How much benadryl can you give a child
Dosage Chart, What It Treats, More
Like many parents, you might have started keeping a stash of medication on hand for when your baby or toddler has little ailments. One popular medicine is Children’s Benadryl, an over-the-counter antihistamine designed to reduce the symptoms of allergies.
But how much do you know about this medication, including when to use it and how much to give to your child, especially your toddler? It’s important to know the safest way to use Children’s Benadryl — and when not to use it.
If you pick up a package of Children’s Benadryl and take a closer look at the label, you’ll see this word: diphenhydramine. Diphenhydramine is a type of antihistamine, which is a medicine designed to reduce your body’s response to a substance called histamine.
Normally, when your body produces this chemical in response to an allergen, you might develop some swelling and itching, or even a runny nose and some congestion. An antihistamine dampens that response and brings you — or in this case, your child — some temporary relief.
Children’s Benadryl is available in a several different forms, including liquid, chewable tablets, and something called meltaway strips that dissolve in your child’s mouth.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warns against giving any cold or cough medicine containing an antihistamine to a child under the age of 2. According to the FDA, this type of medicine could cause serious side effects in toddlers and babies, including rapid heart rate and convulsions.
The manufacturer labels on packages of Children’s Benadryl products tell parents of children under age 2 not to use this product.
When your child is a little older, the situation may be different — but perhaps not as soon as you’d think. These products are generally recommended for children ages 6 and older. The label also directs parents of children between the ages of 2 and 5 not to use the product unless directed by a doctor.
The bottom line: If your child is younger than 6, it’s better to put in a call to your pediatrician before reaching for this medication. And when we talk about toddlers in this article, we’re talking about toddlers above the age of 2.
And when we talk about toddlers in this article, we’re talking about toddlers above the age of 2.
As with any medication that you plan to give to your child, don’t do anything until you read the label. The information will vary from product to product, but in general, product labels list:
- the active ingredients and the inactive ingredients
- the symptoms treated by the medication
- the recommended dosage amounts
Ingestible products like Children’s Benadryl will typically include a statement advising parents of children under 6 not to use the product unless directed by a doctor.
If your child’s doctor does direct you to give a dose of Children’s Benadryl to your toddler, it’s important to give the correct dose as directed by the pediatrician or as instructed by the label. Here’s a look at a suggested dosage chart to help guide you:
| Weight of Child | Liquid suspension* | Chewable tablets* |
|---|---|---|
Under 20 lbs. | Follow doctor directions | do not use |
| 20 to 24 lbs. | 3.75 mL | do not use |
| 25 to 37 lbs. | 5 mL | 1 tablet |
| 38 to 49 lbs. | 7.5 mL | 1 tablet |
| *every 4–6 hours | *every 4–6 hours |
It’s also important to not give too many doses within a certain time period. — no more than six doses in a 24-hour window. However, your child’s doctor may only want you to administer one or two doses to your child, so be sure to ask.
A topical product like Children’s Benadryl Itch Cooling Gel could be useful in situations where it’s not appropriate to give an oral medication to your toddler. Examples include minor skin irritations like insect bites or rashes that itch.
When it comes to Benadryl topicals (like the gel), you can apply a small amount of this product, which contains camphor instead of diphenhydramine, to the affected area on your toddler up to four times per day.
Essentially, allergy symptoms tend to be the main reason that a parent turns to this particular type of medication. Think hay fever-type symptoms:
- sneezing
- sniffling
- watery eyes
- itchy throat
It might also be useful in other situations when an allergic reaction seems to be developing on your child’s skin. For example, the gel might be useful after your child gets a mosquito bite that swells up or has a brush with poison ivy.
Important note
Benadryl often makes children sleepy, but don’t give in to the temptation to give them a dose right before that long car trip! Experts caution that it shouldn’t be used as a sleep aid.
Antihistamines can bring much-needed relief to mild allergic reactions, but they can also cause some side effects. The one that you hear the most about is sleepiness. Your child takes their medicine and then zonks out for an epic nap.
However, some kids experience the exact opposite reaction: The antihistamine stimulates their nervous system, making them hyper and even irritable.
Also, watch out for products containing antihistamines along with other ingredients, so you don’t accidentally double up on a dose.
It’s always a good idea to consult your child’s doctor before giving an antihistamine. Your child’s doctor may give you the green light to go ahead and try a dose of Children’s Benadryl if your child develops an allergic reaction to something. But it’s also possible that your child’s doctor will ask you to steer clear of this particular medication.
If your child does have seasonal allergies, your doctor might also talk to you about trying another type of allergy medication that they can take on an ongoing basis. Benadryl is really designed for short-term use.
Depending on your child’s age, weight, and allergies, possible options might include:
- cetirizine
- loratadine
- fexofenadine
For example, some formulations of Zyrtec are appropriate for toddlers ages 2 and up.
Products containing antihistamines like Children’s Benadryl definitely have their place. But it’s important to use this type of product correctly. For parents of toddlers, it’s best to start with your child’s doctor and go from there.
But it’s important to use this type of product correctly. For parents of toddlers, it’s best to start with your child’s doctor and go from there.
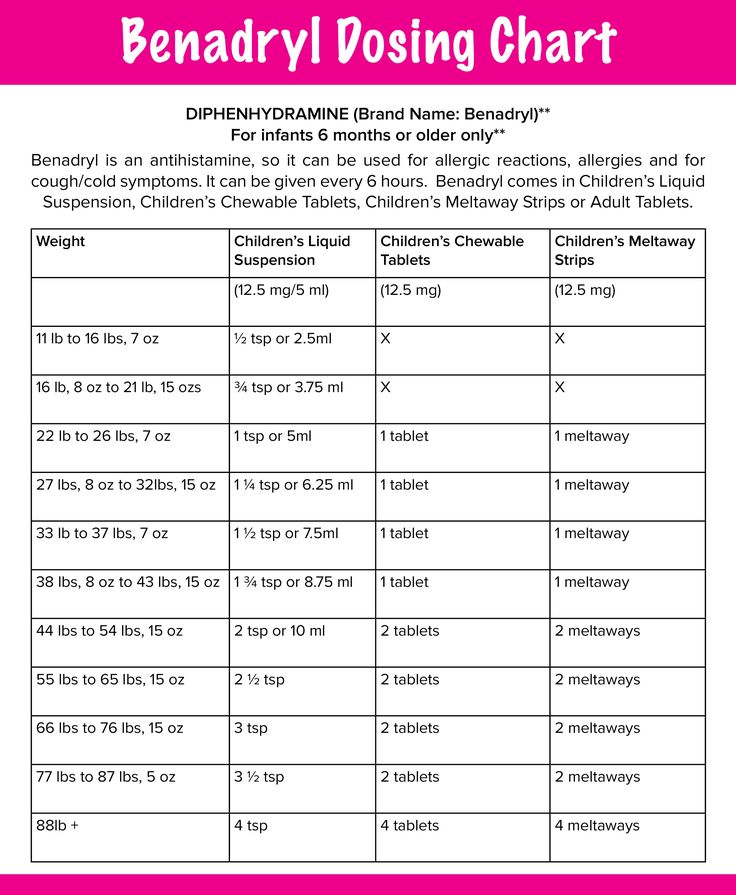
Benadryl Dosing | Framingham Pediatrics
| Child's Weight | 20-24 | 25-37 | 38-49 | 50-99 | 100+ | lbs |
| Liquid 12.5 mg | ¾ | 1 | 1 ½ | 2 | - | tsp |
| Liquid 12.5 mg/5 milliliter (mL) | 4 | 5 | 7 ½ | 10 | - | mL |
| Chewable 12.5 mg | - | 1 | 1 ½ | 2 | 4 | tablets |
| Tablets 25 mg | - | ½ | ½ | 1 | 2 | tablets |
| Capsules 25 mg | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | caps |
Indications: Treatment of allergic reactions, nasal allergies, and hives.
- AGE LIMITS: Avoid Benadryl (diphenhydramine) under 2 years of age unless instructed by healthcare provider.
- DOSAGE: Determine by finding child's weight in the top row of the dosage table
- MEASURING the DOSAGE: Syringes and droppers are more accurate than teaspoons. If possible, use the syringe or dropper that comes with the medication. If you use a teaspoon, it should be a measuring spoon. Never use a kitchen spoon to measure medication dosing.
- 1 measured teaspoon equals 5ml
- 1/2 a teaspoon equals 2.5ml.
- FREQUENCY: May repeat every 6 hours as needed
- ADULT DOSAGE: 50 mg
- CHILDREN’S BENADRYL FASTMELTS: Each Fastmelt tablet contains the equivalent of 12.5 mg of Diphenhydramine HCL and dosed the same as chewable tablets
- RISK of SIDE EFFECTS: May cause drowsiness and occasionally excitation instead.
 DO NOT DRIVE OR OPERATE HEAVY MACHINERY AFTER TAKING BENADRYL.
DO NOT DRIVE OR OPERATE HEAVY MACHINERY AFTER TAKING BENADRYL.
Source: adapted from HealthyChildren.org.
The information contained on this website should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Benadryl Dosing | Contact Us
Benadryl Dosages, Forms and Benefits | SingleCare - Product Information
Home >> Product Information >> Benadryl Dosage: How Much is Safe to Take?
Product information
Benadryl forms and strengths | Benadryl for adults | Benadryl for children | Dosage table of Benadryl | Dosage of Benadryl for Allergies | Dosage of Benadryl for motion sickness | Dosage of Benadryl for insomnia | Benadryl for pets | How to take Benadryl | FAQs
Benadryl is an over-the-counter medication that temporarily relieves allergy symptoms caused by a natural substance in the body called histamine. Diphenhydramine, the active ingredient in the branded drug Benadryl, is an antihistamine that blocks the activity of histamine and reduces symptoms such as runny nose, watery eyes, and itching.
Diphenhydramine, the active ingredient in the branded drug Benadryl, is an antihistamine that blocks the activity of histamine and reduces symptoms such as runny nose, watery eyes, and itching.
Diphenhydramine also causes drowsiness and slows down the part of the brain that controls nausea. For these reasons, Benadryl may also be used to relieve occasional insomnia or prevent motion sickness.
For patients over 12 years of age, the standard dosage of Benadryl Allergy is 25 to 50 mg (milligrams) - one to two tablets or capsules - every four to six hours. Children aged 6 to 11 years can be given Benadryl at a maximum dose of 25 mg (one tablet or capsule) every four to six hours. Benadryl can be taken with or without food.
RELATED: What is a Benadryl Allergy? | Benadryl Allergy Coupons
Benadryl Formulations and Strengths
Benadryl tablets and softgels contain 25mg of diphenhydramine hydrochloride and are usually taken by adults and children 6 years of age and older.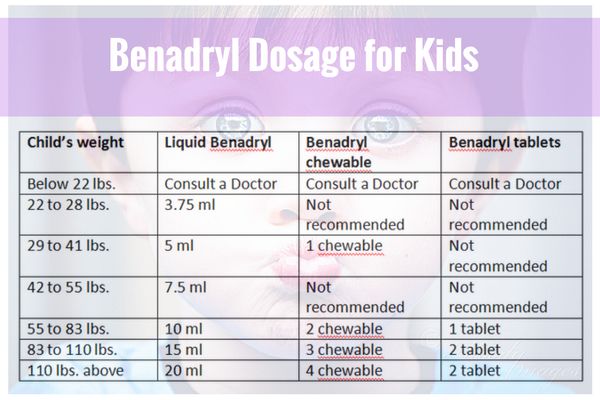 Benadryl Allergy Plus, however, also contains 10 mg of phenylephrine hydrochloride, a nasal decongestant. Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion should not be given to children under 12 years of age unless directed by a doctor.
Benadryl Allergy Plus, however, also contains 10 mg of phenylephrine hydrochloride, a nasal decongestant. Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion should not be given to children under 12 years of age unless directed by a doctor.
- Benadryl Allergy Ultratab : 25 mg of diphenhydramine on tablet
- Benadryl Lov-Geli from allergies without dyes : 25 mg of diphenhydramin for gel capsule Benadril plus strokes : 25 mg Fengizemine /
Benadryl Adult Dosage
The standard adult dose of Benadryl is one to two tablets or softgels (25-50mg) every four to six hours.
- Standard Adult Dose of Benadryl: One to two tablets/capsules (25-50mg) every four to six hours.
- Maximum adult dosage of Benadryl: Two tablets/capsules (50 mg) every four hours, maximum 12 tablets (300 mg) in 24 hours.
Benadryl dosage for children
Benadryl dosages may depend on the age or weight of the children. Children's allergy to Benadryl is more suitable for children aged 6 to 11 years. Contains half the dose of diphenhydramine (12.5mg) as Benadryl Allergy, Children's Benadryl Allergy, sold in a child-friendly liquid and chewable tablet form.
Children's allergy to Benadryl is more suitable for children aged 6 to 11 years. Contains half the dose of diphenhydramine (12.5mg) as Benadryl Allergy, Children's Benadryl Allergy, sold in a child-friendly liquid and chewable tablet form.
- Children's dosage of Benadryl for children 2 to 5 years of age: Do not give unless directed by a physician.
- Benadryl dosage for children 6 to 11 years old: One to two chewable tablets or 5 to 10 ml every four to six hours, maximum 12 tablets or 60 ml in 24 hours.
- Pediatric dosage of Benadryl for children 12 years of age and older: Two to four chewable tablets or 10 to 20 ml every four to six hours, maximum 24 tablets or 120 ml in 24 hours.
RELATED: What is Children's Benadryl? | Benadryl coupons for children
Benadryl (adult drug) can be given to children between 6 and 11 years of age, but should not be given to children under 6 years of age. Although Benadryl Allergy can be used to relieve insomnia. in children 12 years of age and older, it should not be used as a sleeping pill in children under 12 years of age.
Although Benadryl Allergy can be used to relieve insomnia. in children 12 years of age and older, it should not be used as a sleeping pill in children under 12 years of age.
- Standard dose of Benadryl for children under 6 years: Do not give unless directed by a doctor.
- Standard dose of Benadryl for children 6 to 11 years old: One tablet/capsule (25 mg) every four to six hours.
- Maximum dosage of Benadryl for children aged 6 to 11 years: One tablet/capsule (25 mg) every four hours, maximum six tablets (150 mg) in 24 hours.
Children aged 6 to 11 should not be given Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion except under the direction of a pediatrician.
0128

Benadryl dosage for allergy symptoms
Benadryl relieves symptoms caused by allergies, hay fever, or the common cold, including runny nose, nasal congestion, sinus pressure, sneezing, rash, watery or itchy eyes, and itchy nose. It is also indicated for the relief of pruritus (pruritus) caused by the release of histamine due to an allergic reaction (contact dermatitis), urticaria (urticaria), or insect bites.
- Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and older): 25–50 mg every four to six hours.
- Pediatric patients (6-11 years): 25 mg every four to six hours.

- Patients with renal insufficiency:
- Creatinine clearance 10-30 ml/min: No adjustment.
- Dialysis: no adjustment and no additives.
- Other warnings: Talk to your doctor before taking Benadryl if you have any of the following:
- Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and older): 25 to 50 mg 30 minutes before travel and every six to eight hours while traveling.
- Pediatric patients (6-11 years old): 12.5 to 25 mg 30 minutes before travel and every six to eight hours during travel.
Benadryl Dosage for Insomnia
Benadryl may be used for the occasional relief of insomnia or travel-related insomnia in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older.
- Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and older): 25 to 50 mg 30 minutes before bedtime.
- Pediatric patients (6-11 years): Do not give unless directed by a physician.
Benadryl Dosage for Pets
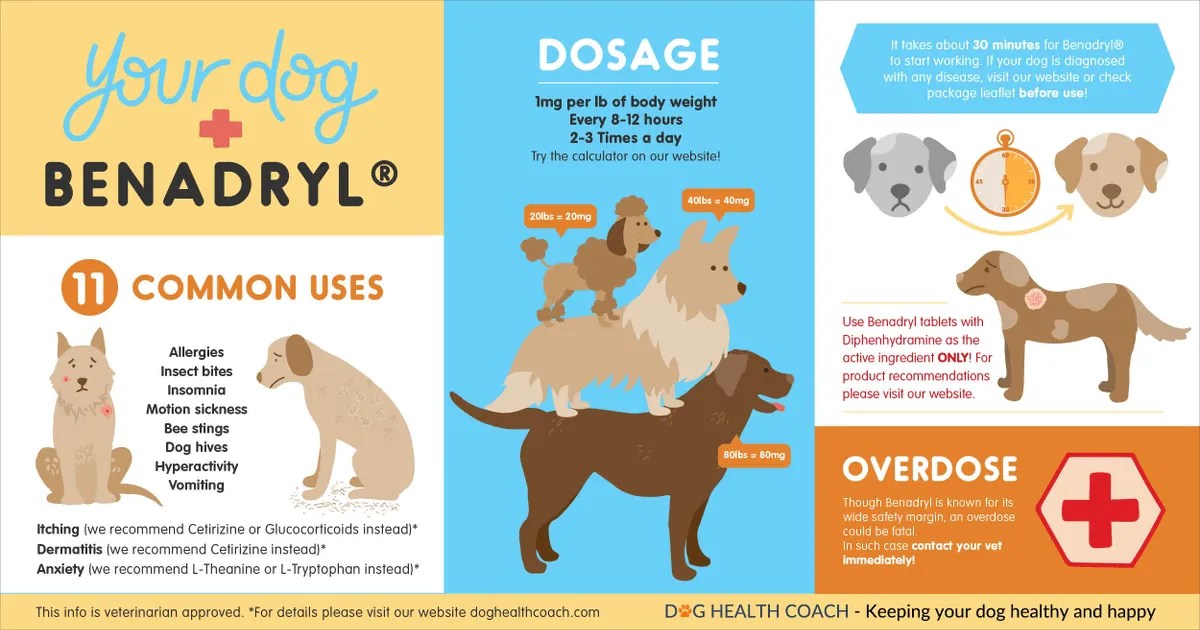
Benadryl is not approved for use in pets, but veterinarians prescribe diphenhydramine in dogs, cats, and large animals to treat allergic reactions, nose allergies, itching, hives, motion sickness, and anxiety problems.
 Veterinarians also use diphenhydramine to treat certain types of cancer (mast cell tumors), shock, life-threatening allergic reactions, and other conditions.
Veterinarians also use diphenhydramine to treat certain types of cancer (mast cell tumors), shock, life-threatening allergic reactions, and other conditions.
The standard veterinary dosage is 2 to 4 mg diphenhydramine per kilogram of body weight (1 to 2 mg per pound) two or three times a day. However, check with your veterinarian before giving your pet Benadryl or any other over-the-counter medication.
RELATED: How to Treat Allergies in Cats and Dogs
How to Take Benadryl
For healthy adults and children 12 years of age and older, take one to two tablets or capsules by mouth every four to six hours or every doctor's instructions. Benadryl can be taken with or without food.
- Follow the instructions on the medicine label if you are taking this medicine without a prescription.
- If you are taking this medicine with a prescription, your doctor will tell you how much to use. Do not use more than indicated.

- Swallow the tablet or softgel whole. Do not crush, break or chew it.
Safety Tips
When taking or using Benadryl, you can consider the following safety and efficacy tips:
- Always check the expiration date. If the medicine has expired, dispose of it safely and buy a new box.
- Benadryl should be stored at room temperature (68°C -77F)
- Check all other medicines you or your child are taking to make sure they also do not contain diphenhydramine or phenylephrine. Both are commonly found in combination with cold, flu, or allergy medications. Pay special attention to topical itch medications that may contain diphenhydramine. These drugs, including topical diphenhydramine, should never be used with Benadryl.
- Do not take Benadryl with alcohol or sedatives.
- People who have glaucoma, breathing problems due to emphysema or chronic bronchitis, or difficulty urinating due to an enlarged prostate should talk to a doctor before taking Benadryl.

- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their physician before taking Benadryl.
- Although Benadryl is approved for use in children 6 years of age and older, Benadryl Allergy should not be used as a sleep aid in children under 12 years of age.
- For motion sickness, take Benadryl 30 minutes before travel or movement. If you are going on a long trip, take the following doses every six to eight hours.
- Record the time for each dose in a diary or schedule so that the next dose is not given too soon.
- Benadryl is a sedative, so do not operate machinery or drive if you feel tired, drowsy or lose concentration. Before taking diphenhydramine, it is recommended to remove obstacles and dangers in the house.
Benadryl Dosage FAQ
How long does Benadryl last?
When taken as directed, Benadryl Allergy usually starts working 30 minutes after ingestion and reaches peak levels in the body in about two hours. In general, food does not affect the absorption of Benadryl and does not reduce its effectiveness.
 However, regular use of Benadryl can lead to tolerance. Over time, the standard dose may gradually lose effectiveness.
However, regular use of Benadryl can lead to tolerance. Over time, the standard dose may gradually lose effectiveness. How long does Benadryl stay in your body?
At the recommended dosage, the effects of Benadryl should last between four and six hours, but this may vary. Generally, the amount of time Benadryl stays in the system increases with age.
Health care providers measure how long a drug stays in the body by its half-life, which is the time it takes for the body to eliminate half the amount of the drug in the body. The half-life of diphenhydramine in children is four to seven hours (average five hours). For adults, the elimination half-life is seven to 12 hours (mean nine hours). For the elderly, the elimination half-life is nine to 18 hours (mean: 13.5 hours).
What happens if I miss a dose of Benadryl?
No problem if you don't take a dose of Benadryl. Take the missed dose at any time. The dosing schedule will be reset, so wait at least four hours before taking your next dose.
 Do not take extra medicine to make up for a missed dose.
Do not take extra medicine to make up for a missed dose. How can I stop taking Benadryl?
You can safely use Benadryl regularly to treat allergic reactions, insomnia, or motion sickness. It should only be used occasionally as a sleep aid. Diphenhydramine - This is sometimes abused. Chronic use of Benadryl, especially to relieve anxiety or insomnia, can lead to addiction and withdrawal symptoms if Benadryl is stopped quickly. High doses of Benadryl can cause severe heart problems, seizures, coma and death. Before you stop taking Benadryl, talk to your doctor about lowering your Benadryl dose or using alternative medications or treatments to reduce anxiety or treat insomnia.
You should stop taking Benadryl and consult your doctor if you experience excessive nervousness, drowsiness, allergic reactions, or if symptoms do not improve after seven days.
What can be used instead of Benadryl Allergy?
Health care professionals generally do not recommend the use of first-generation antihistamines such as diphenhydramine, the active ingredient in Benadryl.
 Second-generation antihistamines are as effective as diphenhydramine but do not cause as much sedation or drowsiness. Instead of Benadryl Allergy, you can choose several second-generation OTC antihistamines such as Claritin (loratadine), Alavert (loratadine), Allegra (fexofenadine), Zyrtec (cetirizine), and Xyzal (levocetirizine).
Second-generation antihistamines are as effective as diphenhydramine but do not cause as much sedation or drowsiness. Instead of Benadryl Allergy, you can choose several second-generation OTC antihistamines such as Claritin (loratadine), Alavert (loratadine), Allegra (fexofenadine), Zyrtec (cetirizine), and Xyzal (levocetirizine). What is the maximum dosage of Benadryl?
The maximum dose is 50 mg (two tablets or softgels) every four hours to a maximum of 300mg (12 tablets or softgels) in any 24 hour period for adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older.
For children aged 6 to 11 years, the maximum dose is 25 mg (one tablet or softgel) every four hours, but not to exceed 150 mg (six tablets or capsules) in any 24 hour period.
What interacts with Benadryl?
Food does not affect the absorption or effectiveness of Benadryl.
Some over-the-counter and prescription drugs may interact with Benadryl, and some may reduce the effectiveness of Benadryl.
 Medicines that depress or slow down the central nervous system, such as tranquilizers, alcohol, or sedatives, may increase the side effects of Benadryl, such as drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, dry mouth, and blurred vision. Always check with your doctor before taking Benadryl Allergy with central nervous system depressants or other medicines.
Medicines that depress or slow down the central nervous system, such as tranquilizers, alcohol, or sedatives, may increase the side effects of Benadryl, such as drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, dry mouth, and blurred vision. Always check with your doctor before taking Benadryl Allergy with central nervous system depressants or other medicines. Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion also contains phenylephrine, a stimulant. When taken with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), a family of medications that includes certain types of antidepressants, antibiotics, and drugs for Parkinson's disease, phenylephrine can cause dangerous and potentially life-threatening increases in blood pressure. Do not take Benadryl with an MAOI or within 14 days of stopping an MAOI inhibitor. Check with your doctor, pharmacist, or other health care provider if you think a medicine you are taking may be an MAO inhibitor.
- Diphenhydramine for Animals, VCA Hospitals
- Chronic Diphenhydramine Abuse and Withdrawal Syndrome, Neurology: Clinical Practice
- Antihistamine Doses, MSD Veterinary Manual
- Pharmacological Treatment of Motion Sickness Pharmacist
- FDA warns of serious problems with high doses of allergy drug diphenhydramine.
 , FDA
, FDA
Benadryl Antialergico - instructions for use, dosages, composition, analogs, side effects / Pillintrip
Usual adult dose for insomnia
mg Benadryl Antiallergic Citrate) at bedtime.
Paracetamol-Benadryl Antiallergic is available in various doses (500 mg-25 mg, 650 mg-50 mg, 500 mg, 38 mg, 500 mg-12.5 mg, 1000 mg, -50 mg, 500 mg-50 mg, 325 mg -12.5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
Usual Adult Dose for Pain
Note: Acetaminophen-Benadryl Anti-Alergic is usually dosed based on the Benadryl Anti-Alergic component to correspond to 50 mg Benadryl Anti-Alergic (76 mg Benadryl Anti-Alergic Citrate) at bedtime.
Paracetamol-Benadryl Antiallergic is available in various doses (500 mg-25 mg, 650 mg-50 mg, 500 mg, 38 mg, 500 mg-12.5 mg, 1000 mg, -50 mg, 500 mg-50 mg, 325 mg -12.5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
Usual Adult Dose for Headache
Note: Acetaminophen-Benadryl Antiallergic is usually dosed based on the Benadryl Antiallergic component to correspond to 50mg Benadryl Antiallergic (76mg Benadryl Antiallergic Citrate) at bedtime.
Paracetamol-Benadryl Antiallergic is available in various doses (500 mg-25 mg, 650 mg-50 mg, 500 mg, 38 mg, 500 mg-12.5 mg, 1000 mg, -50 mg, 500 mg-50 mg, 325 mg -12.5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Insomnia
Greater than or equal to 12 years :
Note: Acetaminophen-Benadryl Antiallergic is usually dosed based on the Benadryl Antiallergic component to correspond to 50mg Benadryl Antialergic (76mg Benadryl Antialergic Citrate) at bedtime.
Paracetamol-Benadryl Antiallergic is available in various doses (500 mg-25 mg, 650 mg-50 mg, 500 mg, 38 mg, 500 mg-12.5 mg, 1000 mg, -50 mg, 500 mg-50 mg, 325 mg -12. 5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Pain
Greater than or equal to 12 years :
Note: Acetaminophen-Benadryl Antiallergic is usually dosed based on the Benadryl Antiallergic component to correspond to 50mg Benadryl Antialergic (76mg Benadryl Antialergic Citrate) at bedtime.
Paracetamol-Benadryl Antiallergic is available in various doses (500 mg-25 mg, 650 mg-50 mg, 500 mg, 38 mg, 500 mg-12.5 mg, 1000 mg, -50 mg, 500 mg-50 mg, 325 mg -12.5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Headache
Greater than or equal to 12 years :
Note: Acetaminophen-Benadryl Antiallergic is usually dosed based on the Benadryl Antiallergic component to correspond to 50mg Benadryl Antialergic (76mg Benadryl Antialergic Citrate) at bedtime.
Paracetamol-Benadryl Antiallergic is available in various doses (500 mg-25 mg, 650 mg-50 mg, 500 mg, 38 mg, 500 mg-12.5 mg, 1000 mg, -50 mg, 500 mg-50 mg, 325 mg -12.5 mg) and as a liquid, capsule. The manufacturer of these products generally recommends 2 doses at bedtime or as directed by a physician.
Renal dose adjustment
No data available
Liver dose adjustment
Use with caution in patients with liver disease. Chronic use of paracetamol is not recommended in patients with liver disease.
Precautions
Patients who consume three or more alcoholic drinks per day should be informed that you will contact your doctor for advice on when and how to take paracetamol. Chronic, heavy alcohol users may have an increased risk of liver damage if you take more than the recommended doses.
Patients and caregivers should consult their physician before continuing to use paracetamol if symptoms worsen. Although rare, there is a possibility of acetaminophen intoxication with chronic use of the drug, and symptoms that appear during the first phase of intoxication (nausea, vomiting, anorexia, malaise and diaphoresis) may cause the use of more doses.