How much to claim a child on taxes
2022 Child Tax Credit: Definition, How to Claim
You’re our first priority.
Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners.
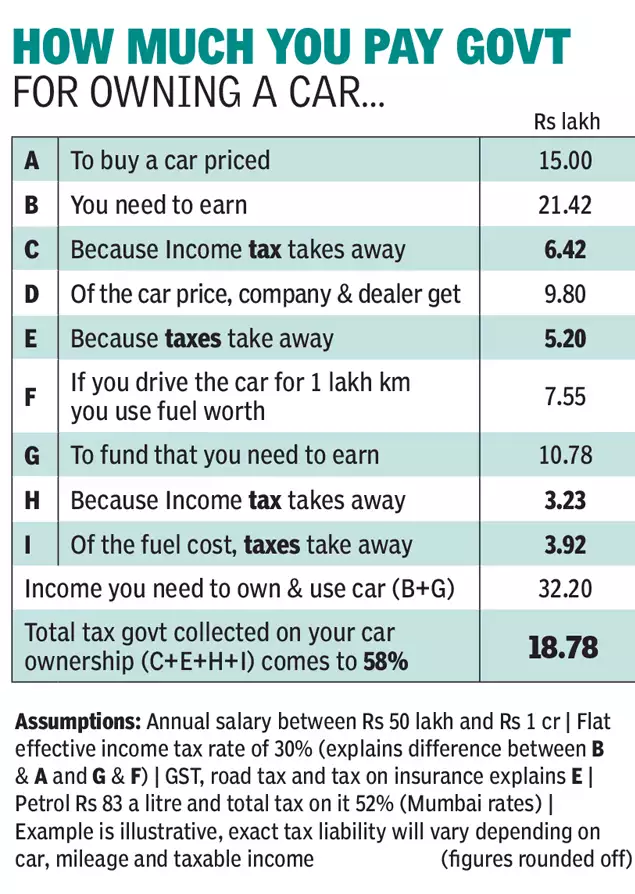
For the 2022 tax year, taxpayers may be eligible for a credit of up to $2,000 — and $1,500 of that may be refundable.
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money.
This article has been updated for the 2022 tax year.
The child tax credit is a federal tax benefit that plays an important role in providing financial support for American taxpayers with children. For the 2022 tax year, people with kids under the age of 17 may be eligible to claim a tax credit of up to $2,000 per qualifying dependent, and $1,500 of that credit may be refundable.
We’ll cover who qualifies, how to claim it and how much you might receive per child.
What is the child tax credit?
The child tax credit, commonly referred to as the CTC, is a tax credit available to taxpayers with dependent children under the age of 17. In order to claim the credit when you file your taxes, you have to prove to the IRS that you and your child meet specific criteria.
You’ll also need to show that your income falls beneath a certain threshold because the credit phases out in increments after a certain limit is hit. If your modified adjusted gross income exceeds the ceiling, the credit amount you get may be smaller, or you may be deemed ineligible altogether.
Who qualifies for the child tax credit?
Taxpayers can claim the child tax credit for the 2022 tax year when they file their tax returns in 2023. Determining your eligibility for the credit begins with understanding which children qualify and what other criteria you need to be mindful of.
Generally, there are seven “tests” you and your qualifying child need to pass.
Age: Your child must have been under the age of 17 at the end of 2022.
Relationship: The child you’re claiming must be your son, daughter, stepchild, foster child, brother, sister, half brother, half sister, stepbrother, stepsister or a descendant of any of those people (e.
 g., a grandchild, niece or nephew).
g., a grandchild, niece or nephew).Dependent status: You must be able to properly claim the child as a dependent. The child also cannot file a joint tax return, unless they file it to claim a refund of withheld income taxes or estimated taxes paid.
Residency: The child you’re claiming must have lived with you for at least half the year (there are some exceptions to this rule).
Financial support: You must have provided at least half of the child’s support during the last year. In other words, if your qualified child financially supported themselves for more than six months, they’re likely considered not qualified.
Citizenship: Per the IRS, your child must be a "U.S. citizen, U.S. national or U.S. resident alien," and must hold a valid Social Security number.
Income: Parents or caregivers claiming the credit also typically can’t exceed certain income requirements. Depending on how much your income exceeds that threshold, the credit gets incrementally reduced until it is eliminated.

Did you know...
If your child or a relative you care for doesn't quite meet the criteria for the CTC but you are able to claim them as a dependent, you may be eligible for a $500 nonrefundable credit called the "credit for other dependents." Check the IRS website for more information.
How to calculate the child tax credit
For the 2022 tax year, the CTC is worth $2,000 per qualifying dependent child if your modified adjusted gross income is $400,000 or below (married filing jointly) or $200,000 or below (all other filers). If your MAGI exceeds those limits, your credit amount will be reduced by $50 for each $1,000 of income exceeding the threshold until it is eliminated.
The CTC is also partially refundable; that is, it can reduce your tax bill on a dollar-for-dollar basis, and you might be able to apply for a tax refund of up to $1,500 for anything left over. This partially refundable portion is called the “additional child tax credit” by the IRS.
How to claim the credit
You can claim the child tax credit on your Form 1040 or 1040-SR. You’ll also need to fill out Schedule 8812 (“Credits for Qualifying Children and Other Dependents”), which is submitted alongside your 1040. This schedule will help you to figure your child tax credit amount, and if applicable, how much of the partial refund you may be able to claim.
Most quality tax software guides you through claiming the child tax credit with a series of interview questions, simplifying the process and even auto-filling the forms on your behalf. If your income falls below a certain threshold, you might also be able to get free tax software through IRS’ Free File.
A word of warning: In the eyes of the IRS, you’re ultimately responsible for all information you submit, even if someone else prepares your return.
🤓Nerdy Tip
If you applied for the additional child tax credit, by law the IRS cannot release your refund before mid-February.
Consequences of a CTC-related error
An error on your tax form can mean delays on your refund or on the CTC part of your refund. In some cases, it can also mean the IRS could deny the entire credit.
If the IRS denies your CTC claim:
You must pay back any CTC amount you’ve been paid in error, plus interest.
You might need to file Form 8862, "Information To Claim Certain Credits After Disallowance," before you can claim the CTC again.
If the IRS determines that your claim for the credit is erroneous, you may be on the hook for a penalty of up to 20% of the credit amount claimed.
State child tax credits
In addition to the federal child tax credit, a few states, including California, New York and Massachusetts, also offer their own state-level CTCs that you may be able to claim when filing your state return. Visit your state's department of taxation website for more details.
History of the CTC
Like other tax credits, the CTC has seen its share of changes throughout the years. In 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, or TCJA, established specific parameters for claiming the credit that will be effective from the 2018 through 2025 tax years. However, the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 (the coronavirus relief bill) temporarily modified the credit for the 2021 tax year, which has caused some confusion as to which changes are permanent.
Here's a brief timeline of its history.
1997: First introduced as a $500 nonrefundable credit by the Taxpayer Relief Act.
2001: Credit increased to $1,000 per dependent and made partially refundable by the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act.
2017: The TCJA made several changes to the credit, effective from 2018 through 2025. This included increasing the credit ceiling to $2,000 per dependent, establishing a new income threshold to qualify and ensuring that the partially refundable portion of the credit gets adjusted for inflation each tax year.

2021: The American Rescue Plan Act made several temporary modifications to the credit for the 2021 tax year only. This included expanding the credit to a maximum of $3,600 per qualifying child, allowing 17-year-olds to qualify, and making the credit fully refundable. And for the first time in U.S. history, many taxpayers also received half of the credit as advance monthly payments from July through December 2021.
2022–2025: The 2021 ARPA enhancements ended, and the credit will revert back to the rules established by the TCJA — including the $2,000 cap for each qualifying child.
Frequently asked questions
1. Does the CTC include advanced payments this year?
The American Rescue Plan Act made several temporary modifications to the credit for tax year 2021, including issuing a set of advance payments from July through December 2021. This enhancement has not been carried over for this tax year as of this writing.
2. I had a baby in 2022. Am I eligible for the CTC?
Yes. You'll likely need to make sure your child has a Social Security number before you apply, though.
3. Is the child tax credit taxable?
No. It is a partially refundable tax credit. This means that it can lower your tax bill by the credit amount, and if you have no liability, you may be able to get a portion of the credit back in the form of a refund.
4. Is the child tax credit the same thing as the child and dependent care credit?
No. This is another type of tax benefit for taxpayers with children or qualifying dependents. It covers a percentage of expenses you made for care — such as day care, certain types of camp or babysitters — so that you can work or look for work. The IRS has more details here.
About the authors: Sabrina Parys is a content management specialist at NerdWallet. Read more
Tina Orem is NerdWallet's authority on taxes and small business. Her work has appeared in a variety of local and national outlets. Read more
Her work has appeared in a variety of local and national outlets. Read more
On a similar note...
Get more smart money moves – straight to your inbox
Sign up and we’ll send you Nerdy articles about the money topics that matter most to you along with other ways to help you get more from your money.
Claiming Dependents As New Parents
First of all: if you recently had a baby, congratulations! You’re in for a lot of changes, and those include changes to the way you file your taxes. Let’s talk about the primary differences you’ll need to be aware of when you file your taxes as a parent for the first time.
First time filing taxes with a child: Dependency requirements
In order to claim a new child as a dependent, your child will have to meet dependency requirements.
Your first step needs to be applying for your baby’s Social Security Number. You will need this number before doing anything else.
To get the number, visit or contact the Social Security Administration to fill out Form SS5, the Application for a Social Security Card. Once you have applied, it will typically take about two weeks for the number to arrive.
Once you have applied, it will typically take about two weeks for the number to arrive.
Another requirement is your child must have lived with you for more than half of the year. A dependent child born during the year is treated as having lived with you for more than half of the year if your home was the child’s residence for more than half of the time he or she was alive during the year.
Time the child spent in a hospital after birth won’t count against you.
If you are single, had a baby, and now support that child, your filing status could change to Head of Household (HH).
The HH filing status gives you a larger standard deduction and more favorable tax brackets. That means – thanks to your new bundle of joy – you could be paying less federal tax as HH than you would as single for the same dollar amount of income.
If you are married, having a child will not generally affect your filing status.
Claiming the Child Tax Credit
Sometimes parents with newborn will ask, “how much can you get back on taxes per child?”
One of the best-known tax breaks for parents is the Child Tax Credit. A taxpayer with a new baby may claim the child tax credit, which lowers their tax bill by up to $2,000 per qualifying child if the taxpayer’s income is not too high. In some cases, the credit may even exceed your taxes, allowing you to get extra money back as a refund. Everyone knows children can be expensive and paying less in taxes means better diapers or nicer toys for your little one.
A taxpayer with a new baby may claim the child tax credit, which lowers their tax bill by up to $2,000 per qualifying child if the taxpayer’s income is not too high. In some cases, the credit may even exceed your taxes, allowing you to get extra money back as a refund. Everyone knows children can be expensive and paying less in taxes means better diapers or nicer toys for your little one.
Claiming tax breaks for child care and medical expenses
If you paid someone to care for your child while you worked – like a daycare center – you may be able to claim the Child and Dependent Care Credit on your federal income tax return. It’s based on your amount of earned income and can be up to 35% of your qualifying child care expenses, up to a max expense of $3,000 for one child, and up to a max expense of $6,000 for two or more children.
The Child and Dependent Care Credit may be reduced if you receive tax-free dependent care benefits from your employer.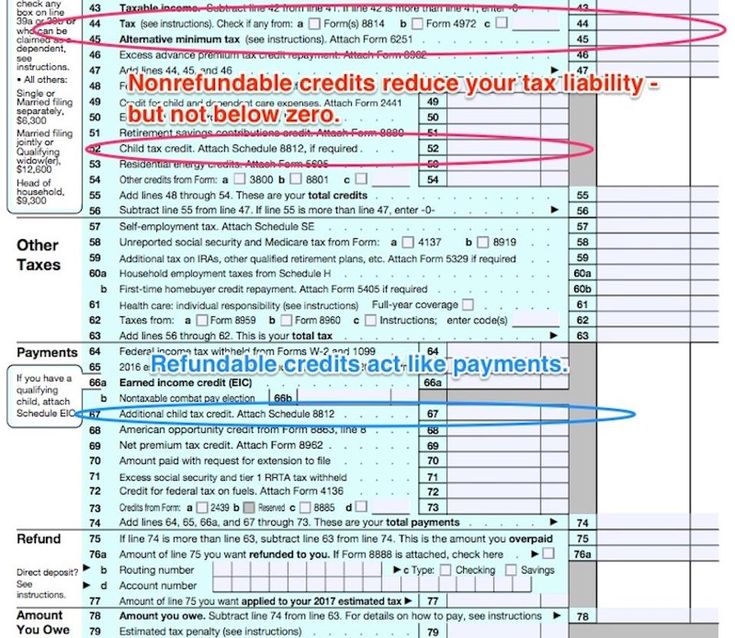
Medical expenses can be deductible if they exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income. The out-of-pocket cost of the hospital stay to birth your baby and related care counts as medical expenses, but mothers are surprised to find out that the cost of breast pumps and lactation supplies are medical expenses as well. These expenses may help you get over that 7.5% hump. To qualify for this deduction, you will need to itemize deductions instead of claiming the standard deduction.
Working taxpayers with a child can claim a credit for qualified child care expenses.
Other tax breaks for parents
Additional tax breaks can be claimed if the following apply:
- You qualify for the Earned Income Tax Credit.
- Gifts (in money or property) from friends, grandparents and other relatives are income tax free to you and your child.
- You participate in a qualified tuition program (QTP, also called “a 529 plan”) offered by your state. QTPs allow you to set aside money for your child’s future secondary and higher education expenses.
 While there is no immediate federal tax break, earnings in the account grow tax free, distributions used for education costs are tax-free, and you may get a state deduction or credit for your contributions.
While there is no immediate federal tax break, earnings in the account grow tax free, distributions used for education costs are tax-free, and you may get a state deduction or credit for your contributions.
Are you filing as a first-time parent?
The experts at H&R Block can look at your personal situation and help make sure you don’t miss any tax breaks you qualify for as a new parent. And if you’d rather file your taxes yourself, know you are still backed by our 100% accuracy and maximum refund guarantees. In an office or online, don’t just get your taxes done. Get your taxes won with H&R Block.
should a minor child pay personal property tax
I recently paid tax for an apartment and realized that it should also be charged for children's shares. But I do not receive any letters from the tax office and do not know how much to pay. I personally do not really want to go to the tax office.
Do I have to pay tax on these shares and how can I find out the amount?
Irina Polovodova
lawyer
Author profile
As soon as you allocated shares to the children, they became the same owners of the apartment as you are. An apartment is a taxable property, and property tax is charged for all its owners, regardless of age.
An apartment is a taxable property, and property tax is charged for all its owners, regardless of age.
You may not have received a child wealth tax notice because you allotted shares in 2021: tax for the year is due by December 1 of the following year. That is, you will see accruals for 2021 in 2022. If you allocated shares in 2020 or earlier, but did not receive anything, then there is also an explanation for this.
I'll tell you more about how the system works, how to find out about children's taxes and how to pay them correctly.
Why a child must pay taxes
A child cannot know about property taxes and pay them. But formally, if a share in property is registered to him, he is considered a taxpayer at any age.
Art. 400 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
At the same time, it does not matter whether the parents received a certificate of assignment of a TIN to the child or not. As soon as the tax office receives information from Rosreestr that the child has become the owner of the property, the TIN appears automatically.
There is no direct obligation of adults to pay property tax for a child in the law, but there is a broader rule: any taxpayer can act through his representative. In the case of a child, parents, adoptive parents, guardians can pay taxes.
Art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The legislation divides children into two groups: minors, that is, up to 14 years old, and from 14 to 18 years old. Parents manage the property of a minor, which means that you still have to pay tax on his behalf. Children from 14 to 18 years old, with the consent of their parents, can independently manage their property and pay taxes.
Art. 26, 28 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
If the property tax is not paid, then it does not matter at what age the child is: the tax office will send a demand to pay the debt to parents, guardians or adoptive parents.
When a child may not pay property tax
There are situations when a child may not pay property tax.
So, children with disabilities, including from childhood, and recipients of a pension, for example, for the loss of a breadwinner, may not pay tax on one piece of real estate. If such a child owns several objects - for example, a share in the parents' apartment and the grandmother's apartment - property tax needs to be paid only for one share of choice.
Who can not pay taxes on property and land or pay less: 7 categories of beneficiaries
This is called a tax credit. To receive it, you need to send an application to the tax office and attach documents that confirm the benefit.
Art. 407 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Regions have the right to independently expand the list of tax benefits. Information about this can usually be found on the website of the Federal Tax Service if you select your subject.
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 13, 2020 No. BS-4-2-21/779
How to find out about the amount of taxes on a child
There is a concept of tax secrecy, and the tax office is not entitled to transfer data on children's taxes to third parties. That is, children's taxes will not be reflected in notifications for adults, and they may not talk about accruals over the phone either. That is why you will not see the amounts of taxes for children in your personal account on the website of the tax authority or in notifications that come to your name.
That is, children's taxes will not be reflected in notifications for adults, and they may not talk about accruals over the phone either. That is why you will not see the amounts of taxes for children in your personal account on the website of the tax authority or in notifications that come to your name.
Taxes on the child's property will be in the notifications that the Federal Tax Service will by default send to the name of the child at the address of his registration. But the most convenient way to receive tax payments for a child is to register a personal taxpayer account for him and receive notifications there.
There are two ways to do this:
- apply to any tax office with a passport and a child's birth certificate. The tax office will immediately issue a username and password from the child's personal account;
- register a child for public services. After that, through public services, it will be possible to automatically enter the taxpayer's personal account.
 You don’t have to go to the tax office, but to register for public services, you need to go through the identity verification procedure - through the MFC or online banking. This method is suitable when the child is already 14 years old or more.
You don’t have to go to the tax office, but to register for public services, you need to go through the identity verification procedure - through the MFC or online banking. This method is suitable when the child is already 14 years old or more.
/newborn-documents/
What documents does a newborn need
What to do if the tax notice has not arrived
Notices of the need to pay property taxes are sent out in August-September. You need to pay before December 1, and the tax service must notify all payers no later than 30 days before this deadline. So, if the notification has not arrived by November 1, it is better to find out for yourself where it is and how much you owe.
Art. 52 NK RF
The specified terms are the same for all types of notifications - both paper and electronic. As soon as you have registered a taxpayer's personal account, notifications stop coming by mail automatically. Rarely, but it happens that notifications do not come to your personal account either - as a rule, this is the result of some kind of error.
/zabral-dengi-za-imuschestvo/
How to save on property taxes
If the notification has not arrived, you can get it:
- in person at the tax office. Take your passport and child's birth certificate. The notification must be issued immediately against receipt;
- at the MFC. The same documents are needed. The notification must be issued within 5 days after the application is submitted. You will have to come to the MFC twice: to write an application and then receive a notification.
There is only one case when a tax notice should not officially come, although property tax is charged - if the tax amount for the year is less than 100 R. For example, children have very small shares in an apartment, and the tax for them is also small. The receipt will be sent when taxes accumulate for a large amount or after three years.
What to do? 10/27/17
There are no letters from the tax office, what should I do?
If you have a taxpayer's personal account, but you want to receive additional paper receipts, file an application for this with the tax office. This function in the taxpayer's personal account is called "Notification of the need to receive documents on paper". It can be found in the section "Life situations" → "Other situations" → "Receive documents on paper"
This function in the taxpayer's personal account is called "Notification of the need to receive documents on paper". It can be found in the section "Life situations" → "Other situations" → "Receive documents on paper" How to properly pay property taxes for a child
Pay taxes for a child in the same way as for an adult. You can do this in the taxpayer's personal account, on the portal of the Federal Tax Service, public services, at banks, at the post office, at the MFC or through a payment terminal.
The fastest way to pay is by UIN, barcode or QR code. All of them are unique for each payment, and you do not need to enter details, payment amounts and payer data.
In the personal account of the child taxpayer, all payment and payer data will also be generated automatically, so it is impossible to make a mistake.
/deadline/
Pay your property tax
If you pay otherwise, it's important not to make the payment in your name. Otherwise, the money will go to the adult's taxes, and the child's property tax will not be paid. In such cases, the purpose of the payment indicates: "Payment of tax for ..." and indicate the data of the child.
Otherwise, the money will go to the adult's taxes, and the child's property tax will not be paid. In such cases, the purpose of the payment indicates: "Payment of tax for ..." and indicate the data of the child.
The deadline for paying property taxes is no later than December 1. This is what threatens if you do not pay the tax on time.
Fines for each day of delay from December 2. Although the interest rate on taxes is small - 1/300 of the key rate of the Central Bank, which is 7.5% per annum as of November 2021 - it still increases the defaulter's debt. For example, with a debt of 5000 R per month, about 40 R will run up.
Art. 45, 69, 70 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Claim for debt payment. IFTS will issue a claim within three months after December 1. The document will come by mail. It must be completed within 8 business days.
Court order. The tax office will receive an order - and the children's debt will be collected from parents, guardians or adoptive parents in a simplified court order. The judge will consider the documents without calling the parties and satisfy the requirement of the Federal Tax Service. The money will be written off from the accounts of both parents, adoptive parents or guardians, because according to the law they are equally responsible for the child.
cl. 1 art. 61, paragraph 1 of Art. 80 SK RF
art. 1 of Law No. 45-FZ
Previously, the tax office filed a lawsuit against the representatives of the debtor child and thus returned the debt.
For example, in June 2015, the tax inspectorate of the Ryazan region sued the parents of a child who had 1/2 share of non-residential premises. The family did not pay the tax, although they received notices and requests to pay it. The court recovered from the parents the child's tax debt, late payment interest and court costs, dividing everything equally.
The family did not pay the tax, although they received notices and requests to pay it. The court recovered from the parents the child's tax debt, late payment interest and court costs, dividing everything equally.
What is the result
In your situation, I would recommend doing this:
- Go to the tax office and take the username and password to access the personal account of the child taxpayer.
- If there is a debt, pay it right away so that you do not have to pay penalties. The debt may accumulate, and it will be collected from you in a simplified manner - you will only find out about this after the money is debited from the card.
- In the future, control accruals through the taxpayer's personal account.
What to do? Readers ask - experts answer
Ask your question
who and how should pay, benefits
www.adv.rbc.ru
www. adv.rbc.ru
adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
Real estate
TV channel
Pro
Investments
Events
RBC+
New economy
Trends
Real estate
Sport
Style
National projects
City
Crypto
Debating Club
Research
Credit ratings
Franchises
Newspaper
Special projects St. Petersburg
Petersburg
Conferences St. Petersburg
Special projects
Checking counterparties
RBC Library
Podcasts
ESG index
Politics
Economy
Business
Technology and media
Finance
RBC Company
www.adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
Are property taxes assessed on a minor child, who pays them and who is entitled to benefits?
Photo: New Africa\shutterstock
Under Russian law, homeowners are subject to property tax. Often, parents who give their children a share in an apartment may have a question: is the tax charged to the child if he is a co-owner, and who pays it.
Often, parents who give their children a share in an apartment may have a question: is the tax charged to the child if he is a co-owner, and who pays it.
Lawyers told how the issue of real estate taxation in relation to minors is regulated.
Do children have to pay property tax
www.adv.rbc.ru
The apartment tax is a tax on the property of individuals. The order of its taxation is established by Ch. 32 of the Tax Code of Russia. The chapter does not contain provisions that children who are owners of taxable property are exempted from paying it. “In this regard, children under the apartment tax bear the same tax liability as adults,” explained Nikolay Pivovarov, a member of the Russian Bar Association.
Art. 400 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers of the property tax of natural persons are persons who have the right to own property, regardless of the age of these persons.
Who pays the tax for the child
Tax authorities are well aware that, as a general rule, children do not have any income due to their age. At the same time, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a direct rule that would oblige parents to pay taxes for their children.
At the same time, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a direct rule that would oblige parents to pay taxes for their children.
Nikolai Pivovarov, member of the Russian Bar Association:
— Parents and guardians are the representatives of children by virtue of the law, including before the tax authorities. Therefore, although children are obligated to pay apartment tax, it is their parents or guardians who will most likely be held liable for non-payment of it. The provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the legal representation of taxpayers - individuals and par. 4 p. 1 art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the tax can be paid by another person.
How to pay tax for a child
When paying tax for a child, in the purpose of payment, you must specify information for which object and for which person the funds are being transferred. If problems arise, you can always write a clarifying letter to the tax authority.