How much can a child earn before paying tax
When Does Your Child Have to File a Tax Return?
How much can a dependent child earn? Learn the rules about when a child must file a tax return because of earned and unearned income.
Say your dependent child is earning money from working, investments, or both. Great, but beware—your child might have to file a tax return. It might seem odd, but the IRS says dependent children who earn more than a threshold amount must file returns.
If a child fails to file, you (the parent) might be liable for the tax. Moreover, if your child can't file a return for any reason, such as age, you're legally responsible for filing one on your child's behalf.
For all these reasons it's vitally important to know how much your dependent child can earn before a tax return has to be filed. But how much can a dependent child earn? Read on to find out.
Types of Income for Dependents
Whether your child is required to file a tax return depends on the applicable standard deduction and how much earned and unearned income the child had during the year.
What is earned income? "Earned income" is income a child earns from working. It includes salary or wages, tips, professional fees, and taxable scholarship and fellowship grants.
What is unearned income? "Unearned income" is investment-type income. It includes taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, unemployment compensation, Social Security benefits, annuities, and distributions of unearned income from a trust.
If Your Child Has Earned Income OnlyA child who has only earned income must file a return only if the total is more than the standard deduction for the year. For 2022, the standard deduction for a dependent child is total earned income plus $400, up to a maximum of $12,950. So, a child can earn up to $12,950 without paying income tax.
If Your Child Has Unearned Income OnlyExample: William, a 16-year-old dependent child, worked part-time on weekends during the school year and full-time during the summer.
He earned $14,000 in wages during 2022. He didn't have any unearned income. He must file a tax return because he has earned income only, and his total income is more than the standard deduction amount for 2022.
A child who has only unearned income must file a return if the total is more than $1,150 for 2022.
Example: Sadie, an 18-year-old dependent child, received $1,900 of taxable interest and dividend income during 2022. She didn't work during the year. She must file a tax return because she has unearned income only, and her total income is more than the unearned income threshold for 2022.
However, if your child's interest and dividend income (including capital gain distributions) total less than $11,500, you can elect to include that income on your (the parents') return rather than file a return for the child. In this event, all income over $2,300 is taxed at your tax rates—you could end up paying more with this method.
If a child has both earned and unearned income, that child must file a return for 2022 if:
- unearned income is over $1,150
- earned income is over $12,950, or
- earned and unearned income together totals more than the larger of (1) $1,150, or (2) total earned income (up to $12,500) plus $400.
Should Your Child File a Return Even If Not Required?Example: Mike, a 19-year-old college student claimed as a dependent by his parents, received $200 taxable interest income (unearned income) and earned $2,800 from a part-time job during 2022 (earned income). He doesn't have to file a tax return. Both his earned and unearned income are below the thresholds, and his total income of $3,000 is less than his total earned income plus $400 ($3,200).
Even if your child doesn't meet any of the filing requirements discussed, that child should file a tax return if:
(1) income tax was withheld from that child's income, or
(2) that child qualifies for the earned income credit, additional child tax credit, health coverage tax credit, refundable credit for prior year minimum tax, first-time home buyer credit, adoption credit, or refundable American opportunity education credit.
See the tax return instructions to find out who qualifies for these credits. By filing a return, your child can get a refund.
What Is Your Child's Income Tax Rate?The first $1,150 of unearned income is covered by the kiddie tax standard deduction, so it isn't taxed. The next $1,150 in unearned income is taxed at the child's tax rate, which is ordinarily lower than the parent's. Income over $2,300 is taxed at the parent's maximum income tax rate.
Figuring the kiddie tax can be complex. For example, if a parent has more than one child subject to the kiddie tax, the net unearned income of all the children has to be combined, and a single kiddie tax calculated.
For federal income tax purposes, the income a child receives for personal services (labor) is the child's, even if, under state law, the parent is entitled to and receives that income. So, dependent children pay income tax on their earned income at their own individual tax rates.
For more on tax rules for children, see IRS Publication 929, Tax Rules for Children and Dependents.
How to File Your Child's First Income Tax Return
As your child moves toward adulthood, you face several milestone decisions that involve, in part, a desire to help your child become more independent and responsible. But one milestone for your child that you may not anticipate—even though it will be part of their growing-up experience—is filing that first income tax return.
Key Takeaways
- Children generally don't receive instruction in school on filing income taxes, so parents should teach their kids when and how to do it.
- Dependents must file under certain circumstances if they have earned or unearned income.
- Other reasons to file include owing taxes, recovering withheld taxes, earning Social Security credits, qualifying for an earned income credit, and opening a retirement account.
- Your child might be allowed to skip filing a separate tax return and include their income on your return under certain circumstances, such as only having unearned income (interest, dividends, or capital gains).
Most students are not taught how to file taxes in school, even though the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides an entire website for educators (titled Understanding Taxes).
Reasons vary, from underfunding and a lack of student interest to a general failure of the education system to identify skills students need.
Most children have only a vague idea of income taxes, let alone the specific rules they must meet. It becomes your role as a parent to help your child initiate this rite of passage by evaluating tax-filing requirements and/or obtaining guidance from tax professionals.
This quick guide for parents covers the basic rules that you should know for determining when your child must (or should) file. It also offers suggestions for helping your child take responsibility for their own tax chores in the future.
Dependent Child Status
To qualify as your dependent, your child must:
- Have a valid Social Security number (SSN)
- Not file a joint return (if married)
- Be your son, daughter, adopted child, stepchild, eligible foster child, sibling, half-sibling, step-sibling, or offspring of any of these
- Be under age 19 at the end of the tax year, or under age 24 if a full-time student, or any age if permanently and totally disabled
- Live with you for more than half the year in the U.
 S.
S.
It's worth noting that, with the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) in 2017, personal exemptions for parents and others with dependents were eliminated.
However, several other tax-saving opportunities remain. These include:
- Head of household filing status
- The child tax credit
- The child and dependent care credit
- The earned income tax credit
- The American opportunity tax credit and lifetime learning credit
- The student loan interest deduction
- The medical expense deduction
When Your Child Must File a Tax Return
Some people mistakenly believe their child's status as a dependent means they don't have to file taxes. But dependent child status does not excuse your child from filing an income tax return in certain situations. A child who meets any one of these tests for the 2021 tax year must file:
- If the child only has unearned income (e.g., from investment interest or gains) above $1,100 (increasing to $1,150 in 2022)
- If the child only has earned income above $12,550 (increasing to $12,950 in 2022)
- If the child has both earned and unearned income, and the child's gross income (earned plus unearned) is greater than either $12,550 or their earned income plus $350, whichever is less (which essentially means a dependent child must file if their unearned income is more than $350 and they have any earned income, although there is a minimum threshold of $1,100 gross income)
- The child's net earnings from self-employment are $400 or more
Additional rules apply for children who are blind, who owe Social Security and Medicare taxes on tips not reported to an employer or wages received from an employer who didn't withhold taxes, or who receive wages from churches exempt from employer Social Security and Medicare taxes.
If filing a return is required by the first test above and the child has no other income besides unearned income, you can avoid filing a separate tax return for your child by making an election described later in this article.
When Your Child Should File a Tax Return
Even if your child isn't required to file an income tax return, it can still be a good idea to file if:
- Income taxes were withheld from earnings
- They qualify for the earned income credit
- They owe recapture taxes (such as the tax from recapture of an education creditor)
- They want to open an IRA
- You want your child to gain the educational experience of filing taxes
In the first two cases, the main reason for filing would be to obtain a refund if one is due. The others are income-dependent or based on taking advantage of an opportunity to begin saving for retirement or to begin learning about personal finance.
Filing to Recover Taxes Withheld
Some employers automatically withhold part of pay for income taxes. By filing Form W-4 in advance, children who do not expect to owe any income tax (and did not owe income tax the previous filing year) can request an exemption.
By filing Form W-4 in advance, children who do not expect to owe any income tax (and did not owe income tax the previous filing year) can request an exemption.
Form 1040EZ, used previously for simple individual taxes, is no longer valid for tax years 2018 and beyond as a result of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
Filing to Report Self-employment Income
Your child can report income from self-employment using Form 1040 and Schedule C to determine profit (as with Form 1040EZ, Schedule C-EZ is no longer used.) If your child has a net self-employment income of $400 or more—or a lower threshold of $108.28 if your child is employed by a church or religious organization exempt from employer Social Security and Medicare taxes—they must file a tax return.
To determine if your child owes self-employment taxes (essentially Social Security and Medicare taxes for those who are self-employed), use Schedule SE. Your child may have to pay self-employment taxes of 15.3%, even if no income tax is owed.
Filing to Earn Social Security Work Credits
Children can begin earning work credits toward future Social Security and Medicare benefits when they earn a sufficient amount of money, file the appropriate tax returns, and pay Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) or self-employment taxes. For the tax year 2021, your child must earn $1,470 to obtain a single credit (increasing to $1,510 in 2022). They can earn a maximum of four credits per year.
If the earnings come from a covered job, your child's employer will automatically take the FICA tax out of their paycheck. If the earnings come from self-employment, your child pays self-employment taxes quarterly or when filing.
Filing to Open an Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
It might seem a little premature for your child to consider opening an individual retirement account (IRA), but it is perfectly legal if they have earned income. By the way, earned income can come from a job as an employee or through self-employment.
If you can afford to, consider matching your child's contributions to that IRA. The total contribution must be no more than the child's total earnings for the year. That lets your child start saving for retirement but keep more of their own earnings.
It also teaches them about the idea of matching funds, which they may encounter later if they have a 401(k) at work. It will probably make sense for the child to open a Roth IRA if they qualify and begin to benefit from decades of compound interest before retirement and tax-free withdrawals when they do retire.
Filing for Educational Purposes
Filing income taxes can teach children how the U.S. tax system works while helping them create sound filing habits for later in life. In some cases, it can also help children start saving money or earning benefits for the future as noted above.
Even if your child doesn't qualify for a refund, doesn't make enough to earn a Social Security credit, and doesn't want to open a retirement account, learning how the tax system works is important enough to justify the effort.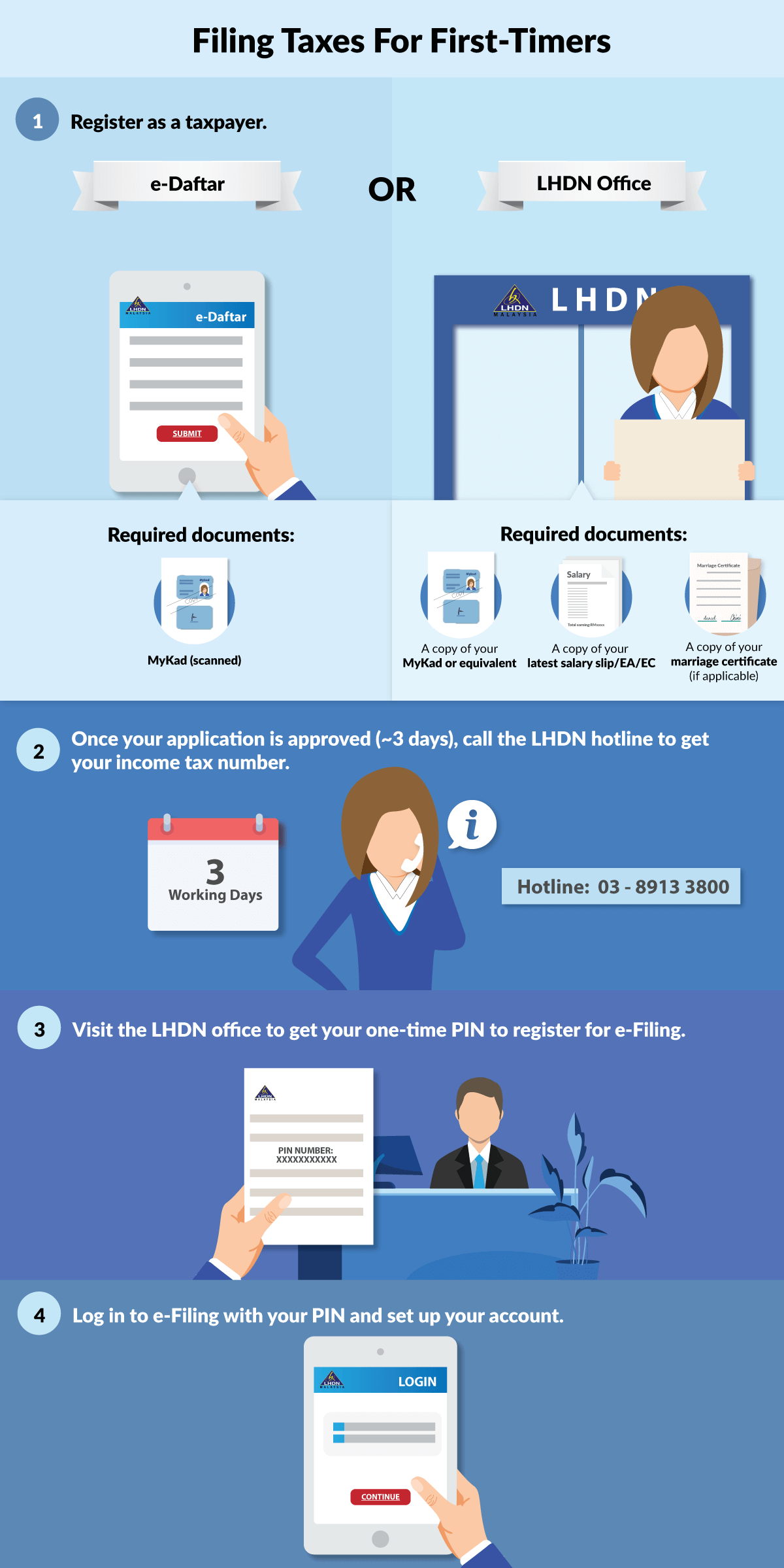
Helping Your Child File a Tax Return
When it comes to helping your child file their income taxes, you should know the following:
- Legally, your child bears primary responsibility for filing and signing their own income tax returns. This responsibility can begin at any age, perhaps well before your child becomes eligible to vote.
- According to IRS Publication 929, "If a child can't file his or her own return for any reason, such as age, the child's parent, guardian, or another legally responsible person must file it for the child."
- Your child can receive tax deficiency notices and even be audited. If this happens, you should immediately notify the IRS that the action concerns a child.
- According to IRS Publication 929, "The IRS will try to resolve the matter with the parent(s) or guardian(s) of the child consistent with their authority."
Reporting Your Child's Income on Your Tax Return
Your child might be allowed to skip filing a separate tax return and include their income on your return, but only if:
- Your child's only income consists of interest, dividends, and capital gains (unearned income).

- Your child was under age 19 (or under age 24 if a full-time student) at the end of the year.
- Your child's gross income was less than $11,000.
- Your child doesn’t file a joint return for the year.
- No estimated tax payments were made for the year, and no overpayments from the previous year (or from any amended return) were applied to this year under your child's name and Social Security number.
- No federal income tax was withheld from your child's income under the backup withholding rules.
- You are the parent whose return must be used when applying the special tax rules for children.
Explain to your child the basics of Social Security and Medicare and the benefits of earning credits in these programs.
Include your child's unearned income on your tax return by using IRS Form 8814. It's important to note that doing so could result in a higher tax rate for you than if the child filed their own tax return. It all depends on the amount of unearned income your child reports.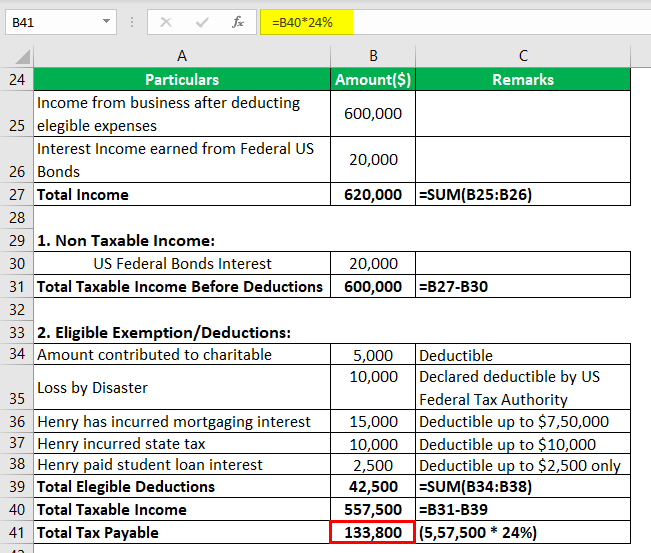
Teaching Your Child About Taxes
When your child starts to earn their own money, start talking about taxes right away.
- Go over that first paycheck stub. Talk about gross earnings, any deductions for income taxes, and any deductions for FICA taxes (Social Security and Medicare).
- Tell your child that, depending on their total income for the year, they can probably receive a refund of income taxes withheld but that FICA deductions will not be refunded and will continue to be withheld from earned wages.
- This would also be a good time to explain the basics of Social Security and Medicare and the benefits of earning credits in these programs.
- If it looks like your child's self-employment income will exceed $400, have the same discussion about that process and the different forms they may have to file, as well as the need to keep receipts of expenses and why.
- Explain that two pieces of information are required on every income tax form: the taxpayer's name and tax identification number (TIN) (usually the Social Security number for children).
 Because the IRS wants these two items to match the data it has on file, remind your child not to use nicknames on tax returns.
Because the IRS wants these two items to match the data it has on file, remind your child not to use nicknames on tax returns. - Emphasize that tax returns are normally due by April 15 each year, but that they can file earlier if they are ready and have all the necessary documentation. The IRS typically begins accepting returns sometime in late January.
- Make sure your child understands that tax records are confidential and that they should not leave them where prying eyes could see.
- Encourage your child to sign their own tax return and forms if they are able. Remind them that they are signing under "penalty of perjury," meaning if their return isn't honest, they will be lying under oath.
- Reinforce the importance of paying attention to taxes, filing on time, and taking IRS obligations seriously.
What Is the Child Tax Credit for 2021?
The Child Tax Credit for 2021 has risen to $3,600 per qualifying dependent in 2021, as per the American Rescue Plan. To receive the credit, certain income requirements must be met.
To receive the credit, certain income requirements must be met.
Do Minors Have to File Taxes?
Minors have to file taxes if their earned income is greater than $12,550 (increasing to $12,950 in 2022). If your child only has unearned income, the threshold is $1,100 (increasing to $1,150 in 2022). If they have both earned and unearned income, it is the greater of $1,100 or their earned income plus $350. If the minor is self-employed, they will owe self-employment tax at $400 and above.
What Is the Standard Deduction for a Child?
If you are a dependent, the standard deduction for 2021 is the greater of $1,100 or your earned income plus $350. The amount cannot be higher than the basic standard deduction of your filing status.
The Bottom Line
As a parent or guardian, it's up to you to discuss and teach income tax filing to your child. The best way to do this is to start early, be patient, and walk your child through the process carefully. Fully explain as much as you need to but don't feel like you have to address every nook and cranny of tax law. After all, that can be pretty tough, even for experienced taxpayers. Finally, consult a tax professional if you get stuck.
After all, that can be pretty tough, even for experienced taxpayers. Finally, consult a tax professional if you get stuck.
Work in Turkey for Russians and citizens of the CIS: vacancies 2022
Salaries in Turkey, when compared with many regions of Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, are higher, and the cost of living, on the contrary, is low. It has a pleasant climate, high-quality products, inexpensive housing. And, what is especially important, there are many vacancies for foreigners, and not only in the tourism sector. It is not difficult to get a job in Turkey, even knowing the local language is not necessary. Detailed instructions are in front of you - bookmark.
In 2022, the Turkish economy entered a period of turbulence. The Turkish lira continues to depreciate, and annual inflation in the country reached 70% in April.
Nevertheless, the country is developing. According to the results of the first quarter of 2022, Turkey's GDP increased by 7.3% year on year - growth exceeds that of most European countries.
According to statistics, there is a high unemployment rate here - 10-14% of the able-bodied population. But we must understand that these figures are largely due to the cultural characteristics of the country. For example, there are few employed women in Turkey simply because many of them prefer to work from home rather than being employed.
In any case, foreigners rarely compete with local residents for jobs: they find jobs in other areas.
Are we needed in Turkey?
A great advantage of working in the country is that there is no need to obtain a visa in case of a seasonal stay. For example, if you decide to work as an animator in a hotel for three months, combining such activities with relaxation, you can do this without any documents.
Turkey is a visa-free country for Russians, Ukrainians, Kazakhs, Belarusians and many others.
Work in Turkey can be combined with a vacation at sea
The main market for foreign labor in Turkey is the former USSR countries (Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Ukraine, Georgia, Russia, etc. ). This is partly due to the fact that Turkish entrepreneurs need employees who speak Russian well. In 2004, the Association of Russian Culture was even created, which helps immigrants find work in the country and adapt faster. Branches of the organization are located in large cities - Alanya, Antalya, Istanbul and Izmir.
). This is partly due to the fact that Turkish entrepreneurs need employees who speak Russian well. In 2004, the Association of Russian Culture was even created, which helps immigrants find work in the country and adapt faster. Branches of the organization are located in large cities - Alanya, Antalya, Istanbul and Izmir.
Seasonal workers are most in demand: animators, guides, dancers, models, English teachers for the summer. In addition, there is a constant shortage of female workers in Turkey, therefore there are many vacancies for nannies and nurses, maids, qualified nurses, waitresses, seamstresses, and hairdressers on the relevant sites.
Due to the rapid development of the real estate market, the country needs builders, engineers and designers. The demand for highly qualified specialists is also strong: doctors, teachers, IT workers.
There are many vacancies for women in Turkey - nannies, nurses, hairdressers...
You can see the statistics of residence permits issued in Turkey, including on the basis of employment, on the official website of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
How to find a job in Turkey for a foreigner
The easiest way to search is to apply to the services of specialized agencies. But there are many "buts" here. First of all, the services of such companies will cost you $200-250. Information about the organization will have to be checked very carefully, since there are a lot of scammers in this area on the market.
And in no case should one agree to unofficial employment: the Turkish authorities carefully monitor this moment, illegal immigrants are punished, and official employees are provided with social guarantees and protection.
The best thing to do is to ask friends and acquaintances who already live in Turkey for recommendations. If not, the first resource to look into is the Turkish Employment Service (İŞKUR). Here you can find up-to-date information about the local labor market, as well as register for a job search, explore training opportunities, consult about starting a business.
About investments, immigration and real estate on the Prian. ru Telegram channel Subscribe
ru Telegram channel Subscribe
Job search and job search sites in Turkey
Before monitoring specialized resources, you should visit the Government Investment Portal. Here you will find important information for immigrants that will help them find a job in the country, and you can also find out the details of obtaining a residence permit and work permit.
You can also contact unofficial, but reputable job sites:
- FLAGMA (Russian language)
- SecretCV.com (Turkish)
- Yenibiris (Turkish)
- Kariyer.net (Turkish)
- CareerJet (Turkish)
- Vacanciesinturkey (English)
Don't forget to join LinkedIn, where you can search for jobs in international companies with offices in Turkey.
If you are interested in tourism, pay attention to the sites of major tour operators - Tui, Teztour, Anextour, Coral Travel, Sunmar. A few months before the peak season, you can often see offers for employees who will interact with Russian tourists.
Internship
Turkey is one of the countries where the AIESEC internship program operates, which provides foreigners with the opportunity to gain work experience in another part of the world. About 4,500 places are provided per year, which can be accessed by specialists and students under the age of 30 years. Often there is an exchange between employees of different companies.
To participate in an internship, you need to register on the site and fill out an application form. Selected candidates will be invited to take an English-language test and try their hand at business games. If you have successfully passed all the "tests", they conclude an agreement with you - and you can start preparing a list of documents for participating in the program:
- visa application form;
- photos;
- copies of passport pages;
- an invitation for an internship and a certificate from the AIESEC unit in your country;
- receipt of payment of the consular fee in the amount of $50.

Requirements for foreign employees
- Language skills
A good command of the Turkish language is only necessary if you get a job in a company whose activities are purely focused on local residents. Such situations are rare for foreigners, so often knowledge of English is more than enough.
If we are talking about temporary work in resorts (service personnel, dancers, hairdressers, etc.), then it is generally not necessary to speak a foreign language. The only exception is animators and guides. Good knowledge of English in their case significantly increases the salary, as it allows them to work in prestigious hotels with visitors from different countries.
- Diploma confirmation
Applies to highly qualified specialists only. The most difficult thing in this case is the doctor (in fact, as in most other countries). The employer will need not only a confirmed diploma and experience, but also passing a professional exam. But in return - high earnings on a par with Turkish specialists.
But in return - high earnings on a par with Turkish specialists.
Features of working in Turkey
By applying for a job in a country with the official permission of the local authorities, you fall under the protection of all labor standards in Turkey. If you decide to work illegally, the opposite is true: you have no rights in your relationship with the employer.
Illegal work, in addition to the dismissive attitude of the employer, is fraught with a number of other consequences.
- Penalties
Both employer and employee. The first one gets a $9 fine75, the second - $389. If you are doing business in the country without a permit, get ready to pay $780. And if you harbor illegal workers without reporting them to the authorities, you will be fined $64. Moreover, all the indicated amounts are for those who violated the law for the first time; repeated fines are two to three times higher.
If you have been repeatedly spotted by law enforcement, you face deportation for at least three years.
- Job search
Without a work visa and a guaranteed job, you have a lot of additional competitors in your new place: in addition to the Turks, there are many illegal immigrants from Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, Georgia, Uzbekistan. But it's not only that it will be much more difficult for you to find a job - your salary will also be lower than that of officially working immigrants, and its size is unstable.
It is allowed to work in the country from the age of 12, the norm of the working day is 8 hours, and the week is 45 hours. Regional labor departments control these norms, allowing overtime work per day - no more than three hours, but no more than 90 additional hours per year. The minimum duration of each paid vacation is 12 working days.
Most of the vacancies in Turkey are in the tourism sector
Obtaining a work permit and residence permit
Step 1. Work permit
There are three types of work permit in Turkey.
- Temporary (Süreli Çalışma İzni)
Issued to foreigners who make such an application for the first time. The validity period is one year. It can be extended for three years, but work cannot be changed. After another three years, the permit can be renewed again, while you can change the employer, but not the specialty.
- Permanent (Süresiz Çalışma İzni)
Issued to foreigners who have either legally worked in the country for at least six years or have lived in Turkey for at least eight years.
- For entrepreneurs (Bağımsız Çalışma İzni)
A permit allowing you to run your own business is only available to those who have lived in the country for at least five years and can prove that their business will be useful or economically beneficial for Turkey.
Individual citizens are issued a work permit without reference to the terms and place of work. This includes refugees, EU citizens and their families, professional athletes, as well as spouses and children of Turkish citizens. But in the latter case, the child must enter the country before he is 18 years old and graduate from a school or university in the local territory.
This includes refugees, EU citizens and their families, professional athletes, as well as spouses and children of Turkish citizens. But in the latter case, the child must enter the country before he is 18 years old and graduate from a school or university in the local territory.
Where to get a work permit
You can get a work permit directly in Turkey. But this is only suitable for foreigners who have a residence permit in the country for a period of at least six months.
The second option is at the Turkish Consulate in your country, where you will need to submit a package of papers: the original employment contract, a document confirming the signature of the head of the company, as well as copies of these documents. After the application is accepted, you are assigned a number that you need to inform the employer. Within the next ten days, he must submit the following documents to the Turkish Ministry of Labor.
- Work Permit Application (completed and printed)
- Company tax report for the year
- Extract from the Commercial Register, which indicates the amount of capital and the composition of shareholders
- Passport of a potential employee, as well as diploma and certificate, translated into Turkish and certified by a notary
Consideration period - one to one and a half months. The decision is communicated by phone or email.
The decision is communicated by phone or email.
Pay attention!
If you plan to live in Turkey permanently and want to have unlimited access to the labor market (without issuing work permits), you can think about obtaining local citizenship. Turkey has a state program under which a passport can be obtained in three months. One of the conditions is to buy real estate in the amount of $400,000 or more.
Owners of real estate worth between $50,000 and $75,000 can obtain a residence permit. This type of residence permit does not give the right to work (permission will have to be obtained separately), but after five years of residence in Turkey, it will be possible to apply for citizenship through naturalization.
Step 2. Work visa and residence permit
If everything is in order with the work permit, you need to re-apply to the consulate of the Republic of Turkey and submit the following papers.
- A completed application form, which can be found on the website of the consulate
- A copy and original of the international passport with a validity period sufficient for the proposed visa, as well as a certified translation into Turkish
- Two photographs
- Employment contract with a signature circular and an application from the employer with a request to open a visa for a potential employee
- Diploma/certificate translated into Turkish and notarized
- Company certificate indicating the type of activity
Registration of all documents and obtaining a visa will cost approximately $200.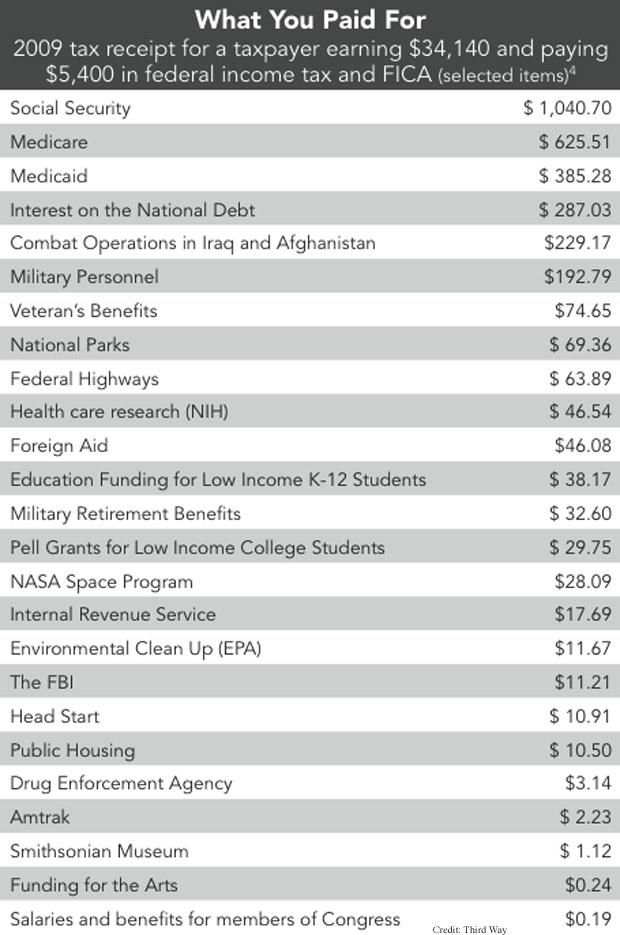 After obtaining a work visa, you must enter the country within 180 days, after which, within a month, obtain a residence permit at the local police department.
After obtaining a work visa, you must enter the country within 180 days, after which, within a month, obtain a residence permit at the local police department.
See also: Visa regime, residence permit and citizenship of Turkey
Demanded specialties and vacancies
If you look at the vacancies offered on job sites, you can distinguish three categories of specialists most in demand in Turkey.
- Highly qualified : teachers (Russian and English, exact sciences), engineers, programmers, system administrators, doctors, designers, architects.
- Specialization : builders, welders, fitters, electricians, turners, equipment operators, furniture designers and assemblers, manicurists, hairdressers, nurses, masseurs and physiotherapists.
- Without special knowledge : animators, waiters, nannies and nurses, maids, administrators, cleaners, salesmen, models and dancers.
The most demanded specialists in the service sector, tourism and construction.
The construction business is developing rapidly, there are many vacancies in this field
Salaries in Turkey
By the beginning of 2022, the official minimum wage in Turkey reached 4,253 lira, an increase of 50% in a year. This is the highest growth in the last 50 years, but given the depreciation of the local currency, the amount still remained low - less than $300. True, it should be borne in mind that in large cities and in qualified specialties, salaries are higher.
Of course, these are not the highest figures in comparison with Europe. But in most CIS countries the situation is worse.
If you have a work permit and a work visa, your salary must be at least the official minimum wage. Failure to comply with this requirement will result in fines being imposed on the employer.
The fixed average salary in Turkey is not officially established - it varies depending on the region and specialty.
According to local employment agencies, the average salary in Turkey in 2022 is 10,000 liras per month ($650), and after taxes 7,825 liras ($525). These figures are relevant for metropolitan areas such as Istanbul and Ankara.
These figures are relevant for metropolitan areas such as Istanbul and Ankara.
The most profitable industries are IT, information and communications, finance, healthcare, scientific activities, real estate and construction. The monthly income here is $1.5–2.5 thousand and more. Administrators and employees of the hotel and restaurant business earn the least - approximately $ 500-650 per month.
Average salary by profession in Turkey (before taxes)
- Programmers - $2,000-2,500
- Physicians - $1,600-$2,000
- Engineers – from $1,700
- Teachers - $1,200-$2,500
- Welders - $1,300 - $1,500
- Masters, foremen - up to $1,500
- College educated managers - $800-$1,200
- Electricians, installers, builders - $600-800
- Vendors - $500-600
- Animators, guides - $500-600
- Babysitters, nurses - $500-700
- Governess (with special education, experience, knowledge of English and Turkish) – from $600
- Clerks - $400-600
- Cleaners, waitresses - $400-500
In Istanbul and other big cities people earn more. You can also count on a higher level of payment, having a diploma from a Turkish or prestigious European university.
You can also count on a higher level of payment, having a diploma from a Turkish or prestigious European university.
Read also: Prices in the country. How much does life cost in Turkey
As you can see, finding a job in Turkey is not such an impossible task. The only question is the salary that suits you. After all, people who have a certain specialty and have the opportunity to confirm their skills receive the most here. Highly qualified specialists, professionals in the construction and installation sector will earn decently in relation to the standard of living and prices in the country.
But low-skilled offers are a good option only for temporary employment and if you want to combine work with leisure (as, for example, in the case of guides, animators). If you are mainly interested in salary, you may want to look at other European countries.
Read instructions for job search in other countries
- Spain
- Italy
- France
- Switzerland
- Greece
- Germany
Conditions for citing materials Prian. ru
ru
Average Salary in Germany - What are the Income in Germany
The average level of wages in Germany for 2019. How much do representatives of different professions earn on average in Germany.
Salary in Germany
The average monthly salary of a German full-time worker in 2019 is 3880€ gross without bonuses and overtime pay.
Let's define that for comparison of incomes the monthly or annual payment for work on hire is accepted as a basis. Hourly wages or profits of legal entities are not included in the statistics.
In German, salary - Gehalt - remuneration received by employees on a monthly basis.
The main problem of finding out the level of wages in Germany - Germans are extremely reluctant to share this information . In private conversations, asking colleagues about income is expressly prohibited by contracts in many firms. It is unlikely that acquaintances will be able to talk about this topic. Even when vacancies are published, the salary is usually not indicated, but is negotiated separately at the interview. As a result, those sitting at neighboring tables in the office, with almost the same indicators, can earn differently, and significantly.
Even when vacancies are published, the salary is usually not indicated, but is negotiated separately at the interview. As a result, those sitting at neighboring tables in the office, with almost the same indicators, can earn differently, and significantly.
It's good that there are data from the labor exchange, which are regularly published on the official website.
These are average values. In each case, the salary differs in one direction or another.
The next source is websites that collect income information anonymously. People share information on the condition of anonymity, everything is entered into a common database, which makes it possible to calculate certain average values for various parameters. Relying on such data is not particularly worth it. No one checks the accuracy of the information entered.
For those who work in Germany (or plan to work here), there is a good way to find out the approximate salary level for their situation. The service is in German, but the main thing is to know the name of the profession - in order to choose the right specialty from the list. The service is free, but it requires you to leave an email and subscribe to the newsletter, from which you can unsubscribe immediately after receiving the result. So, follow the link
The service is free, but it requires you to leave an email and subscribe to the newsletter, from which you can unsubscribe immediately after receiving the result. So, follow the link
Gehalt-Check
Next, step by step, enter your age, gender, level of education, whether you work now, profession, managerial position, index of the city in Germany to which the check belongs - and email. You receive a letter containing a link to a page with results and, interestingly, with vacancies that match the specified conditions.
Separately, for migrants, I note: often the earnings of foreigners are lower than those of German colleagues , simply because otherwise why hire a foreigner? The reason is not only differences in qualifications or more working hours per week. Large differences in wages are noticeable even among professionals who are at the same level in experience and education.
When comparing German salaries, for example, with Russian ones, keep in mind that in Germany the amount before taxes is indicated in the contract . First of all, it is interesting how many people get their hands on it. For a complete understanding of wages in Germany, it is necessary to understand how the net is calculated from the German gross salary, as well as get more statistics.
First of all, it is interesting how many people get their hands on it. For a complete understanding of wages in Germany, it is necessary to understand how the net is calculated from the German gross salary, as well as get more statistics.
In the countries of the former USSR, as a rule, the employer names the amount that the employee receives in his hands, and pays taxes and social contributions additionally. If you mentally add to Russian earnings the costs incurred by the employer, the contrast with German incomes will not be so striking.
In Germany, a person is considered to be below the poverty line if their income is 60% of the average monthly income in the country.
Dependence of income on specialty
Profession - the main criterion for the level of remuneration.
Higher education in Germany does not guarantee a high salary. But in general, in comparison with other groups of workers, on average, university graduates earn more.
If German students chose their future profession solely on the basis of income, the choice would be obvious - an engineer, a doctor or a lawyer.
| Specialty | Average annual gross income |
|---|---|
| Medical | 79538€ |
| Law | 74013€ |
| Engineer | 70288€ |
| Programming | 68133€ |
| Natural sciences | 66954€ |
| Economy | 65404€ |
| Architecture | 55822€ |
| Psychology | 55204€ |
| Geology and other geosciences | 53713€ |
| Politics and society | 52974€ |
| Pedagogy | 50000€ |
| Philosophy | 47022€ |
| History and culture | 46836€ |
| Design | 46075€ |
| Child rearing, social pedagogy | 45116€ |
Doctors in Germany receive more than 5700 per month
The statistics do not give an accurate idea of income above 5700€, as it is collected by the amount of pension contributions, which grow only up to a certain limit, and then remain fixed.
In addition to the above professions, management companies and other managers could have come to the first lines, but there the connection with the specialty in the diploma is not so obvious.
Worse than other holders of higher education in Germany, linguists and sociologists earn. Linguists have a problem with a large number of applicants: there are 25 unemployed for one open vacancy.
Wages do not always determine supply and demand. Yes, in the industrial sector, the lack of specialists has a positive effect on the income of workers, but the situation is different in the civil service.
For example, the situation with social workers. They can often only find a job in the civil service, averaging €3,750 gross. At the same time, due to the influx of refugees in Germany, for every 100 unemployed with a degree in social sciences, there are 92 vacancies.
Professions not requiring higher education
To get a decent salary in Germany, it is not necessary to have a university degree. Statistics show that among professions requiring secondary education, there are enough of those that allow you to earn at the level of higher education holders.
Statistics show that among professions requiring secondary education, there are enough of those that allow you to earn at the level of higher education holders.
And here there are clear leaders - this applies primarily to aviation.
A clerk in a bank or an important account manager in a German trading company in the first 3 years after graduation receives an average of bachelor's level.
| Occupation | Gross salary per year |
|---|---|
| Air traffic controller | 67558€ |
| Pilot | 62986€ |
| Key account manager | 39540 |
| Logist | 39175€ |
| Clerk at a financial institution | 38084 |
| IT consultant | 37083€ |
| Programmer after Ausbildung | 35006 |
| Insurance agent | 34436€ |
| An employee in an insurance company | 33905€ |
| Machine dealer | 33693€ |
| Production Designer | 33682€ |
| Builder | 33152€ |
| Draftsman | 31894€ |
| Locksmith | 31405€ |
Secondary vocational education in Germany often allows you to earn no worse than higher education holders.
The lowest wages in Germany for beauticians, hairdressers, waiters.
| Occupation | Annual income in € |
|---|---|
| Cosmetologist | 21820 |
| Hairdresser | 21832 |
| Waiter | 22628 |
| Baker | 23649 |
| Dental technician | 23682 |
| Dental assistant | 23763 |
| Call center employee | 24200 |
| Receptionist | 24216 |
| Chef | 24540 |
| Sales Consultant | 24999 |
| Optic | 25313 |
| Physician assistant | 25393 |
| Auto mechanic | 25795 |
| Paralegal | 26000 |
| Physiotherapist | 26165 |
| Travel agency employee | 26268 |
Dependence of payment on activity
Wages in Germany are highly dependent on the German industry branch in which the firm does business. There are traditionally more "rich" money directions, where the mere belonging to the labor market forces you to pay more, because otherwise good specialists will be taken away by competitors.
There are traditionally more "rich" money directions, where the mere belonging to the labor market forces you to pay more, because otherwise good specialists will be taken away by competitors.
| Monthly pay | Field of activity |
|---|---|
| 5338€ | Finance and insurance |
| 5126€ | Information technology |
| 5041€ | Energy |
| 4900€ | Freelancers |
| 4367€ | Education and teaching |
| 4128€ | Real Estate |
| 4092€ | Mining |
| 4024€ | Arts, entertainment, recreation |
| 4012€ | Industry |
| 3893€ | Medicine |
| 3636€ | Trade |
| 3444€ | Water supply |
| 3219€ | Construction |
| 3055€ | Transport, logistics |
| 2425€ | Hotel business |
Firm size has a significant impact on the average income of workers in Germany.
- 1-20 persons - 36165€
- 21-50 - 40867€
- 51-100 - 43204€
- 101-1000 - 49451€
- >1000 - 61108€
Therefore, when looking for a job in Germany, keep in mind that in large companies, a potential candidate has the right to hope for a higher pay.
Comparison of wages for men and women
Anyone who is at least a little interested in Germany probably knows that feminism is firmly on its feet here and politicians are fighting for gender equality as if the onset of a brighter future depends on it. However, the fact remains that women earn on average 21% less per hour than men. The wage gap between German men and women is one of the largest in the European Union.
The gap between the wages of women and men in Germany is narrowing very slowly.
Over the years, this difference is gradually decreasing, but the rate is extremely low. The problem here is not so much in inequality as in the fact that women usually work part-time . Without being present 40 hours a week at work, it will be extremely difficult to talk about a promotion with your boss. In addition, the accumulation of experience is slower. Well, women themselves are often more interested in the availability of a job than in the growth of their wages, so they do not particularly apply for an increase. There are also enough careerists among German women, but in general the picture is this.
The problem here is not so much in inequality as in the fact that women usually work part-time . Without being present 40 hours a week at work, it will be extremely difficult to talk about a promotion with your boss. In addition, the accumulation of experience is slower. Well, women themselves are often more interested in the availability of a job than in the growth of their wages, so they do not particularly apply for an increase. There are also enough careerists among German women, but in general the picture is this.
In 2017, Germany passed a law allowing employees of enterprises with more than 200 employees to request information on the salaries of colleagues in comparable positions. And firms with more than 500 employees are required to regularly publish data on the average salary for all positions. According to the government, these measures will allow women to gain more arguments in a conversation with the boss about wage increases. In turn, the authorities, by publishing such data, can slow down the growth of incomes for men.
In Germany, men earn higher wages on average
Dependence of wages on age
Intuitively, the older a person gets, the more experience he accumulates and the higher the income. It makes no sense to draw a direct dependence of wages on age in Germany - no one pays workers more, just because they are older. But an indirect relationship between experience and income can be traced.
| Age | In the age group |
|---|---|
| 20 | 30025€ |
| 25 | 36956€ |
| 30 | 42170€ |
| 35 | 46542€ |
| 40 | 48424€ |
| 45 | 48958€ |
| 50 | 49660€ |
| 55 | 49823€ |
| 60 | 50064€ |
Dependence of German wages on the region
Looking at the place of residence, the highest wages in Germany are paid in Hesse, which is not surprising. There is Frankfurt am Main - the European financial center. Slightly less on average earn in Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria and Hamburg. The lowest level of earnings in the states of eastern Germany. Capital Berlin is in this plan approximately in the middle.
There is Frankfurt am Main - the European financial center. Slightly less on average earn in Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria and Hamburg. The lowest level of earnings in the states of eastern Germany. Capital Berlin is in this plan approximately in the middle.
| Earth | As a percentage of the average German |
|---|---|
| Hesse | 114.1% |
| Baden-Württemberg | 108.6% |
| Hamburg | 105.9% |
| Bavaria | 105.1% |
| North Rhine-Westphalia | 100.8% |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | 98.3% |
| Bremen | 95.8% |
| Saarland | 95% |
| Berlin | 94.5% |
| Lower Saxony | 91.8% |
| Schleswig-Holstein | 88.3% |
| Thuringia | 81% |
| Saxony | 79. 9% 9% |
| Brandenburg | 78.9% |
| Saxony-Anhalt | 78.9% |
| Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | 75.9% |
Dynamics of salary growth in Germany
On average, incomes of Germans grow by 2-3% annually. Such growth covers inflation, because prices also rise by about this amount, which is completely normal for the capitalist model of the world.
| Year | Gross |
|---|---|
| 2018 | 35380€ |
| 2017 | 34306€ |
| 2016 | 33396€ |
| 2015 | 32486€ |
| 2014 | 31600€ |
| 2013 | 31089€ |
| 2012 | 30432€ |
| 2011 | 28333€ |
| 2010 | 27997€ |
| 2009 | 27728€ |
| 2008 | 27827€ |
| 2007 | 27196€ |
| 2006 | 26765€ |
It is even more interesting to look at the dynamics of the net income of burghers.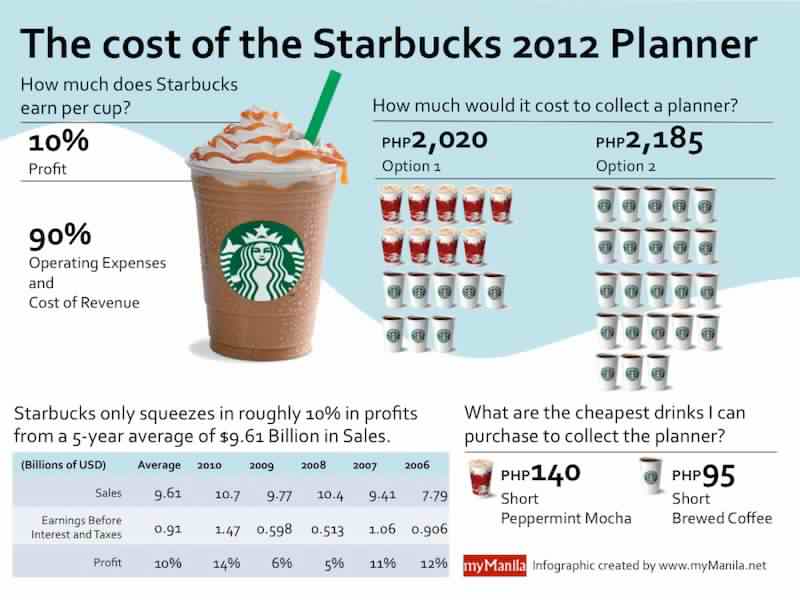
| Year | Net |
|---|---|
| 2018 | 23345€ |
| 2017 | 22652€ |
| 2016 | 22162€ |
| 2015 | 21607€ |
| 2014 | 21134€ |
| 2013 | 20594€ |
| 2012 | 20212€ |
| 2011 | 19729€ |
| 2010 | 19240€ |
| 2009 | 18498€ |
| 2008 | 18479€ |
| 2007 | 18161€ |
| 2006 | 17981€ |
Examples of German salaries for specific occupations
Civil servants
Policeman - 2800-4059€
Police service (Polizist) in Germany takes place in various types of police, from service at the city station to the criminal department. The salary of a German policeman is highly dependent on the specific position and class.
Depending on the direction of service (Laufbahn), the requirements for those wishing to become police officers are different, but in general, the absence of offenses, an impeccable reputation, good physical shape and psychological stability are required. School grades play a big role when you want to become an investigator or forensic scientist.
Police officers in Germany are paid decent salaries up to €4000 gross per month.
Soldier - 2210-3486€
Germany has a professional army, therefore, any soldier (Soldat) has a salary, like other professionals.
Physically healthy, psychologically stable young people are chosen to replenish the ranks of the Bundeswehr. However, the army also requires other specialists, ranging from plumbers to programmers, so in principle anyone can become a military man in Germany if he can fulfill the admission standards.
The salary of the military depends on the length of service, position, rank and availability of military specialties.
White collar - office workers
Judge - 4187-6449€
In order to work as a judge in Germany (Richter), you need to graduate from a university, pass a state exam, then go through two or three years of training, pass two more exams, and then you can start working with a probationary period of two years, during which you are constantly threatened with removal from office at any time and without explanation.
It goes without saying that judges must be independent, including financially, so the salary of the arbiter in Germany is much higher than the average.
Lawyer - 2248-4444€
To work as a lawyer in Germany (Anwalt), you will have to get a higher education in the field of law and pass a state exam. Then you need to pass the practice (Referendar), which ends with the second state exam.
A lawyer is most often employed in a lawyer's office until he starts his own business as a self-employed person. It is also possible to get a job in various companies that provide legal services, checks of contracts and other documents. It will not be superfluous to have a lawyer in a company earning in the field of production or trade.
It will not be superfluous to have a lawyer in a company earning in the field of production or trade.
Work of a lawyer - consultations in the field of legislation, preparation of lawsuits, protection of the client's interests in court.
Tax consultant - 4552-7206€
Tax consultants (Steuerberater) in Germany is one of the most prestigious professions. The process of learning in the field of taxes is complex - endless study of laws, rules, filling out forms will require attentiveness, concentration and perseverance.
Tax consultants work as private entrepreneurs, in tax consultations, or as employees in large companies.
The main activity of tax consultants in Germany is assistance in filling out tax returns for individuals and financial reporting for companies.
Accountant - 2977-4064€
Accounting (Buchhalter) is not a separate profession in Germany. The specialty is obtained in courses or as part of another educational process, for example, in the course of training as a tax consultant.
In German companies, bookkeeping is rarely done by a single employee. The person who is engaged in maintaining financial statements has a lot of other responsibilities.
Small firms do not have an accountant on staff, but resort to the services of external consultants, hiring them on an hourly basis when necessary. In Germany, accountants are often entrepreneurs serving several firms at once.
Interior designer - 2350-3419€
Interior designers (Innenarchitekt) - a profession at the intersection of architecture, materials science and art. The task is to design the room in such a way that it is practical, safe and beautiful.
Very often it is the latter that influences the salaries of interior designers the most. The ability to create beauty without forgetting about reliability and practicality will allow you to accumulate an impressive portfolio.
There are two ways to obtain the title of Innenarchitekt - through direct study at a university, or as an additional title for sculptors or artists, acquired through practice and theoretical studies.
Musician - 2479-5017€
A musician in Germany (Musiker) often works as a self-employed person. The basis of income is teaching children to play musical instruments, performing in orchestras or groups.
For thousands of hours of study at a music school or university, a professional gets the opportunity to work on the special status of Freiberufler - as a free worker, which leads to significant tax benefits.
It is clear that the size of a musician's earnings depends on personal professional qualities and the ability to devote himself to his work.
The earnings of a musician in Germany are unstable and rarely tied to employment.
Notary - 1919-3035€
Notary (Notar) acts as an intermediary in the conclusion of serious transactions, certifies copies and translations of documents.
In Germany, this work is combined with other legal activities. Of the 6,000 notaries in Germany, 75% are simultaneously practicing law.
Training for the profession of a notary lasts 3 years and allows you to work only in this specialty. But you can get permission to conduct notarial activities to any lawyer who meets the required conditions: legal education, 5 years of work experience, an exam.
But you can get permission to conduct notarial activities to any lawyer who meets the required conditions: legal education, 5 years of work experience, an exam.
Secretary - 2003-3071€
The secretary (Sekretär), and more often the secretary (Sekretärin), is responsible for supporting the boss in organizing work activities. Papers, planning meetings and business trips, other "turnover" - this is the responsibility of the secretaries.
There is no separate education for the profession, usually specialists in the organization of office work - Bürokaufmann / -frau work in positions.
Excellent knowledge of the language, and not only German, is practically necessary.
Social worker - 2490-3300€
Social workers (Sozialarbeiter) work in Germany in orphanages and nursing homes, care centers for the helpless and shelters for the homeless, support the disabled and the elderly.
Social workers can find employment in government agencies, medical facilities, legal clinics, and emergency services.
Vocational training in the specialty takes 3 years, after which it is necessary to pass the state exam. Candidates will need excellent knowledge of German, resistance to stressful situations, as well as the ability and desire to communicate with people.
Occupations related to medicine
Nurse - 2309-3146€
There are several names for the nursing profession in Germany - Krankenpflegerin, Krankenschwester or Pflegefachkraft.
The essence is the same - after three years of training in basic medical skills and nursing, you can go to look for work in a hospital, clinic, nursing home and other places where hard work is required for those in need of help.
Although the profession is responsible and very difficult, nurses and brothers do not earn much. There are not enough people who want to earn a living in this specialty in Germany, so there is an acute shortage of workers in the field of patient care.
There are many foreigners among the medical staff in Germany. Earnings do not inspire Germans, but attract immigrants.
Earnings do not inspire Germans, but attract immigrants.
Head of Care Service - 3072-4204€
Germany has a well-developed network of special services that support people in difficult times of life when they become helpless due to illness or accidents (Pflegedienst). Orderlies work in this service, and managers - Pflegedienstleitung manage.
The task of the head of the service is to organize the work of subordinates.
Due to a shortage of workers, managers often have to act as orderlies themselves and look after the wards. This position is mainly filled by experienced workers who have spent thousands of hours in the role of a nurse or assistant.
Nurse - 2380-3688€
Nurse (Pfleger) is one of the most sought-after professions in Germany. Caring for the helpless sick, the disabled, and the elderly requires special qualities that not everyone possesses.
You need to be physically strong and healthy, as you will have to lift and carry a lot of those who are not able to walk themselves. Possess a lot of knowledge of a medical and domestic nature, so as not to harm the wards. We must not forget about human qualities in order to take care of people in the most difficult periods of life. Moral stability is a must!
Possess a lot of knowledge of a medical and domestic nature, so as not to harm the wards. We must not forget about human qualities in order to take care of people in the most difficult periods of life. Moral stability is a must!
To work as a nurse in Germany, you need to get a vocational education and pass a state exam. This is one of the few professions that a migrant without a higher education, but with a medical secondary education, can take, although this will require at least a year of work as a trainee.
Physiotherapist - 1907-2507€
Physiotherapist (Physiotherapeut) in Germany is educated in 3 years. Its task is to help people recover from injuries or develop the physical abilities of the disabled through exercise, gymnastics and massage.
This specialty allows you to work in clinics and rehabilitation centers. Also, the services of a physiotherapist may be needed in a hotel with a SPA service, in a sports club or fitness center.
The highest earners are good physiotherapists who open their own private offices where they see patients on prescription and carry out prescribed procedures.
Ergotherapist - 1979-2706€
Ergotherapeut (Ergotherapeut) - a specialist in the rehabilitation of sensory motility, reaction, sense of touch. His job is to help recover from severe injuries associated with partial or complete loss of coordination. Occupational therapists also work with people with disabilities, trying to develop their weaknesses through games and exercises.
Usually a profession is obtained through a three-year training process in vocational schools. There is also an opportunity to get higher education in this specialty.
Occupational therapists usually work in their clinics, as private entrepreneurs or assistants, as well as in large rehabilitation centers, as employees.
Pharmacist - 2520-2998€
A pharmacist (Pharmazeut) in Germany works in the development, research and production of medicines. Also, pharmacists often take a place at the counters of pharmacies, as workers well versed in medical preparations.
You can also find a place in government agencies involved in the admission of drugs to the market and conducting testing.
In terms of education, this is usually secondary vocational education for 3 years, but there is also a higher education that allows you to work in research areas.
Apothecary - 2518-2984€
Pharmacist (Apotheker) in Germany is not the one who sells medicines in a pharmacy, but the owner of the pharmacy itself. Although nothing prevents pharmacists from working in other areas of pharmaceuticals, from the production of medicines to marketing.
After graduating as a pharmacist, you must complete another year of practice - Approbation - to obtain the status of a pharmacist. You can then choose whether to open your own business or join an existing one.
Blue collar workers - blue collar workers
Confectioner - 1510-2264€
Konditor bakes various sweets. To work, you will have to undergo serious professional training for three years and pass the state exam.
Confectioners work in bakeries, cafes and restaurants, sometimes in hotels with a large number of guests, as well as in enterprises producing sweet pastries.
It's a pretty hard job with the need for night shifts, but the salaries of confectioners in Germany are not the highest.
Confectioner is one of the lowest paid professions in Germany.
Painter - 2044-2694€
The painter (Maler) is engaged in exterior and interior painting of buildings. It sounds very simple, but in fact, the correct high-quality interior decoration is a whole science!
Painter training lasts three years, most of the time is spent on practical activities. You will have to master the painting and varnishing of various materials, study the impact of the external environment and many other aspects of work.
We must not forget about the creative component of the profession, because in the end the goal of the painter is to make it beautiful!
Carpenter - 1929-2615€
Carpenter (Zimmerer or Zimmermann) - a profession so ancient that now it even seems outdated. But if you think about it, woodworking is still relevant!
Roof framing, doors, wooden furniture, fences, interior decoration and many other things require the processing of wooden materials, which means that the carpenter's hands are still valuable.
Professional training lasts 3 years. A funny detail - they prefer to take physically strong guys with strong backs as students, since in work they often have to lift and carry weights.
Plumber - 2130-3330€
Plumber (Installateur) in Germany is engaged in the installation and maintenance of various sanitary equipment: plumbing, sewerage, gas supply, and the like.
Training does not last 3 years and includes a large number of practical exercises.
Electrician - 2354-3356€
Electricians (Elektriker) are responsible for the assembly, repair and maintenance of electrical networks.
Education in Germany lasts three and a half years, usually theory is combined with active practice.
Recently, the profession has been renamed Elektroniker, expanding the scope of work towards the infrastructure of information systems, telephone networks and other methods of data transfer.
Electrician - 2336-3352€
Electrical technicians (Elektroniker) work in Germany in a wide variety of branches. Energy, construction, industrial automation, other industries where electronic mechanisms need to be taken care of.
Energy, construction, industrial automation, other industries where electronic mechanisms need to be taken care of.
The training process for electrical engineering in Germany is usually limited to three to three and a half years.
Mechanical engineer - 3280-4859€
Mechanical engineer (Maschinenbauer) can work in Germany in the production, adjustment and repair of machine tools, robots and other industrial machines. There are many specializations for the profession.
Often, in addition to theoretical knowledge of mechanical engineering, mechanics also have quite practical skills, such as plumbing or welding.
The specific specialty of mechanics in Germany can be achieved in three years through a vocational education.
Specialties related to auto and transport
Car dealer - 2394-3934€
Car dealers in Germany (Automobilverkäufer) help customers choose the make and model of the car, advise on various issues of operation, place an order.
To become a car dealer in a German car dealership, you need a secondary education in the field of trade. Other technical automotive specialists can also retrain in the field of sales of automotive equipment. Autohouses first train salespeople for six months, of which at least 3 weeks are devoted to theory. To gain specialization in certain types of models or in various brands, employees undergo seminars.
The most important component of the work of a car seller is the ability to communicate with customers, inspire confidence and positive emotions.
Bus driver - 1901-2549€
In addition to holding the relevant German license categories, a bus driver (Busfahrer) in Germany must complete a vocational training course that lasts 3 years.
Just being able to turn the steering wheel is not enough! The driver must provide services to passengers, sell tickets, monitor the condition of the bus.
Bus driver's job is urban transport, intercity flights or school routes.
Subway driver - 1978-2719€
Train driver in the subway (U-Bahn-Fahrer) - a special case of a locomotive driver who is focused on working in the subway.
The task of the subway driver is to drive the train according to the schedule, control the disembarkation and embarkation of passengers, monitor the state of the train.
Work in the German underground is a prestigious, highly paid occupation that does not require a long process of obtaining an education.
Working as a subway driver in Germany has the advantage of a fast learning process.
Pilot - 4386-11139€
The profession of a pilot in Germany is in demand on passenger airlines, in the military and transport sectors.
Pilot training is linked to a specific company or organization in professional schools. Training is paid. To obtain a license to fly, you must listen to the theory, pass the practice and pass the exams. This will take two or three years. A pilot's license for a small motorized aircraft will cost around 20,000€.
Then you need to look for a job and not lose your skills - a simple pilot leads to the loss of a license. Whoever is lucky will be able to get a job in a big company, where they will pay for retraining. However, in Germany there is no shortage of pilots, many licensed do not progress beyond amateur flying at the air clubs.
Unskilled work
Maid - 1461-1699€
Cleaning women in hotels (Zimmermädchen) in Germany is one of the low-paid occupations that do not require high qualifications. Anyone can work as a maid.
However, hotel directors and recruiters started out as Roomboys. Having gained experience in the hotel business, seeing everything from the very bottom of the career ladder, it is easier to comprehend many details of hotel organization.
Hotel Administrator - 1748-2409€
The visiting card of the hotel is the person at the reception (Rezeptionist). In Russian, the name of the profession can most adequately be translated as "hotel administrator".