makes you sweat, but it may also cause your hands to swell.
In most cases, swollen hands while exercising aren’t anything to worry about. However, if you’re an endurance athlete, it could be a sign of hyponatremia. This refers to having low levels of sodium in your blood. If you have hyponatremia, you’ll likely experience nausea and confusion as well.
Here are a few steps you can take to reduce swelling in your hands while exercising:
- Remove all your jewelry before exercising.
- Do arm circles while exercising.
- Expand your fingers and clench them into a fist repeatedly while exercising.
- Elevate your hands after exercising.
When you’re suddenly exposed to unusually hot temperatures, your body may struggle to cool itself down. Normally, your body pushes warm blood toward the surface of your skin, where it cools down by sweating. On hot and humid days, this process may not work properly. Instead, fluid might accumulate in your hands instead of evaporating through sweat.
Other symptoms of extreme heat exposure include:
- rash
- increased body temperature
- dizziness or fainting
- confusion
It may take your body a few days to acclimate to hot weather. Once it does, your swelling should go away. You can also try using a fan or dehumidifier for relief.
Your body maintains a delicate balance of salt and water that’s easy to disrupt. Your kidneys filter your blood all day long, pulling out toxins and unwanted fluid and sending them to your bladder.
Eating too much salt makes it harder for your kidneys to remove unwanted fluid. This allows fluid to build up in your system, where it may collect in certain areas, including your hands.
When fluid builds up, your heart works harder to circulate blood, which increases blood pressure. High blood pressure puts extra pressure on your kidneys and prevents them from filtering fluid.
Following a low-sodium diet can help restore the proper balance.
Lymphedema is swelling caused by a buildup of lymph fluid. This condition is most common among people who’ve had their lymph nodes removed or damaged during cancer treatment.
This condition is most common among people who’ve had their lymph nodes removed or damaged during cancer treatment.
If you’ve had lymph nodes removed from your armpit during breast cancer treatment, you have a higher risk of developing lymphedema in your hands months or years after treatment. This is known as secondary lymphedema.
You can also be born with primary lymphedema, though it’s more common to have it in your legs than your arms.
Other symptoms of lymphedema include:
- swelling and aching in the arm or hand
- a heavy feeling in the arm
- numbness in the arm or hand
- skin feels tight or taut on the arm
- jewelry seems to be too tight
- decreased ability to flex or move your arm, hand, or wrist
While there’s no cure for lymphedema, lymphatic drainage massage can help to reduce swelling and prevent fluid from building up.
Preeclampsia is a condition where blood pressure rises and causes other organ dysfunction.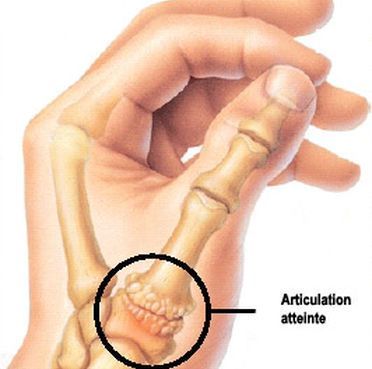 It is common after 20 weeks gestation, but can sometimes occur earlier in pregnancy or even postpartum. This is a serious condition that can be life threatening.
It is common after 20 weeks gestation, but can sometimes occur earlier in pregnancy or even postpartum. This is a serious condition that can be life threatening.
A certain amount of swelling is expected during pregnancy, especially in your hands and feet. However, a sudden increase in blood pressure due to preeclampsia can cause fluid retention and rapid weight gain. If you’re pregnant and experience any of the following symptoms with swollen hands, contact your doctor immediately:
- abdominal pain
- severe headaches
- seeing spots
- a change in reflexes
- urinating less or not at all
- blood in the urine
- dizziness
- excessive vomiting and nausea
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that affects people who have psoriasis. Psoriasis is a skin condition marked by red patches of scaly skin. Most people are diagnosed with psoriasis first, but it’s possible for arthritis symptoms to begin before skin symptoms appear.
Psoriatic arthritis can affect any part of your body. It often tends to affect your fingers, toes, feet, and lower back. Your fingers, in particular, can become extremely swollen and “sausage-like.” You might also notice swelling in your fingers before any signs of joint pain.
Other symptoms of psoriatic arthritis include:
- joints that are painful and swollen
- joints that are warm to the touch
- pain in the back of your heel or sole of your foot
- lower back pain
There’s no cure for psoriatic arthritis. Treatment focuses on managing pain and inflammation, usually through nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or steroid injections.
Angioedema is caused by an allergic reaction to something you came in contact with. During an allergic reaction, histamine and other chemicals are released into your bloodstream. This can cause sudden swelling underneath your skin, either with or without hives. It usually affects your lips and eyes, but can also show up in your hands, feet, and throat.
Angioedema is very similar to hives, but it happens just beneath your skin’s surface. Other symptoms include:
- large, thick, firm welts
- swelling and redness
- pain or warmth in the affected areas
- swelling in the lining of the eye
Angioedema usually goes away on its own. Its symptoms can also be treated with oral antihistamines.
Swollen hands can be uncomfortable, but they’re usually nothing to worry about. Try making a few lifestyle changes and see if that helps. If you’re pregnant or have had lymph nodes previously removed, talk to your doctor. You may have preeclampsia or lymphedema.
Why Do My Hands Swell When I Walk or Run? Is Swelling a Concern?
- Hands swelling is a common issue runners experience in hot weather.
- Swinging your arms while you run and increased blood flow are two additional reasons it might occur.
- Moving your workouts to cooler parts of the day can help decrease your odds of experiencing this.
If you’ve ever noticed your hands swelling midrun or plopped down after the fact to see some swollen fingers, you’re definitely not alone. While it’s often only subtle, it’s actually a pretty common occurrence, so we tapped William O. Roberts, M.D., professor in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at the University of Minnesota, to give us the details on this phenomenon.
According to Roberts, your hands usually swell when it’s hot out—but it’s not a sign of dehydration. Rather, it’s the opposite: Hands and fingers swelling can be a sign of hyponatremia, which occurs when you drink too much fluid over the course of a run, he says.
Related Story
- Every Hydration Question, Answered
“During exercise, circulation increases, and the hand has a large network of small blood vessels that open up,” he tells Runner’s World. “With the increased blood flow, there is some fluid leak between the cells. This leakage is probably the cause of your fingers swelling.”
This leakage is probably the cause of your fingers swelling.”
Additionally, swinging your arms as you run may also contribute to fluid retention in your hands, since this motion increases air movement across your skin to improve heat exchange with the air.
“This fluid is eventually reabsorbed into the cells or cleared by the lymph system,” he says. “This process is going on while you are running, but the rate of removal is slower than the rate of accumulation. Once you stop exercising, the fluid will reabsorb into the vascular system or surrounding cells or be removed by lymph flow.”
The solution? Roberts says if you notice that your hand swelling is worse when you run in the heat, moving your hard or long workouts to the cooler parts of the day—mornings or night—could help.
Related Story
- How to Carry Water on a Run
Taking off any rings you’re wearing is also not a bad idea—the last thing you want to deal with after a 20-miler is wrestling to get them off of your swollen fingers. (If you really like to keep something like a wedding ring on, you can opt for a rubber version.)
(If you really like to keep something like a wedding ring on, you can opt for a rubber version.)
And most importantly, dial in your hydration plan, especially for long runs that last over an hour or have to happen in heat and humidity. One recent study, published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology, suggests that drinking water whenever you want (when you feel thirst) will lead to adequate hydration at the end of a two-hour run despite the temperature. Listen closely to your body to prevent over-hydrating which can lead to symptoms of hyponatremia.
4 Great Hydration Belts to Consider for Your Runs
Danielle Zickl
Senior Editor
Danielle Zickl for Runner's World and Bicycling.
This content is imported from OpenWeb. You may be able to find the same content in another format, or you may be able to find more information, at their web site.
SM-Clinic cardiologist spoke about the causes of hand swelling in adults
Edema of the hands occurs quite often, and can be a manifestation of physiological changes or one of the symptoms of pathology. When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member
St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists
ANDREY GRACHEV
Leading cardiologist of the holding
SM-Clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Swelling of the hand is a cause for concern if it occurs frequently or almost daily, is accompanied by additional symptoms, is aggravated or is not eliminated by simple methods.
What you need to know about arm swelling
- Why your arm swells
- How to remove swelling
- Questions and answers
Why the hand swells in adults
Swelling of the arm or both at once may be physiological or be a sign of pathology. It may be localized or spread to surrounding tissues.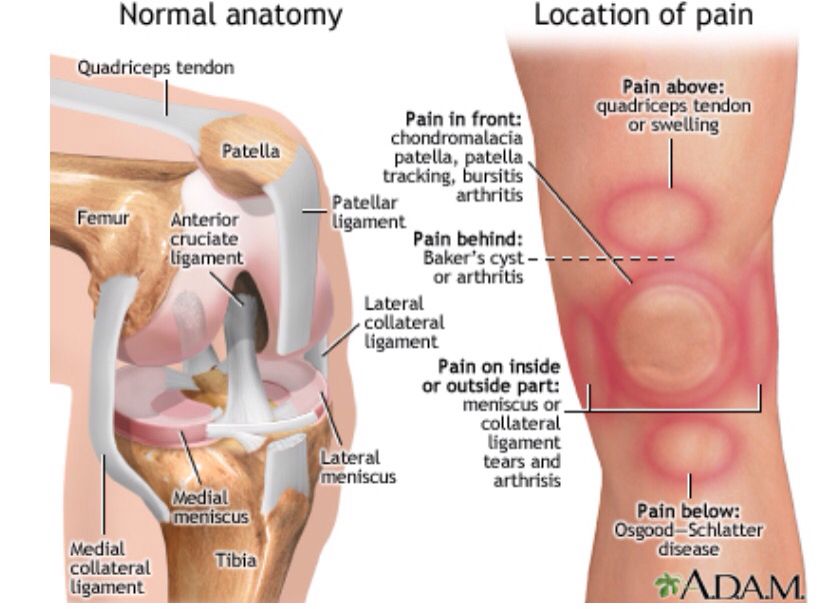 With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
Swelling in the right or left arm occurs when the blood or lymphatic vessels are compressed by items of clothing during sleep. Swelling of the fingers and hands, which is especially noticeable if you remove rings or watches, occurs after alcohol or excess salty foods, fluids at night.
Right hand
A small local edema, if the mobility of the limb is preserved, is possible with bruises. In the area of edema, there may be soreness, redness, bruises or abrasions may appear. If it is a hematoma, the edema will be more pronounced, a seal is determined under the skin, in the center of which fluctuation (fluid movement) is felt. Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture. Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the arm.
Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the arm.
Edema is possible with fractures of bones, dislocations of joints. Then there is pain, limb deformity, complete impossibility of movement.
Edema may appear with frostbite of the fingers, burns, infectious processes in the area of the hand, forearm or shoulder.
Left hand
Swelling of the finger of the left hand (as well as the right one) is possible with panaritium - suppuration in the phalanx. If it is a deeper lesion, the edema passes to the hand. Carbuncles or boils on any part of the arm can also lead to swelling. In this case, cyanosis or a purple area with suppuration is visible in the center of the inflamed focus. Edema is possible with suppuration of wounds, erysipelas, purulent arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Joint damage in other forms of arthritis also leads to tissue swelling. With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
Edema is typical for joint damage - thrombosis. In addition to edema, a feeling of fullness, pain, thickening of tissues, discoloration of the skin, crawling, and a change in sensitivity are typical.
Morning
Lymphatic edema is possible after operations to remove the mammary gland, if the axillary lymph nodes were excised. Puffiness may increase or appear in the morning with malformations of the lymphatic capillaries, with post-burn scars, thrombophlebitis, lymphadenitis. Without treatment, swelling can become permanent.
Hand edema also occurs against the background of heart failure. In the morning they are minimal, intensify in the evening. In contrast, renal swelling of the hands is most pronounced in the morning and decreases or disappears during the day.
Pregnancy
Puffiness in the fingers or hands is due to hormonal changes, especially as the pregnancy progresses. In the first trimester, a slight swelling of the fingers is typical, which is almost not noticeable. By the third trimester, swelling can be pronounced, making it difficult to wear rings, watches, bracelets. Puffiness gradually disappears in the first days after childbirth.
However, in pregnant women, pathological edema associated with hypertension, overweight and the development of preeclampsia is also possible. Then the appearance of protein in the urine, a pronounced weight gain per week, severe swelling of the arms and legs, face, and body are typical.
How to relieve hand swelling in adults
At home or for first aid, you need to give your hand an elevated position.
If this is an injury, the hand should be immobilized with a bandage or splint, a cold compress should be applied to the affected area, and an anesthetic should be taken.
If these are diseases of the joints, it is necessary to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs locally and orally. If the swelling develops quickly, with severe pain and dysfunction of the hand, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors have two options for treating edema - conservative and surgical. It depends on the cause, the severity of the condition, and possible complications. In case of injuries, emergency care, bandages, anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthesia are indicated.
In vascular edema, antispasmodic, angioprotective and phlebotonic drugs are used.
Physiotherapy, gymnastics, massage or manual therapy are also prescribed.
If the injury is serious or severe lesions of blood vessels, bones, joints are detected, the edema is not eliminated, surgical interventions are used.
Popular questions and answers
Edema can be a short-term phenomenon and does not threaten anything. But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem.
But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem.
Why is hand swelling dangerous?
Swelling is often a sign of a serious infection, cancer, heart or kidney problems. And if the swelling is persistent, then the disease has worsened or is rapidly progressing. Edema can be complicated by tissue malnutrition, skin inflammation, stretch marks, and discoloration.
When should I see a doctor for swollen hands?
In any situation when you notice swelling of the hands - in the morning, in the evening or during the day, you need a doctor's consultation and at least a minimal set of tests and examinations. Edema itself is a symptom of problems in the body, and you need to find out what caused it.
Is it possible to remove swelling of the hands with folk remedies?
There are a number of diuretic decoctions and infusions, but it is extremely dangerous to use them on your own, not knowing what the causes of edema are. This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
In addition, various traditional medicines can cause allergies, worsen the condition, negatively affect the effects of the drugs taken and have a number of contraindications for taking. Folk remedies are not equal to the concept of "safe".
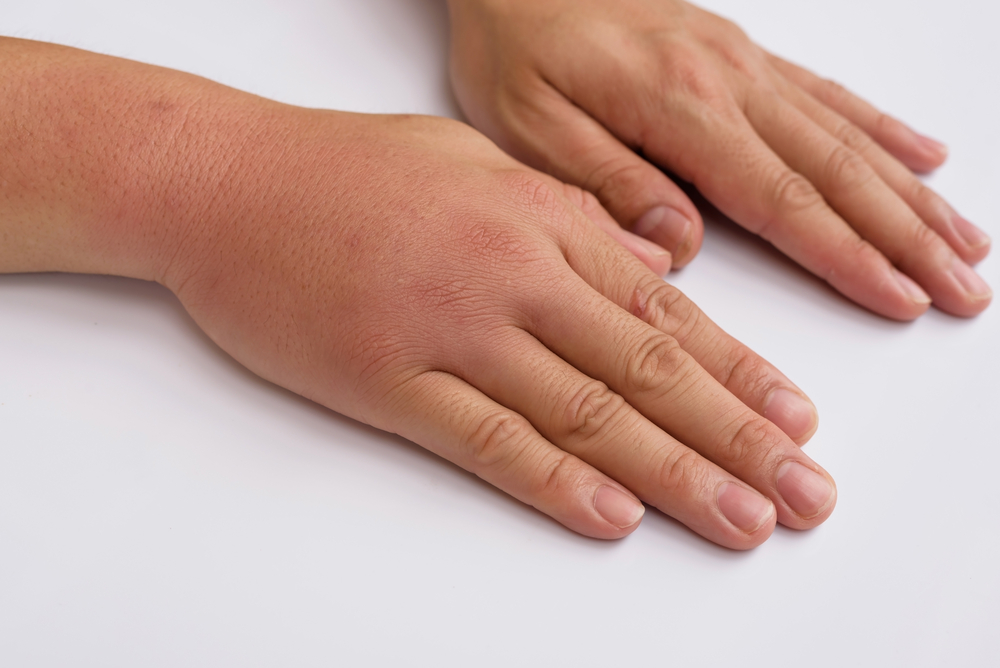
What if only one arm is swollen?
If one arm is swollen, see a surgeon or physician, depending on the suspected cause. At the time of the examination, it is worth disturbing the sore arm less, giving it an elevated position so that the liquid flows more easily, do not sleep on this side, do not press the arm to the body. Also, do not massage the swollen hand, carry out any activities without the permission of the doctor.
Published on the portal kp.ru
Why do the hands and fingers swell when walking or running
Admin
Content
- Why Do I swelling
- Metabolic changes
- This fluids
- hyponatremia
- prevention
- Promote better blood flow
- Balance your water intake
- Use the muscles in your arms and hands
- Exercise in cool weather
- Word from Drink-Drink
Many people get swollen fingers or hands when walking or running. This can be a confusing and frustrating symptom, even if it disappears shortly after the workout ends.
This can be a confusing and frustrating symptom, even if it disappears shortly after the workout ends.
There are no studies examining the causes of hand swelling during moderate exercise, but there have been some suggestions that hand movements, metabolic changes, or heat-related problems may play a role.
Why swelling occurs
Extensive research has been done on elite endurance athletes (eg marathon runners) and the changes that occur in their bodies during prolonged or intense exercise under adverse conditions. Some of these studies indicate that swelling or swelling may occur along with other potentially life-threatening symptoms.
But it would be a stretch to assume that these acute conditions are the cause of swollen fingers when you take your dog for a walk in the neighborhood or go hiking on a sunny day.
Evidence does not support this connection. But there are a few clues from these studies to understand why you're experiencing finger swelling when you walk or run.
Movement of the hand
A published research report has shown that approximately one in four people experience swelling of the hands or fingers while walking. This study also found that women were more than twice as likely to report swelling of their hands after exercise. But this one limited study only looked at hand swelling while walking the dog.
This study, published in 2011, is the only study on post-ambulatory hand edema, also called "big hand syndrome". The authors of the study noted that this issue is “completely ignored by the scientific literature.”
The study authors did not investigate the causes of hand swelling in their study, but referred to another study of hand movement during walking. They summarized their interpretation of this study:
“The only theory for swelling of the hands after walking was proposed by Collins et al., who suggested that the cause could be incorrect hand movements, excess fluid entering the hands due to ‘centrifugal force’, or alternatively, change in metabolic rate during exercise.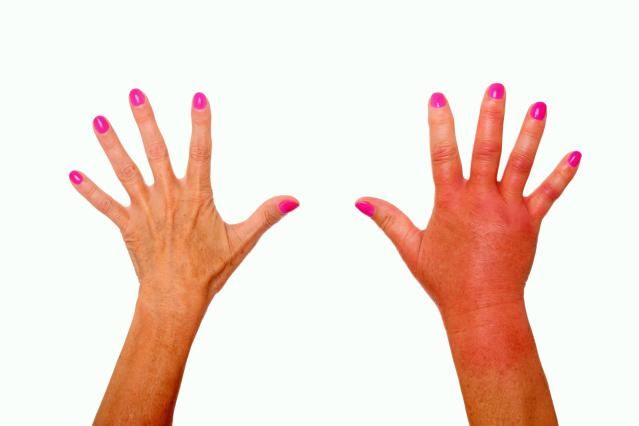 ."
."
Unfortunately, a deep dive into this Collins study reveals that there is no mention of centrifugal force, hand swelling, or any related terms. The study by Collins looked at the metabolic costs of various arm swing patterns while walking, but did not look at swelling or fluid changes in the arms or any other part of the body.
So, could centrifugal force from waving your hand play a role in your swollen fingers after walking? Maybe. Many walkers use strong arm swings, and some of them get swollen fingers.
It is also not uncommon to notice that putting your hands in your pockets or lifting them up for a few minutes will reduce the swelling. It would be reasonable to assume that the simple forces of gravity and possibly centrifugal force could cause fluid to accumulate in your fingers.
But you shouldn't assume that your arm span needs to be adjusted. In fact, according to Collins' research, double-sided arm swings (which most walkers use) are not wrong, but rather undesirable. normal hand wave.
normal hand wave.
Metabolic changes
The authors of a 2011 study mention another potential cause of hand swelling when walking: changes in metabolic rate during exercise. Collins' research found that the normal (two-way) swing of the arm used in a typical human gait uses the least amount of energy.
However, he compared this to walking with the hands tied, walking with the hands completely still, and the "anti-normal" pattern of the right arm swinging forward as the right leg steps forward, and vice versa. You are unlikely to use any of these arm swings during your daily run or walk.
But, walking and running do increase your metabolic rate, even if your body mechanics are efficient. Can the normal changes in your metabolism during exercise lead to swollen fingers?
Here's what we know
- Endurance exercise (such as walking or running) increases blood flow to meet the body's increased oxygen demand. You will notice that your heart beats faster and you start to breathe deeper when you start walking or running.
- During exercise, your working muscles require more oxygen, so blood flow is directed from your extremities (such as your fingers and toes) to the muscles that need it, such as your quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings.
- When the flow of blood is directed away from the hands and fingers, they become colder. As a result, the blood vessels in your arms may begin to open wider, causing them to swell, especially if you exercise in cold weather.
hot
If the cooling effect can cause hand swelling, you can assume that exercising in the heat will have the opposite effect. But it is not always the case.
There are several evidence-based reasons why exercising in hot weather can also cause swollen fingers. However, not all of them apply to your normal walking or running.
Fluid imbalance
Studies have shown that during dynamic exercise in a hot environment, skin blood flow and circulation are disturbed, and body temperature regulation is disturbed even during light exercise.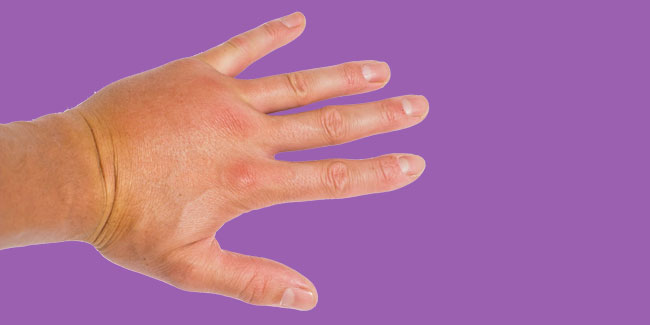 Vasodilation—or the opening of blood vessels—occurs to cool the body through sweating.
Vasodilation—or the opening of blood vessels—occurs to cool the body through sweating.
Depending on your fluid intake and your body's ability to cool itself, you may experience fluid imbalances. According to medical experts, this can lead to edema (excess fluid in the skin and tissues).
hyponatremia
Walking or running in hot weather can also cause other complications. Research has looked at a condition called hyponatremia, which can lead to symptoms such as swelling and bloating. In severe cases, it can also cause dizziness, fatigue, headache, vomiting, agitation, coma, and even death.
Exercise-related hyponatremia is a condition in which the body develops low levels of sodium in the blood during or immediately after physical activity. The condition is usually caused by excessive fluid intake.
Some media reports have cited this condition as a potential cause of hand swelling while walking or running. While this is possible, evidence suggests that certain unfavorable (and perhaps unlikely) conditions must exist for hyponatremia to occur.
However, it is true that most athletes who develop hyponatremia experience an increase in total body water. And swelling is mentioned as a common side effect.
Hyponatremia develops when you consume too much hypotonic fluid in addition to sweat, urine, and other body fluid losses. Hypotonic fluids are those that contain a higher concentration of salt and sugar than the human body (eg PowerAde). In combination with other factors such as loss of sodium in sweat, reduced sodium intake, and rapid absorption of fluid from the gastrointestinal tract, hyponatremia may occur. Hyponatremia is more common in women than in men.
Many of the studies examining this condition evaluate ultra-endurance athletes (both elite and amateur) such as marathon runners, long-distance cyclists and triathletes. These athletes often sweat excessively for several hours in extreme heat, may experience gastrointestinal distress, and may consume large amounts of water and sports drinks during long races.
Investigators have reported cases of hyponatremia during or after other activities such as walking or yoga, but much less frequently. So, is it possible that hyponatremia causes swollen hands when walking or jogging at a moderate temperature?
This is possible if you have been training for a very long time, in hot weather, and if you have been drinking too much liquid. Your doctor can make an individual diagnosis.
But experts advise to prevent this condition from occurring by drinking as much as you are thirsty during and immediately after exercise in a temperate climate lasting less than 17 hours.
prevention
If swollen hands and fingers are causing you discomfort or anxiety, try one of these tips to fix or reduce the problem.
Promote better blood flow
Before walking, remove your rings and loosen your bracelets. If your fingers are very swollen, rings can restrict blood flow and cause discomfort. Leave them safe at home.
Also, loosen the band on your watch or fitness band. If your fitness band or smartwatch needs to be tight for heart rate detection, wear it higher on your wrist or forearm, rather than at the narrowest part of your wrist.
Balance your water intake
Drink according to your thirst when you exercise. Carry fluids with you, especially if you are exercising at high temperatures or for long periods of time. It is likely that you will need to consume fluids such as water or a sports drink after the first hour of walking and sweating.
You can also weigh yourself before, during and after your walk to determine your perspiration level.
This method can provide guidance so you can see if you are drinking too much or too little. Your weight should remain the same. For endurance walks, use the calculator to estimate fluid requirements.
Walking Water Calculator
Use Arm and Arm Muscles
Promote healthy circulation in your arms by using them while walking:
- Bring a cane and change hands as you walk.